AQA GCSE Geography - Paper 1
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Paper 1 - Section B: The Living World + Section C: Coasts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What is a destructive wave?
A short, steep wave that tend to erode the beach
Strong backwash & weak swash
What is a constructive wave?
A long, gentle wave that deposits sediment onto the beach.
Strong swash & weak backwash
What is mechanical weathering?
The physical breakdown of rocks
What is chemical weathering?
The breakdown of rocks due to chemical reactions
What is mass movement?
The downward movement of sediment, due to gravity and weathering
What is rockfall?
The abrupt movement of rock fragments due to quick erosion
What is a landslide?
Blocks of rock slide downhill when layers of rock dip towards the sea
What is erosion?
Erosion is the removal of material by waves
What is abrasion?
When the sediment in destructive waves are launched at the coast until it wears away
What is attrition?
When sediment within the sea hit each other and breaks down
What is coastal hydraulic action?
When destructive waves crash against the cliff base, compressing air & water into the crack until it weakens/breaks
Describe the formation of caves, arches, stacks and stumps
A joint or fault in resistant rock
Abrasion and hydraulic action widen the joint to form a cave
Waves make the cave larger until it cuts through the headland to make an arch
The arch is eroded and the roof becomes too heavy and collapses
This leaves a tall stack
The stack is eroded and collapses, leaving a stump
What is a wave cut platform?
Narrow flat area found at the edge of a sea cliff.
What is a headland?
Headlands are formed of rocks which are more resistant to erosion, therefore erode more slowly.
What is a bay?
= an inlet of the sea where the land curves inwards (often at a beach)
What is deposition & what causes it?
When waves lose their energy and drops sediment at the coastline
Causes:
Wave type: constructive waves deposit more
Wind speed: lower wind speed reduces wave energy, depositing more
What are spits?
Spits are piles of sand that create sheltered zones on the coast.
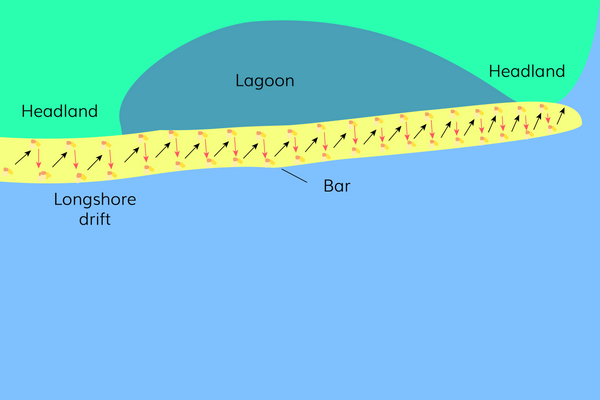
What are bars?
A bar is created when a spit grows across a bay. Lagoons are often created behind a bar.
What are sand dunes?
Sand dunes are hills of sand created at the back of the beach.
What is longshore drift? (+ describe the process)
The movement of sediment along a coastline by wave action
Waves approach the coast at an angle.
Swash carries sediment up the beach at an angle.
Backwash carries sediment down the beach with gravity – perpendicular to the beach.
This creates a zig-zag movement of sediment along the beach.
What is managed retreat?
The controlled flooding of coastal areas by removing existing defences
What are the advantages of managed retreat?
Managed retreat protects the land behind the mangroves or swamps. Managed retreat costs no money & no maintenance is needed. Swamps and mangroves are often biodiverse. Managed retreat moves the coastline. Because of this, it can be called coastal realignment.
What are the disadvantages of managed retreat?
Land is lost to the sea. Some people may lose their land or livelihoods if farmland is allowed to be flooded. Someone's house could be lost if they lived in the area that would become marshland.
Identify the erosional & depositional landforms found at the Dorset Coastline
Erosional: headland & bay
Depositional: beaches, spits, bars
(contains both concordant & discordant coastlines)
What is a sea wall?
Concrete or rock barrier against the sea placed at the foot of the cliff, usually curved.
What is a groyne?
Timber or rock structures built out to sea from the coast. They trap sediment being moved by longshore drift and enlarge the beach.
What is rock armour?
Piles of large boulders dumped at the foot of a cliff.
What are gabions?
Wire cages filled with rocks that can be built up to support a cliff.
What is beach nourishment?
The addition of sand to an existing beach to make it higher or wider.
What is dune regeneration?
Action taken to build up dunes and increase vegetation.
What is dune fencing?
Construction of fences along the seaward face of the dune to reduce wind speed.
How do waves form?
