Topic 2 - Control of Sexual Behaviour
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
two stage sof sexual behvaior
appetitive behvior
consummatory behvior
Appetitive Behaviour:
Behaviour aimed at finding and obtaining a sexual partner
Consummatory Behaviour:
Behaviour of the actual sexual act
Appetitive Behaviour: Sexual Motivation
external
internal
external Appetitive Behaviour: Sexual Motivation
• Usually related to opposite-sex conspecifics
• Can be chemical stimuli we’re not consciously aware of (pheromones)
Can also be learned and of different sensory modalities
internal Appetitive Behaviour: Sexual Motivation
• Hormones
• Brain mechanisms
Pheromones:
species-typical molecules that trigger a specific response in another animal of the same species (e.g. sexual interest)
Putative role of pheromones in human sexual interest
• In other mammals, pheromones are detected by the vomeronasal organ- sepracte organ in the nasal passage
• There is debate about whether humans have a functional vomeronasal organ- we dont have a distinction of a spefic organ
• Olfactory epithelium can detect some pheromones in humans (and pigs)- thay have detection in the nasal cavety without a specific organ
so it may be the case that phemones do effect humans
what effect can pheromons have
Women’s t-shirts smell sexier during fertile phase of menstrual cycle- t shirt study about wether they think thay are attrective - smell sexier - unconsous
Androstadienone (in men’s sweat) triggers alertness, good mood and sexual arousal in women (but poor mood in men)- place on the upper lips of participants
Estratetraene activates male, but not female hypothalamic areas. third trimester of pregnacey in urine
armpits and grouns have hair to spred pheromones
femal and make molectules thay are thought to be the phemone molecules in humans
Estratetraene female
Androstadienone male
Role of sex hormones in sexual interest males
• Suppression of testosterone (T) reduces sexual interest (but not performance)
its in between their own levels not leves on avrage of males
• Anticipation of sexual encounter increases Testotrone
dosnt effect the factc to have ahveing an erection
• No correlation with individual differences in T
• Only motivation that is changes- sexual preditors not chanage who they are into
Role of sex hormones in sexual interest Females:
• Sexual interest fluctuates with cycling ovarian hormones (esp. oestradiol)
• Androgens (testosterone from ovaries, androstenedione from adrenal gland) increase effect of oestradiol up to 3 times
• Increase in T in females also with anticipation of sexual activity
Fluctuation in sexmotivation in teh menstaral cycles
increases over ovvulation
decreases in midlutial
slightly more in the premestral than middlutial
Similar patterns for masturbation
Shows the menstarl cycle and plots the percentage- lon term hetrosexal cupple
- Innituate the sex
Testosterone in females responds to anticipated sexual activity
Long distance cupples – when come together they wil have sex
Mesure the t at baseline- day to day
Day before visted, after visting patnerthay have an increase in T
consummatory sexual behvior: 4 stagges of arousal
- Excitement
- Plateau
- Orgasm
- Resolution
Excitement and Plateau: Parasympathetic Nervous System
early stages of phyiilogocal arousal for an exrection and clit growing and lubrication
parasypathetic nerouvs systen orgnised into two stages
pregangual neurons - acetylechline (mnicinic receptors)
postagngulan nerons - acetylcholine (muscarine receptors
pregangual neurons -
nerons taht sit begfore the ganaggulan
ganalgulan is a group on neralic cell bodies witch stit nxt to the target orgens
use acetecholone
niciten receptors
postagngulan neron
sit behind the agangilion onto the organs
uses acetylechline
musscarine receptors
Excitement and Plateau: the Mechanics
• Parasymphathetic stimulation relaxes smooth muscle in blood vessels
• More blood enters the genitals
into cavities with make the dick clit swell up
• Penile/Clitoral erection (“tumescence”)
• Engorgement of labia
• Vaginal lubrication
• Smooth muscle relaxation involves signalling by Nitric Oxide (NO)- if the blood goes in the to prevent it from going back out again muscle
• This increases the levels of cyclic GMP (cGMP)- responsible for the relaxation
how Viagra works
• Viagra inhibits the breakdown of cGMP by Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5), keeping the smooth muscle relaxed
dost cause an erection just keeps the erection going
the excitment cercit
5 is post gangilonic
4- pre ganglioninc
3 exictory inter neron in spinal cord- witch get input from 3 diffrent places
2- first ordern nreon of the sensroy system in the spinal cord witch gets stimulated by
1 witch is a sesory neron a perifiral sensory neron- sensation in genitasl
6&7 are exitory adn inhibitory input form the barin
local reflex arc just ahppinging in the area - soinal cord damage it happens but cant feel
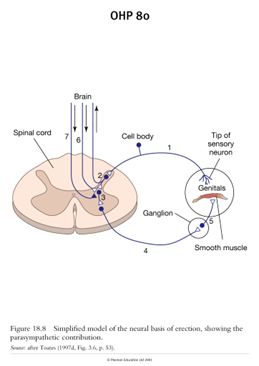
system
sensory imput
periphiral sesnory nuron
first ordern nreon of the sensroy system in the spinal cord
inter exctory spinal neon witch can also be stimulates by
extatory or inhibitory brain nerons from the spine
pregangulan
postgangula
to gentials
erectial disfunction
- Always “physical”
- Stress leads to increased sympathetic activity, which causes vasoconstriction
- Learned aversions can have central effects
- Many of these are difficult to tease apart
Orgasm: Sympathetic Nervous System