3.2 Costs and Economies of Scale
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Fixed costs
Costs that do not vary with the level of output
Variable costs
Costs that vary with the level of output
Total costs
The sum of all costs that are incurred in producing a given level of output (including opportunity cost)
Average costs
Total cost divided by the quantity produced, sometimes known as unit cost
Marginal costs
The cost of producing an additional unit of output
Short run
The period in which at least one factor of production is fixed
Long run
The period over which the firm is able to vary all its factors of production (inputs)
The law of diminishing returns
States that if a firm increases its inputs of one factor of production while holding inputs of the other factors fixed, eventually the firm will experience diminishing marginal returns from the variable factor
Economies of scale
These occur for a firm when an increase in the scale of production leads to production at lower long-run average cost
Internal economies of scale
Economies of scale that arise from the expansion of a firm
External economies of scale
Economies of scale that arise from the expansion of the industry in which a firm is operating
Diseconomies of scale
These occur for a firm when an increase in the scale of production leads to higher long-run average costs
Minimum efficient scale
The level of output at which long run average cost stops falling as output increases
Short run costs
Fixed and variable
Fixed costs: capital inputs such as machinery, buildings, capital equipment, rent
An increase in the output level will not lead to an increase in fixed costs. Fixed costs will be incurred even if the firm shuts down production
Variable costs: such as labour, raw materials and energy
We assume that in the short run the quantity of capital inputs is fixed and that production can only be changed by changing variable inputs
Sunk costs
A cost which cannot be recovered if the firm closes down
E.g. costs of infrastructures, research and development expenditure, advertising
Short run cost formulas
Average total cost: Total cost/quantity
Average fixed cost: Total fixed cost/quantity
Average variable cost: Total variable cost/quantity
Marginal cost: Change in total cost/total variable cost due to an additional unit of production
Short run cost curves
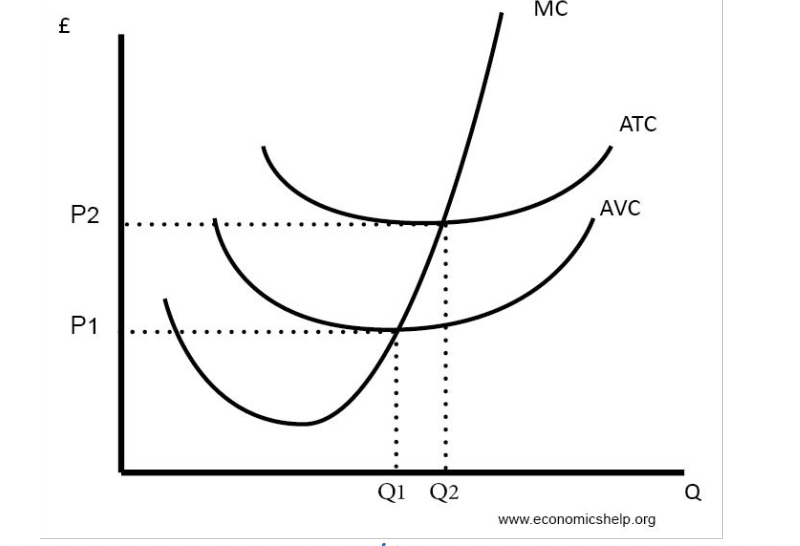
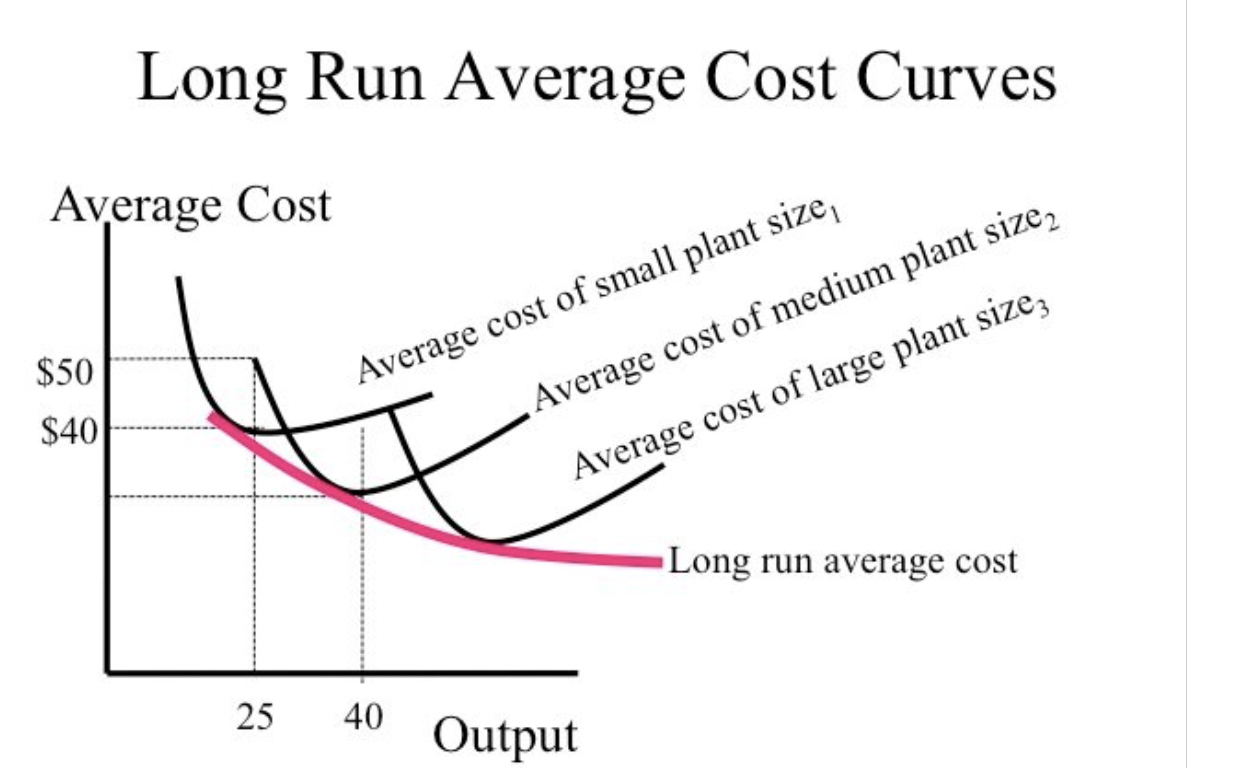
Long run average cost curve
The long run is a period of time sufficiently long enough to allow the firm to change the combination of all of the factors of production which it is using.
