Anatomical directional terms
1/16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
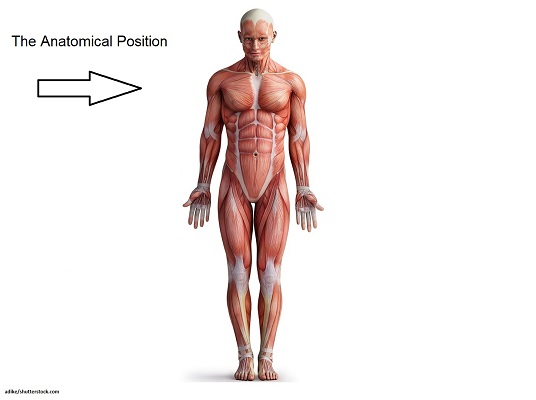
Anatomical Position
A standard position of the body used as a reference point in anatomy, where the body is facing forward, arms at the sides, and palms facing forward, and feet point forward.
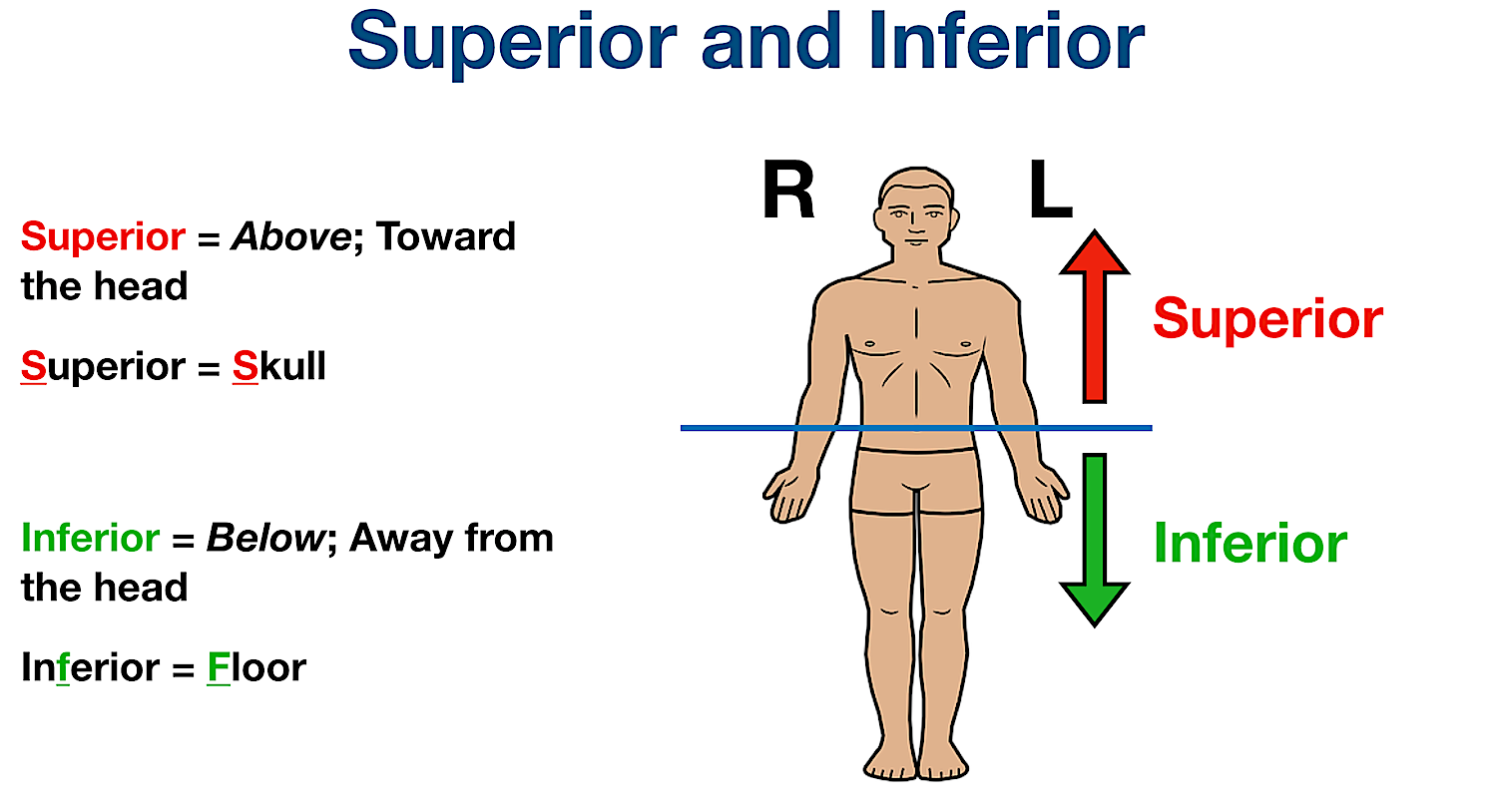
Superior
Refers to a position above or higher than another part of the body. Above toward the head. (Superior = skull)
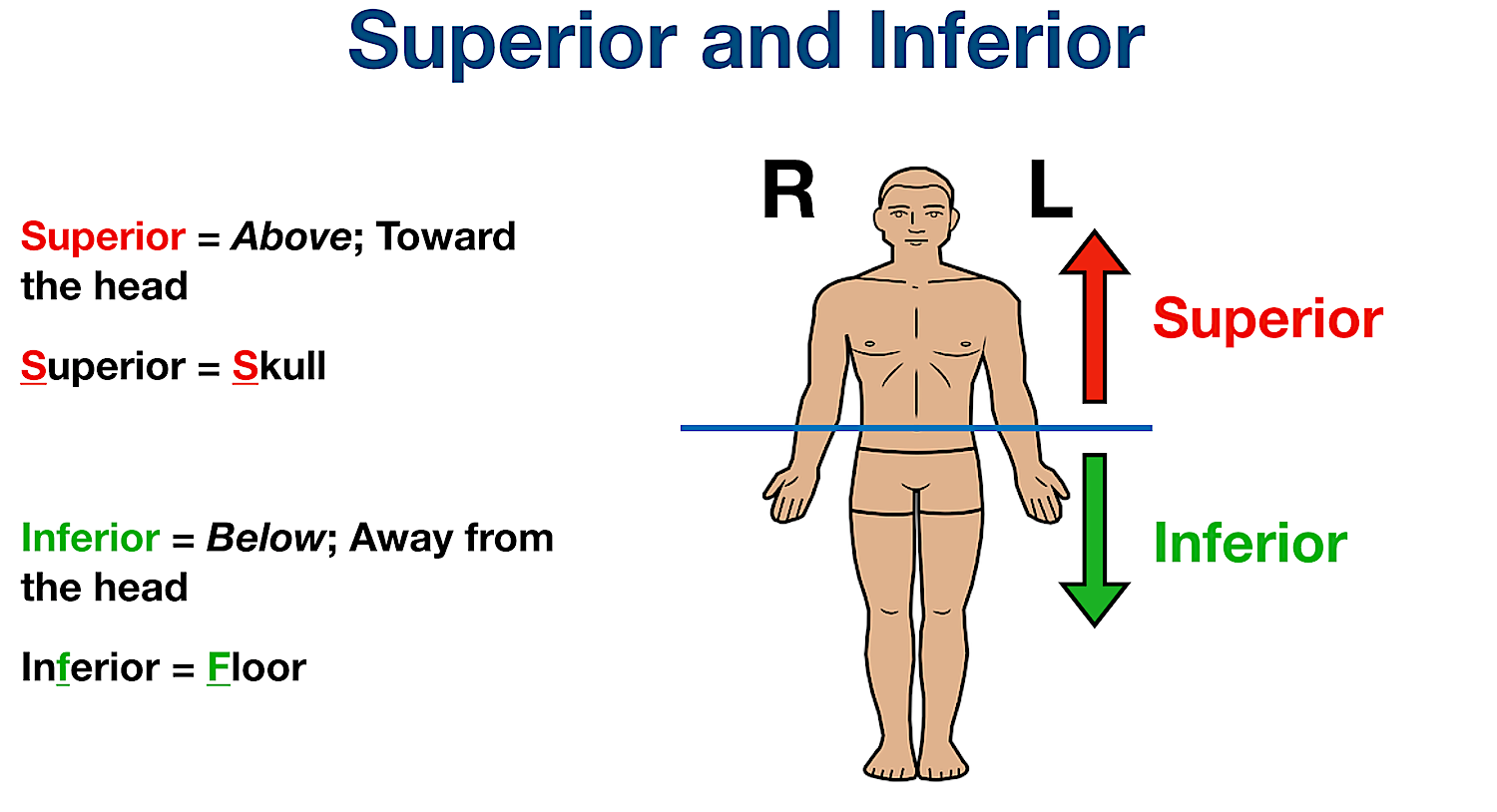
Inferior
