Rehab Essentials Part 16: Cancer Chemotherapy
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What is the goal of cancer chemotherapy?
Selective toxicity of neoplastic cells
What are primary methods of cancer chemotherapy? (2)
1. Disrupt DNA/RNA function
2. Inhibit mitosis and initiate cell death
What are the functional drug groups for chemotherapy?
1. Direct effect on DNA
2. Direct effect on mitosis
3. Hormones
4. Targeted therapies
5. Immunothearpies
6. Miscellaneous
What are drugs that affects DNA synthesis and function?
1. Alkylating agents
2. Antitumor antibiotics
3. Platinum drugs
4. Topoisomerase inhibitors
5. Antimetabolites
What do alkylating agents do?
1. Bind strongly to DNA bases
2. Form cross-link within/between DNA strands
What does alkylating agents forming cross-links between DNA strands ultimately do?
1. Prevent DNA replication/translation
2. Cause breaks in DNA chain
What are examples of alkylating agents?
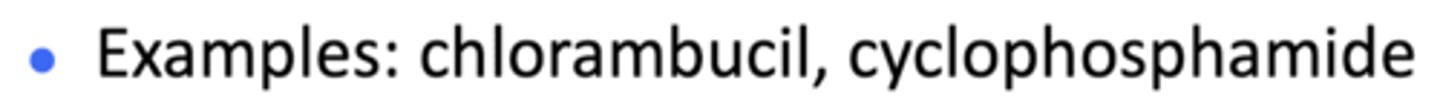
What are antitumor antibiotics?
Antibacterials that are reserves for cancer because of toxicitiy
What do antitumor antibiotics do as they are inserted into DNA strand?
1. Inhibit transcription
2. Cause breaks in DNA chain
What are examples of antitumor antibiotics?

What are platinum coordination complexes?
Drugs that contain platinum and form strong cross-links in DNA, inhibiting replicatoin
What are examples of platinum coordination complexes?
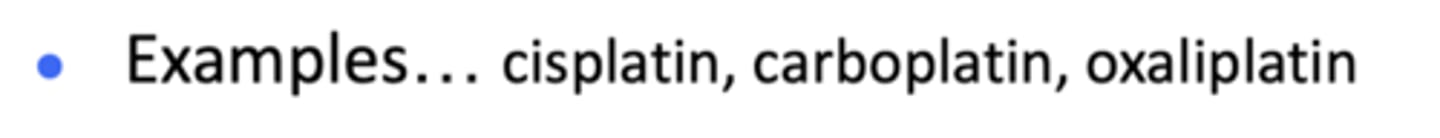
What is topoisomerase?
Key enzymes needed for DNA replicaiton
What are topoisomerase inhibitors?
Drugs that inhibit the enzyme, causing breaks in DNA chain
What are the two types of topoisomerase inhibitors?
Type I
Type II

