Endo/Repro Exam 1: Adrenal Gland Physiology (Dr. Sun)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
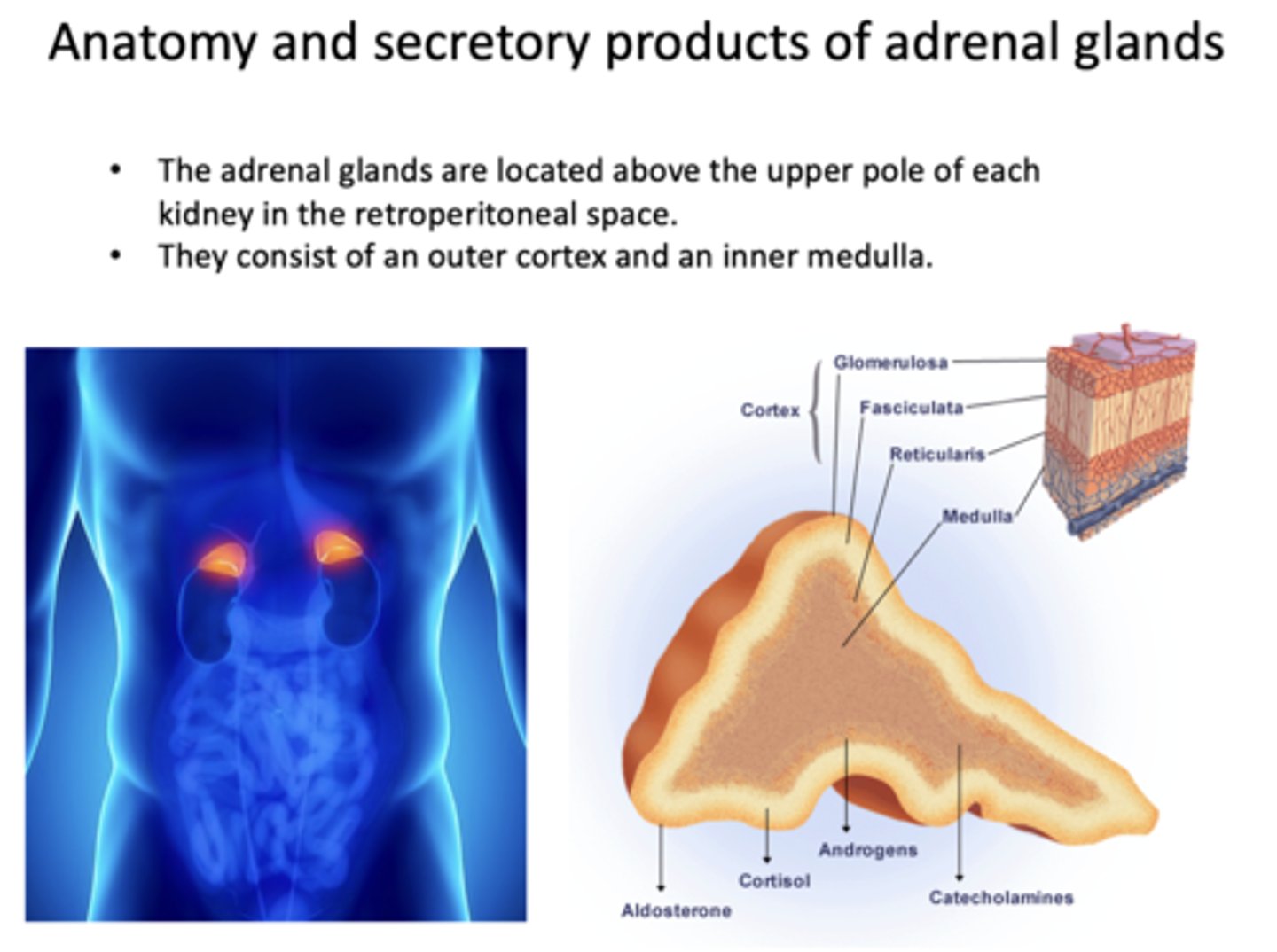
Where are adrenal glands located?
Upper pole of each kidney in the retroperitoneal space
Zona Glomerulosa (ZG) releases what type of hormones?
mineralcorticoids
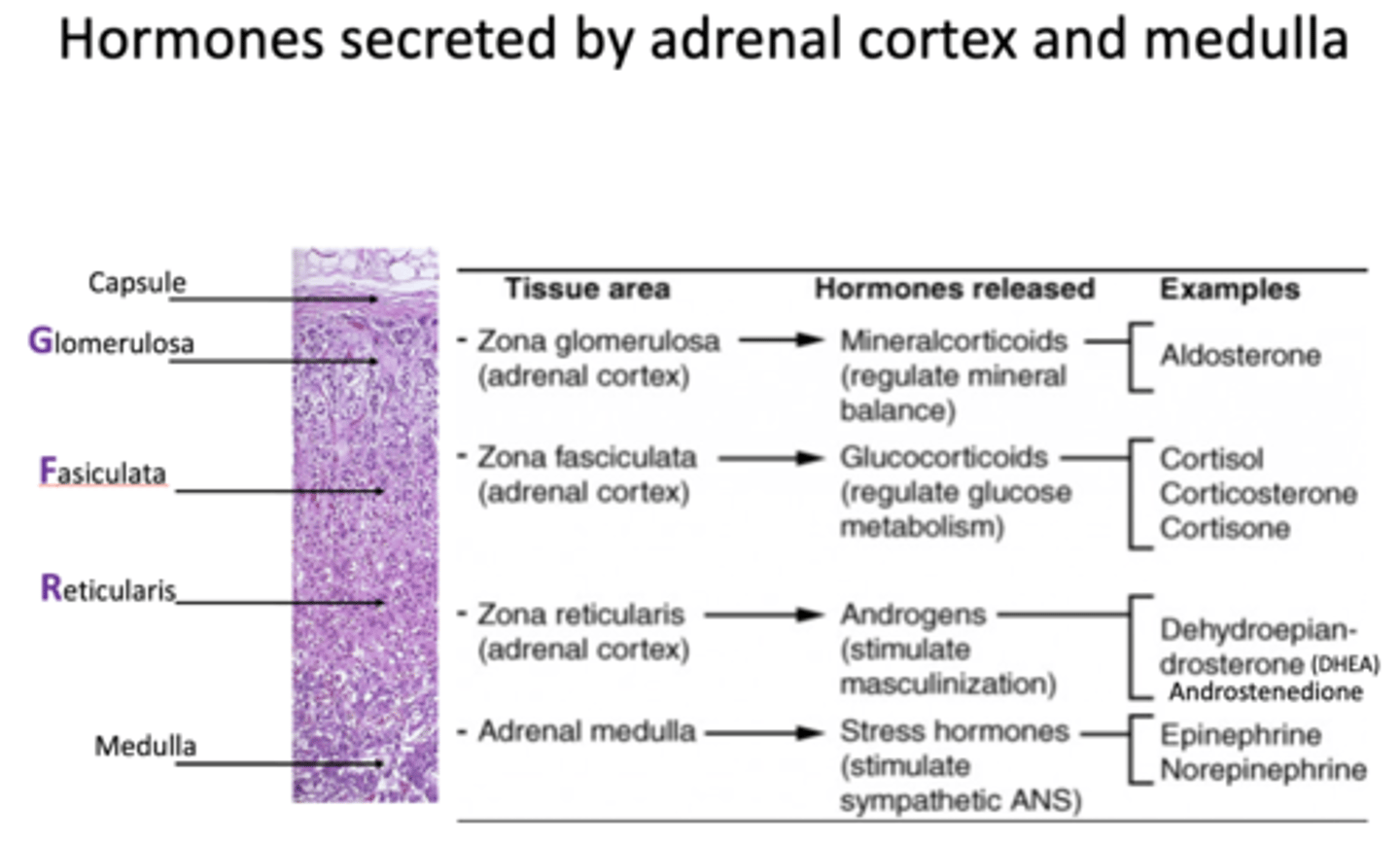
What is an example of a hormone released from Zona Glomerulosa?
Aldosterone (mineralcorticoid)
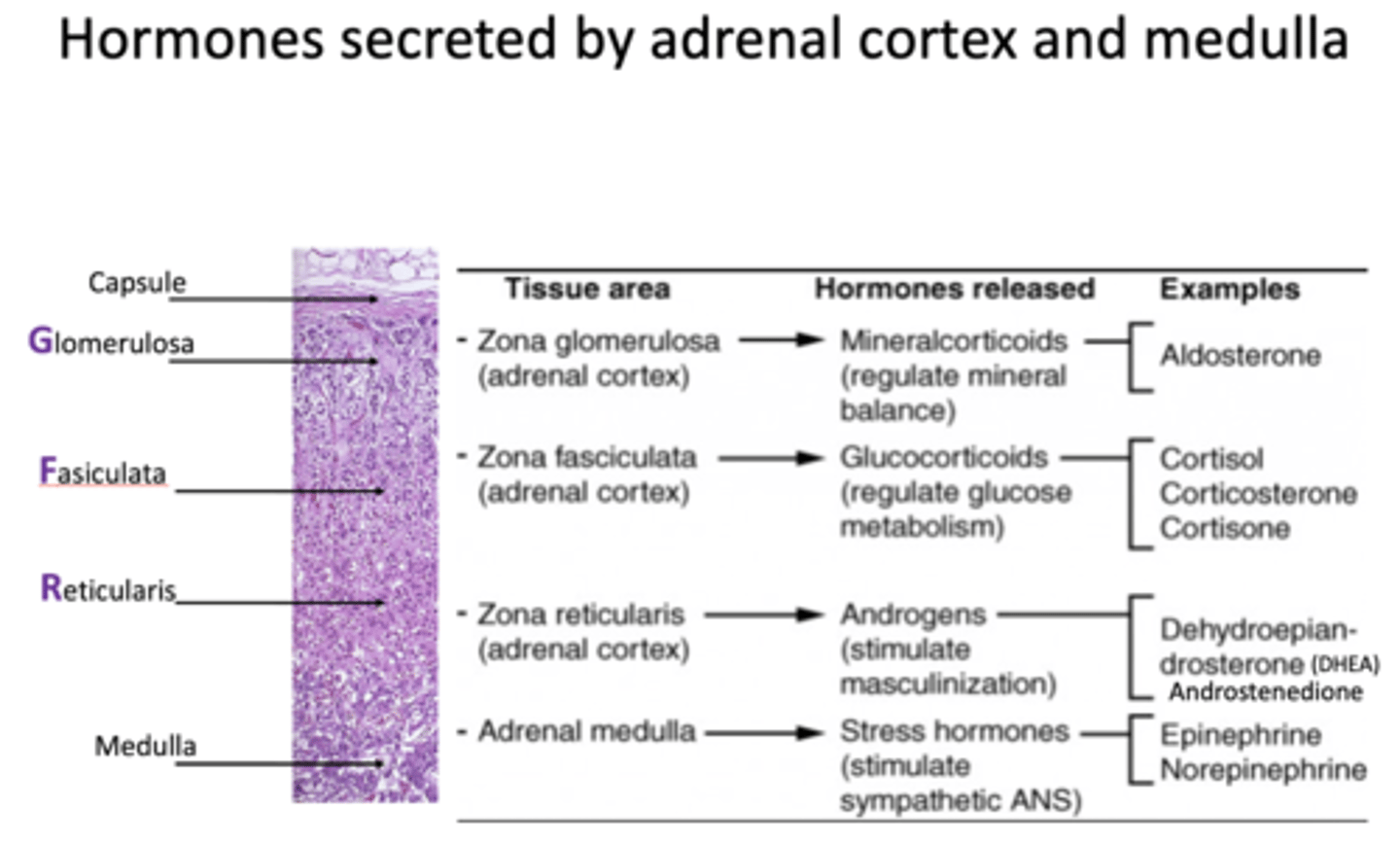
Zona fasciculata (ZF) releases what type of hormones?