Refers to a position below or lower than another part of the body. The foot is inferior to the hand. Below or toward the bottom of body. (inferior = further)
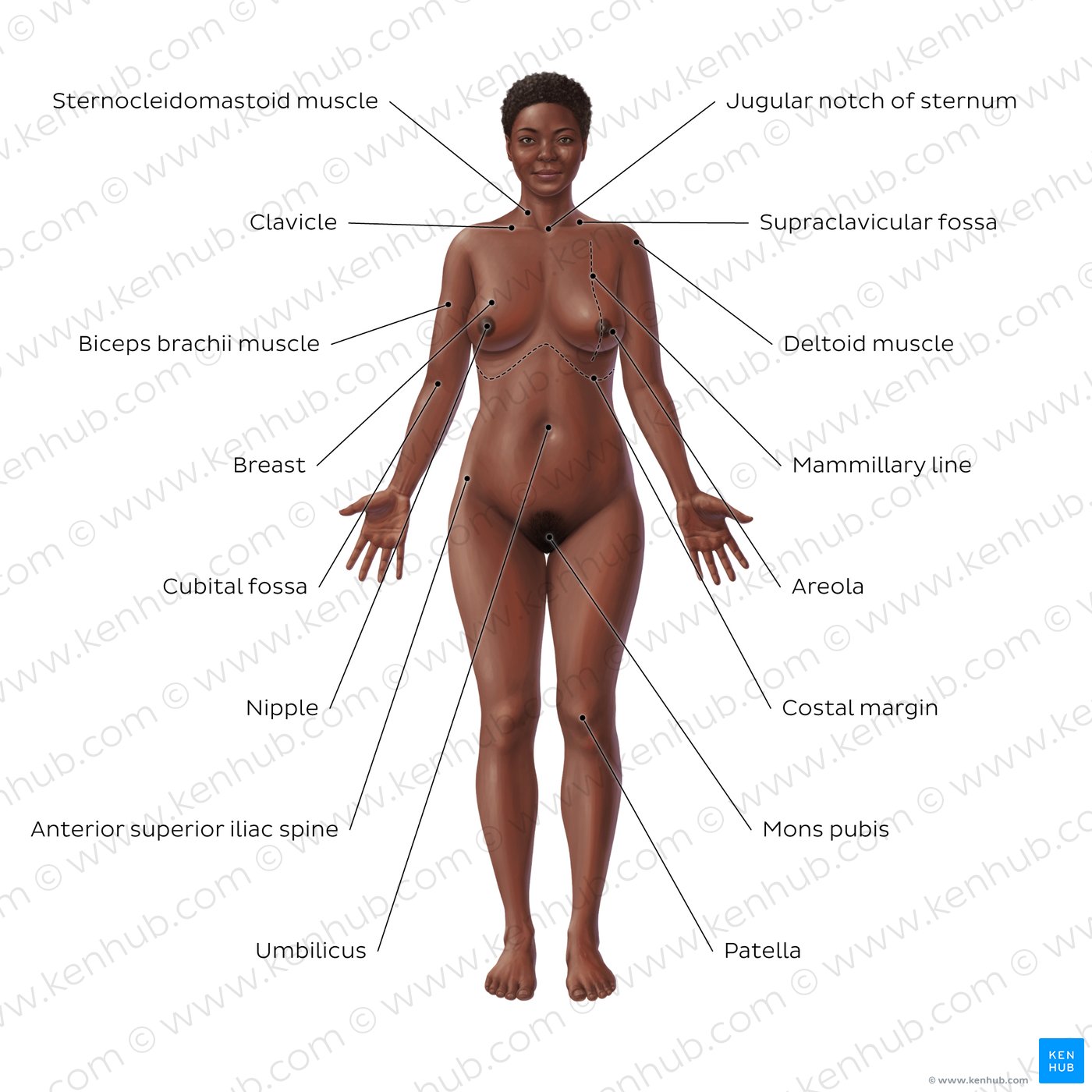
Anterior
Refers to the front side of the body. Knee caps are anterior part of the body. Ventral.
