NPTE Gait
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Gait cycle
Begins with heel strike of one extremity and ends with heel strike of the same extremity
= stride
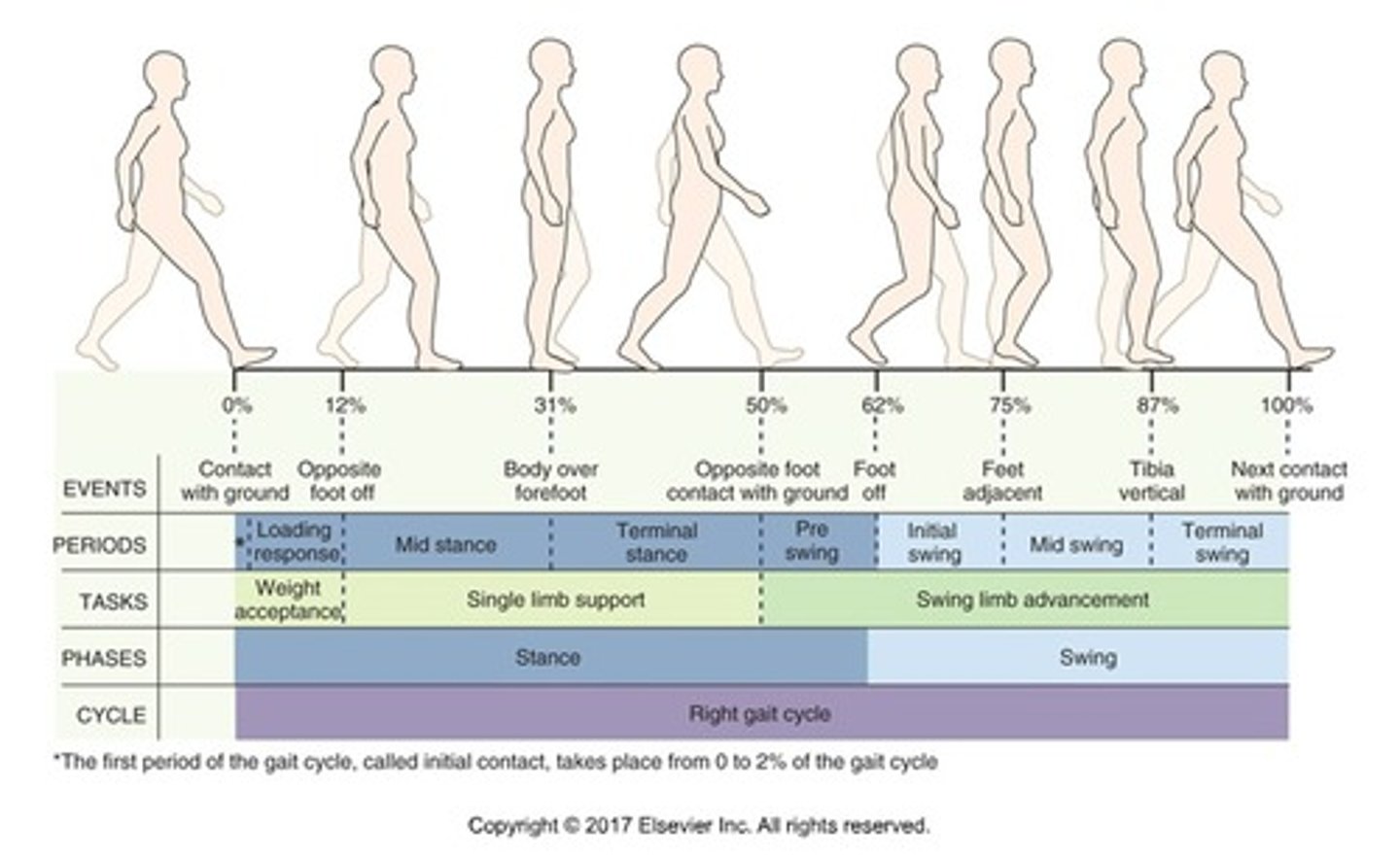
Step
Beginning of event by one lib until beginning of same event with CL limb
How to remember what hip flexor tightness causes in gait: FLOP
hip FLexor tightness = OPposite side step length reduces

ROM required for gait (hip, knee and ankle)
Hip
Stance: 0-30 flexion and 0-10-20 hyperextension
Swing: 20-30
Knee
Stance: 0-40 flexion
