APBio Unit 7 Evolution
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

38 Terms
Adaptation
A characteristic that improves an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment.
Allele frequency
The measure of the relative frequency of an allele at a genetic locus in a population; expressed as a proportion or percentage.
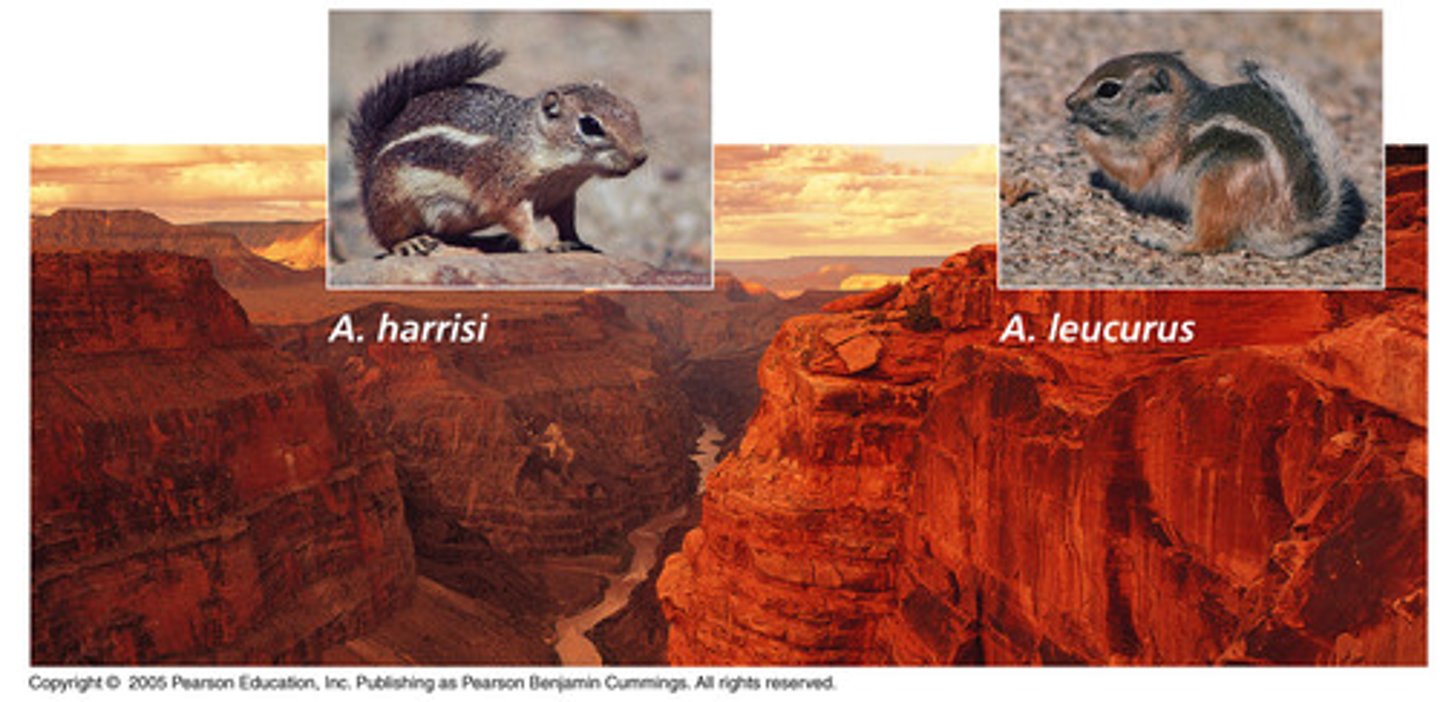
Allopatric speciation
The formation of a new species as a result of an ancestral population's becoming isolated by a geographic barrier.

Analogous structure
Similarities among unrelated species that result from convergent evolution, body parts that share a common function but not structure
Artificial selection
Selective breeding of plants and animals to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in offspring