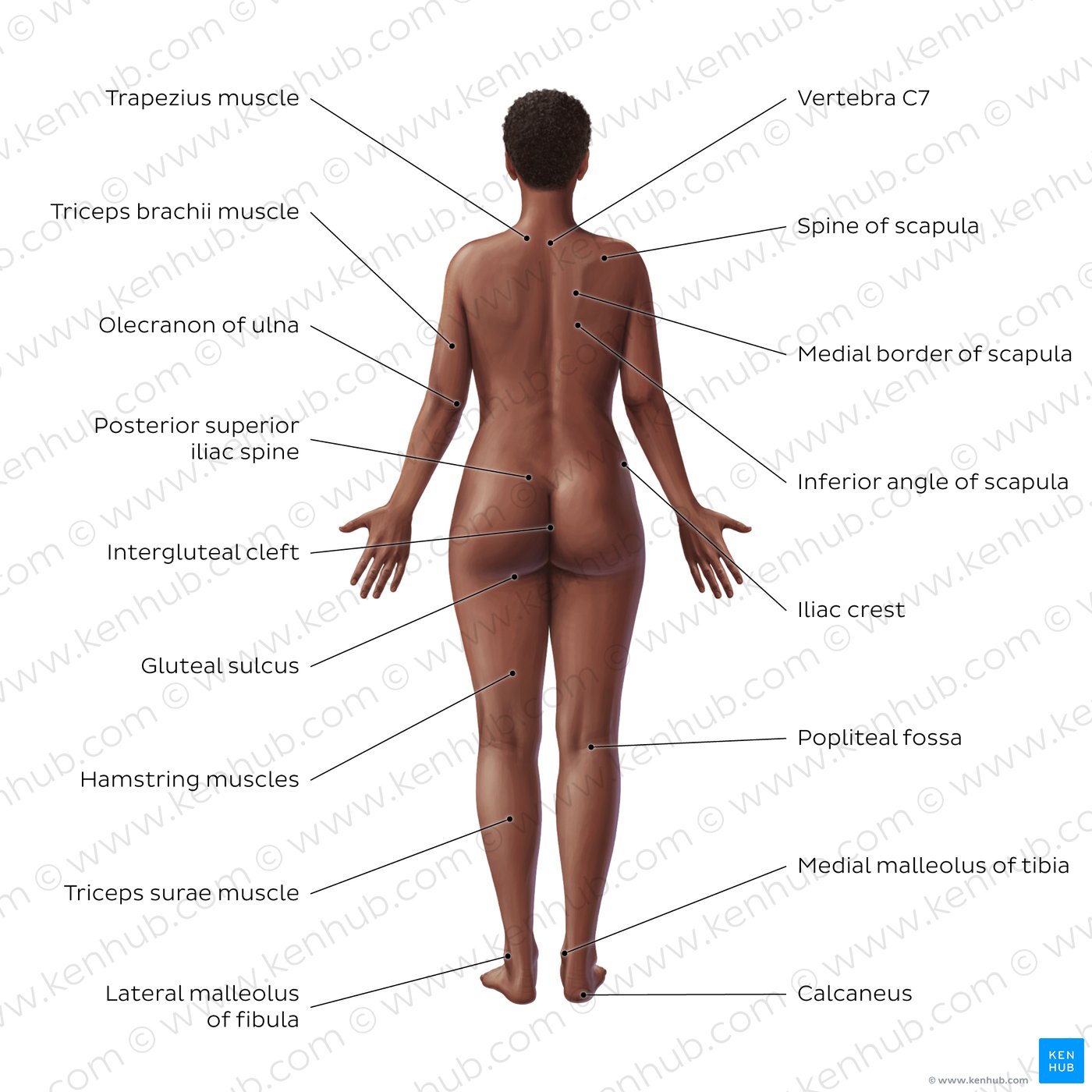
Posterior
Refers to the back side of the body toward the back. Dorsal.
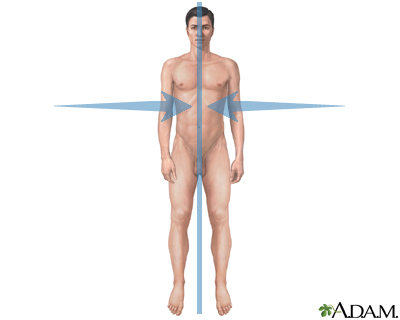
Medial
Refers to a position closer to the midline of the body.