Swing: 0-60 flexion
Ankle
Stance: 0-10 DF and 0-20 PF
Swing: 0-10 DF

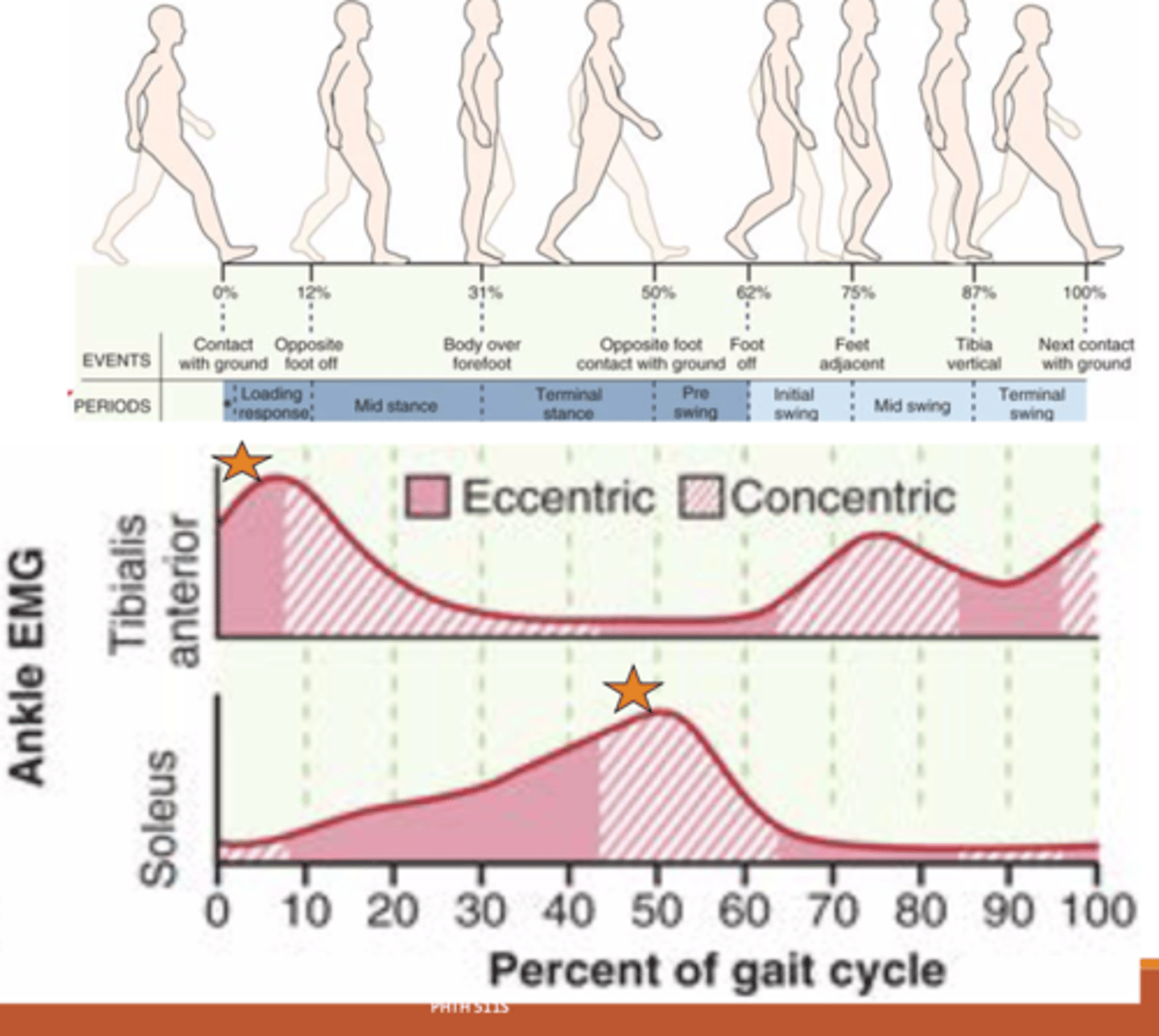
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Pretibial muscles
mm: Tibialis Anterior, EDL, EHL (Deep peroneal nn. L4-S1)
Prior to and during heel strike:
-Eccentric -> lower foot down
Prior to and during swing:
-Concentric -> DF to clear toes
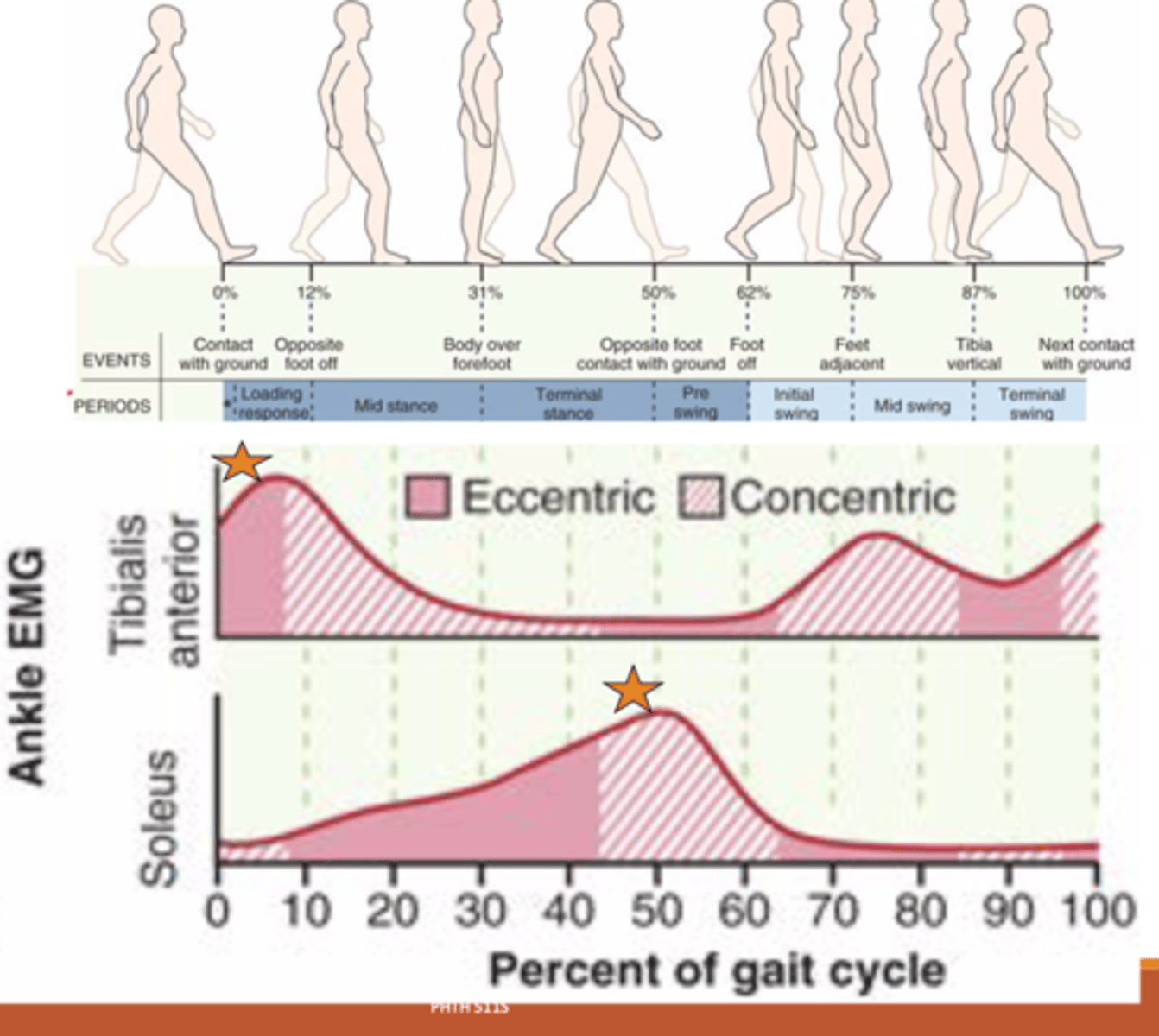
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Calf Muscles
mm: Soleus, Gastric, FDL, FHL, Tibialis Posterior
(Tibial nn. L4-S3)
Mid stance:
-Eccentric -> control tibia over foot
Heel off:
-Concentric -> PF
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Quadriceps
mm: Vastus medialis/lateralis/intermedius, RF
(Femoral nn. L2-L4)
Before heel strike:
-Eccentric -> control rapid knee flexion to prevent buckling
Pre-swing:
-eccentric -> slow down tibia
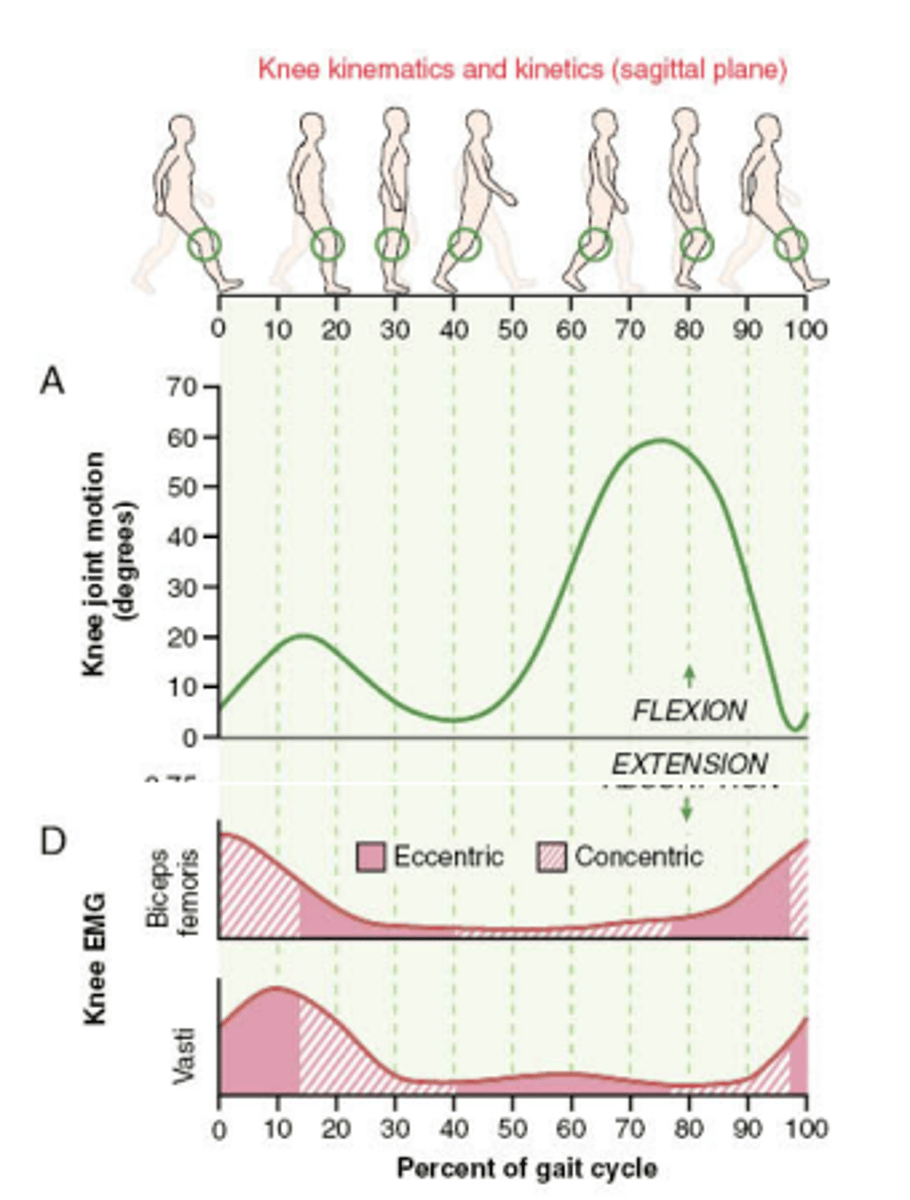
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Hamstrings
mm: Biceps, semitendinosus, semimembranosus (Sciatic nn L4-S3)
Heel strike:
-Eccentric -> protects knee from hyperextension
