Additive manufacturing MECH3775
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is Photolithography?
Photolithography is a process that uses light to transfer a geometric pattern from a photomask to a light sensitive chemical called a photoresist.
What are some manufactured electronics photolithography can be used to make?
semiconductors
MEMS (micro-electrical-mechanical systems)
PCBs
LCD and OLED displays
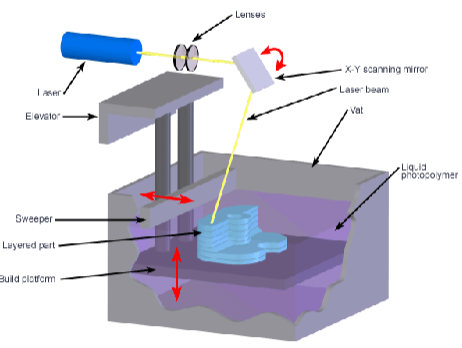
What was the original SLA process?
used a uv wavelength laser
the laser scans the liquid surface and causes the liquid to polymerise
the platform drops and layer and repeats
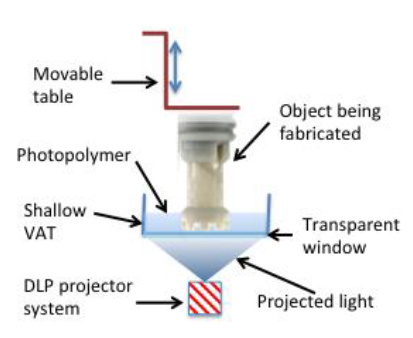
What is projection based SLA?
typically uses a DLP but LCD are now emerging
image is projected from below and polymerises a layer at a time
the part is moved up and this repeats
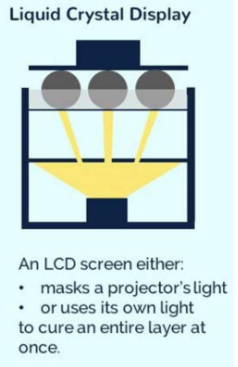
What is LCD SLA?
Uses a LCD screen to mask regions of light
the systems can be low cost
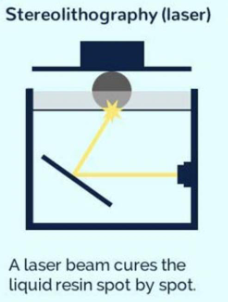
What is SLA? (method of patterning with light)
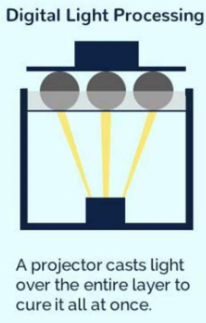
What is DLP? (method of patterning with light)
What is LCD? (method of patterning with light)
What are the advantages of top down projection methods?
resolution of the part is higher
the current later only adheres to the previous layer
simplicity for retrofitting
What are the Disadvantages of top down projection methods?
surface characteristics of the resin can affect the part quality
the process is usually longer due to the re coating step
viscosity of the resin determines the thickness of the part
What are the advantages of bottom up projection methods?
so specific re coating stage needed
ultra thin layers can be produced
reduce of waste materials
What are the disadvantages of bottom up projecting?
light has to pass through more surfaces causing aberrations and less intensity
the current layer may adhere to the surface of the vat (damaging the part)
harder to retrofit components
what are the materials used for Stereolithography?
light curable resins
resins consist of a monomer, photo initiator and an inhibitor
How does photopolymerisation work?
Photopolymerisation is initiated by excitement of the photoinitiator by UV radiation which produces free radicals
Photopolymerisation causes the linking of small molecules (monomers) to larger chain like molecules (polymers)
Why do the materials used for Photopolymerisation contain additives and what are they?
to try to simulate common engineering materials
they are all based on epoxy/acrylic formulations of non-polymerised liquid
some can change the colour/improve stability/are used for specialised applications
What is post-processing of materials for Photopolymerisation?
ensures complete polymerisation
ensures complete cross linking of polymer bonds
more stable and integrity
curing time depends on mass and material
What are some positives of the post processing for Photopolymerisation?
supports can be easier to remove before final cure
materials can mimic traditional engineering polymers
process energy input low compared to thermal AM systems
Very accurate / very good surface finish
parts can be mechanically/chemically smoothed
What are some negatives of the post processing for Photopolymerisation?
the machine is expensive
support structures are always required
stereolithogrpahy resins are often toxic (PPE is needed)
materials must be photo-curable resins
parts age in the sunlight
material change requires thorough cleaning
part orientation affects surface finish