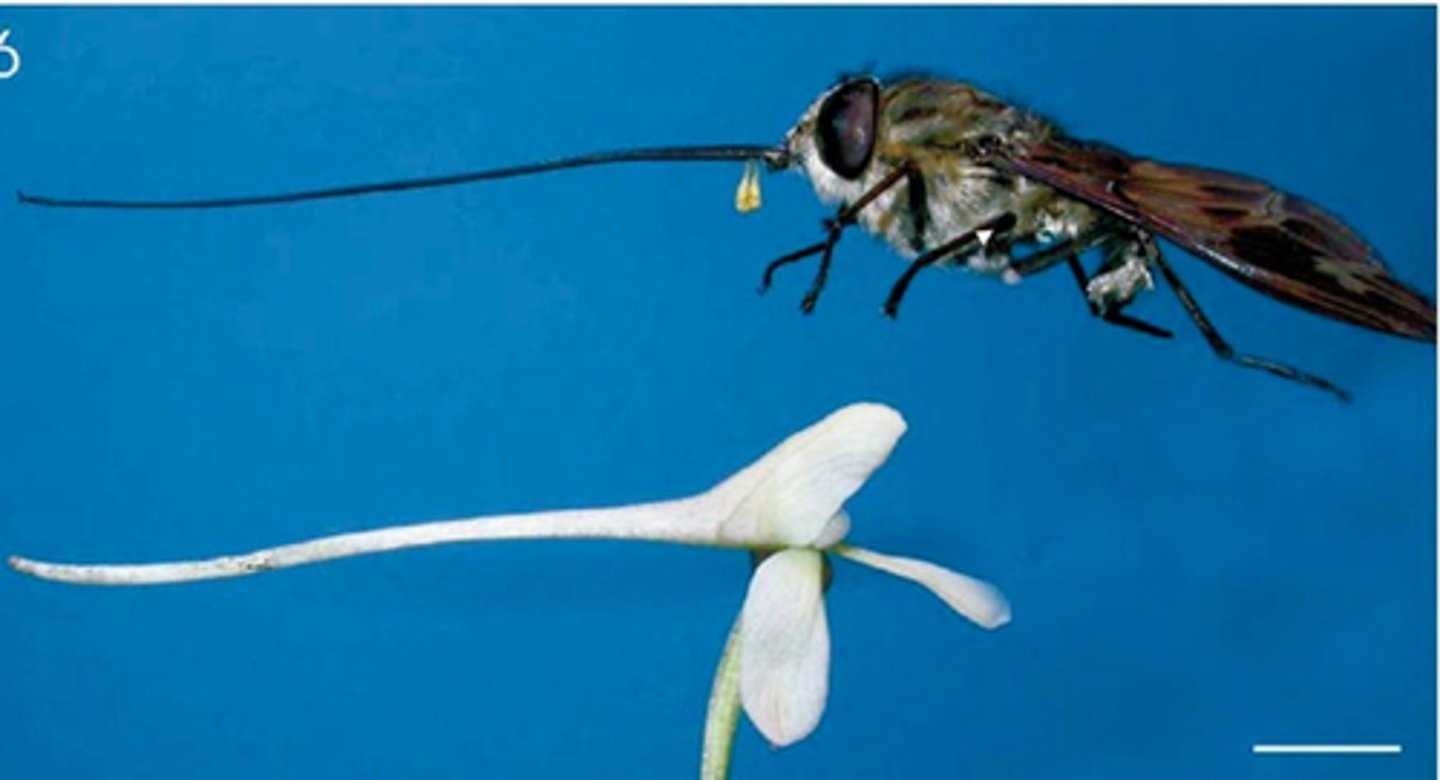
Coevolution
The evolution of two or more species that is due to mutual influence, often in a way that makes the relationship more mutually beneficial

Convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
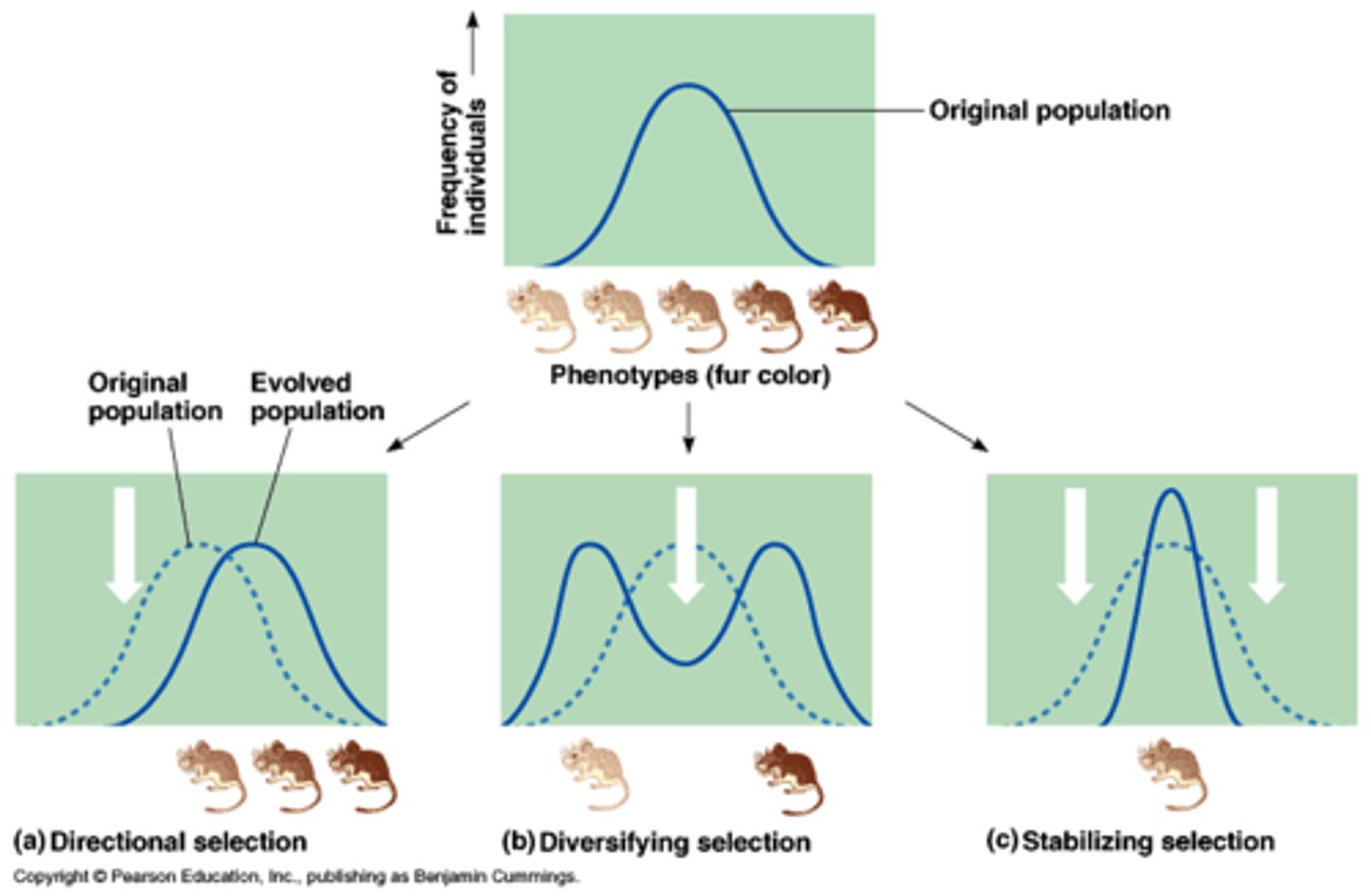
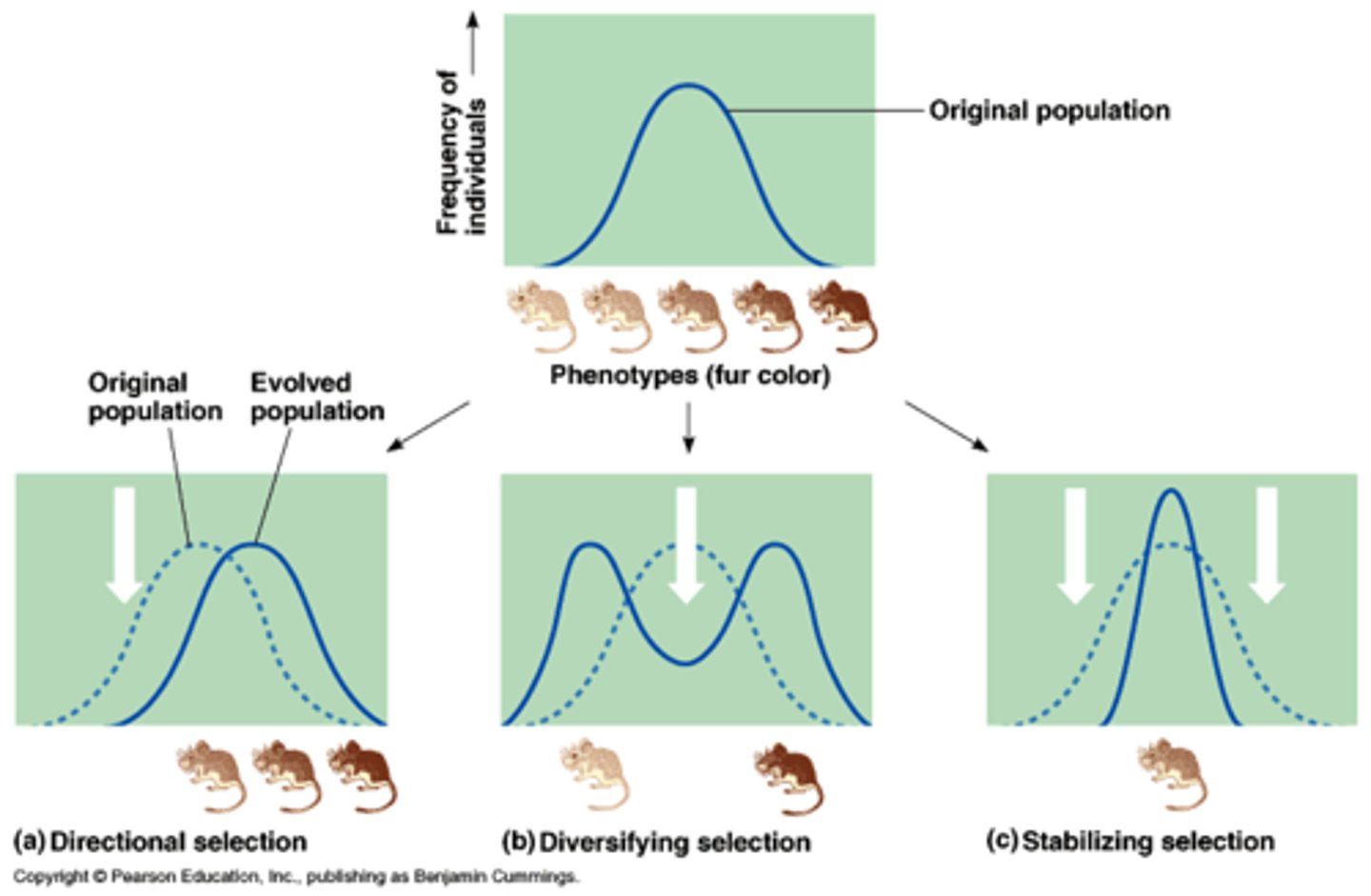
Directional selection
Natural selection in which individuals at one end of the phenotypic range survive or reproduce more successfully than do other individuals.
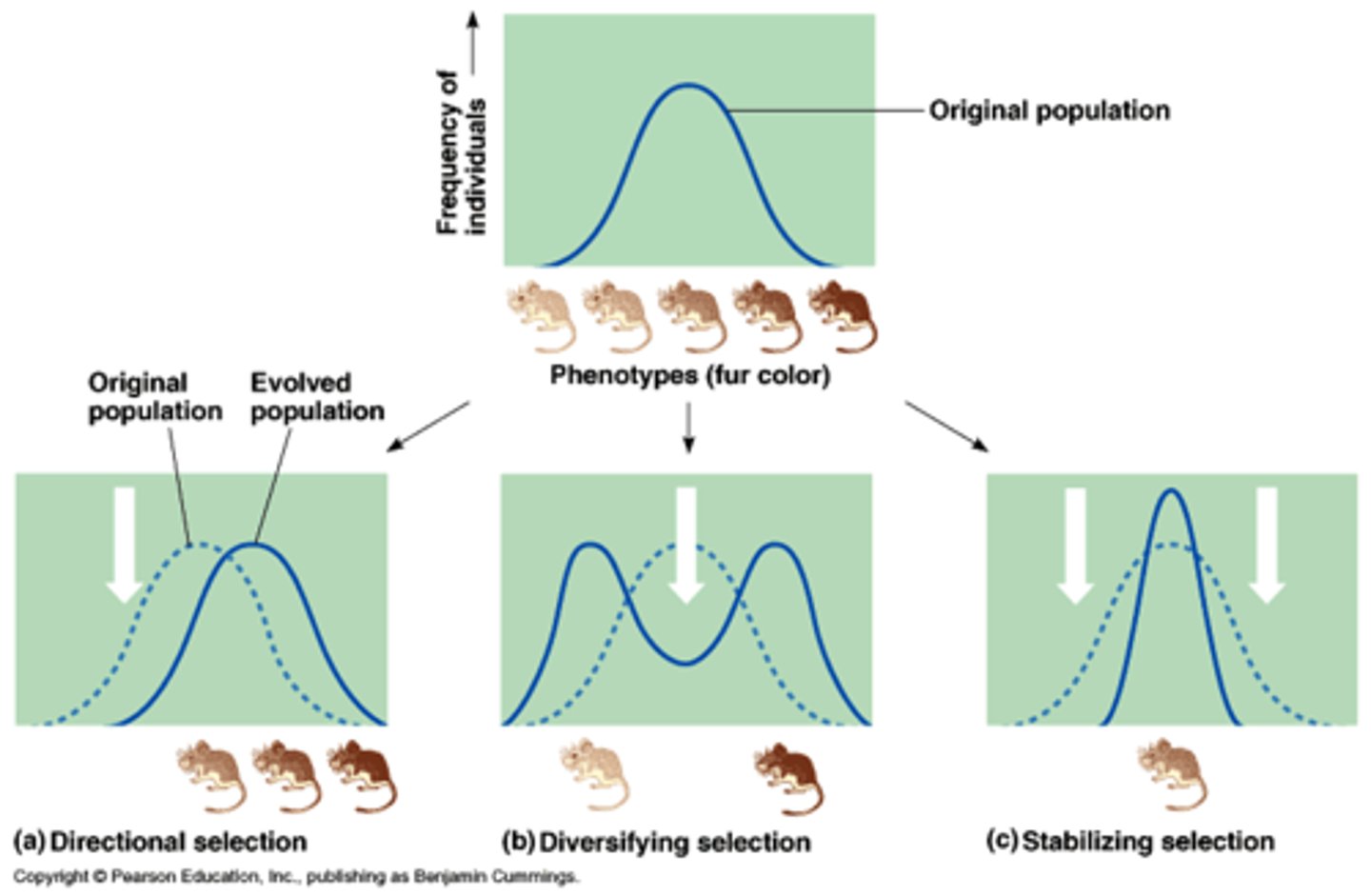
Disruptive selection
Natural selection in which individuals on both extremes of a phenotypic range survive or reproduce more successfully than do individuals with intermediate phenotypes.
