BIOL 185L - Bacteria and Archaea
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
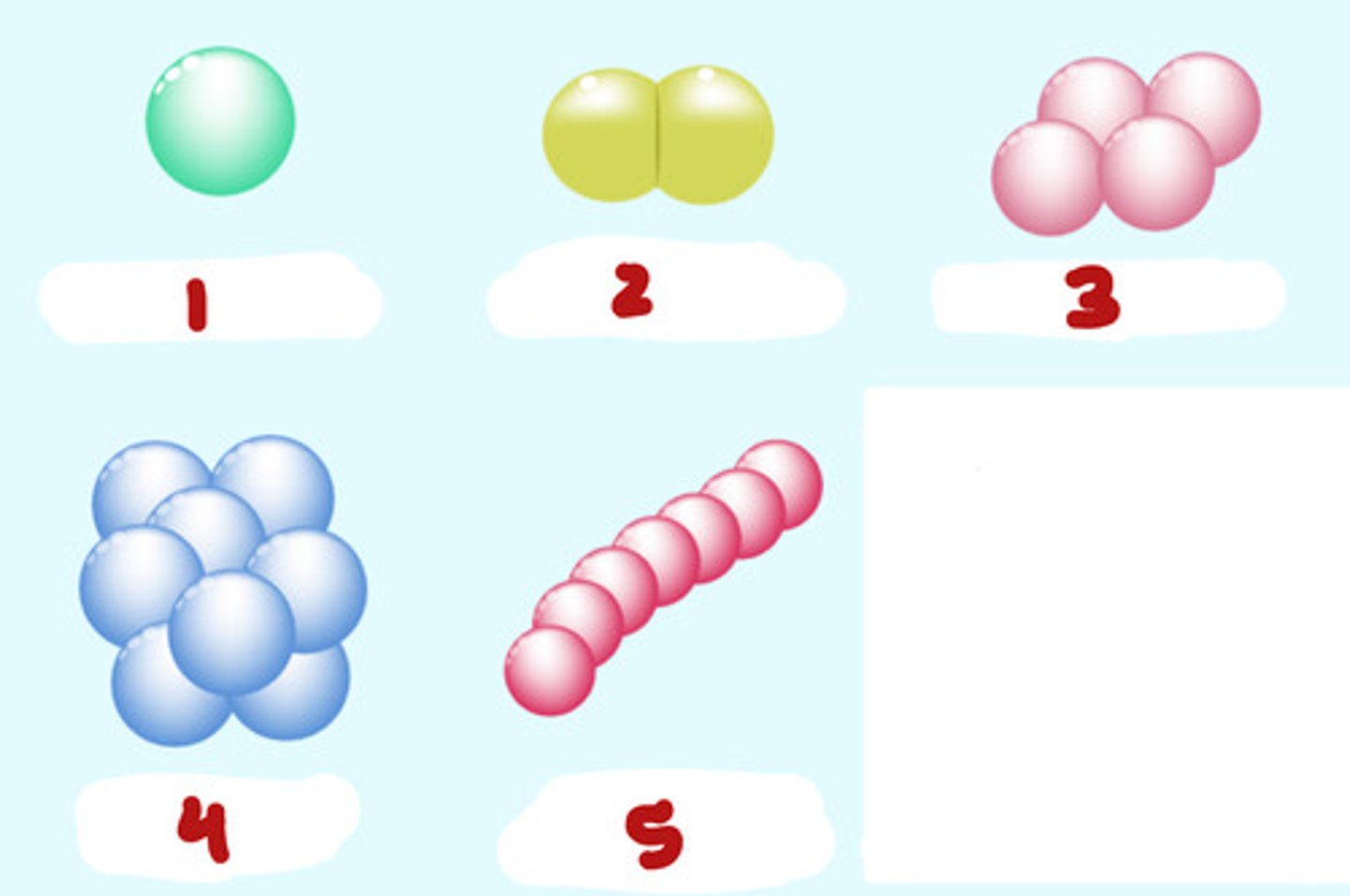
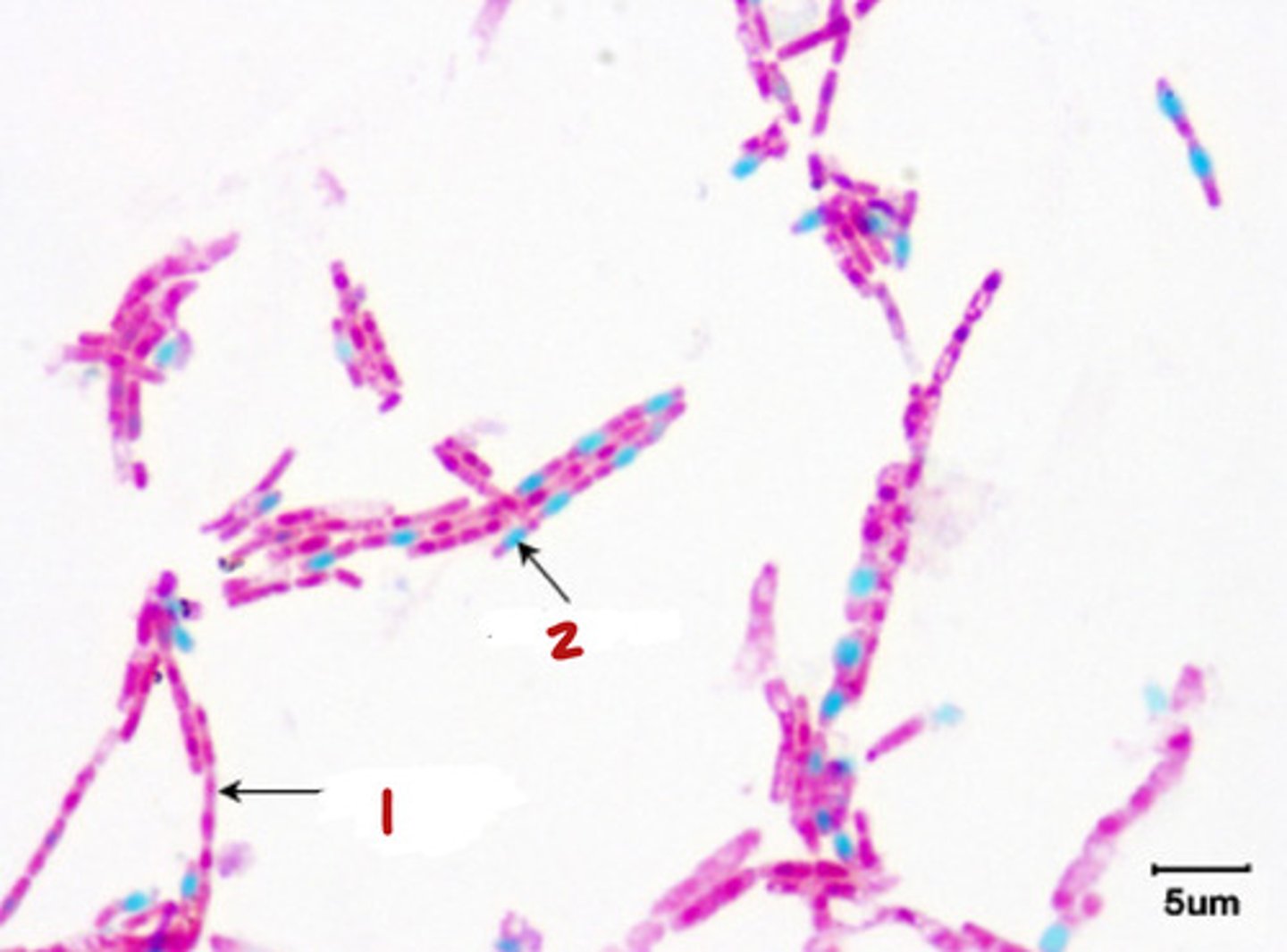
1- Monococcus (single)
2. Dicoccus (pairs)
3- Tetrads (4's)
4- Sarcina (cuboidal)
5- Streptococci (chains)
Name and describe the shapes
Coccus (spherical), Bacillus (rod-shaped), Spirochete (spiral)
Name and describe the major shapes
aggregations of bacteria living on a solid surface, typically linked together by an extracellular matrix composed of primarily proteins and polysaccharides
What are biofilms?