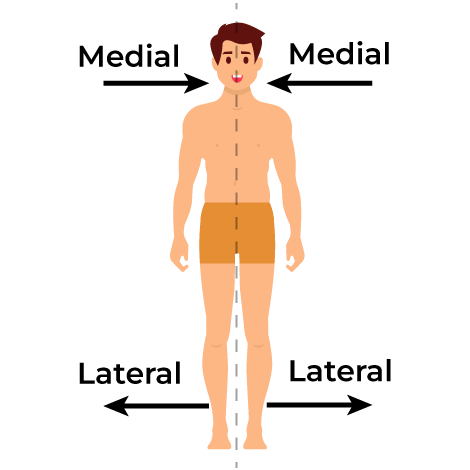
Lateral
Refers to a position further away from the midline of the body. (closer to the side)
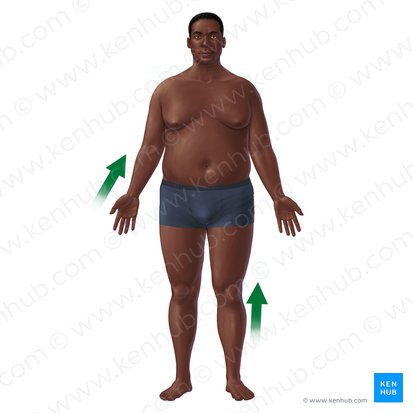

Proximal
Refers to a position closer to the centre/ trunk of the body or point of attachment. (The knee is proximal to the ankle) - knee closer to centre
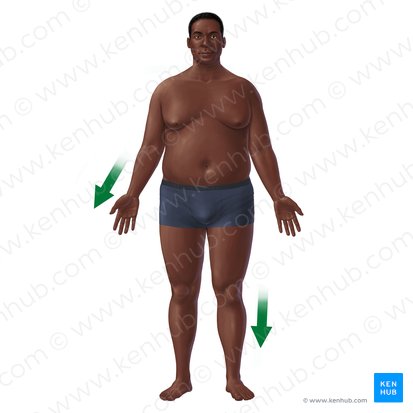
Distal
