Intro to Professional Nursing - Legal (Chapter 6)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Learning Objectives:

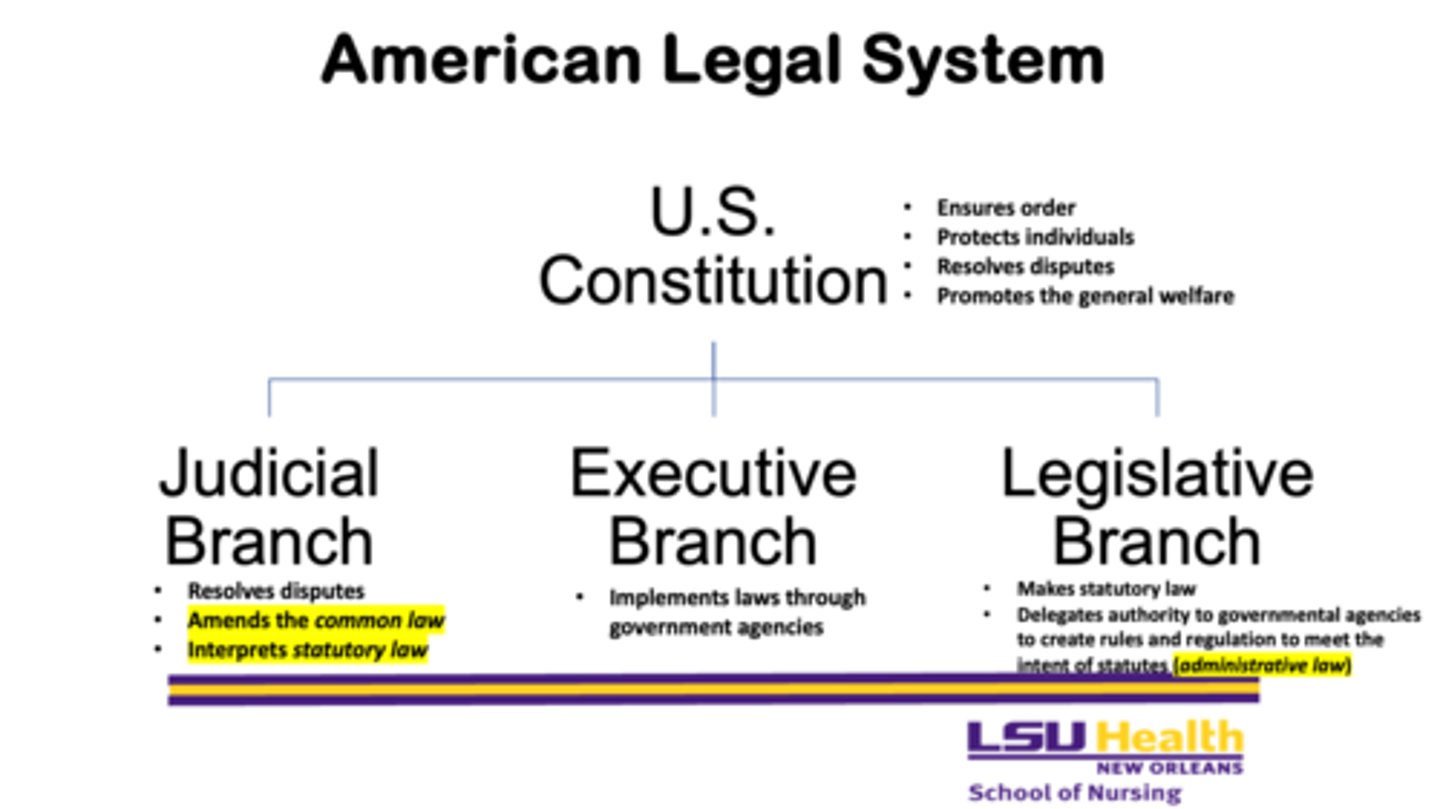
What are the three branches of the American legal system?
1. judicial branch
2. executive branch
3. legislative branch
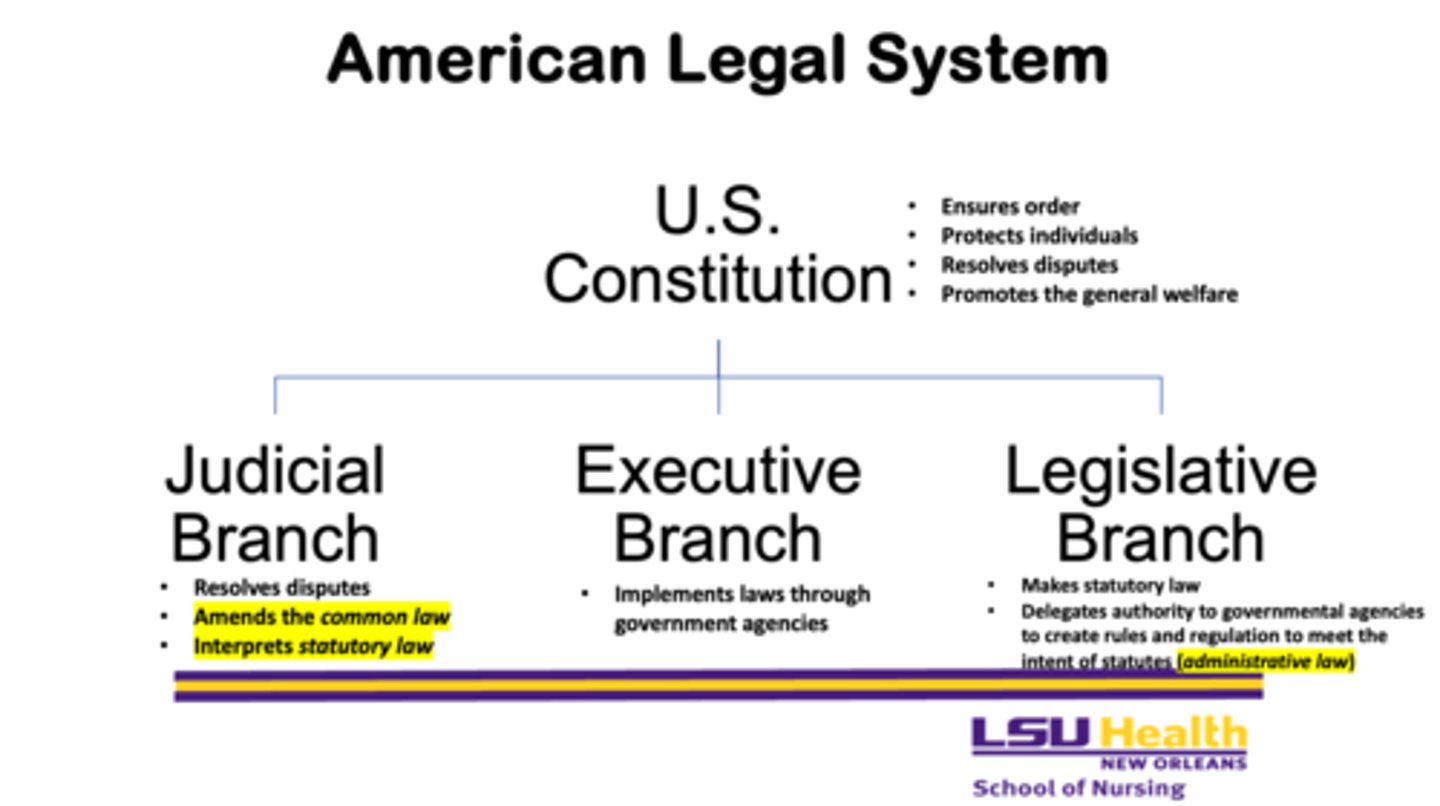
What are the four reasons that the U.S. Constitution is important?
1. ensures order
2. protects individuals