A.
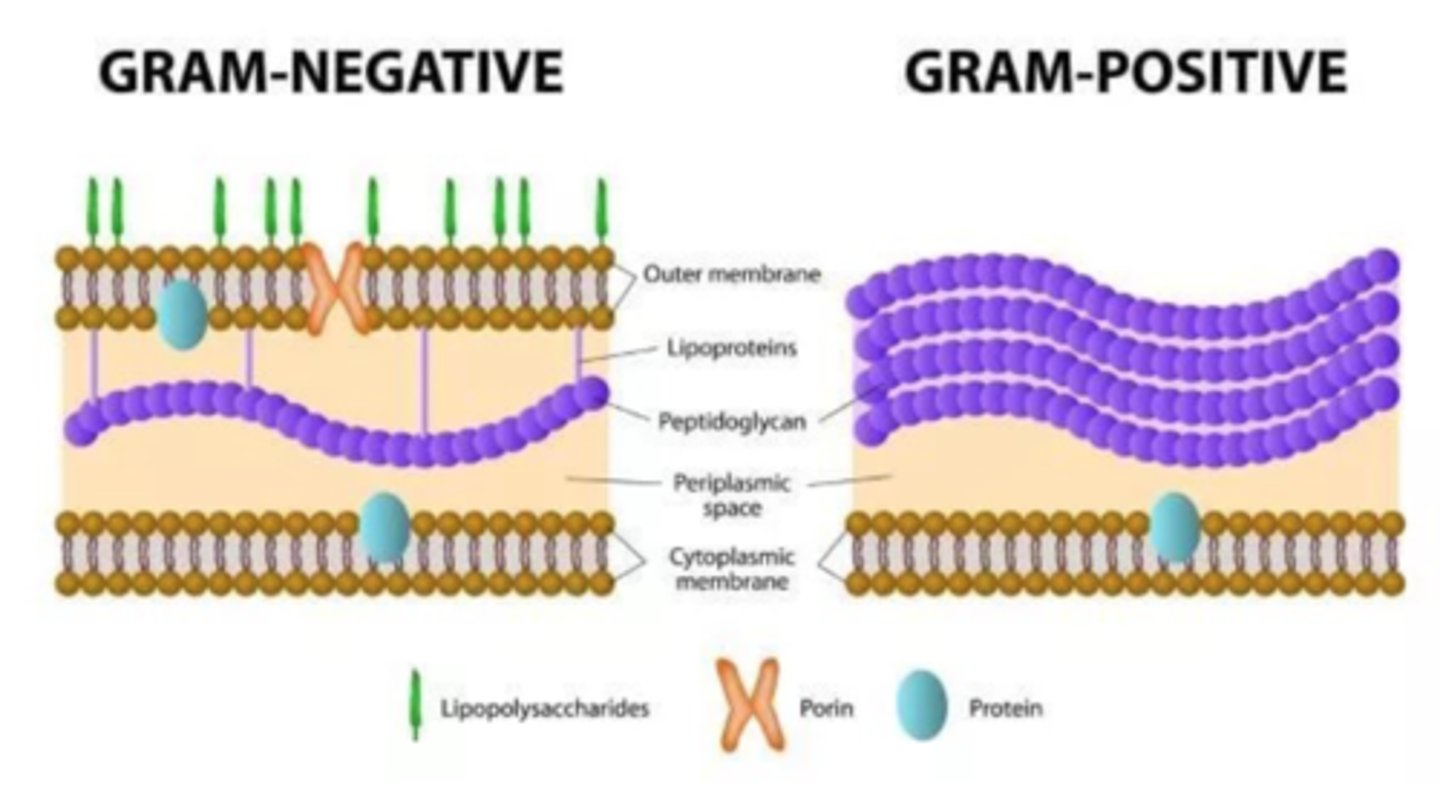
- Gram-positive bacteria: appear purple (crystal violet interacting with iodine); typically monoderms
- Gram-negative bacteria: appear pink/red (safranin); typically diderms
B.
Bacteria: stain either
Archaea: stain both (due to variability of cell wall structures)
A. What are the two different types of gram stainings? Describe the color it appears and what causes it?
B. What do bacteria stain? What do archaea stain?
A. Monoderm: single plasma membrane, thick cell wall, typically stain gram (+); peptidoglycan in bacteria and pseudopeptidoglycan (all archaea, few bacteria)
B. Diderm: two membranes (most bacteria)
- Innermost: lipid bilayer plasma membrane
- Thin cell wall: containing peptidoglycan
- Outermost: lipopolysaccharide
- In between inner and outermost - periplasmic space
Differentiate between monoderm and diderm prokaryotes.
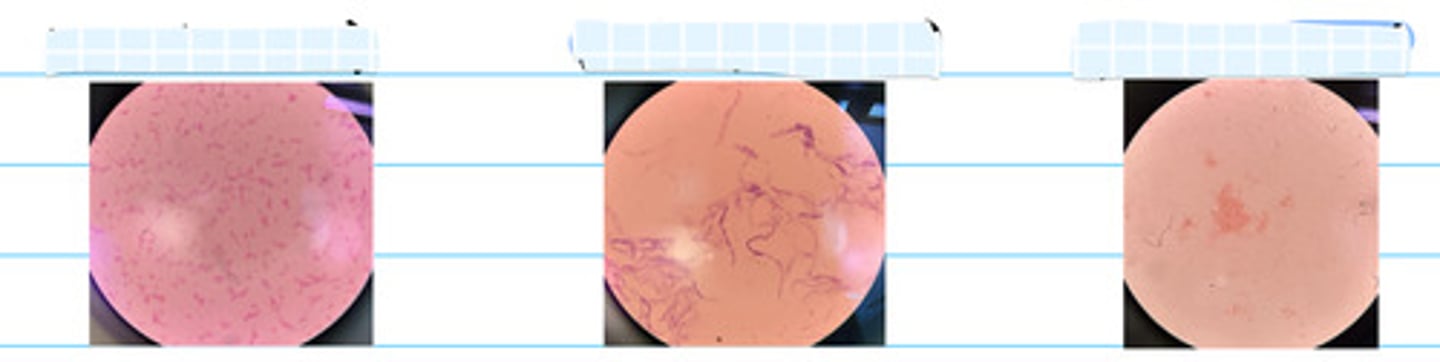
1. Size: how large/wide the colony is
2. Color: color of colony
3. Configuration: overall shape of colony
4. Margin: shape of edge of colony
5. Elevation: vertical element of colony's appearance
6. Opacity: translucence of colony
What are some morphological traits to describe a colony?
Small, medium, large
How can you describe a colony's size (as a whole)?
Yellow, green, pink, etc.
How can you describe a colony's color?