Refers to a position further away from the centre/trunk of the body or point of attachment. (The wrist is distal to elbow) - wrist further from the centre than elbow
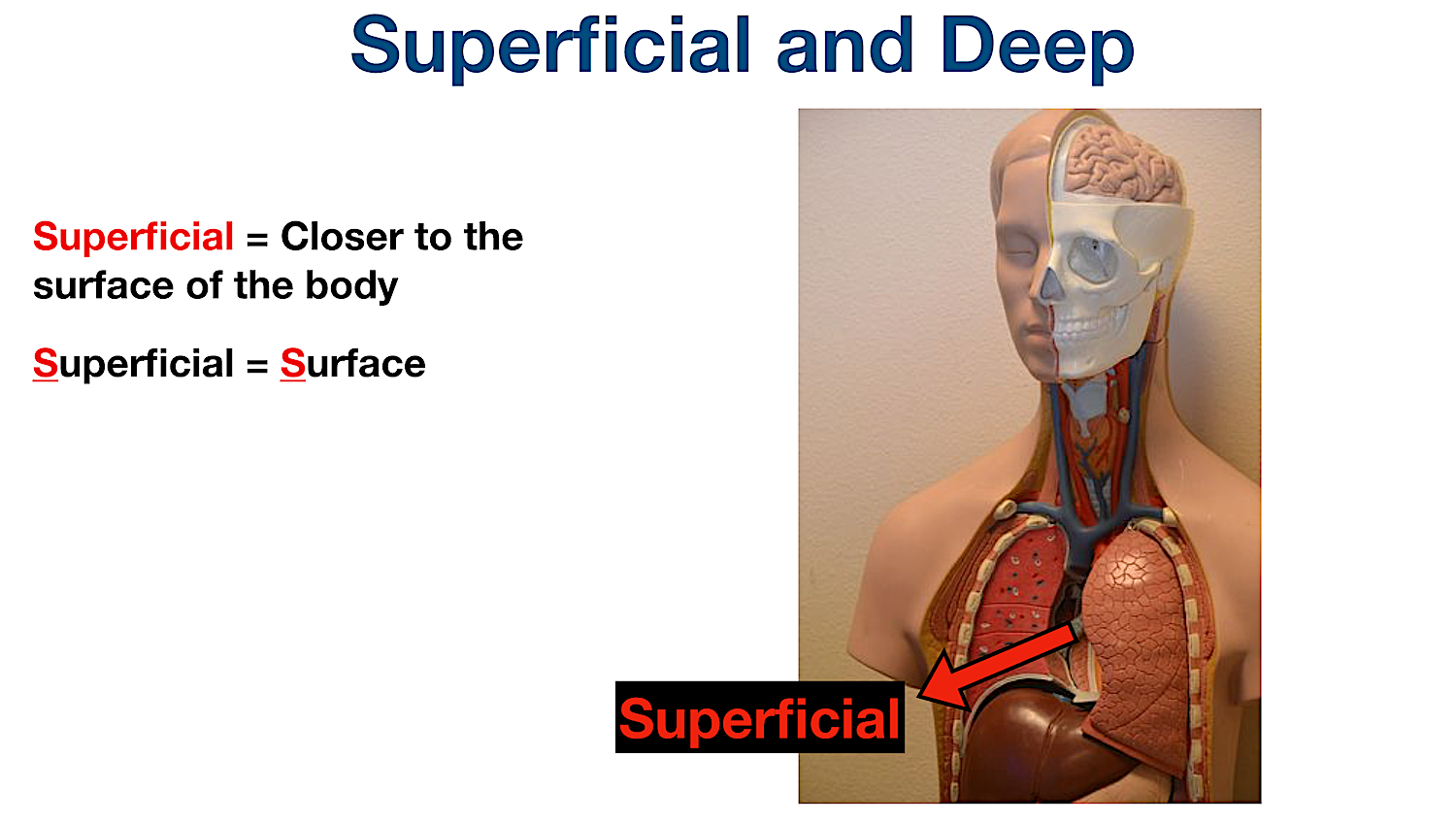
Superficial
Refers to a position closer to the surface of the body. (The skin superficial to muscles) (the skull superficial to brain) (superficial = surface)
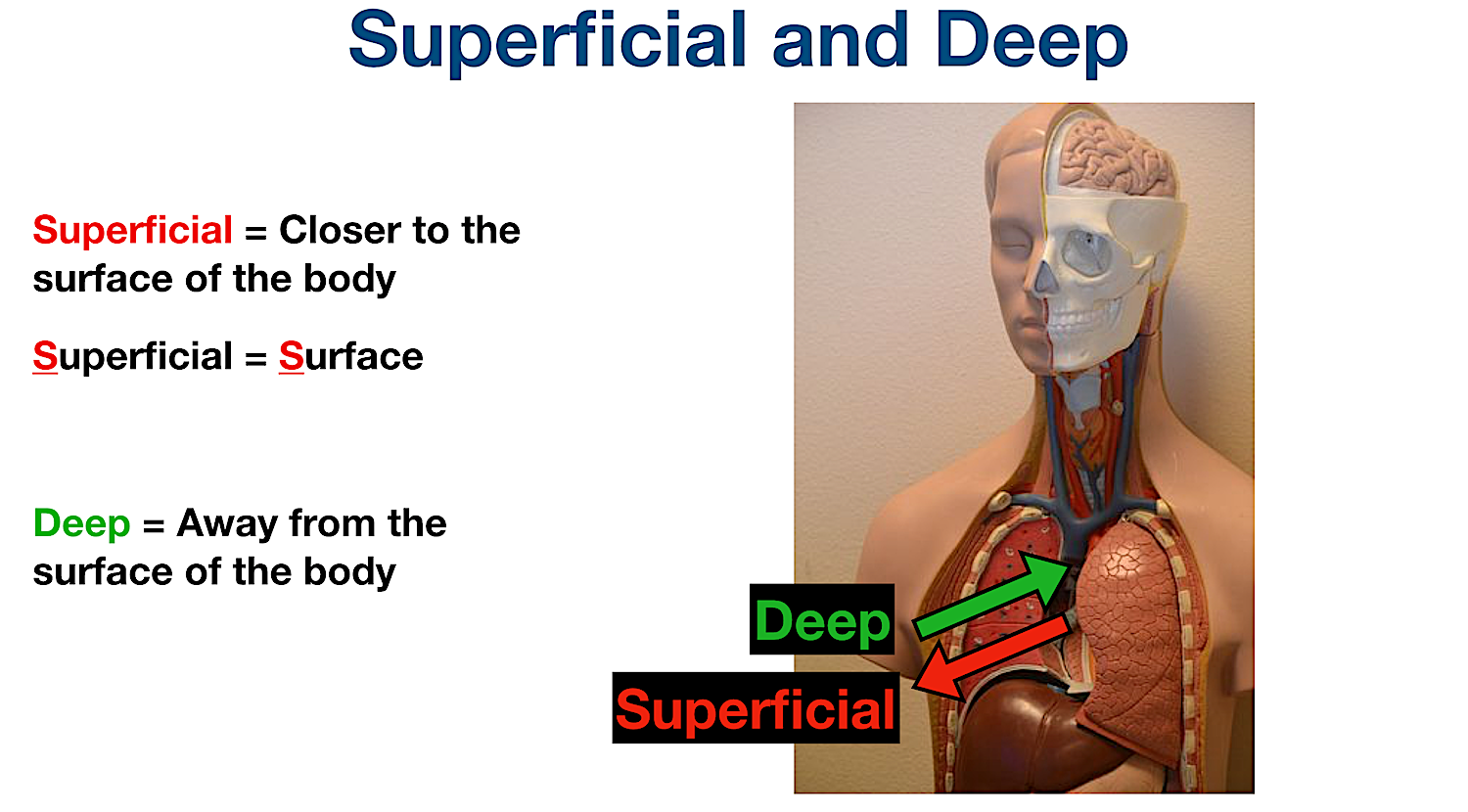
Deep