Wind makes contact with the sea, causing ripples
Ripples turn into waves
(in deep water) water molecules in wave move circularly, until increasing contact with sea bed causes crest to curve & break
Explain an example of mechanical weathering
Freeze thaw weathering:
Water enters crack in rock
It freezes & expands (due to trapped bubbles), widening the crack
Repeats until rock splits
Explain an example of chemical weathering
Acid rain:
Carbonic acid in the rain breaks down & dissolves rock over time
What is slumping?
Occurs in areas of permeable and impermeable layers of rock
How is a wave cut platform formed? (4 main points)
Destructive waves erode base of cliff, forming wave-cut notch
Height of wave-cut not determined by high/low tides
Overhang cracks (due to weathering) & falls off
Process repeats & wave-cut platform formed on sea floor where the cliff originally was
How & where are headlands and bays formed? (4 main points)
Formed by erosion at discordant coastlines
The hard rock remains standing, forming a headland
The soft rock erodes away, forming a bay
A beach is formed in the bay as waves lose energy & deposit material
How & where do caves form into arches to stacks to stumps? (5 main points)
In hard rock headlands
Hydraulic action & abrasion causes a crack in the headland, widening into a cave
The cave erodes until there is a gap all the way through the headland, forming the arch
The roof of the arch falls, becoming a stack
Stumps are smaller, eroded stacks
What are the 2 types of beaches ?
Sandy & shingle beaches
How do sandy beaches form? + Describe 2 characteristics
In sheltered bays:
Swash is greater than backwash so constructive waves deposit slowly
Gentle slope & wide beach width
How do shingle (pebble) beaches form? + Describe 2 characteristics
At exposed parts of the coastline:
Backwash is greater than swash, so destructive waves wash away finer sand, leaving large pebbles
Steep slope + narrow beach width
How are sand dunes formed? + Outline its 5 main stages
Embryo dune - newly formed dune close to sea
Fore dune- marrow grass takes hold as embryo dune grows
Yellow dune- larger dune with yellow sand
Grey dune - more biodiversity & roots hold sand in place
Dune slack forms where dune hollows out below water level
Mature dune - climatic climax is reached and full ecosystems form
How are spits formed?
Longshore drift carries sediment along a coastline in the direction of prevailing winds
Spit forms when: coastline changes shape OR longshore drift meets an estuary
Material is deposited & spit grows until material is removed faster than deposition
Salt marsh behind spit forms - sheltered area causes deposition
How is a bar formed?
Longshore drift carries sediment straight across a bay
What are 4 examples of hard engineering strategies (+ outline what they are)
Sea walls - concrete walls at beaches that are physical barriers to the sea
Rock armour - Large rocks highly resistant to erosion that absorb wave energy
Gabions - Permeable cages of rock that absorb wave energy
Grognes - wooden/rock structures that interrupt longshore drift
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of hard engineering strategies?
Pros:
Effective at reducing erosion/flooding
Long-term solution
Cons:
High set-up & maintenance costs
Can harm ecosystems & habitats
What are 3 coastal soft engineering strategies? (+ outline what they are)
Beach nourishment - Piling sediment from the sea floor onto the beach to replace eroded sediment
Beach reprofiling - Mechanically moving around sediment to create high ridges in sand to absorb wave energy
Dune regeneration- planting xerophytes into sand dunes to create natural barrier
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of soft engineering strategies?
Pros:
Environmentally friendly
More aesthetic to locals & tourists
Cons:
Short term solutions
Less effective in severe weather
What is managed retreat?
Controlled flooding of low-lying coastal areas
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of managed retreat?
Pros:
Creates natural habitats
Cheaper than sea defences
Cons:
Land & property are lost
Landowners need to be compensated
What is the name of a UK coastal management scheme?
Lyme Regis Improvement Scheme
Why was coastal management needed in Lyme Regis? (3 reasons)
Geology - clay is prone to erosion
Threat to homes/businesses - built on unstable cliffs
Area’s reliance on tourism - summer population increase from 4k to 15k
What strategies were used for Lyme Regis (+ total cost)
4 phases - £43 million total (completed in 2015):
Sea wall near river Lym
Rock armour at the Cobb
Cancelled as cons outweighed pros
New sea wall for extra protection
What are 2 pros and 2 cons of the Lyme Regis Improvement Scheme?
Pros:
Improved tourism → better beaches & protected harbour
Area protected from sea storms
Cons:
Complaints that sea defences ruin natural coastline
Erosion may worsen in other areas of coast
What is an ecosystem?
= a natural system where plants & animals interact with each other and their environment
What are the 2 main components of an ecosystem?