Round, irregular, filamentous (furry/fuzzy)
How can you describe a colony's configuration (overall shape, ignoring the margin)?
Smooth, wavy, filamentous
How can you describe a colony's margin (shape of edge of colony)?
Flat, convex (rises off surfact of agar), umbonate (distinct peak in center), crateriform (noticeable depression in center)
How can you describe a colony's elevation (vertical element)?
...
Practice: Describe the morphology of as many colonies possible.
A. Bacteria
B. Cyanobacteria
C. 1- heterocysts (nitrogen fixation), 2- vegetative ells (photosynthesis)
A. Domain
B. Clade
C. Label with function
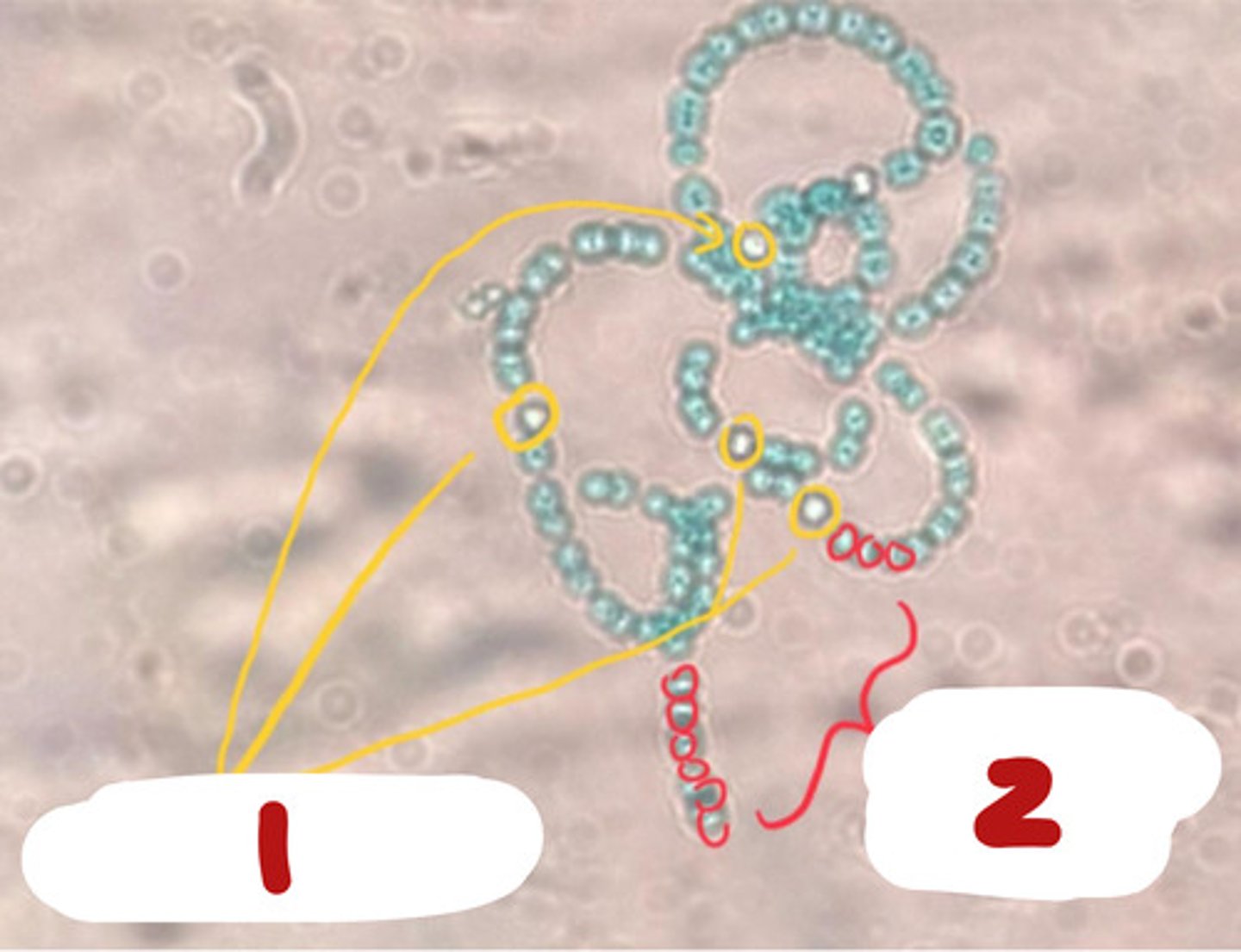
A. Bacteria
B. Cyanobacteria
C. Trichomes (light harvesting, mvmt, nitrogen fixation)
A. Domain
B. Clade
C. Label with function
