Lecture 1: The Cerebrum
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
CNS
where information is processed:
brainstem, cerebellum, diencephalon, cerebrum, basal ganglia
-spinal cord
components of the central nervous system:
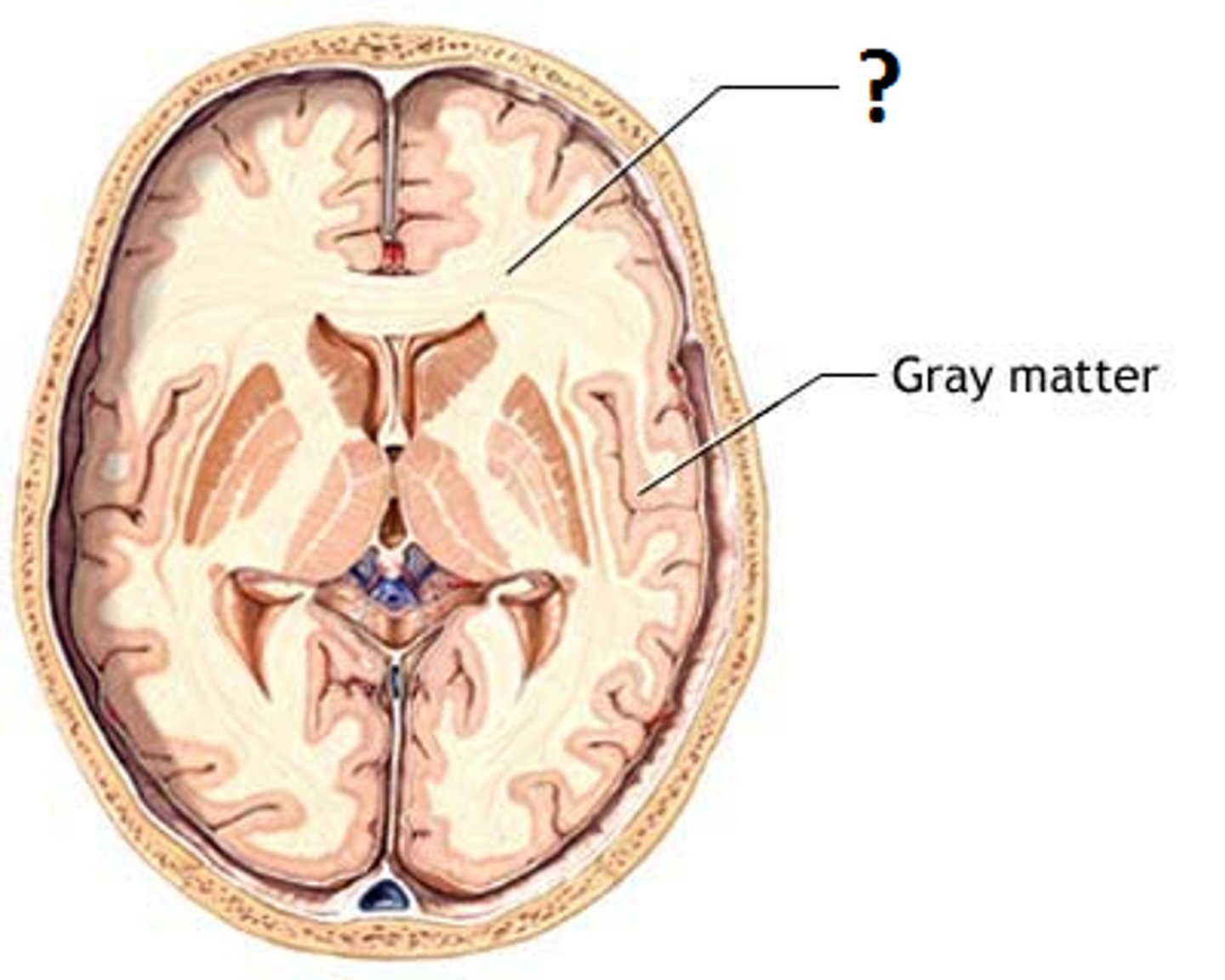
grey matter
The portions of the central nervous system that are abundant in cell bodies of neurons rather than axons. Unmyelinated.
ganglion
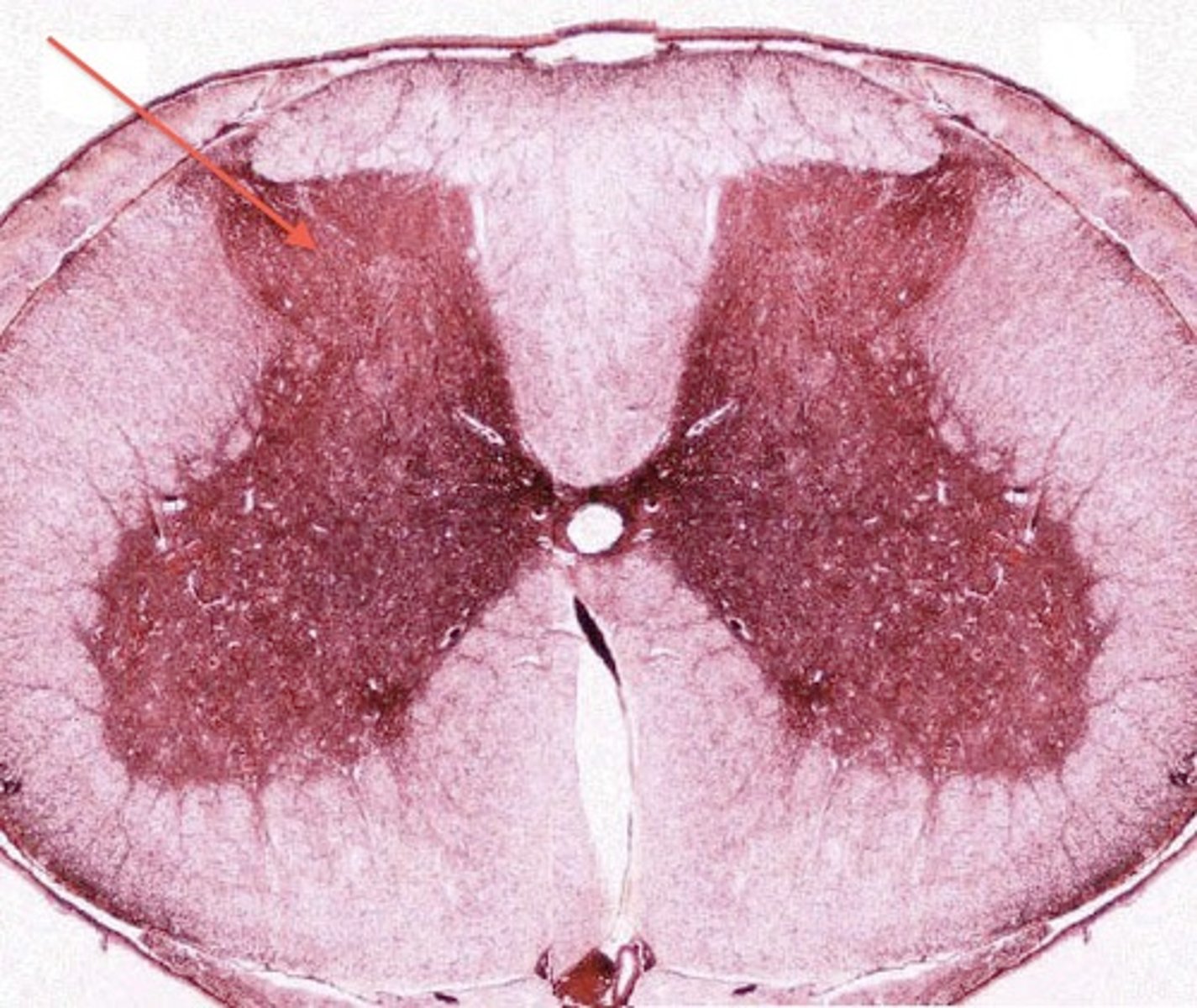
-grey matter
collection of neuron cell bodies outside the CNS
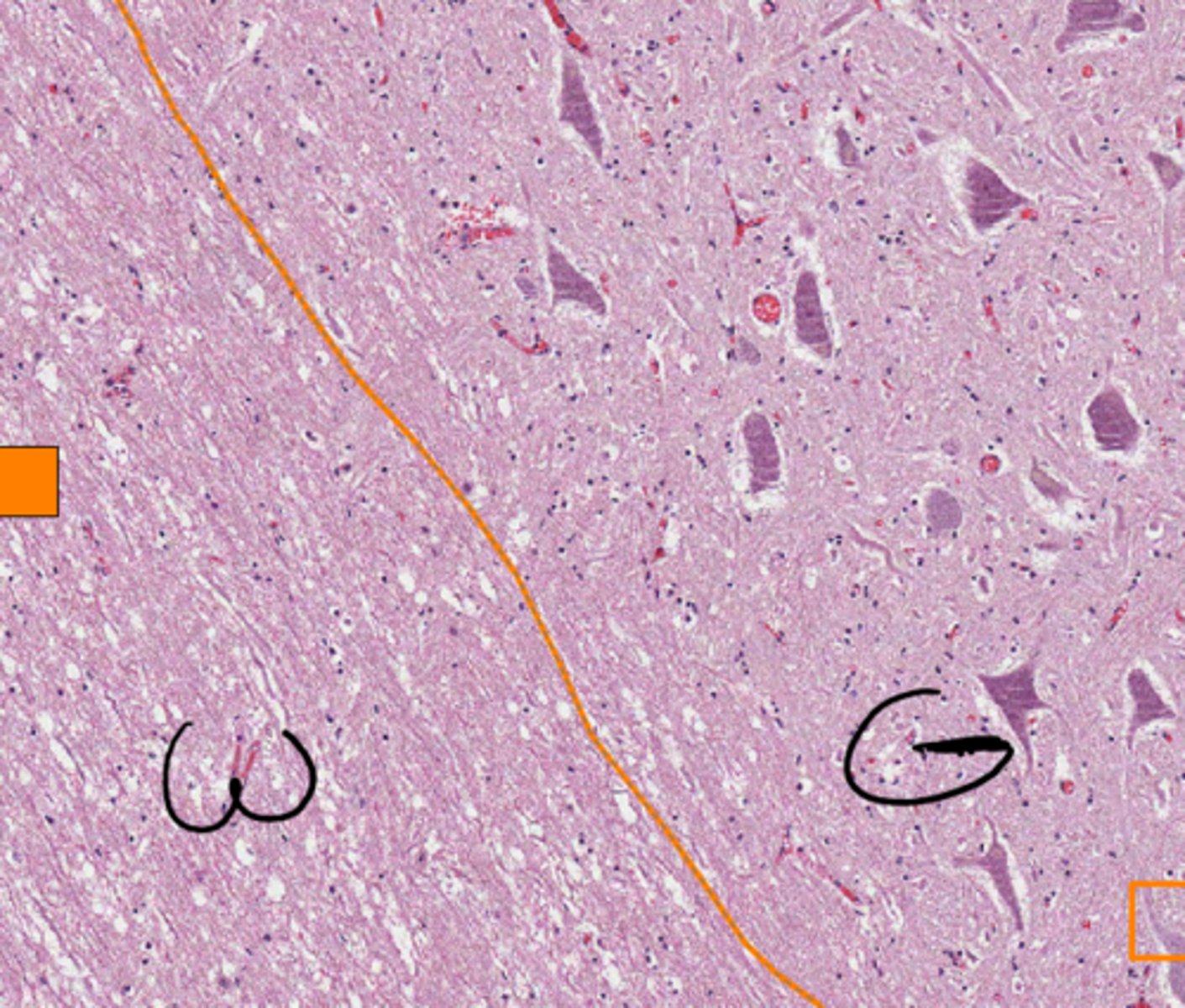
axons connecting neighboring or distant nuclei of cerebral cortex
define tract of white matter:
telencephalon
the cerebrum is aka
thalamus, hypothalamus
what structures make up the diencephalon?
midbrain, pons, medulla
components of the brain stem
tract
name for a bundle of axons running together
gray matter
a portion of the CNS consisting of (cell bodies), their dendrites and synaptic connections
white matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.
Telencephalon
the cerebrum is also known as
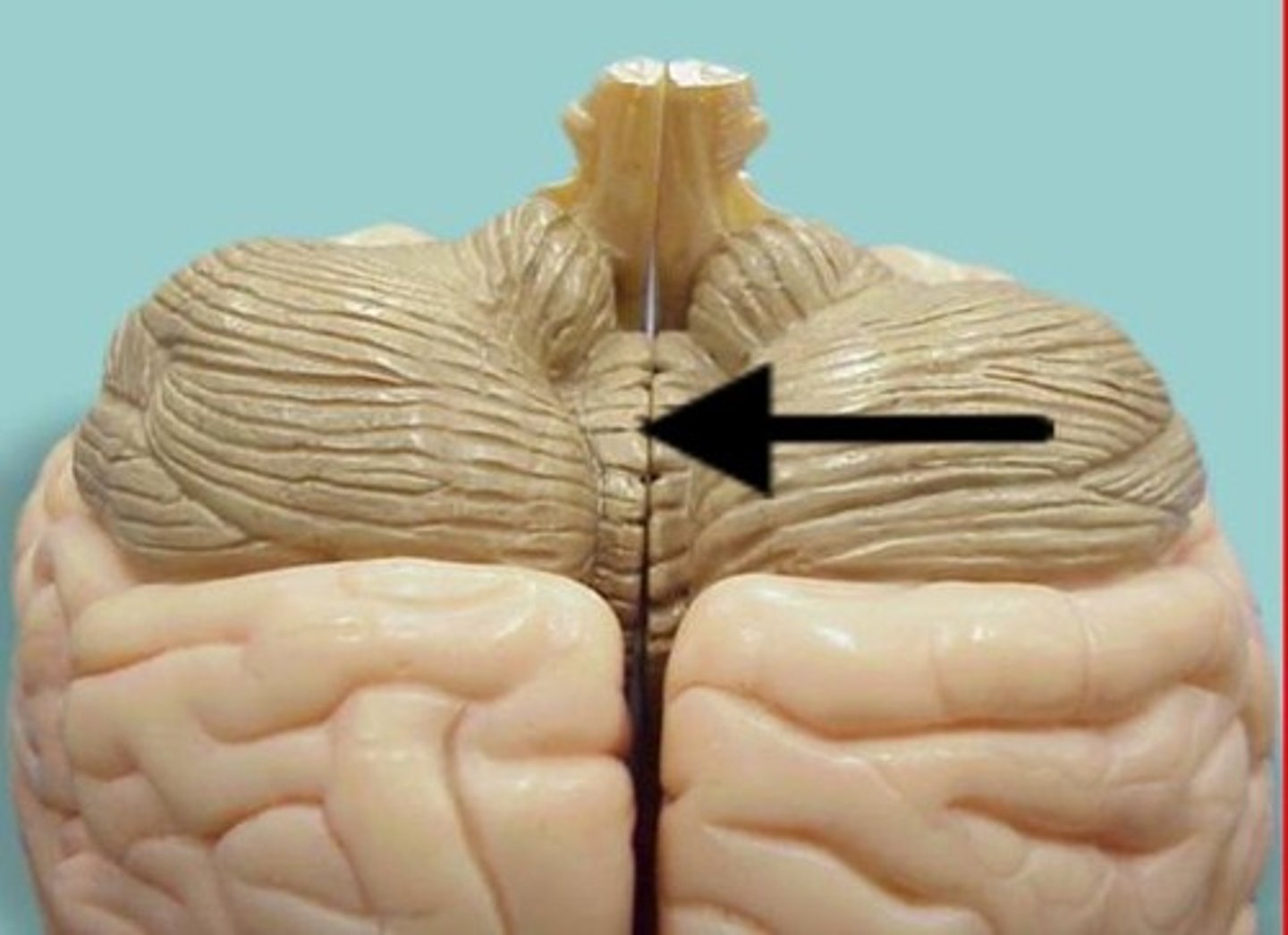
corpus collosum
the two hemispheres of the cerebrum are connected by
Sulcus
groove
gyrus
A ridged or raised portion of a convoluted brain surface.
