914 Biology Final
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
Chapter 11 Test: Mitosis
.
As a cell becomes larger its:
A. volume increases faster than its surface area
B. surface area increases faster than its volume
C. volume increases, but its surface area stays the same
D. surface area stays the same, but its volume increases
A. volume increases faster than its surface area
All of the following are problems that growth causes for cells EXCEPT:
A. DNA overload
B. excess oxygen
C. obtaining enough food
D. expelling wastes
B. excess oxygen
When during the cell cycle is a cell's DNA replicated?:
A. G1 phase
B. G2 phase
C. S phase
D. M phase
C. S phase
Which event occurs during interphase?:
A. the cell grows
B. centrioles appear
C. spindle fibers begin to form
D. centromeres divide
A. the cell grows
During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle of the dividing cell?:
A. prophase
B. telophase
C. metaphase
D. anaphase
C. metaphase
Which of the following represents the phases of mitosis in their proper sequence?:
A. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
B. interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
C. interphase, prophase, metaphase, and telophase
D. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis
A. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
What is the role of the spindle during mitosis?:
A. It helps separate the chromosomes
B. It breaks down the nuclear membrane
C. It duplicates the DNA
D. It divides the cell in half
A. It helps separate the chromosomes
The two main stages of cell division (NOT the cell cycle) are:
A. mitosis and interphase
B. synthesis and cytokinesis
C. the M phase and the S phase
D. mitosis and cytokinesis
D. mitosis and cytokinesis
Cyclins are a family of closely related proteins that:
A. regulate the cell cycle
B. produce p53
C. cause cancer
D. work to heal wounds
A. regulate the cell cycle
Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost the ability to control their:
A. size
B. spindle fivers
C. growth rate
D. surface area
C. growth rate
As a cell grows it:
A. places more demands on its DNA
B. uses up food and oxygen more quickly
C. has more trouble moving enough materials across its cell membrane
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
The process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells is called:
A. cell division