glucocorticoids
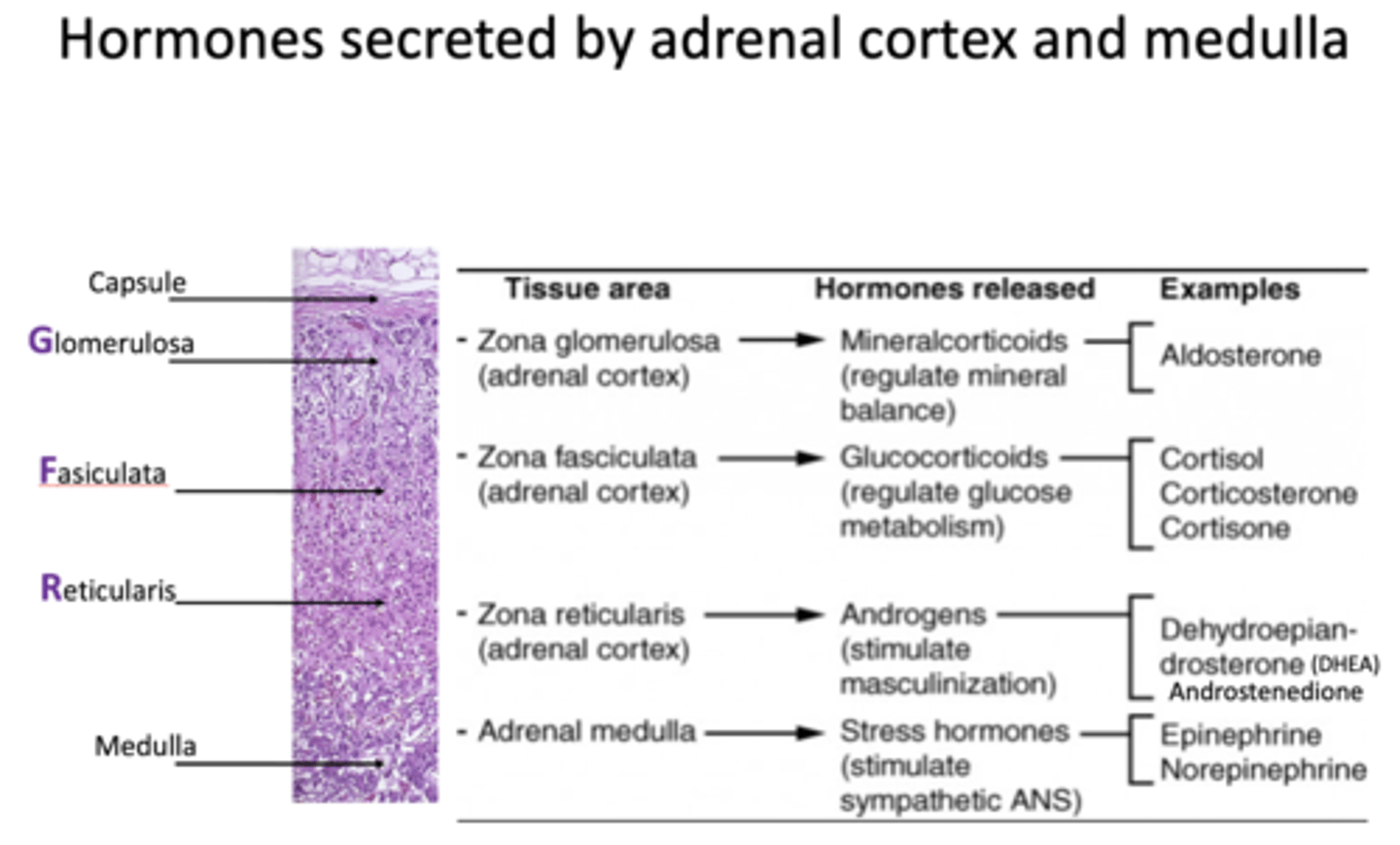
What are examples of hormones released from Zona fasciculata?
- Cortisol
- Corticosterone
- Cortisone
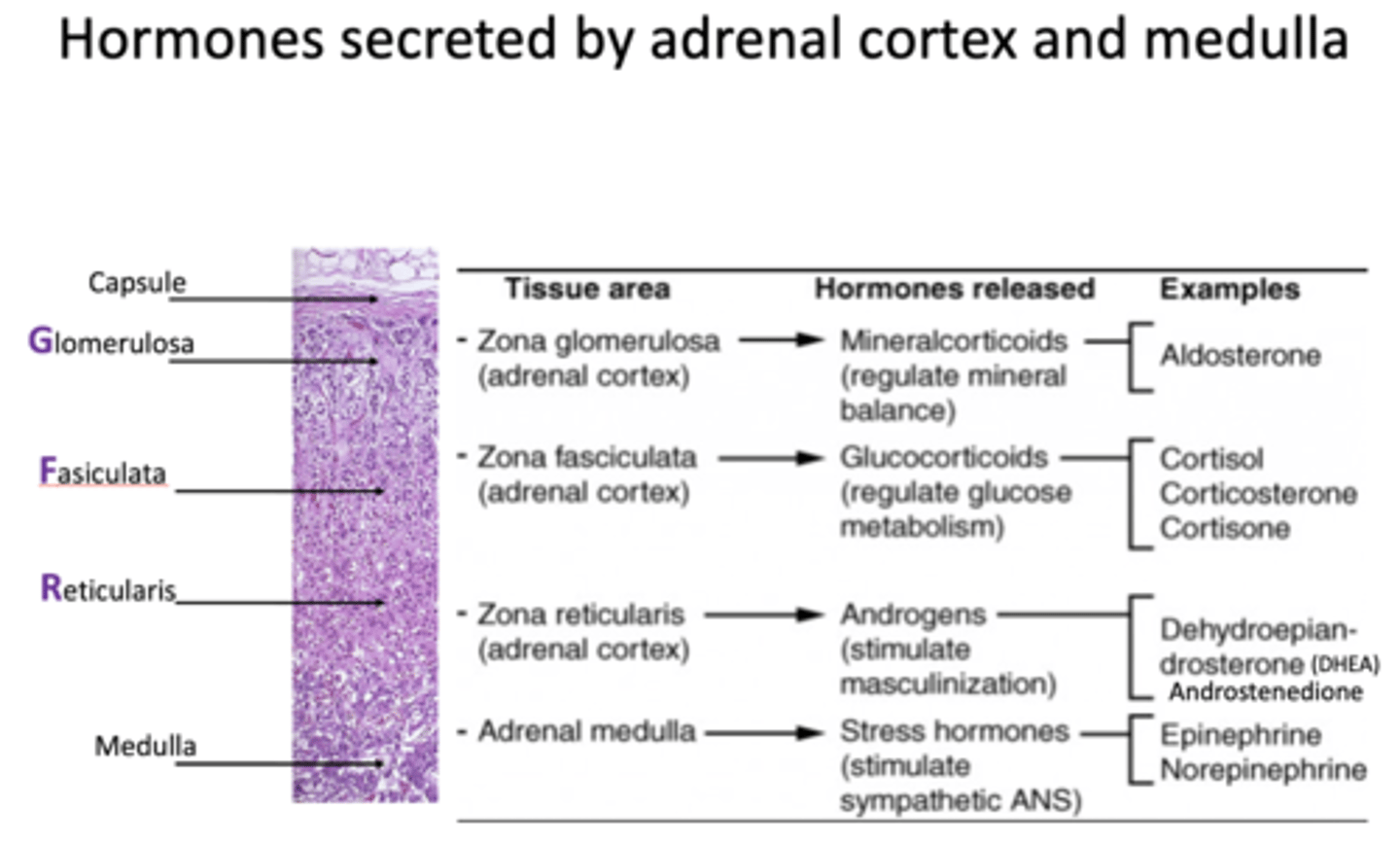
Zona reticularis (ZR) releases what type of hormones?
androgens
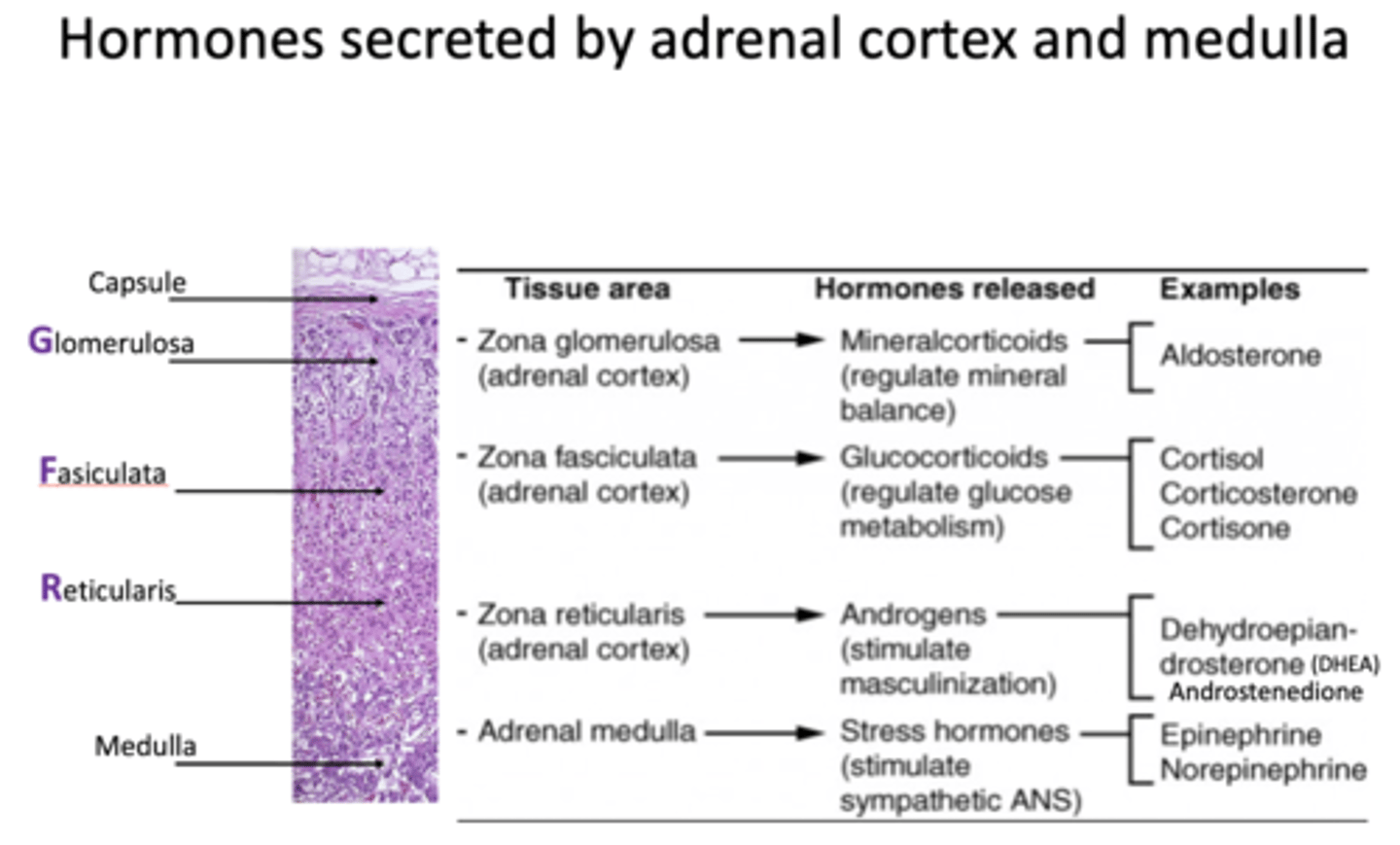
What are examples of hormones released from Zona reticularis?