Endosymbiosis
A process in which a unicellular organism (the "host") engulfs another cell, which lives within the host cell and ultimately becomes an organelle in the host cell; also refers to the hypothesis that mitochondria and plastids were formerly small prokaryotes that began living within larger cells.
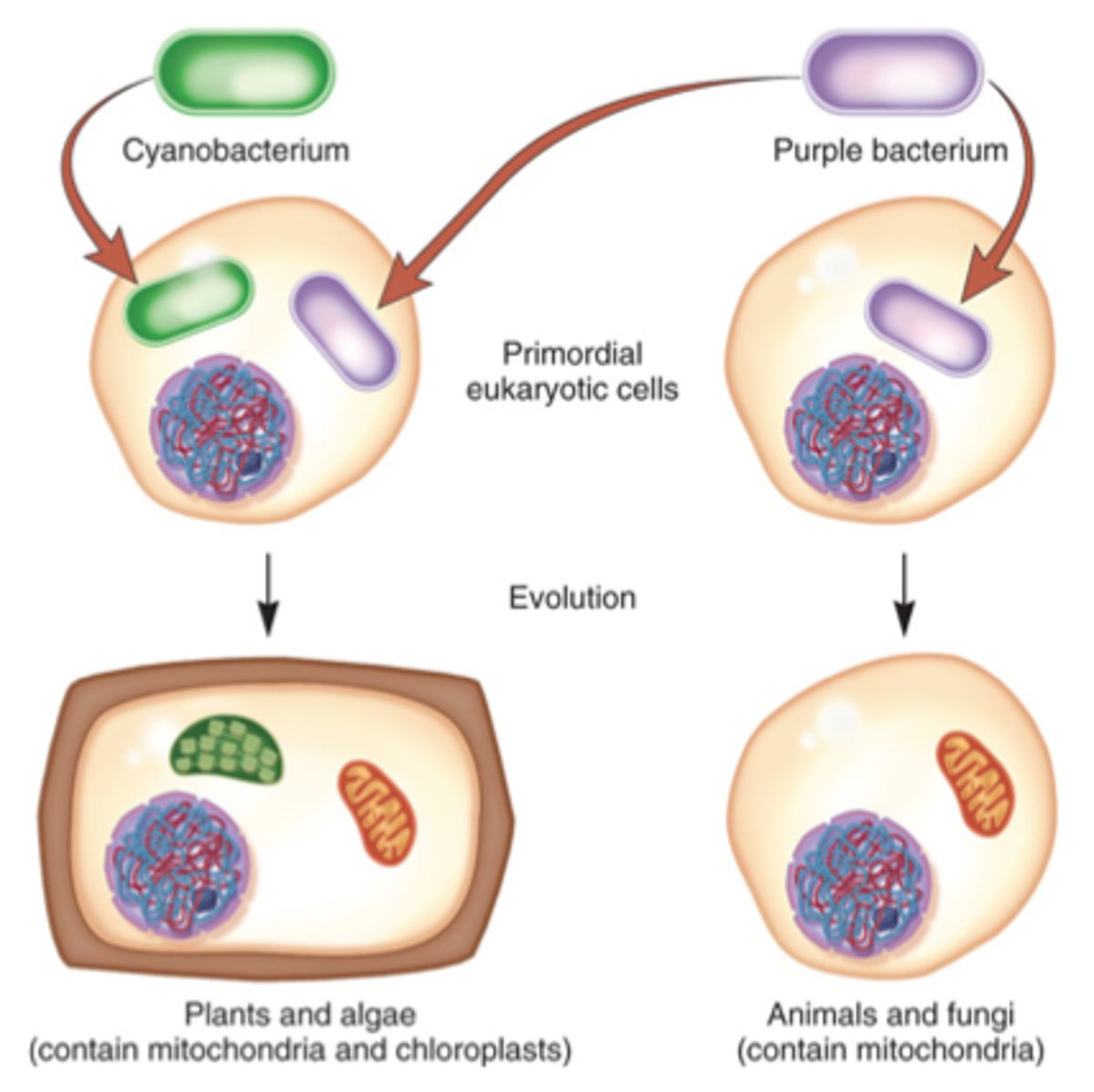
Evolution
Change in allele frequency of a population over time.
Evolutionary fitness
success in passing genes to the next generation

Extinction
The disappearance of all members of a species from Earth

Fixing of alleles
When all but one allele gos extinct and only one remains

Fossil