B. metaphase
C. interphase
D. mitosis
A. cell division
Which of the following is a phase of the cell cycle?:
A. G1 phase
B. G2 phase
C. M phase
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
The cell cycle is the:
A. series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
B. period of time between the birth and death of a cell
C. time from prophase until cytokinesis
D. time it takes for one cell to undergo mitosis
A. series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
Use this to help with the next few questions
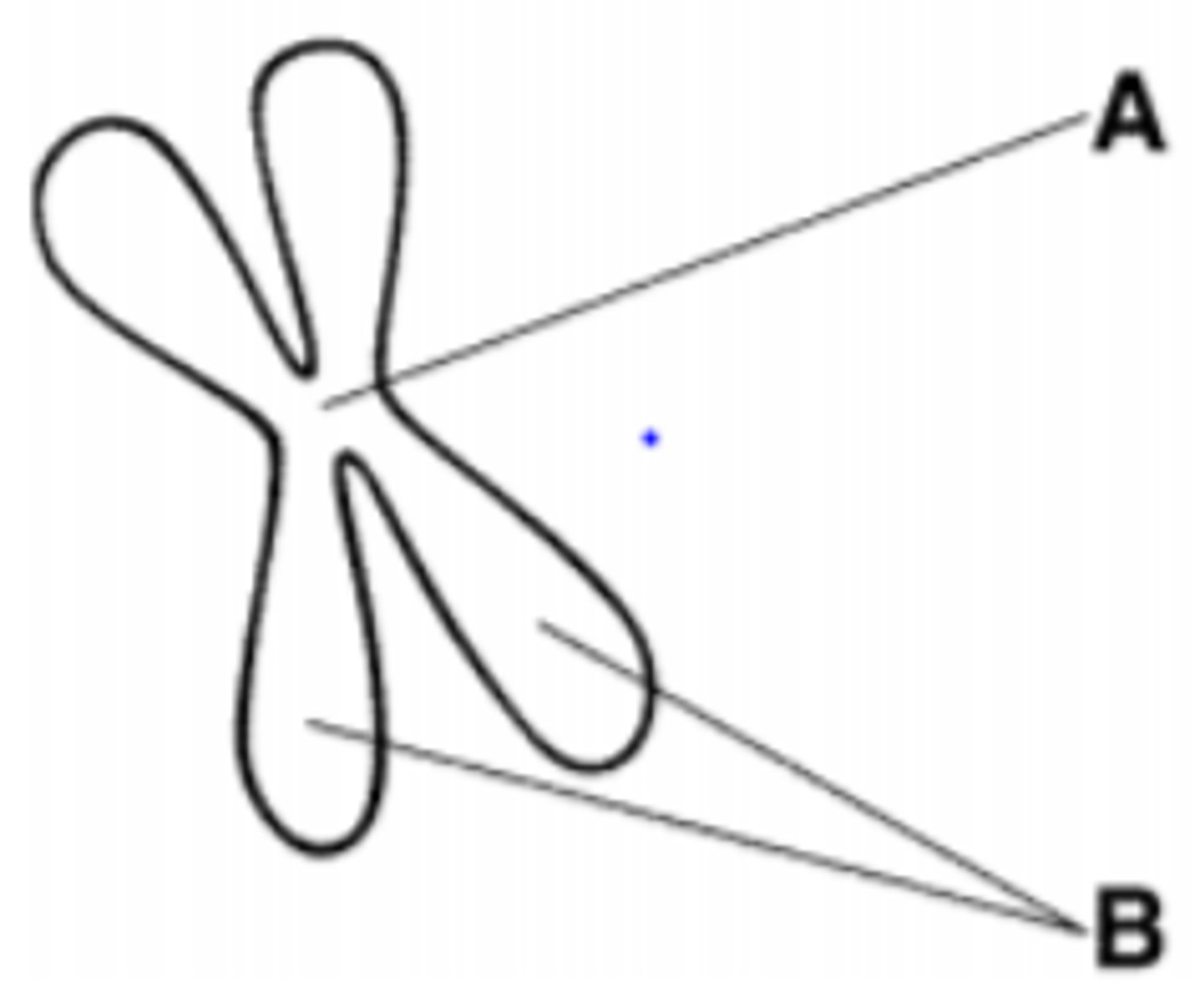
The structure labeled A is called the:
A. centromere
B. centriole
C. sister chromatids
D. spindle
A. centromere (centro=center)
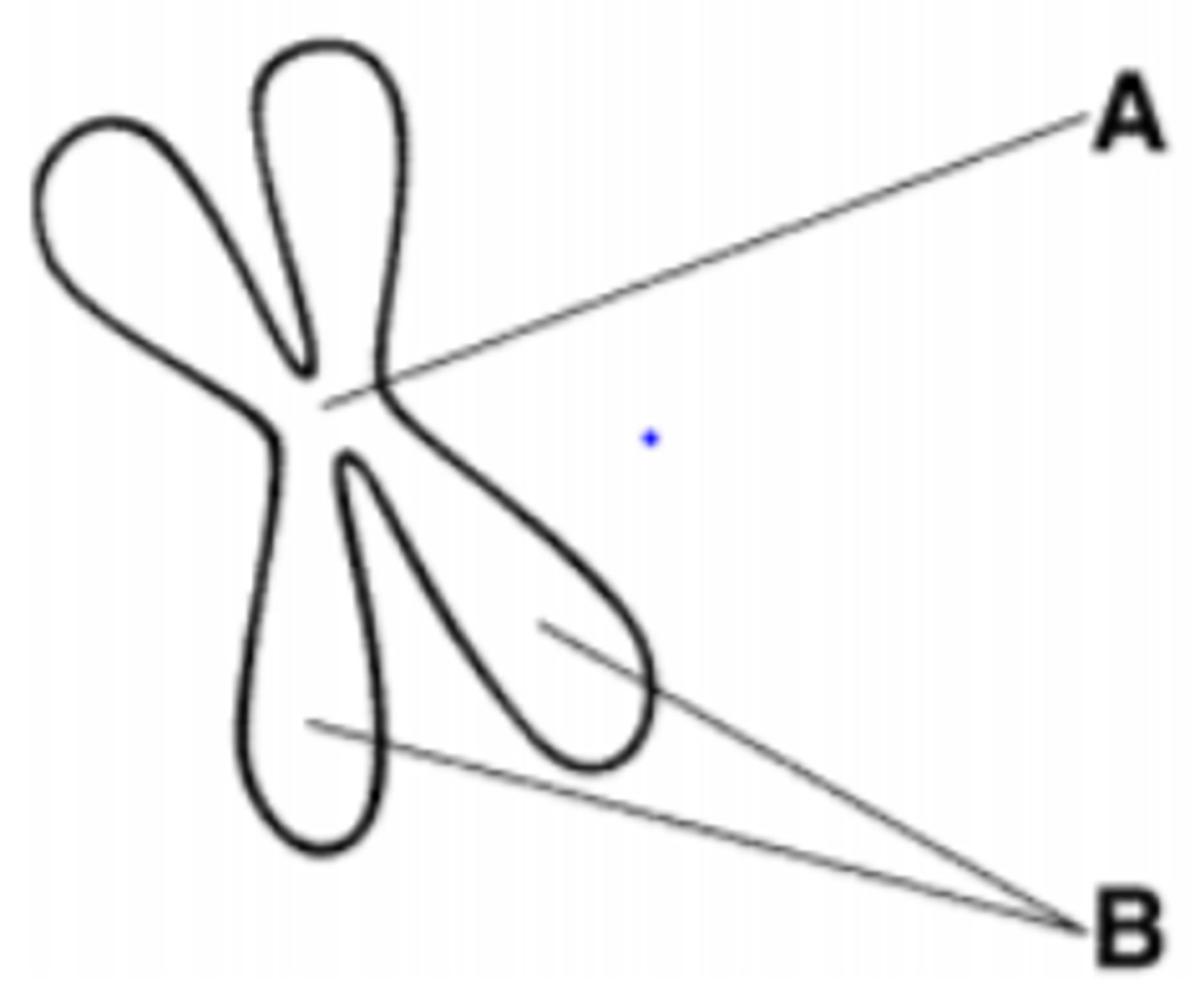
The structure labeled B is called the:
A. centromere
B. centriole
C. sister chromatids
D. spindle
C. sister chromatids
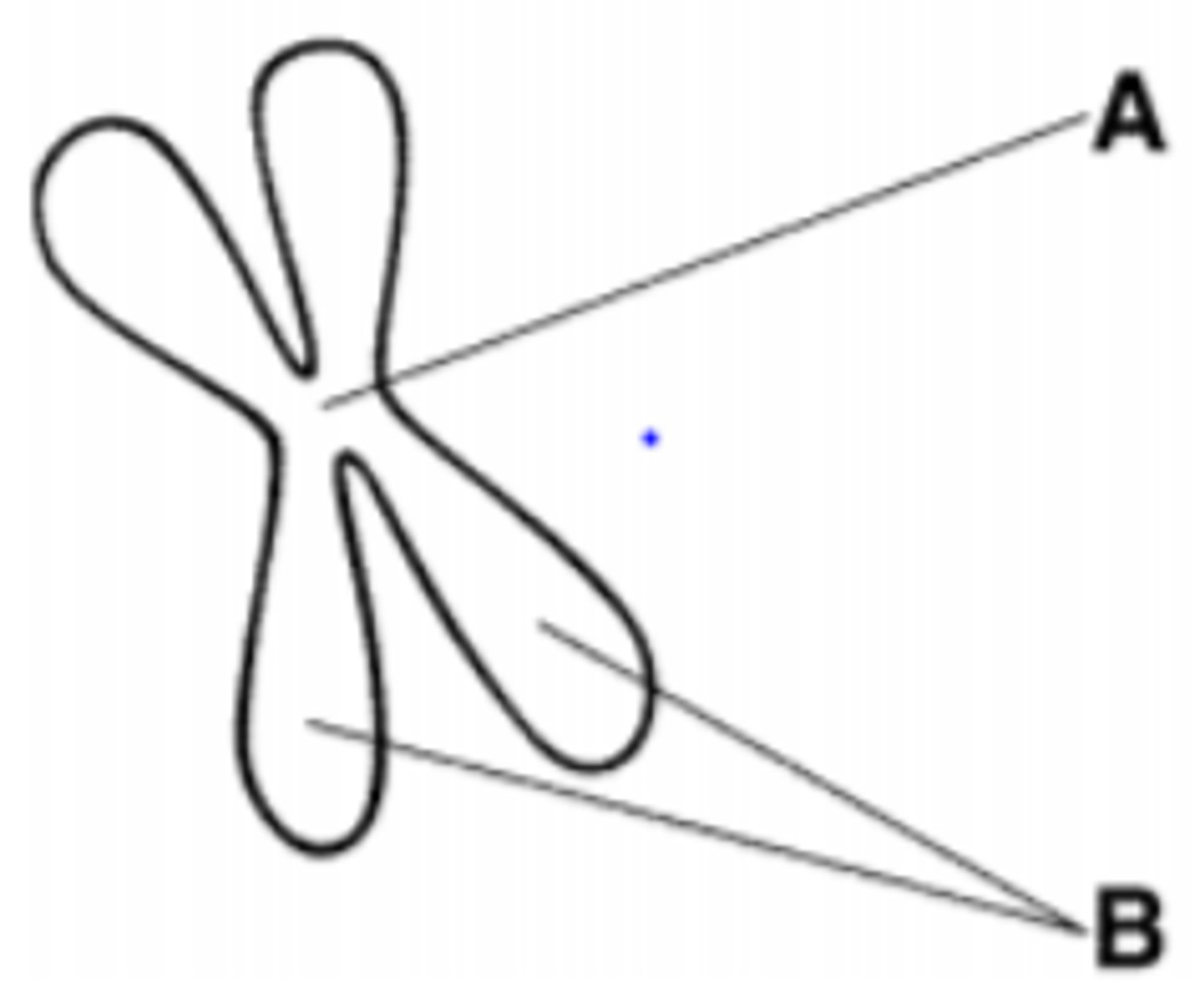
Which of the following is a phase of mitosis?:
A. cytokinesis
B. interphase
C. anaphase
D. S phase
C. anaphase
Cell division is represented by what letter in the chart?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
D. D
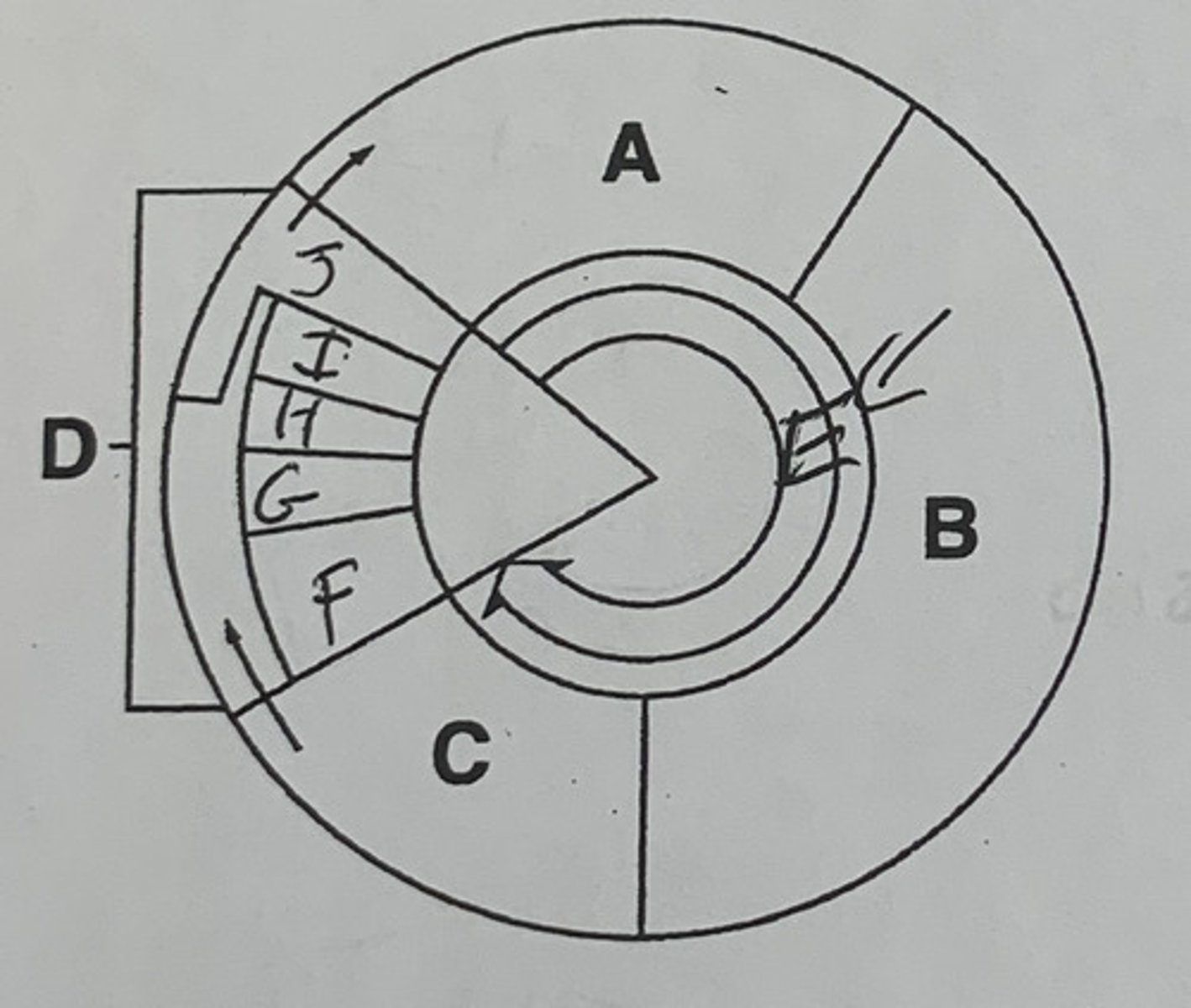
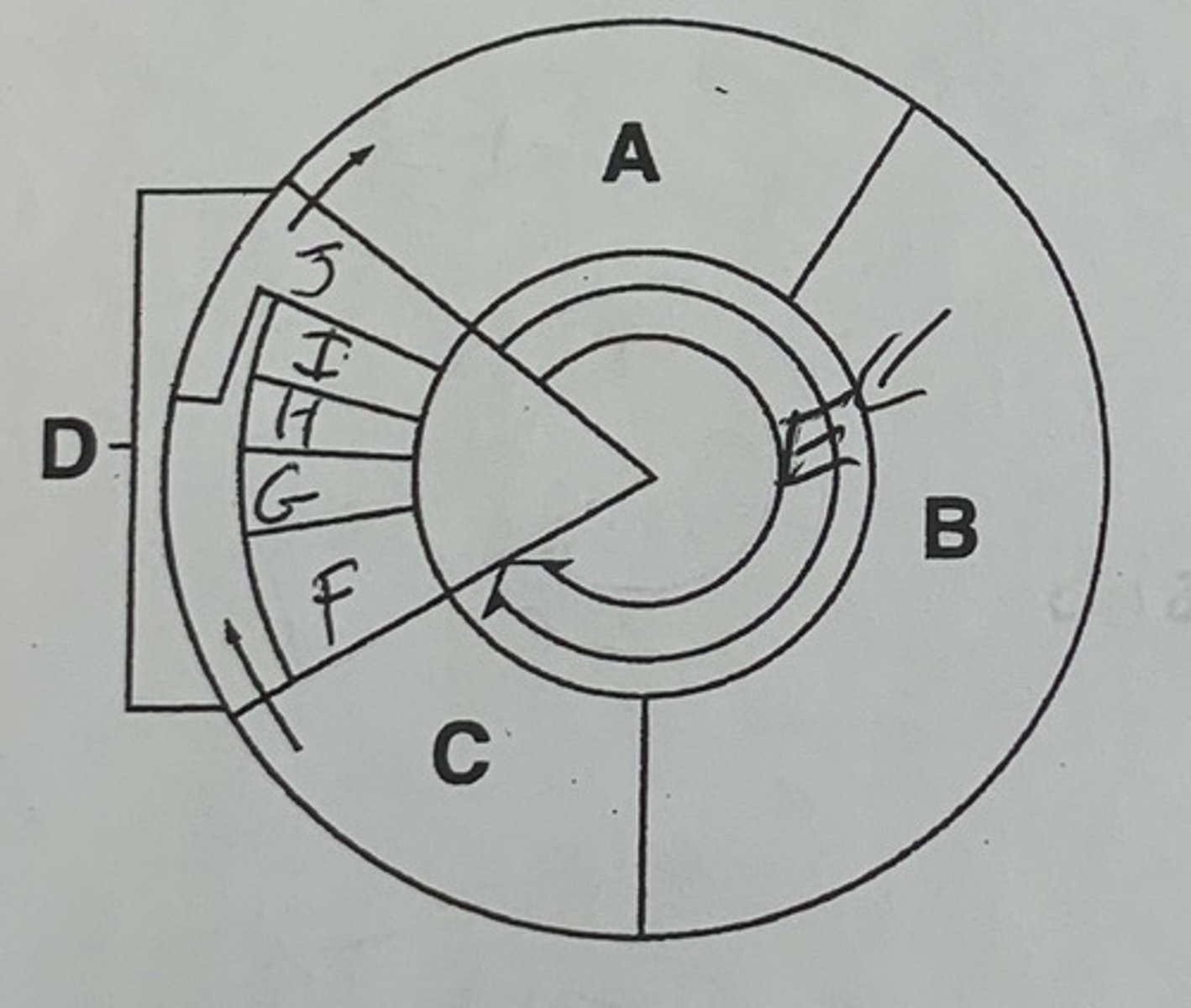
Label A, B, C, D, E and briefly describe each
A. G1 phase: where cells grow
B. S phase: DNA replicates and chromosomes synthesize
C. G2 phase: cell prepares for mitosis
D. M phase: cell division
E. Interphase: a 3-phase process of the cell growing and preparing for division
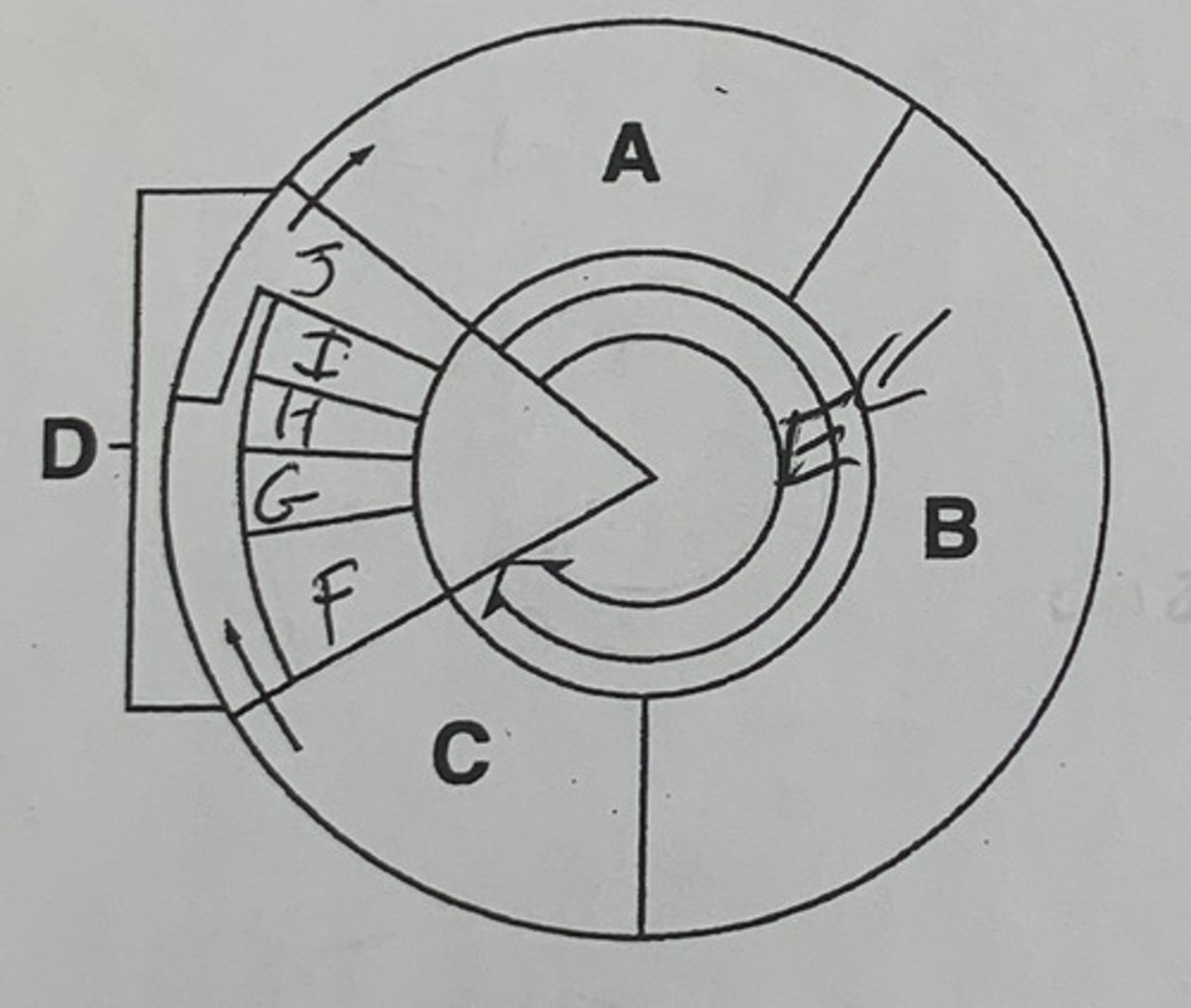
Label F, G, H, I, J, and briefly describe each
F. Prophase: the chromosomes and the nucleus membrane starts to dissolve/disappear
G. Metaphase: the chromosomes line up along the center of the cell and the spindles attach to the centromere
H. Anaphase: chromosomes split and the spindles drag the half of the sister chromatids onto opposite sides of the cell
I. Telophase: the nucleus is completely split and the nuclear membrane starts to reform
J. Cytokinesis: the cytoplasm separates to form the other 2 daughter cells
What does the figure represent?
the 4 phases of mitosis
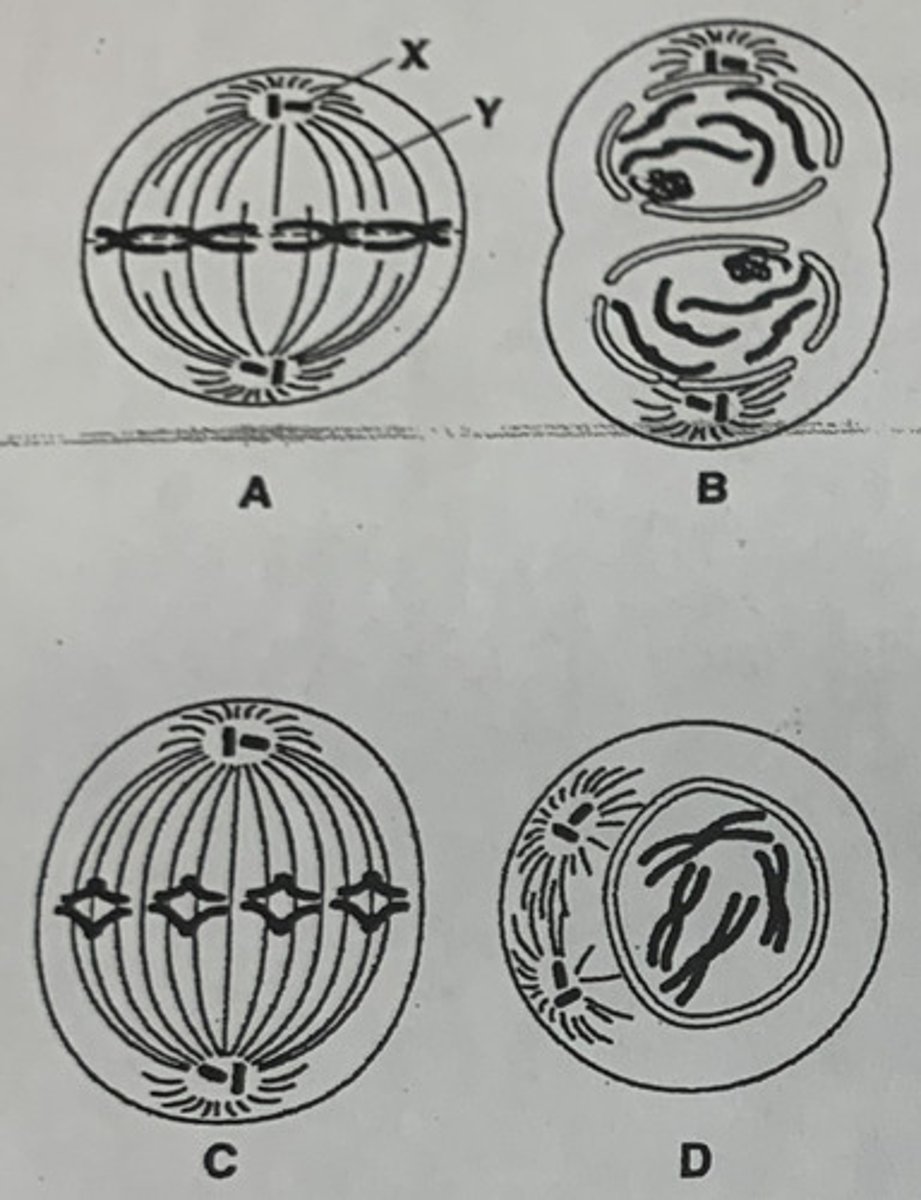
Identify the structures labeled X and Y
X: centriole
Y: spindle
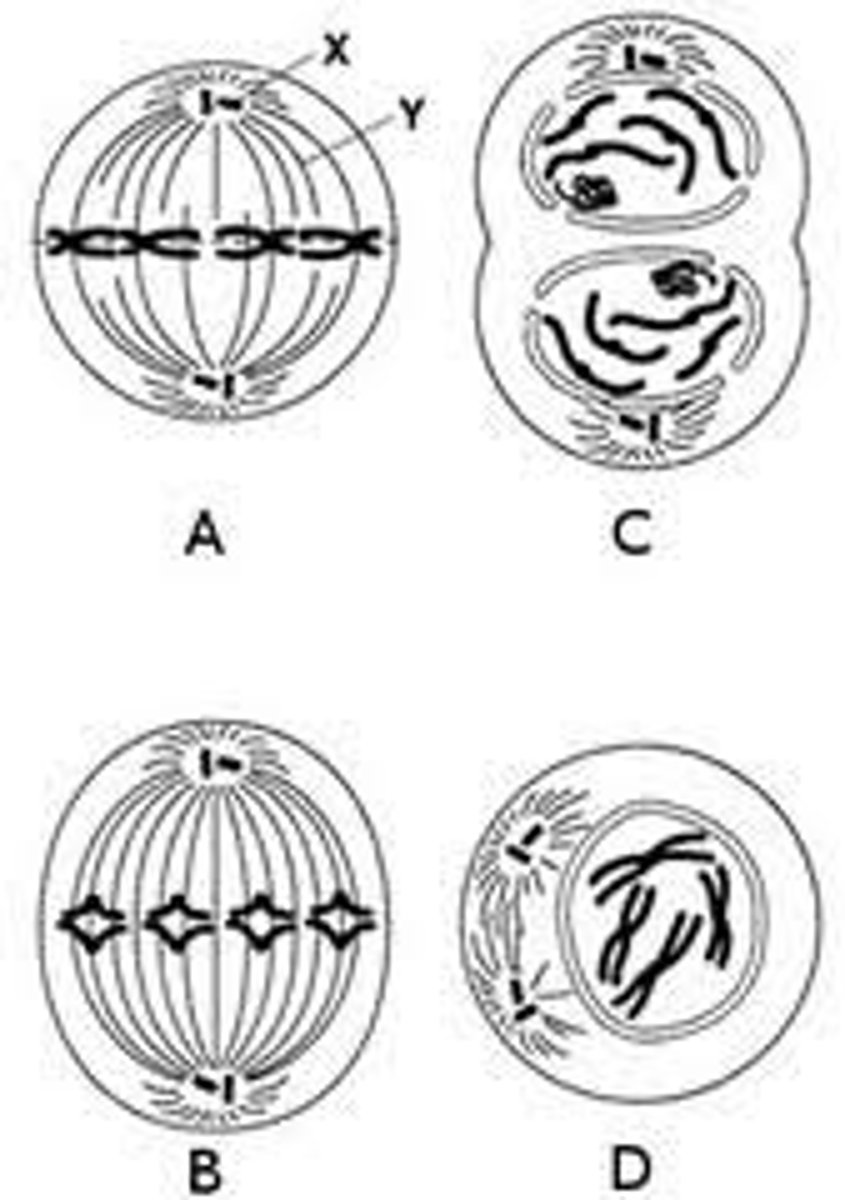
List the correct order for the diagrams
D, A, C, and B
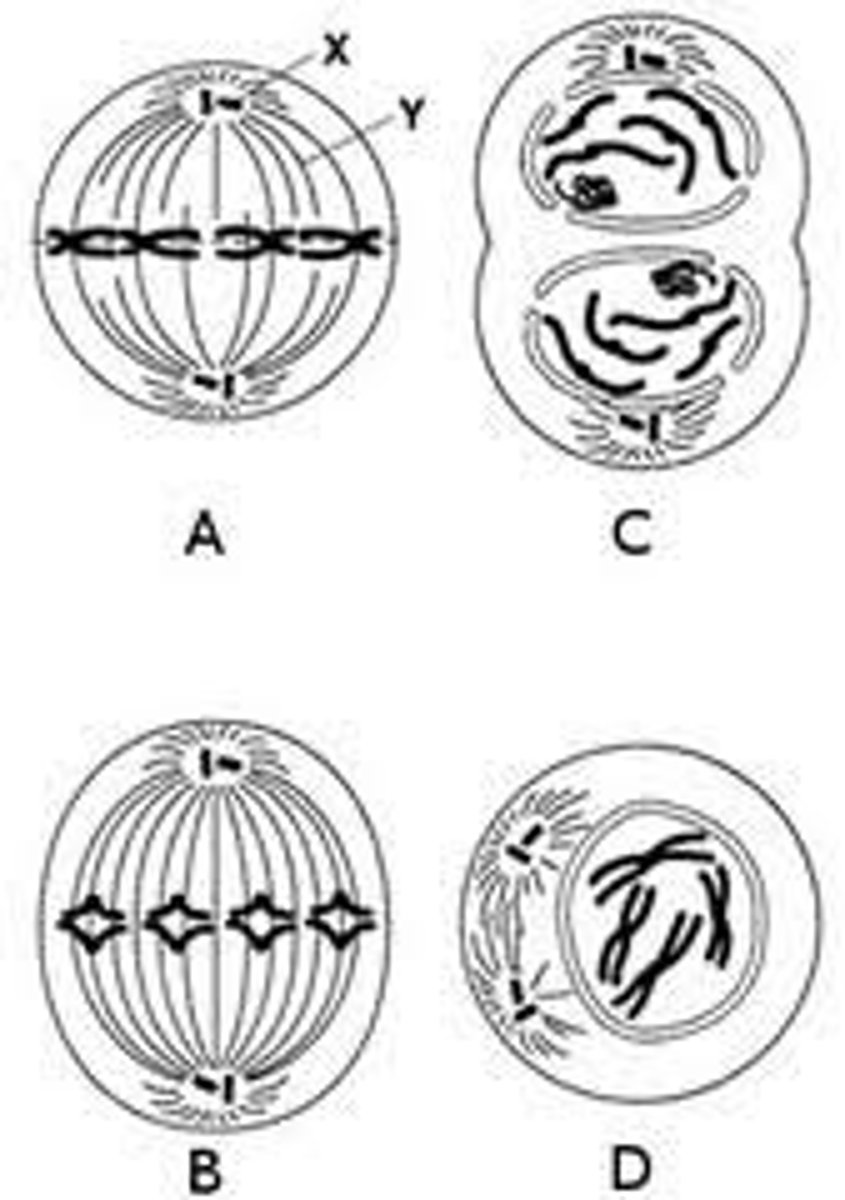