- DHEA
- Androstenedione
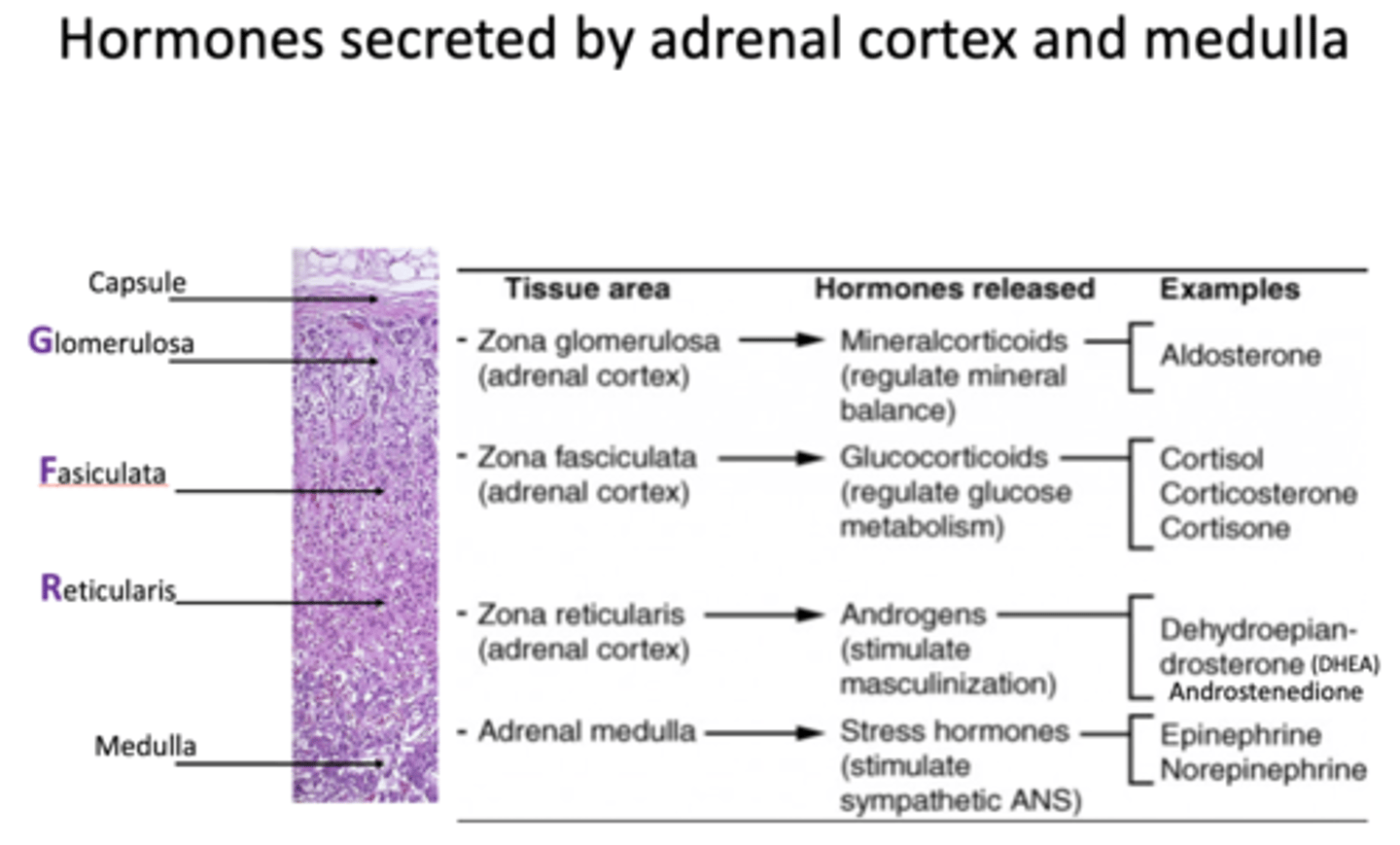
Adrenal medulla releases what types of hormones?
stress hormones
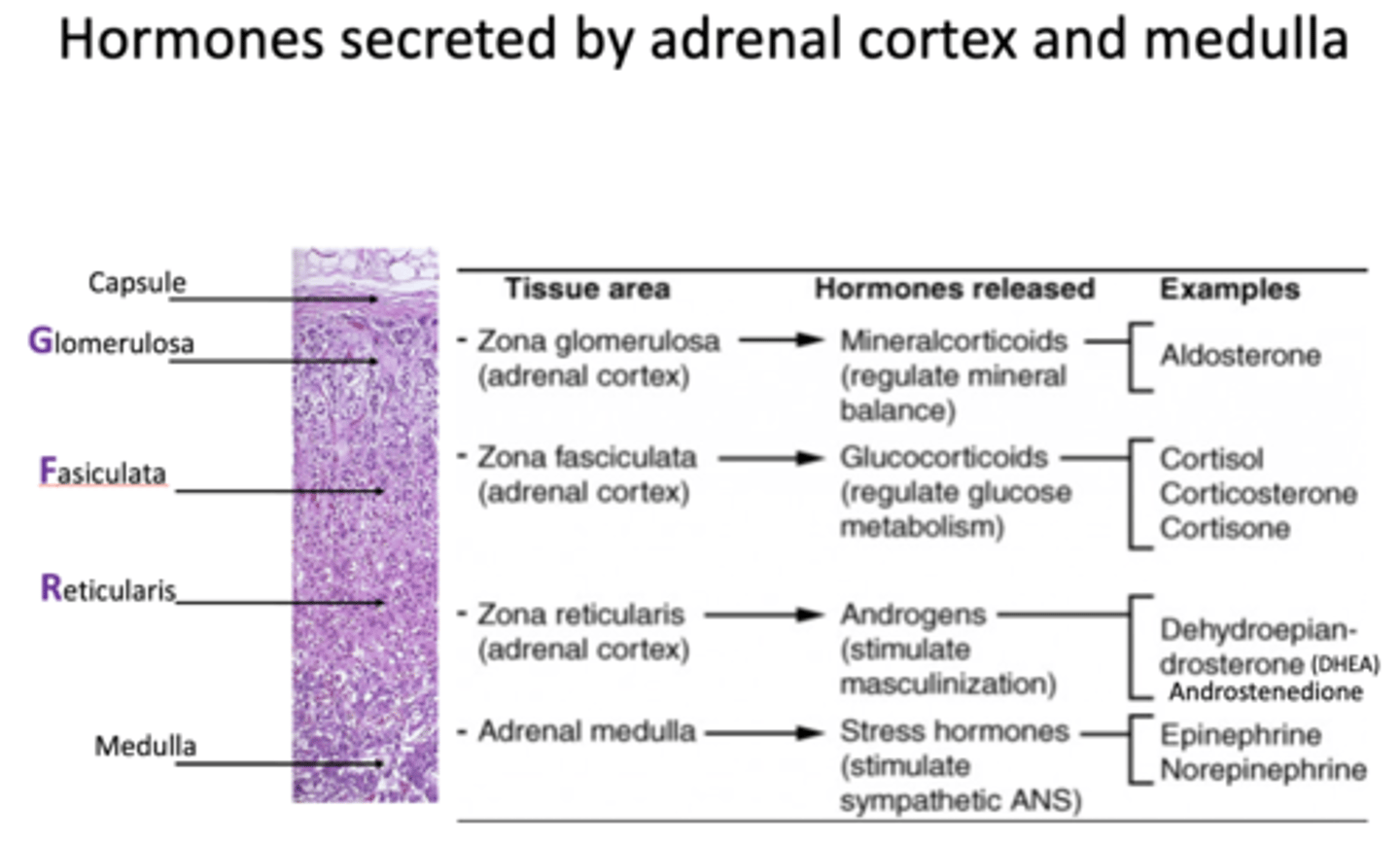
What are examples of hormones released from the adrenal medulla?
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
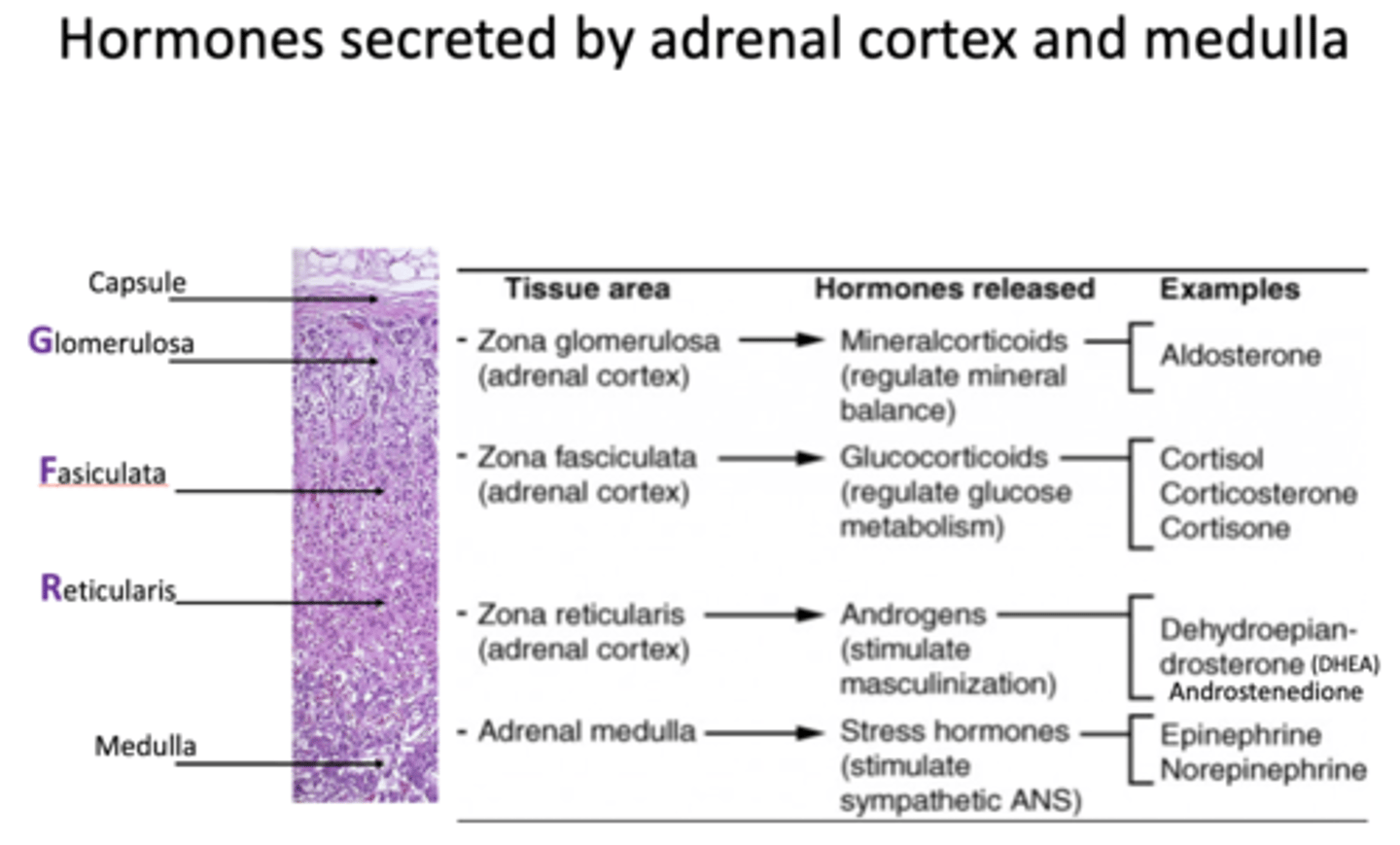
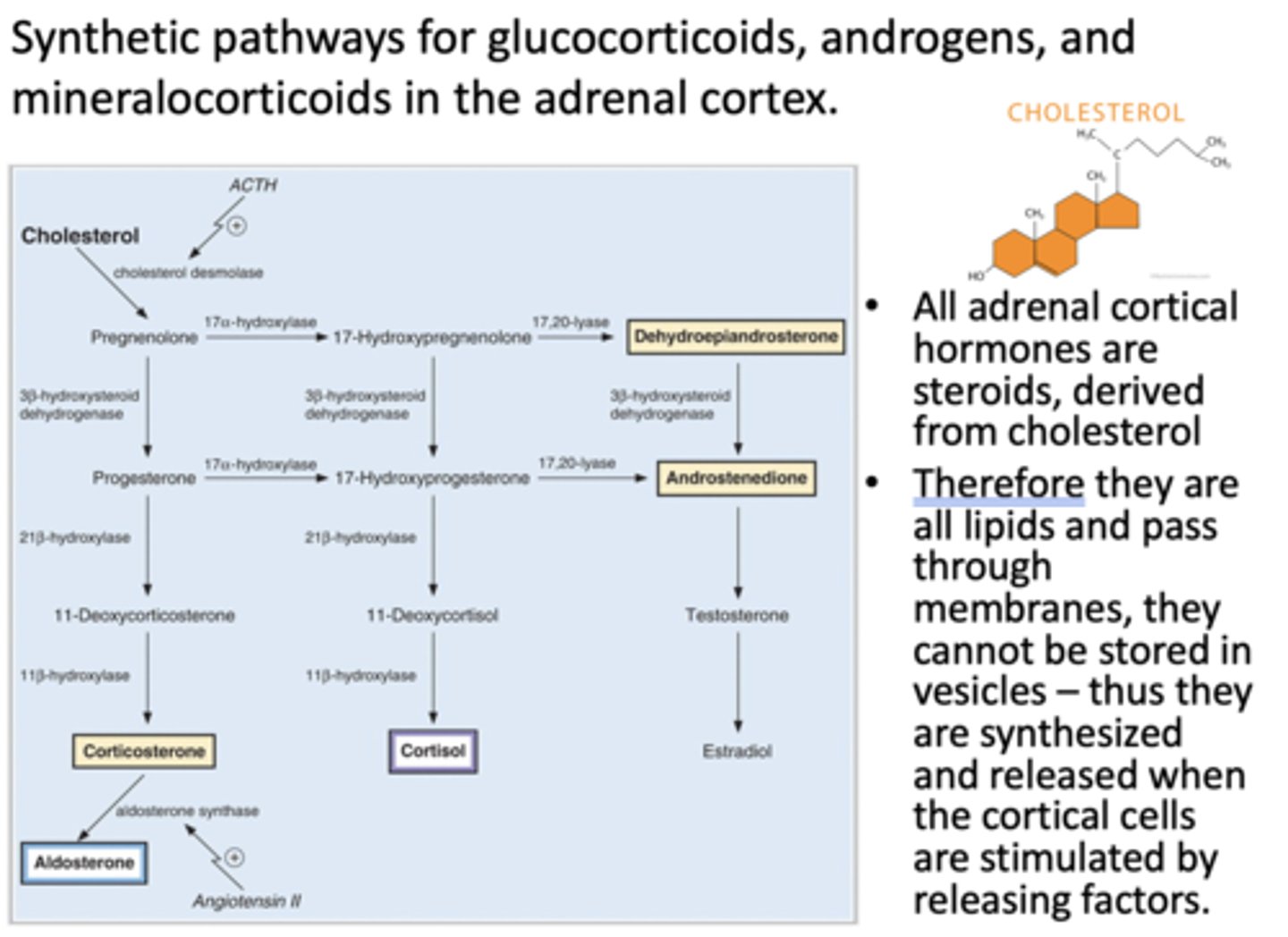
Synthetic pathways for glucocorticoids, androgens, and mineralocorticoids are where?