The trace or remains of an organism that lived long ago, most commonly preserved in sedimentary rock
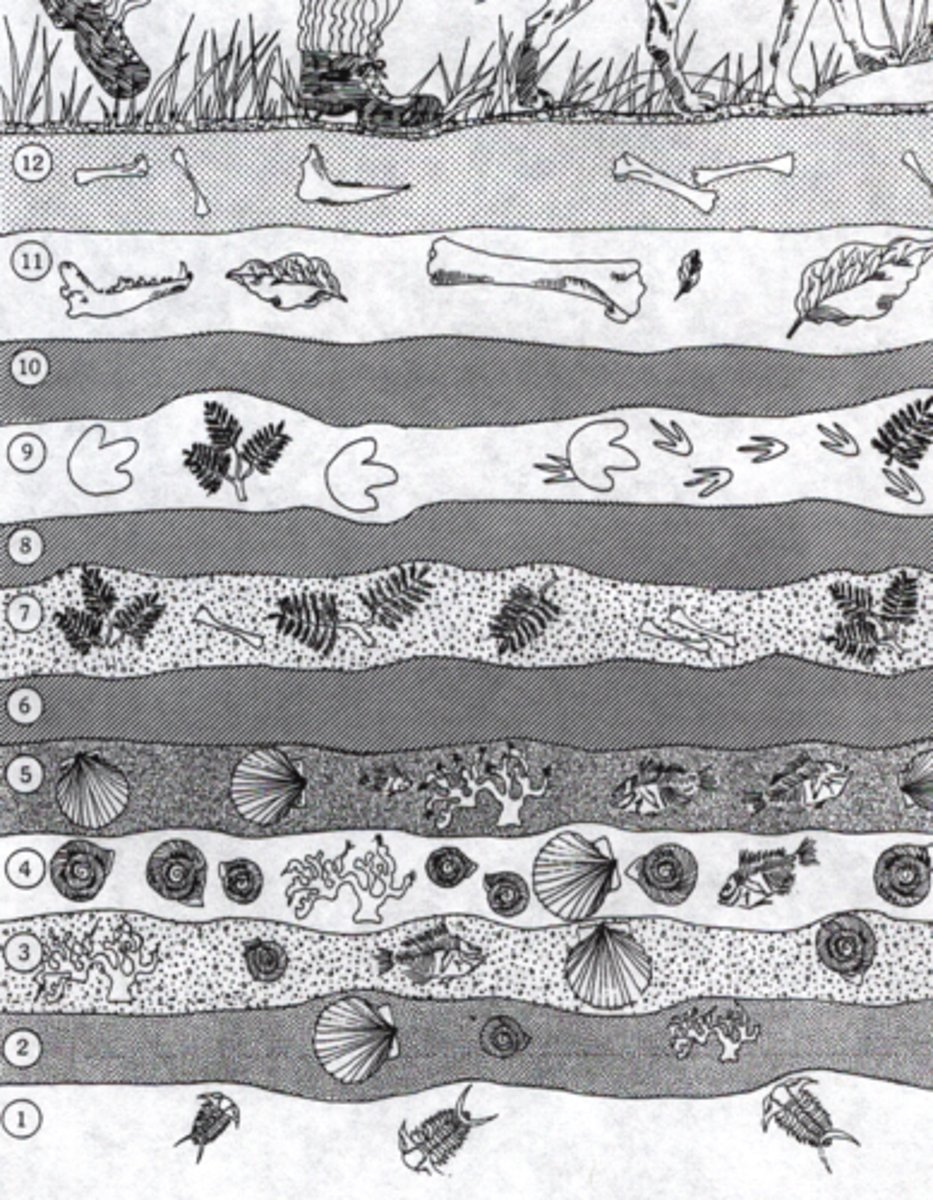
Fossil record
A term used by paleontologists to refer to the total number of fossils that have been discovered, as well as to the information derived from them
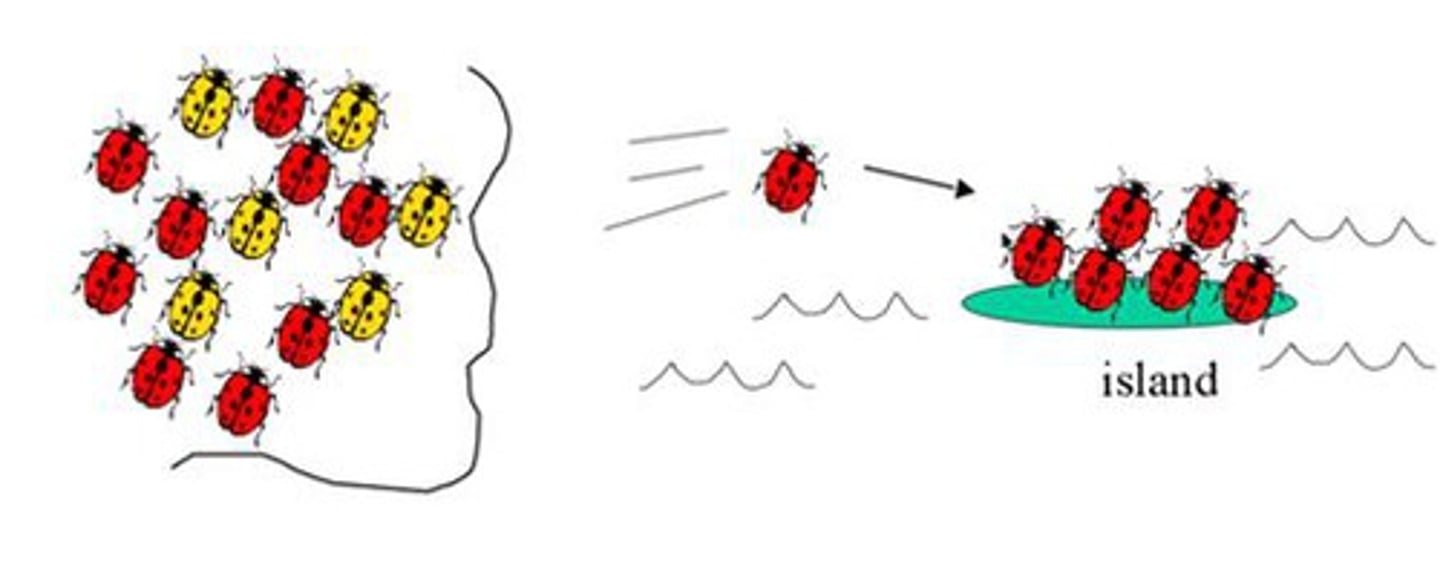
Founder effect
Genetic drift that occurs after a small number of individuals colonize a new area
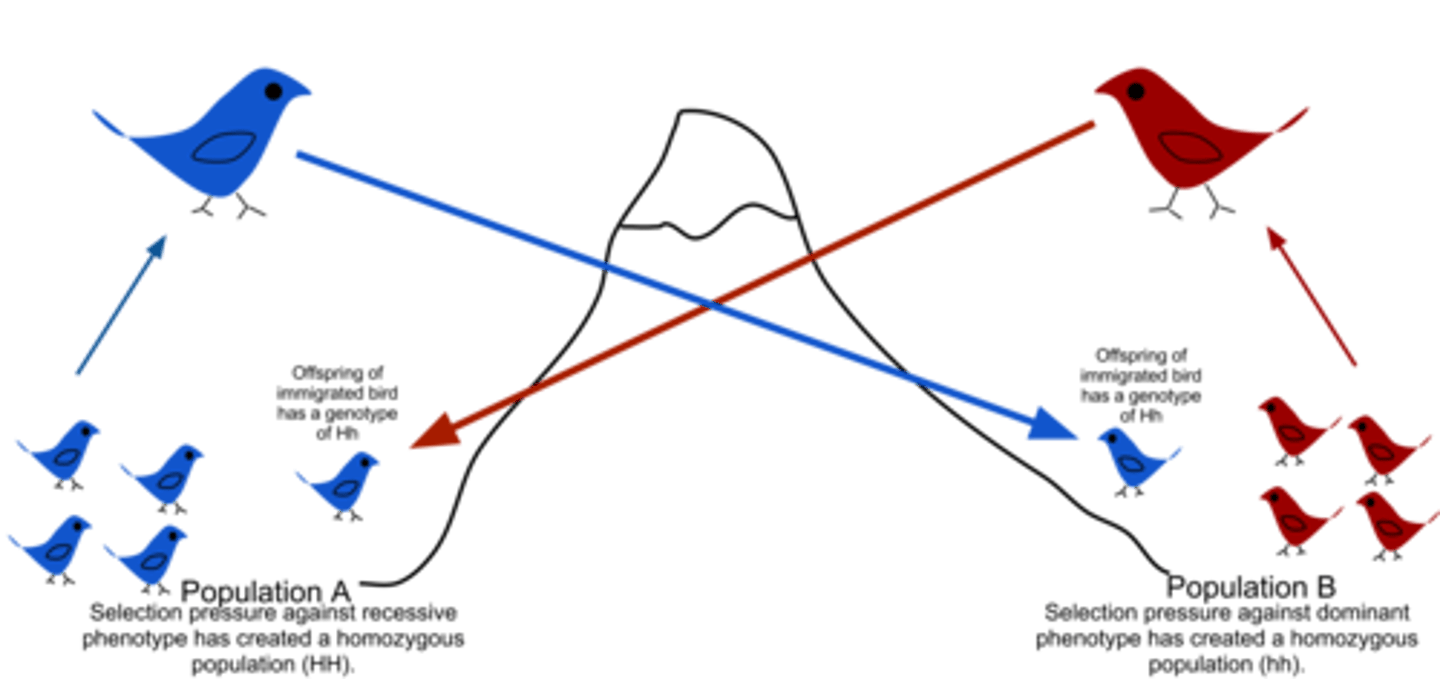
Gene Flow
Movement of alleles into or out of a population due to the migration of individuals to or from the population
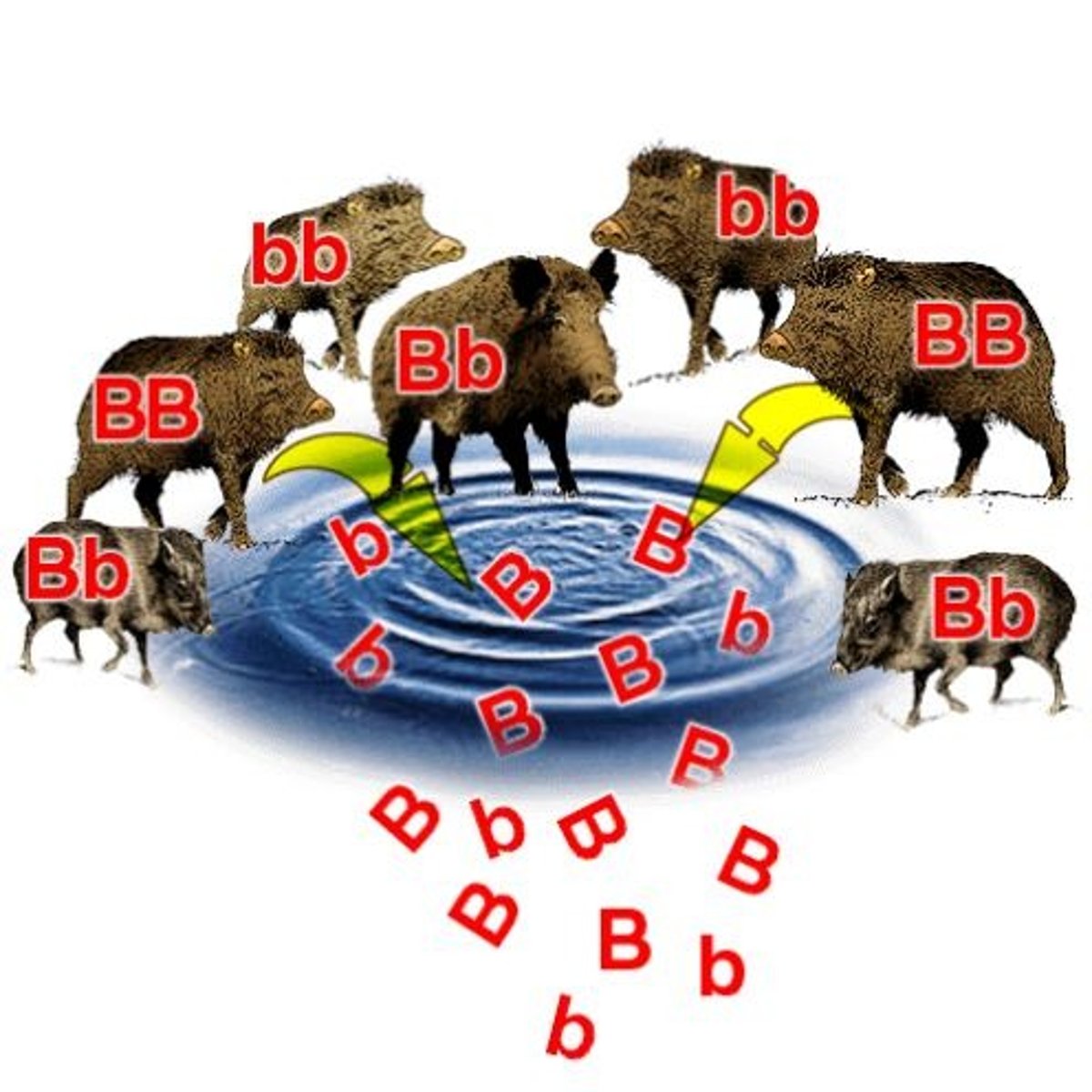