Which phase takes the longest time, about 55%?
prophase
How do you know if they are plant cells or animal cells?
Animal cells have centrioles
Plant cells don't have centrioles
Chapter 12 Test: Genetics
.
What are the genotypes and phenotypes of a tall plant and short plant crossing?
Genotypes: Tt, Tt, Tt, and Tt
Phenotypes: 4 tall (4:0)
Explain what happened to the short gene in this cross.
The short gene was masked by the tall gene
Take two of the genotypes from the last answer (Tt,Tt) and cross them. What are the genotypes and phenotypes?
Genotypes: TT, Tt, Tt, and tt
Phenotypes: 3 tall and one short
Explain what happened to the short gene in this cross.
The short gene was masked twice (Tt,Tt), not shown once (TT), and visible once (tt)
Offspring that result from crosses between true-breeding parents with different traits:
A. are true breeding
B. are called hybrids
C. make up the parental generation
B. are called hybrids
When Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short plants, all the offspring were tall because:
A. the allele for tall plants is recessive
B. the allele for short plants is dominant
C. the allele for tall plants is dominant
D. they were true-breeding like their parents
C. the allele for tall plants is dominant
A Punnett Square shows all of the following EXCEPT:
A. all possible results of a genetic cross
B. the genotypes of the offspring
C. the alleles in the gametes of each parent
D. the actual results of a genetic cross
D. the actual results of a genetic cross
Use this to answer the next question
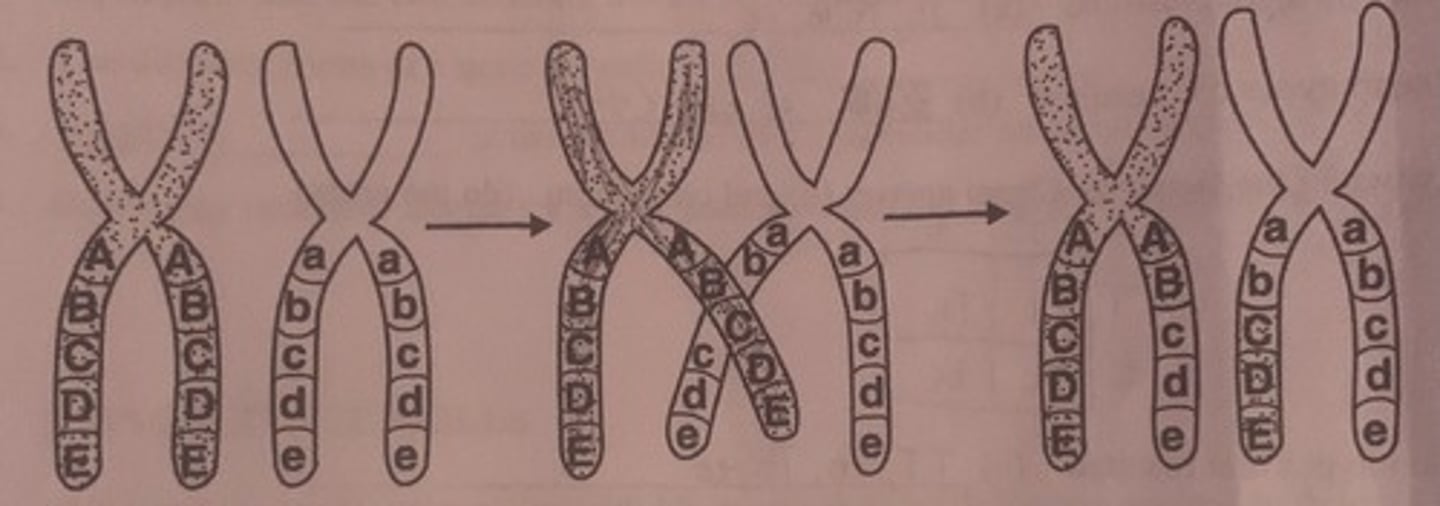
What is shown in this figure?:
A. independent assortment
B. anaphase 1 of meiosis
C. crossing over
D. incomplete dominace
C. crossing over
How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY?:
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
A. 2
A cross of a white hen with a black rooster produces erminette-color offspring. This type of inheritance is known as:
A. incomplete dominance
B. polygenic inheritance
C. codominance
D. multiple alleles
C. codominance
Which of the following statements about Thomas Hunt Morgan is true?:
A. Morgan chose to use fruit flies in his study of genetics because fruit flies produce a large number of offspring
B. Morgan chose to use fruit flies in his study of genetics because fruit flies take a long time to produce offspring
C. Morgan continued Mendel's study of pea plants