Refers to a position further from the surface of the body. (The brain is deep within skull) (the heart is deep to the skin)
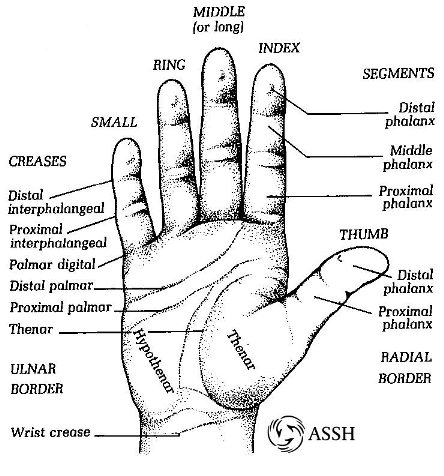
Palmar
Refers to the palm side of the hand.
Plantar
Refers to the sole of the foot.
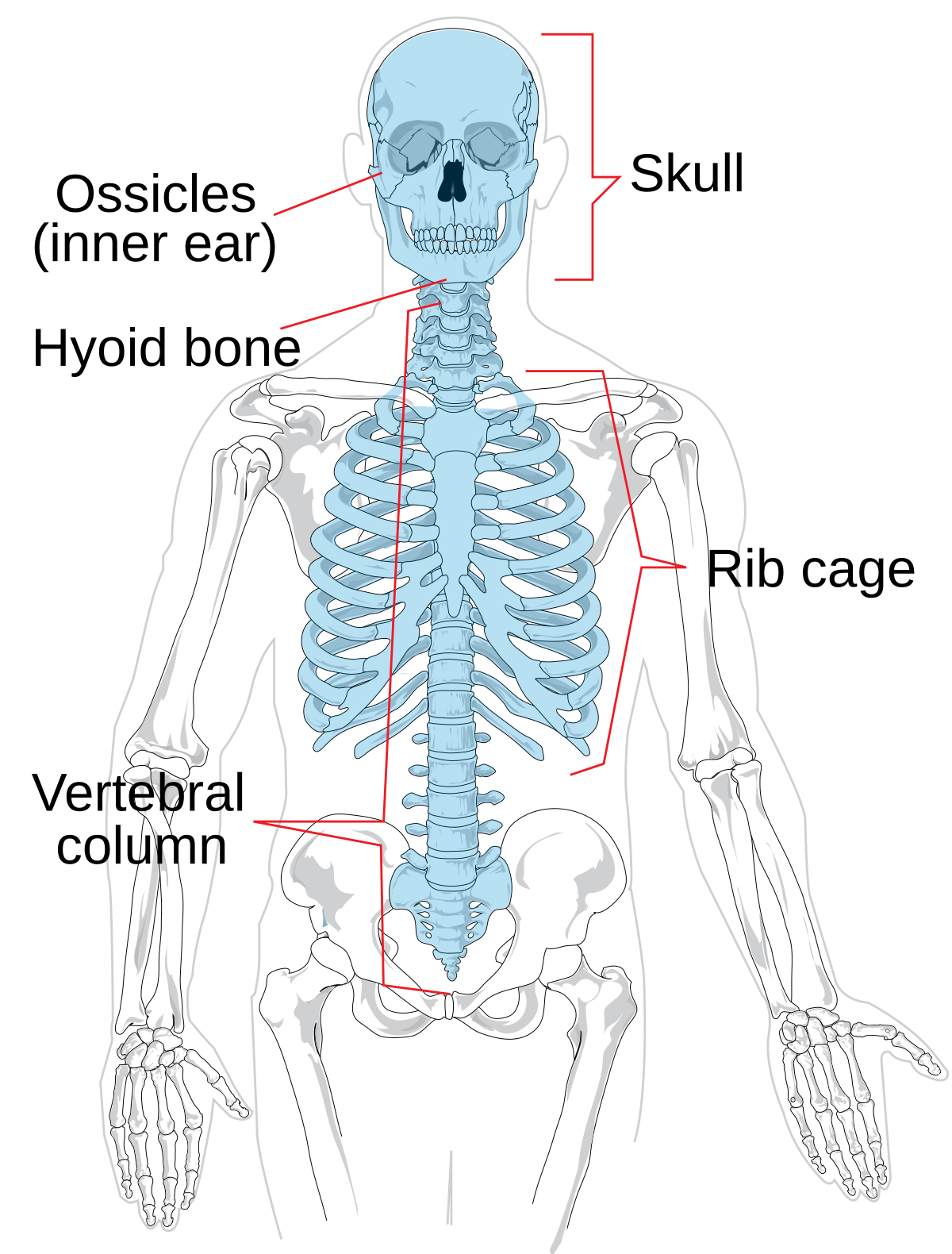
Axial
Refers to the head and trunk of the body.
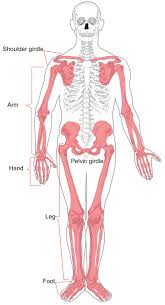
Appendicular