3. resolves disputes
4. promotes the general welfare
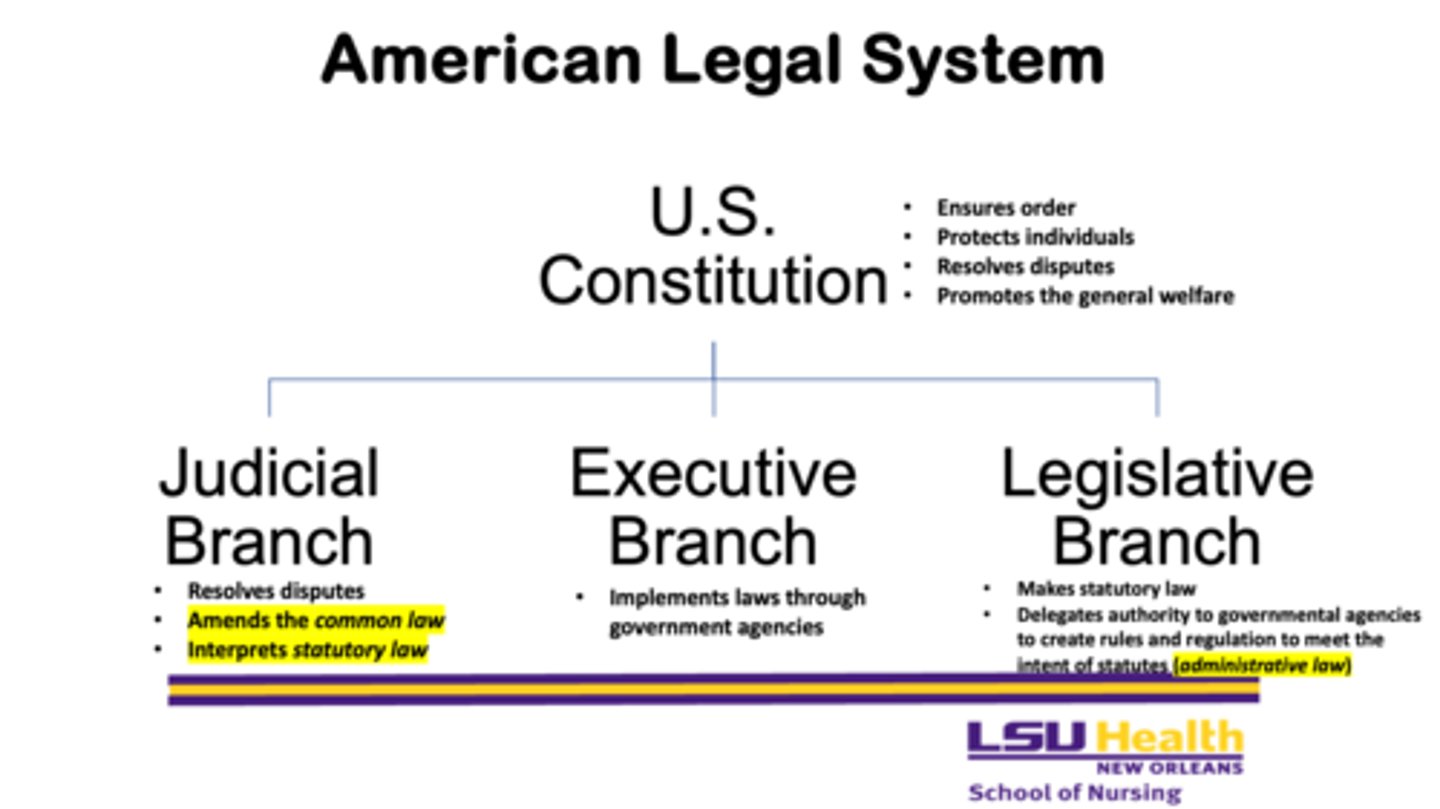
What does the judicial branch do? Why is it important?
- resolves disputes
- amends the common law
- interprets statutory law
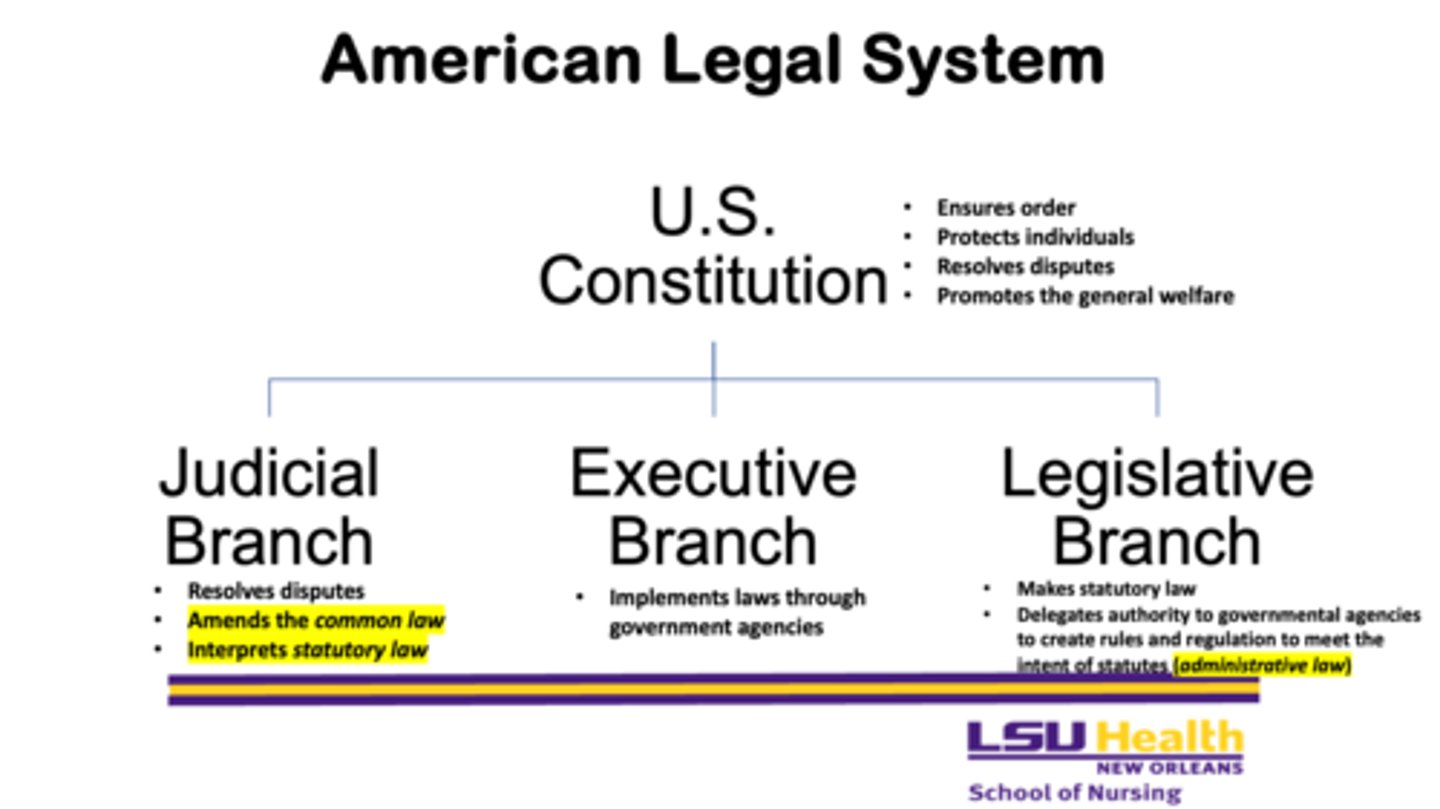
What does the executive branch do? Why is it important?
- implements laws through government agencies
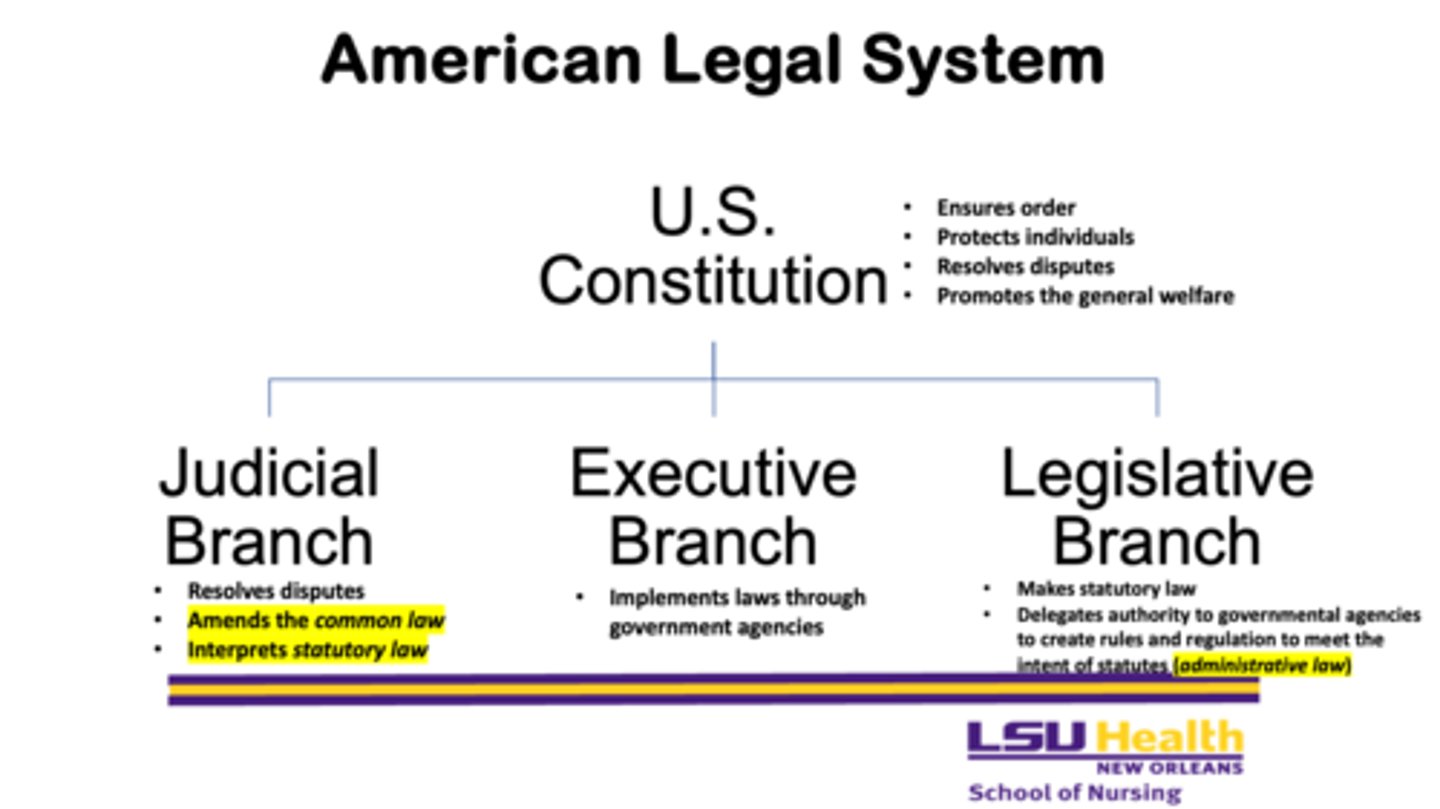
What does the legislative branch do? Why is it important?
- makes statutory law
- delegates authority to government to create rules and regulations to meet the intent of statutes (administrative law)
Which branch interprets statutory law and amends the common law?
Judicial Branch
Which branch creates administrative law by delegating authority to agencies?
Legislative Branch
What is an example of an administrative law as it pertains to nursing?
Title 9