Therefore, when the firm knows what quantity it will be producing, it will opt for the combination of the factors of production which gives the lowest AC for that quantity.
Sources of economies of scale
Technical Economies of Scale
Managerial Economies of Scale
Organisational Economies of Scale
Purchasing Economies of Scale
Financial Economies of Scale
Technical economies of scale
More advanced machinery and low amount of specialised labor (high fixed costs, low variable costs) mean large fixed costs of purchasing machinery are spread over higher levels of output
Marketing economies of scale
As a business gets larger, it is able to spread the fixed cost of marketing over a wider range of products and sales, cutting the average marketing cost per unit
Purchasing economies of scale
As businesses grow they need to order larger quantities of production inputs
As the order value increases, a business has more bargaining power with suppliers
It may be able to obtain discounts and lower prices forthe raw materials
Managerial economies of scale
Large firms have the money/resources to attract the most productive/efficient/specialist managers who make the most effective business decisions and increase efficiency over time
Financial Economies of Scale
Large firms can benefit from cheaper loans and wider sources of cheap finance (investment from shareholders)
Risk-Bearing Economies of Scale
Large firms benefit from having wider, more diversified product range. This means that they are better able to withstand the risk of a fall in demand for one good or service
Sources of diseconomies of scale
Lack of motivation: Workers in large companies may feel demotivated, leading to absenteeism and lateness. This could cause a reduction in productivity, lower output per worker and increased unit costs
Lack of communication: As the size of the workforce increases there will be less face-to-face communication leading to less effective communication. This could cause more mistakes to be made, more wastage and higher average unit costs
Lack of coordination: As a company grows and takes on new staff/makes new products/buys new premises all of this needs to be coordinated. Workers may need monitoring which can add to costs as hiring more managers increases average cost per unit
Sources of external economies of scale
A pool of skilled labour becomes widely available to all firms in the industry
The expansion of an industry creates higher demand for new specialised labour - training/university courses may become more profitable and expand, leading firms to reduce their training costs and therefore to lower their total cost
New transport infrastructures and new specialised infrastructures and services become available to all firms