Lecture 2, part 2 - Anatomy of deep forebrain
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Amygdala, hippocampus, basal gangli, thalami
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the types of white matter fibers that connect grey matter structures of the cerebrum?
Association fibers - connects cortical areas on the same side of the brain (anterior/posterior)
Commissure fibers - connect cortical areas on opposite sides of cerebrum (left/right)
Projection fibers - connect cortex with subcortical areas/other brain structures (Superior/inferior)
What are association fibers? List 2.
White matter fibers that connect cortical areas on the same side of the brain (anterior/posterior)
Cingulum
Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus
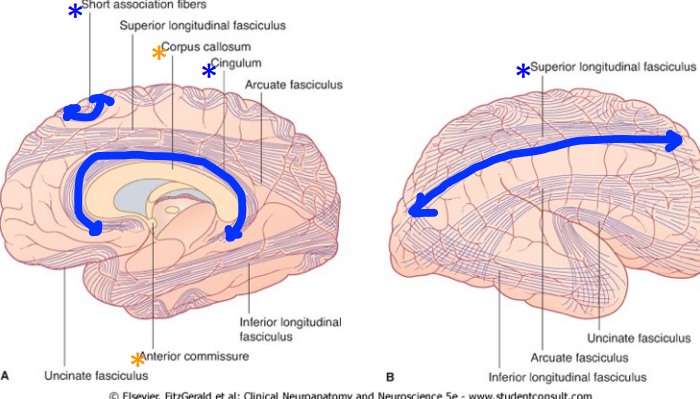
What are commissure fibers? Name 2.
Commissure fibers connect cortical areas on opposite sides of the cerebrum.
Corpus callosum (biggest commissure fiber bundle!)
Anterior commissure
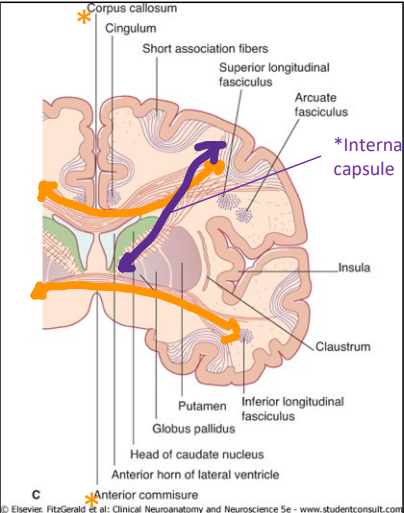
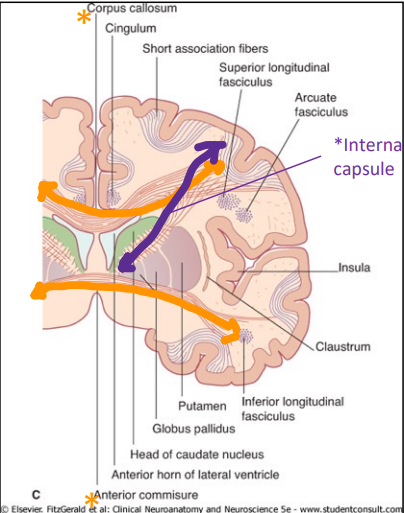
What are projection fibers?
Projection fibers connect the cortex with subcortical areas.
The corona radiata is a large bundle of projection fibers, with its axons funneling into a compact projection bundle called the internal capsule
Hippocampus - what is it involved in and where is it located relative to the lateral ventricle?
The hippocampus is important in learning and memory and also spatial localization.
They’re located medial to the inferior horn of the lateral ventricles.