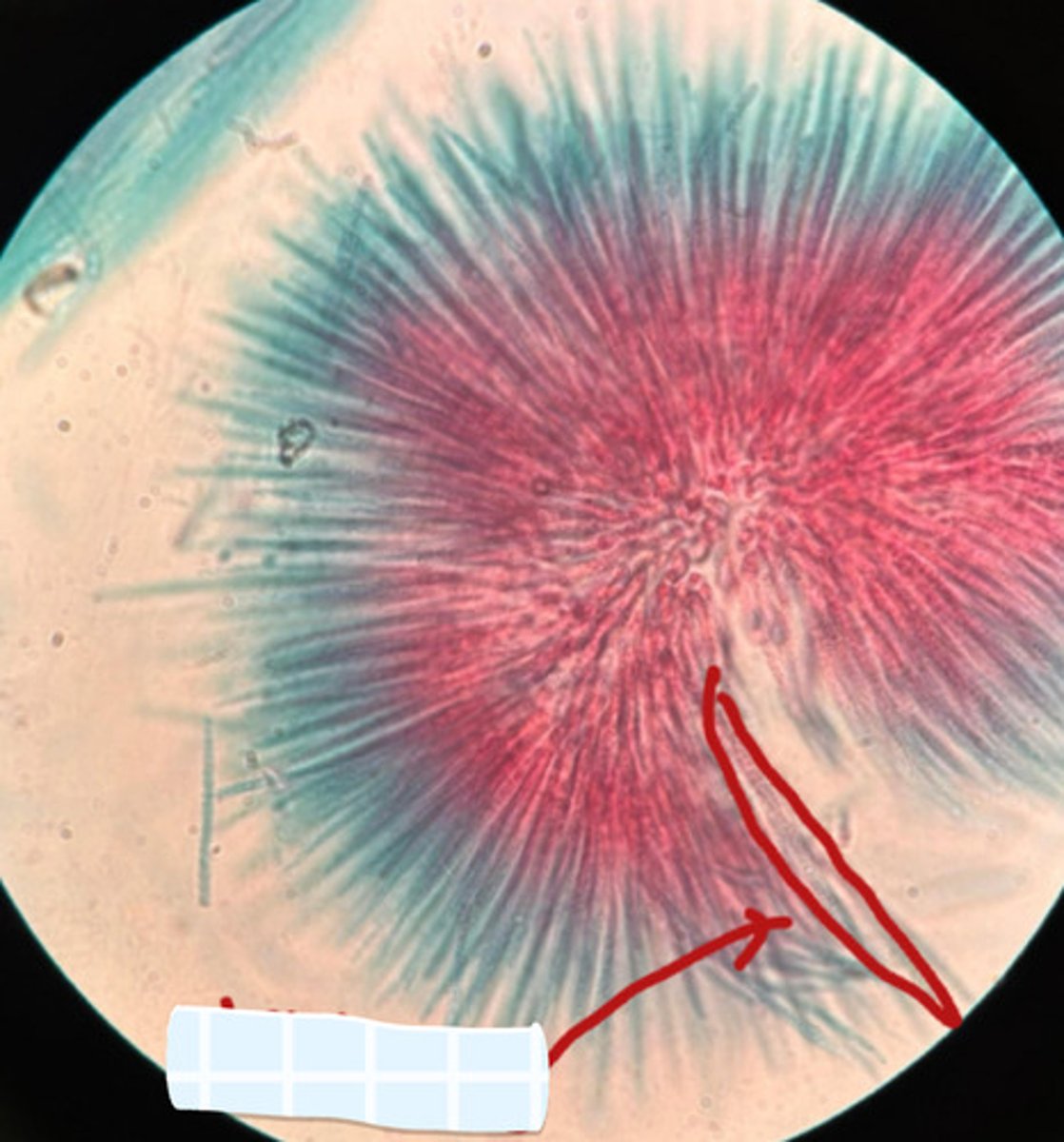
A. Bacteria
B. Cyanobacteria
C. 1- rhizobia (nitrogen-fixing bacteria), 2- root nodule (house rhizobia), 3- root cross-section
D. Eukarya, Plantae
E. Symbiosomes (facilitate nutrient exchange between plant host and bacteria, ensure efficiency of nitrogen fixation)
A. Domain (of 1)
B. Clade (of 1)
C. Label with function
D. What is the domain and family of 3?
E. Where does 1 grow in? Function of this?
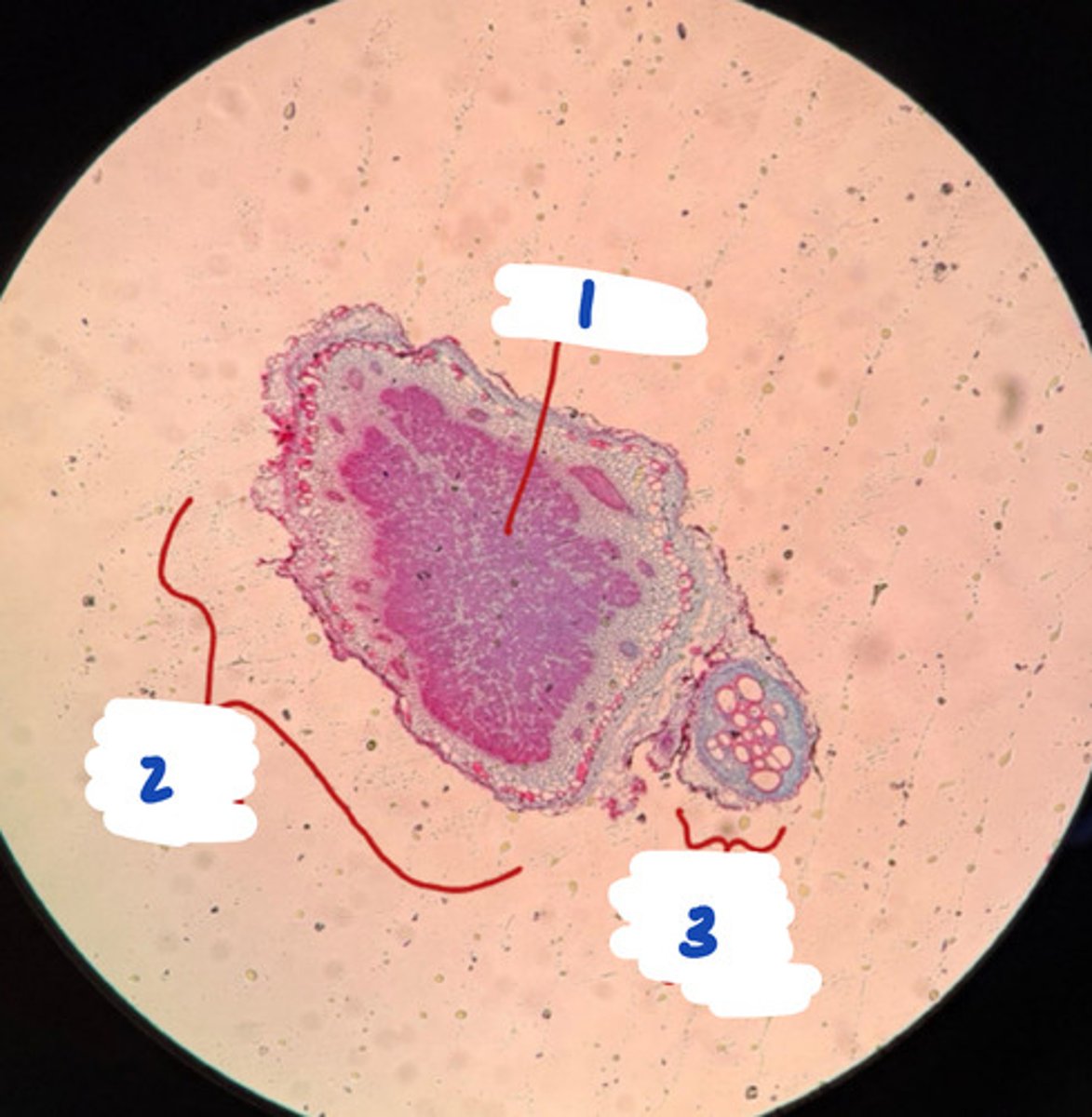
A. Bacteria
B. Firmicutes
C. 1- vegetative cells (form endospores when stressed), 2- endospores (resistant to environmental stress)
A. Domain
B. Clade
C. Label with function
Color, smell (hydrogen sulfide, etc.), texture, taste & smell
What are some signs to determine the presence of bacteria/archaea?
