week 1 treatment planning
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Keys steps of treatment planning
1. Prescription- The physician determines the radiation dose and treatment area.
2. Planning - Experts create a precise plan for safe and effective dose delivery.
3. Treatment - The plan is executed to deliver radiation to the patient.
Planning Process Overview
•Goal: Customize and optimize radiation treatment for each patient.
•Uses:
Machine settings + patient data + calculations.
Collect Patient Data
•CT scan, tumor location, and critical structures.
Machine & Beam Data
•Radiation quality, PDD, beam profiles.
•Source or beam placement optimization.
Required Patient Information for Treatment Planning
• Radiation therapy is localized → Focuses on a specific area.
• Target details → Location, volume, and shape of the tumor.
• Secondary targets → Any nearby areas that also need treatment.
• Critical structures → Important organs/tissues to protect.
• Radiobiology → How radiation affects tumor and normal tissues.
• Dose AND volume → Amount of radiation needed for both tumor and normal structures.
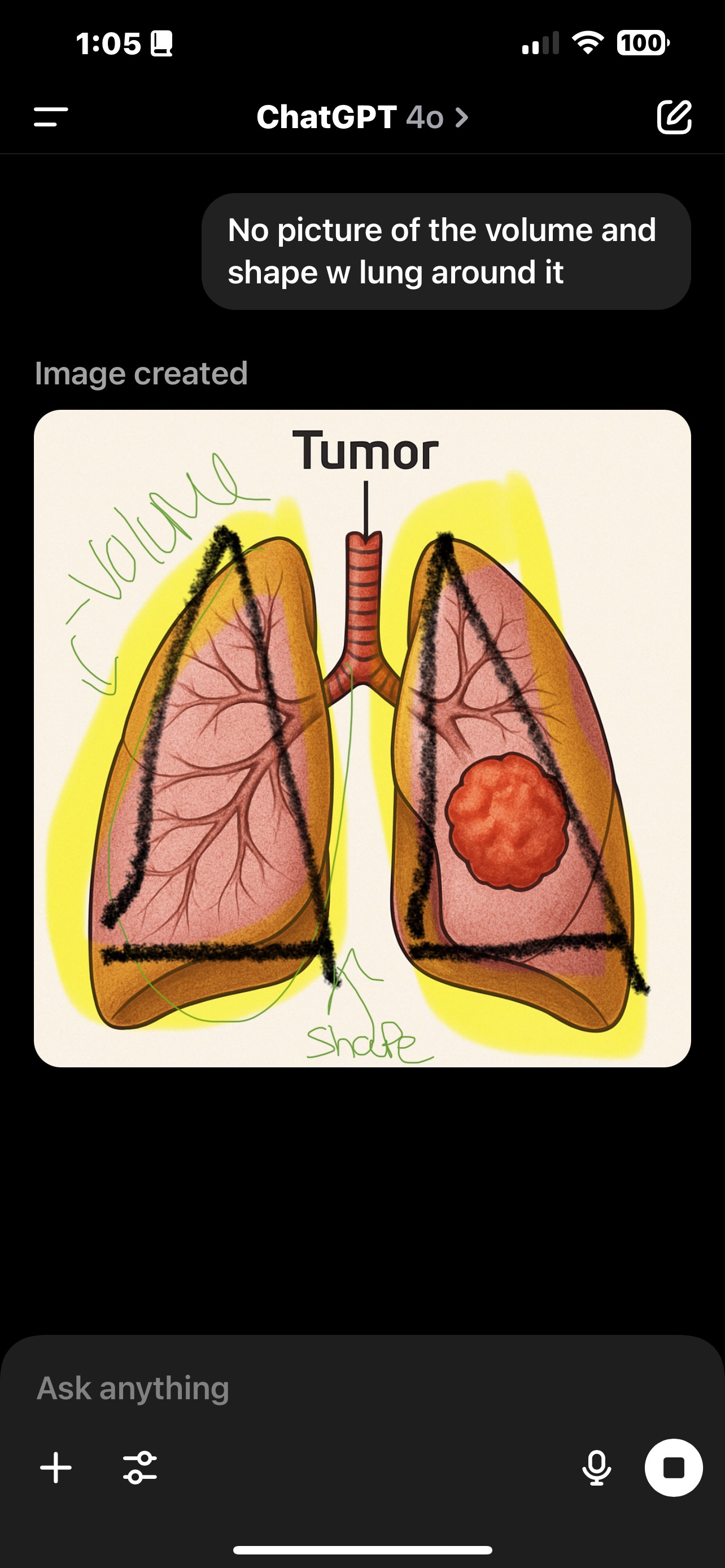
Target Volumes (ICRU Standard)
•Purpose:
Standardizes treatment planning & allows comparison across cancer centers.