Gene Pool
All of the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population
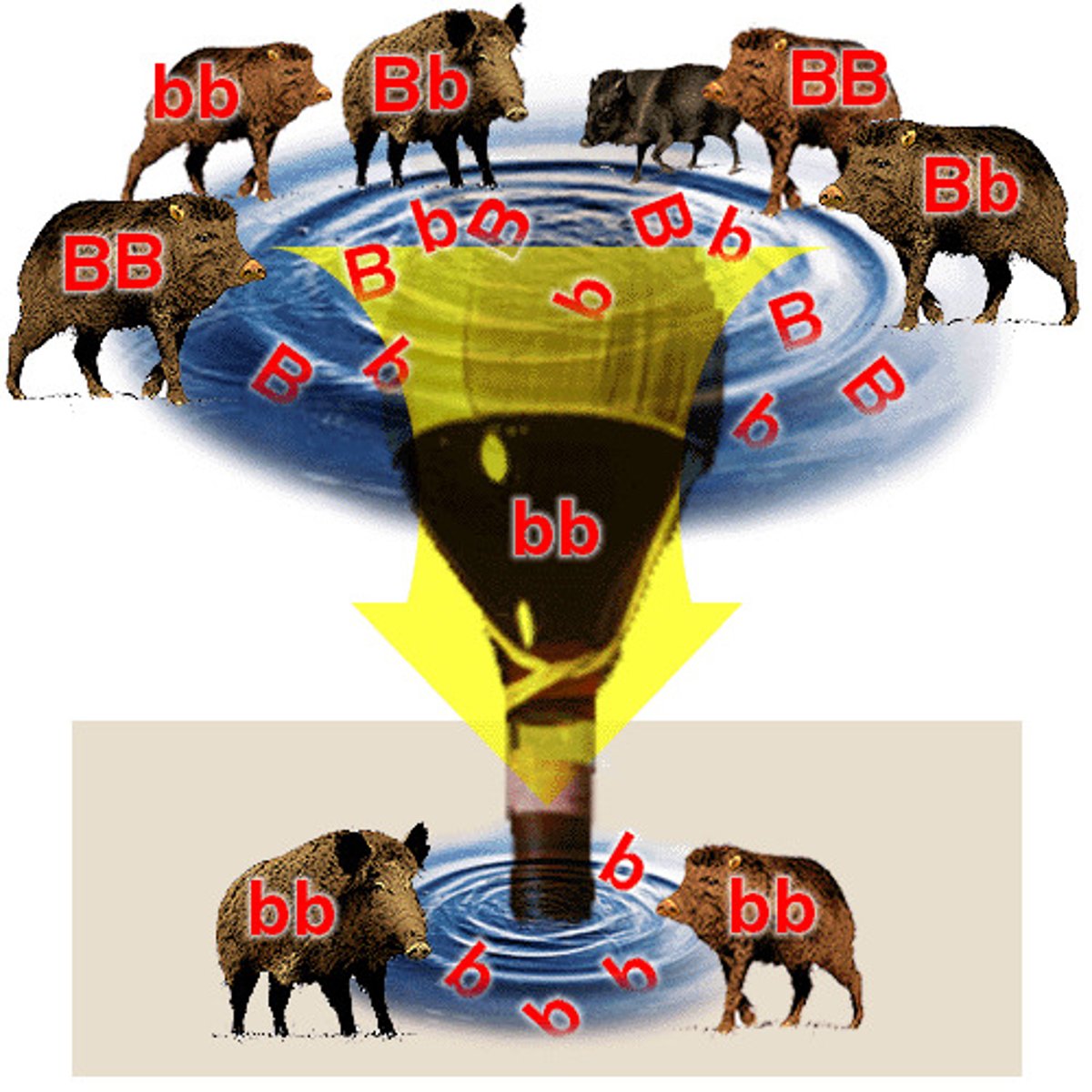
Genetic Bottleneck
The reduction of diversity that occurs when an event drastically reduces the number of organisms in a population. May lead to genetic drift.
Genetic Drift
Random change in allele frequency caused by a series of chance occurrences that cause an allele to become more or less common in a population

Genetic Variation
variations of genomes between members of species, or between groups of species thriving in different parts of the world as a result of genetic mutation.

Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism
Hardy Weinberg equation
Mathematical equation that can be used to calculate the genetic variation of a population at equilibrium
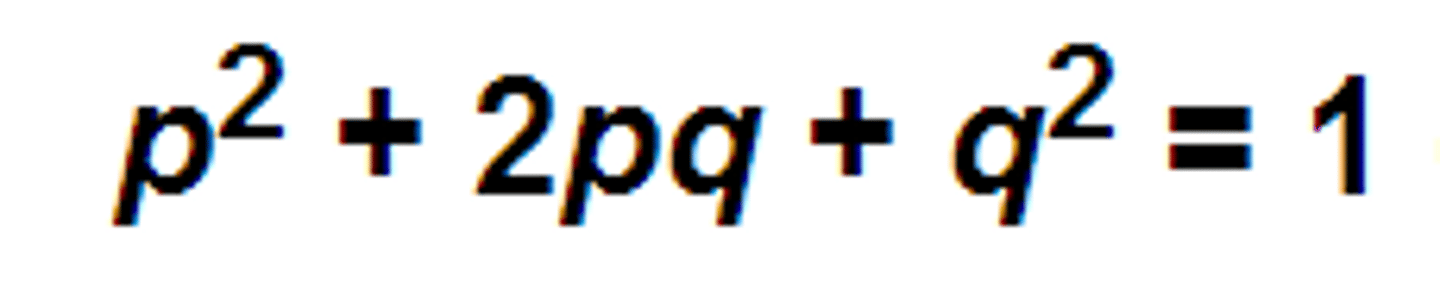
Homologous Structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
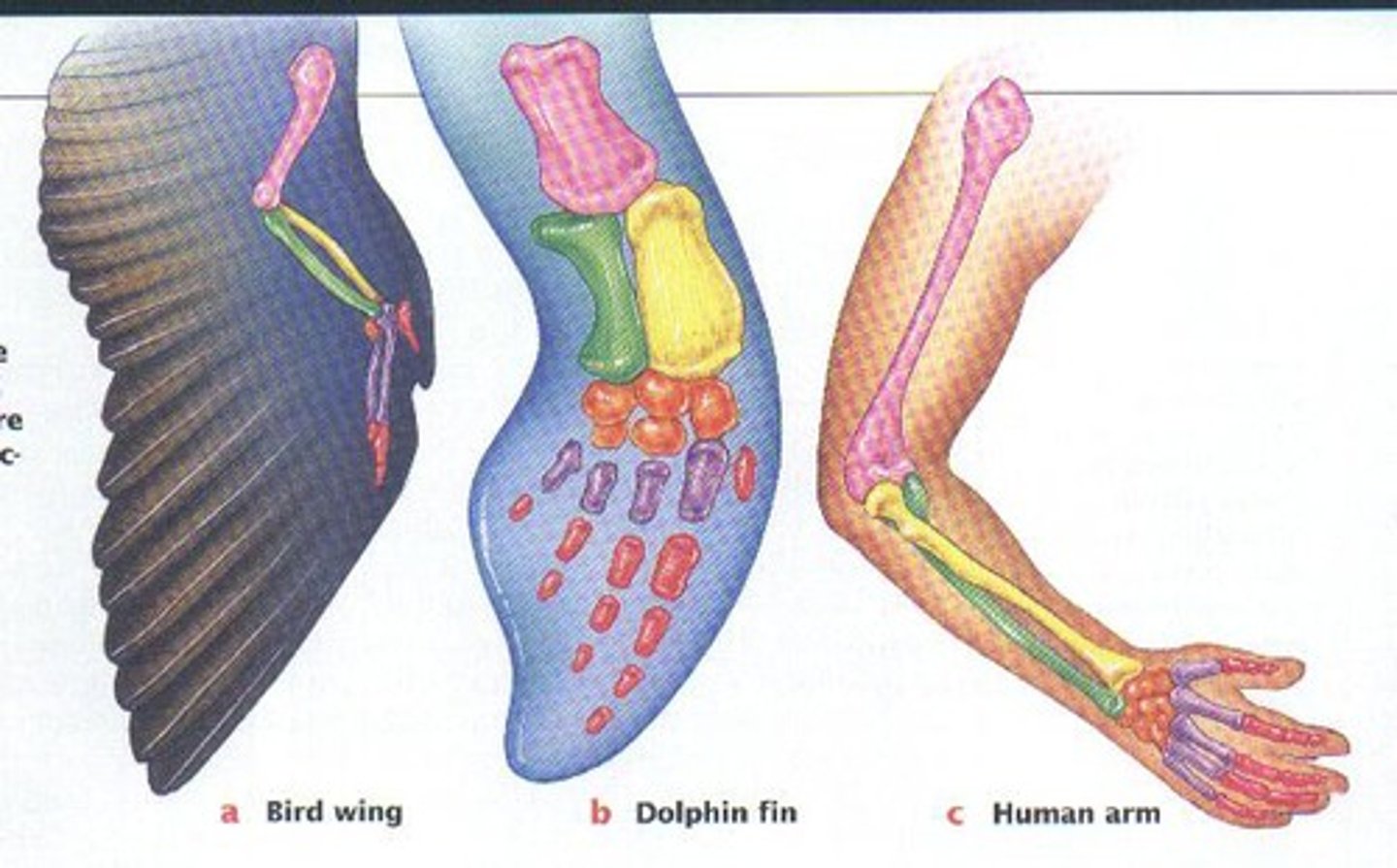
Mutation
A change in the nucleotide sequence
Natural selection
1 - Overproduction of offspring
2 - Variation in offspring
3 - Competition for limited resources
4 - Unequal reproductive success
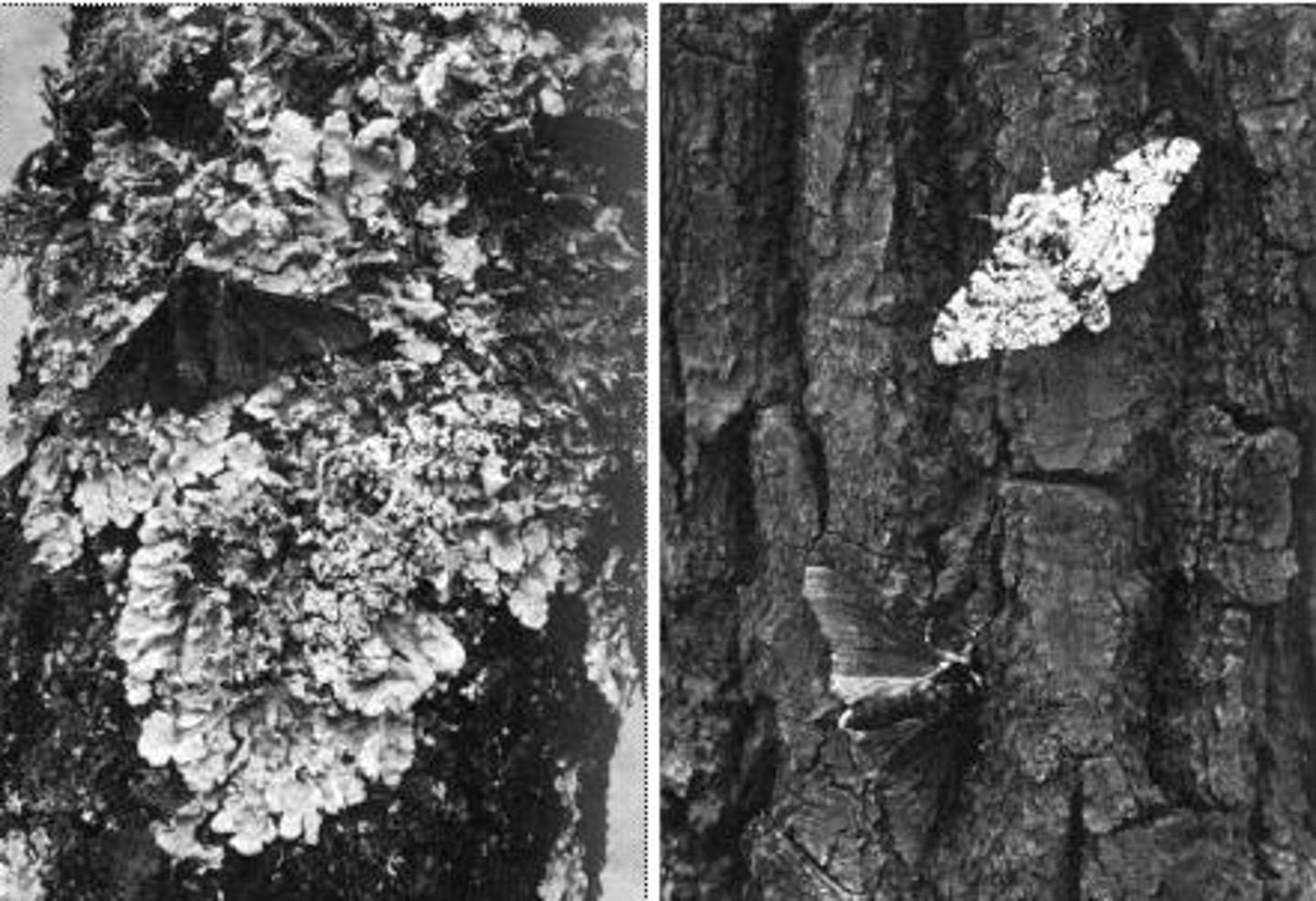

Phenotype
How a trait appears or is expressed
Phylogeny