What do antimetabolites do?
Act on pathways for DNA synthesis to impair DNA synthesis
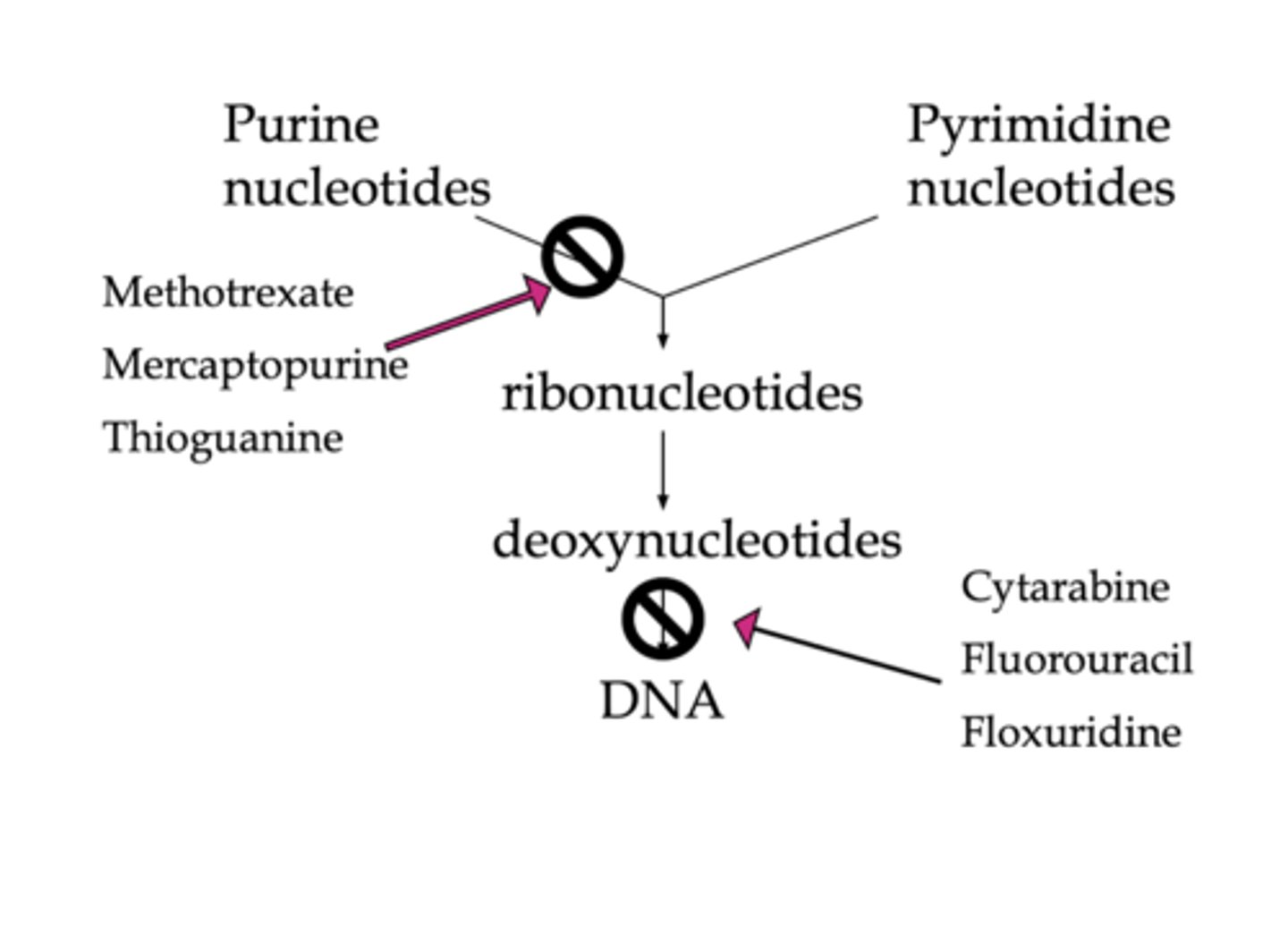
How do antimetabolites impair DNA synthesis?
1. Inhibit enzymes
2. Act as bogus ingredients
What are examples of antimetabolites?

How do anti-cancer drugs directly effect DNA synthesis and function?
1. By binding strongly to DNA
2. INhibiting DNA enzymes
3. Inhibiting steps in DNA/RNA synthesis
What drugs bind strongly to DNA? (3)
1. Alkylating agents
2. Antitumor antibiotics
3. Platinum drugs
What drugs inhibit DNA enzymes?
Topoisomerase inhibitors
What drugs inhibit steps in DNA/RNA synthesis?
Antimetabolites
What do drugs affecting DNA synthesis/function cause?
Severe/toxic side effects because they do not discriminate between cancer cells and healthy cells
What are drugs that directly inhibit mitosis?
Antimicrotubule agents
What are microtubules?
Located in mitotic apparatus, and must function properly during cell division
What can certain drugs affect?
Microtubules, impairing cell division
What are the types of antimicrotubule agents?
1. Vinka alkaloids
2. TAxanes
What do vinka alkaloids do?
Inhibit formation of microtubules
What do taxanes do?
Inhibit breakdown of microtubules
What are examples of vinka alkaloids?

What are examples of taxanes?