D. Morgan discovered that Mendel's principles of genetics do not apply to fruit flies
A. Morgan chose to use fruit flies in his study of genetics because fruit flies produce a large number of offspring
If an organisms diploid number is 6, its haploid number is:
A. 12
B. 6
C. 24
D. 3
D. 3
Chromosomes form tetrads during:
A. prophase of meiosis I
B. metaphase of meiosis I
C. prophase of meiosis II
D. metaphase of meiosis II
A. prophase of meiosis I
The principle of dominance states that:
A. all alleles are dominant
B. all alleles are recessive
C. some alleles are dominant and others are recessive
D. alleles are neither dominant nor recessive
C. some alleles are dominant and others are recessive
Two plants with the genotypes TT and Tt:
A. would have the same phenotype
B. would have different phenotypes
C. have all dominant alleles
D. have all recessive alleles
C. have all dominant alleles
Organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to be:
A. hybrid
B. homozygous
C. heterozygous
D. dominant
B. homozygous
What principle states that during gamete formation alleles separate?:
A. principle of dominance
B. principle of independent assortment
C. principle of probabilities
D. principle of segregation
D. principle of segregation
Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over another allele for that gene are called:
A. multiple alleles
B. incomplete dominance
C. codominant alleles
D. multiple genes
B. incomplete dominance
Mendel's principles of genetics apply to:
A. plants only
B. animals only
C. pea plants only
D. all organisms
D. all organisms
Gametes are produced by the process of:
A. mitosis
B. meiosis
C. crossing-over
D. replication
B. meiosis
Traits that are produced by the interaction of several genes are said to be:
A. polygenic
B. codominant
C. haploid
D. diploid
A. polygenic
Gene maps are based on:
A. the frequencies of crossing-over between genes
B. independent assortment
C. genetic diversity
D. the number of genes in a cell
A. the frequencies of crossing-over between genes
A pea plant that has two different alleles for the same trait is said to be ___________
heterozygous
The different forms of a gene are called ___________
alleles
____________ is the likelihood that a particular event will occur
probability
How many recessive alleles for a trait must an organism inherit in order to show that trait?