adrenal cortex
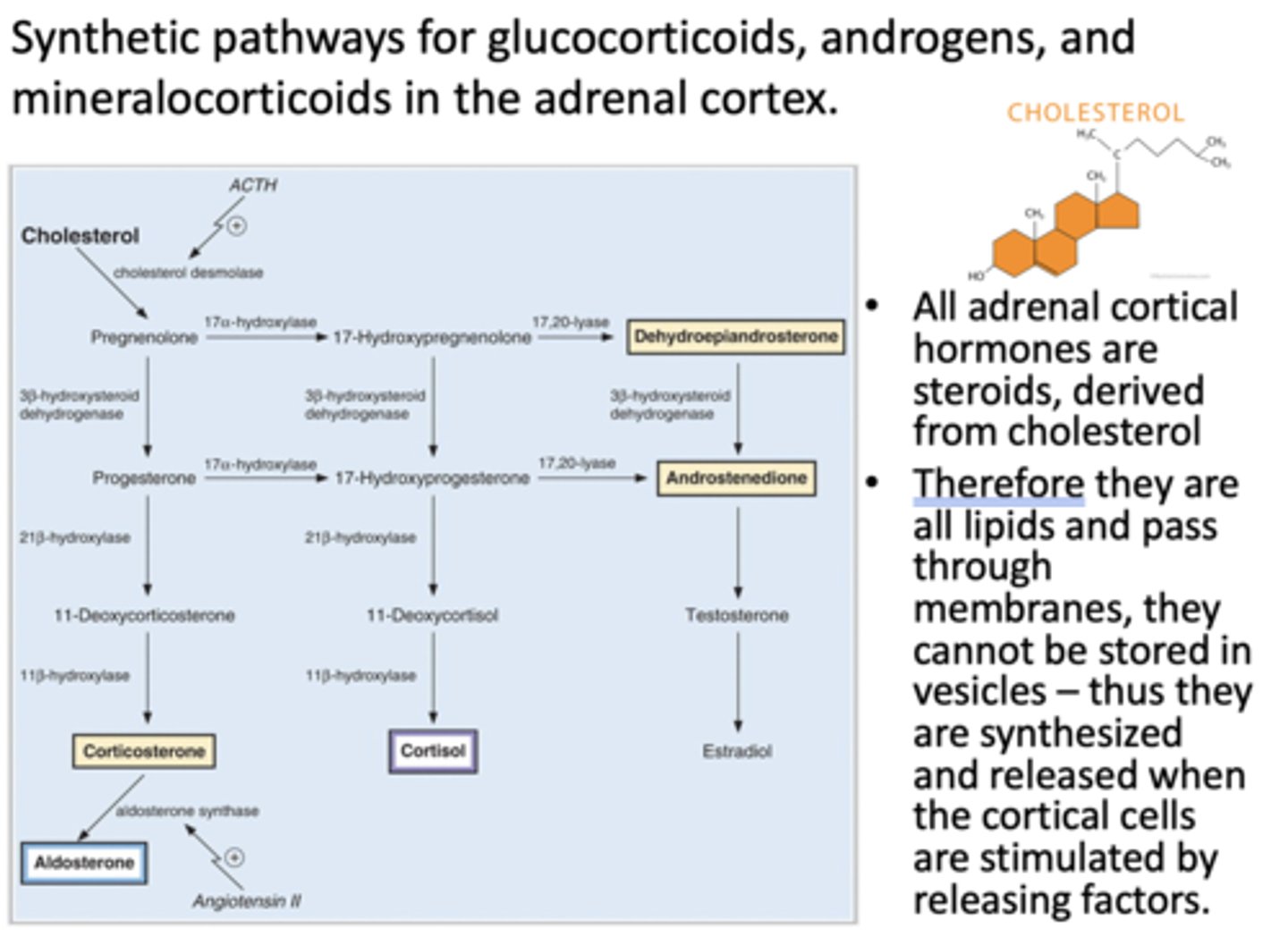
All adrenal cortical hormones are steroids derived from what?
cholesterol
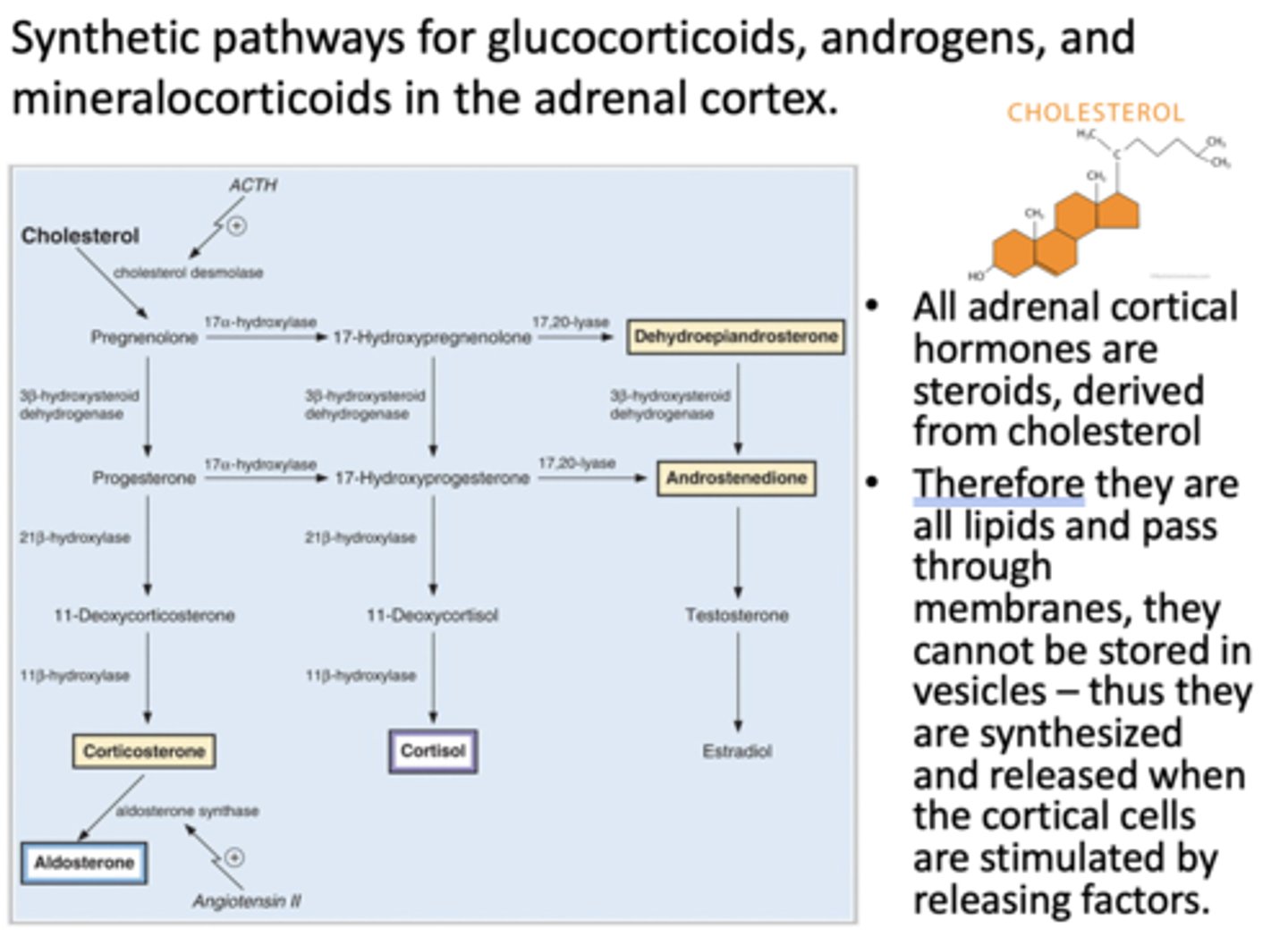
T/F: Since all adrenal cortical hormones are steroids, they pass through membranes so they are synthesized and released when cortical cells are stimulated by releasing factors
true
What is released by the hypothalamus and acts on the anterior pituitary corticotrophs to release ACTH in pulses which are highest in the early morning hours?
CRH

What is released in the event of psychological, physiological or biochemical stresses such as illness, fatigue, hypoglycemia, etc, higher centers in the brain can boost secretion?