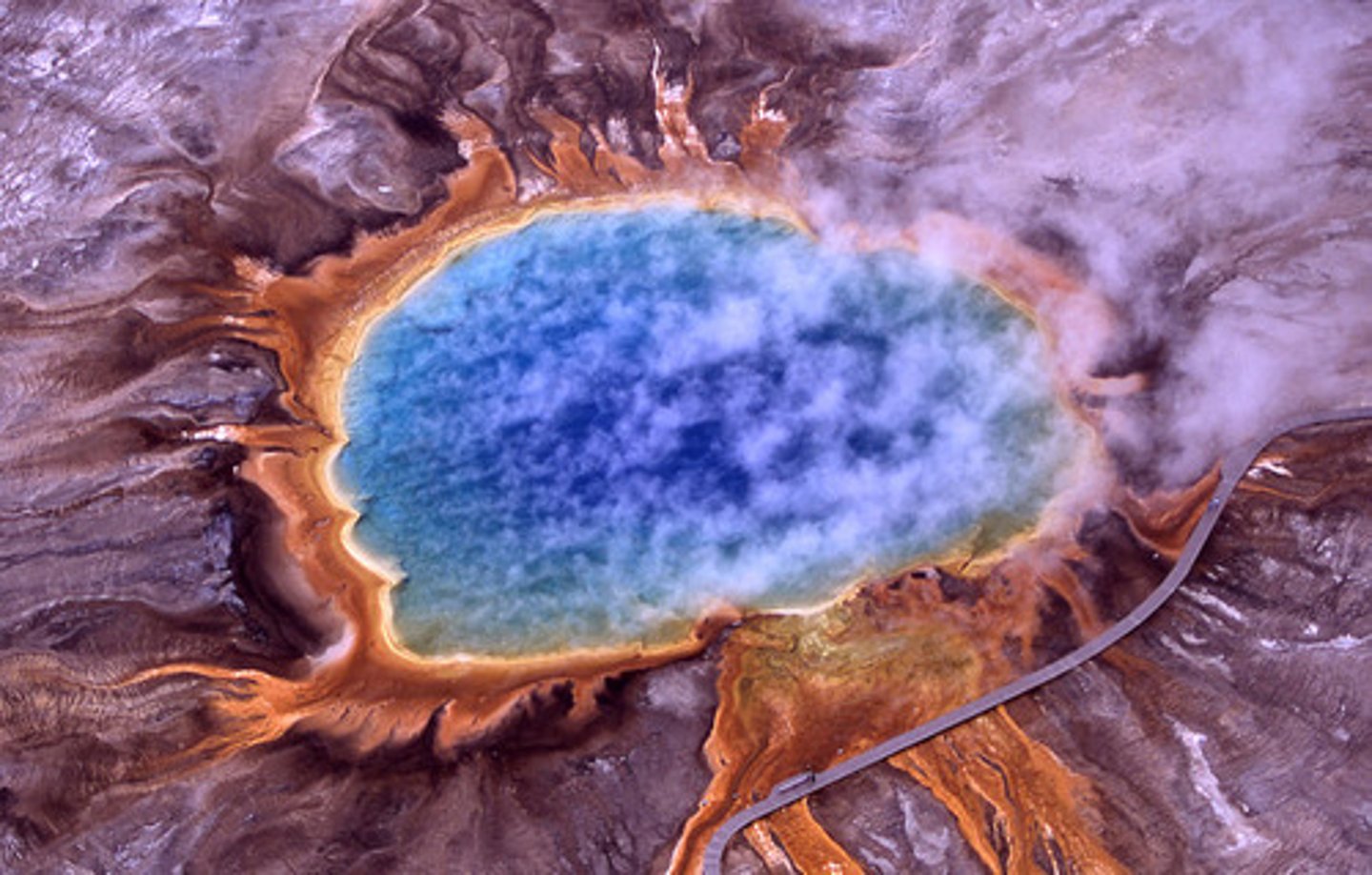
A. Archaea, Euryarchaeota
B. Either
C. Monoderm
D. Lack peptidoglycan
A. Domain, Clade name
B. Gram +/-
C. Mono/diderm
D. One characteristic
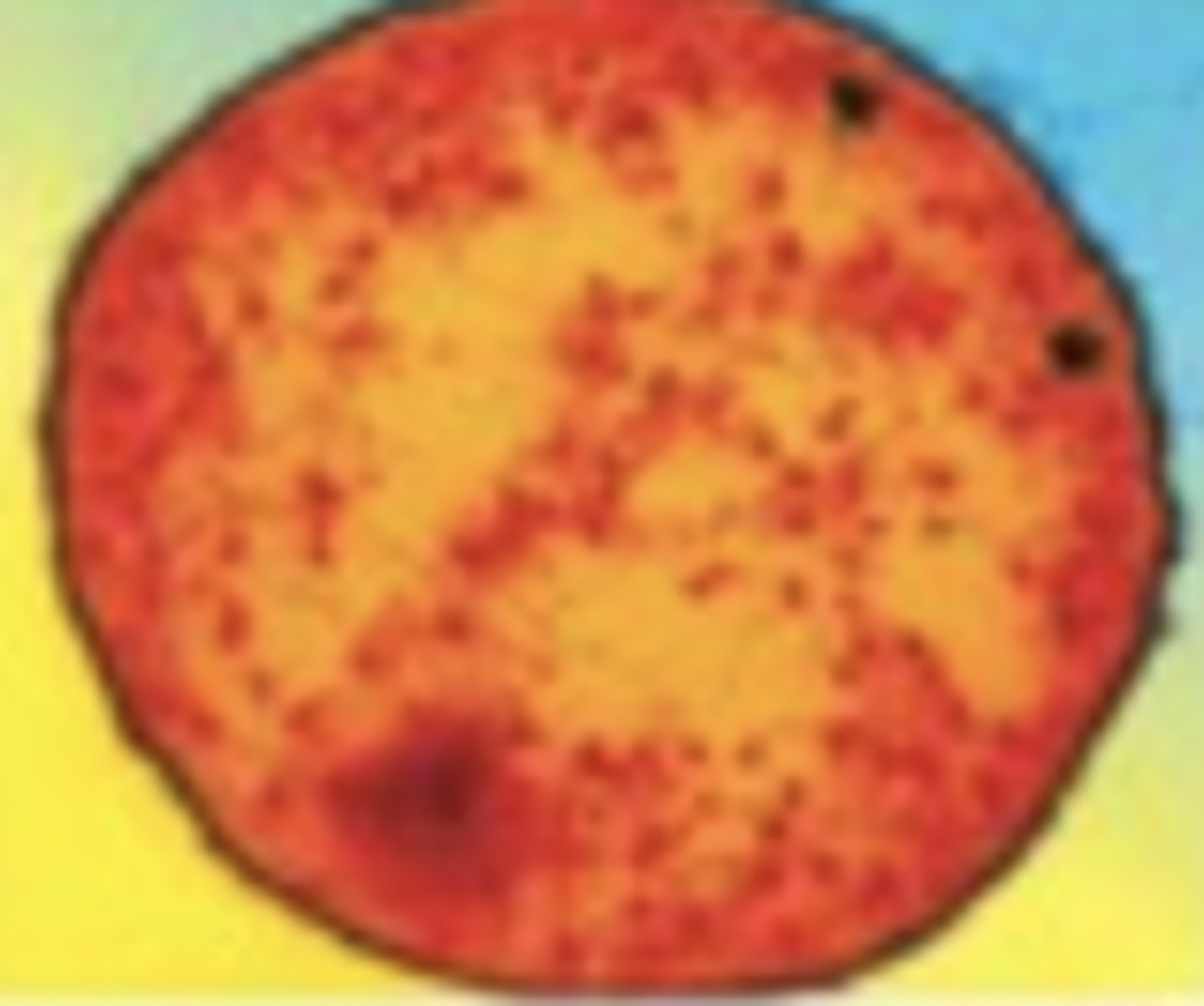

A. Archaea, Crenarchaeota
B. Either
C. Monoderm
D. coccus & bacillus
A. Domain, Clade name
B. Gram +/-
C. Mono/diderm
D. One characteristic
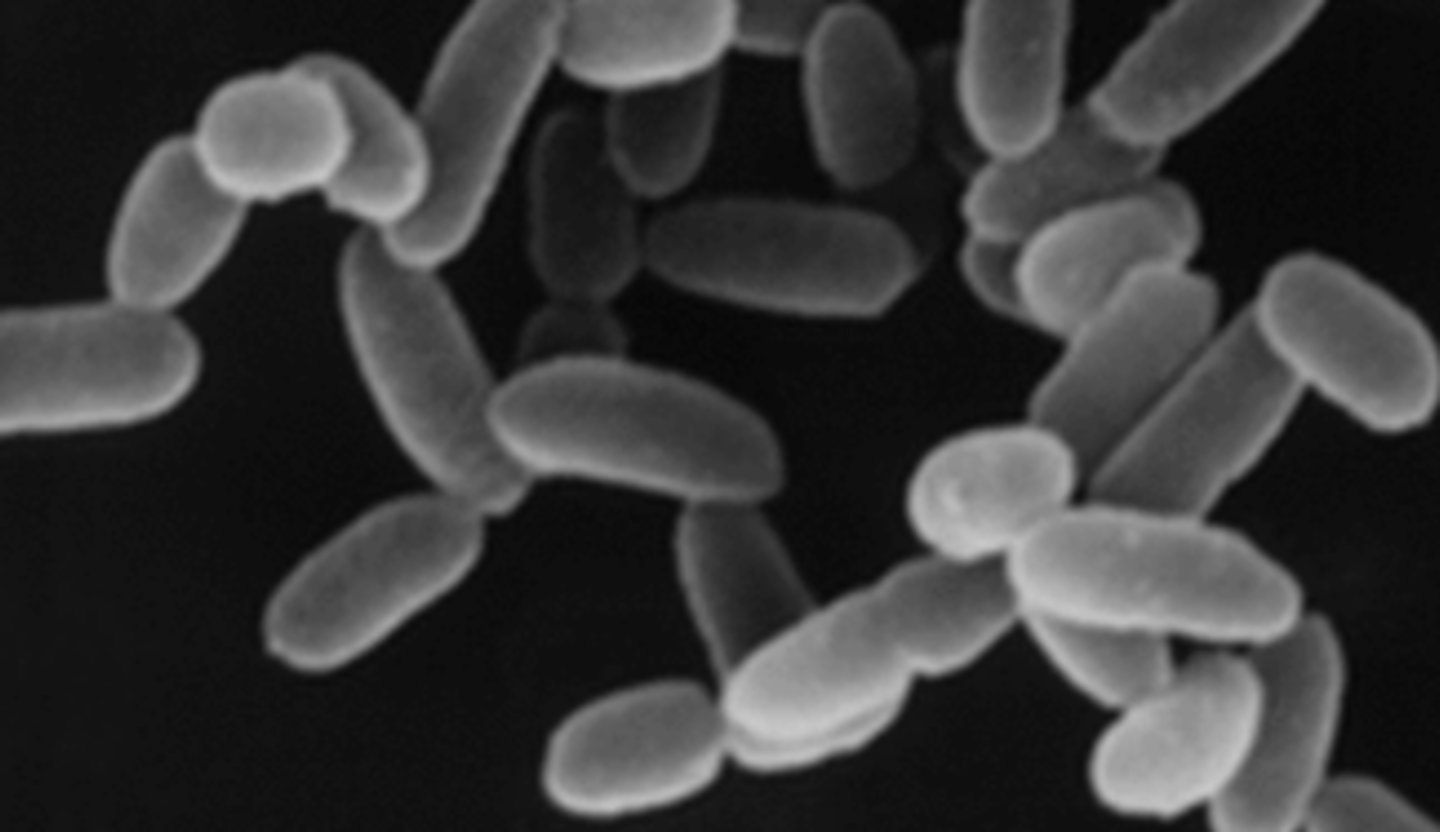

A. Bacteria, Actinobacteria