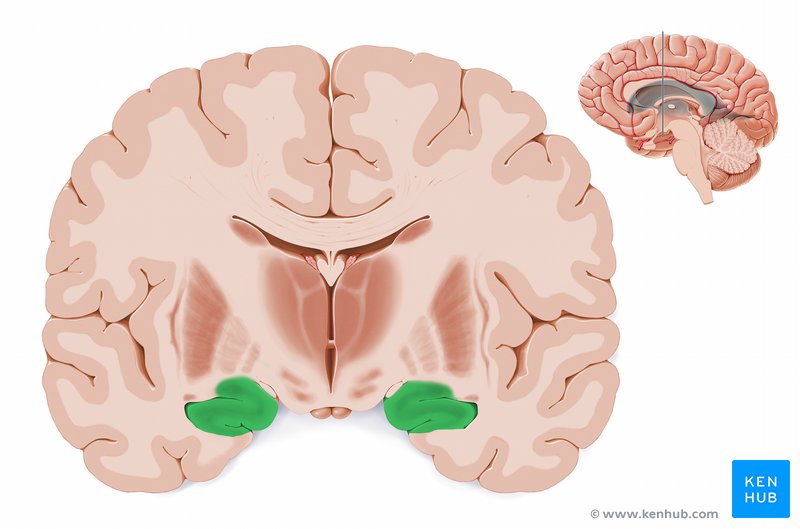
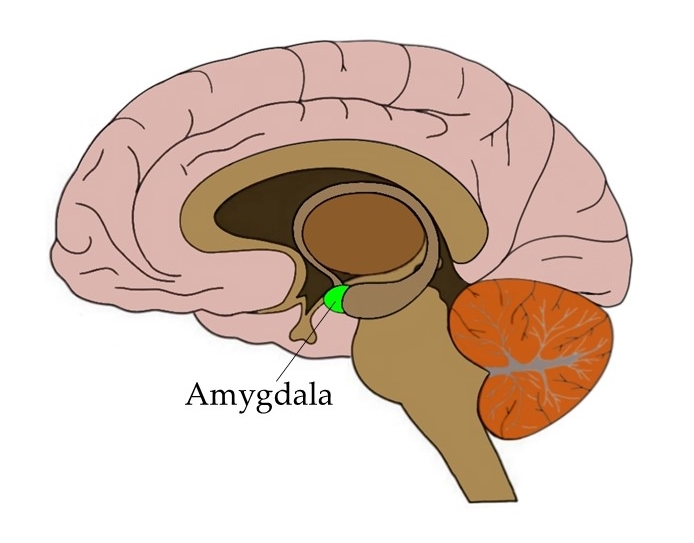
Amygdala - what is it involved in and where is it located relative to the lateral ventricle?
Recieves info from all sensory systems and mediates intense emotion (FEAR, FIGHT, FEED, FORNICATE)
Located anterior to the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle.
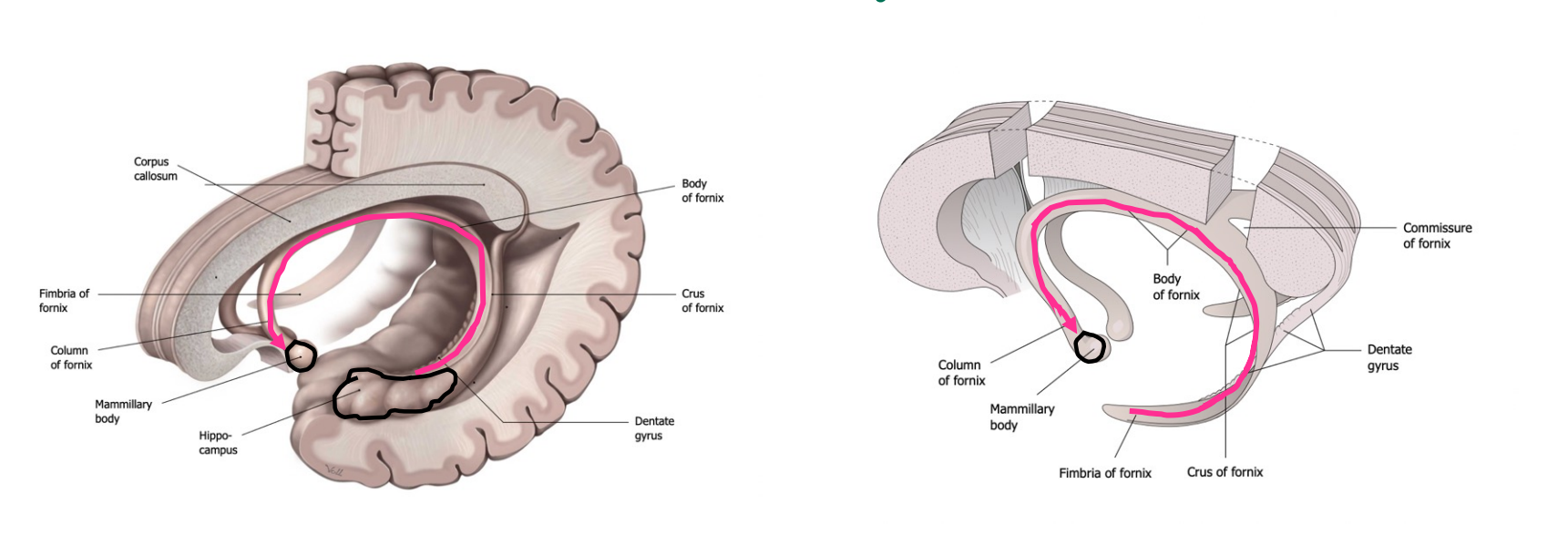
Fornix
White matter tract - projects from the hippocampus to the mammillary body (part of the hypothalamus), wrapping underneath the corpus callosum.
