Unit 2 AP MARCO
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:13 PM on 2/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
When was Macroeconomics created?
**The field of macroeconomics was born during the** __**Great Depression**__**.**
2
New cards
Why study the whole economy?
1. **Measure the health of the whole economy.**
2. **Guide government policies to fix problems.**
3
New cards
What are all countries’ three major economic goals?
1. **Promote Economic Growth**
2. **Limit Unemployment**
3. **Keep Prices Stable (Limit Inflation)**
4
New cards
**What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?**
**GDP is the dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders in one year.**
5
New cards
**What is One Year-GDP?**
**Measures annual economic performance.**
6
New cards
**What are Final Goods?**
**GDP does not include the value of intermediate goods. Intermediate goods are goods used in the production of final goods and services.**
7
New cards
**What is Dollar value?**
**GDP is measured in dollars.**
8
New cards
**Intermediate Goods**
No Multiple Counting, Only Final Goods
9
New cards
What are examples of **Intermediate Goods?**
**Price of finished car, not the radio, tire, etc.**
10
New cards
What are **Nonproduction Transactions?**
**Financial Transactions (nothing produced)**
**Used Goods**
**Used Goods**
11
New cards
What is an example of Used Goods?
**Old cars, used clothes**
12
New cards
What is an example of Financial Transactions?
**Stocks, bonds, Real estate**
13
New cards
What is an example of **Non-Market (Illegal) Activities?**
**Illegal drugs, unpaid work, babysitting (literally anything that you are paid in cash that the IRS does not tax)**
14
New cards
Name Two Ways of calculating GDP:
\-Expenditures Approach
\-Income Approach
(Both ways generate the same amount since every dollar spent is a dollar of income.)
\-Income Approach
(Both ways generate the same amount since every dollar spent is a dollar of income.)
15
New cards
Expenditures Approach
Add up all the spending on final goods and services produced in a given year.
16
New cards
Income Approach
Add up all the income that resulted from selling all final goods and services produced in a given year.
17
New cards
What are **Investments?**
**When** __**businesses**__ **put money back into their own business.**
18
New cards
What is an example of **Government Spending?**
**Bombs or tanks,** ***NOT social security***
19
New cards
**How do you calculate Net Exports?**
**Exports (*****X*****) – Imports (*****M*****)**
20
New cards
Who calculates national income and product accounts?
Bureau of Economic Analysis, a division of the U.S. government’s Department of Commerce.
21
New cards
What is National income?
tracks the spending of consumers, sales of producers, business investment spending, government purchases, and a variety of other flows of money among different sectors of the economy.
22
New cards
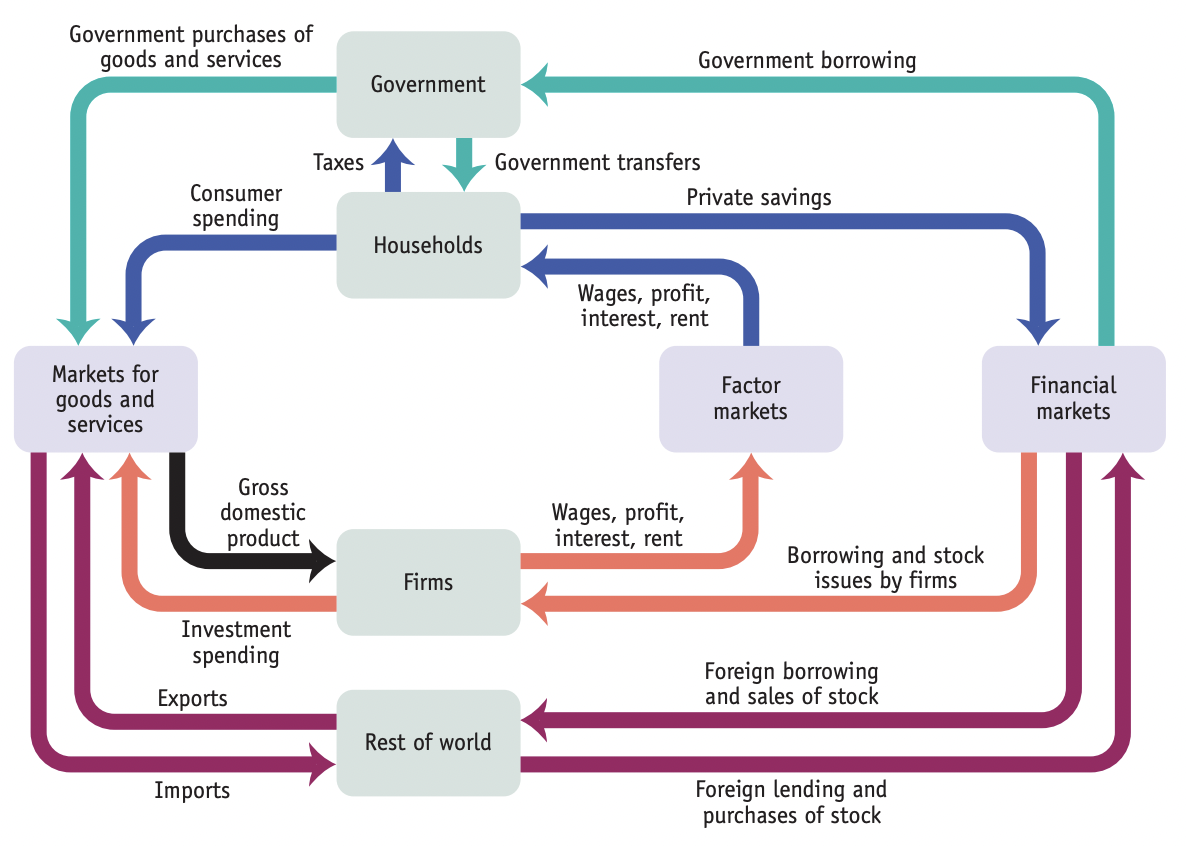
What diagram is this?
