9 - Hypothesis Testing
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering vocabulary from a week 10 revision lecture, focusing on hypothesis testing and related concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
HATPC
A framework for hypothesis testing involving hypotheses, assumptions, test statistic calculation, p-value determination, and conclusion.
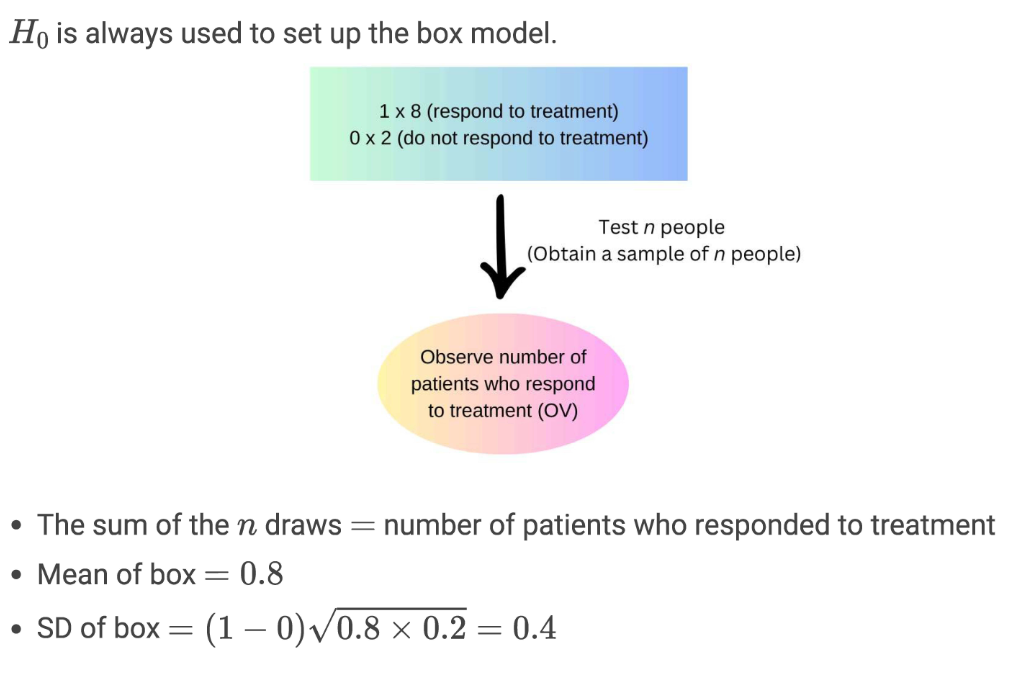
Null Hypothesis
A statement that postulates a single value, usually with an equal sign, and serves as the basis for the box model in hypothesis testing.
Assumes difference between observed value (data) and expected value (EV) is due to chance alone.
Alternative Hypothesis
A range of values that contradicts the null hypothesis, often involving inequalities like less than or greater than.
Assumes difference between observed value (data) and the expected value (EV) is not due to chance alone.
Two-Sided Alternative
An alternative hypothesis that considers both directions (greater or less) from a central value.
Assumptions in Hypothesis Testing
Underlying requirements of a model that must be stated and justified, without which the tests and results may be invalid.
P-Value Method
Retaining or rejecting the null hypothesis, given if there is data consistent with H0 or there is evidence against H0.
Significance Level
The cutoff point (e.g., 0.05) used to determine statistical significance, though it's more of a convention and can vary by context.
Test Statistic Formula
Observed Value – Expected Value divided by Standard Error.
Box Model