The evolutionary history of a species or group of related species
Polymorphism
2 or more versions of a trait are present for a species

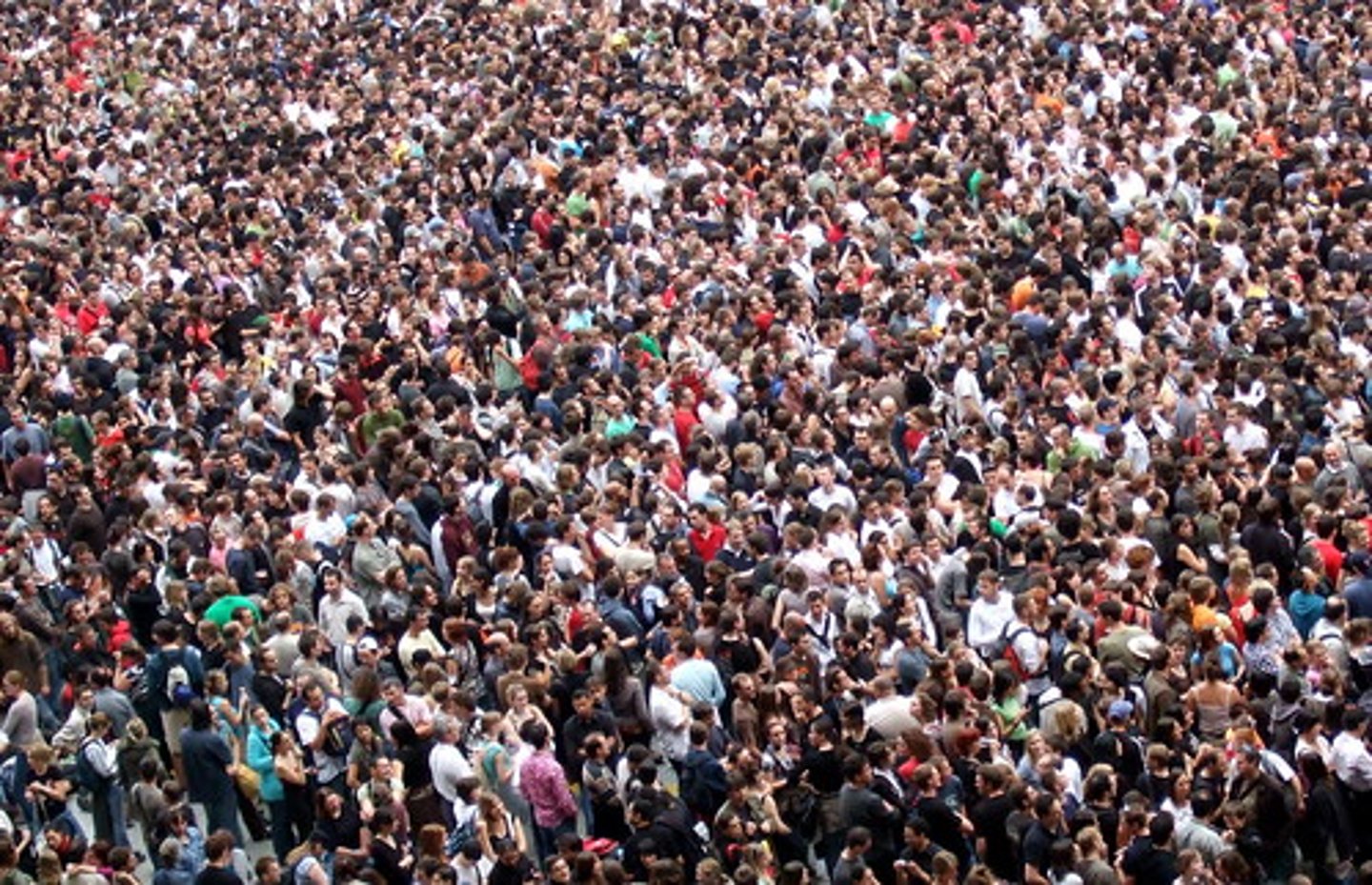
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area

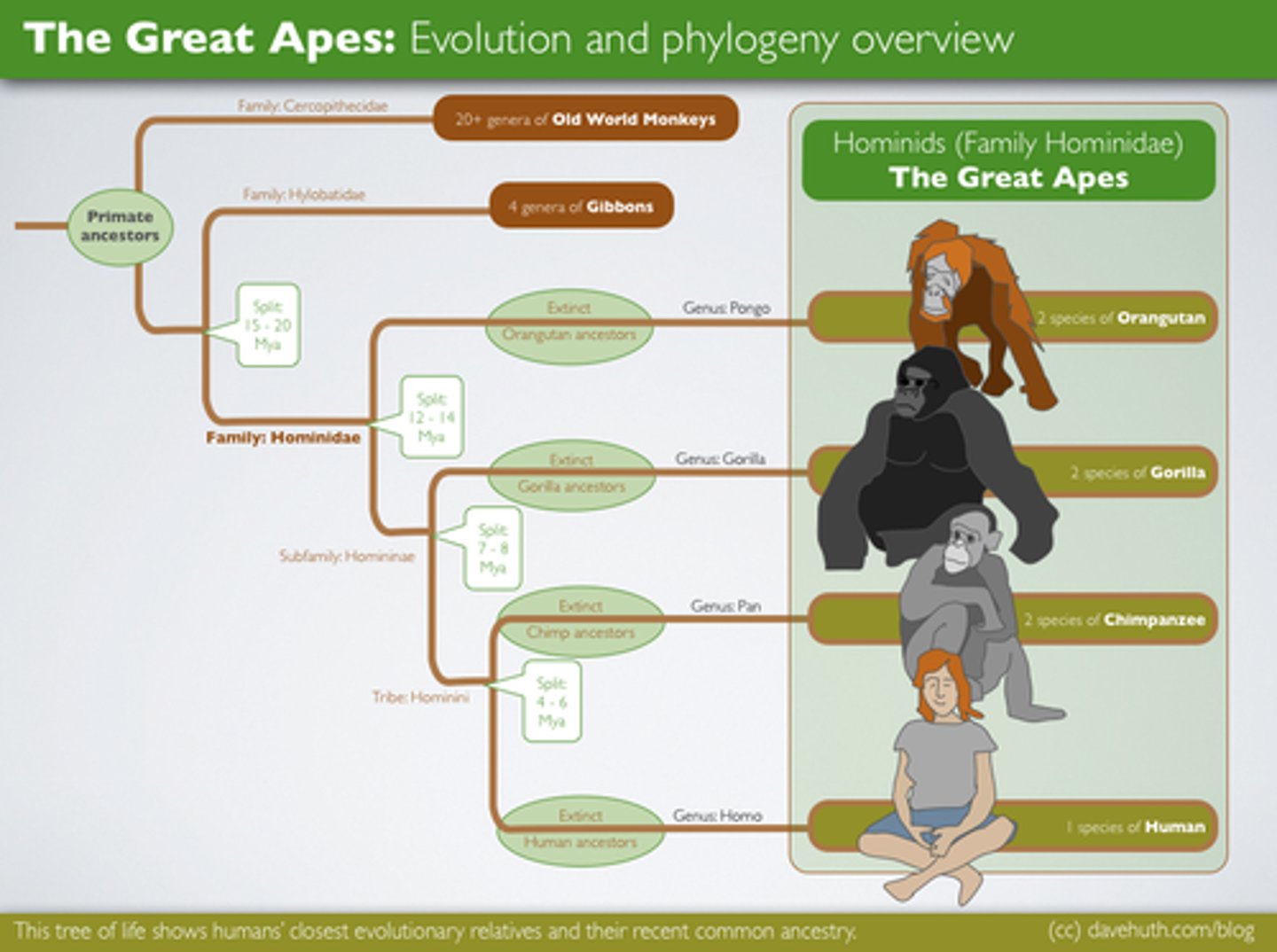
Postzygotic isolating mechanism
A type of reproductive isolation in which zygotes are produced but are unable to develop into reproducing adults; these mechanisms may range from inviability of zygotes or embryos to adults that are sterile.

Prezygotic isolating mechanism
Prevents reproduction by making fertilization unlikely through geographical, ecological, behavioral, or other differences.