What do anticancer hormones act on?
Hormone-sensitive cancers
What are anticancer hormones used to do?
1. Inhibit production of a hormone
2. Block or reduce effects of a hormone
3. Inhibit cell growth or induce growth in certain cells
What drugs inhibit production of a hormone?
Aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer
What drugs block or reduce effects of a hormone?
Androgen receptor blockers in prostate cancer
What drugs inhibit cell growth or induce death in certain cells?
Prednisone in leukemia, lymphoma
Why do conventional anticancer drugs often cause severe side effects?
Most of these drugs do not discriminate between healthy tissues and cancerous cells
What do conventional anti-cancer drugs do?
Decrease mitosis in cancer and healthy cells
What do targeted therapies do?
Focus on a specific abnormal trait in the cancer cell that is not present in healthy cells
What are primary targeted therapies?
1. Monoclonal antibodies
2. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
What are monoclonal antibodies (MABs) derived from?
Cell cloning techniques used to manufacture antibodies that bind to a specific antigen on tumor cells..."targeting" effect
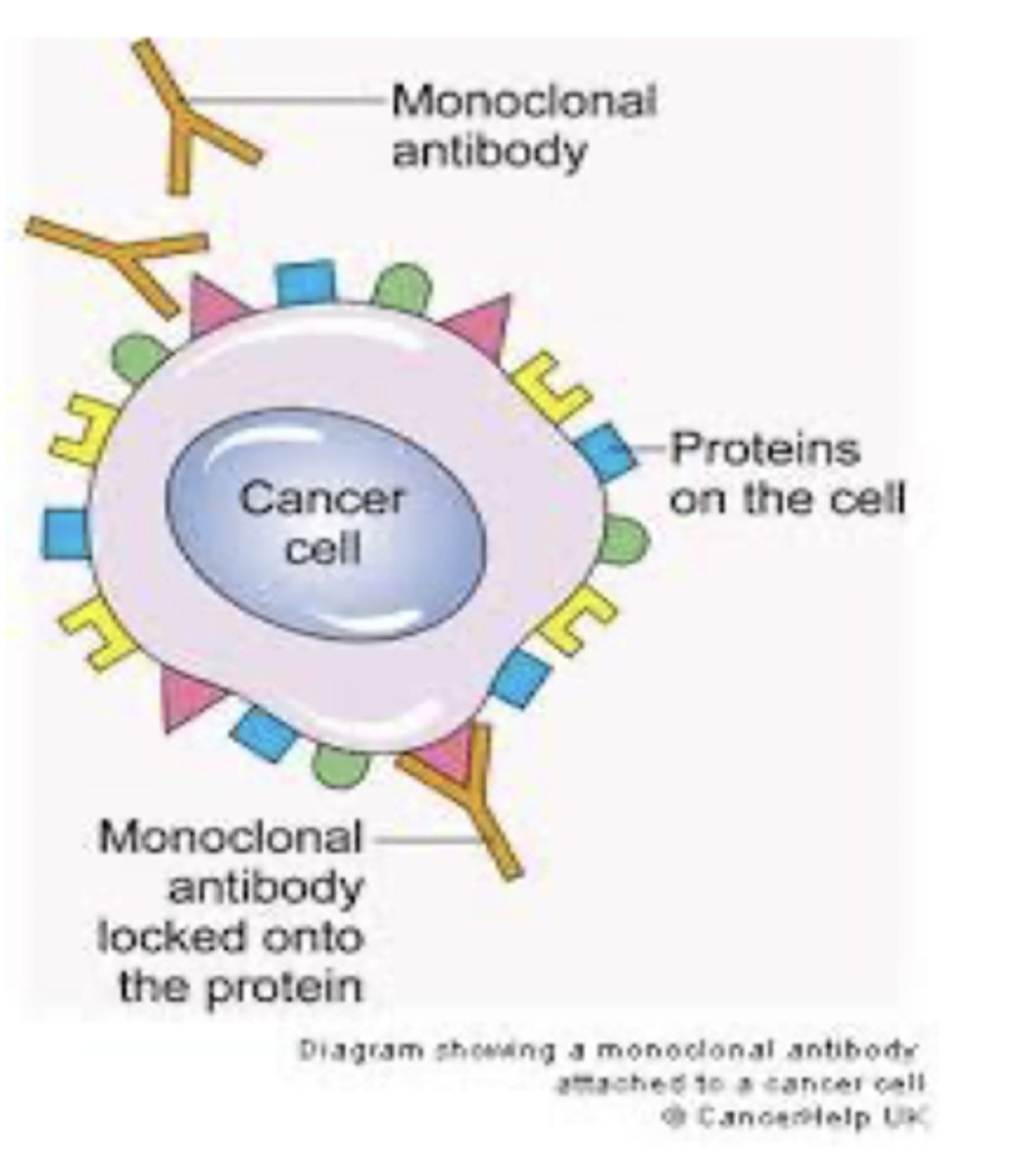
Can MABs have direct effect on cancer cells?
Yes
What can MABs do after binding to an antigen?
1. Block signaling pathways that cause mitosis
2. Initiate programmed cell death (apoptosis)
3. Inhibit angiogenesis
What are examples of MABs for specific cancers?