B. Gram +
C. Monoderm
D. coccoid & rod
A. Domain, Clade Name
C. Gram +/-
D. Mono/diderm
E. One characteristic
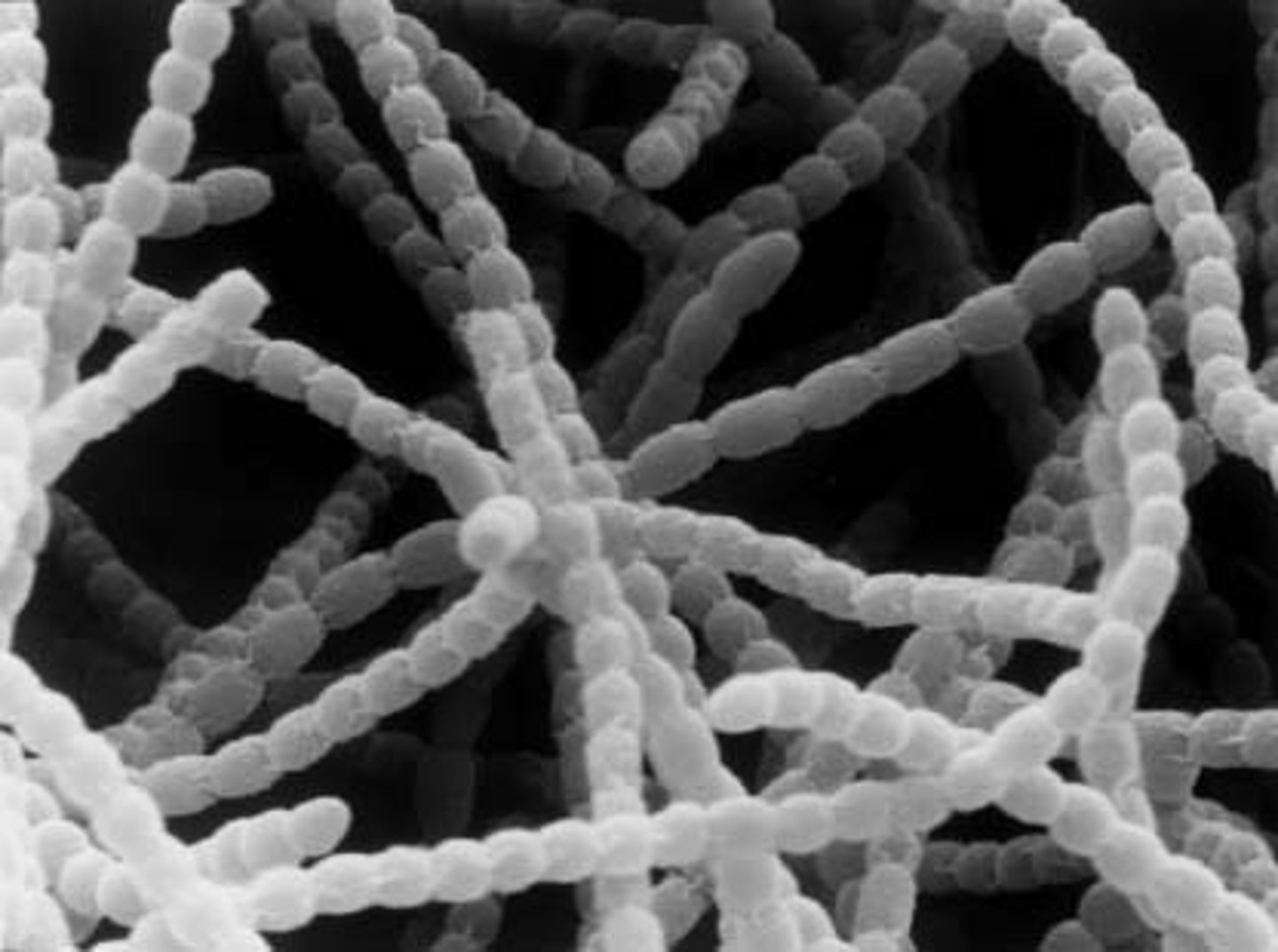

A. Bacteria, Firmicutes
B. Gram +
C. Monoderm
D. endospore formation
A. Domain, Clade Name
C. Gram +/-
D. Mono/diderm
E. One characteristic
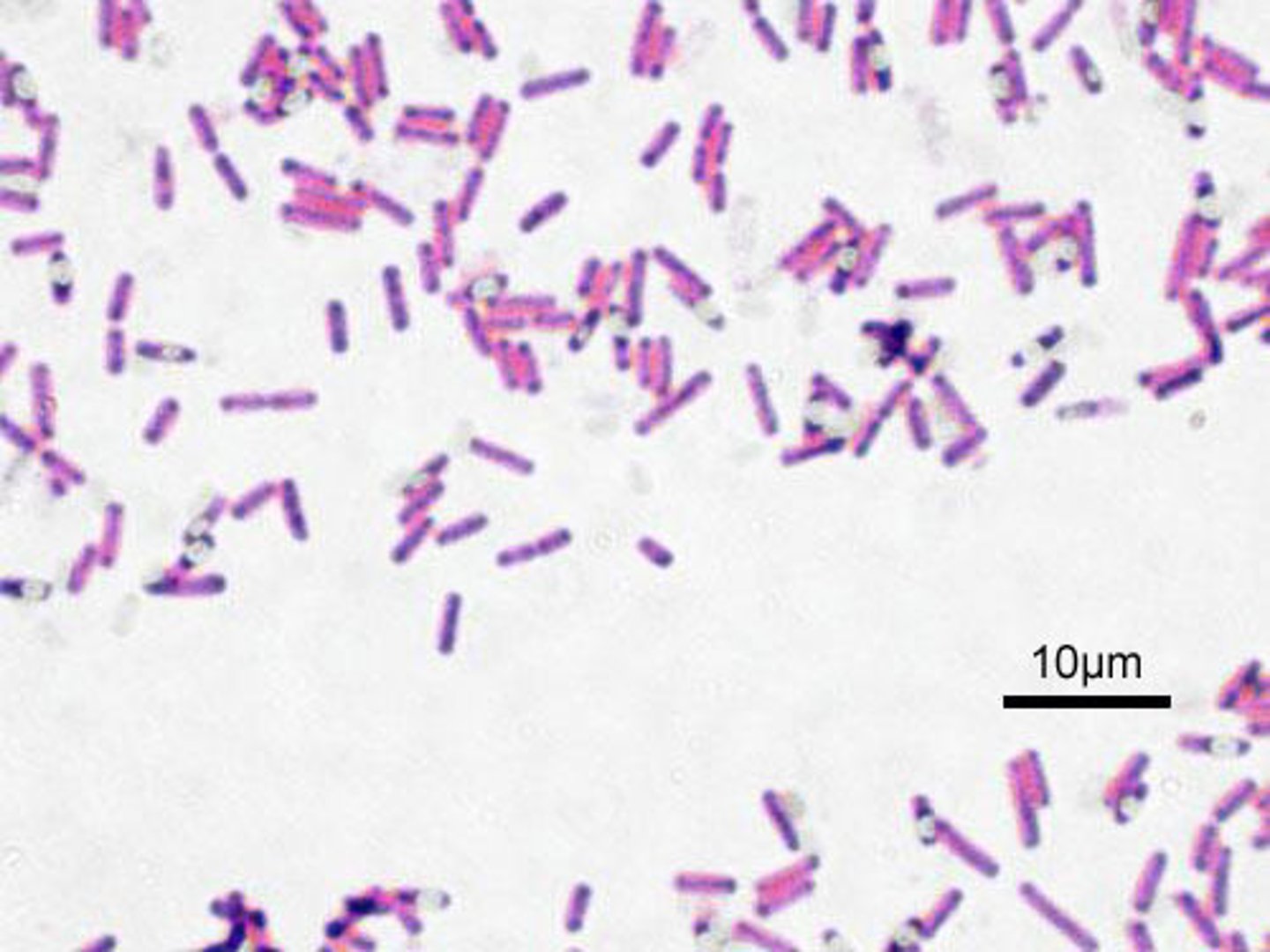
A. Bacteria, Chlamydiales
B. Gram -
C. Monoderm
D. Coccus
A. Domain, Clade Name
