APPP: L3 Gross Anatomy of the CNS II
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Name the segments of the spinal cord and how many in each segment
7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal
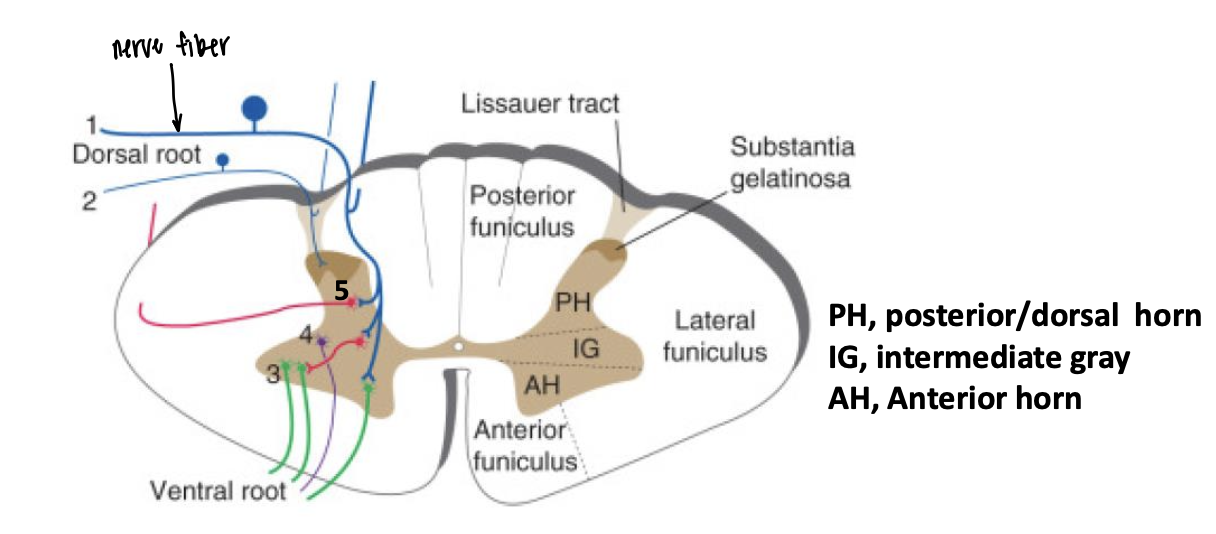
…-diameter and …-diameter sensory neuron fibers enter through the … horn and feed into motor neurons involved in rapid … movements (reflex arc), and signaling to the …
Large, small, dorsal, involuntary, cortex
Reflex arc:
Incoming sensory signals from the body (afferent sensory nerve fibers) synapse at the … horn with … found in the … gray
Interneurons signal to efferent motor nerve fibers, in the … horn, to stimulate … movement
posterior/dorsal, interneurons, intermediate
anterior, muscle
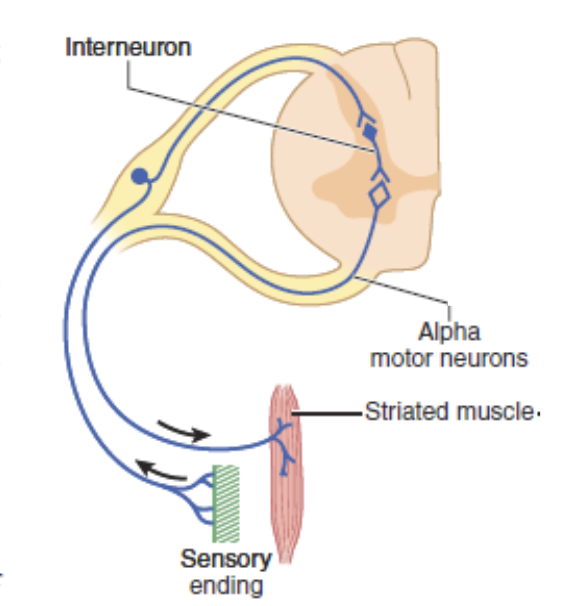
… nerves propagate information to actions at specific sites in the brain
Afferent
… nerves propagate information away from the central nervous system to a muscle or gland
Efferent
Links to the autonomic system:
Intermediate grey matter contains .. neurons with axons that leave through … roots
autonomic, ventral
What are the 3 major pathways in the spinal cord located in the white matter?