vermis
the 2 hemispheres of the cerebellum are connected by
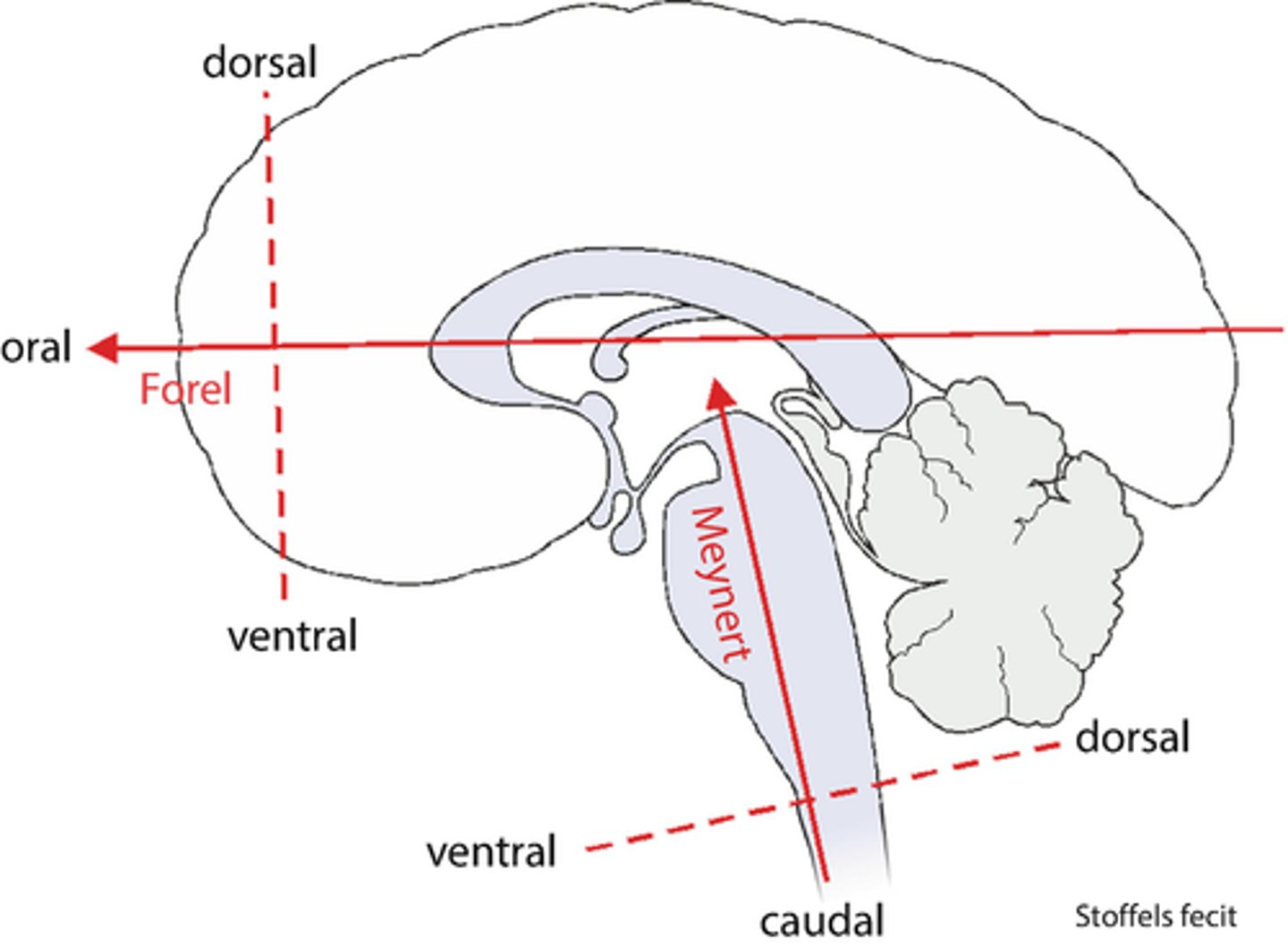
Forel Axis
horizontal axis in relation to cerebrum
-separates superior/inferior
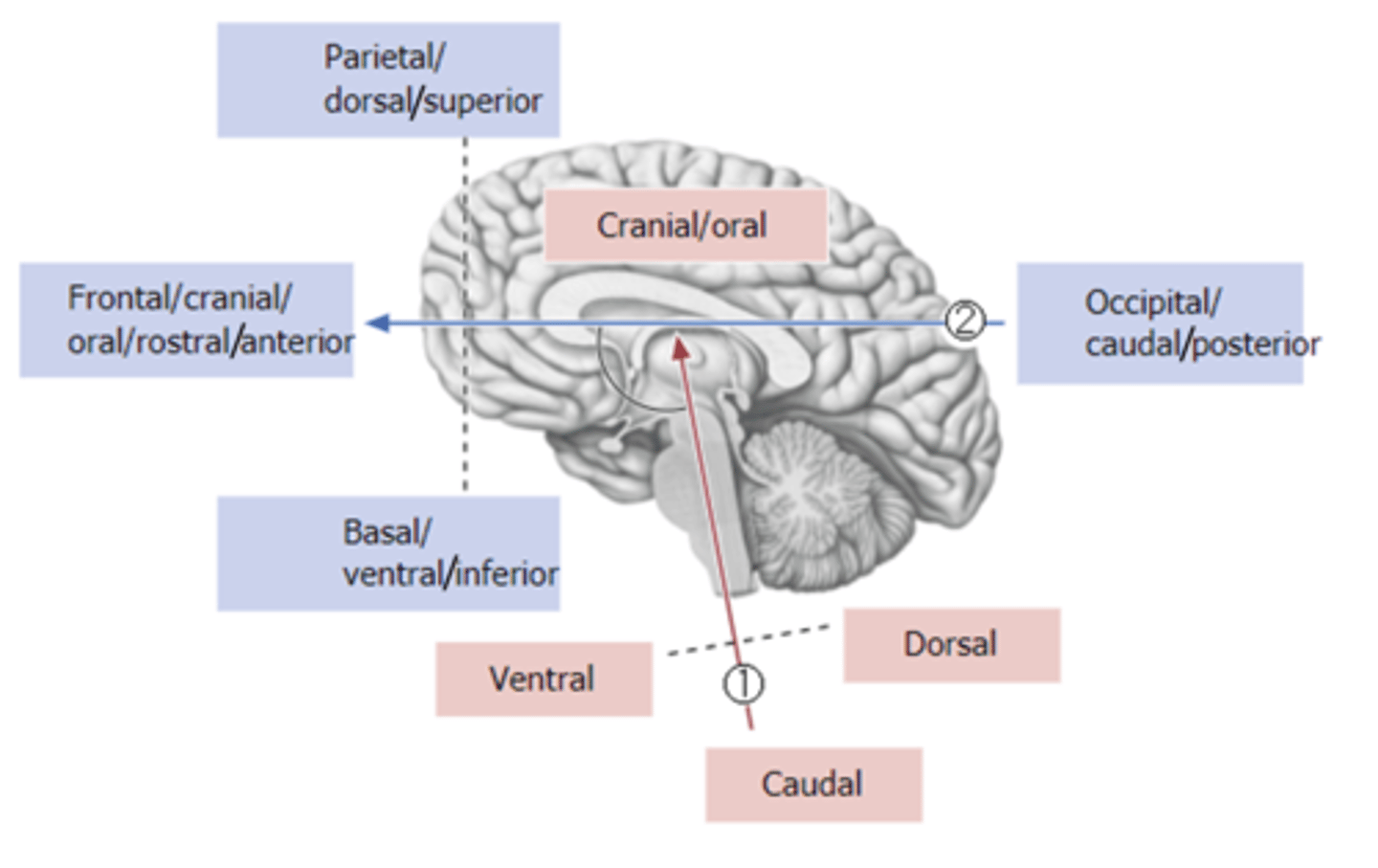
Maynert Axis
brain axis through the spinal cord, brain stem, and cerebellum
-ventral, dorsal, caudal
Rostrum of Corpus Callosum
ID
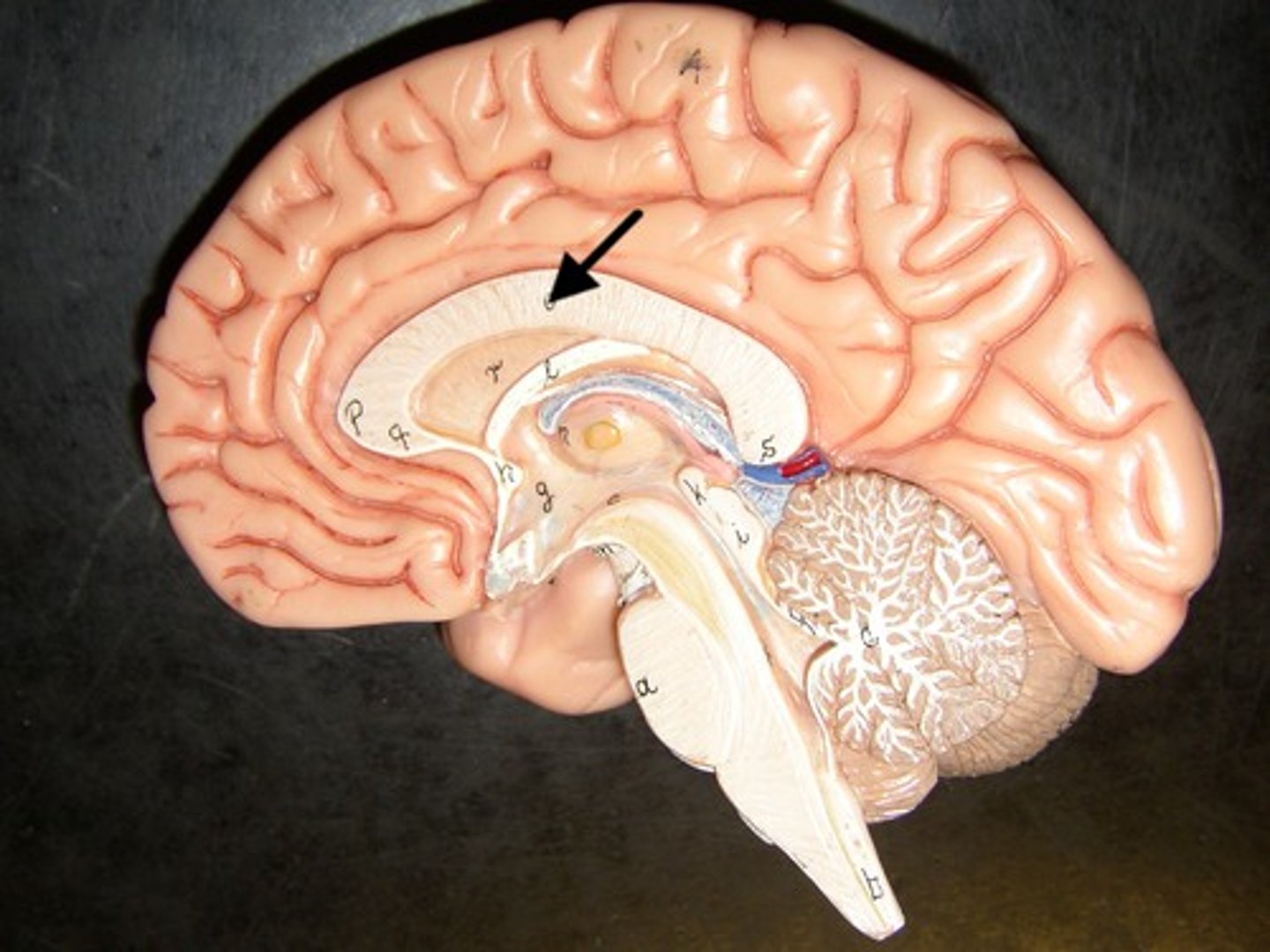
Genu of Corpus Callosum
ID (be specific)
trunk of corpus callosum
ID (be specific)
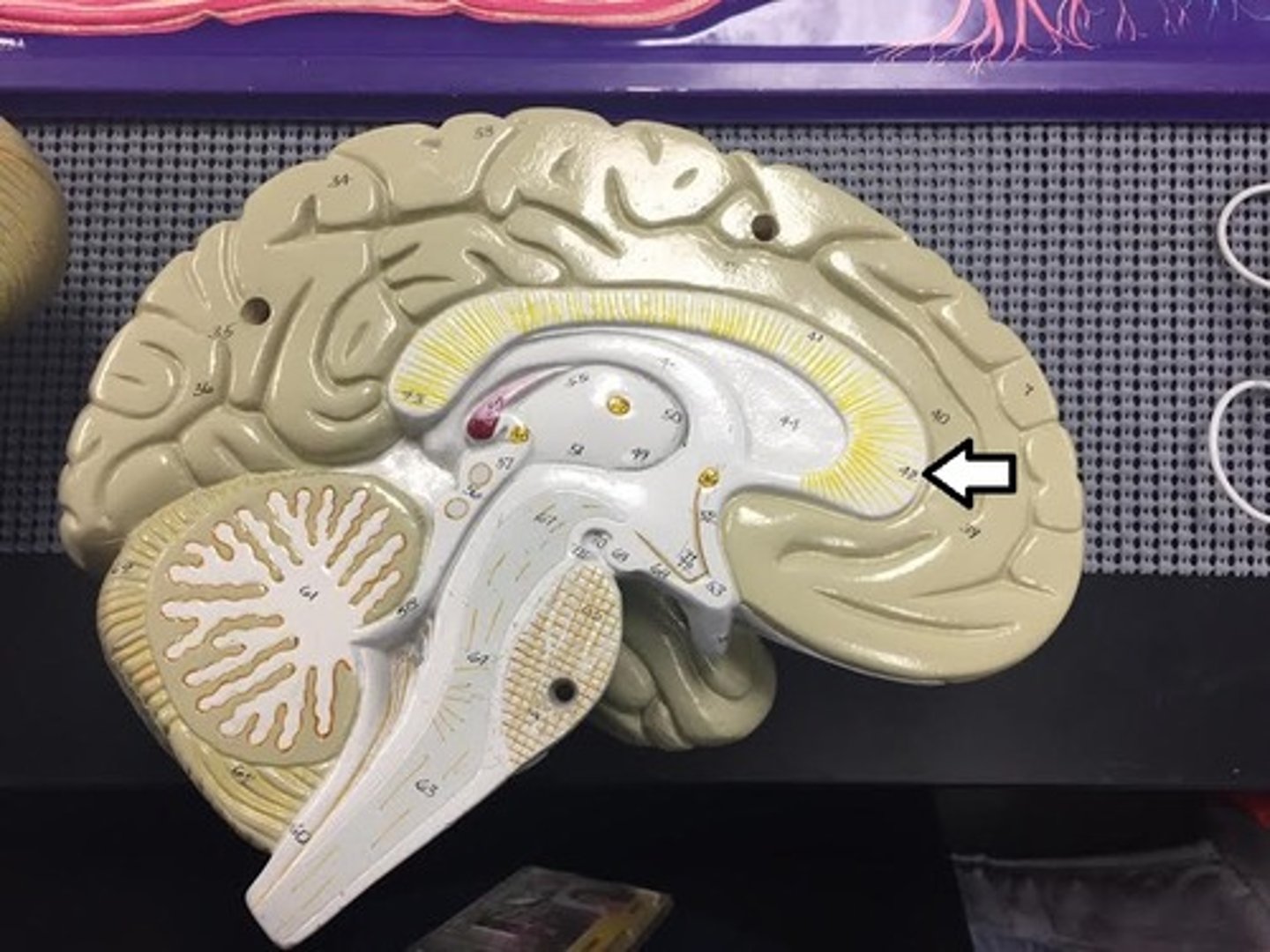
splenium of corpus callosum
ID (be specific)
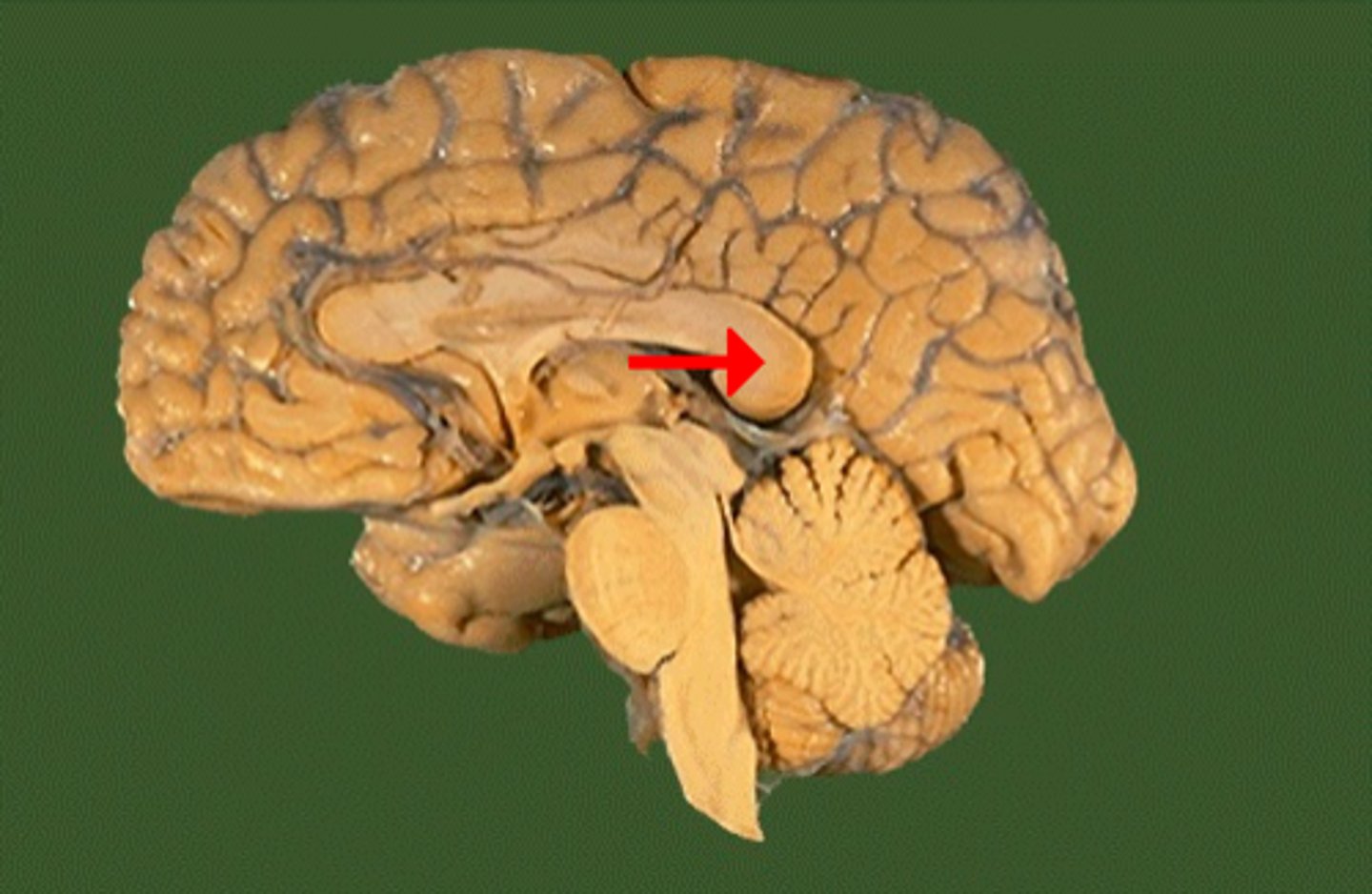
particularly deep sulcus
define fissure:
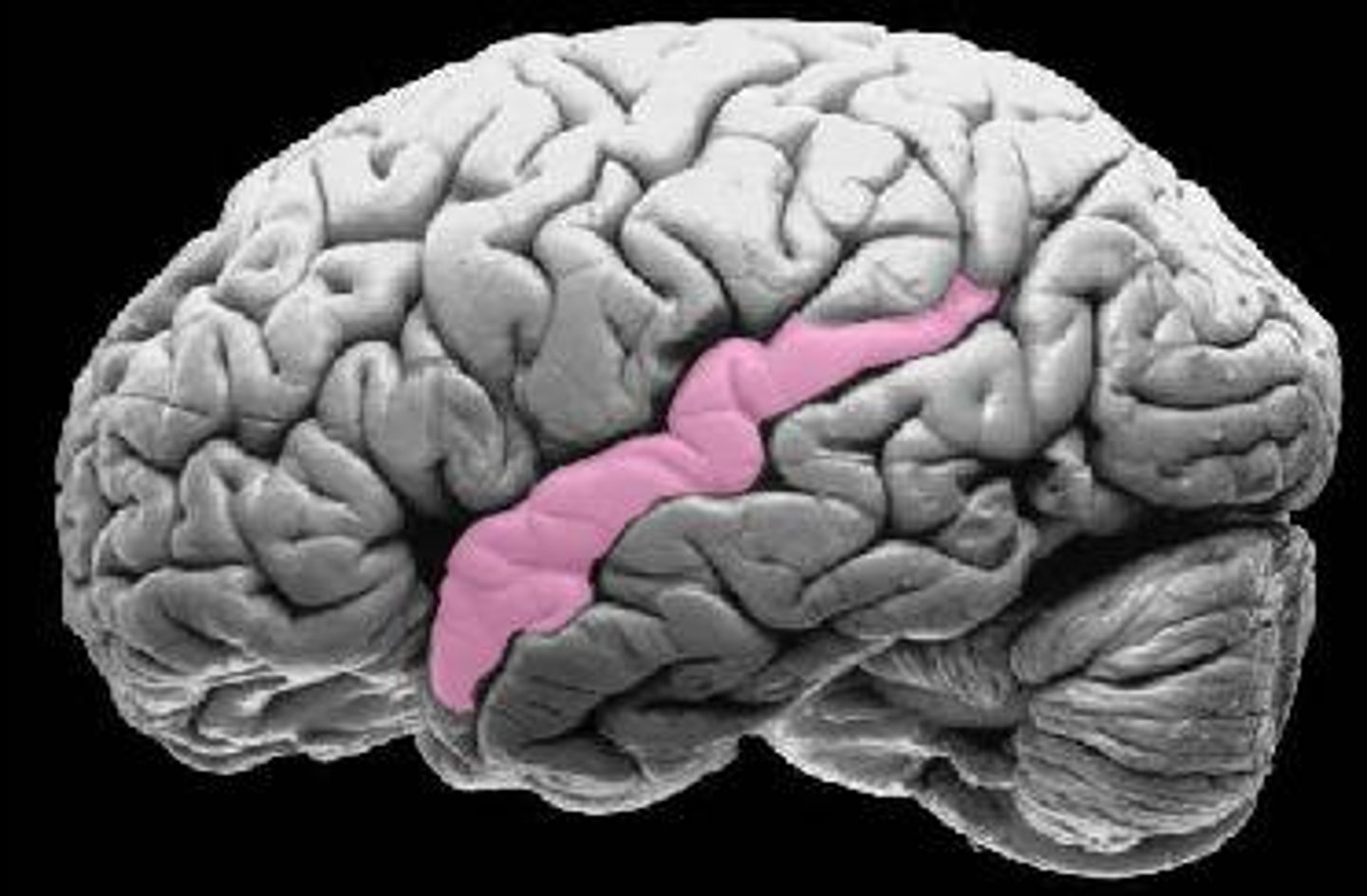
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
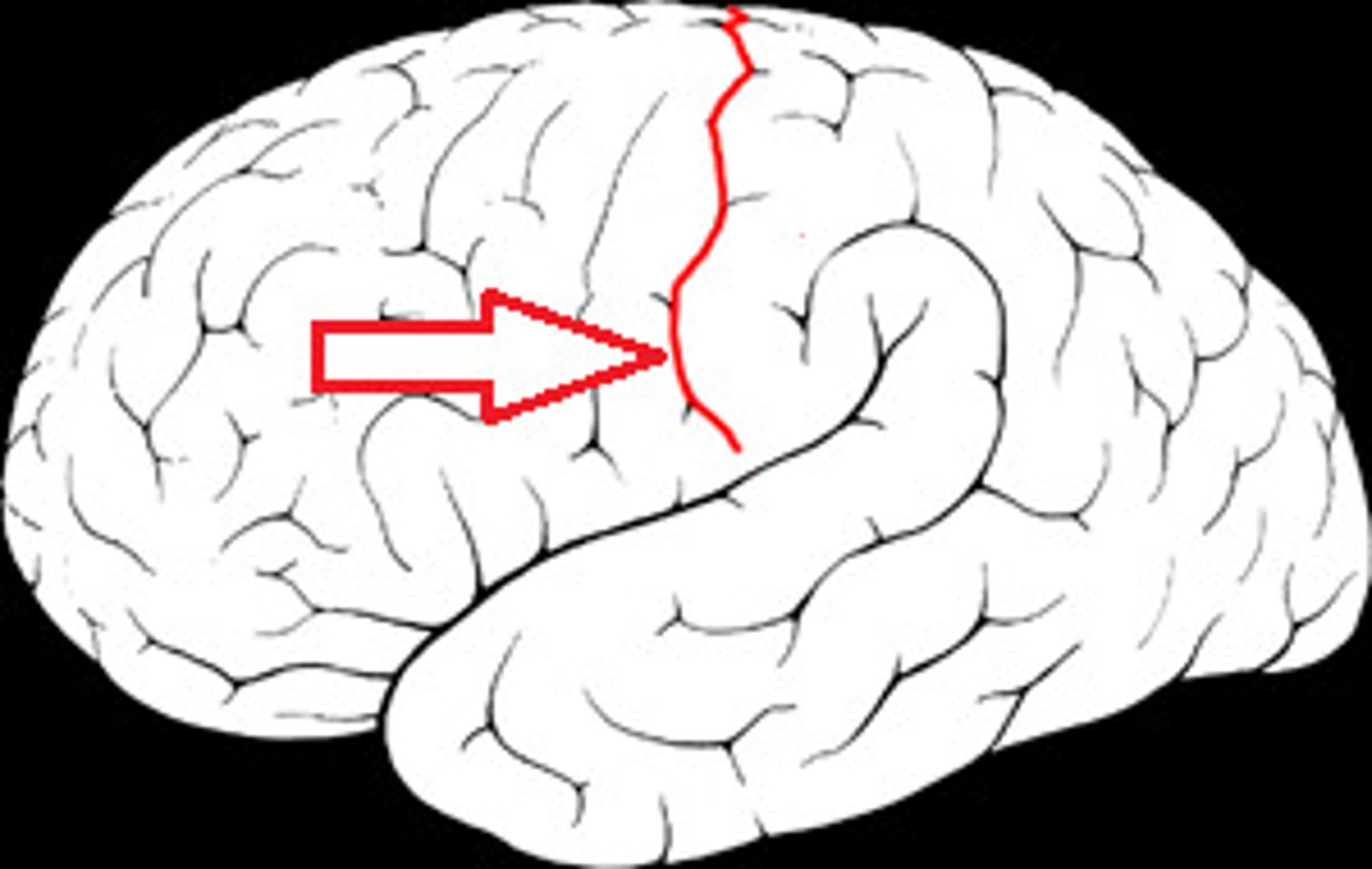
lateral fissure