C. Gram +/-
D. Mono/diderm
E. One characteristic
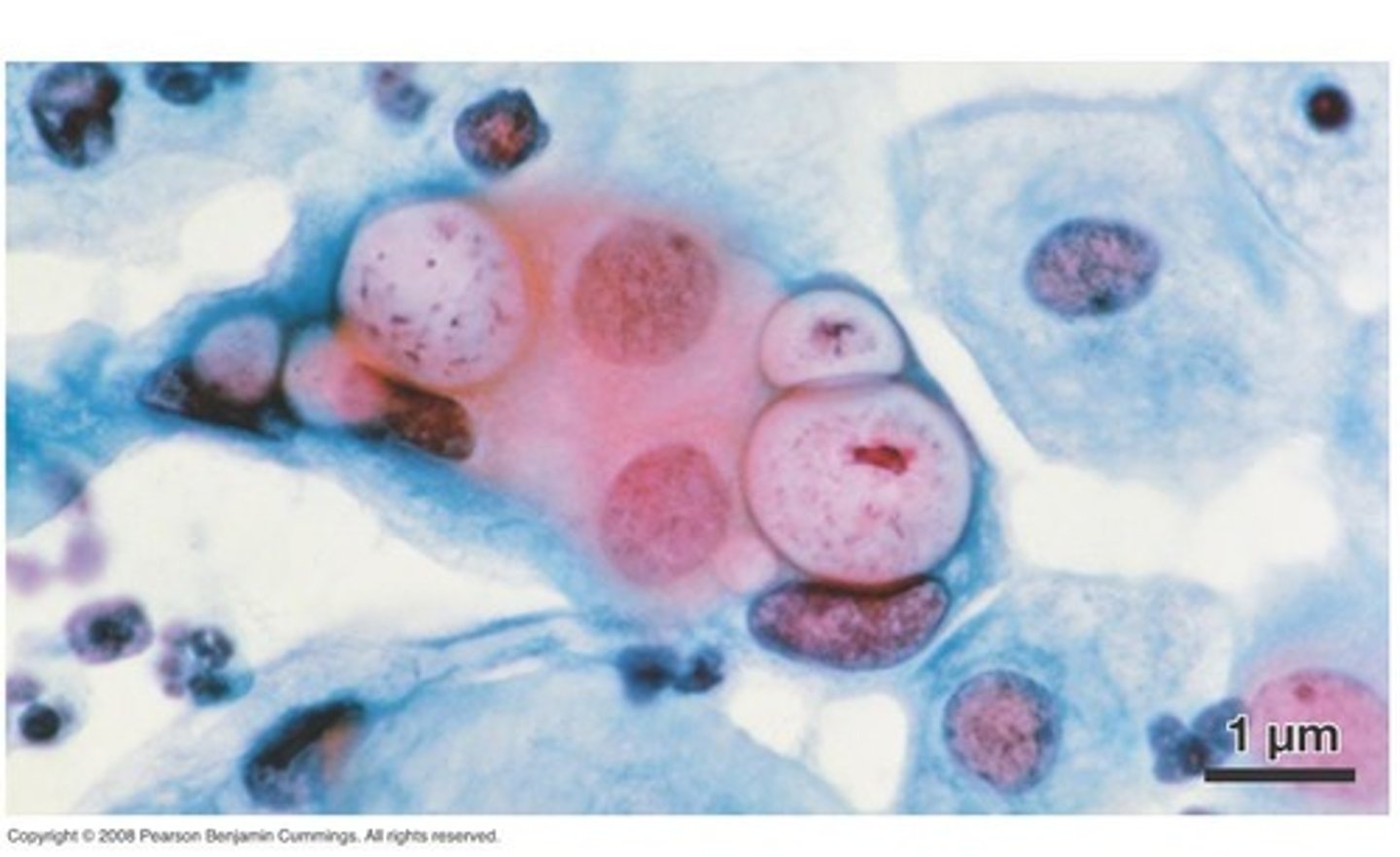
A. Bacteria, Cyanobacteria
B. Gram -
C. Diderm
D. Photosynthetic
A. Domain, Clade Name
C. Gram +/-
D. Mono/diderm
E. One characteristic
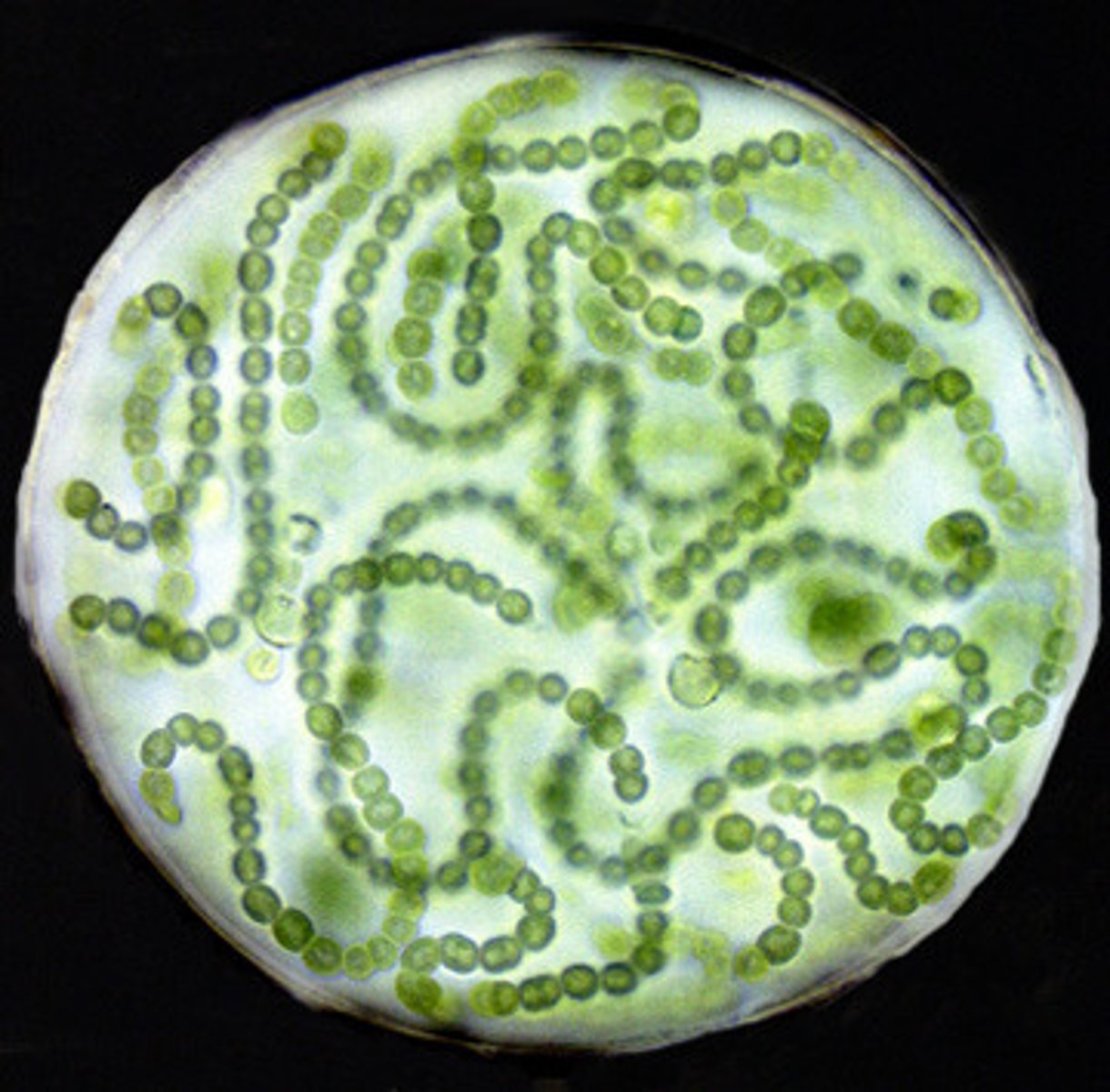
A. Bacteria, Spirochetes
B. Gram -
C. Diderm
D. Spiral
A. Domain, Clade Name
C. Gram +/-
D. Mono/diderm
E. One characteristic
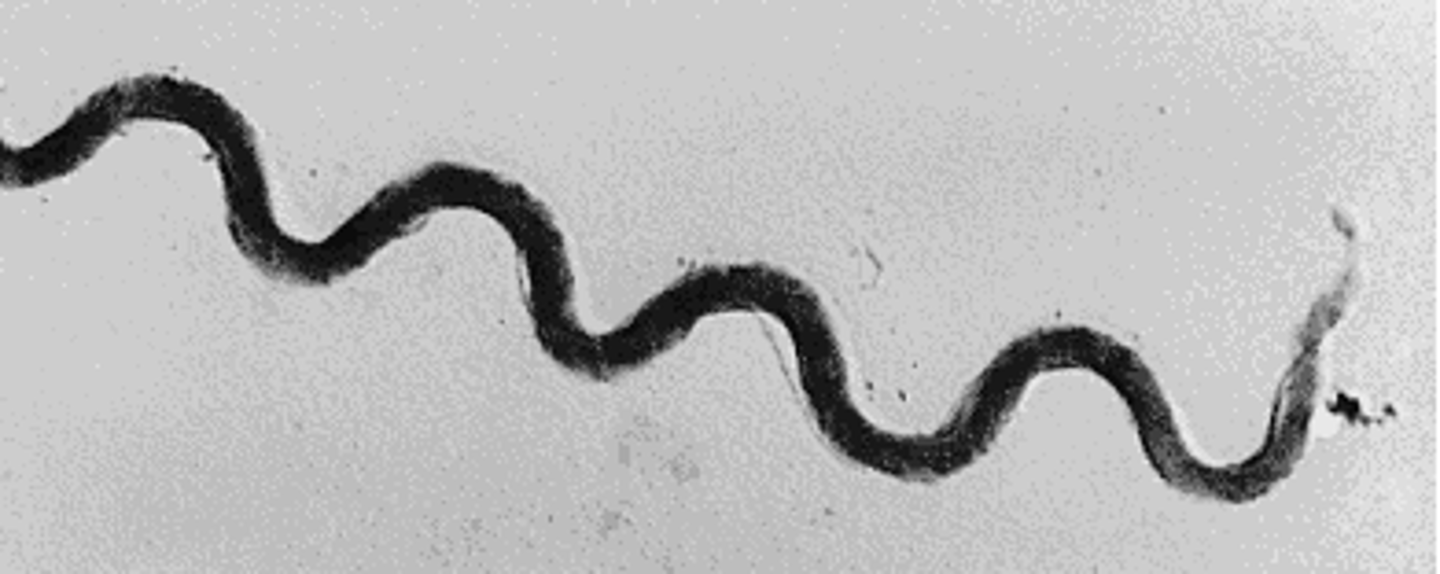
A. Bacteria, Green Sulfur
B. Gram -
C. Diderm
D. Anaerobic photosynthesis
A. Domain, Clade Name
C. Gram +/-
D. Mono/diderm
E. One characteristic
Prokaryotes, unicellular, cell wall, flagella, obtaining energy and carbon
What are the characteristics of domain bacteria?
Prokaryotes, extremophiles, unicellular, cell wall, flagella, obtaining energy and carbon
What are the characteristics of domain archaea?