Posterior columns, lateral corticospinal tract, and spinothalamic tract
What are the posterior columns responsible for?
Touch and position
What does the lateral corticospinal tract do?
Commands for voluntary movements
What is the spinothalamic tract responsible for?
Pain and temperature
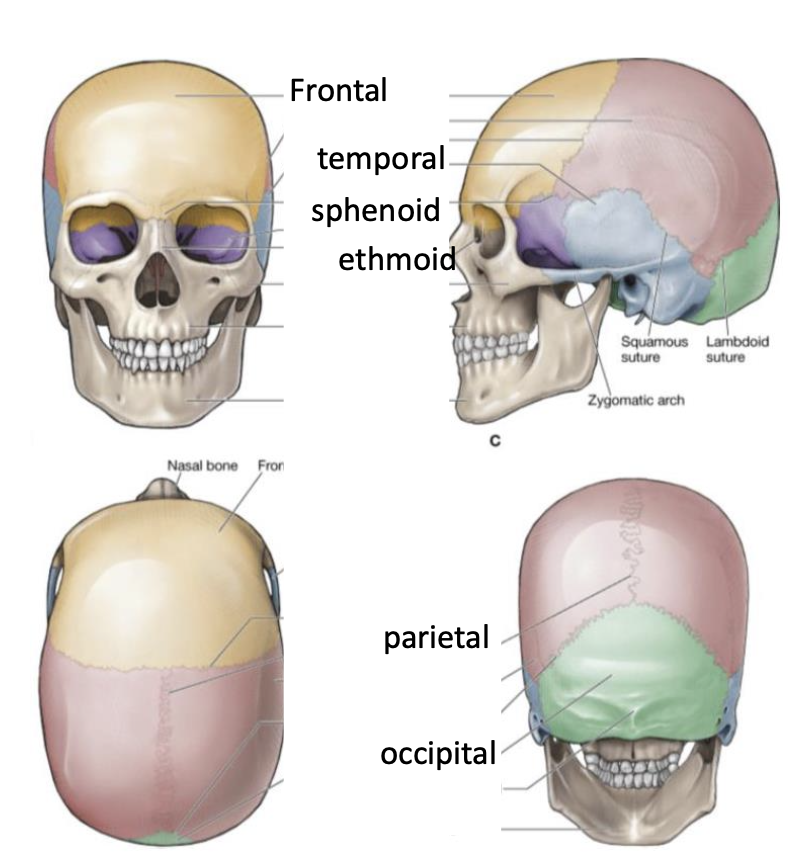
How many bones are in the skull?
22
What are the 6 cranial bones that enclose and protect the brain?
Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, sphenoid, and ethmoid
What is the spine protected by?
Vertebrae
What forms the major part of the mechanical suspension of the CNS and is necessary to keep it from self destructing?
Meninges
What are the 3 layers to the meninges?
Dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater
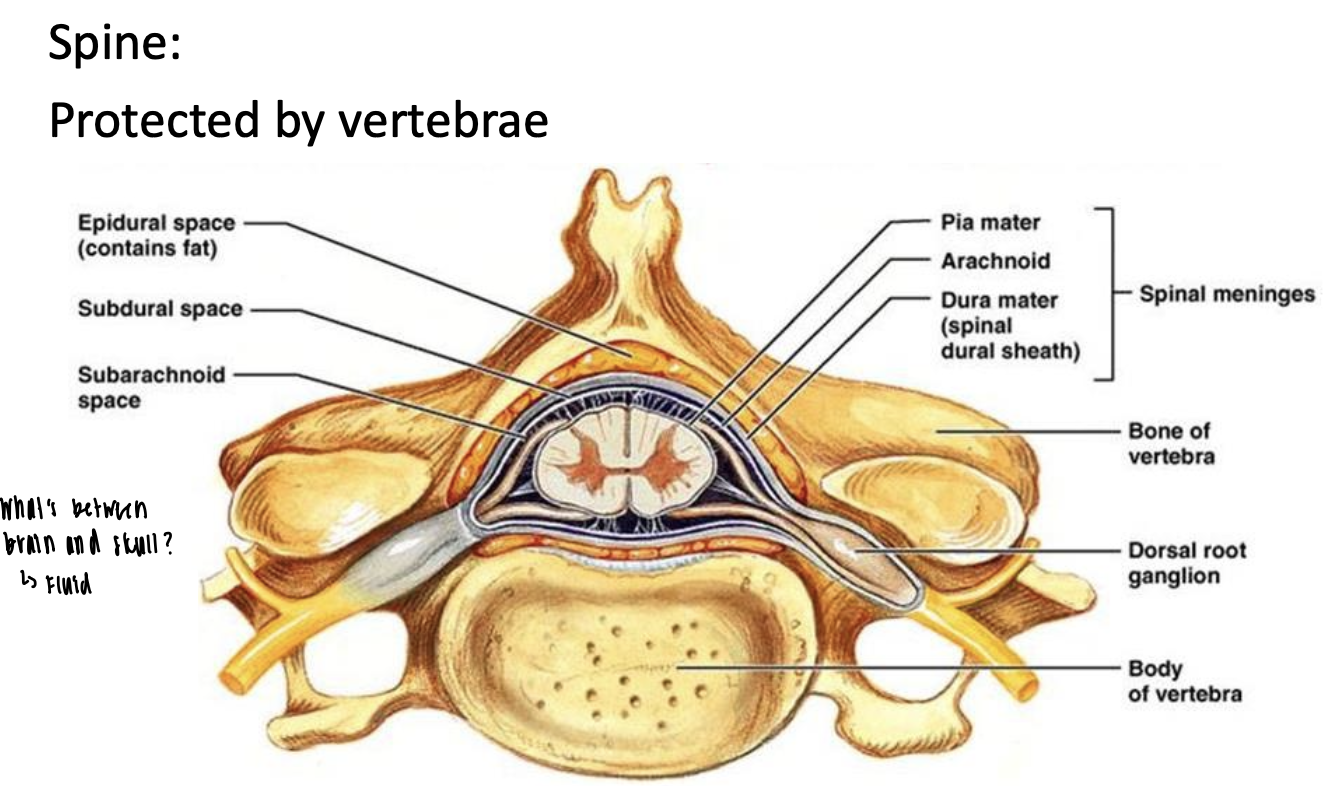
What is the dura matter?
Thick connective tissue membrane
What are the arachnoid and pia?
Thinner collagenous membrane
What does the dura provide?
Mechanical strength
The … connects the skull to the … cell layer
dura, arachnoid
The … connects to the … mater cell layer by delicate strands of connective tissue (arachnoid trabeculae) and suspends the CNS in its bath of cerebrospinal fluid
arachnoid, pia
How much of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) coat the brain?
~ 150 mL
The cerebral spinal fluid contains … and is formed by the filtration of …
nutrients, blood
Where the CSF enter the venous circulation through?
Arachnoid villi
What are arachnoid villi?
Outpouchings that poke through holes in the walls of the venous system
What do arachnoid villi do?
Act like valves:
When CSF pressure higher than venous, moves into venous system
In reverse, villi snap shut and venous fluid does not enter subarachnoid space
What is epidural hematoma?
Bleeding that occurs between the dura mater and the skull
What can epidural hematoma lead to?
Increased pressure on, and damage to, brain tissues
What are the symptoms of epidural hematoma?