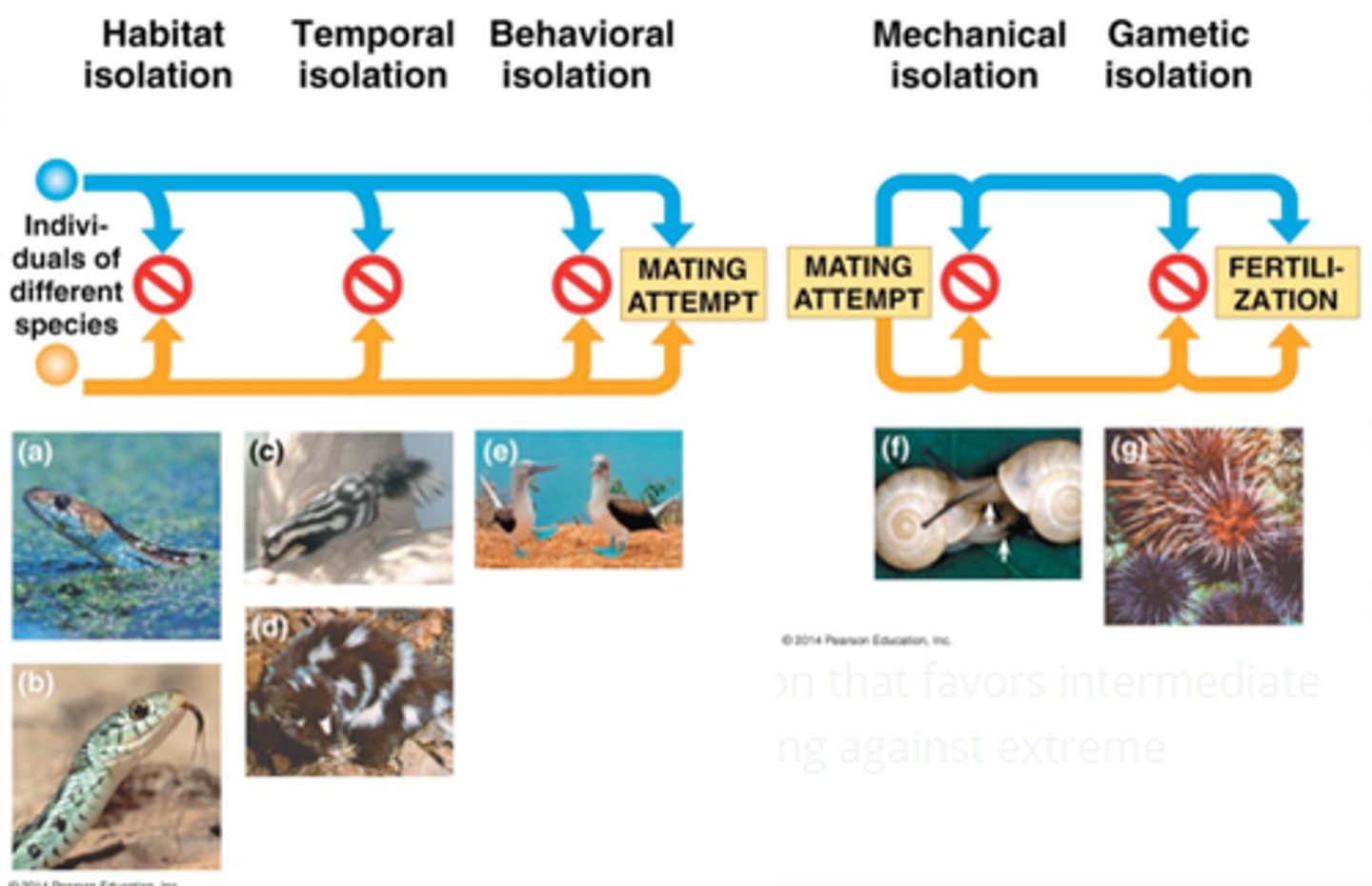
Reproductive isolation
Condition in which a reproductive barrier (physical or behavioral) keeps two species from interbreeding
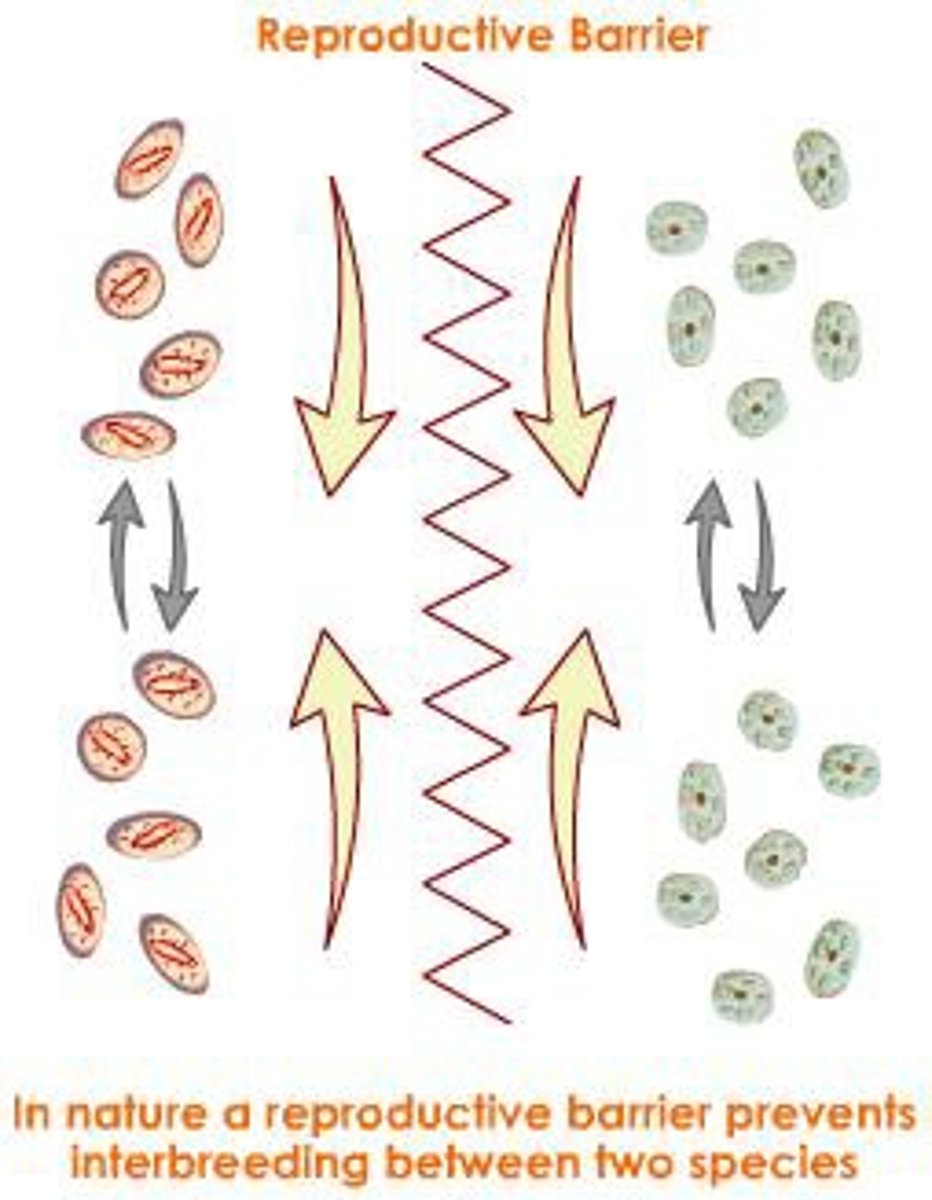
Speciation
A process typically caused by the genetic isolation from a main population resulting in a new genetically distinct species.
Species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
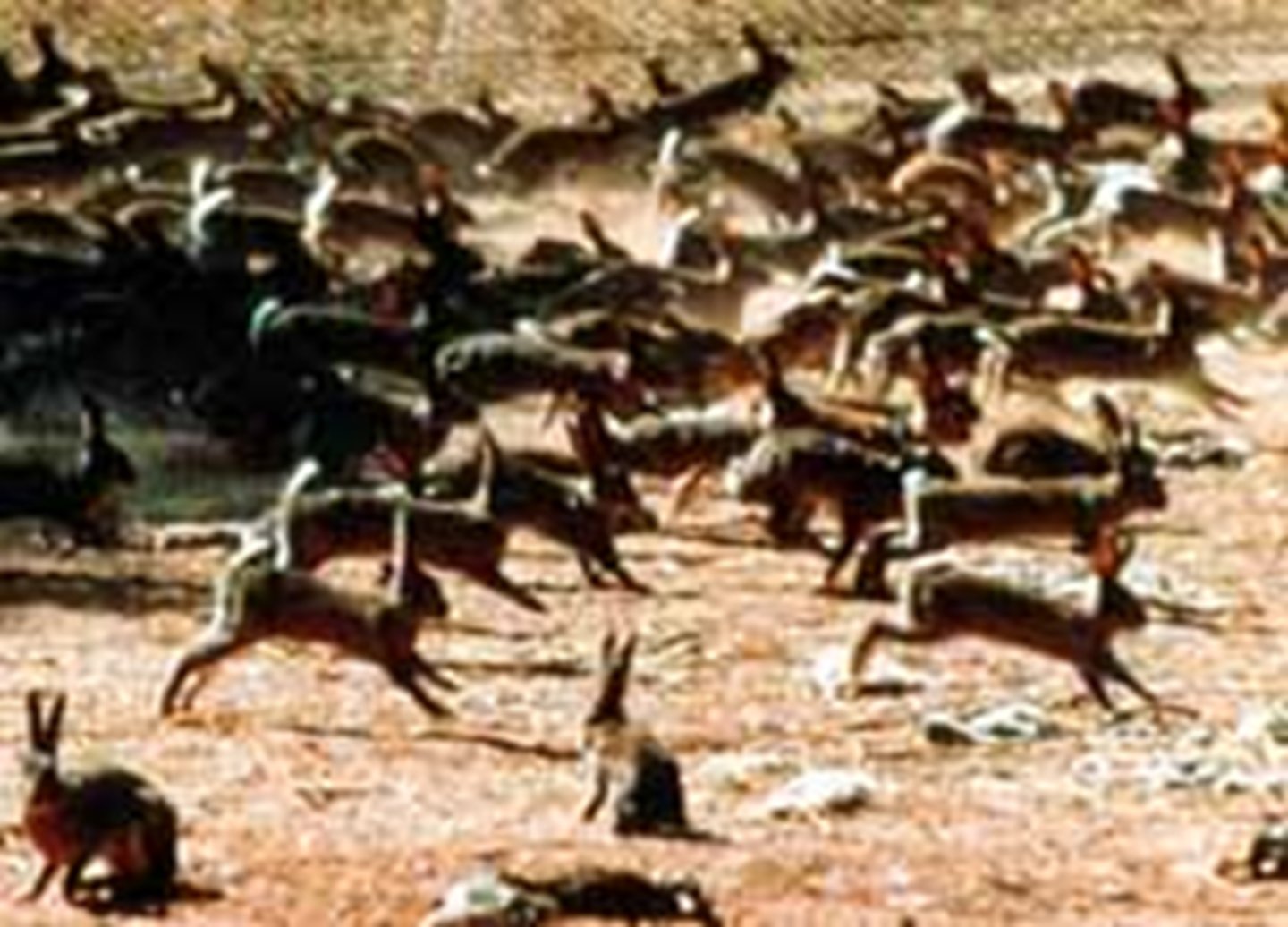

Stabilizing Selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
Sympatric speciation
The formation of new species without geographic isolation; such as polyploidy or behavioral isolation