What is tyrosine kinase?
Receptor/enzyme on cell surface that signals the cell to divide
What happens to tyrosine kinase in cancer cells?
Malfunctioning or too many of them; or causing them to divide too much
What do certain cancers have?
Abnormal tyrosine kinases (ex. HER2, ErbB-1)
What does activiation of these abnormal tyrosine kinases cause?
Uncontrolled cell proliferation
What do tyrosine kinase inhibitors do? (2)
1. Bind to tyrosine kinase site, inhibiting receptor activation
2. Prevents receptor from initiating signals that cause cell division
What are examples of tyrosine kinase inhibitors?

What do drugs that impair microtubule function do?
Directly inhibit mitosis
What are specific hormones used in?
Hormone sensitive cancers to decrease cell proliferation
What do targeted treatments allow?
Anti-cancer drug to more selectively affect cancer cells with fewer toxic effects on healthy cells
What do immunotherapies encourage?
Body's immune system to deal with cancer system (aka. biological therapies)
What are examples of immunotherapies?
1. Cytokines
2. MABs
3. Others
What are cytokines?
Small proteins that plan an important role in immune responses
What are the two primary strategies of cytokines?
1. Interferons (INF alpha 2b)
2. Interleukins (IL-2)
What are the effects of cytokines?
1. Directly activate pathways that inhibit cell division, promote cell death
2. Encourage cytotoxic immune cells (T lymph, NK cells) to attack cancer cells
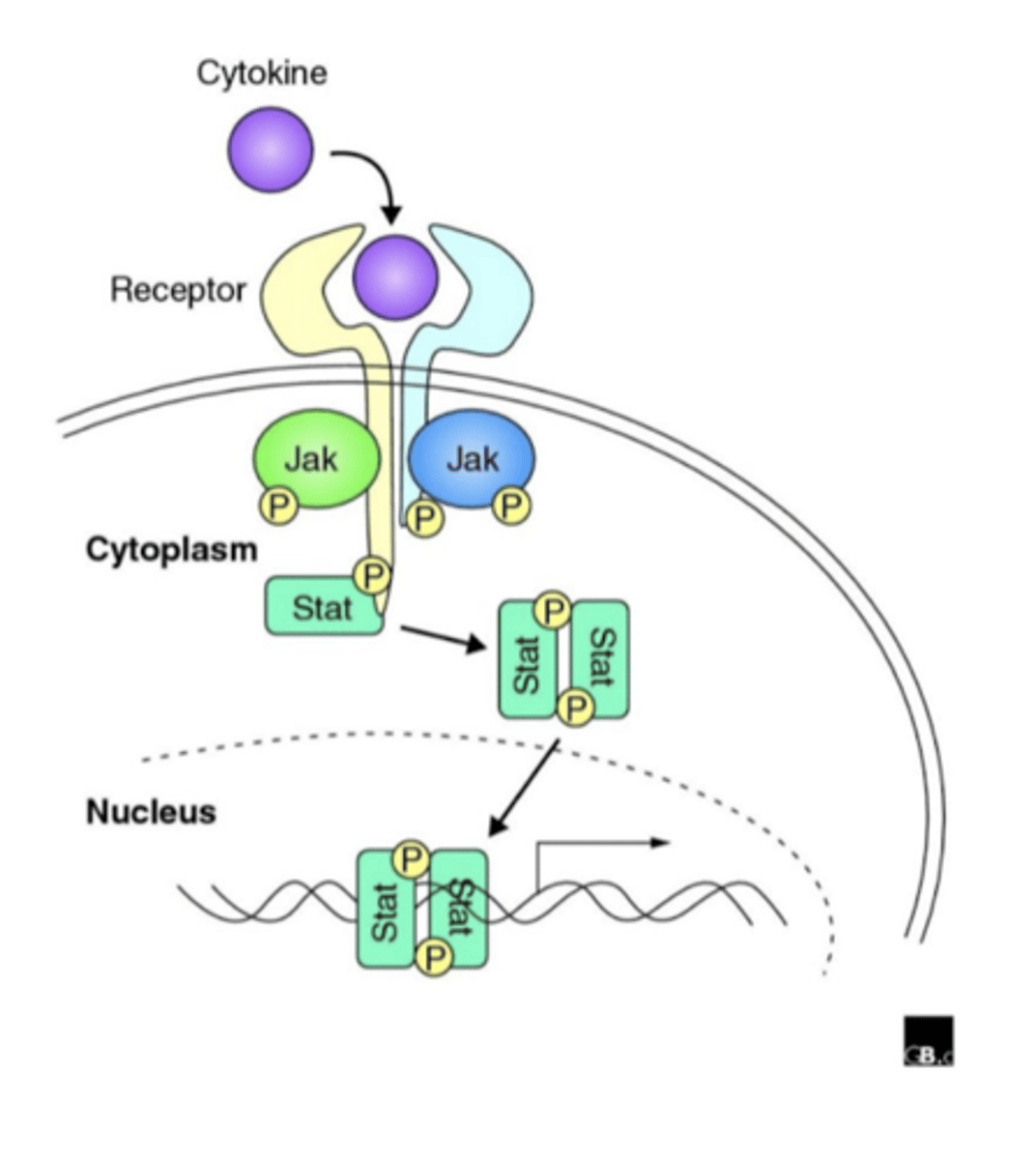
What do some MABs do?
Sensitize cancer cell to attack from T lymphocytes
What do some other monoclonal antibodies do?
They inhibit proteins that are suppressing the immune cells that normally attack cancer "checkpoint inhibitors"; different than targeted therapies
What are some examples of other immunotherapies?
1. Anticancer vaccines (HPV, Hep B)
2. Adoptive cell transfer (grow pt's T cells in lab, reinsert into patient)
3. Modify and engineer T cells to attack specific cancers (could get really sick)
What do some miscellaneous agents do?
Generally disrupt DNA structure or cancer cell metabolism
What does asparaginase do?
Deprive tumor cells of asparagine
What do histone deacetylase inhibitors do?
Affect proteins that package DNA in a cell
What do retinoids do?
Enhance cell differentiation
What is the combination of chemotherapy agents ABVD used for?
Hodgkin lymphoma