separates temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes
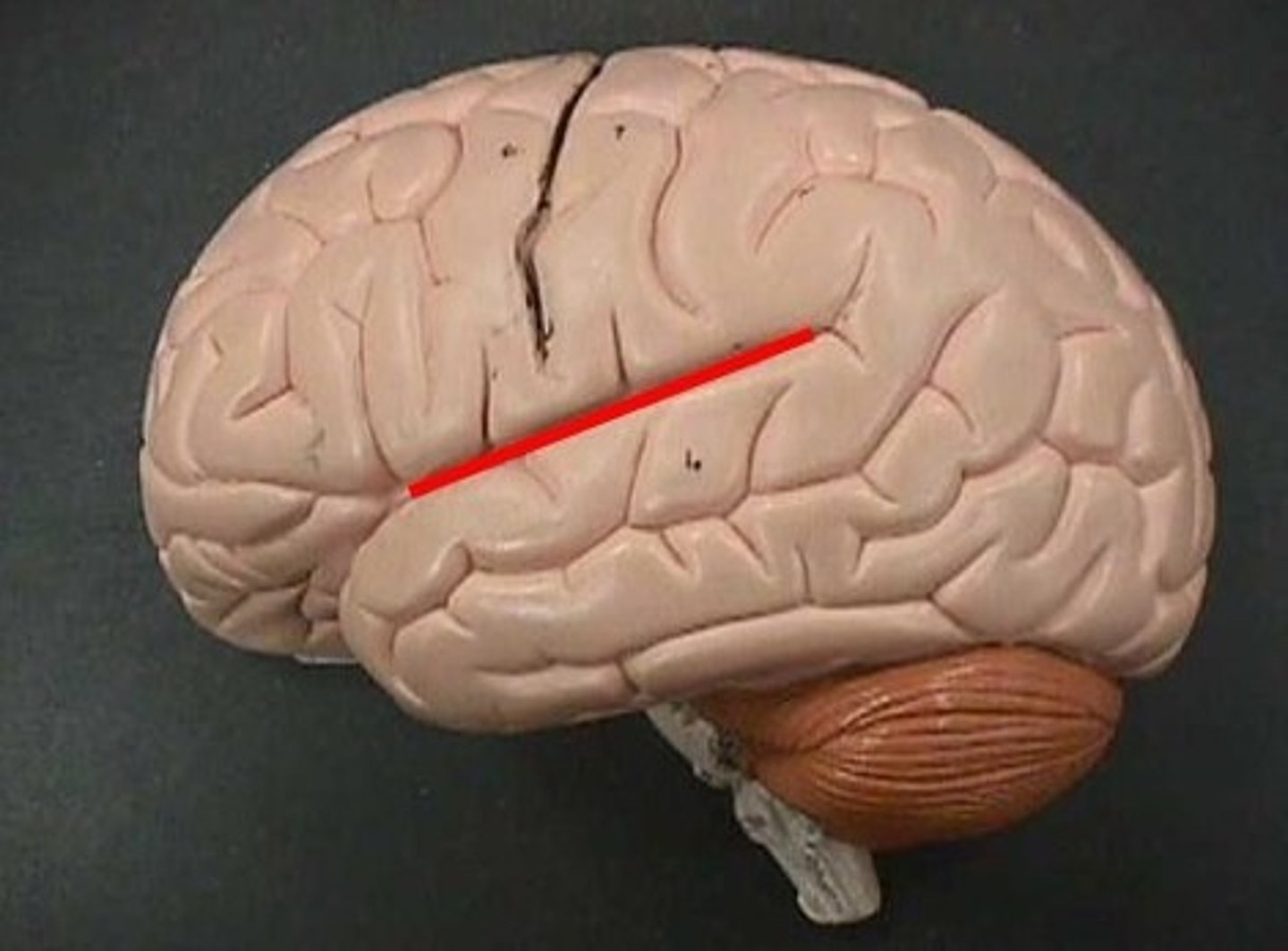
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates parietal and occipital lobes
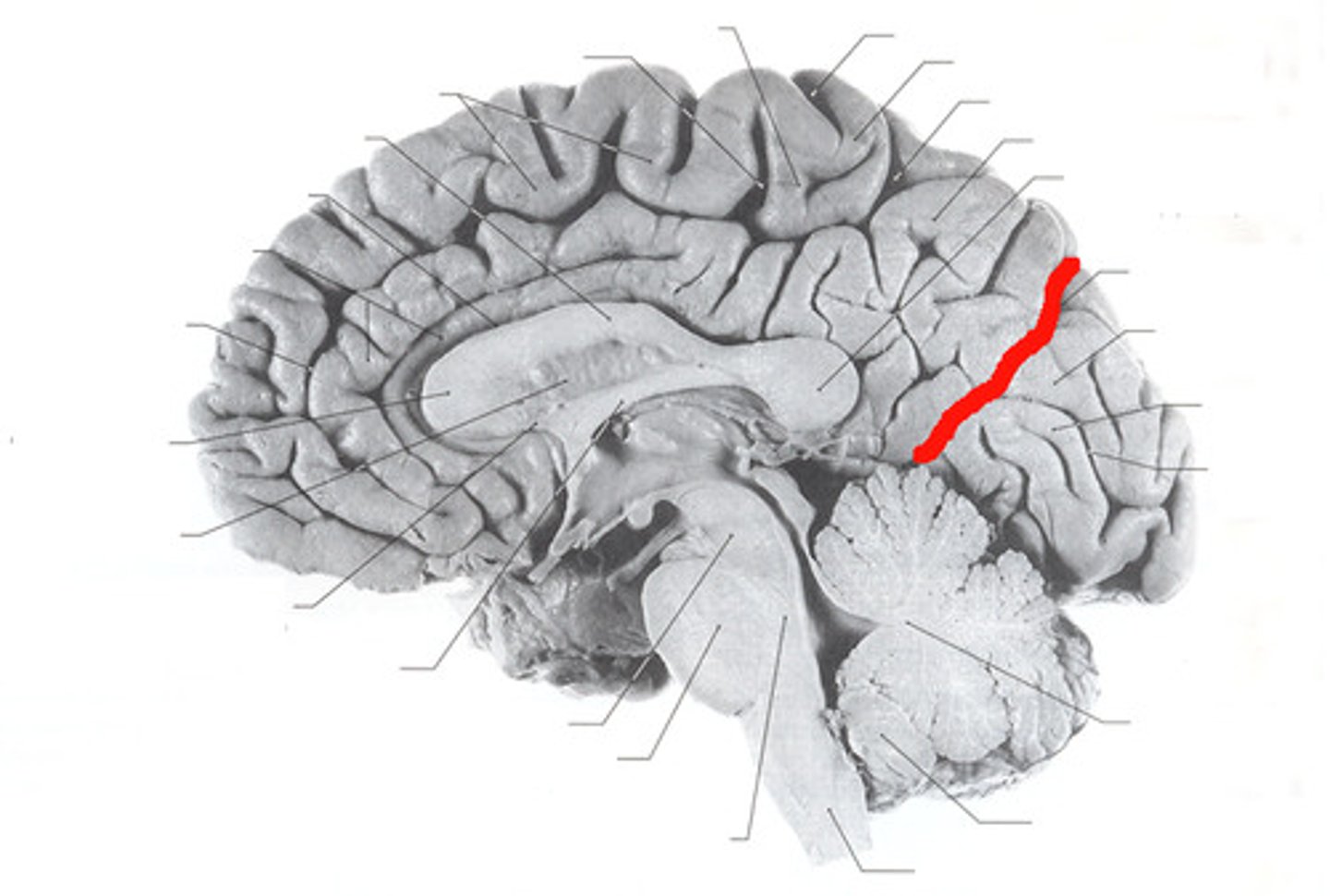
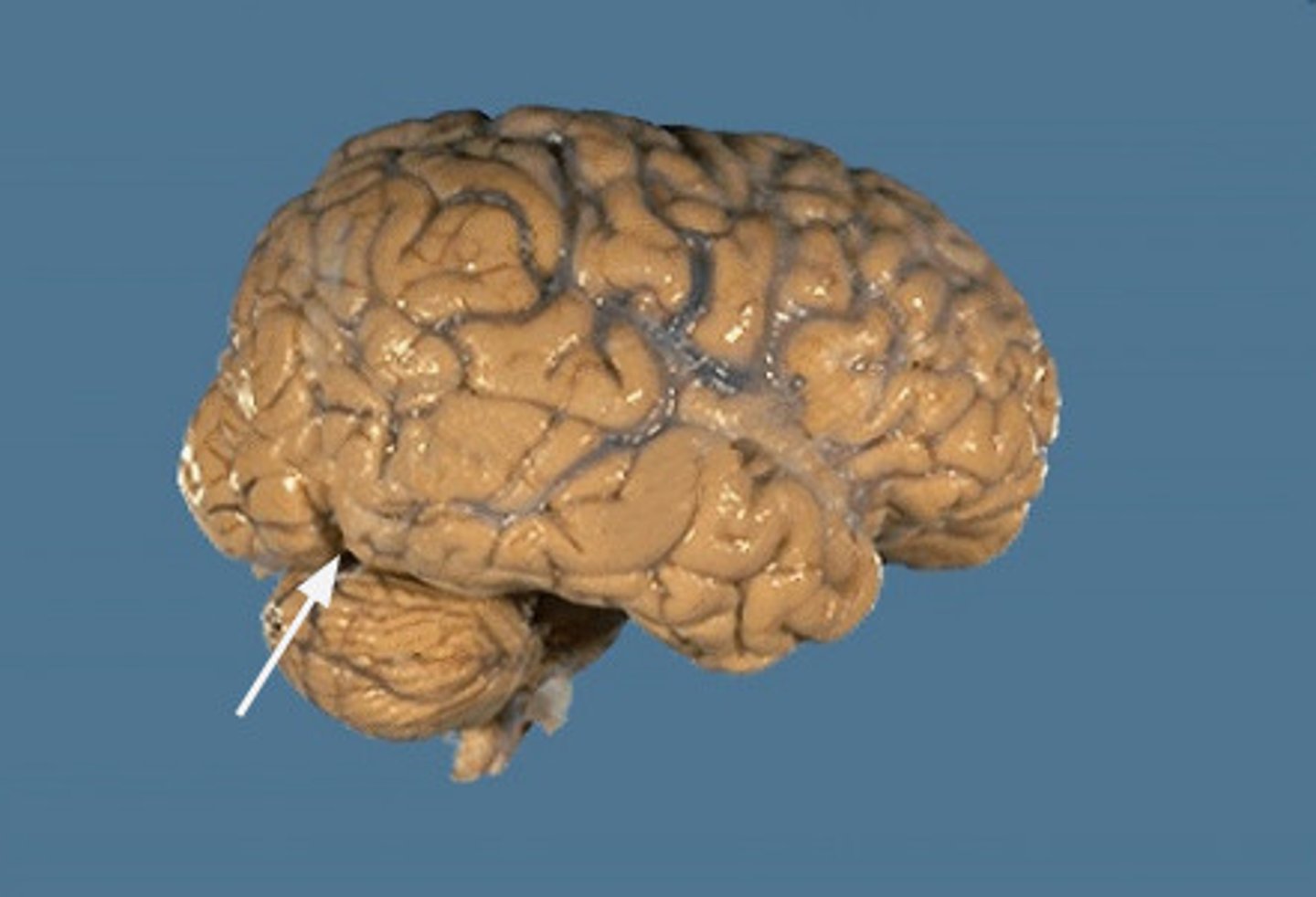
pre-occipital notch
the notch that serves as the bottom point of the imaginary dividing line between the temporal and occipital lobes; the top of the parieto-occipital sulcus is the top point
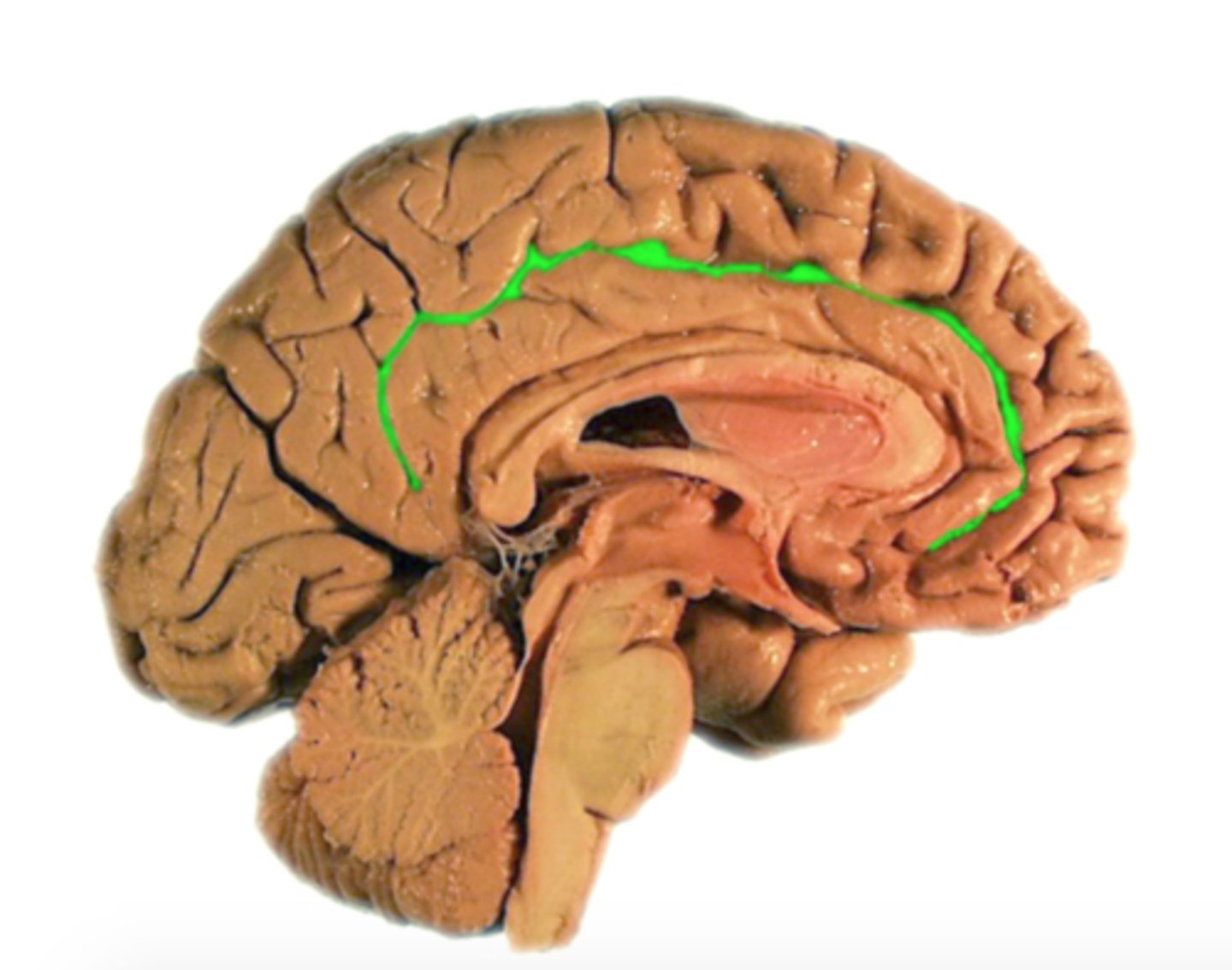
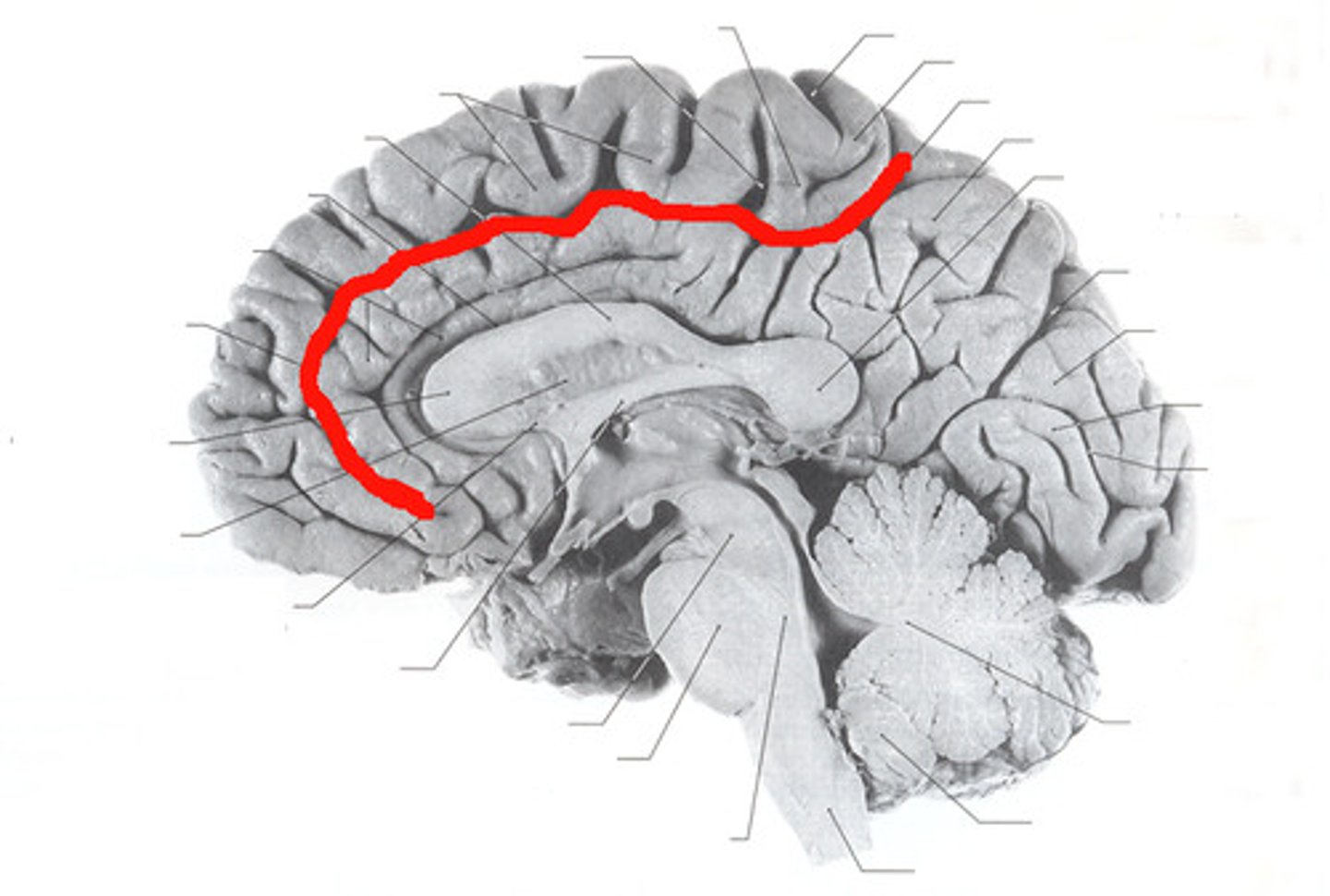
cingulate sulcus
Separates frontal and parietal lobes from cingulate gyrus
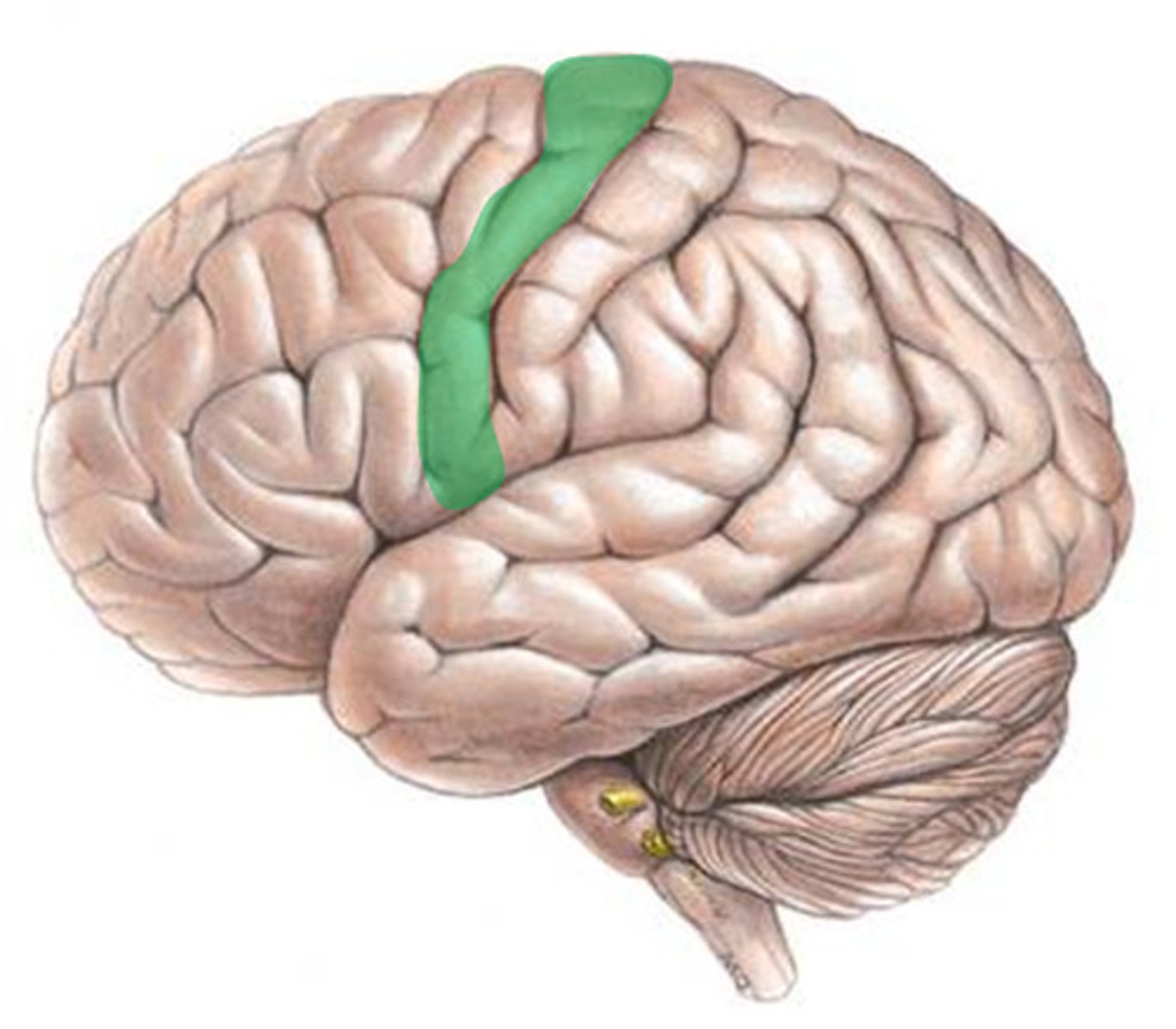
precentral gyrus
ID
superior frontal gyrus
the frontal lobe gyrus that runs horizontally along the top of the lobe
-medial