2
Chapter 13 Test: DNA
.
What did Griffith observe when he injected into mice a mixture of heat-killed disease-causing bacteria and live harmless bacteria?:
A. The disease-causing bacteria changed into harmless bacteria
B. The mice developed pneumonia
C. The harmless bacteria died
D. The mice were unaffected
B. The mice developed pneumonia
Which of the following is a nucleotide found in DNA?:
A. ribose + phosphate group + thymine
B. ribose + phosphate group + uracil
C. deoxyribose + phosphate group + uracil
D. deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine
D. deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine
DNA replication results in two DNA molecules:
A. each with two new strands
B. one with two new strands and the other with two original strands
C. each with one new strand and one original strand
D. each with two original strands
C. each with one new strand and one original strand
Avery's experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by:
A. RNA
B. DNA
C. proteins
D. carbohydrates
B. DNA
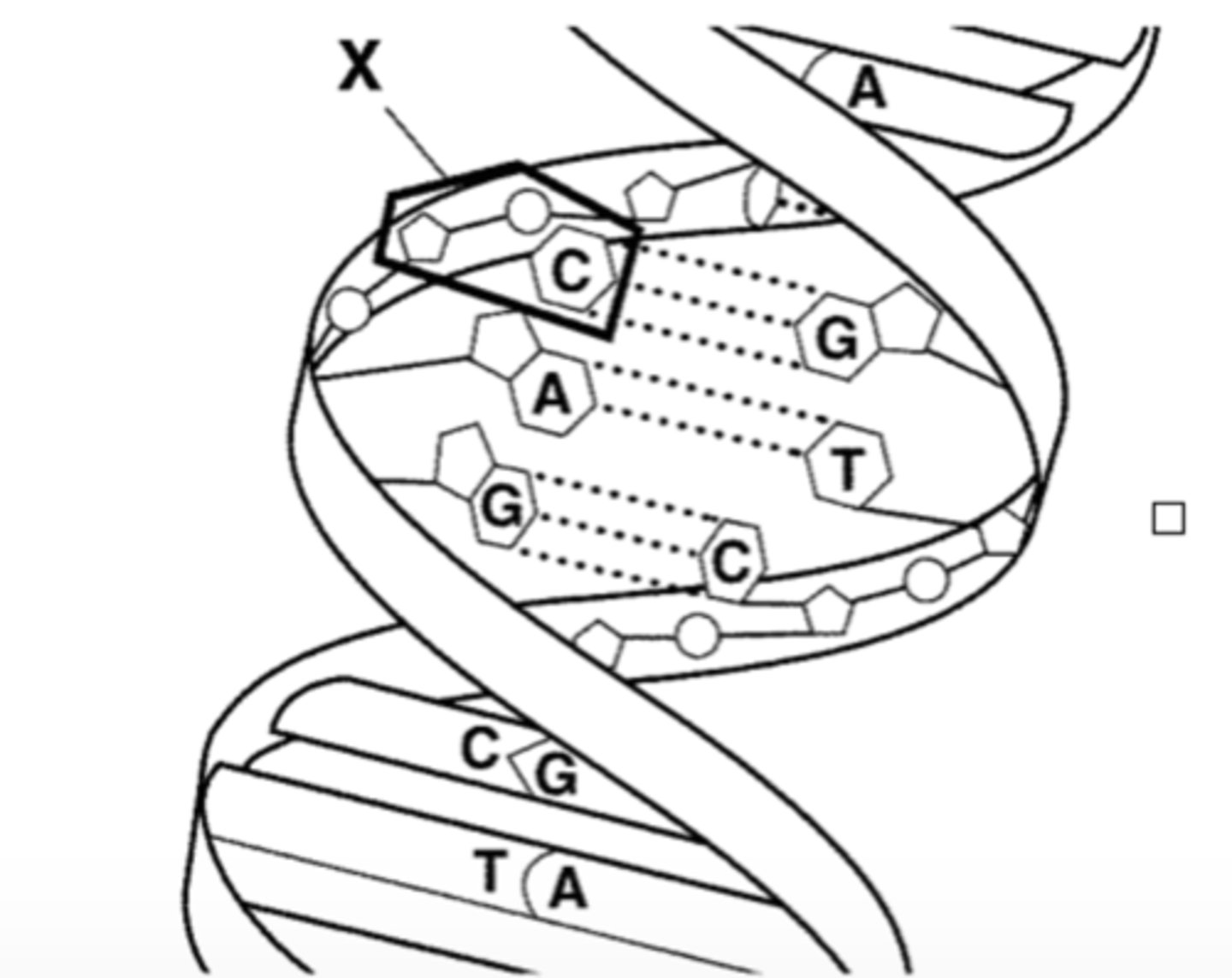
The whole picture is showing the structure of a(an):
A. DNA molecule
B. amino acid
C. RNA molecule
D. protein
A. DNA molecule
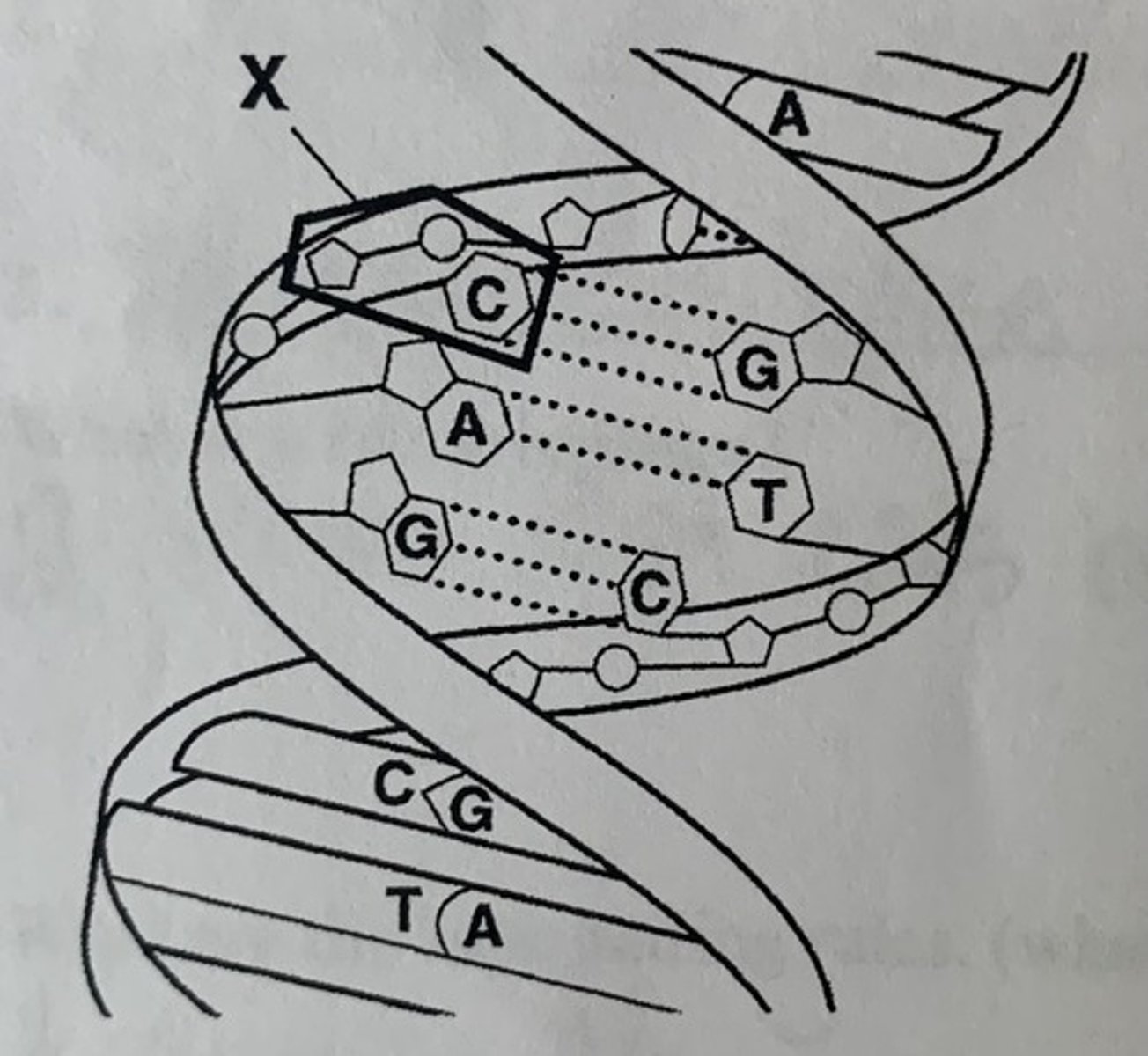
The structure labeled X is a ____________
nucleotide
DNA is copied during a process called:
A. replication
B. translation
C. transcription
D. transformation
A. replication
In eukaryotes, DNA:
A. is located in the nucleus
B. floats freely in the cytoplasm
C. is located in the ribosomes
D. is circular
A. is located in the nucleus
What are the three main parts of a DNA nucleotide?
1. Phosphate group
2. 5-Carbon Sugar
3. Nitrogenous base
What are the base pairing rules?
A goes with T and C goes with G
What did Fredrick Griffith do?
Fredrick Griffith used mice and found out that bacteria can transform.
What did Oswald Avery do?
Oswald Avery continued the work of Griffith and used enzymes to kill parts of the bacteria. They found out that DNA was a transforming factor.
What did Erwin Chargaff do?
Erwin Chargaff came up with rules, these rules stated that Adenine goes with Thymine and Guanine goes with Cytosine. This is called base pairing.
What did Rosalind Franklin do?
Rosalind Franklin took an x-ray picture of DNA.
Which type(s) of RNA is(are) in protein synthesis?:
A. transfer RNA only
B. messenger RNA only
C. ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA only
D. messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA
D. messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA
What did Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase do?
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase used bacteriophages and radioactivity as "tracers" to find out what was being transferred. They found out that DNA was the injected material.
During transcription, an RNA molecule is formed:
A. that is complementary to both strands of DNA
B. that is complementary to neither strand of DNA
C. that is double-stranded
D. inside the nucleus
D. inside the nucleus
How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids?:
A. 3
B. 6
C. 9
D. 12
A. 3
What did James Watson and Francis Crick do?
James Watson and Francis Crick used Franklin's x-ray picture to make a model of DNA which looked like a double helix.
Which type of RNA functions as a blueprint of the genetic code?:
A. rRNA
B. tRNA
C. mRNA
D. RNA polymerase
C. mRNA
Chapter 14 Test: RNA and Protein Synthesis
.