Who establishes and regulates the boundaries of nursing practice?
- established and regulated at the state level (the boundaries of the practice of nursing and many others)

What are State Boards of Nursing (SBNs)?
- the regulatory bodies by which nursing practice acts are administered and enforced

What does the State Board of Nursing (SBN) do to expand the law?
- publicizes rules and regulations that expand the law, giving full meaning to the nursing practice act in each state

Who lobbies for updates to nursing practice acts?
- state nurses associations lobby state legislators for appropriate updating of nursing practice acts

State boards of nursing (SBNs) are the __________ by which nursing practice acts are __________ and __________
- regulatory bodies; administered; enforced

What is the purpose of the Nurse Practice Act in each state?
- to define and regulate the practice of nursing by outlining standards, qualifications, and disciplinary guidelines

What are the six objectives of the Nurse Practice Act?
1. Defines the standards and scope of professional nursing
2. Describes the authority, power, and composition of the board of nursing
3. Defines educational program standards
4. Sets the minimum educational qualifications and other requirements for licensure
5. Determines and protects the legal titles and abbreviations nurses may use
6. Provides for disciplinary action of licensees for certain causes

What is the purpose of the NCSBN Model Nursing Practice Act (2012)?
- to guide states in developing consistent and comprehensive nursing practice laws and regulations

According to the NCSBN Model Nursing Practice Act (2012), what should be clearly differentiated?
- advanced nursing practice and generalist nursing practice

What authority should state boards of nursing have regarding advanced nursing practice?
- they should have authority to regulate advanced nursing practice, including prescription writing

What authority should boards of nursing have over unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)?
- authority to oversee unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)

What does the NCSBN Model Act clarify about nurses' responsibilities?
- clarifies the nurse’s responsibility for delegation to and supervision of their personnel

What type of licensure does the NCSBN Model Nursing Practice Act support?
- it supports mandatory licensure for nurses while maintaining flexibility for the changing nature of nursing practice

In many states, what type of law is the Nurse Practice Act (NPA)?
- a statutory law that affects nursing practice within the bounds of the state

Why is the Nurse Practice Act (NPA) important to professional nurses?
- it defines legal boundaries, protects public safety, and sets professional standards for nursing practice

Who developed and suggested language for the content of state NPAs?
- the American Nurses Association (ANA) and the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN)

What does the 1996 ANA Model Practice Act encourage?
- consideration of issues within nursing practice acts and awareness of state legislative and regulatory realities