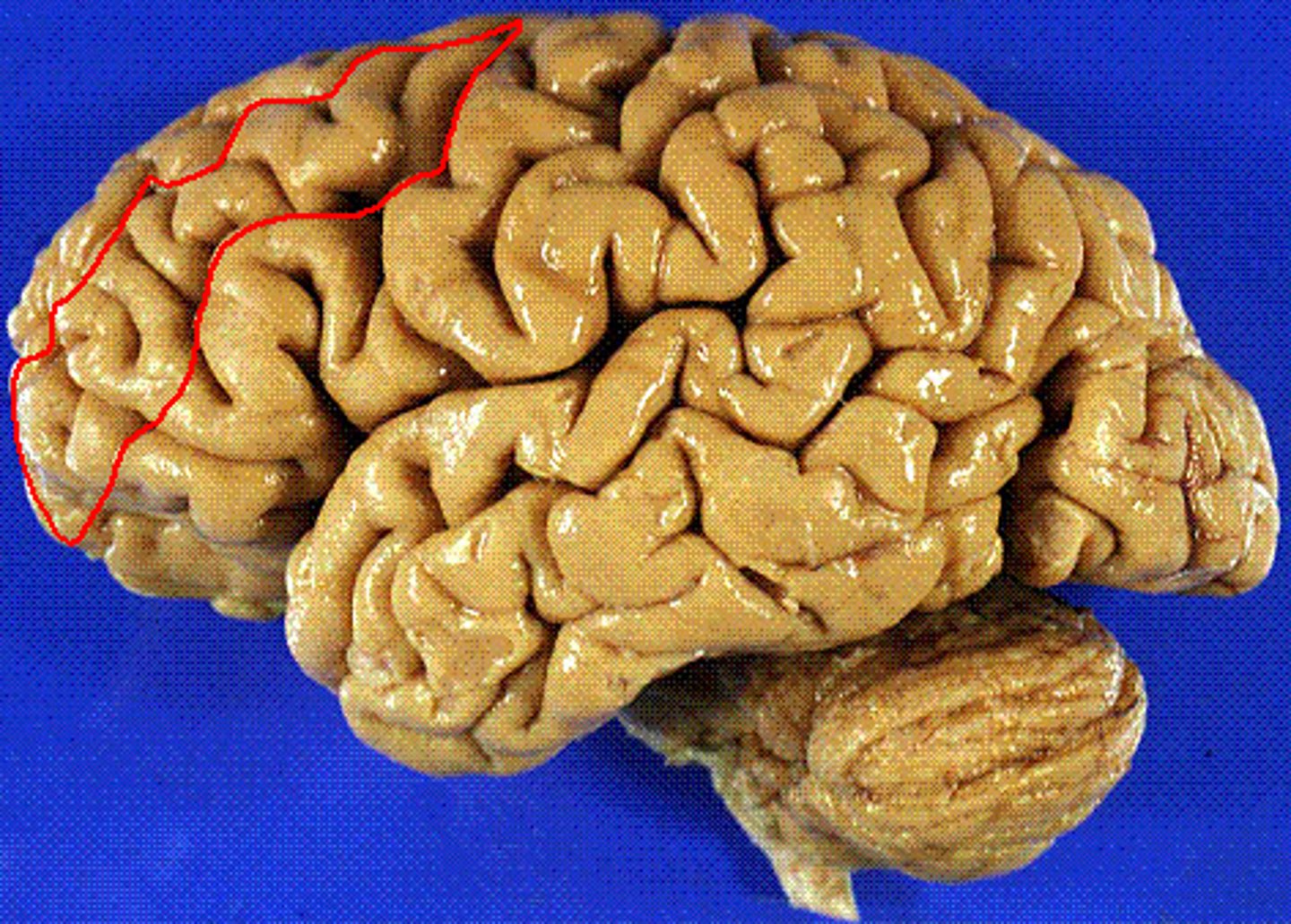
middle frontal gyrus
the frontal lobe gyrus that is located between the superior and inferior frontal gyri
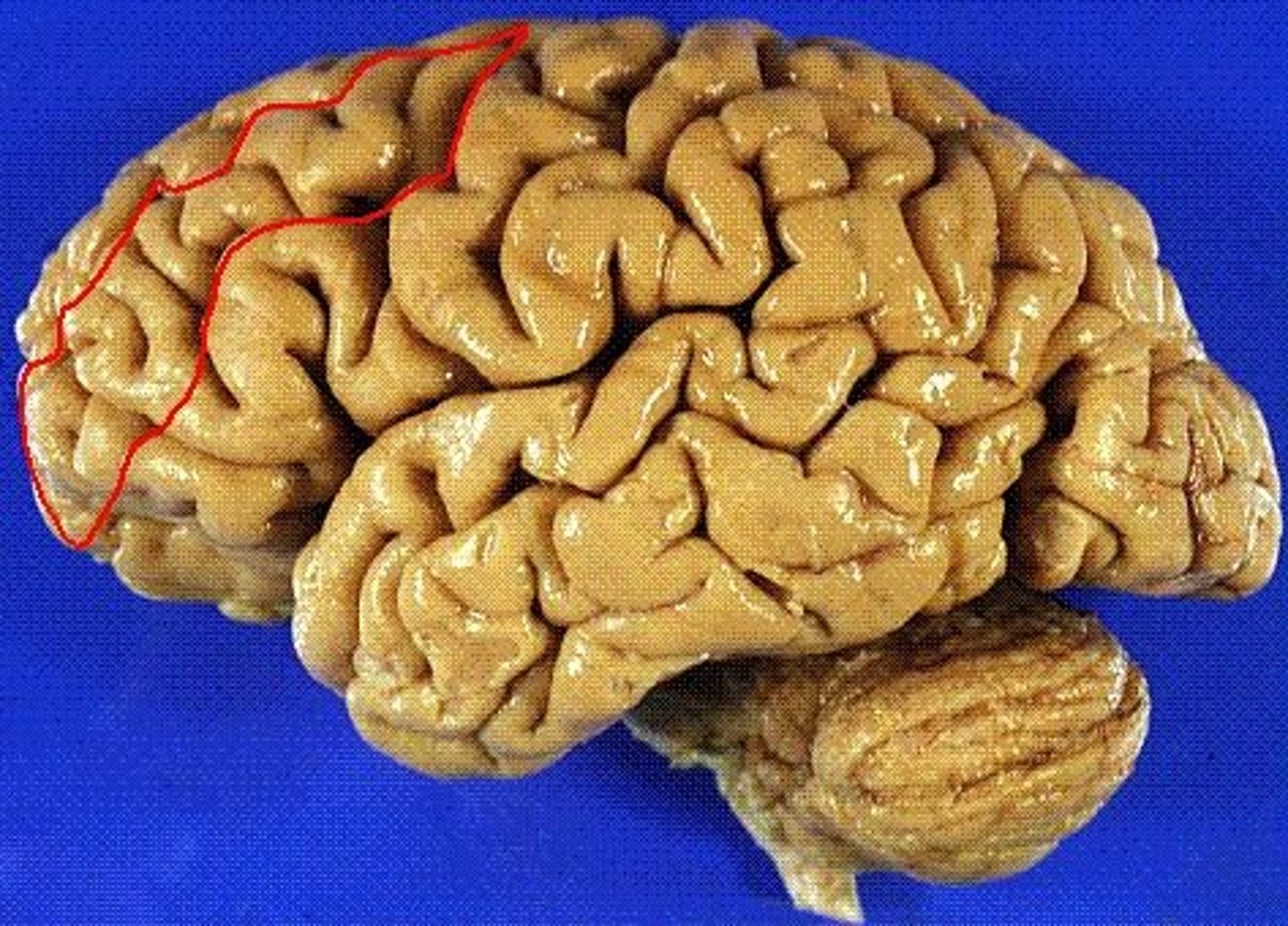
inferior frontal gyrus
the frontal lobe gyrus that is located just inferior to the middle frontal gyrus
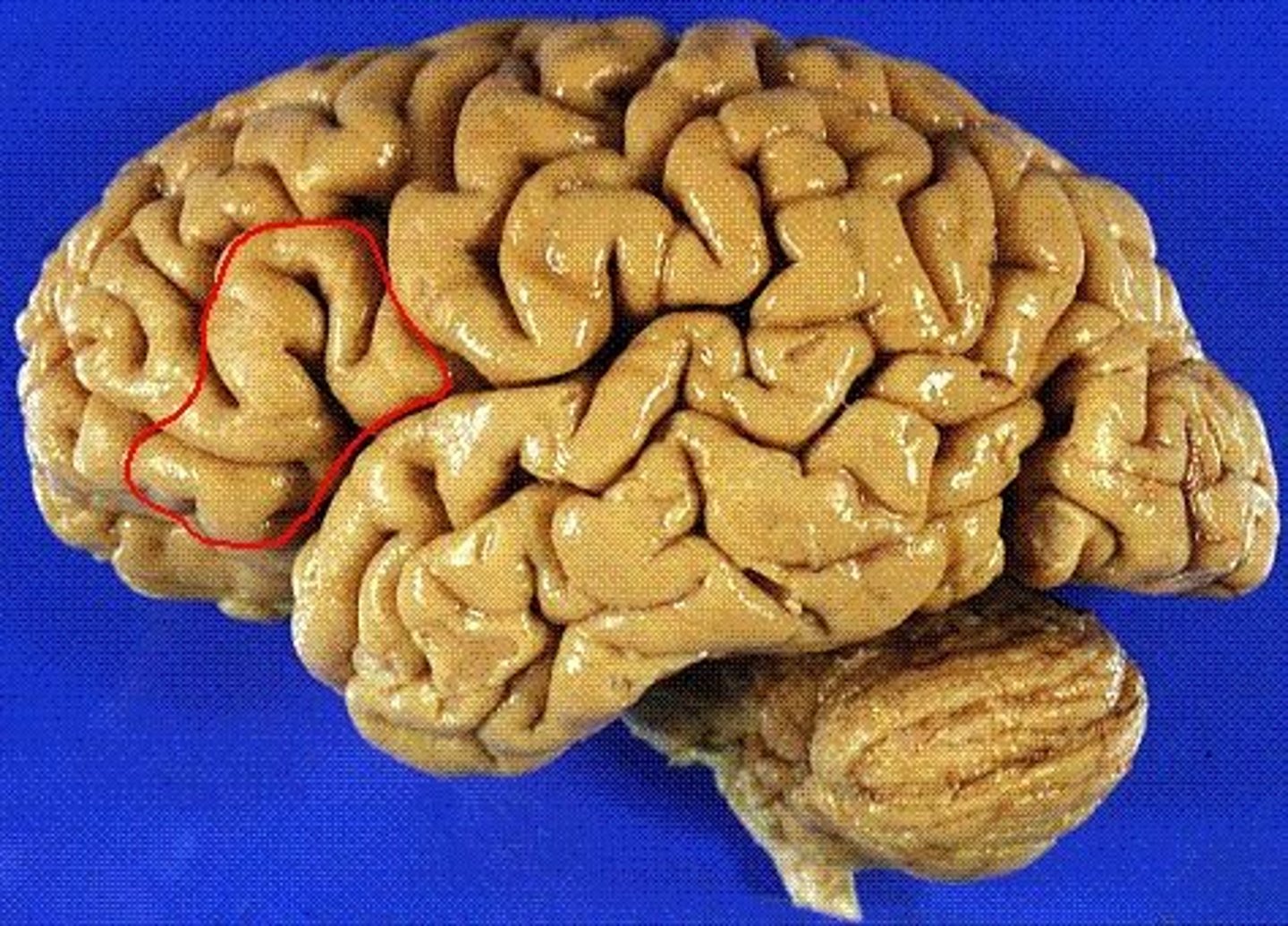
orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus
most anterior portion of inferior frontal gyrus
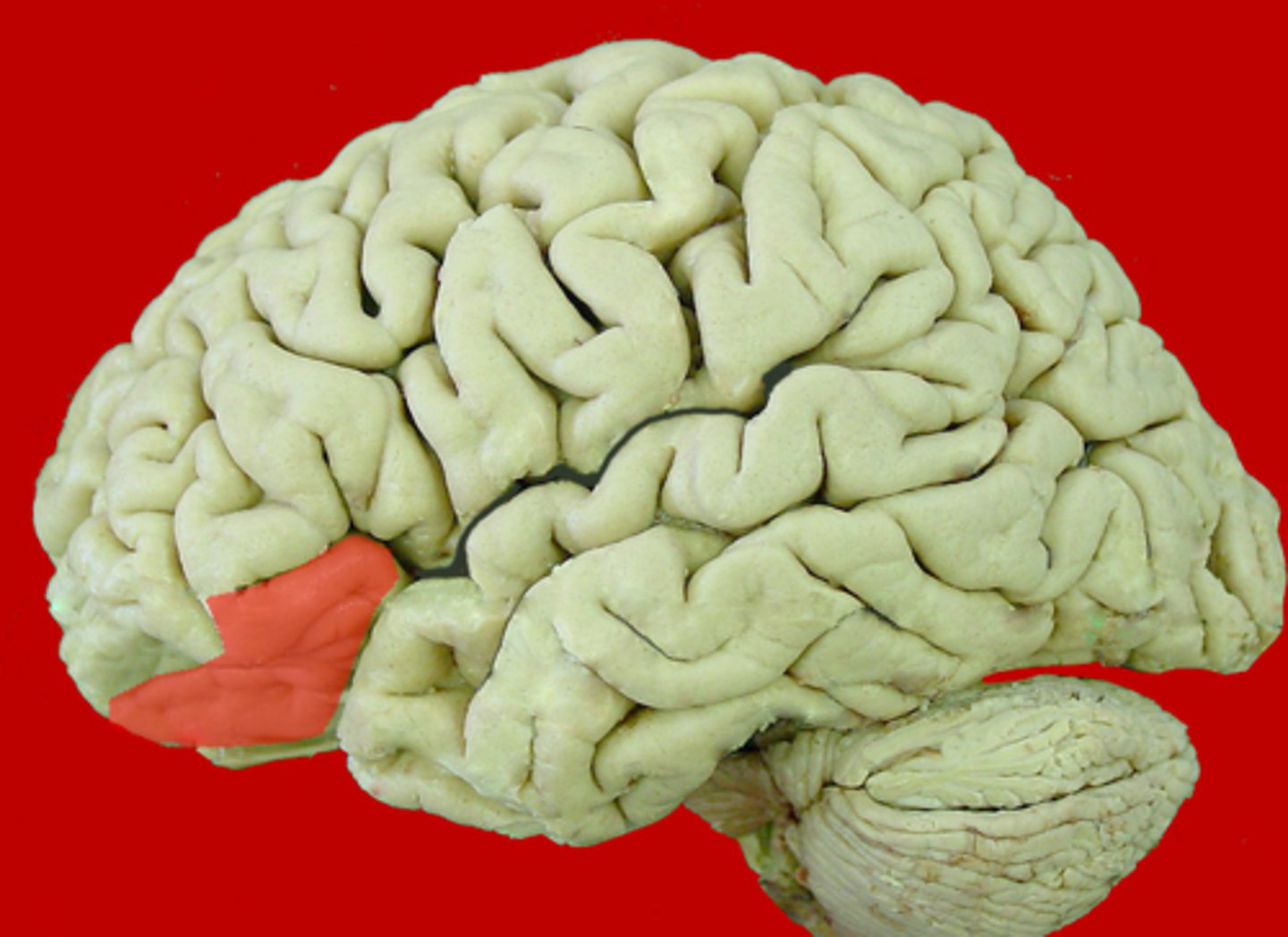
postcentral gyrus
between central sulcus and postcentral sulcus
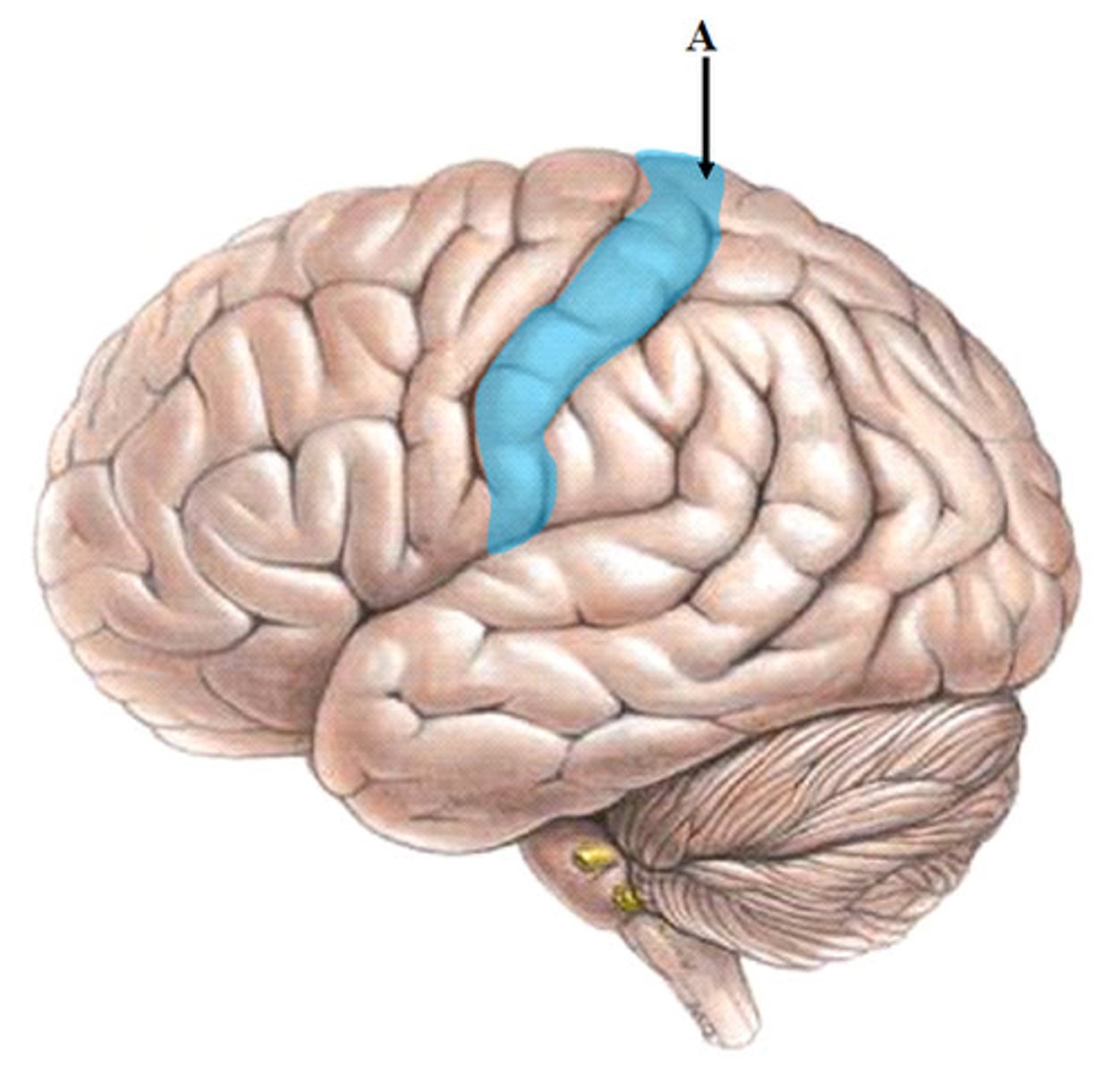
intraparietal sulcus
Separates superior and inferior parietal lobules
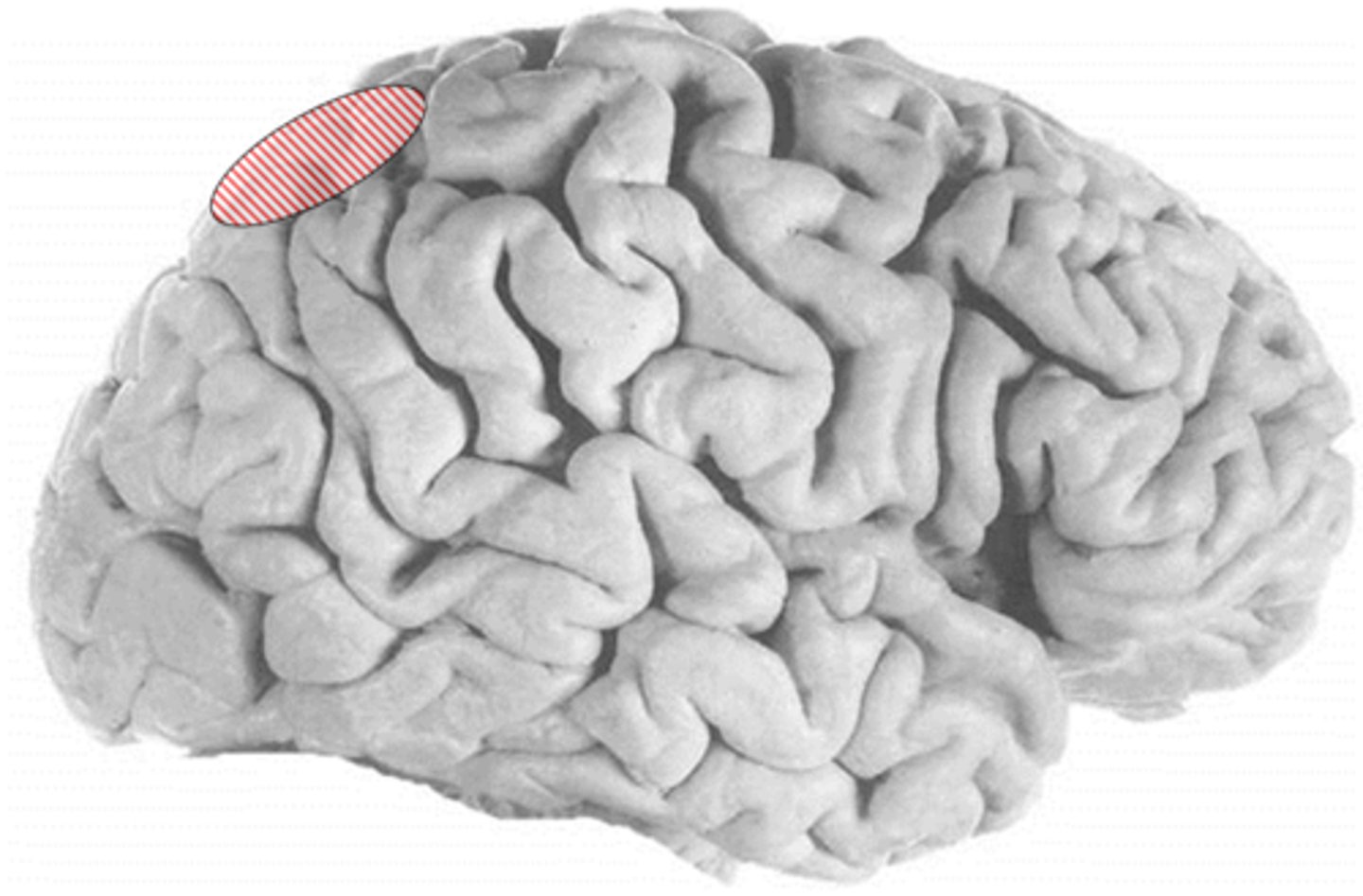
superior parietal lobe
ID
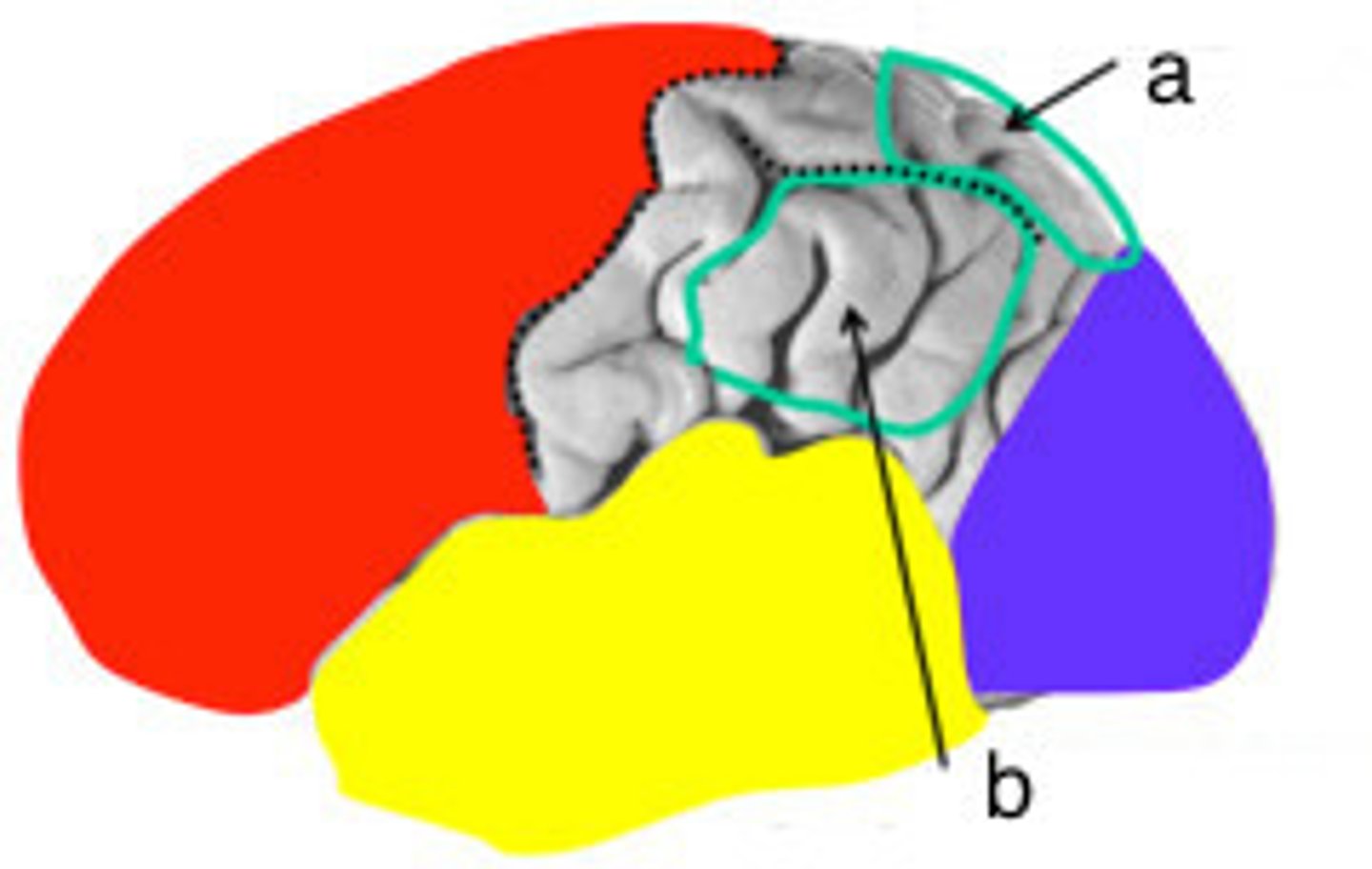
inferior parietal lobule
ID B
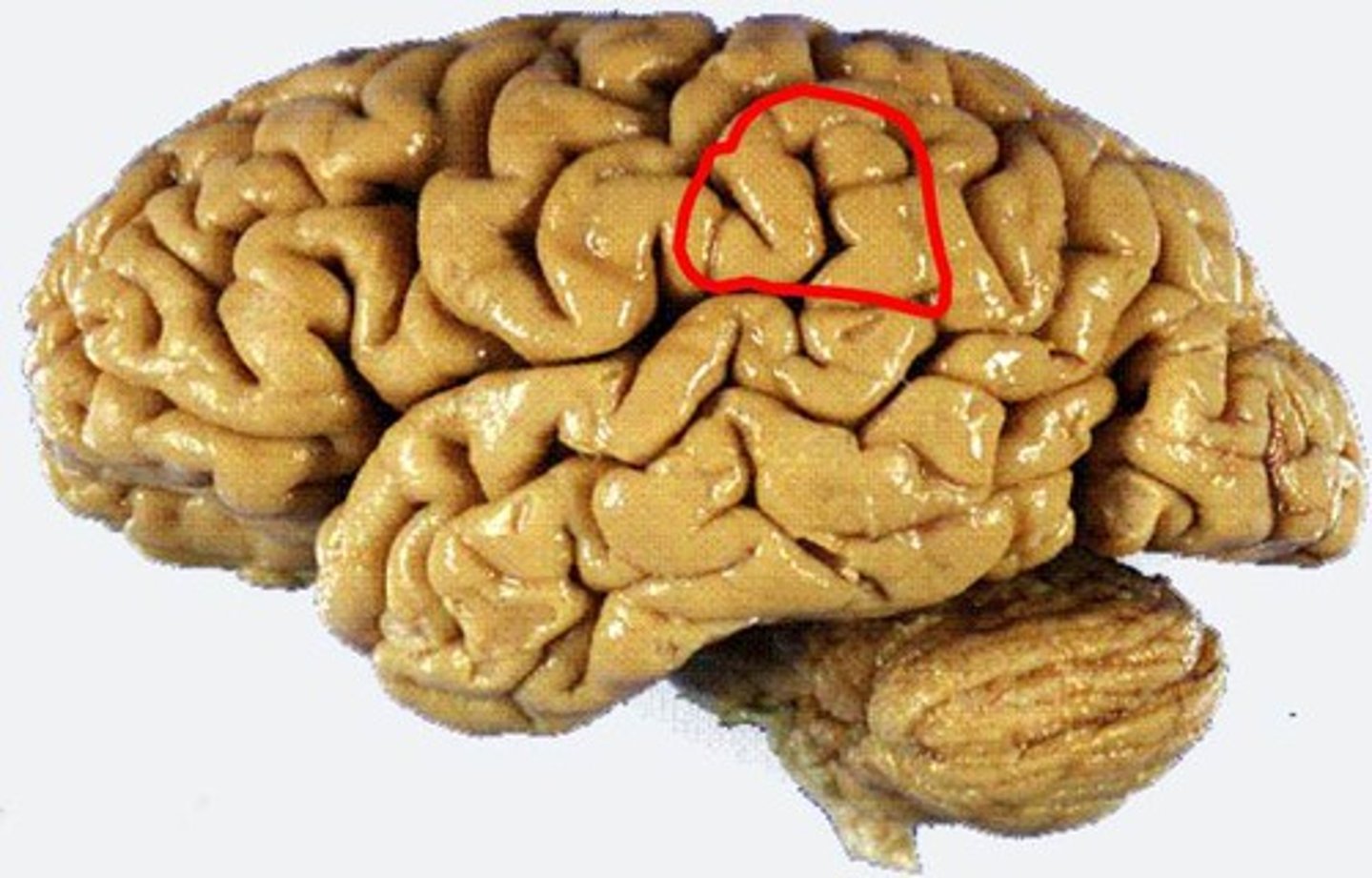