Refers to the limbs of the body. (Appendicular)
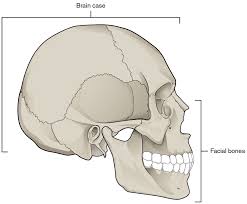
Cranial
Refers to anything pertaining to the skull or the head (toward the head). For example, the cranial cavity houses the brain.
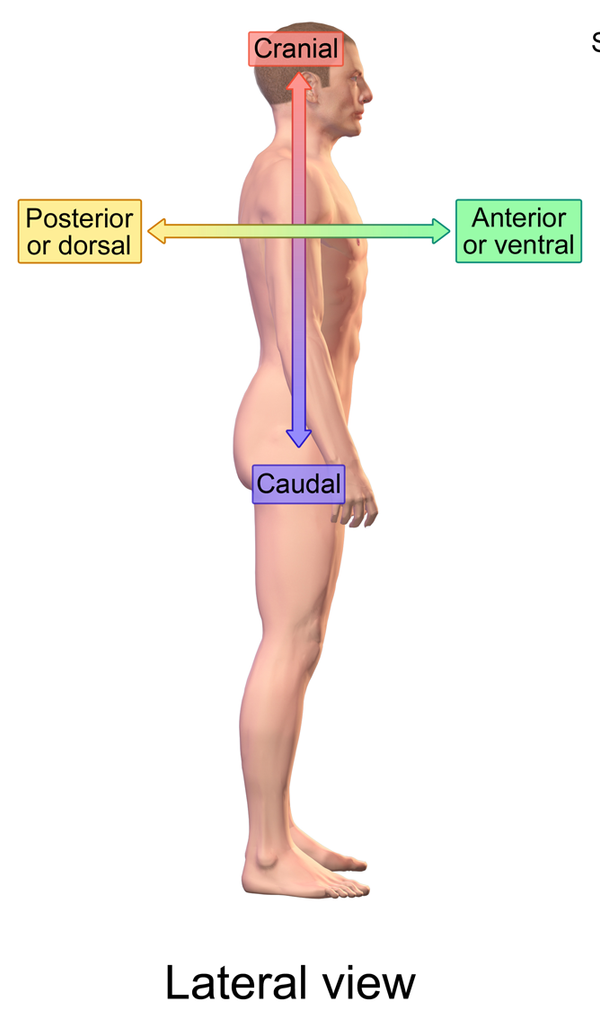
Caudal
Refers to a position toward the tail or the lower part of the body. For example, in a quadruped anatomy, structures that are caudal are toward the tail end.