Biotic components - living components of an ecosystem
Abiotic components - non-living components of an ecosystem
Give 3 examples of biotic components of an ecosystem
Plants, animals, microorganisms
ps - dead things are also biotic
Give 3 examples of abiotic components of an ecosystem
Temperature, rainfall, landforms
What are the 4 roles in an ecosystem
1. Producers - convert energy from the environment into sugars
2. Primary consumers - animals that gain energy from eating plants
3. Secondary consumers - animals that gain energy from eating each other
4. Decomposers - break down plant/animal material , returning nutrients to the soil
Give 2 examples of each role in an ecosystem
1. Producers - flowers, trees
2. Primary consumers - herbivores: eg. insects, cows
3. Secondary consumers - eagles, lions
4. Decomposers - bacteria, worms
What is the nutrient cycle?
= the circulation of nutrients between the biotic elements of an ecosystem
Explain the 3 main stages of the nutrient cycle
1. Producers take up nutrients for growth
2. consumers eat producers and use their nutrients for energy & growth
3. Producers/consumers die and decomposers break down organic matter into nutrients
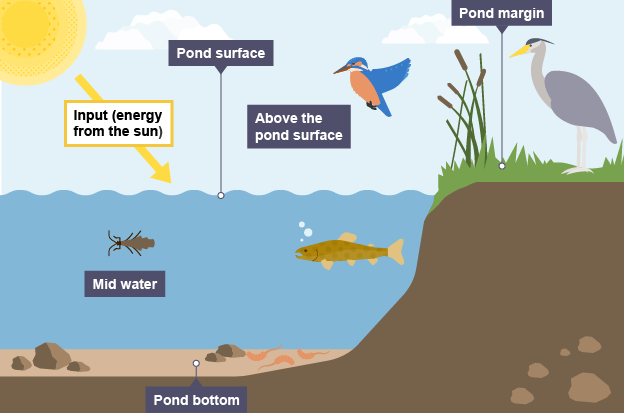
What are the main zones of a freshwater pond?
Pond bottom
Mid water
Pond surface
Pond margin
Above pond surface
What types of organisms and conditions can be found in different zones of a pond ecosystem?
Pond bottom:
Conditions: Little oxygen and light.
Organisms: Decomposers - eg. Water worms
Mid water:
Organisms: Fish (main predators) + animals that breathe through gills
Pond surface:
Conditions: Plenty of oxygen and light.
Organisms: Ducks, tadpoles + animals that breathe through gills, skin, or lungs
Pond margin:
Conditions: Lots of light and oxygen; plants thrive.
Organisms: Frogs & insects sheltered by plants.
Above the pond surface:
Organisms: birds (eg. Kingfishers) + flying insects (eg. dragonflies)
What are the main characteristics of a tropical rainforest?
Very warm & wet
Soil isn’t very fertile
High biodiversity
Describe the 4 layers of the rainforest
Emergent: highest layer with trees approx 50M
Main canopy: where most life is found that recieves 70% of sunlight
Under canopy: contains younger trees competing for light in dark conditions
Shrub layer: lowest layer - is dark & dense with small vegetation
How does the nutrient cycle work in the rainforest?
Warm & wet conditions allow dead material to rapidly decompose
Rich nutrients in the top soil are quickly absorbed by plants
Soil is relatively infertile as a result
What are 2 plant adaptations for the tropical rainforest?
Buttress roots: tall, above-ground roots to absorb top soil nutrients + keep tree stable
Drip tips: waxy leaves with pointed tips to allow water run off without damaging plant
What case study illustrates deforestation & its effects?
Malaysian rainforest
What are the 3 causes of deforestation in Malaysia?
Mining for metals/materials
Construction of dams/pipelines/roads
Logging to produce timber
Land for farming
What are the impacts of deforestation in Malaysia?
Economic development from developing infrastructure (mines, roads etc) - generate foreign income
Soil erosion: water washing away nutrient dense top soil stops nutrient cycle & makes it infertile
Climate change: less trees to absorb C02, global warming
Why is the rainforest important? (3 reasons)
Helps regulate atmospheric composition (by absorbing CO2)
Provide medicines (eg rosy periwinkle for leukaemia)
Raw materials (eg timber)
What are 4 ways to sustainably manage the rainforest?
Selective logging: most valuable trees removed without damaging others, then replanting
Conservation: preserving rainforest for science & education
Ecotourism: small scale tourism that implements natural world
International agreements: global environmental agreements/pledges
What are the main characteristics of a hot desert?
Dry & arid (less than 250mm per year)
Very hot during day, very cold at night
Sandy stony soils
What are 2 animal/plant species adapted to the desert & how?