supramarginal gyrus
part of inferior parietal lobulus
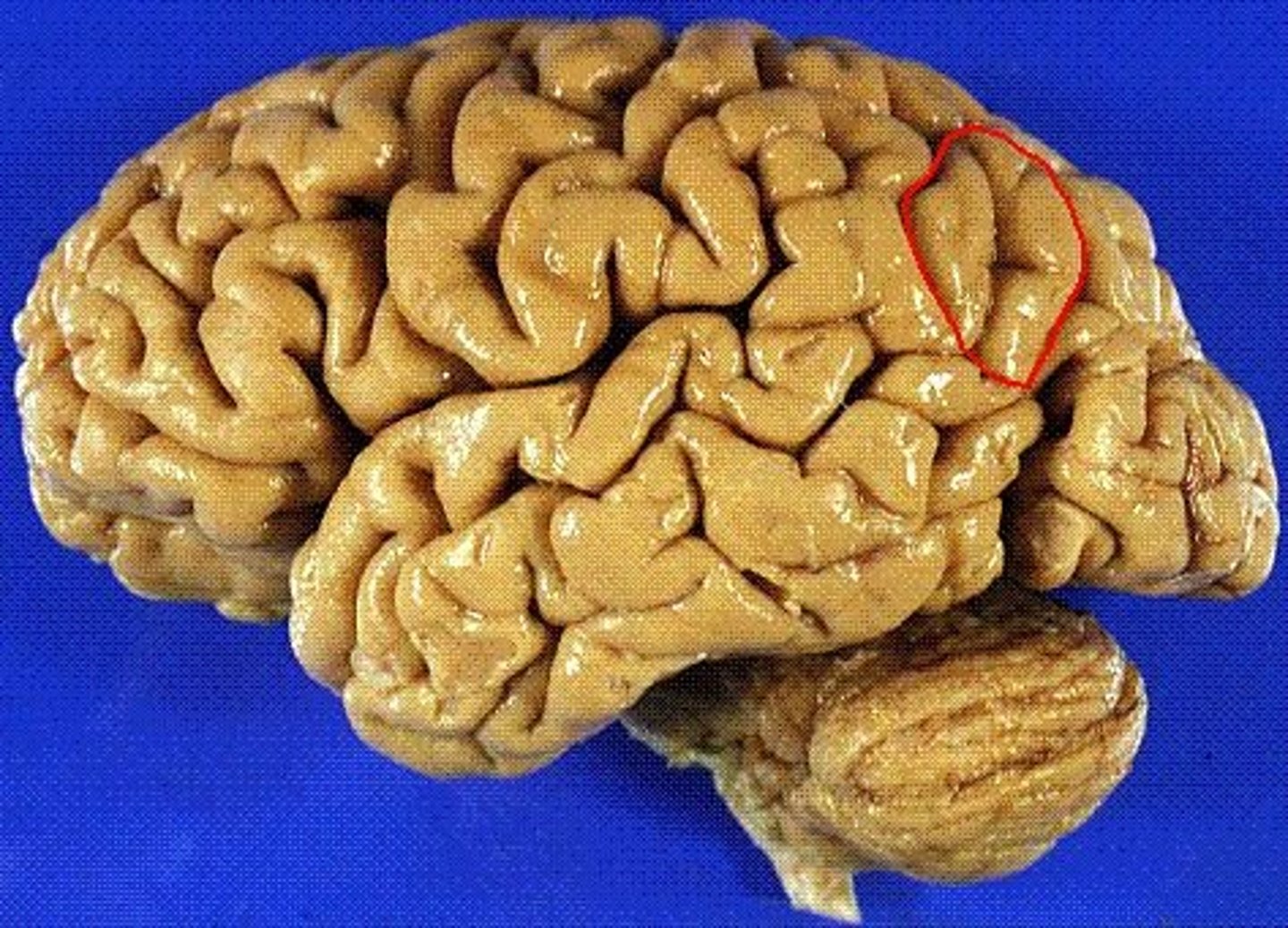
angular gyrus
part of inferior parietal lobe
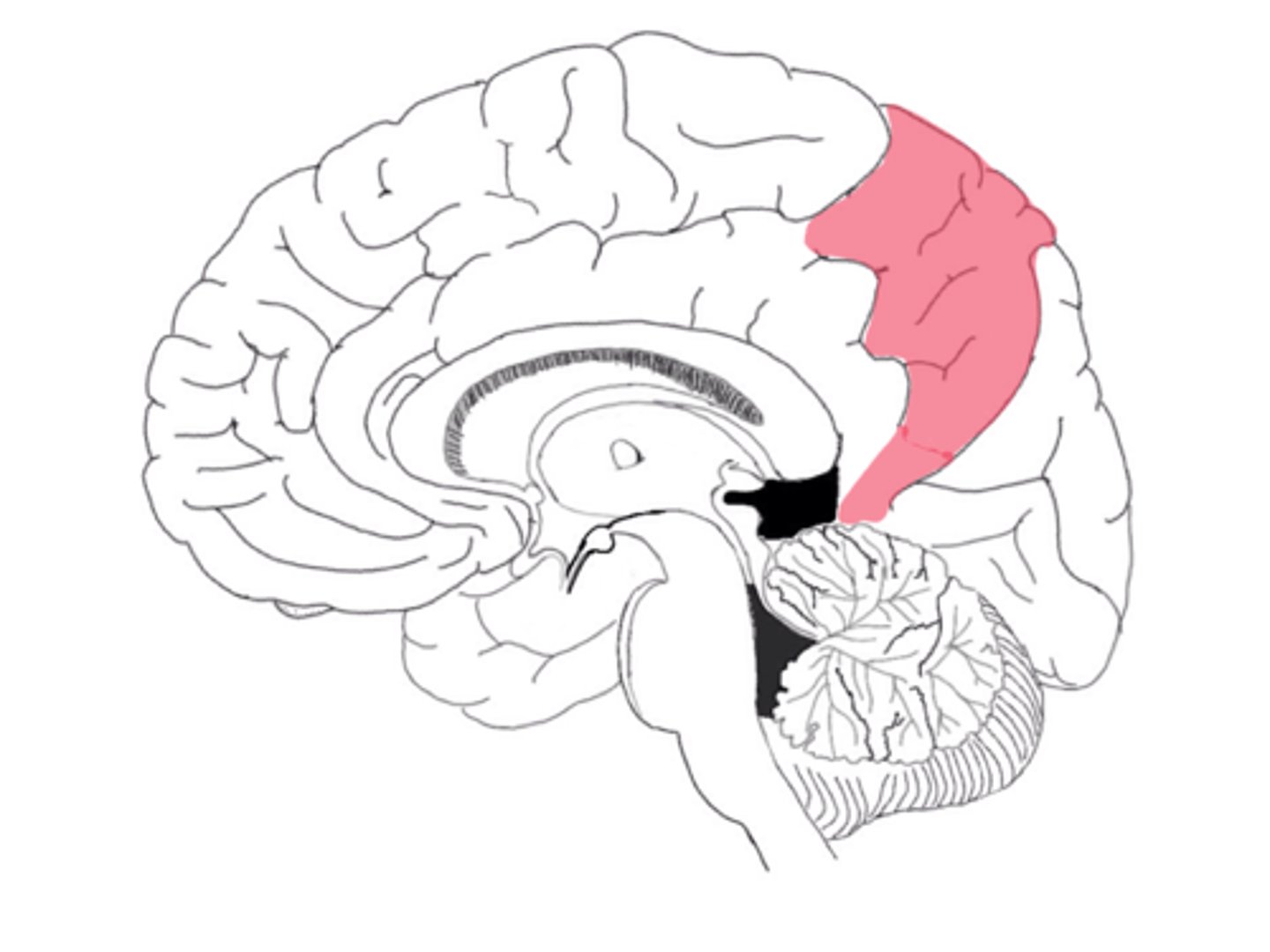
posterior paracentral lobule
on the medial surface of parietal lobe
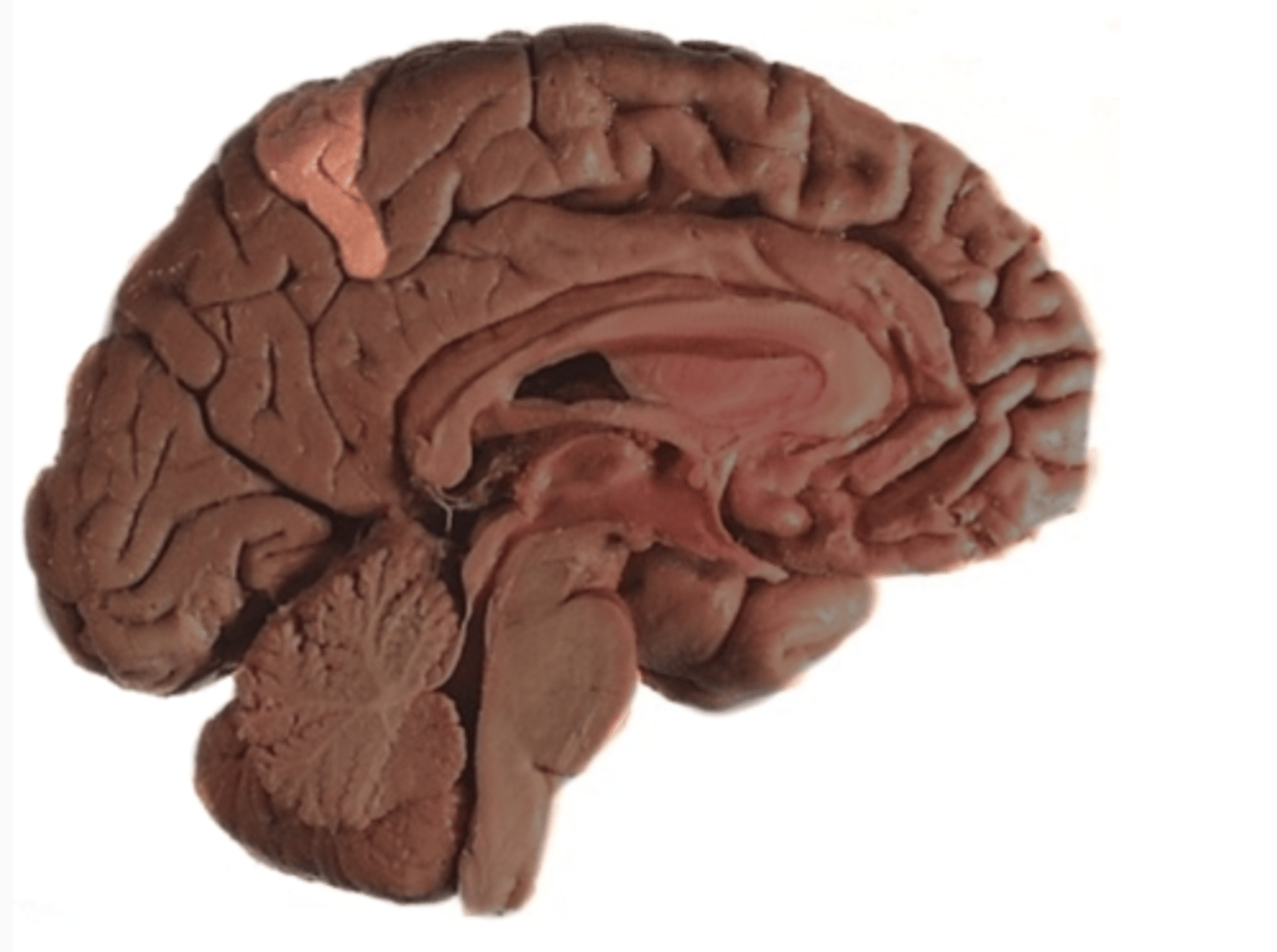
precuneus
ID landmark of the parietal lobe
superior temporal gyrus
ID
middle temporal gyrus
ID
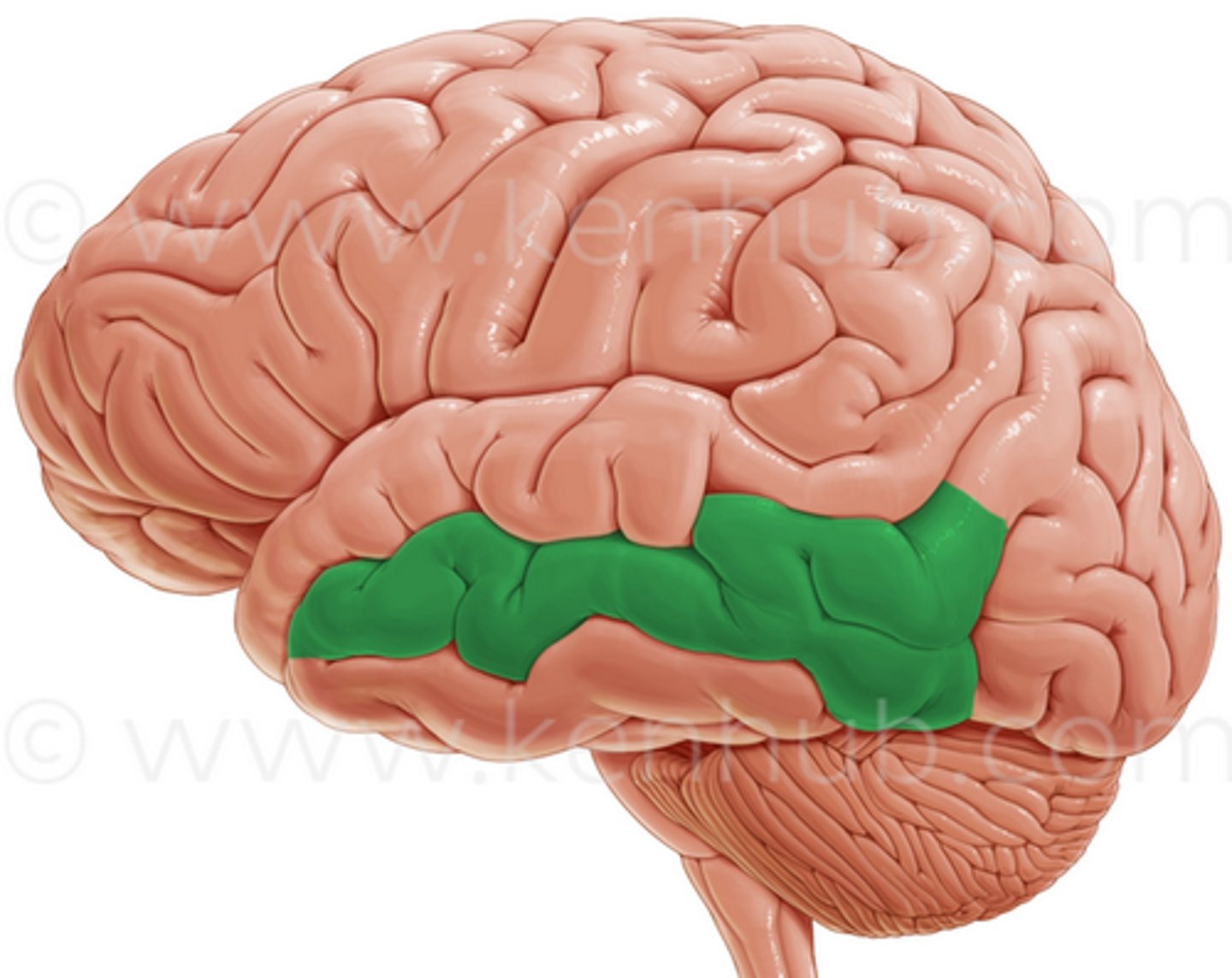
inferior temporal gyrus
ID
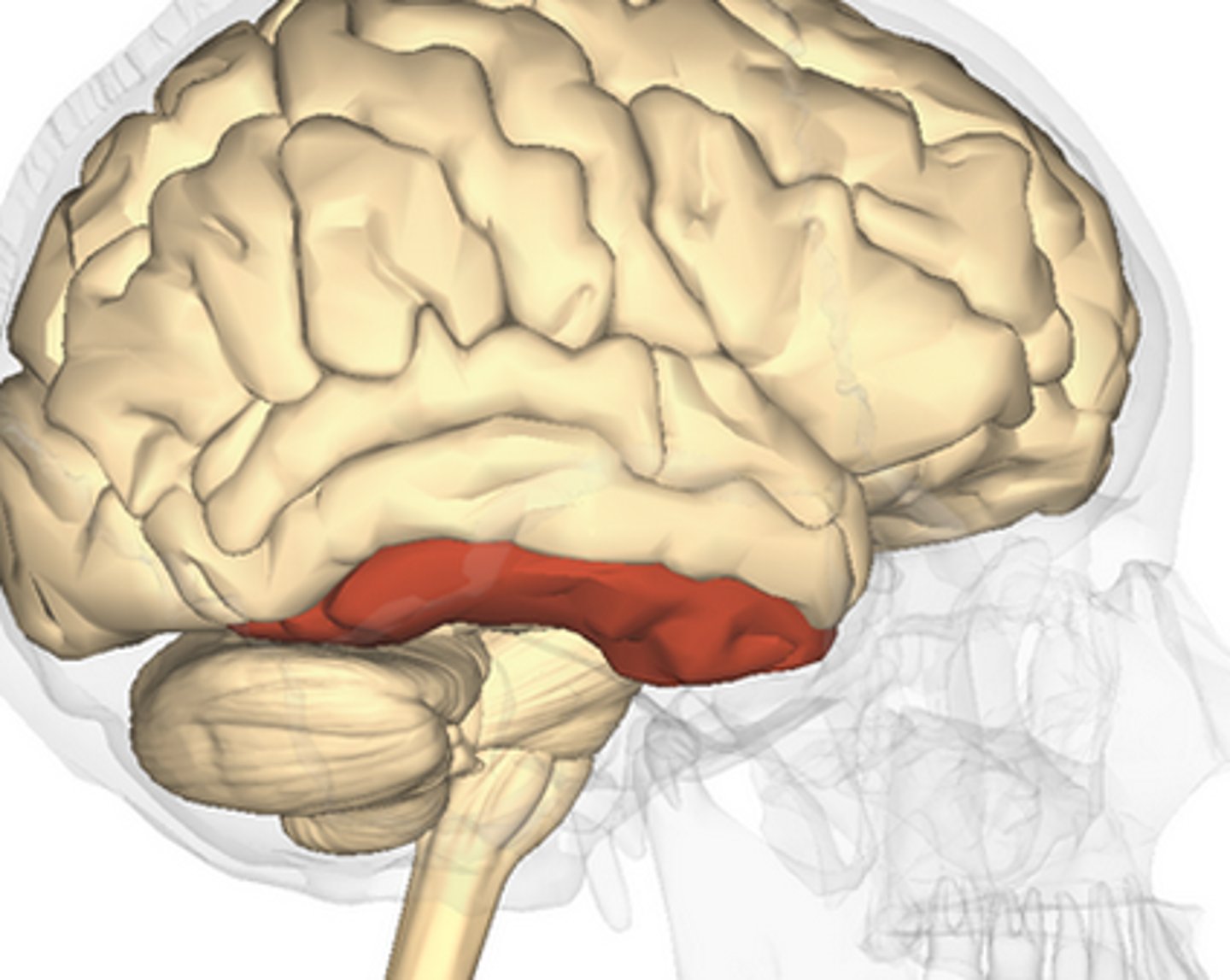
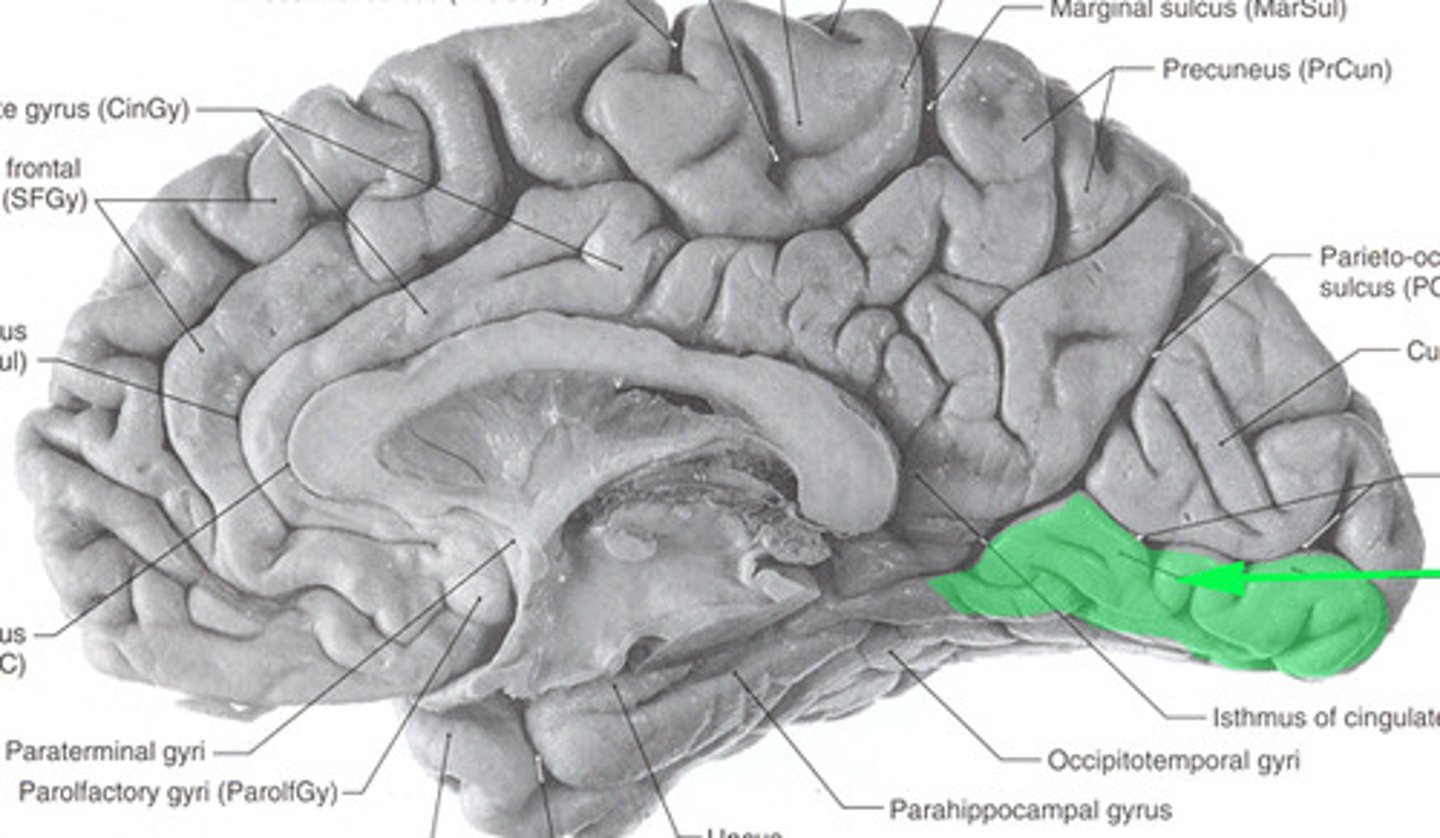
occipitotemporal gyrus
-separated from limbic lobe by collateral sulcus
-partly in temporal and partly in occipital lobes
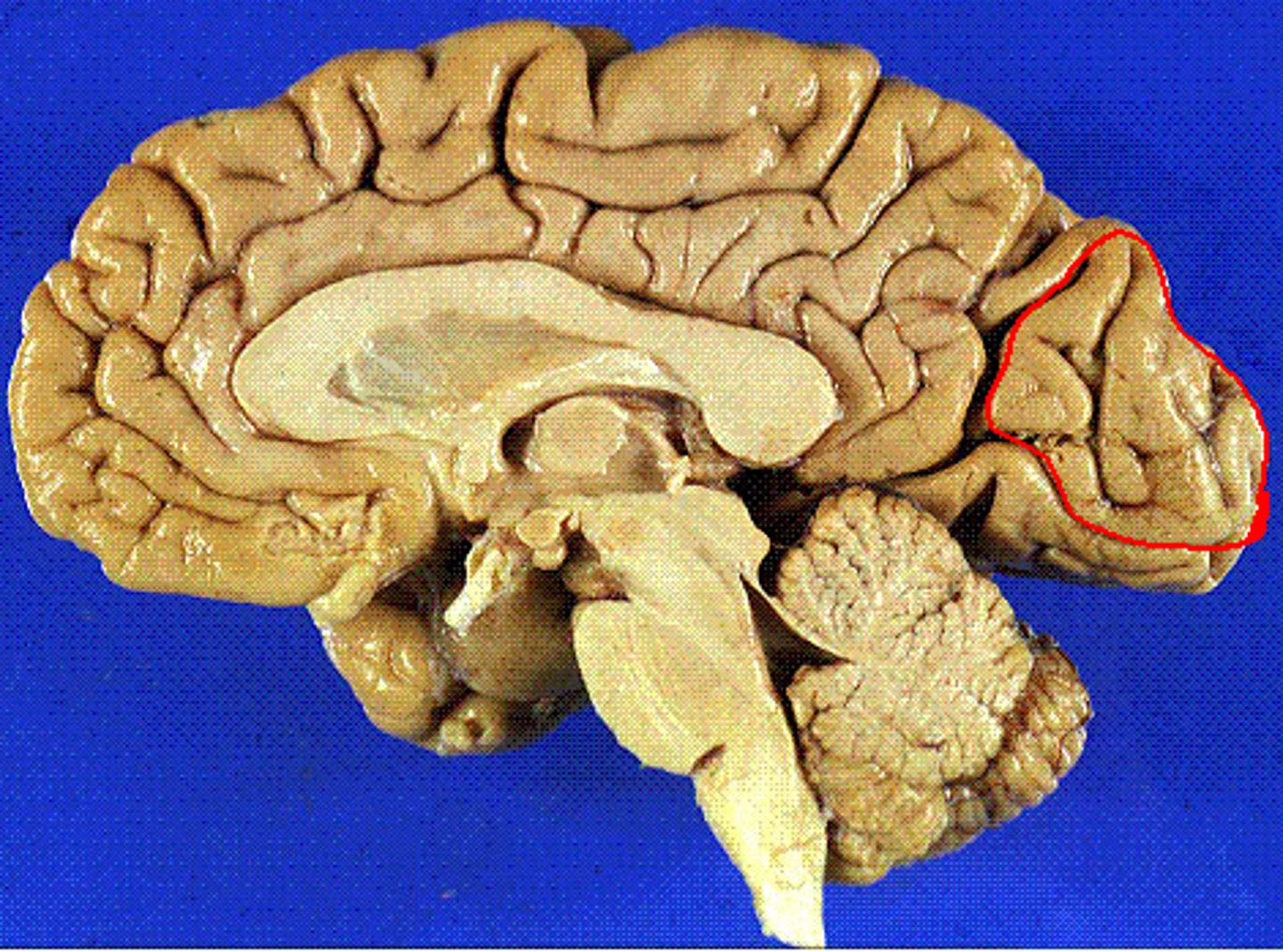
cuneus
wedge shaped lobe on occipital lobe
-bw parietoccipital and calcarine sulci