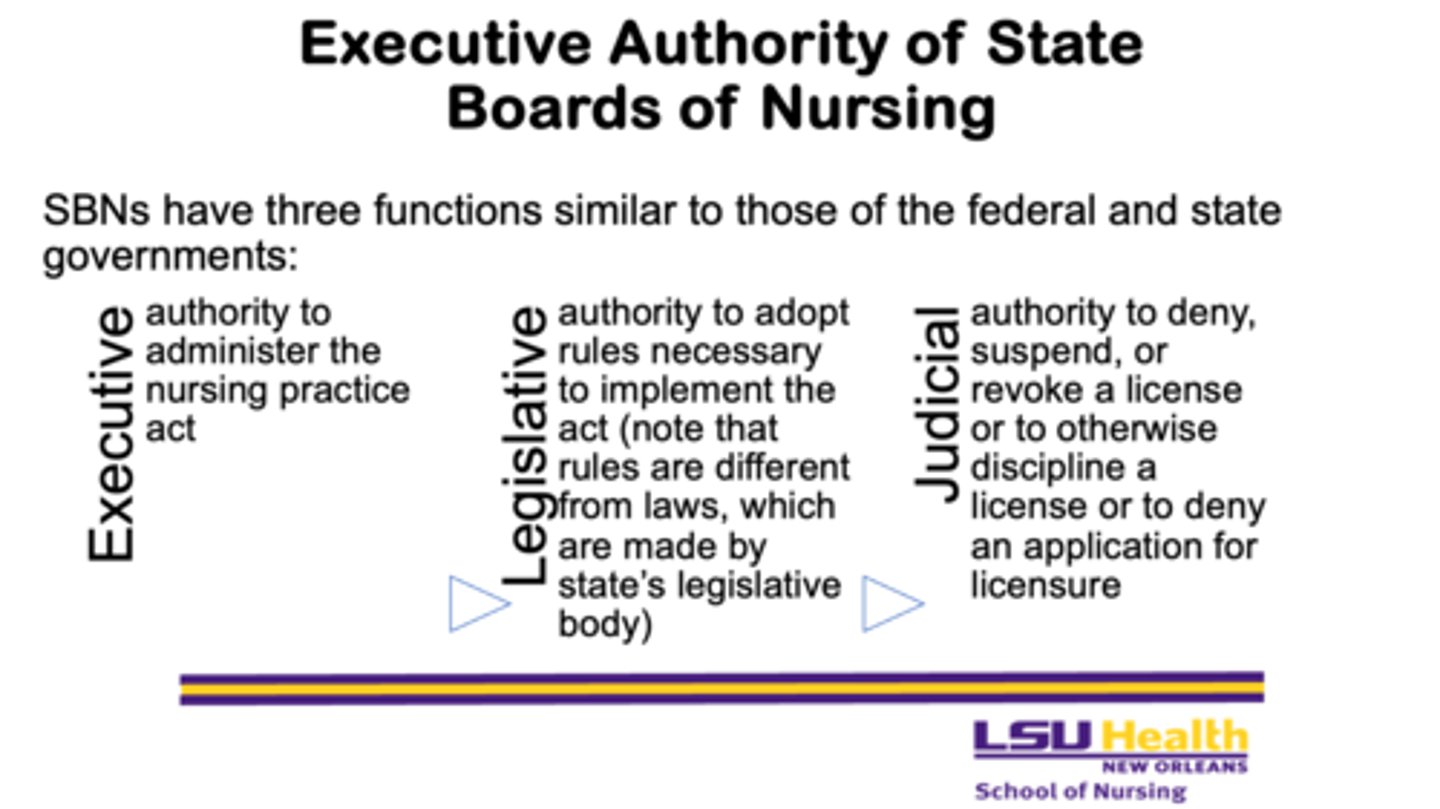
What are the three functions of State Boards of Nursing (SBNs)?
1. Executive
2. Legislative
3. Judicial
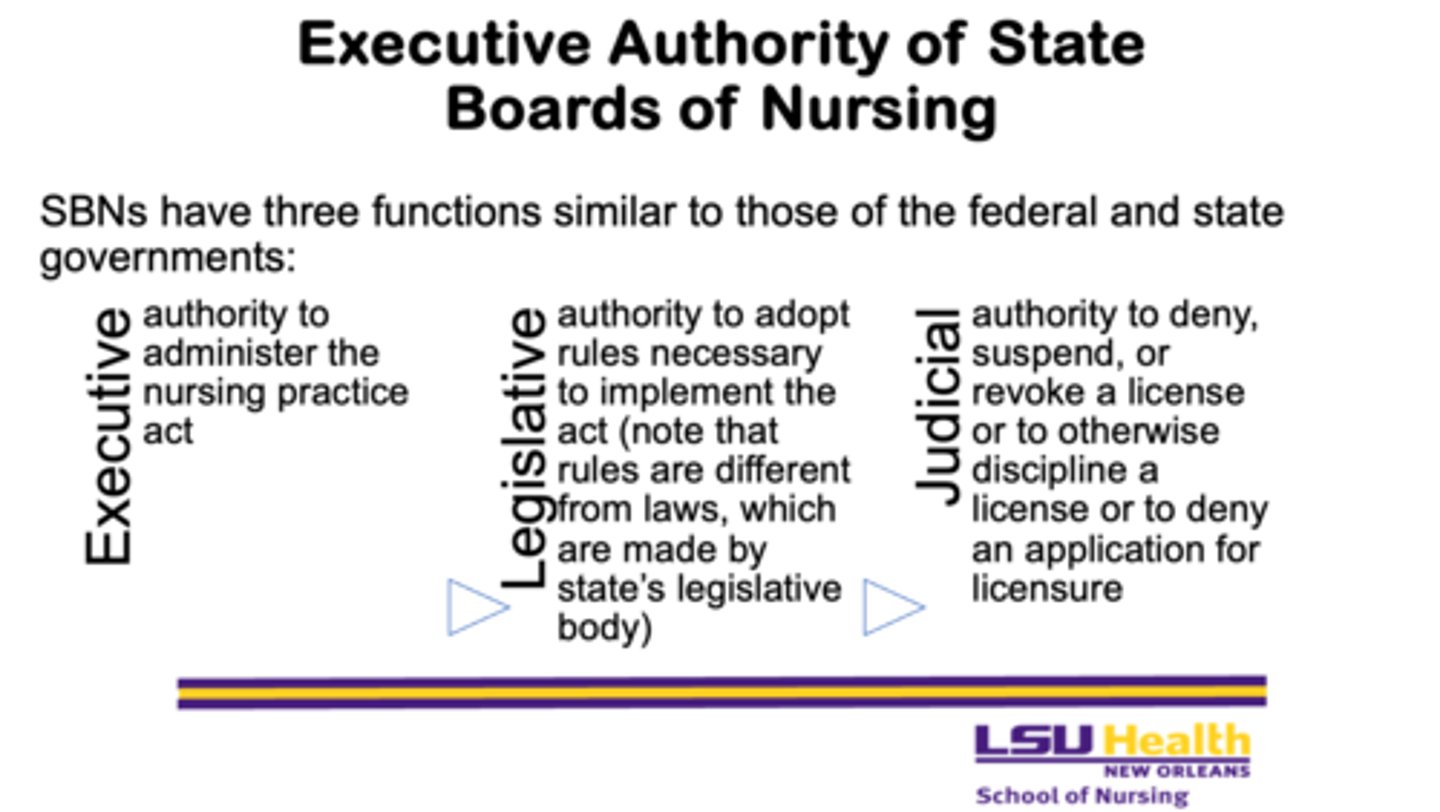
What is the executive function of State Boards of Nursing?
- the authority to administer the nursing practice act
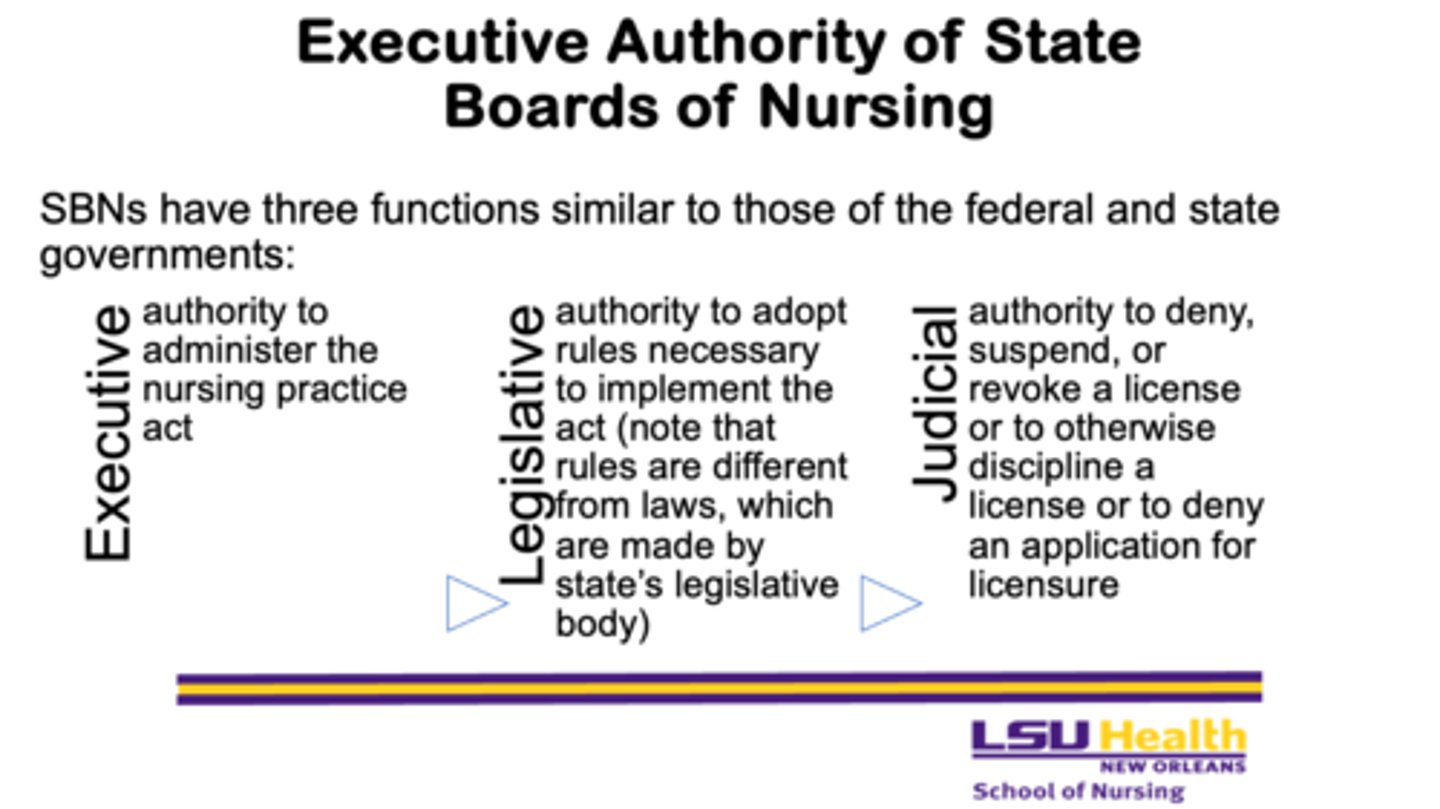
What is the legislative function of State Boards of Nursing?