RNA contains the sugar:
A. ribose
B. deoxyribose
C. glucose
D. lactose
A. ribose
Which RNA molecule carries amino acids?:
A. messenger RNA
B. transfer RNA
C. ribosomal RNA
D. RNA polymerase
B. transfer RNA
What is produced during transcription?:
A. RNA molecules
B. DNA molecules
C. RNA polymerase
D. proteins
A. RNA molecules
What happens during the process of translation?:
A. Messenger RNA is made from DNA
B. The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins
C. Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA
D. Copies of DNA molecules are made
B. The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins
Genes contain instructions for assembling:
A. purines
B. nucleosomes
C. proteins
D. pyrimidines
C. proteins
A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a(an)?:
A. chromosomal mutation
B. inversion
C. point mutation
D. translocation
C. point mutation
What codons specify the amino acid arginine?
AGG, AGA, CGA, CGC, CGU, CGG
What is the start codon?
AUG
What amino acid does the start codon code for?
methionine
Why do some kinds of point mutations cause greater changes in proteins than others?
________________________________
What are the three main differences between a DNA and RNA molecule?
1. RNA has uracil, DNA has thymine
2. RNA is single-stranded, DNA is double-stranded
3. RNA has sugar ribose, DNA has deoxyribose
Name the 4 types of chromosomal mutations A, B, C, and D
A. Deletion
B. Duplication
C. Inversion
D. Translation
Use this to help with the next question
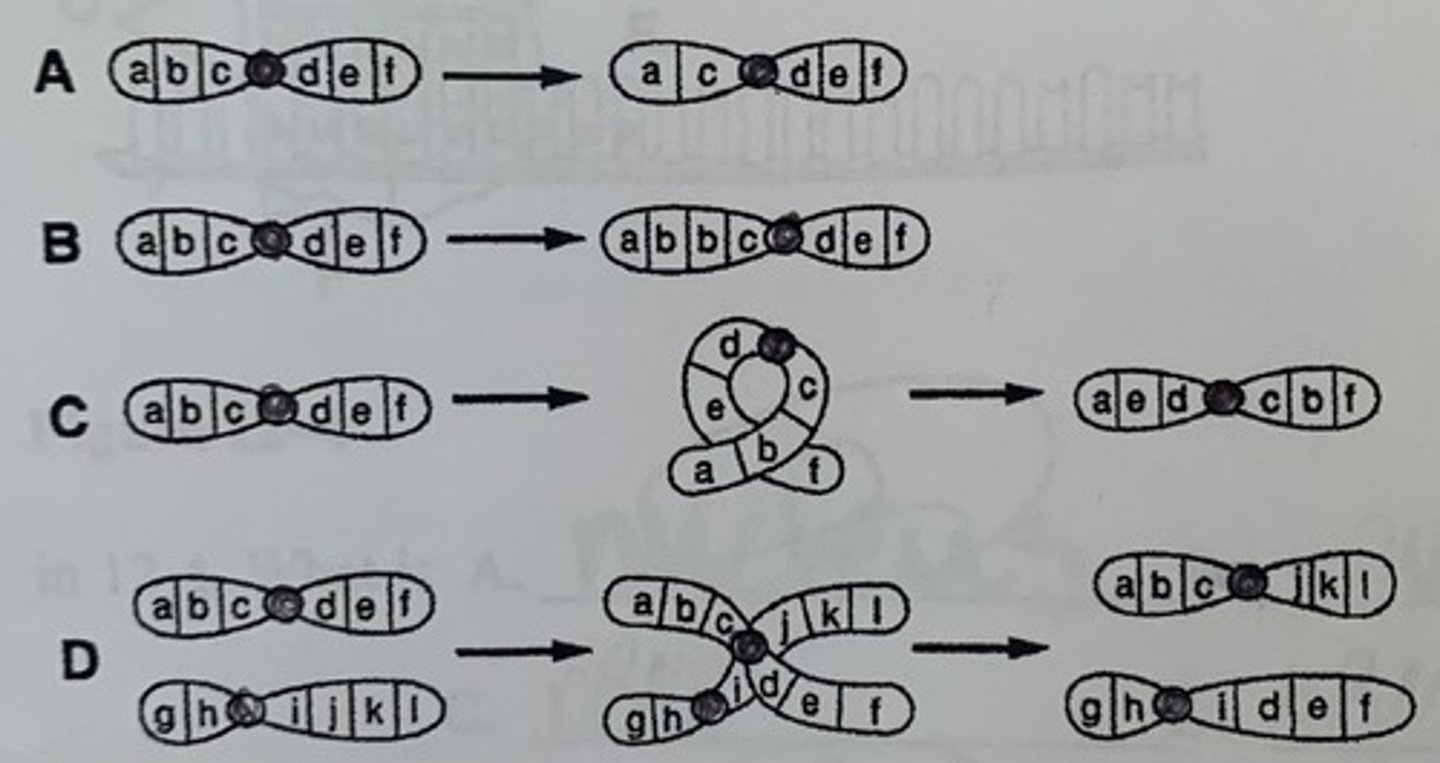
What are the three types of gene/point mutation?
1. Substitution
2. Insertion
3. Deletion
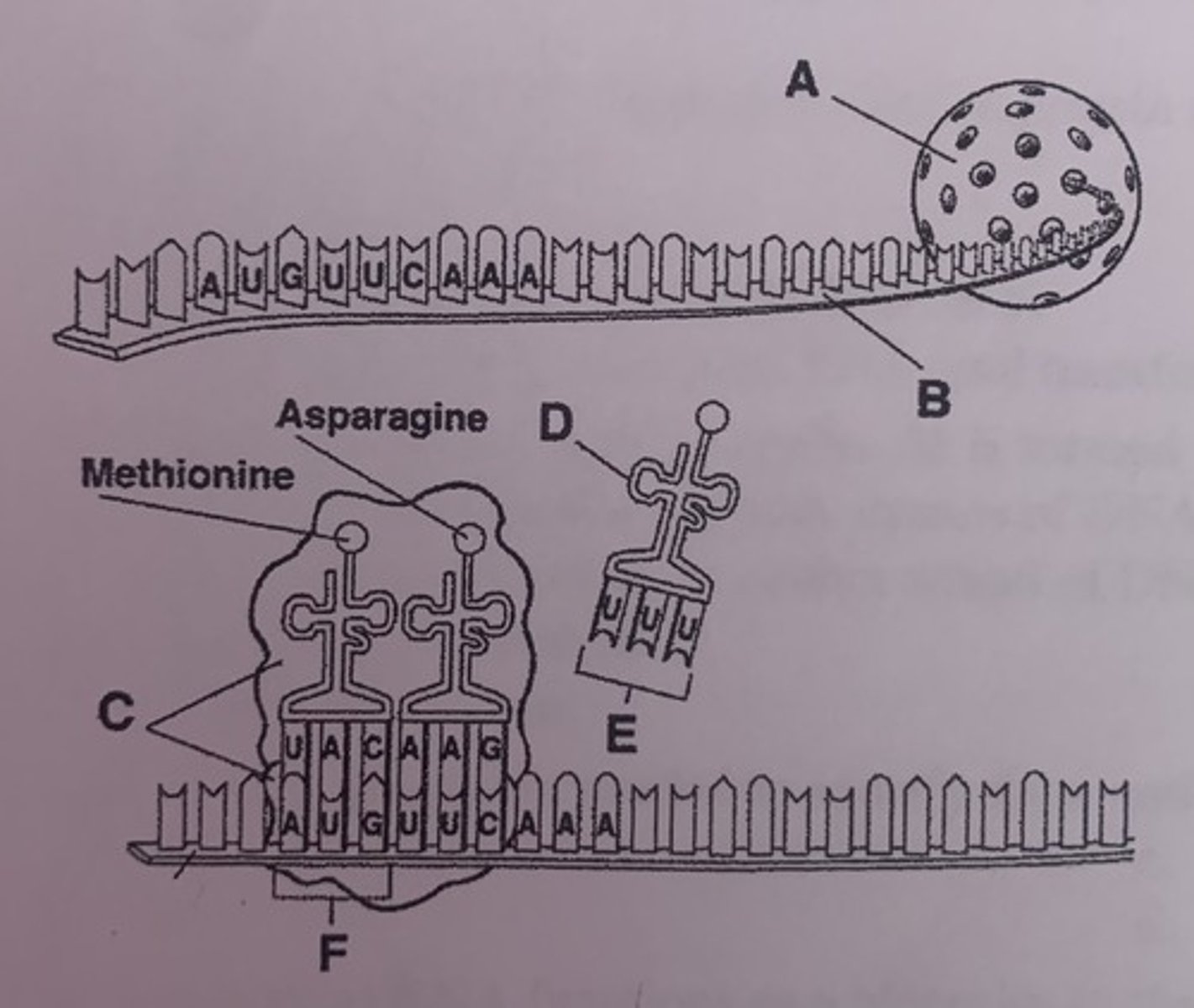
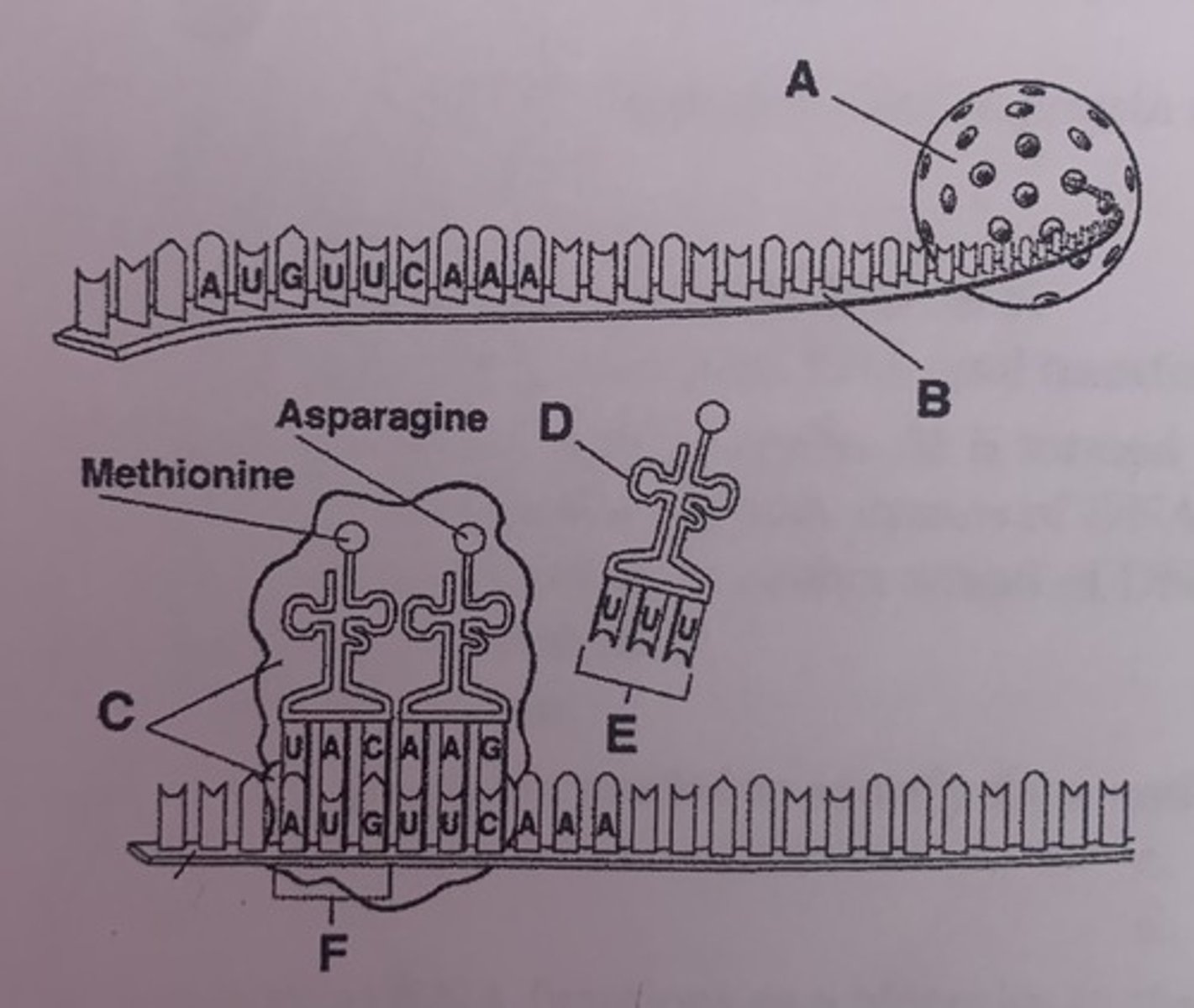
What is B?