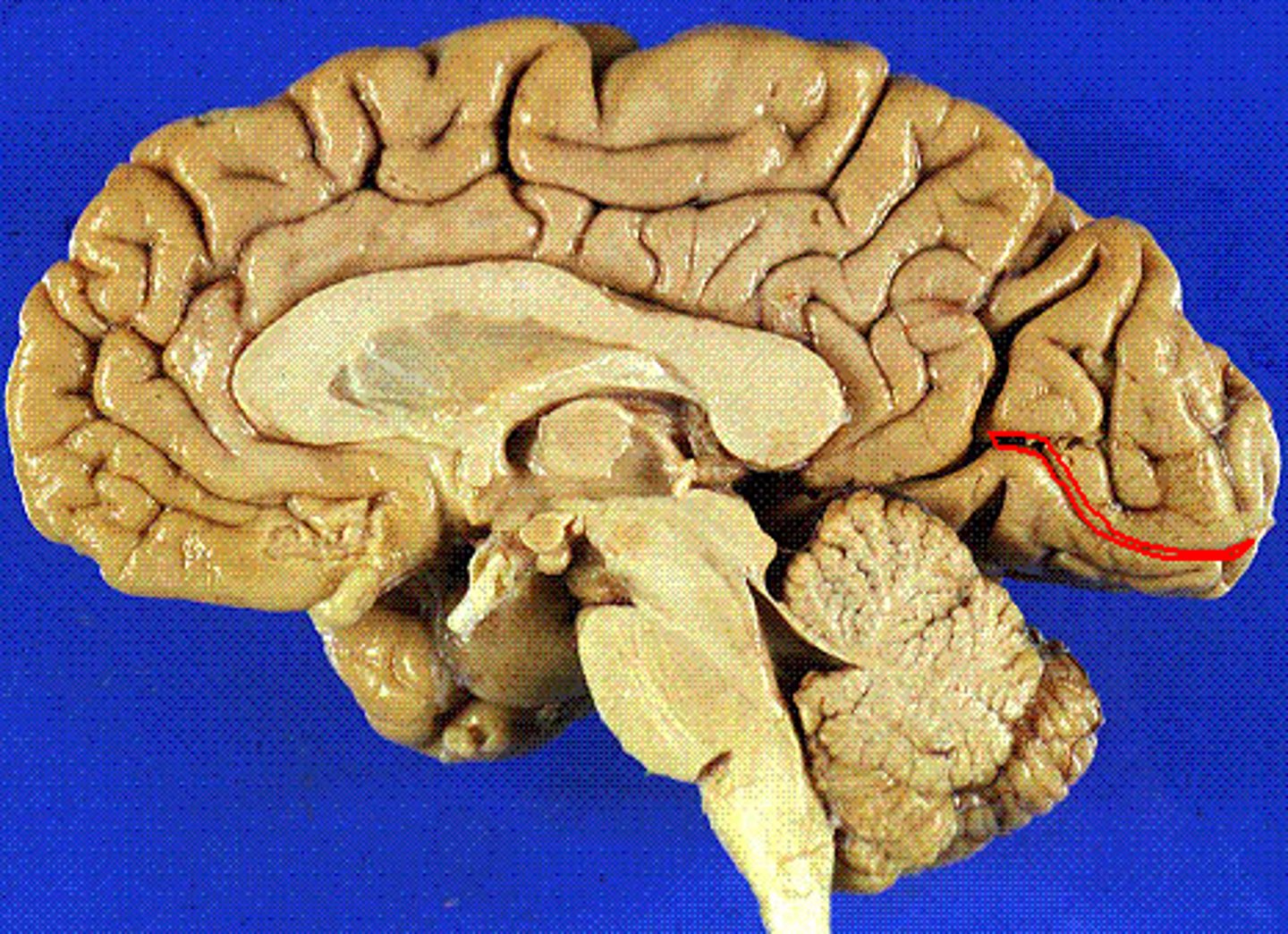
calcarine sulcus
located between cuneus and lingual gyrus
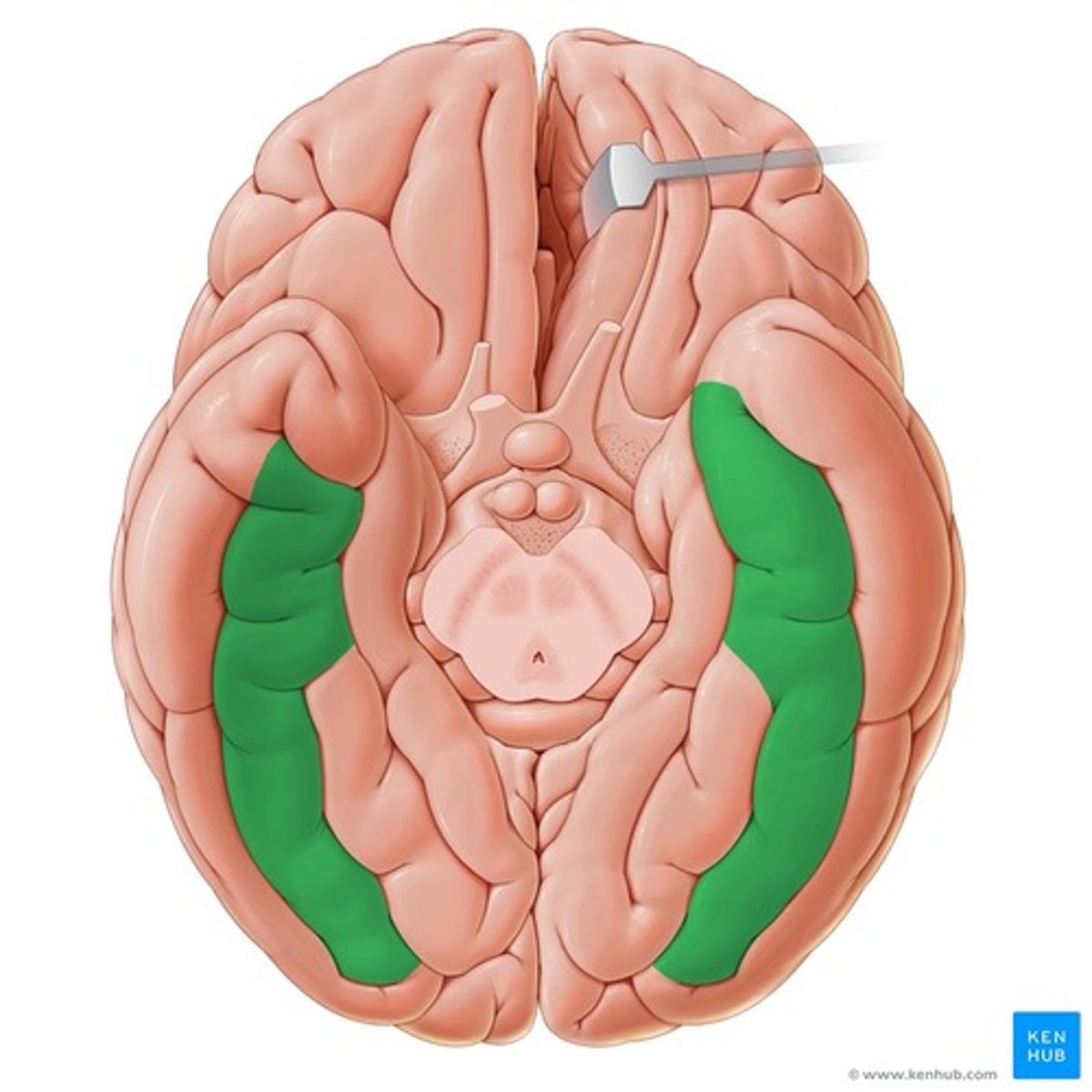
lingual gyrus
-in temporaal and occipital lobe
-inferior to alcarine sulcus
-continuous with parahippocampal gyrus
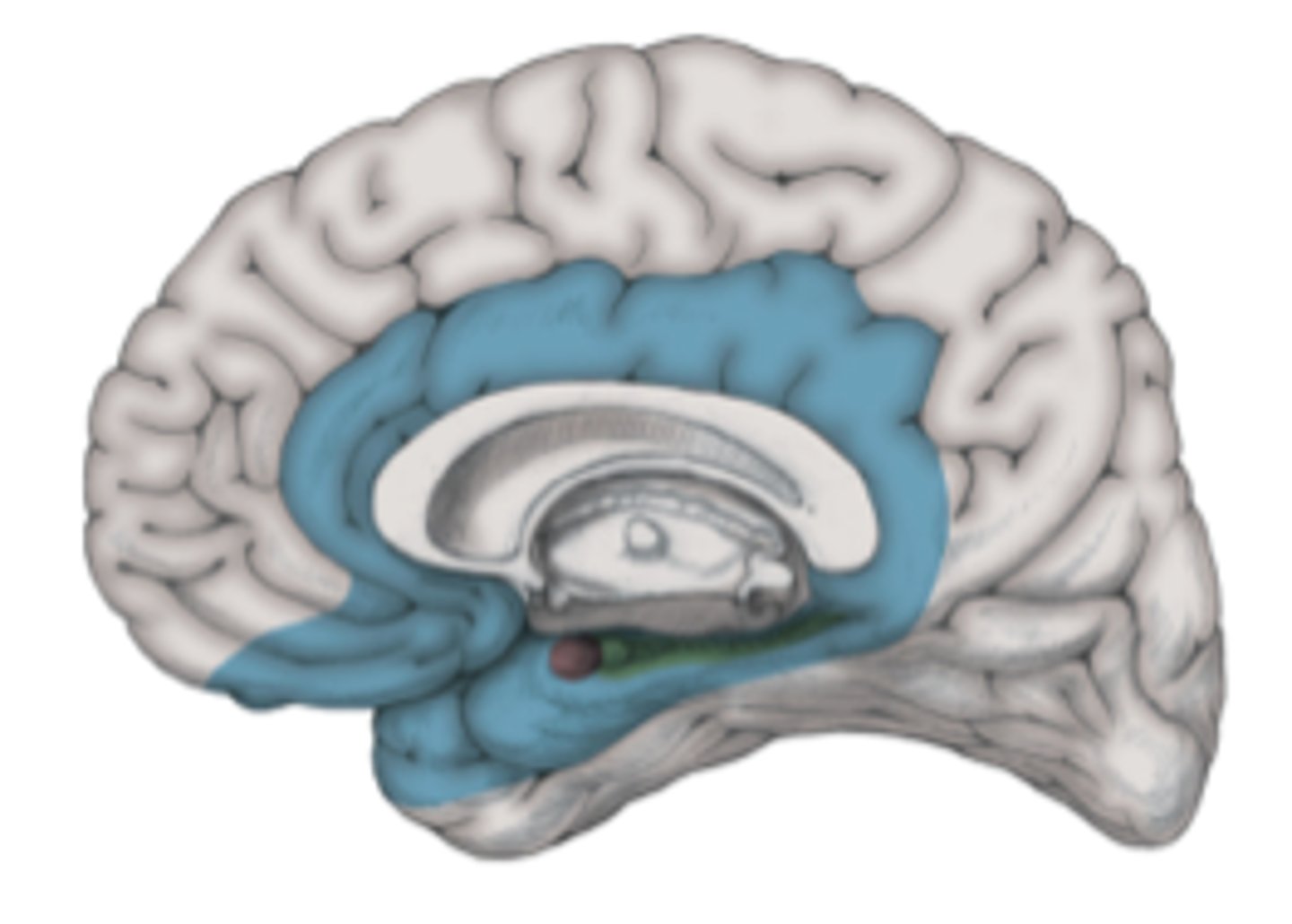
limbic lobe
encircles telencephalon-diencephaalon junction
cingulate sulcus
Separates frontal and parietal lobes from cingulate gyrus
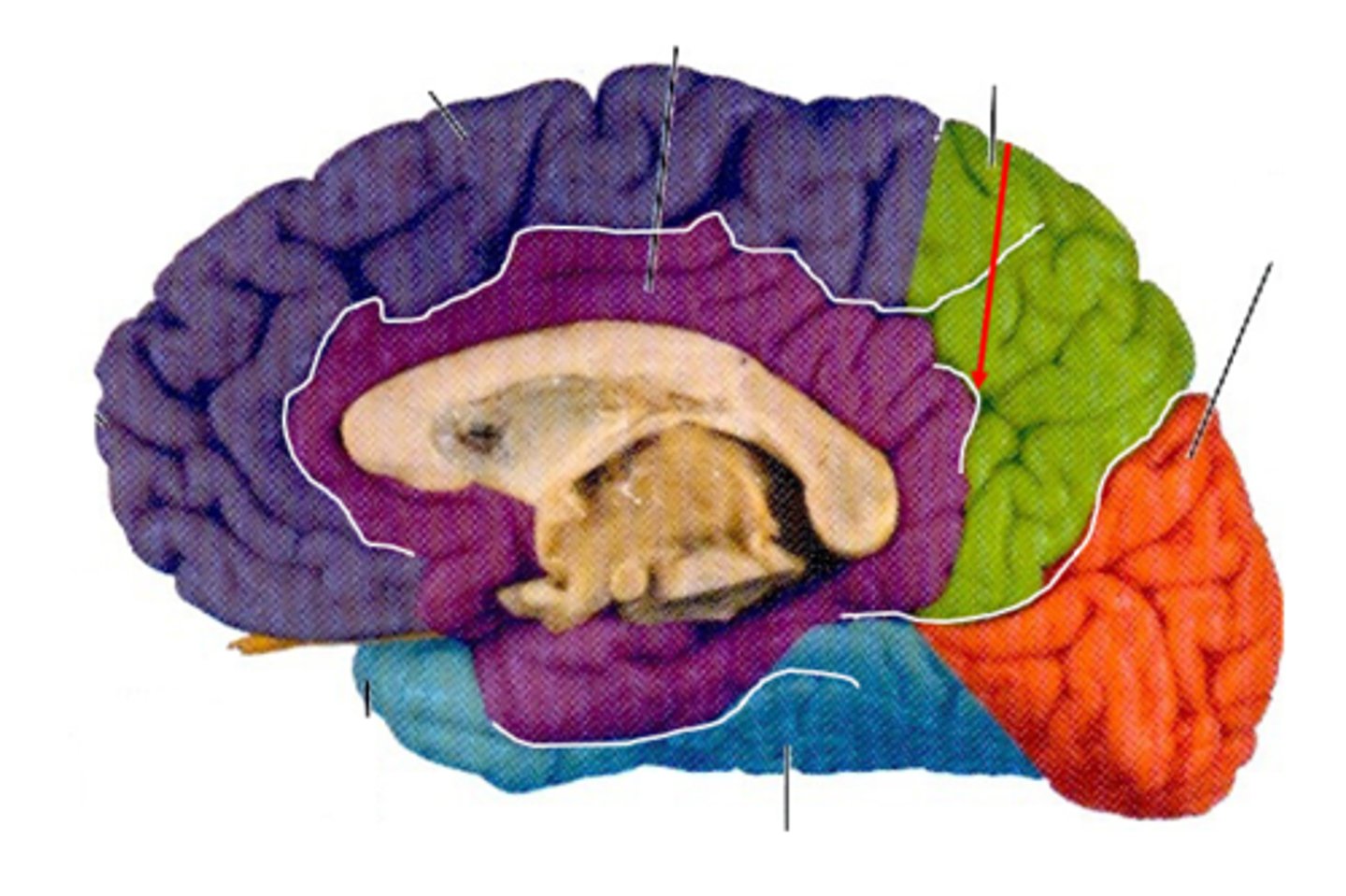
subparietal sulcus
separates limbic and parietal lobes
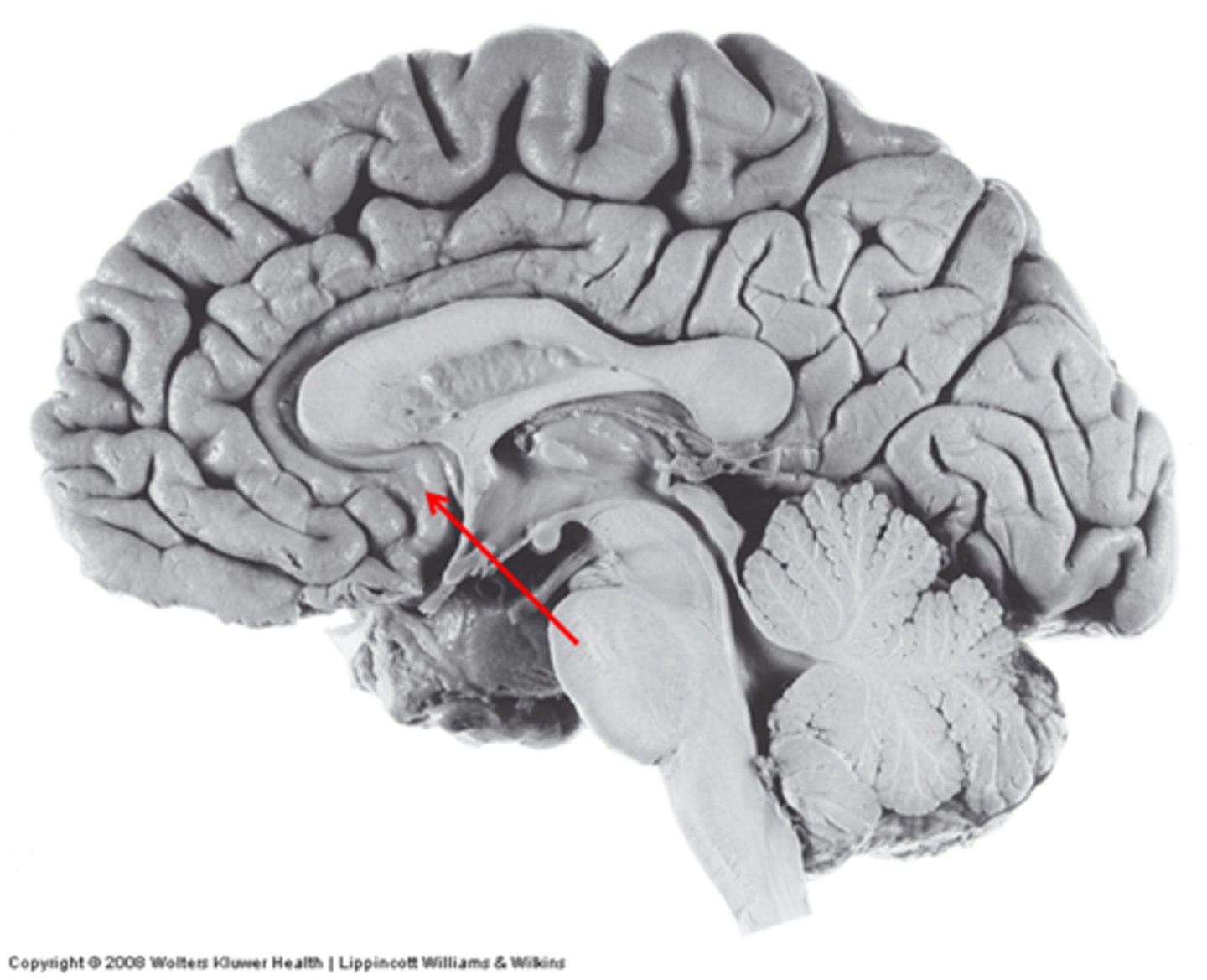
parahippocampal gyrus
a fold of tissue near the hippocampus that is often included in the limbic system
-inferior continuation of cingulate gyrus
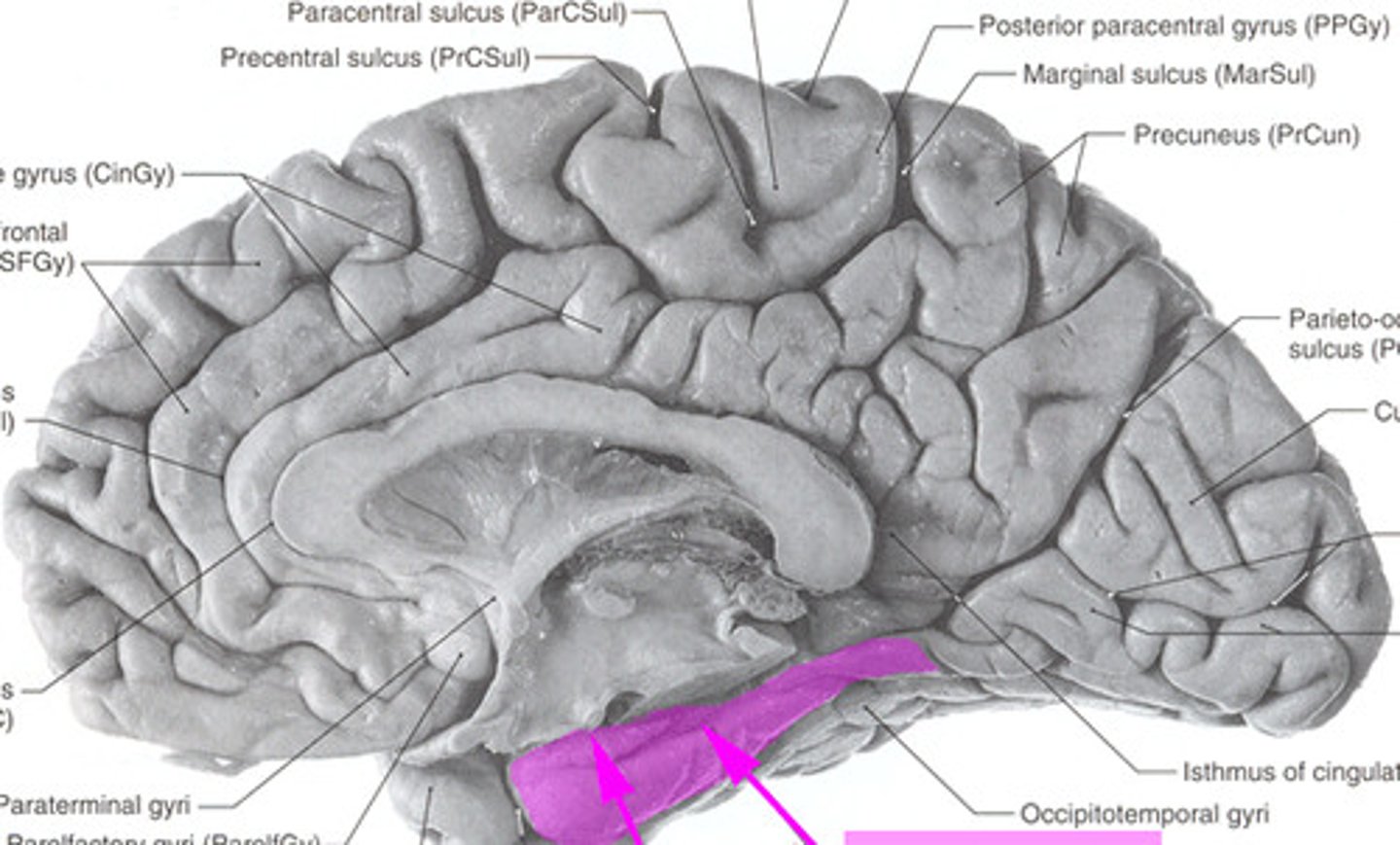
subcallosal area
inferior to genu of corpus callosum