- the authority to adopt rules necessary to implement the act, noting that rules differ from laws, which are made by the state’s legislative body
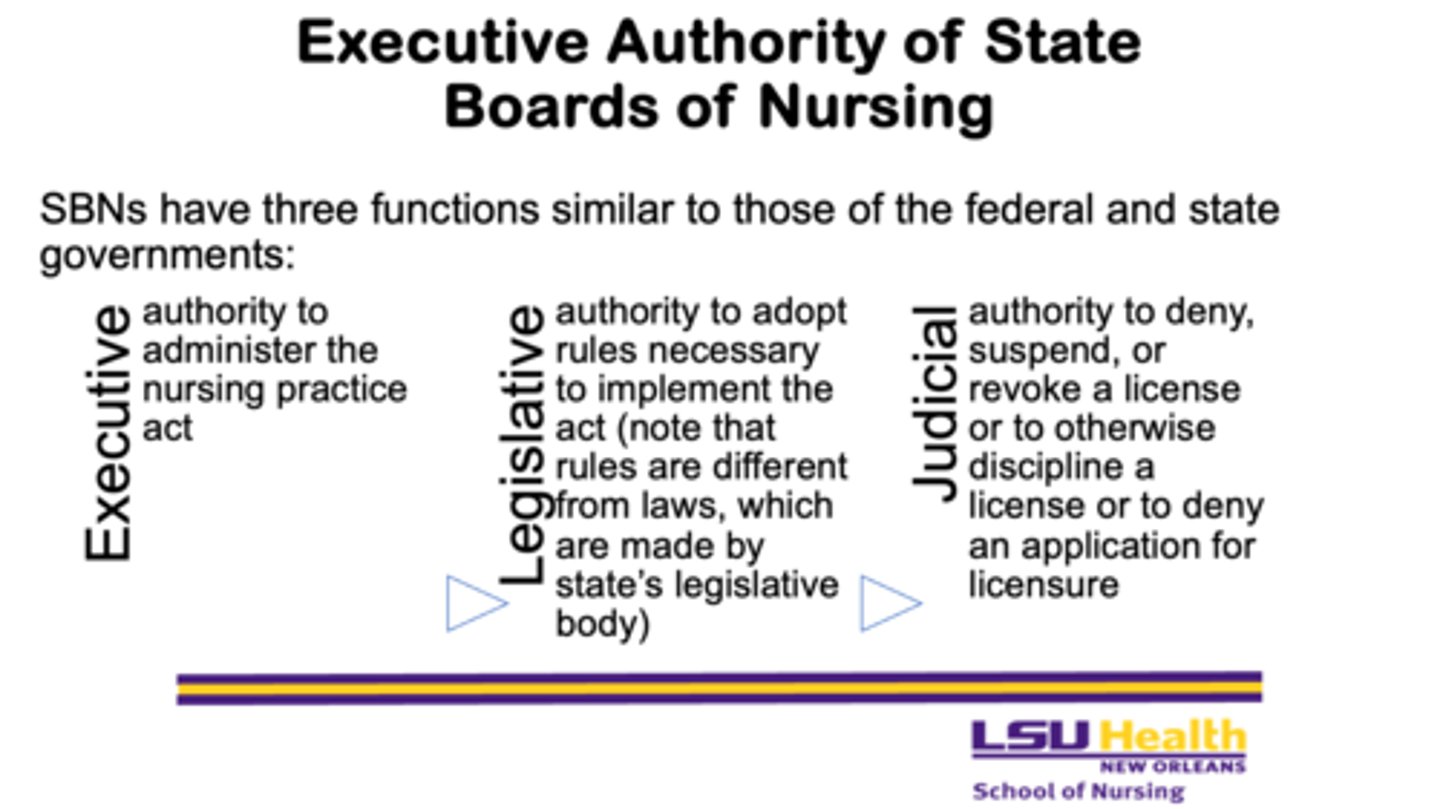
What is the judicial function of State Boards of Nursing?
- the authority to deny, suspend, or revoke a license, to discipline a licensee, or to deny an application for licensure
What does a mandatory law require regarding nursing practice?
- it requires any person who practices the profession or occupation to be licensed