Swing Phase:
-Concentric -> knee flexion, hip extension
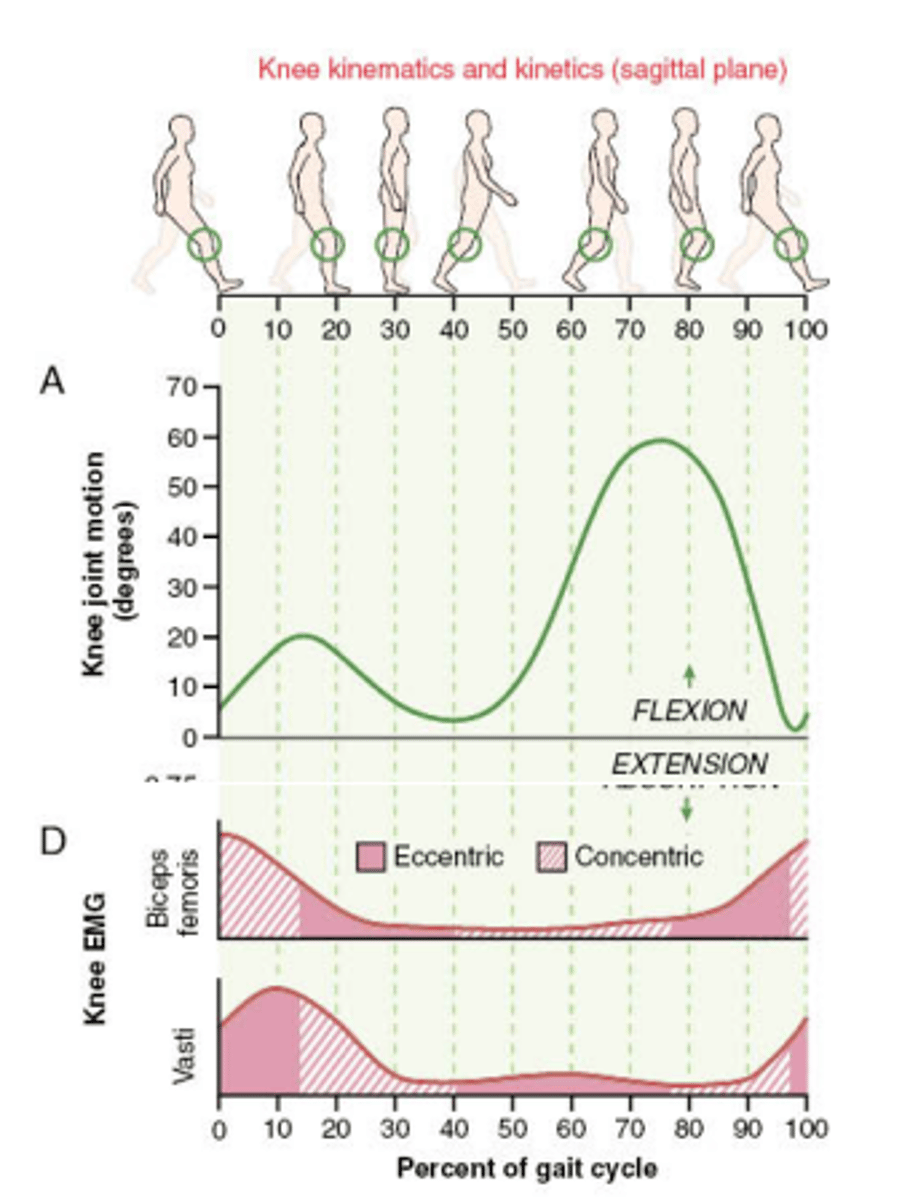
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Hip Abductors
mm: Glute med, glute min and TFL
(Superior Gluteal nerve L4-S1)
Stance:
-eccentric -> control pelvis
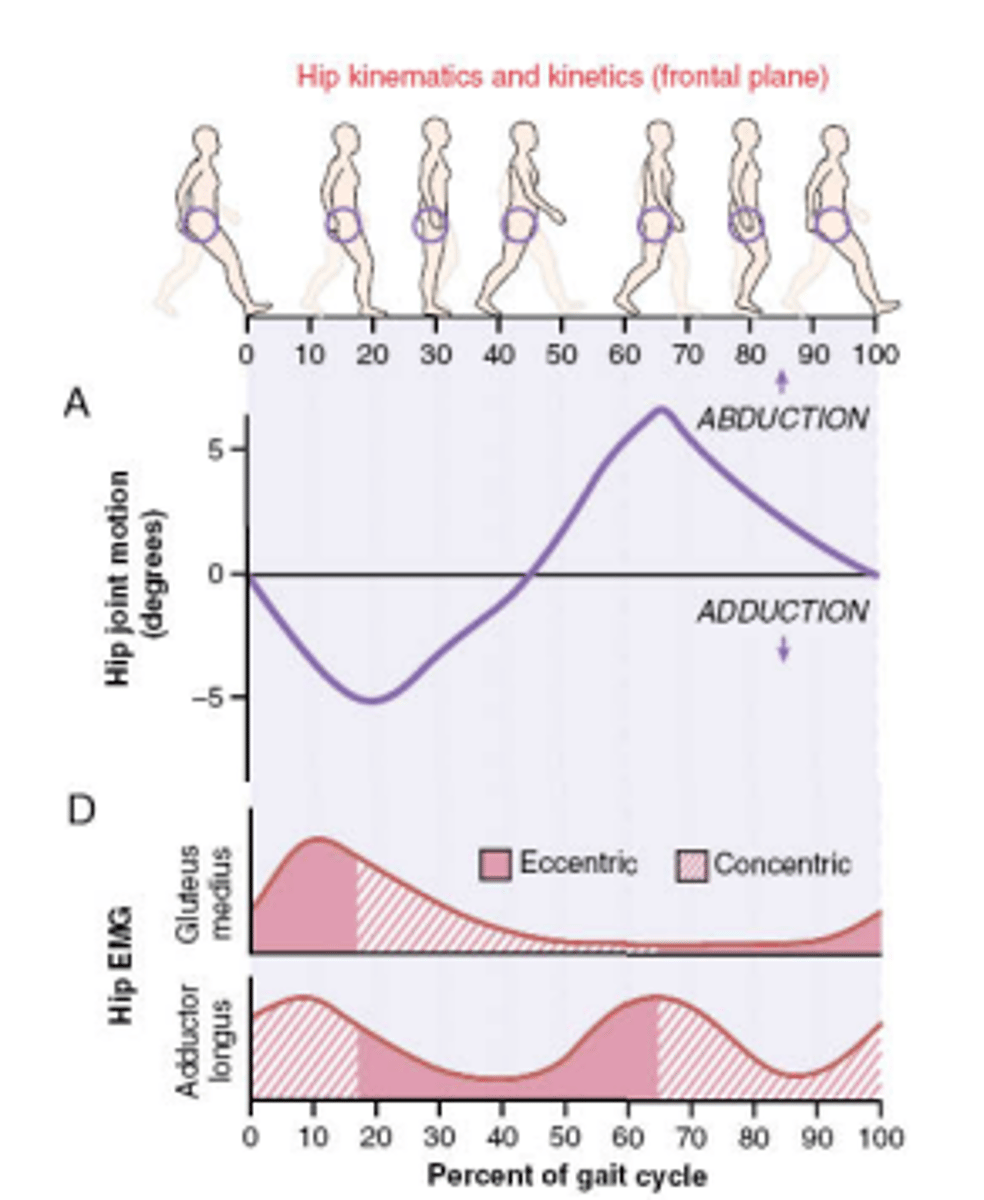
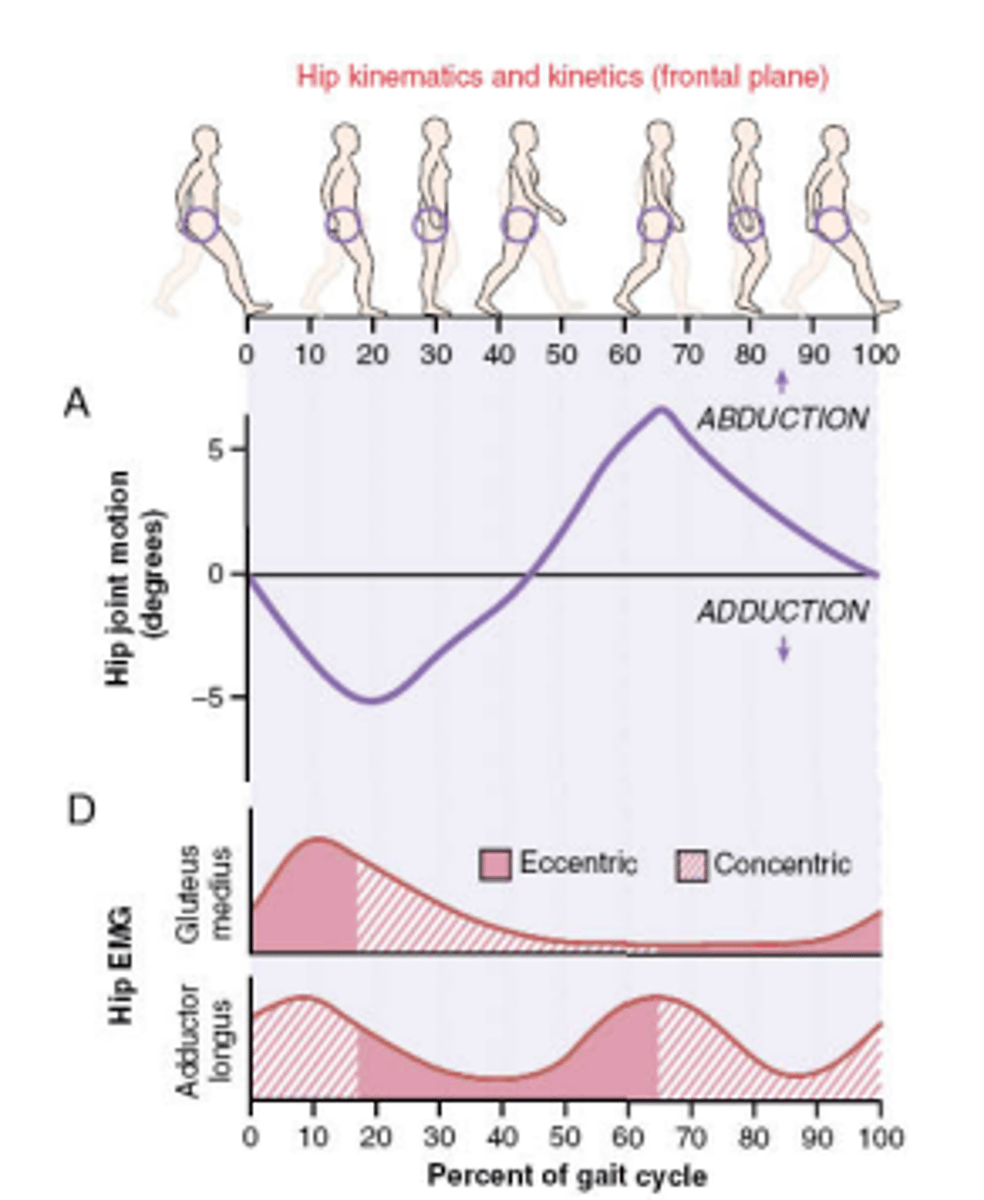
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Hip Adductors
mm: adductor longus/brevis, gracilis, adductor magnus (obturator nm L2-L4)
Early and late stance:
- Concentric ->stabilize pelvis