brodmann
scientist who organized the brain based on shape aand arrangement of neurons
precentral gyrus
-brodmann area 4
location of primary motor cortex
Brodmann Area 3,1,2
primary somatosensory cortex brodmann areas:
post central gyrus
where is the primary somatosenosry cortex located?
basal ganglia
cluster of nuclei deep in brainstem
- component of subcortical grey matter
commissural fibers
horizontal fibers that connect white matter of two hemispheres
arcuate fibers
short association fibers that connect two adjacent gyri within one hemisphere
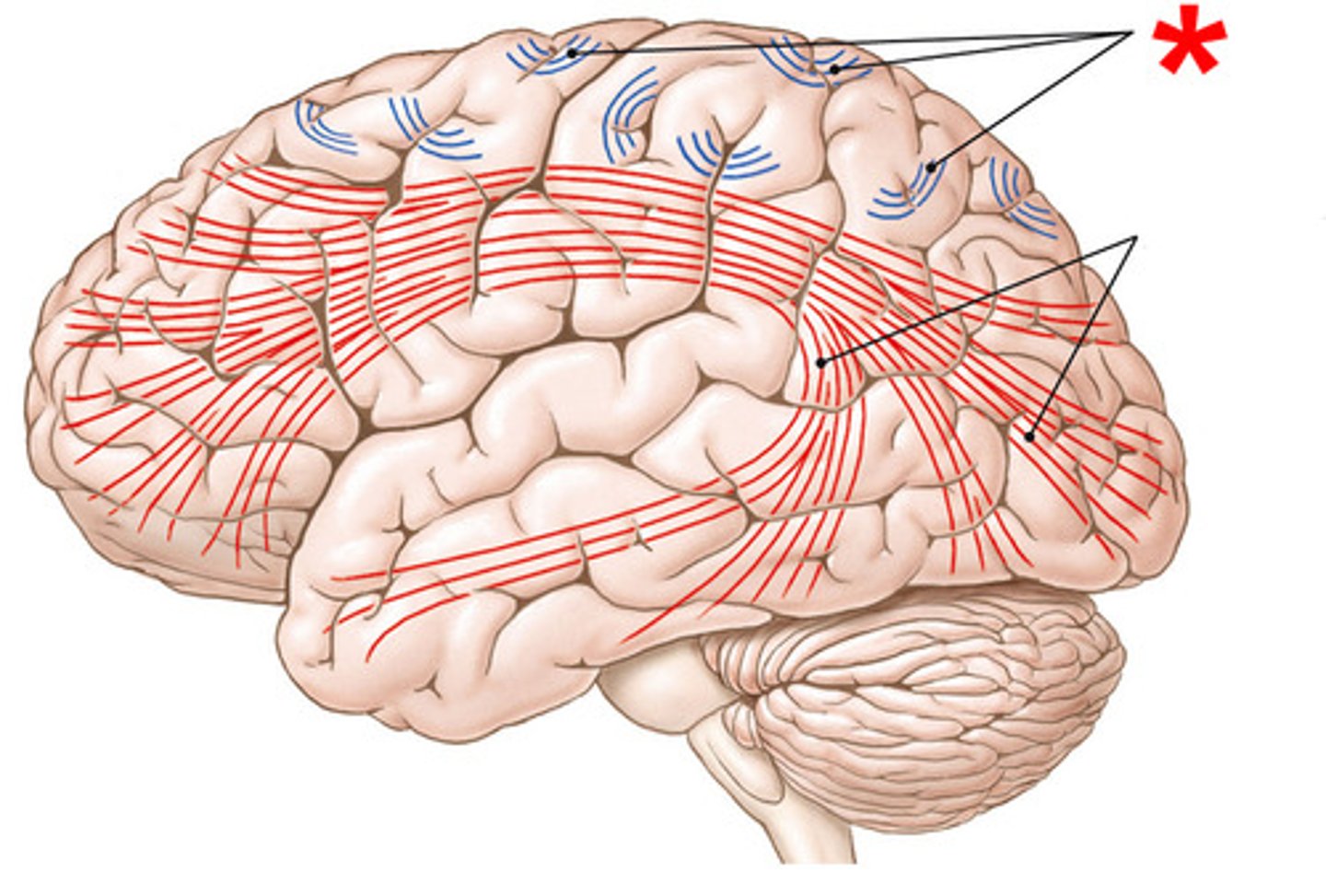
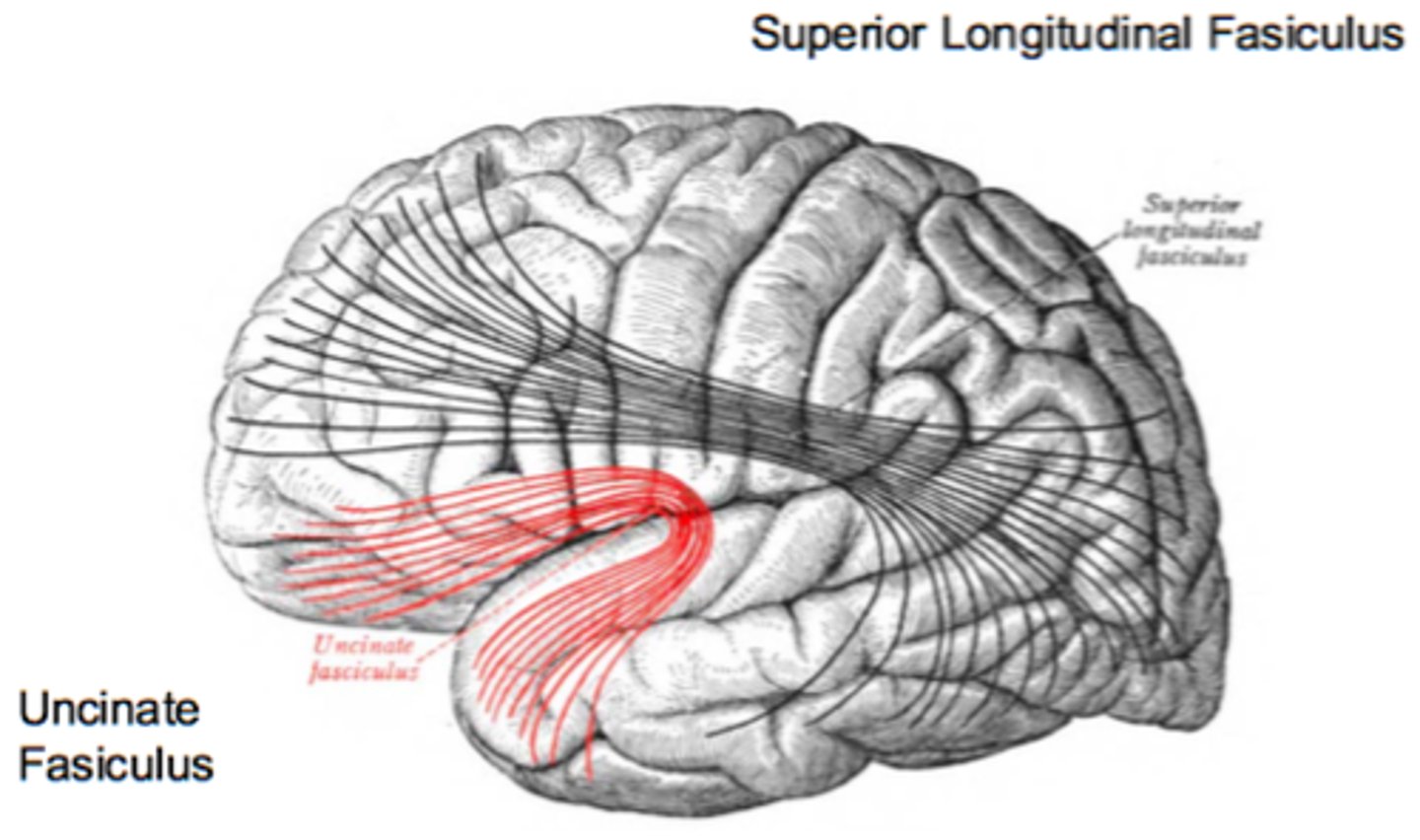
superior longitudinal fasiculus
Connects frontal, parietal, and occipital lobes
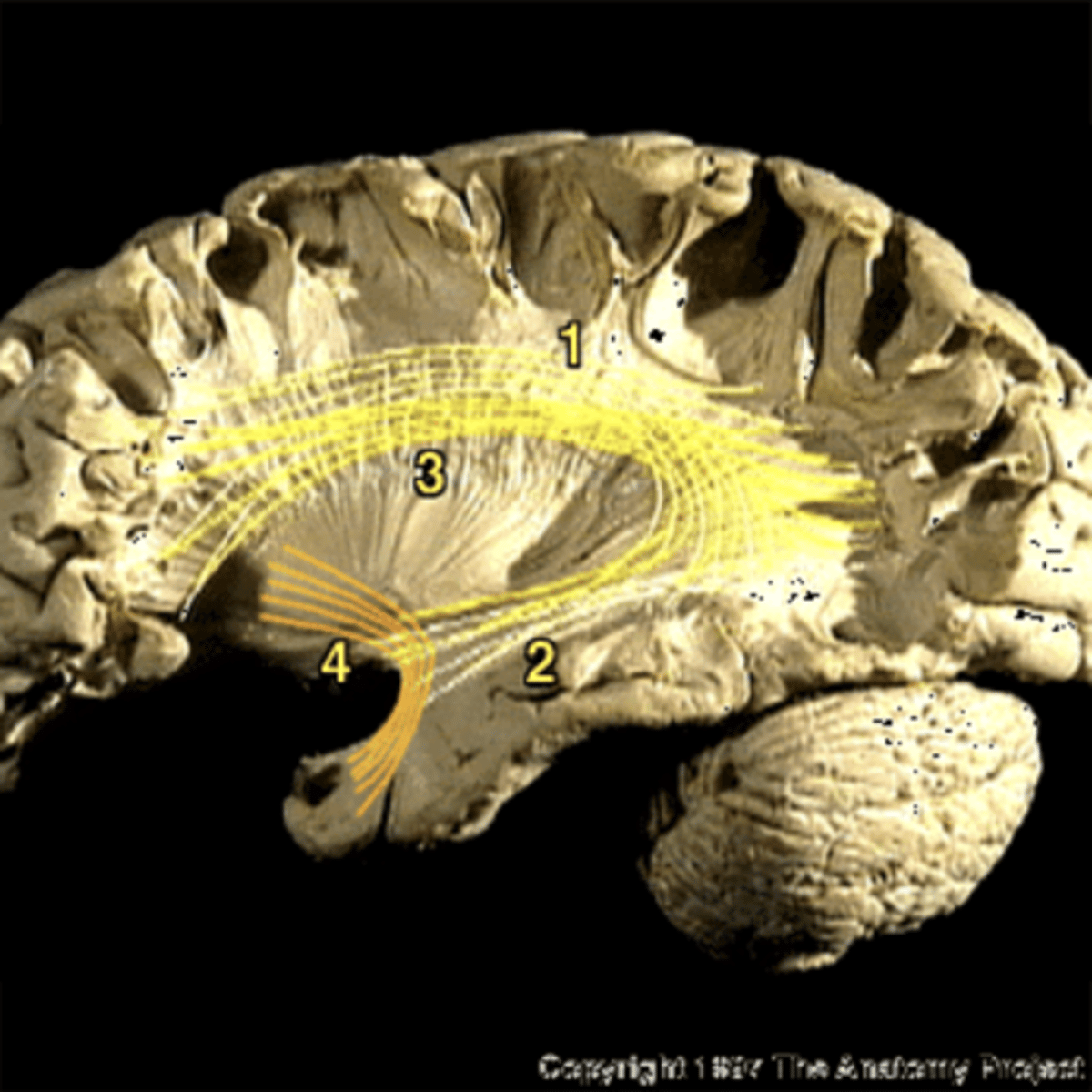
arcuate fasiculus
connects Wernicke's area and Broca's area