What authority do State Boards of Nursing (SBNs) have in most states?
- they have the authority to set and enforce minimum criteria for nursing education programs

What is one major responsibility of SBNs related to licensing?
- SBNs grant licenses to nurses

Besides granting licenses, what additional power do SBNs have?
- they have the power to sanction a nurse for performing professional functions in a way that is dangerous to patients or the public

What are possible sanctions the State Board of Nursing can impose?
- probation, suspension, or revocation of a nursing license

What is the most common reason nurses are disciplined by State Boards of Nursing (SBNs)?
- practicing while under the influence of alcohol or other substances, often narcotics

What is the goal of State Boards of Nursing (SBNs) regarding nurses with substance use issues?
- to return nurses who have been identified as having problems with drugs and/or alcohol safely back into practice

What does the NCLEX-RN stand for?
- National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses

What does the NCLEX-RN test?
- it tests critical thinking and nursing competence in all phases of the nursing process

What type of testing format does the NCLEX-RN use?
- computer adaptive testing (CAT)

What is the minimum number of questions on the NCLEX-RN?
- 75 questions

What is the maximum number of questions on the NCLEX-RN?
- 256 questions

How much time is allowed to complete the NCLEX-RN, including breaks?
- 6 hours

If a candidate is unsuccessful on their first NCLEX-RN attempt, what must they do?
- they must pay fees and wait 45 days before retesting

What do high first-time NCLEX pass rates indicate about a nursing program?
- they reflect the quality of the education program and how well it prepares graduates for professional nursing practice

What does licensure by endorsement allow registered nurses (RNs) to do?
- it allows RNs to practice in different states without having to take another licensing examination

What does NLC stand for?
- National Licensure Compact

What is the enhanced NLC (eNLC)?
- an updated mutual recognition model for licensure that allows nurses to have one multistate license to practice across member states

What is the main goal of the Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC/eNLC)?
- to improve the mobility of nurses while still protecting public health, safety, and welfare

In what situations does nursing mobility typically occur?
- travel nursing, crossing state lines for work, telehealth practice, or moving to another state for personal or career reasons

What is the main legal concern discussed in the "Legal Risks in Professional Nursing Practice" slide?
- nurses spending too much time documenting in the electronic health record (EHR) rather than providing direct patient care, a practice sometimes called defensive practice

What is "defensive practice" in nursing?
- focusing excessively on perfect documentation to protect against malpractice rather than prioritizing patient care

How can excessive focus on documentation impact patient care?
- it can impede the delivery of safe, timely, and effective care to patients

What should nurses consider when documenting patient care?
- focus on using documentation to enhance patient care, not just to protect themselves legally

How might excessive documentation harm a nurse in a malpractice case?
- overly detailed or unnecessary documentation can highlight inconsistencies or errors, potentially strengthening a malpractice claim against the nurse

What are three key areas of legal risk for nurses?
1. delegation
2. informed consent
3. confidentiality

What is the primary legal concern for healthcare professionals?
- malpractice

How is malpractice defined?
- negligence applied to the acts of a professional

Are nurses accountable for their own practice in malpractice suits?
- yes, nurses can be named in a malpractice suit just like any other practitioner

What is informed consent?
- written permission obtained from a patient before performing a procedure or treatment

What is implied consent?
- consent that is assumed through a patient’s actions, such as reaching out when a nurse approaches with medication

What is the most important question in a malpractice case?
"Was the prevailing standard of care met?"