Expanded Circular-Flow Diagram
23
New cards
What is a household?
a person or group of people who share income.
24
New cards
What is a Firm?
is an organization that produces goods and services for sale.
25
New cards
What is Product markets?
are where goods and services are bought and sold.
26
New cards
What is Factor markets?
are where resources, especially capital and labor, are bought and sold.
27
New cards
What is Consumer spending?
is household spending on goods and services.
28
New cards
. So, for example, the total flow of money out of households—the sum of taxes paid, consumer spending, and private savings—must equal the total flow of money into households—the sum of wages, profit, interest, rent, and government transfers.
29
New cards
in what three ways does the world participates in the U.S. economy?
\-First, some of the goods and services produced in the United States are sold to residents of other countries.
\-Second, some of the goods and services purchased by residents of the United States are produced abroad.
\-Third, foreigners can participate in U.S. financial markets. Conversely, foreign borrowing—borrowing by foreigners from U.S. lenders and purchases by Americans of stock in foreign companies—leads to a flow of funds out of the United States to the rest of the world.
\-Second, some of the goods and services purchased by residents of the United States are produced abroad.
\-Third, foreigners can participate in U.S. financial markets. Conversely, foreign borrowing—borrowing by foreigners from U.S. lenders and purchases by Americans of stock in foreign companies—leads to a flow of funds out of the United States to the rest of the world.
30
New cards
What is Real GDP?
**is GDP expressed in constant, or unchanging, dollars.**
31
New cards
What is Nominal GDP?
**is GDP measured in current prices. It does not account for inflation from year to year.**
32
New cards
**What is Inflation?**
**A rising general level of prices.**
33
New cards
**What is Real GDP per capita?**
**is real GDP divided by the total population. It identifies on average how many products each person makes.**
34
New cards
What is the **best way to measure a nation’s standard of living?**
**Real GDP per capita**
35
New cards
What affects Productivity?
1. Technology
2. Economic System
3. Capital
4. Human Capital (Knowledge)
5. Natural Resources
36
New cards
How do you calculate **The Unemployment rate?**
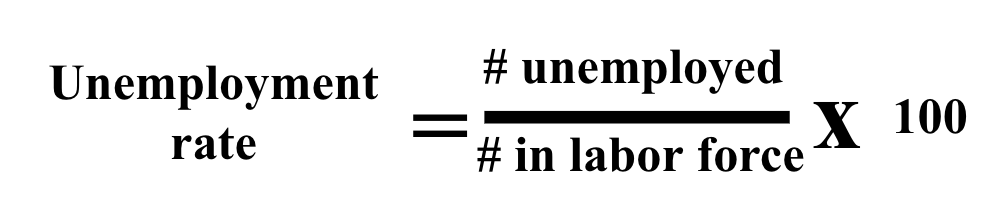
37
New cards
**Who is in the Labor Force?**
* **Above 16 years old**
* __**Able**__ **and** __**willing**__ **to work**
* **Not institutionalized (jails, hospitals)**
* **Not in military, in school full time, or retired**
* __**Able**__ **and** __**willing**__ **to work**
* **Not institutionalized (jails, hospitals)**
* **Not in military, in school full time, or retired**
38
New cards
**Why is a stay at home mom/dad not unemployed?**
**Cause they aren’t actively looking for a job.**
39
New cards
What is **Frictional Unemployment?**
**“Temporarily unemployed” or being between jobs.**
**Individuals are qualified workers with transferable skills but they aren’t working.**
**Individuals are qualified workers with transferable skills but they aren’t working.**
40
New cards
What is **Structural Unemployment?**
**Changes in the structure of the labor force make some skills obsolete.**
**Workers** __**DO NOT**__ **have transferable skills and these jobs will never come back.**
**Workers** __**DO NOT**__ **have transferable skills and these jobs will never come back.**
41
New cards
**What is Seasonal Unemployment?**
**This is a specific type of frictional unemployment which is due to time of year and the nature of the job.**
42
New cards
What is **Technological Unemployment?**
**Type of structural unemployment where automation and machinery replace workers causing unemployment**
43
New cards
**Cyclical Unemployment**
**Unemployment that results from economic downturns (recessions).**
**As demand for goods and services falls, demand for labor falls and workers are fired.**
**As demand for goods and services falls, demand for labor falls and workers are fired.**
44
New cards
**What are the Two ree types of unemployment that are unavoidable?**
**Frictional unemployment**
**Structural unemployment**
**Structural unemployment**
45
New cards
**What makes up the natural rate of unemployment?**
**Frictional unemployment**
**Structural unemployment**
**Structural unemployment**
46
New cards
What is “normal” unemployment?
**The number of jobs seekers equals the number of jobs vacancies.**
47
New cards
What is the “normal” unemployment rate?
**4-6% Unemployment = Full Employment**
48
New cards
**What is wrong with the unemployment rate?**
**It can misdiagnose the actual unemployment rate because of the following:**
**-Disgruntled job seekers**
**-Part-Time Workers**
**-Race/Age Inequalities**
**-Illegal Labor**
**-Disgruntled job seekers**
**-Part-Time Workers**
**-Race/Age Inequalities**
**-Illegal Labor**
49
New cards
what is **“market basket”?**
**is made up of about 300 commonly purchased goods**
50
New cards
**What is The Inflation Rate?**
**% change in prices in 1 year**
**They also compare changes in prices to a given base year (usually 1982)**
**They also compare changes in prices to a given base year (usually 1982)**