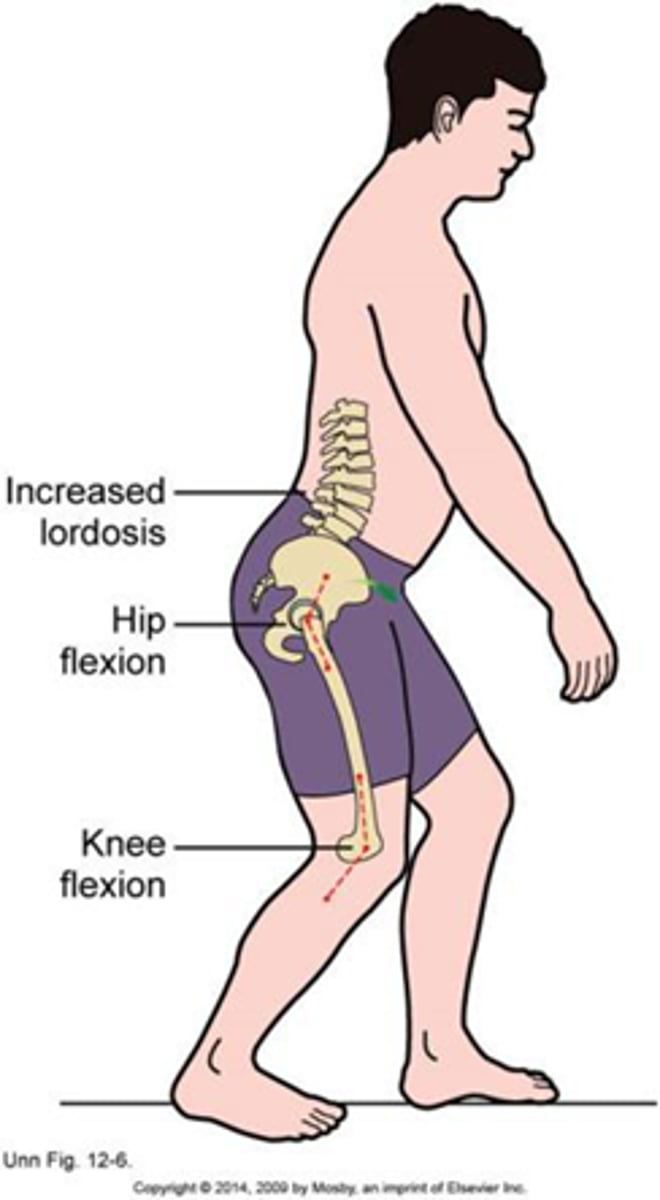
Contractures will ____________ (decrease/increase) ROM of the ___________ (opposite/same) motion in gait
Contractures will decreaseROM of the opposite motion in gait
Example: Hip flexion contracture will lead to decreased hip extension and decreased step length on the OPPosite side
Weakness will ____________ (decrease/increase) ROM of the ___________ (opposite/same) motion in gait
Weakness will decrease ROM of the same motion in gait
Example: Weakness of hip flexors will cause decreased hip flexion and decrease step length on the same side
