4.1.7(Antibodies)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Describe what antibodies are and their role
They are proteins or glycoproteins found on the surface of cells that stimulate an immune response
They are specific to each antigen and are produced when foreign antigens are detected by the immune system
Their is to bind onto antigens to form an antigen-antibody complex so the phagocyte or lymphocyte is then able to engulf it
State what antigens are also known as
they are known as immunoglobulins
Describe the structure of antibodies
They are a Y-shaped molecule that consists of 4 polypeptide chains
2 identical light polypeptide chains
2 Identical heavy polypeptide chains
The polypeptide chains are held by disulphide bridges
Each polypeptide chain is a tertiary structure that consists of distinct domains - variable region and constant region
They have a hinge region that contains disulphide bridges which gives flexibility so the molecule is able to bind with more than one antigen
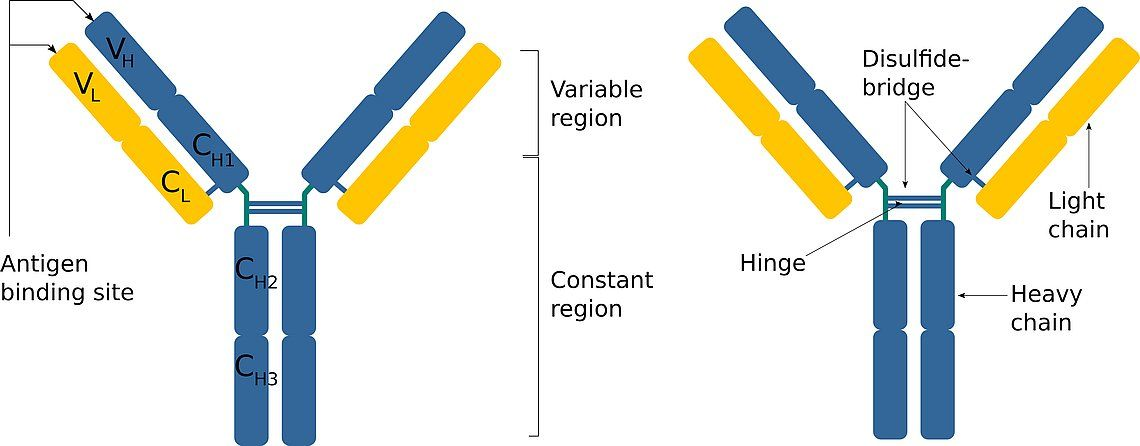
Describe what distinct and variable regions are
Variable regions are parts on antibodies which have a shape specific to the shape of the antigen
Constant regions are parts on antibodies which are the same in all antibodies- it may have a site for easy binding of phagocytic cells
Describe and explain how antibodies are specific
The variable region of the polypeptide chains have a different amino acid sequence for every antibody
This creates a different tertiary structure for the binding site on each antibody
This means that only one antibody will be able to bind to a specific antigen
Each antibody is complementary to each antigen
State the 3 types of antibody
Opsonins
Agglutinins
Anti-toxins
State where opsonins and phagocytes bind to pathogens
Opsonins bind to the pathogens at the variable region
Phagocytes bind to pathogens at the constant region
Describe and explain the role of opsonins
opsonins are protein markers that bind to the antigens on the plasma membrane on a pathogen once detected as a foreign antigen and aid phagocytosis.
They do this by acting as binding sites for phagocytic cells, so that these phagocytes can more easily bind and kill the pathogen
Describe the process of neutralisation using opsonins
Pathogens may use their antigen molecules as a binding site used for attachment to a host cell
The opsonin in this case binds to the specific antigen and stops the antigen from binding to the host cell
This stops pathogens from entering a host cell
Describe and explain the role of agglutinins
Each antibody can bind to 2 different antigens at the same time as theyhave 2 identical binding sites, they are able to use this to for crosslinks by bindning an antigen of one pathogen with one binding site and then an antigen on another pathogen with its other binding site
When this process is repeated many times, crosslinks clump pathogens together which is called Agglutination
State the 2 advantages of agglutination
The agglutinated pathogens are immobilised so they can no longer enter host cells
Agglutinated pathogens are readily and easily engulfed by phagocytes
Describe and explain the role of antitoxins
They bind to toxic molecules which are released by pathogens
Antitoxins undergo neutralisation as well and bind to toxins which stops toxins from binding to pathogens
Describe and explain what happens during primary and secondary responses
Primary response:
The primary response is the first response when the pathogen enters the host for the first time
Its slow and it takes a few takes for the number of antibodies in the blood to rise to a level that can combat the infection successfully, this is due to the lack of B cells that make the specific antibody needed to bind to foreign antigen
Once the pathogen has been removed, the number of antibodies drops quickly but B memory cells stay in the body
Secondary response:
The secondary response is anytime after the first time a new pathogen has entered the host
Its much quicker and much more effective. This is due to B and T memory cells that remained in the blood after the primary response:
B memory cell: Quickly divide to form plasma cells which secrete the correct Ab to the antigen
T memory cells: Quickly divide into the right type of T-cells to kill cells carrying the pathogen
These can recognise the foreign antigen and can stimulate a much quicker immune response
This causes a rapid rise in concentration of specific antibodies in the blood