GTV
Gross Tumor Volume) → Visible or palpable tumor.
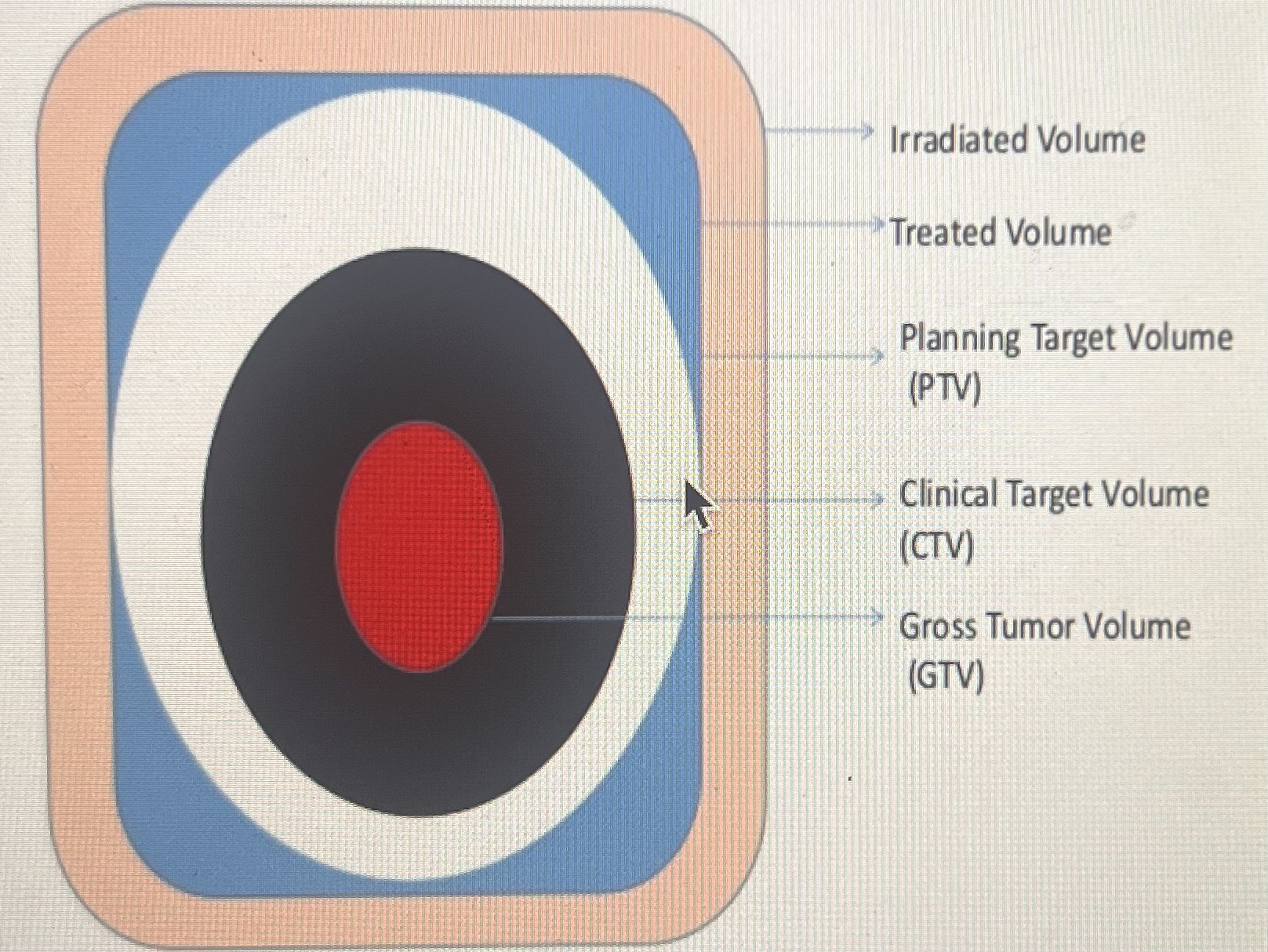
CTV
Clinical Target Volume) → EXPANDS from GTV + microscopic disease (possible spread).
PTV
Planning Target Volume) → CTV + margins (for setup uncertainties).
ITV
Internal Target Volume) → CTV + internal motion margins (e.g., breathing).
Treated Volume
Area that actually gets the prescribed dose.
How quickly a tumor grows depends on 3 factors
Division rate of cells proliferation
Growth factor
Degree of cell death- exfoliation death