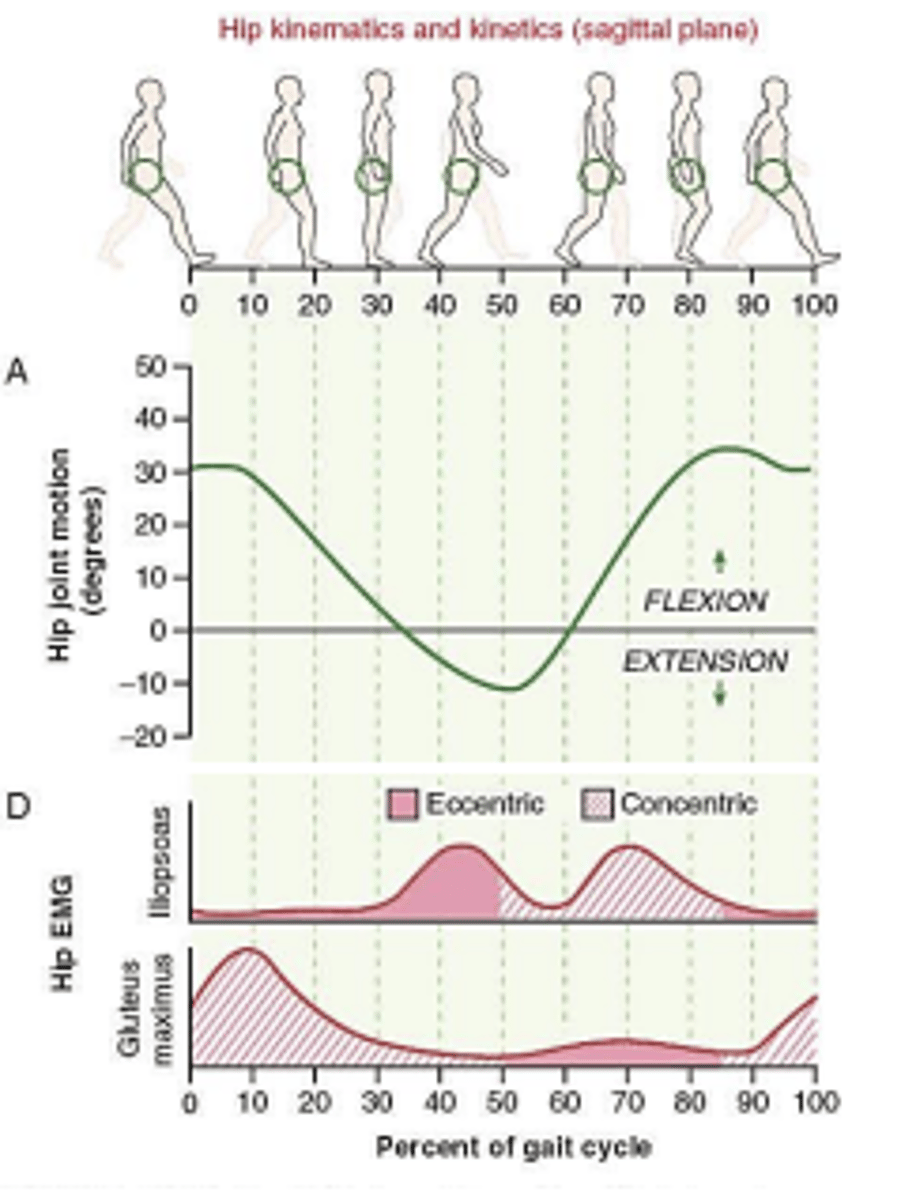
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Glute max
(inferior gluteal nn. L5-S2)
Stance Phase:
-eccentric -> decelerate forward momentum
Pre-swing phase:
-concentric -> hip extension
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Erector Spinae
Heel strike through toe-off:
-maintain trunk posture
Causes for backward trunk lean
Stance Phase:
-Weak hip extensors
-Hip flexion rigid contracture
Swing:
-hip flexor weakness (lean back to fling leg forward and get further)