glucocorticoids
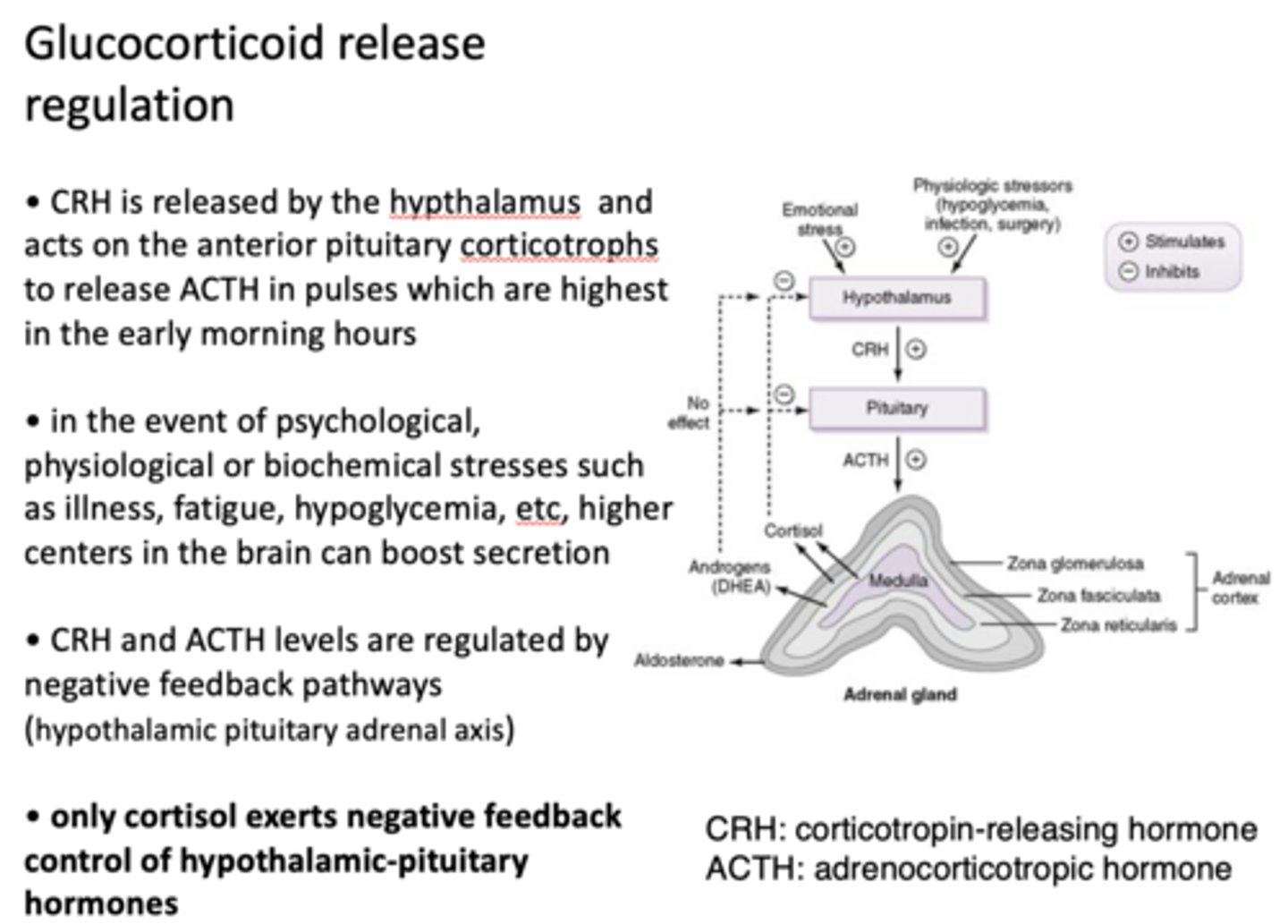
________ and ________ levels are regulated by negative feedback pathways (hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis)
CRH, ACTH
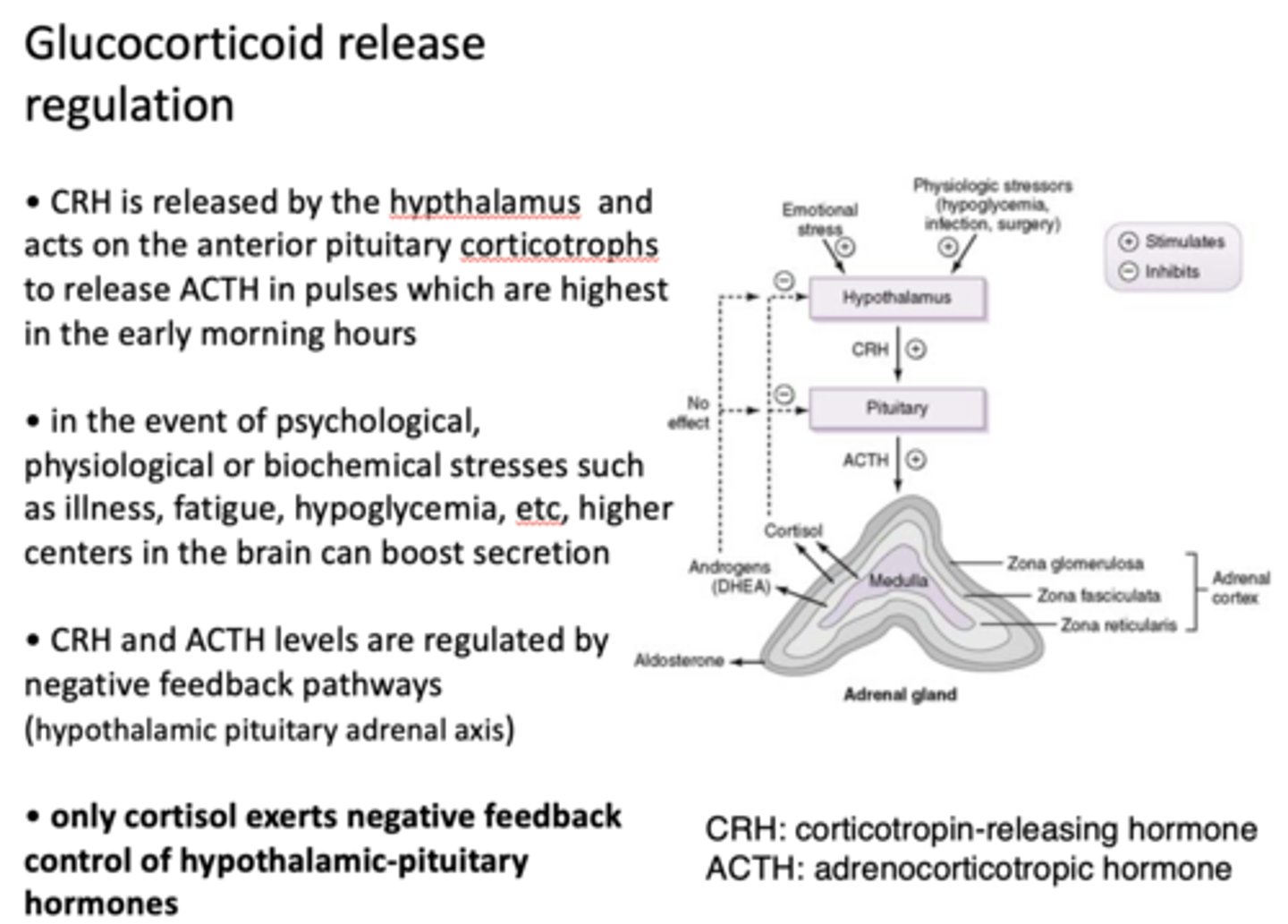
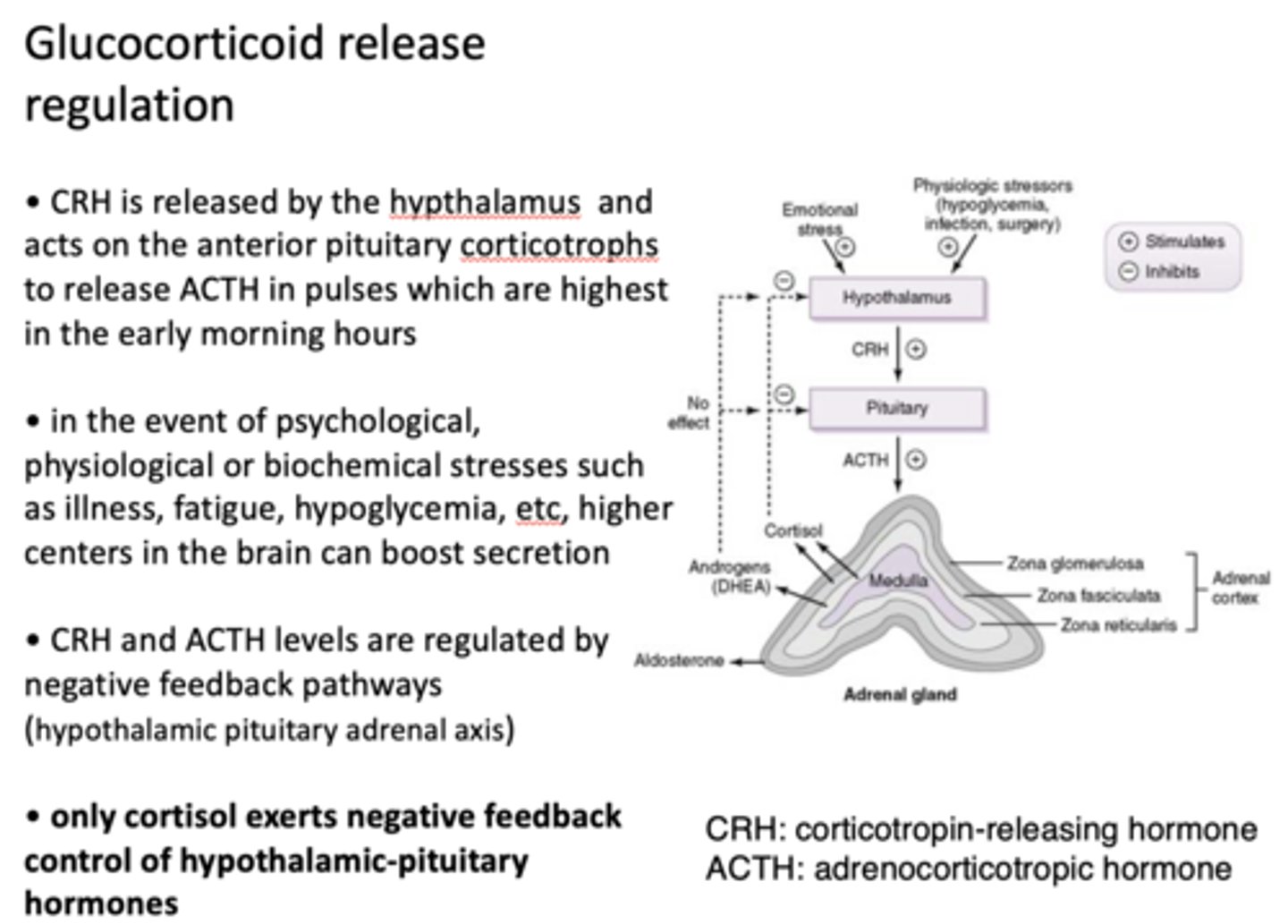
What is the only hormone released by the adrenal gland that exerts negative feedback control of HPA ?
cortisol
ACTH is synthesized as what prohormone?
POMC
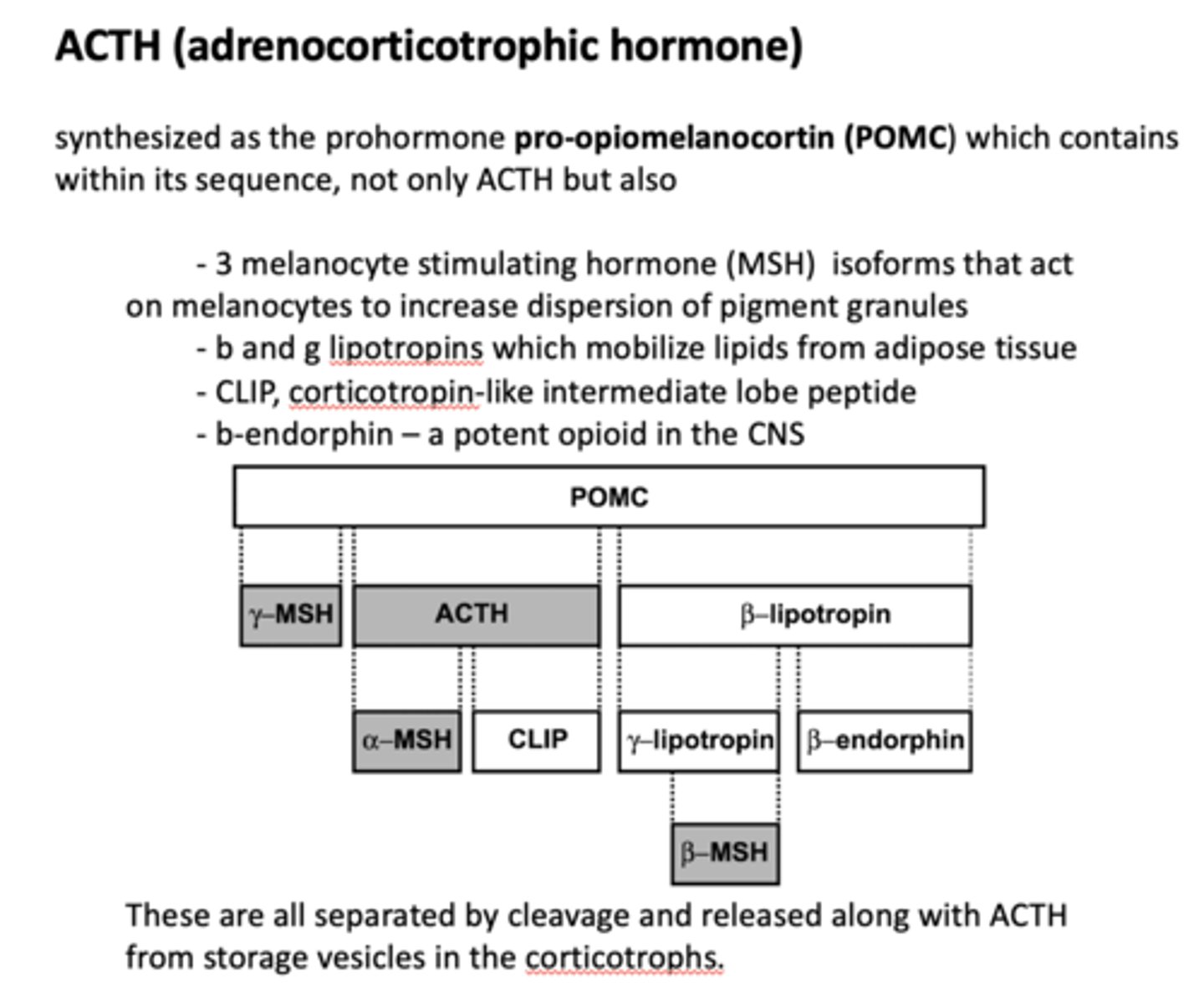
POMC synthesizes ACTH along with what other four products?