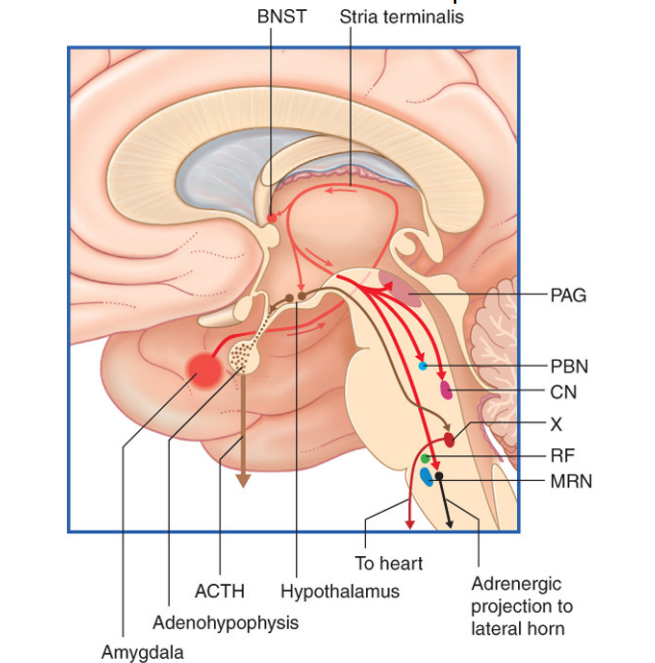
Stria terminalis
Main fiber bundle that projects from the central nucleus of the amygdala to the bed nucleus (BNST) - outputs include autonomic centers of brainstem and HPA axis (amygala is important in aggression and fear).
Basal ganglia
A collection of deep grey matter nuclei associated with the lateral ventricles and involved in motor regulation.
3 structures: caudate nucleus, globus pallidus, putamen
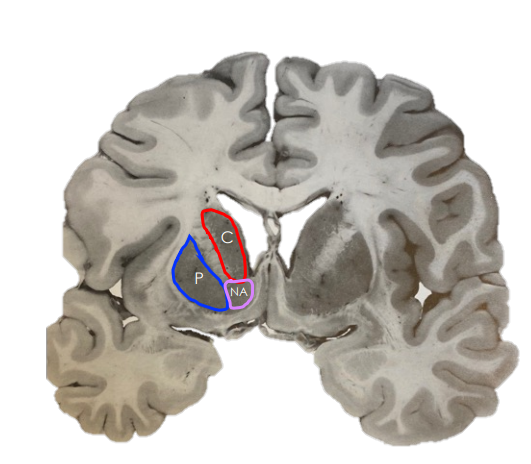
Describe the location of the caudate nucleus
Lateral to the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
What tract separates the caudate from the globus pallidus and putamen?
The internal capsule.
What is the grey matter structure that the internal capsule would “dead end” in some coronal section?
The nucleus accumbens
Involved in pleasure pathways and substance abuse (mesocorticolimbic reward pathway).