What does the standard of care represent?
- the minimum level of prudent care based on the ethical principle of non-maleficence (“do no harm”)

Who provides expert testimony in malpractice cases?
- nurse expert witnesses, hired by both the plaintiff and the defendant, testify whether the nurse met the prevailing standard of care

What evidence is used to determine whether the standard of care was met?
- expert witness testimony, patient records, nursing standards, and direct testimony from patients, nurses, and others

Standards of Care & Six Major Categories of Negligence "Box 6.2 and 6.3"** go over (slide 16)
Who can nurses delegate to?
1. LPNs
2. CNAs
3. Techs
4. other nurses (in certain circumstances)

What is the nurses responsibility when delegating?
- know that "you're ultimately responsible"

What are the three major conditions of informed consent?
1. disclosure
2. capacity
3. voluntariness

In informed consent, what is disclosure?
- "disclosing" information to the patient

In informed consent, what is capacity?
- the medical ability for the patient to understand what's happening
- capacity can be fluid

In informed consent, what is voluntariness?
- patient is acting on their own free will

What does HIPAA stand for, and when was it established?
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Established in 1996

Who signed HIPAA into law? What type of law is HIPAA?
- president Bill Clinton
- federal law

What is the ethical principle behind HIPAA?
- the principle of confidentiality, which protects patient privacy and limits the sharing of health information

What are nurses legally and ethically required to protect under HIPAA?
- patients' health information and privacy

What does HIPAA require nurses to protect, and what happens if they violate it?
- nurses must protect patients’ health information and privacy
- violating HIPAA means the nurse has broken federal law and may also have violated state laws.

How does HIPAA relate to nurses' social media use?
- HIPAA’s confidentiality rules apply to all forms of communication, including social media, meaning nurses must never share or reference patient information online

What do "assault" and "battery" mean in legal terms?
- assault - intimidation or threatening behavior
- battery - actual physical contact or touching without consent

Who is HIPAA based on?
- arthur ashe

What are some examples of evolving legal issues in nursing practice?
- issues related to role changes, supervision of unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)
- payment mechanisms
- implementation of the Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA)

What is a Legal Nurse Consultant?
- a registered nurse who provides advice and expertise to lawyers in cases involving medical or nursing issues

What is prescriptive authority?
- the legal acknowledgment of prescription writing as an appropriate and regulated nursing function, particularly for advanced practice nurses

What is the goal of prescriptive authority laws?
- to establish a uniform, state-wide model for prescribing practices while ensuring nurses stay within their legal scope of practice

What must generalist nurses understand about prescriptions?
- they must know whom they can accept medication orders from and ensure that prescribers are authorized within their scope of practice

What are three major evolving legal issues affecting nursing?
1. Supervision of unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)
2. Payment mechanisms for nurses
3. Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA)

What was the significance of the 1997 Balanced Budget Act for nurses?
- it allowed advanced practice nurses (APNs) to receive direct reimbursement for services under state Medicaid agencies

Which nurses were affected by the reimbursement legislation under the Balanced Budget Act?
- nurse practitioners (NPs)
- nurse-midwives
- certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs)

What law reformed the U.S. healthcare system in 2010?
- the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), which aimed to increase the quality, availability, and affordability of healthcare

What is the purpose of the Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA)?
- ensure patients are informed about their rights to make decisions regarding medical care, including end-of-life preferences and treatment options

What role do nurses play under the PSDA?
- nurses help patients and families understand their rights, discuss advance directives, and support them in documenting treatment preferences for future care

What are key ways nurses can protect themselves from legal problems?
- practice in a safe setting
- communicate effectively with other health professionals, patients, and families
- meet the standard of care
- carry and understand professional liability insurance
- promote positive interpersonal relationships

Why is communication important in preventing legal issues?
- good communication helps prevent misunderstandings and errors, and accurate patient records serve as critical legal evidence for safe, consistent practice

What is the importance of professional liability insurance for nurses?
- it provides financial protection and ensures the nurse is covered in case of a malpractice claim or legal dispute

Why should nurses own and understand four key professional documents?
- because nurses are accountable for practicing within their scope, and these documents help them stay current with changes that affect nursing practice and ethical standards

What are the four documents every professional nurse should own?
1. A copy of the nursing practice act of the state in which you practice
2. Nursing’s Social Policy Statement: The Essence of the Profession
3. Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice
4. ANA’s Code of Ethics for Nurses with Interpretive Statements

What is the main purpose of these four nursing documents?
- to ensure nurses understand their professional responsibilities, ethical obligations, and legal boundaries while maintaining high standards of care

What are the components of a model nursing practice act?
- it defines the standards and scope of nursing, outlines authority and composition of state boards, and establishes educational and licensure requirements

What is the authority of state boards of nursing?
- they have executive, legislative, and judicial powers to administer, enforce, and interpret the nursing practice act

What conditions must be present for malpractice to occur?
1. Duty to the patient must exist
2. Duty is breached
3. Proximate cause (circumstances link breach to harm)
4. Cause and fact must be proven
5. Damage occurs to the patient