- MSH (3)
- Lipotropin (2)
- CLIP
- Endorphin
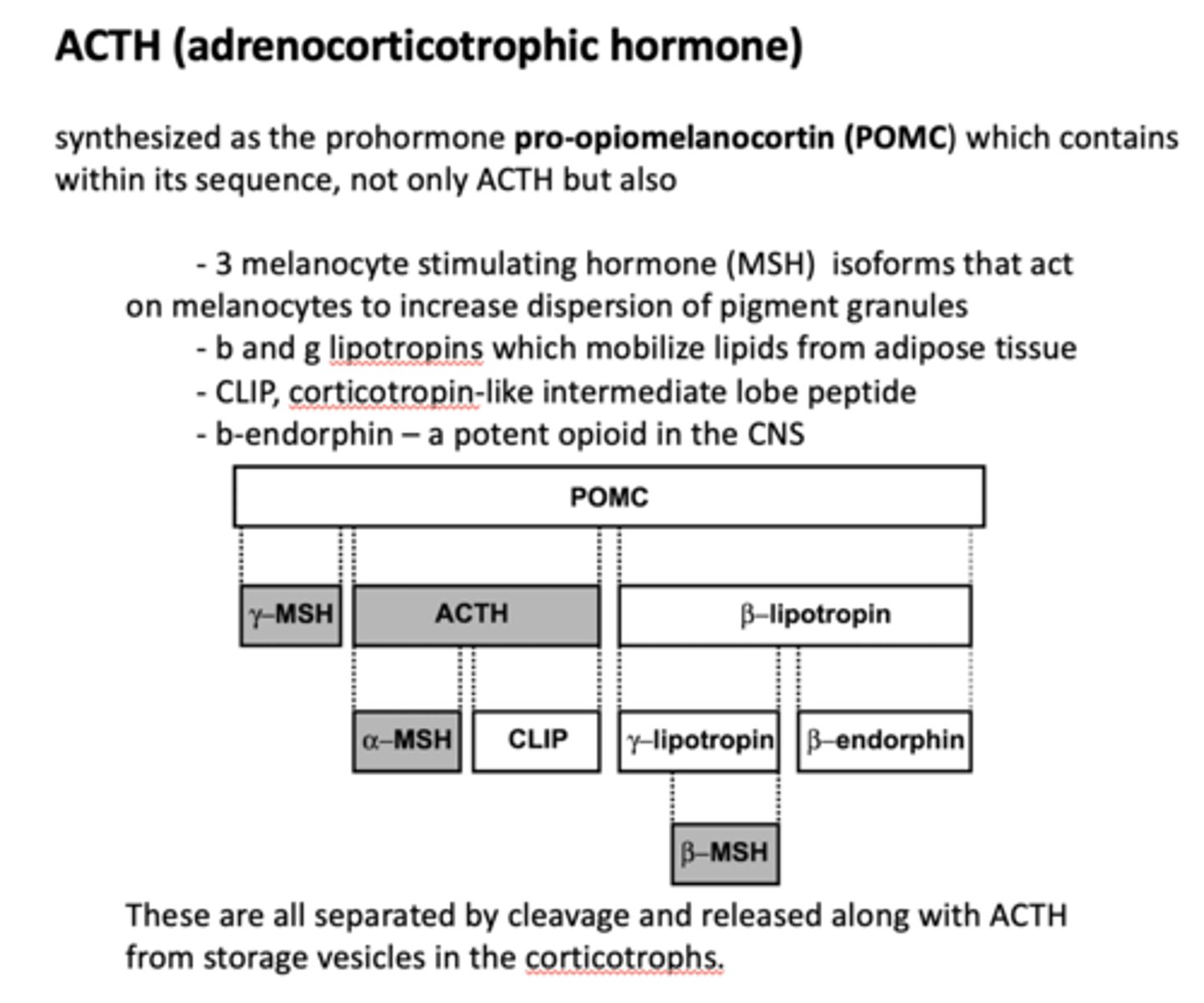
Which product of POMC?
Isoforms that act on melanocytes to increase dispersion of pigment granules
MSH
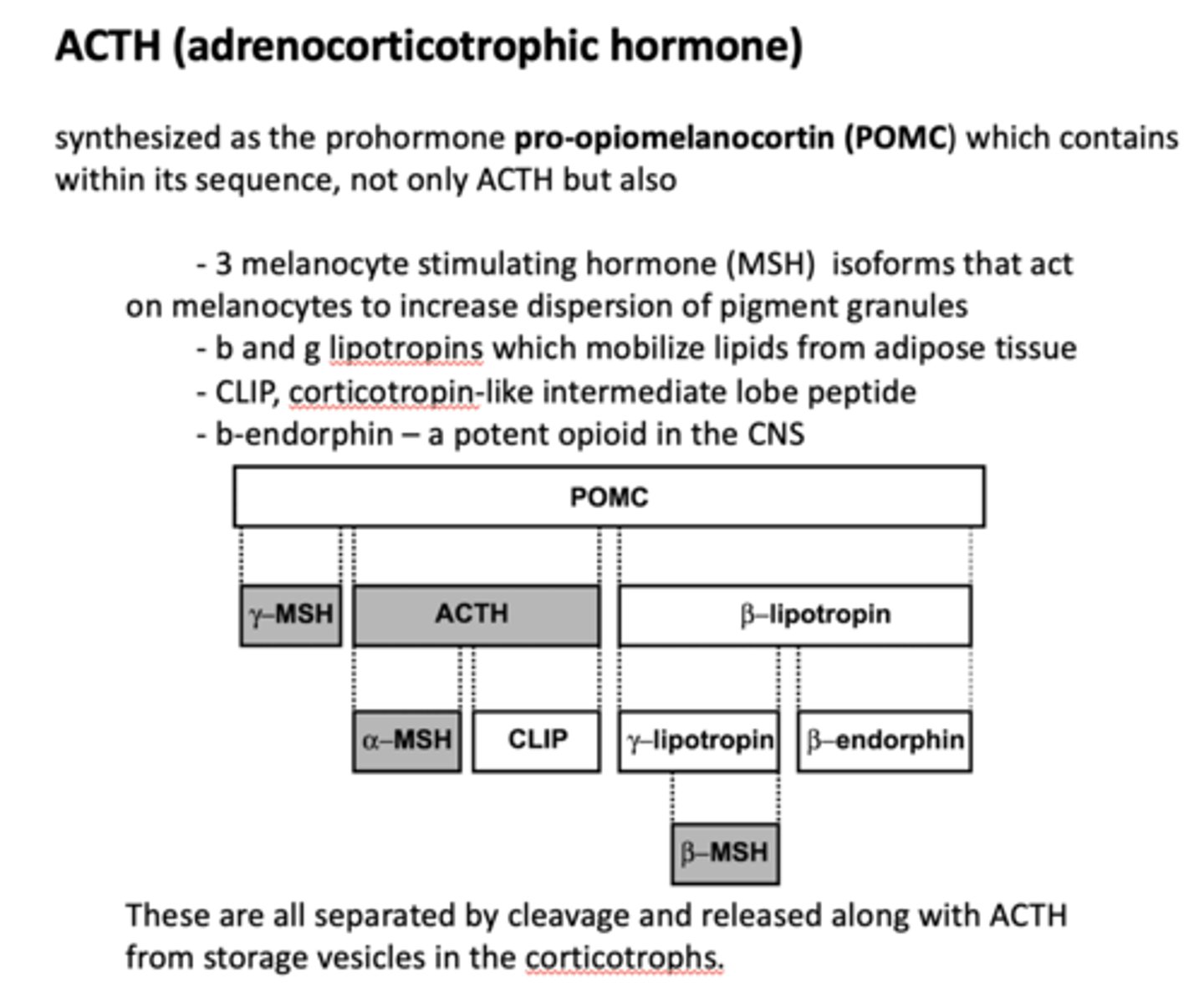
Which product of POMC?
Mobilize lipids from adipose tissue
lipotropins
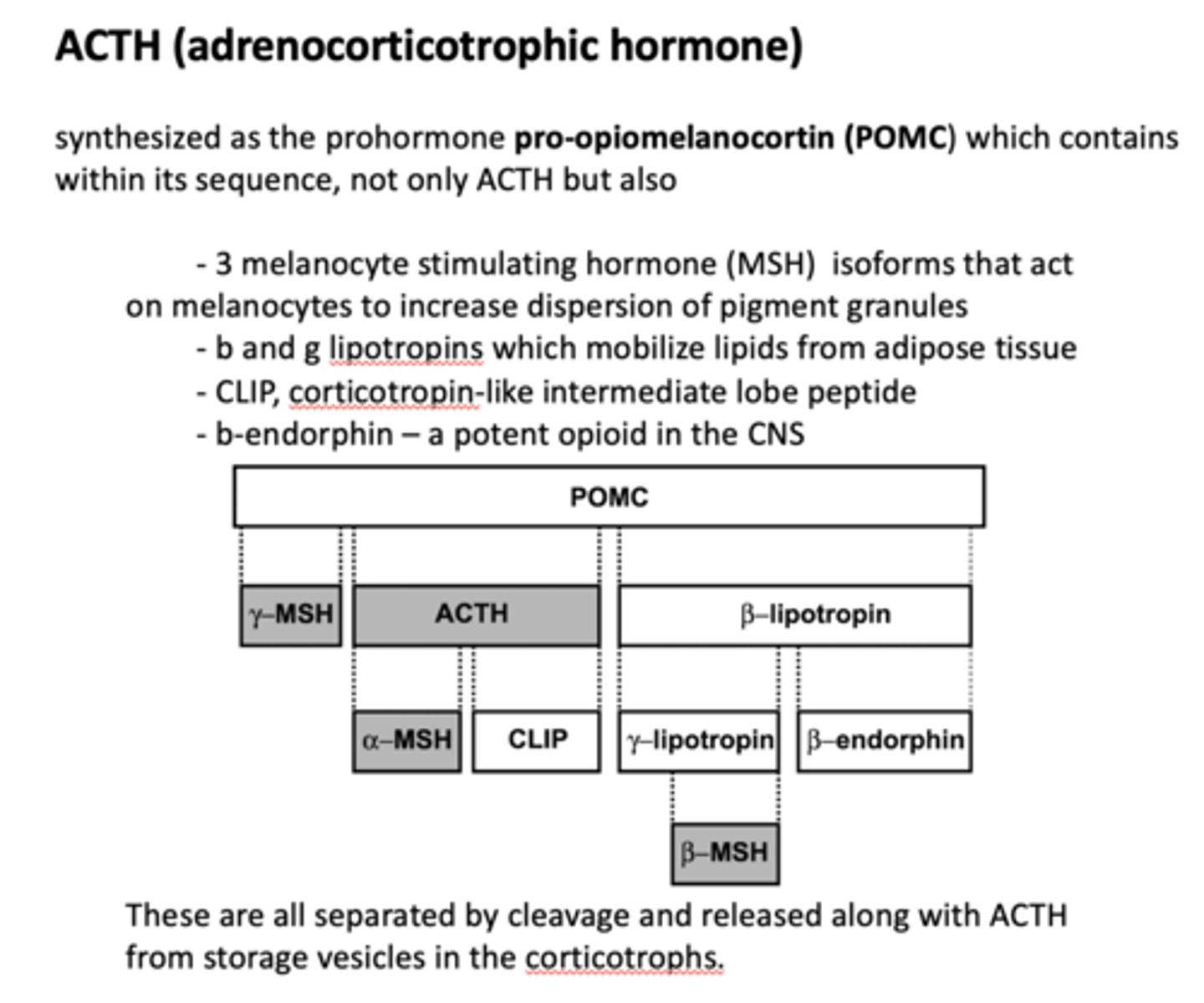
Which product of POMC?