mRNA
Use this to help with the next few questions
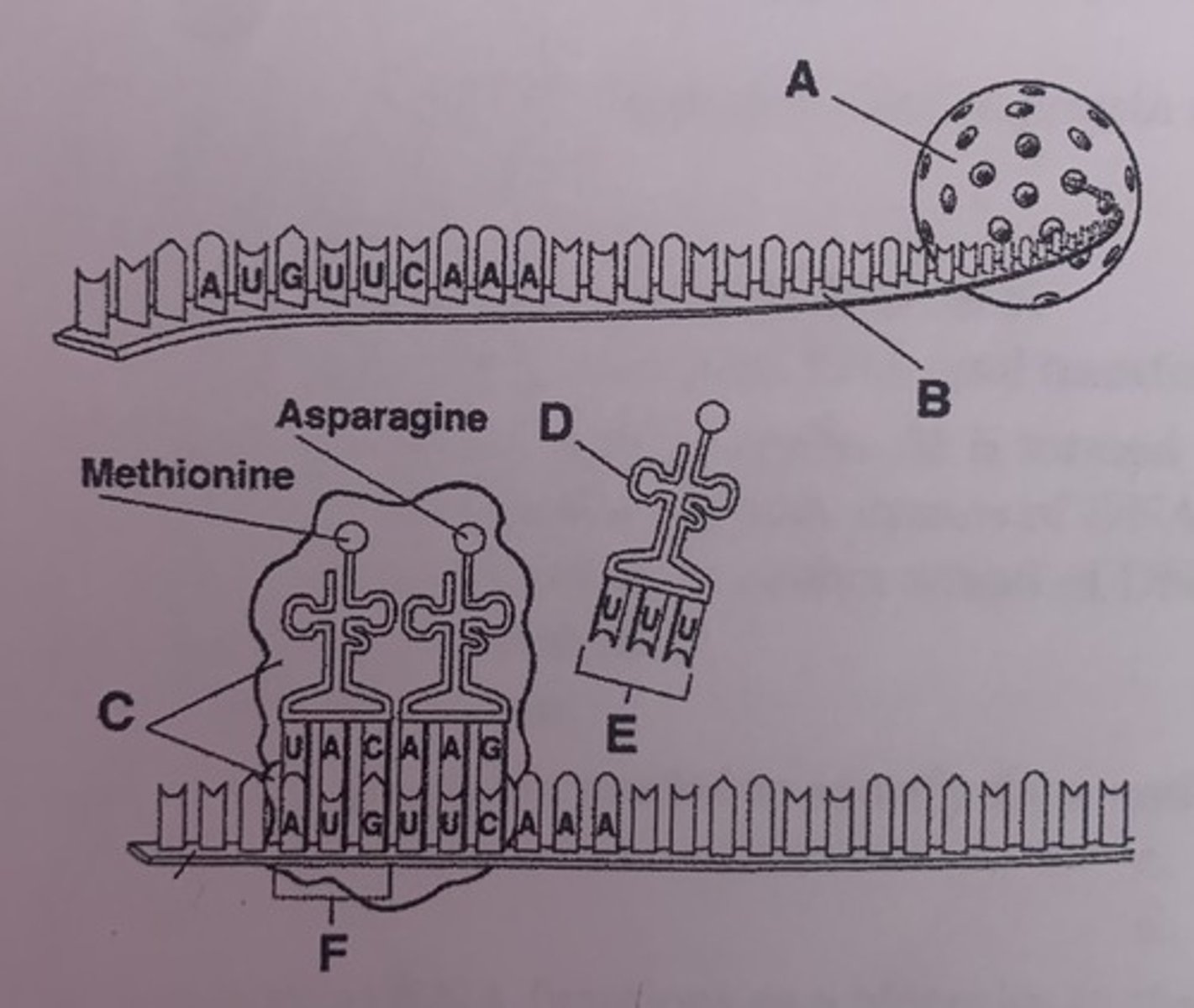
What is C?
rRNA
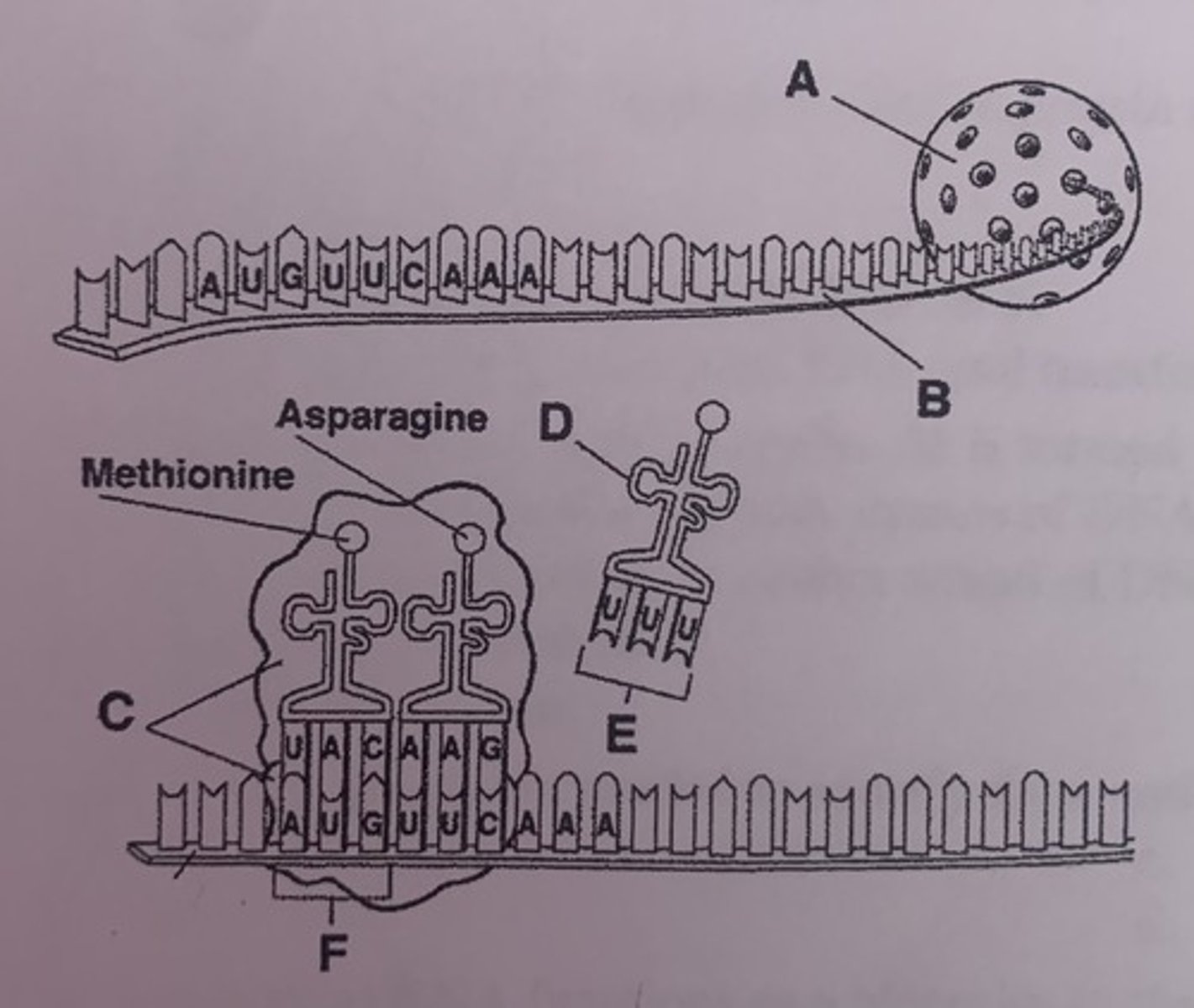
What is A?