What is the combination of chemotherapy agents CMF used for?
Early stage breast cancer

What is the combination of chemotherapy agents FOLFOX used for?
Colorectal cancer

What are side effects of chemotherapy?
1. Hair loss
2. GI problems
3. Anemia
4. Fatigue
5. Neurotoxicity
6. Cardiotoxicity
7. Skin rashes
8. Others
What are side effects of chemotherapy caused by?
Inhibiting cell replication
What have newer targeted therapies caused?
Less side effects
What are some rehab concerns for those in cancer treatment/
1. Pain support, help manage pain
2. Exercise
How does exercise play a role in cancer treatment?
Exercise should occur before, during, after chemo to increase strength, ROM, CV function as indicated/tolerated
What is the overall success of cancer chemotherapy?
Decreased cancer mortality over last 30 years
What are some current issues with cancer therapy? (2)
1. Success is limited in certain cancers (lung, pancreatic)
2. Drug resistance
What are some future perspectives of cancer therapy? (4)
1. More, better targeted therapies
2. More vaccines
3. Drugs that protect healthy cells from chemo drugs
4. Personalized oncology
What is personalized oncology?
Tailoring treatment based on characteristics of tumor in each individual
What remains one of the best anti-cancer strategies?
Prevention
What are some strategies that can help prevent cancer?
1. Regular exercise
2. Quit smoking
3. Eat a low-fat, high fiber diet
4. Use sunscreen, and avoid excessive UV exposure
5. Early detection regular screens
What do certain anti-cancer drugs to?
Activate or mimic the immune system's ability to find and kill cancer cells
What role should PTs have in cancer treatment?
Make their patients aware of ways to prevent cancer, and screening techniques that should be used for early detection of cancer