Corticotropin-like intermediate lobe peptide
CLIP
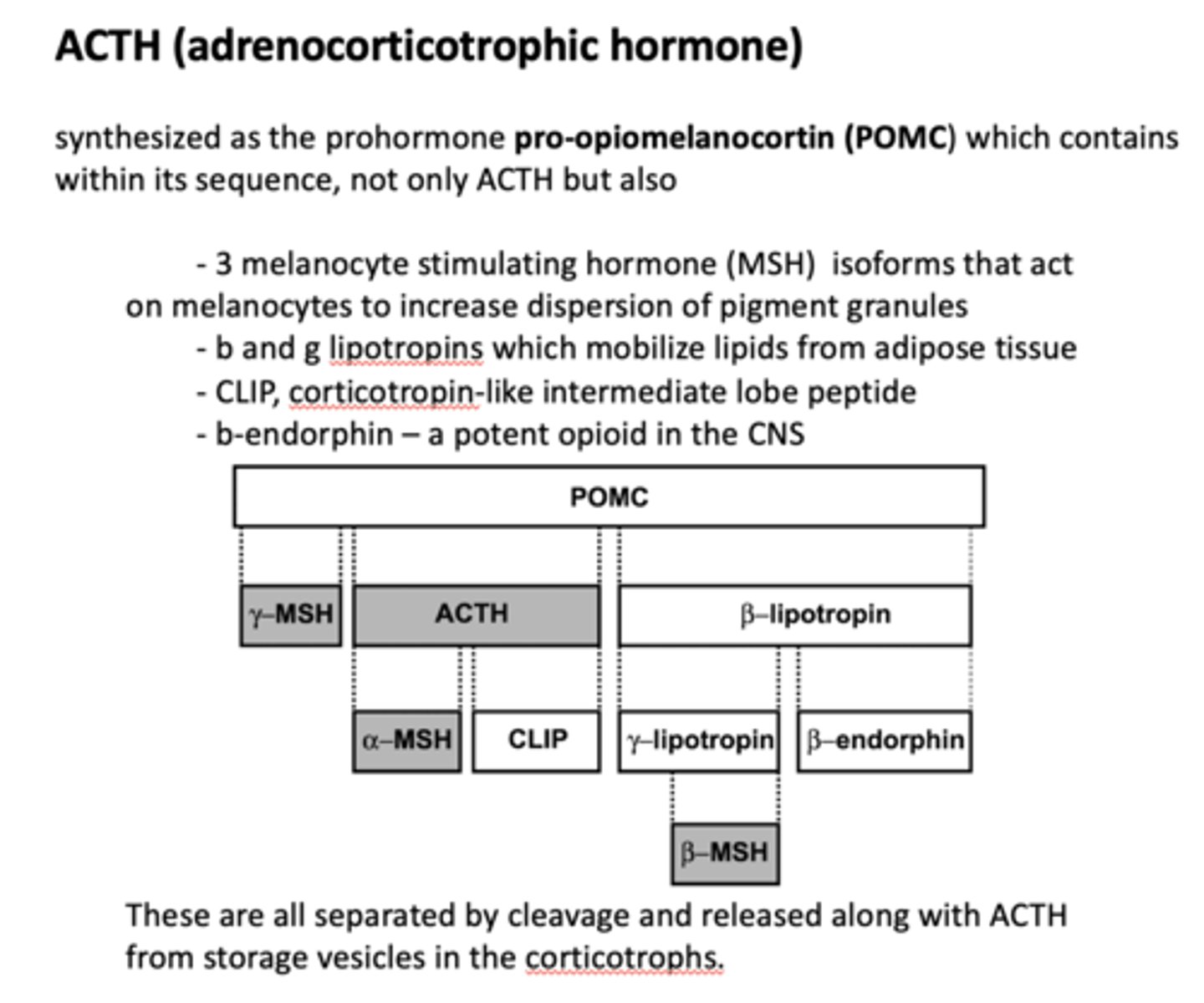
Which product of POMC?
A potent opioid in the CNS
B-endorphin
___________ binds to hormone receptors on all three layers of the adrenal cortex and acts through the G-protein-mediated activation of the PKA pathway to stimulate several enzymes in synthetic pathway.
ACTH
ACTH has a minor effect on the maintenance of the zona glomerulosa but the synthesis of aldosterone is mainly under the influence of ___________ and ___________
angiotensin II, K+
In the absence of ACTH, what two zones will atrophy?
- Zona fasciculata
- Zona reticularis
In the absence of ACTH, what zone will NOT atrophy?
Zona glomerulosa
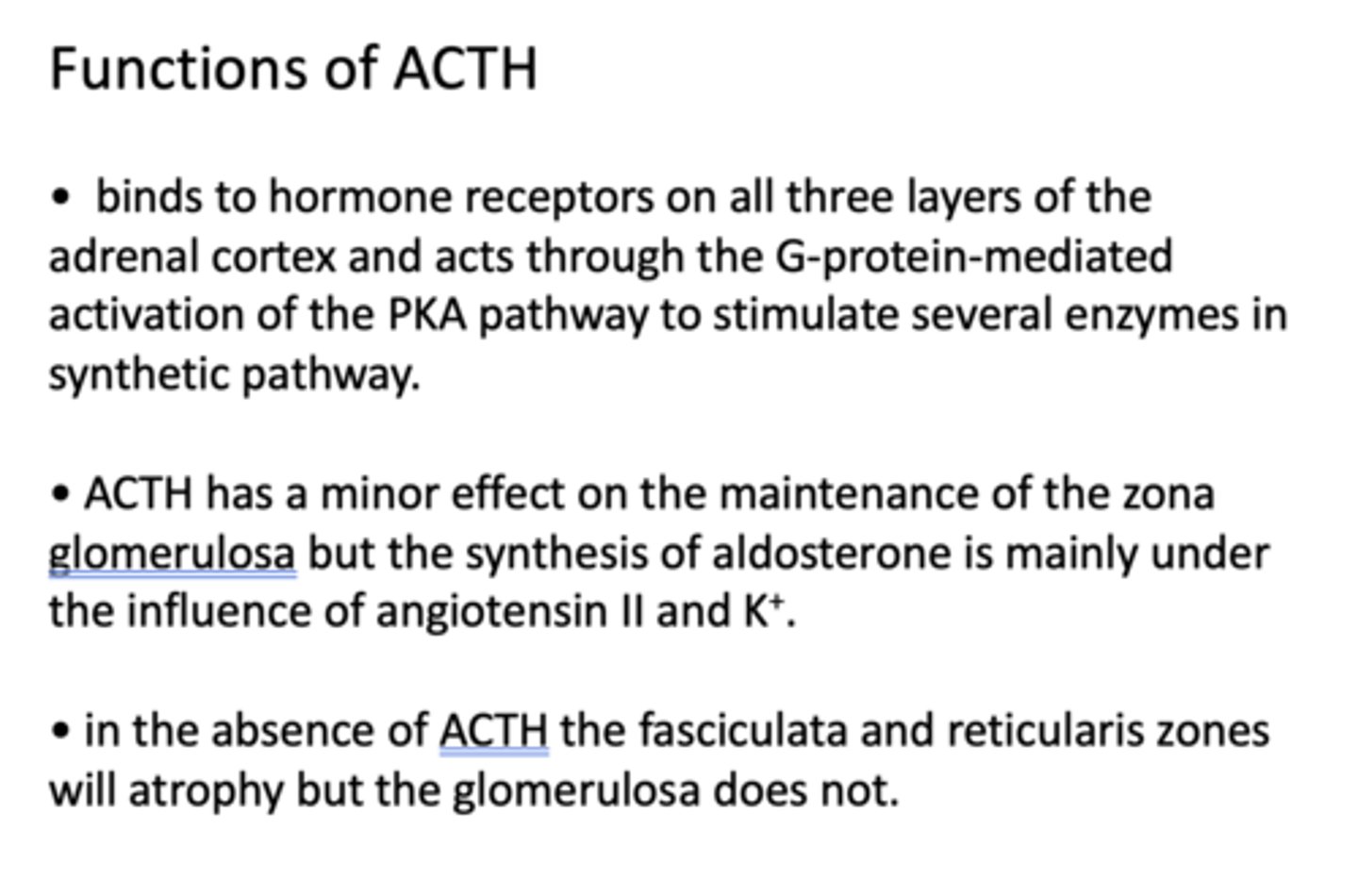
When plasma K+ are increased, what is released?
aldosterone
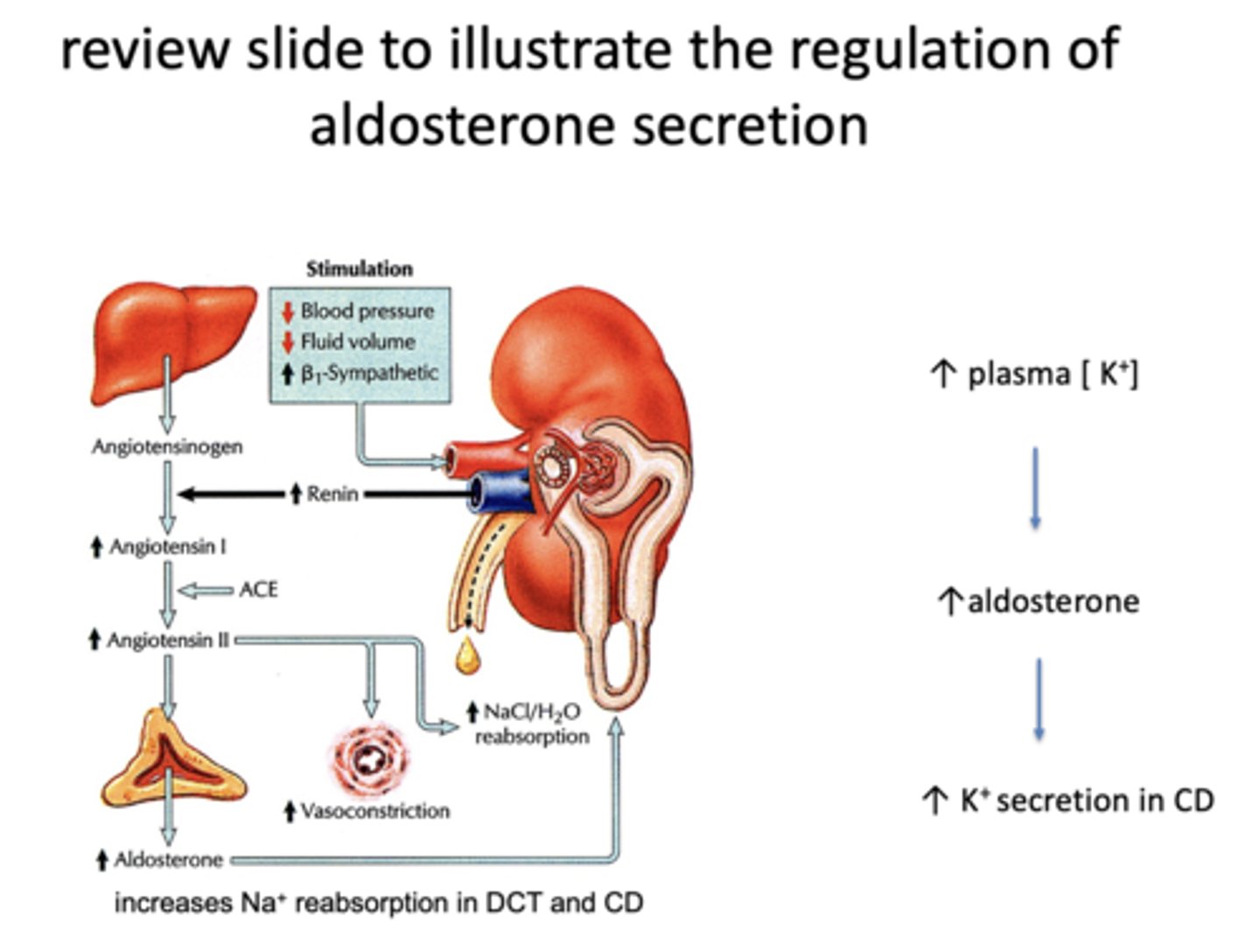
Aldosterone has what effect on K+ secretion in the CD?