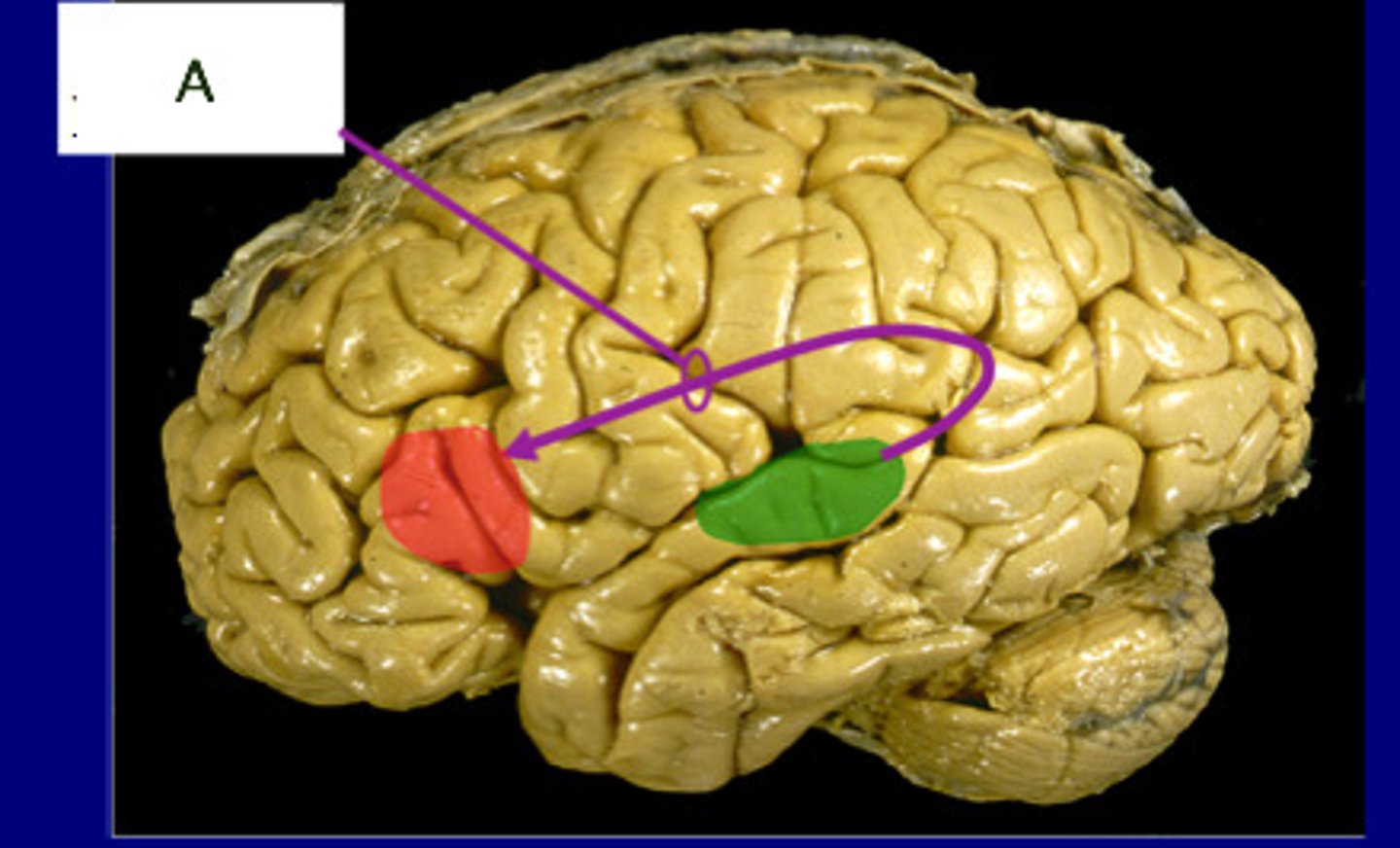
uncinate fasiculus
connects inferior frontal gyrus to anterior temporal lobe
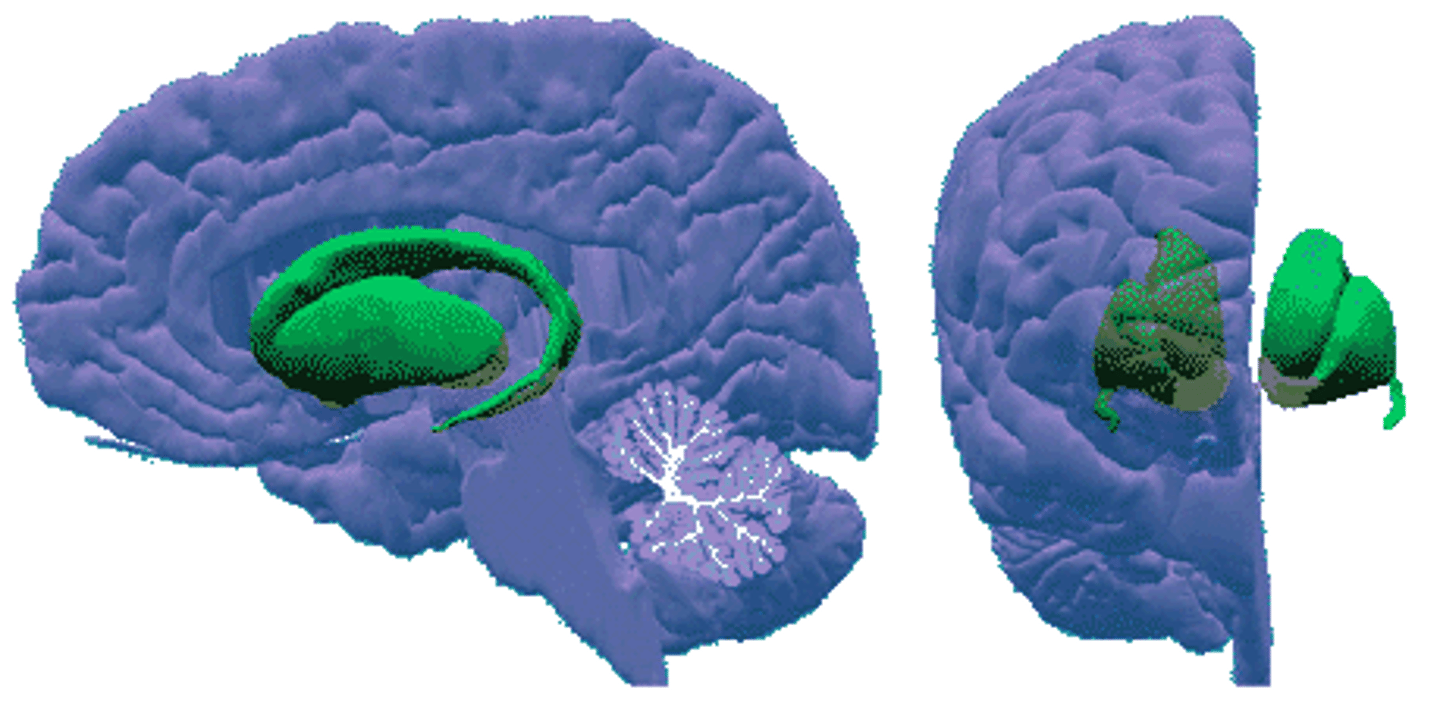
corpus callosum
largest commissural tract
anterior commissure
bundle of axons that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex
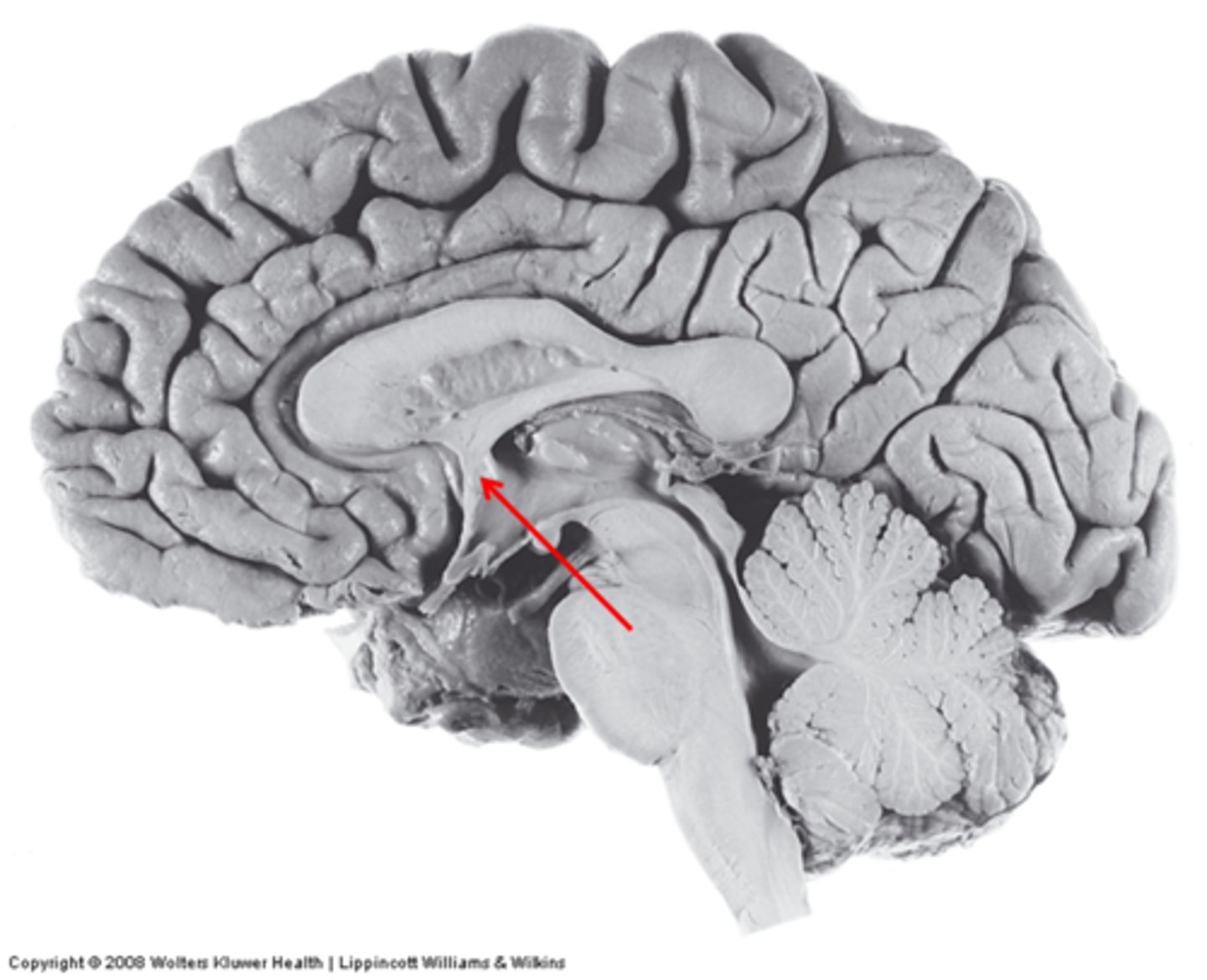
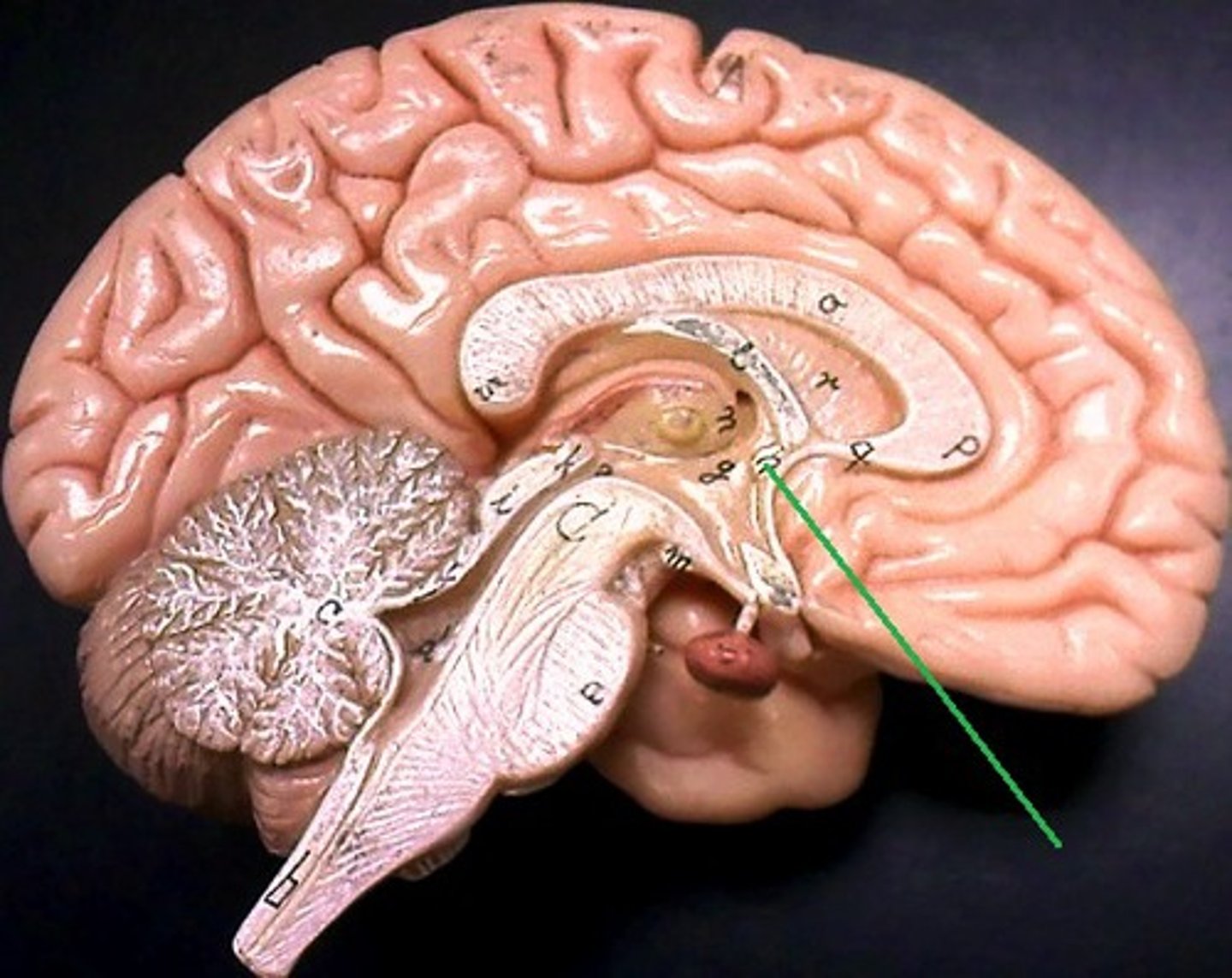
anterior commissure
Name the structure.
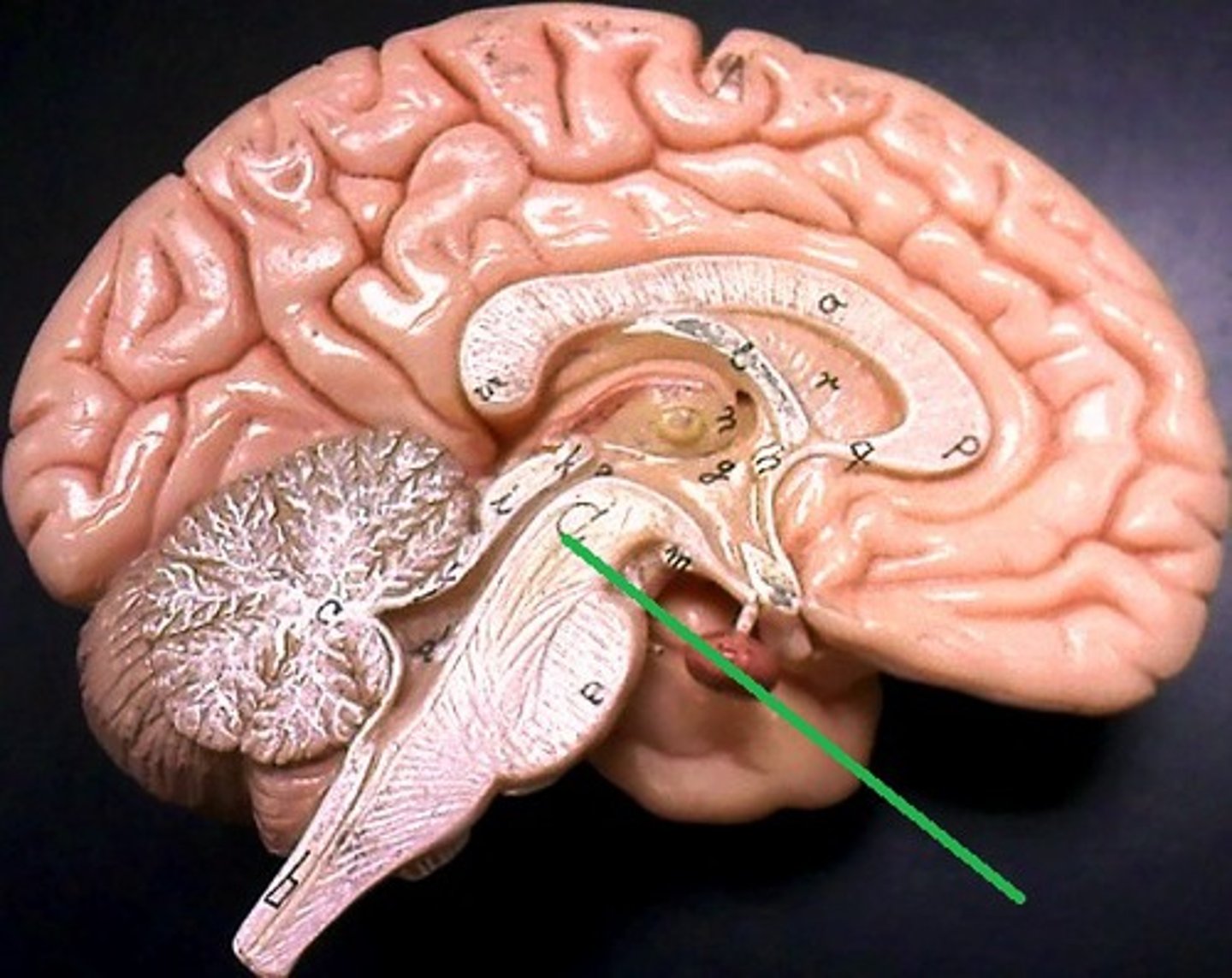
corona radiata
axons from cortical neurons descending and converging on brainstem
cerebral peduncle
contiuous with corona radiata and internal capsule
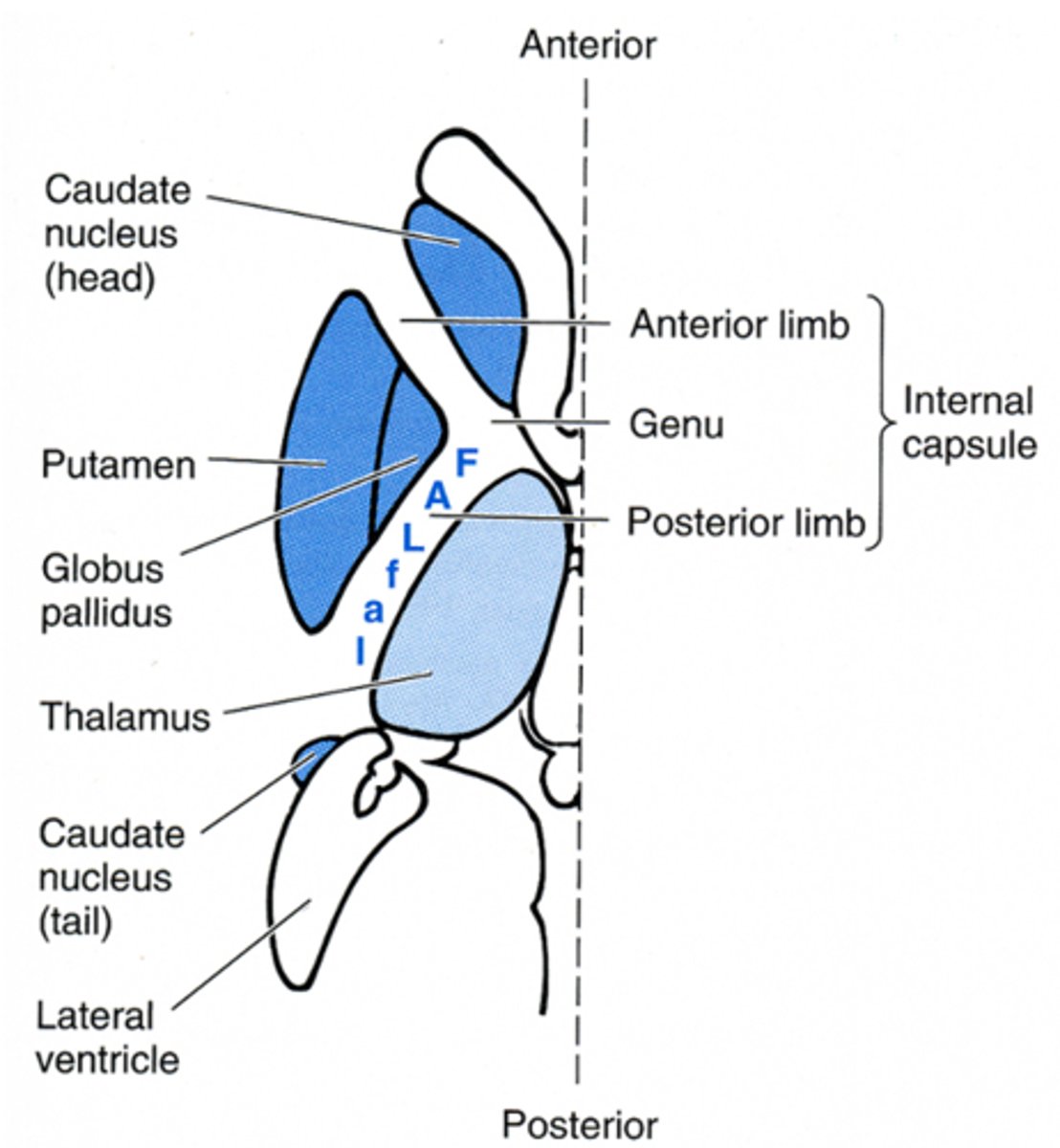
somatotopic organization of internal capsule
motor fibers are anterior (face, arm, leg)
sensory fibers are posterior (face, arm, leg)