Principles of Chemistry I - Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:13 PM on 9/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
B
Arrange from shortest to longest
A) Single bonds, double bonds, triple bonds
B) Triple bonds, double bonds, single bonds
C) None of the above
A) Single bonds, double bonds, triple bonds
B) Triple bonds, double bonds, single bonds
C) None of the above
2
New cards
A
Bond strength is __________ proportional to the number of bonding electrons between two atoms.
A) Directly
B) Indirectly
C) Not
D) All of the above
A) Directly
B) Indirectly
C) Not
D) All of the above
3
New cards
Electronegativity
A measure of the decrease in the energy of a system if bonding electrons are localized in the vicinity of a given type of atom.
4
New cards
Electronegativity
A measure of the probability of finding the electrons in a bond localized in the vicinity of that atom.
5
New cards
x
Symbol for electronegativity
6
New cards
Radical (or Free Radical)
A very reactive atom with one unpaired electron.
7
New cards
A
E Pair Geometry: 2 electron domains
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal pyramidal
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal pyramidal
8
New cards
B
E Pair Geometry: 3 electron domains
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal pyramidal
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal pyramidal
9
New cards
C
E Pair Geometry: 4 electron domains
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal bipyramidal
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal bipyramidal
10
New cards
D
E Pair Geometry: 5 electron domains
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal bipyramidal
A) Linear
B) Trigonal Planar
C) Tetrahedral
D) Trigonal bipyramidal
11
New cards
B
Bond angle: bent (one lone pair)
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
12
New cards
E
Bond angle: bent (two lone pairs)
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
13
New cards
C
Bond angle: trigonal planar
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
14
New cards
A
Bond angle: tetrahedral
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
15
New cards
D
Bond angle: linear
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
A) 109.5
B) >120
C) 120
D) 180
E)
16
New cards
Ketone
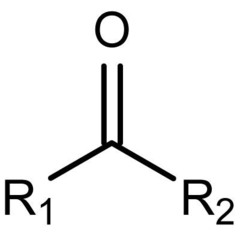
17
New cards
Aldehyde
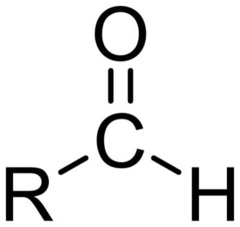
18
New cards
Carboxyl
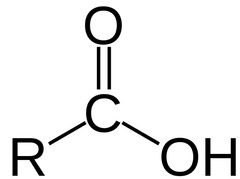
19
New cards
Alkoxy
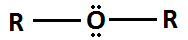
20
New cards
Amine
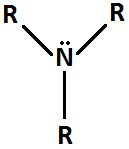
21
New cards
Phenyl
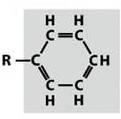
22
New cards
Hydroxyl
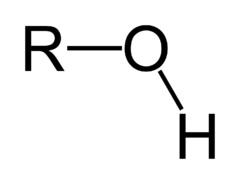
23
New cards
Anything asymmetric (asymmetric stretch, bend vibration, etc)
Vibrations that absorb IR radiation
24
New cards
Anything symmetric
Vibrations that do not absorb IR radiation
25
New cards
Geometry, bond polarity, molecular polarity
What things affect how a molecule interacts with other particles?
26
New cards
Polarizability, molecular polarity, bond polarity
The strength of IMFs depends on....
27
New cards
Polarizability
A measure of how easily an electron cloud is distorted or shifted by an electric field.
28
New cards
More
More electrons and a larger radius means a molecule is (more/less) easily polarizable
29
New cards
B, C
A molecule has a large surface area and more e-. Which is true?
A) Lower polarizability
B) Lower vapor pressure
C) High BP
D) Low BP
A) Lower polarizability
B) Lower vapor pressure
C) High BP
D) Low BP
30
New cards
A
Which intramolecular forces are present in this molecule?
CH4
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Hydrogen bonds
CH4
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Hydrogen bonds
31
New cards
B
Which intermolecular forces are present in this molecule?
HCl and HCl
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Hydrogen bonds
HCl and HCl
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Hydrogen bonds
32
New cards
D
Strongest?
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
33
New cards
A
Weakest?
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
34
New cards
E
Ion with a NP molecule
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
35
New cards
C
NP Molecule with a Polar Molecule
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
36
New cards
A
Same as instant dipole-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
37
New cards
Lower
More "branches" (more circular of a structure) means (higher/lower) IMFs.
38
New cards
E
Lower IMFs mean lower...
A) Melting Points
B) Boiling Points
C) Vaporization Energy
D) Viscosities
E) All of the above
A) Melting Points
B) Boiling Points
C) Vaporization Energy
D) Viscosities
E) All of the above
39
New cards
E
Lower IMFs mean higher...
A) Melting Points
B) Boiling Points
C) Vaporization Energy
D) Viscosities
E) Volatilities
A) Melting Points
B) Boiling Points
C) Vaporization Energy
D) Viscosities
E) Volatilities
40
New cards
B
2 polar molecules
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
41
New cards
D
Ion & a polar molecule
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
A) London Dispersion
B) Dipole-Dipole
C) Dipole-induced dipole
D) Ion-dipole
E) Ion-induced dipole
42
New cards
C
A substance wants to be in the state with the ___________ energy and the __________ # of configurations
A) Highest, highest
B) Highest, lowest
C) Lowest, highest
D) Lowest, lowest
A) Highest, highest
B) Highest, lowest
C) Lowest, highest
D) Lowest, lowest
43
New cards
B
To determine if two substances mix, pick the state with the....
A) Highest energy
B) Highest # configs
C) Lowest energy
D) Lowest # configs
A) Highest energy
B) Highest # configs
C) Lowest energy
D) Lowest # configs