nucleus
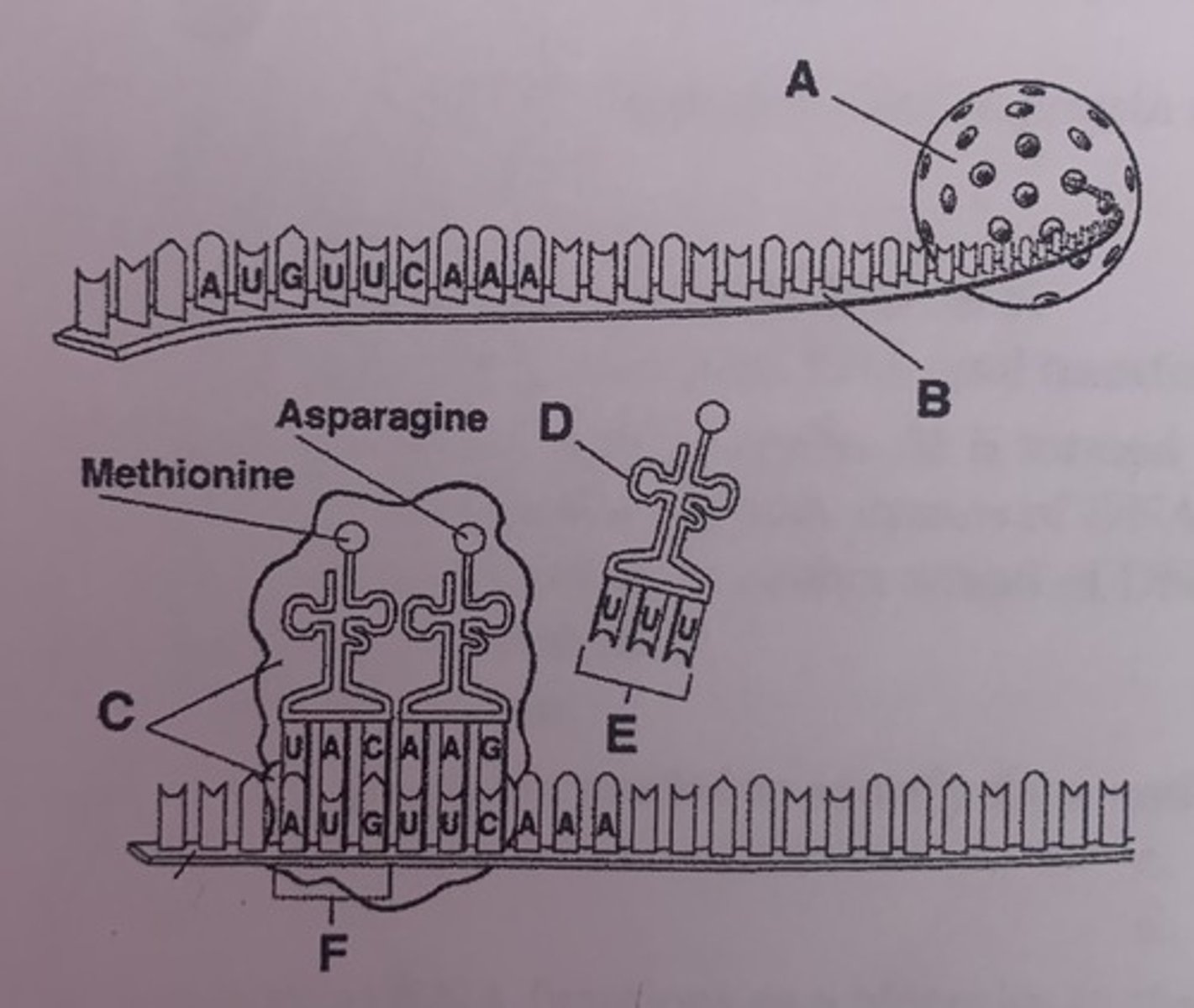
What is D?
tRNA
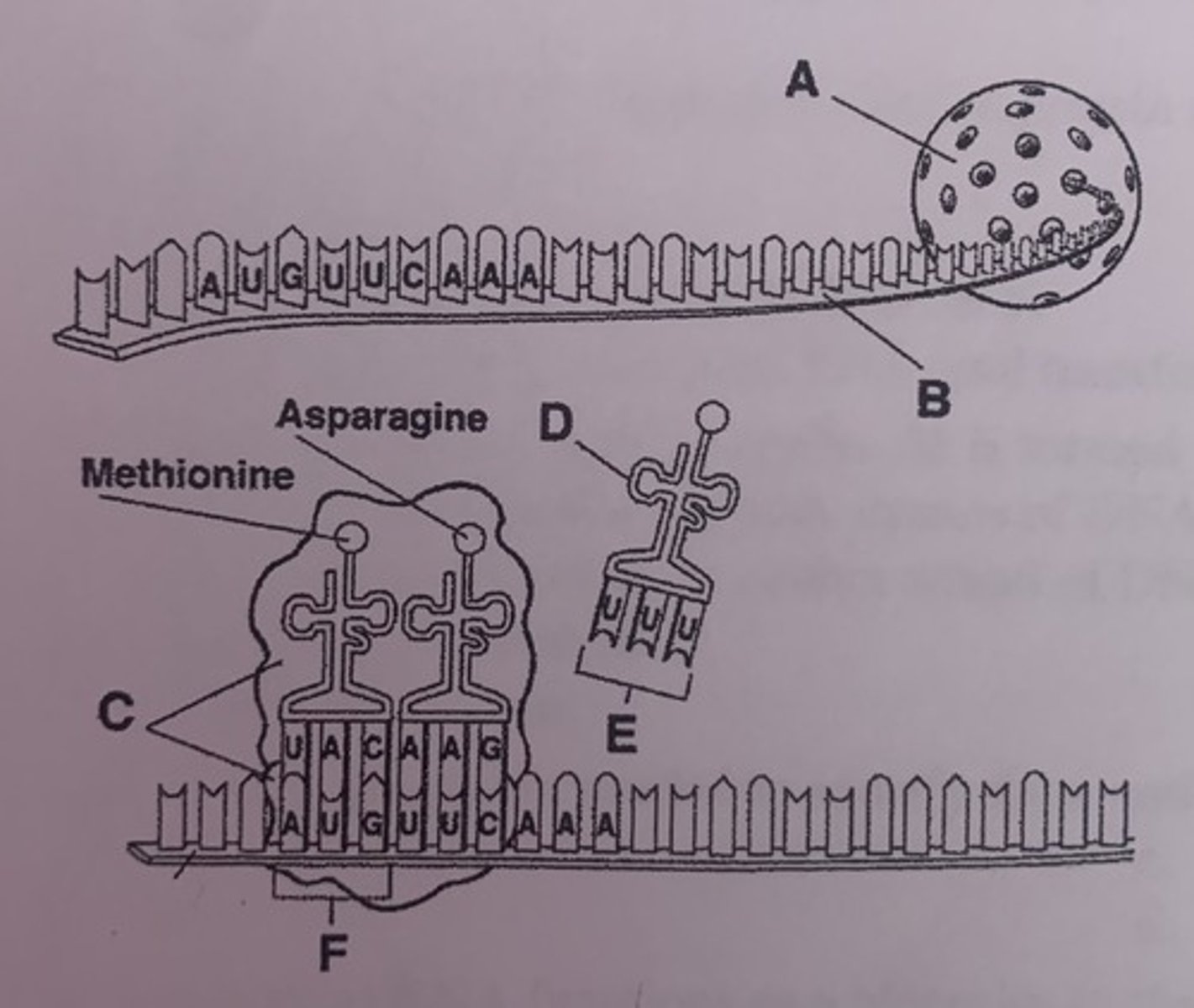
What is E?
anticodons
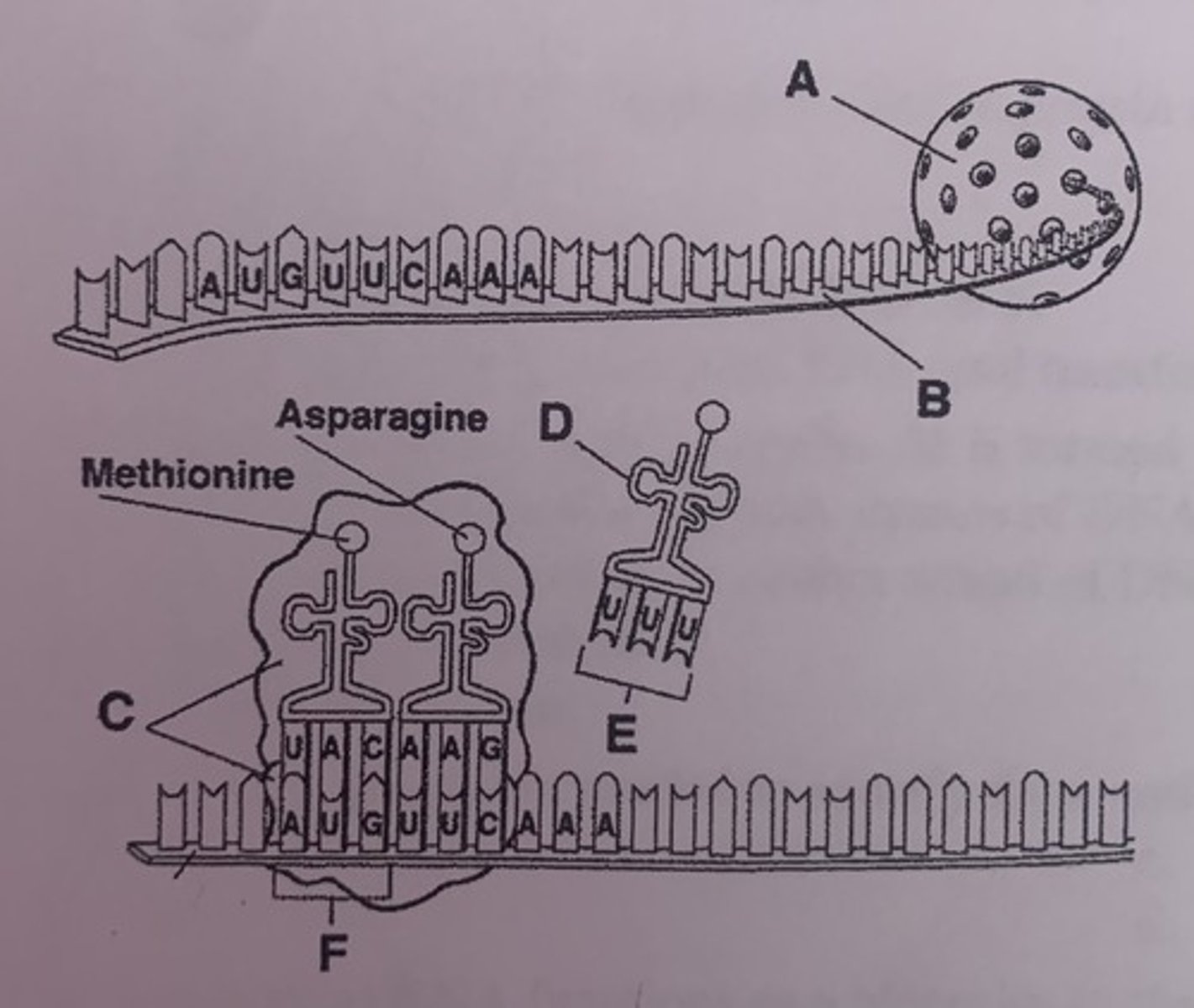
What is F?
start codon
Chapter 15 Test: Genes
.
Which of the following are shown in a karyotype?:
A. homologous chromosomes
B. sex chromosomes
C. autosomes
D. all of the above
D. all of the above