Camel: sat hump to store energy, thick fur for cold nights
Cactus: waxy layer reduce water loss, spikes provide shade + reduce water loss via transpiration
What case study shows the opportunities and challenges in a desert?
Moroccan Sahara
What are 3 opportunities created in hot deserts?
Mineral extraction: phosphate in Morocco
Energy production: CSP enough to power 1 million Moroccan homes
Tourism: Atlas Studios located in Sahara - sets for movies
What are 3 challenges created by hot deserts?
Harsh temperatures: hard to live and work in this
Lack of water: water supplies can are unreliable (eg reliance on underground wells)
Inaccessibility: limited road networks to the Sahara, making transport expensive
What is desertification?
= the spread of desert conditions in arid regions due to human activities, drought and climate change
What are some causes of desertification ?
Climate change: global warming
Overgrazing: increase in farming leaving soil exposed to erosion
Population growth: places strain on resources (eg water, wood)
What are 3 ways to reduce desertification?
Planting more trees: holds soil together & reduces soil erosion
Replace grazing animals with crops: prevents overgrazing
Appropriate technology: eg earth dams to store water during wet season
Describe the 4 main types of river erosion? (think HAAS)
Hydraulic action = force of the river against the banks causes air compression in cracks
Abrasion = rocks carried by the river scraping along the bed & banks
Attrition = river rocks collide and break up
Solution = sea water eroding certain types of rocks
Describe the 4 main types of river transportation & where is it most prevalent? (think TripleS)
Traction = larger heavy pebbles roll along river bed (mostly at river source)
Suspension = lighter sediment suspended within the water (mostly at river mouth)
Solution = transport of dissolved chemicals (location varies)
Saltation = pebbles bouncing along river bed (mostly at river source)
What are 3 factors that lead to river deposition?
Shallow water
Water getting to the river’s mouth
Decreased volume of water
What are 3 erosional river landforms? (+ what river course do they appear?)
Interlocking spurs
Waterfalls
Gorges
UPPER course
What are 2 river landforms that are both erosional & depositional? (+ what river course do they appear?)
Meanders
Oxbow lakes
MIDDLE course
What are 3 depositional landforms? (+ what river course do they appear?)
Levées
Flood plains
Estuaries
LOWER course
How are interlocking spurs formed? (3 main points)
UPPER COURSE: there is more vertical erosion, so it cuts into the valley
Due to low velocity, the river erodes soft rock but bends round harder rock
This forms interlocking spurs
How are waterfalls and gorges formed? (4 + 1 main points)
UPPER COURSE: when there’s a drop in the river course, there is hard rock layered on soft rock
The soft rock erodes faster than the hard rock and forms an overhang
Abrasion & hydraulic action erode to form a plunge pool
This increases the size of the overhang until it collapses - waterfall formed!
Valley from the sides of where the waterfall once was is = gorge
How are meanders formed?
MIDDLE COURSE - As river gains more velocity:
Water is highest velocity on the outside of a bend
Hydraulic action + abrasion erosion forms river cliff
Water is lowest velocity on the inside of a bend (because of more friction)
Deposited sediment forms slip off slope
How are oxbow lakes formed?
MIDDLE COURSE - As erosion & deposition occurs in meandering rivers:
Outer banks are eroded, inner banks have sediment deposited
The bend becomes more pronounced until the narrow neck of the meander breaks during a flood
This leaves a new straighter channel + isolated oxbow lake
How are levées formed? (+where?)
LOWER COURSE- when an increased volume of water forms & flooding occurs:
Transported sediment floods across floodplain
River loses energy so larger sediment deposited first on river banks & smaller sediment further away
After lots of floods, sediment builds up, forming levées
What is a floodplain?
= low lying area surrounding a river that is prone to flooding
How is a floodplain formed?
Material from river deposits during flood
Over time height increases
What is an estuary & how is it formed?
= where the river meets the sea
river spreads out & slows down when it reaches sea causing deposition
What is an example of river Valley in the UK?
River Severn
What physical and human factors increase flood risk?
Physical:
Heavy rainfall (saturated soils- > runoff)
Impermeable rock surfaces
Relief - steep valleys increases floodrisk
Human:
Land use - urban areas → impermeable surfaces → surface runoff
What is the rising limb & falling limb on a hydrograph?
Rising limb = increase in river discharge
Falling limb = decrease in river discharge
What are 3 examples of hard engineering strategies for flood management?
Dams
Channel straightening (by cutting off meanders)
Embankments (creating leeves/building walls)
What is a pro and con of dams for flood managament?
Pro: stores lots of water esp during heavy rainfall
Con: lots of land need to be flooded (displaces people)