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Peroneus longus and brevis
(Superficial Peroneal nn L4-S2)
Stance phase:
-concentric -> maintain medial/lateral stability of foot
Muscle activity in gait cycle: Foot intrinsics
(Tibial nn L4-S3)
Stance phase:
-Concentric -> support plantar fascia
Inadequate hip extension caused by
hip flexion contracture = decreased step length on opp side, (+) thomas test and anterior pelvic tilt
Excessive knee extension (hyperextension) is caused by:
-Quad weakness
-Excessive ankle PF: causes shortened stride length and reduced velocity
Substitutions:
1) premature heel of
2) knee hyperextension
3) forward trunk lean
Vaulting is caused by
-leg length discrepancy
-CL prosthesis is too long
-CL foot stuck in PF
Delayed heel of is caused by
-Weak PF
-Excessive DF mobility
-Tibial nerve palsy (loss of PF)
-Anterior foot pain
Early heel off is caused by
-Limited posterior talocrural capsular mobility
-Tight or spastic PF
-Heel pain
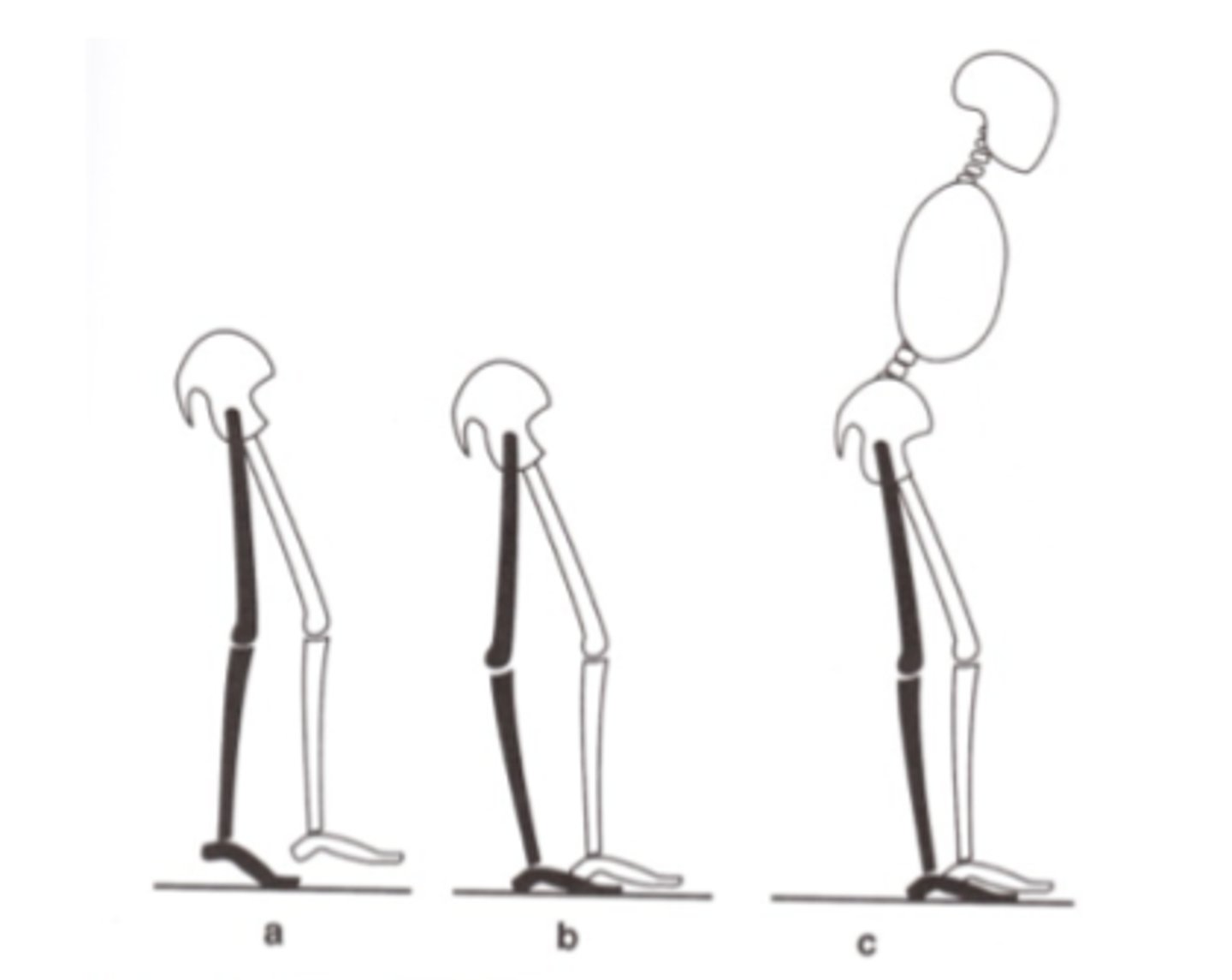
Forward trunk lean caused by
-Weak quadriceps