Biotech in the Pharmaceutical Industry Vocabulary
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:41 AM on 2/5/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Hybridoma
A B lymphocyte fused to a tumor cell; the “cell”/substance that is exposed to the antigen in the making of monoclonal antibodies.
2
New cards
Monoclonal antibody
“Custom-designed” antibodies that are made in a lab and are made to target/bind to a specific molecule (they are much more specific than normal antibodies).
3
New cards
How are monoclonal antibodies made (differently/similarly to polyclonal antibodies)?
The process of making them is similar to making polyclonal antibodies, but everything is much more specific:
* an animal is still used, but only a specific antibody is wanted, not a variety
* the B lymphocyte collected from the lab animal is fused with a tumor cell (hybridoma) to replicate
* the hybridoma is then exposed to the antigen to produce the antibody that specifically attacks the antigen
* this __specific__ B lymphocyte is then harvested and sold
* an animal is still used, but only a specific antibody is wanted, not a variety
* the B lymphocyte collected from the lab animal is fused with a tumor cell (hybridoma) to replicate
* the hybridoma is then exposed to the antigen to produce the antibody that specifically attacks the antigen
* this __specific__ B lymphocyte is then harvested and sold

4
New cards
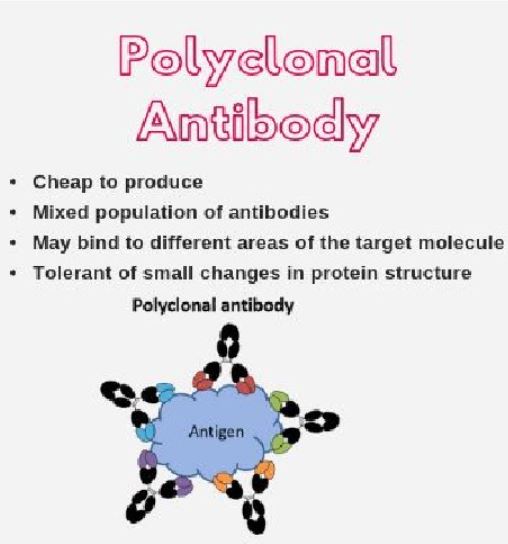
Polyclonal antibody
The traditional way of making antibodies:
* The antigen is injected into a lab animal
* lab animal produces B lymphocytes that produce (a **variety**) antibodies to attack antigen
* the B lymphocytes are harvested and sold
* The antigen is injected into a lab animal
* lab animal produces B lymphocytes that produce (a **variety**) antibodies to attack antigen
* the B lymphocytes are harvested and sold
5
New cards
ELISA test
the test that indicates if one has the specific disease/substance in oneself; it detects the presence of an antibody or antigen (ex: rapid COVID, pregnancy, drug, air quality tests)
6
New cards
Indirect ELISA
An unlabeled primary antibody that attacks the antigen is put into the sample and an enzyme-labeled secondary antibody is also used in the sample. This ELISA test is used when sensitivity is very important (ex: HIV).
7
New cards
Direct ELISA
A primary antibody is combined with an enzyme to detect the antigen. The primary antibody has to be labeled individually (time-consuming and expensive).
8
New cards
Assay
To test or analyze (for) something (usually a certain substance).
9
New cards
Antigen
any substance the immune system recognizes as foreign (ex: viruses, bacteria, allergens) and generates an immune response (production of antibodies)
10
New cards
Antibody
proteins created by the immune system that attack and disable antigens and activate when the body is infected by an antigen
11
New cards
Epitope
regions on the surface of an antigen where an antibody attaches
12
New cards
Primary Antibody
antibodies that only attach to the antigen
13
New cards
Secondary Antibody
antibodies that only attach to a primary antibody
14
New cards
Vaccine Injury
A serious health problem caused by a vaccine such as a severe allergic reaction or disability.
15
New cards
Herd Immunity
A form of protection against a contagious disease due to a large population of people in a certain area obtaining natural immunity from the disease by either being infected or vaccinated.
16
New cards
Vaccine
A biological preparation that contains a small dosage of a disease and is injected into the body to stimulate the production of antibodies and to gain immunity to the disease.
17
New cards
HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus; A sexually transmitted infection (STI) that directly attacks the immune system
18
New cards
Gene Therapy
the use/altering of genes to treat or prevent disease (and eventually to treat genetic disorders).
19
New cards
CRISPR
A (DNA) defense system found in the prokaryotic genome that can specifically and easily alter DNA sequences.
20
New cards
B lymphocyte
B cells (of lymph nodes) that produce antibodies
21
New cards
Biologic
medicine made of biologically based molecules (ex: proteins)
22
New cards
Chimeric protein
a type of biologic in which parts of different proteins are engineered together to make a very specific protein (ex: Etanercept or Enbrel)
23
New cards
What are the 3 types of biologics?
substances that mimic the body’s own proteins (ex: insulin), monoclonal antibodies, chimeric/fusion proteins