Sever headache, nausea and vomiting, and slurred speech
Skull fracture causing a blood vessel rupture —> epidural bleeding —> …
epidural hematoma
Spontaneous rupture of blood vessel —> subarachnoid bleeding —> …
stroke
What is the BBB?
A protective functional separation of the circulating blood from the CNS
What is the role of the BBB?
Keep toxins and pathogens out, and facilitates the select transport of molecules
Arachnoid mater represents an … barrier to the CNS; cells are joined by … junctions
impermeable, tight
Pia mater meninges are … and joined by … junctions
impermeable, tight
What are the 4 layers of the BBB?
Endothelial cell layer, pericyte layer, protecting basement membrane, glial barrier formed by astrocyte endfeet
Both the … cell layer and … layer contribute to the maintenance and regulation of endothelial cell tight junctions (length, width, and complexity)
pericyte, glial barrier
… has specific transport systems that permit the supply of nutrients, ions, and bioactive molecules
Endothelial cell layer
…, …, and … are small and nonpolar (transcellular diffusion)
CO2, O2, and lipid-soluble molecules
… can do diffusion, active transport, and receptor mediated and adsorptive transcytosis
Endothelial cell layer
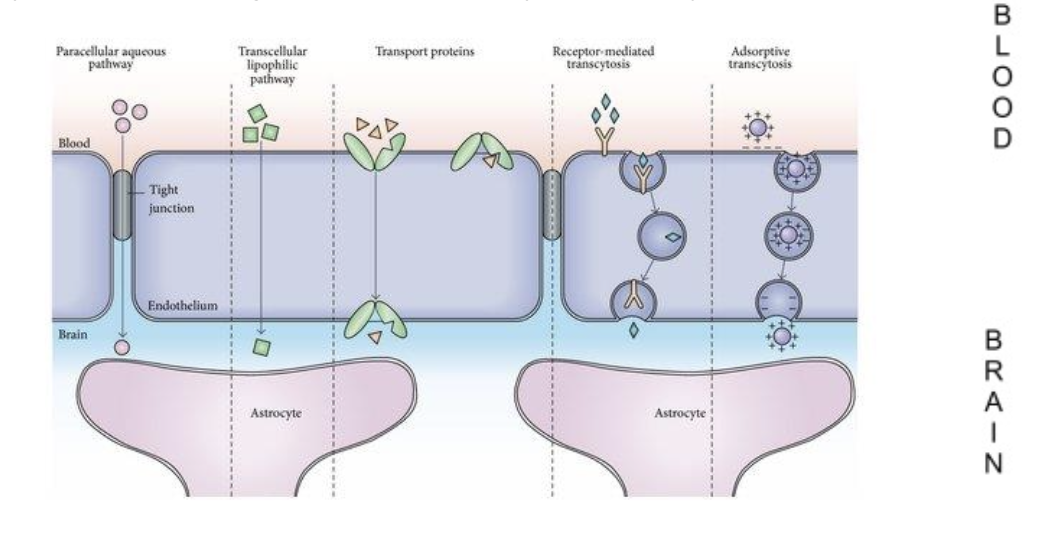
Transport of … into the BBB often requires the drug to engage specific transport mechanisms
drugs
If drugs are not desired in the brain, creating more … compounds reduces uptake
polar
What are the 3 glia cell types?
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia
What do astrocytes do in addition to their role in the BBB?
Provide nutrients to nerve cells and control the chemical composition of fluids around nerve cells, enabling them to thrive
What do oligodendrocytes do?
Make myelin, a fatty substance that insulates nerve axons and speed the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers
What does microglia do?
Help protect the brain against infection and help remove devris from dead cells
Dysregulation of … can either cause the disease (e.g. multiple sclerosis) or lead to further progression (e.g. Alzheimer’s)
microglia
What happens when microglia is dysregulated?
Abnormal protein aggregation, failure in protein degradation pathways, and impaired axonal transport