increase
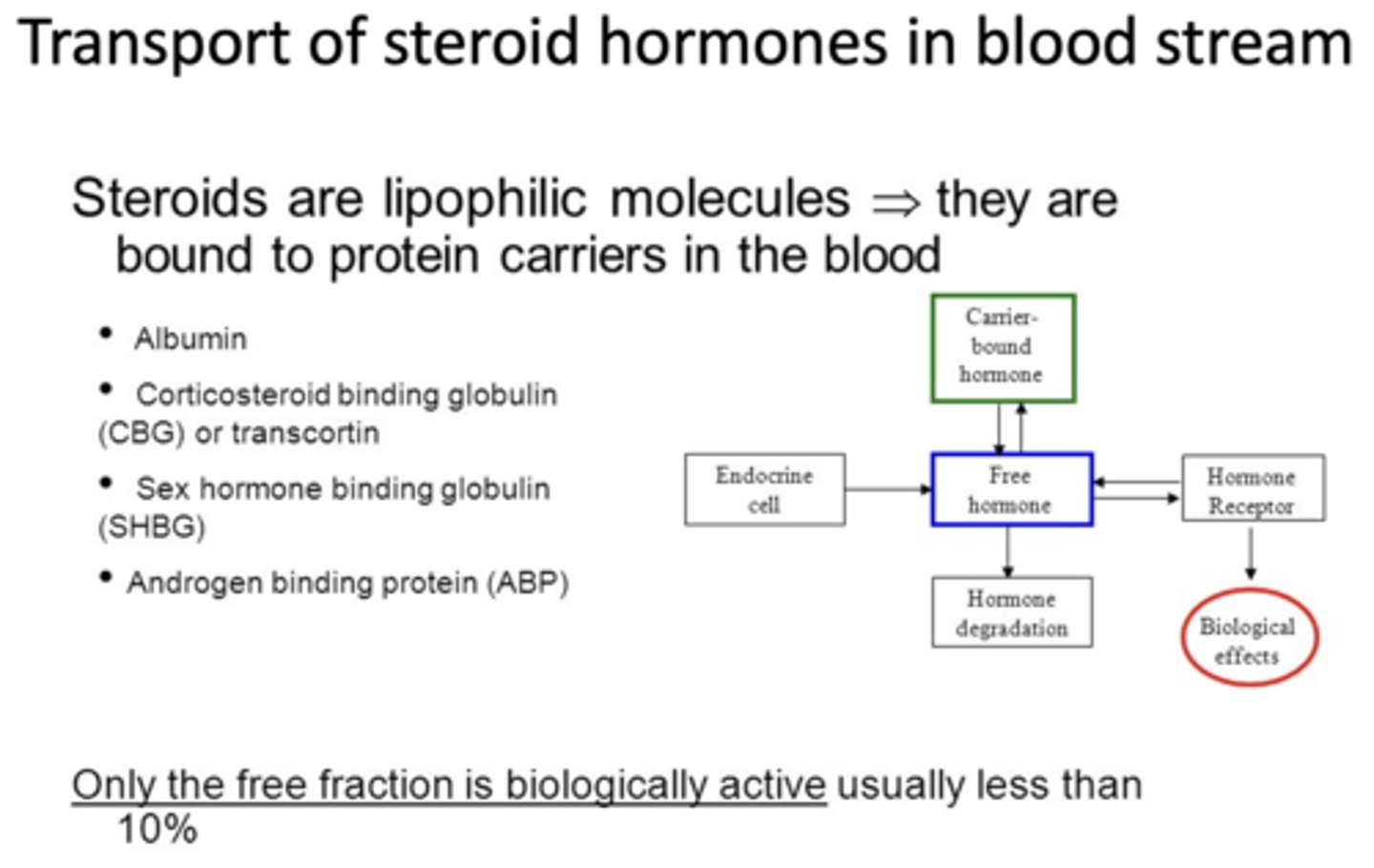
Steroids are what type of molecules that are bound to protein carriers in the blood?
lipophilic
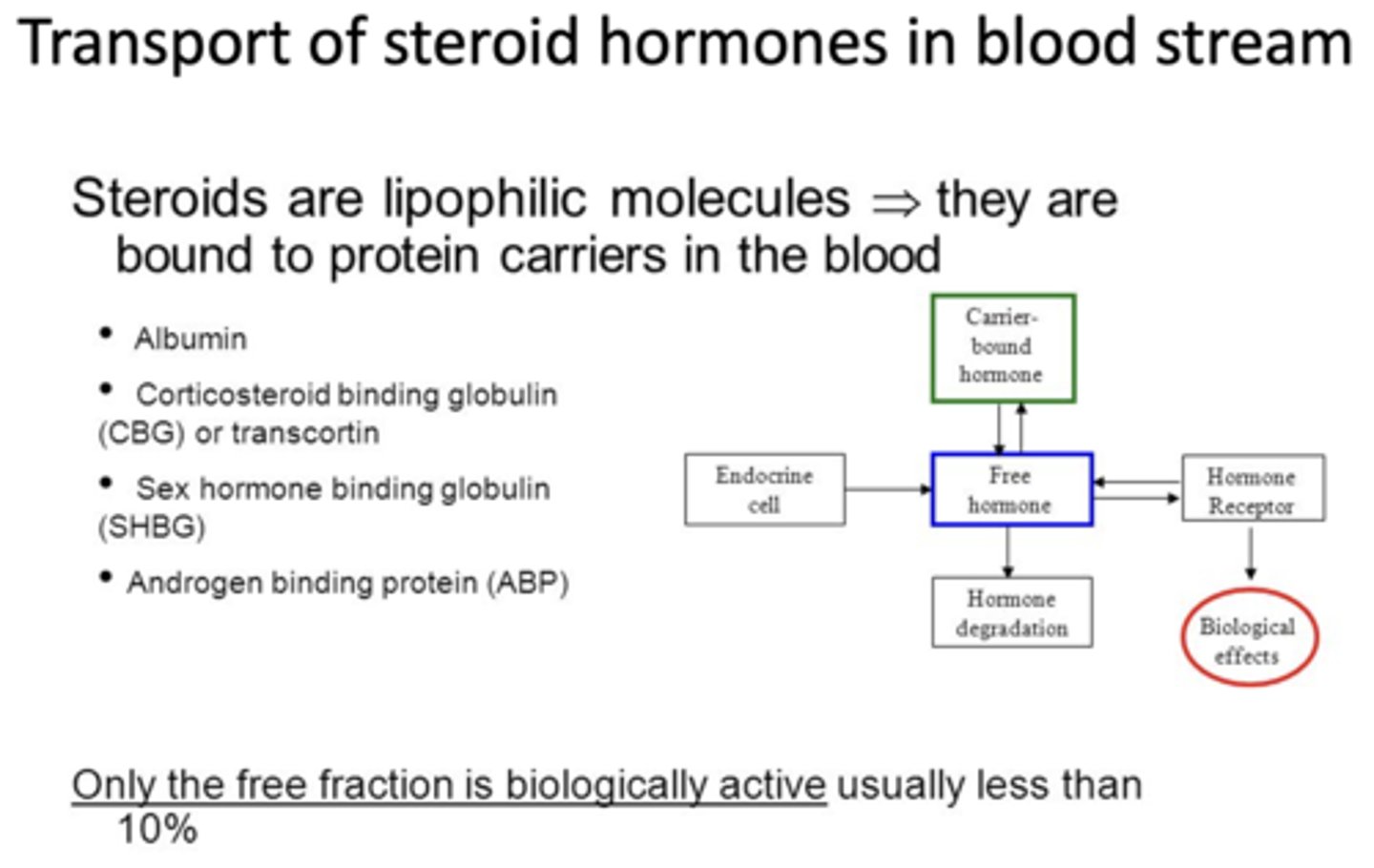
Are the bound or free steroids biologically active?
free (less than 10%)
What are the primary targets for cortisol?
- Liver
- Skeletal muscle
- Adipocytes
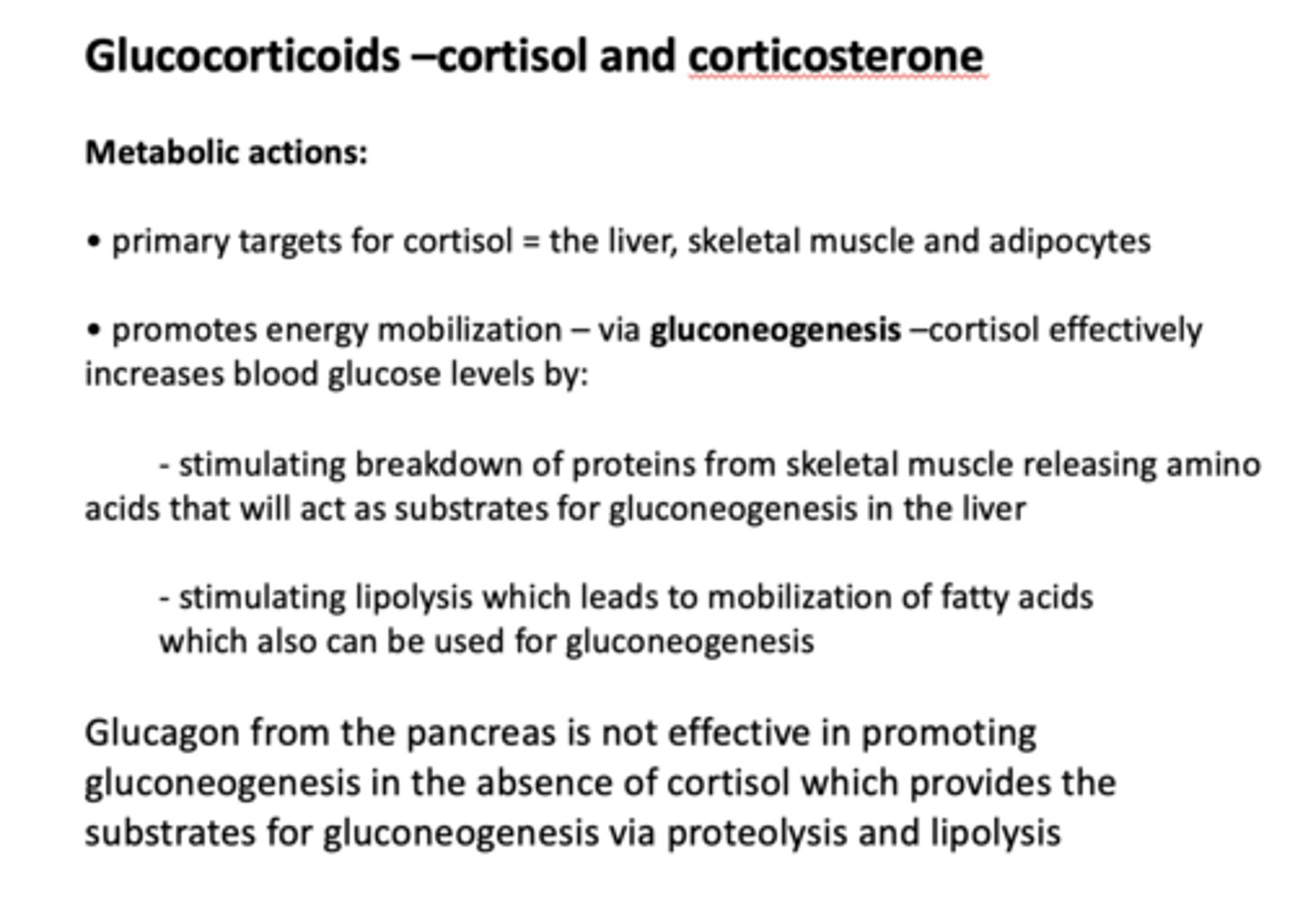
Cortisol increases blood glucose levels by what process?
gluconeogenesis
What two processes occur to make substrates for gluconeogenesis?
- Stimulating breakdown of proteins
- Stimulating lipolysis
T/F: Glucagon from the pancreas is not effective in promoting gluconeogenesis in the absence of cortisol which provides the substrates for gluconeogenesis via proteolysis and lipolysis
true

What is the effect of glucocorticoids on GLUT-4-mediated uptake?
inhibits (spares glucose for other tissues)

What is the effect of glucocorticoids on the cardiovascular system?
Maintains normal function and vascular response to adrenergic (a1) receptors

What is the effect of glucocorticoids on the kidney?
- Increases GFR
- Increases salt and water retention

What is the effect of glucocorticoids on the CNS?
necessary for fetal development

Excess glucocorticoids have what effects on bones?
Decrease bone formation (stimulate osteoclast formation, decrease collagen synthesis, inhibit osteoblasts--> osteoporosis, decrease Ca2+ uptake in gut)

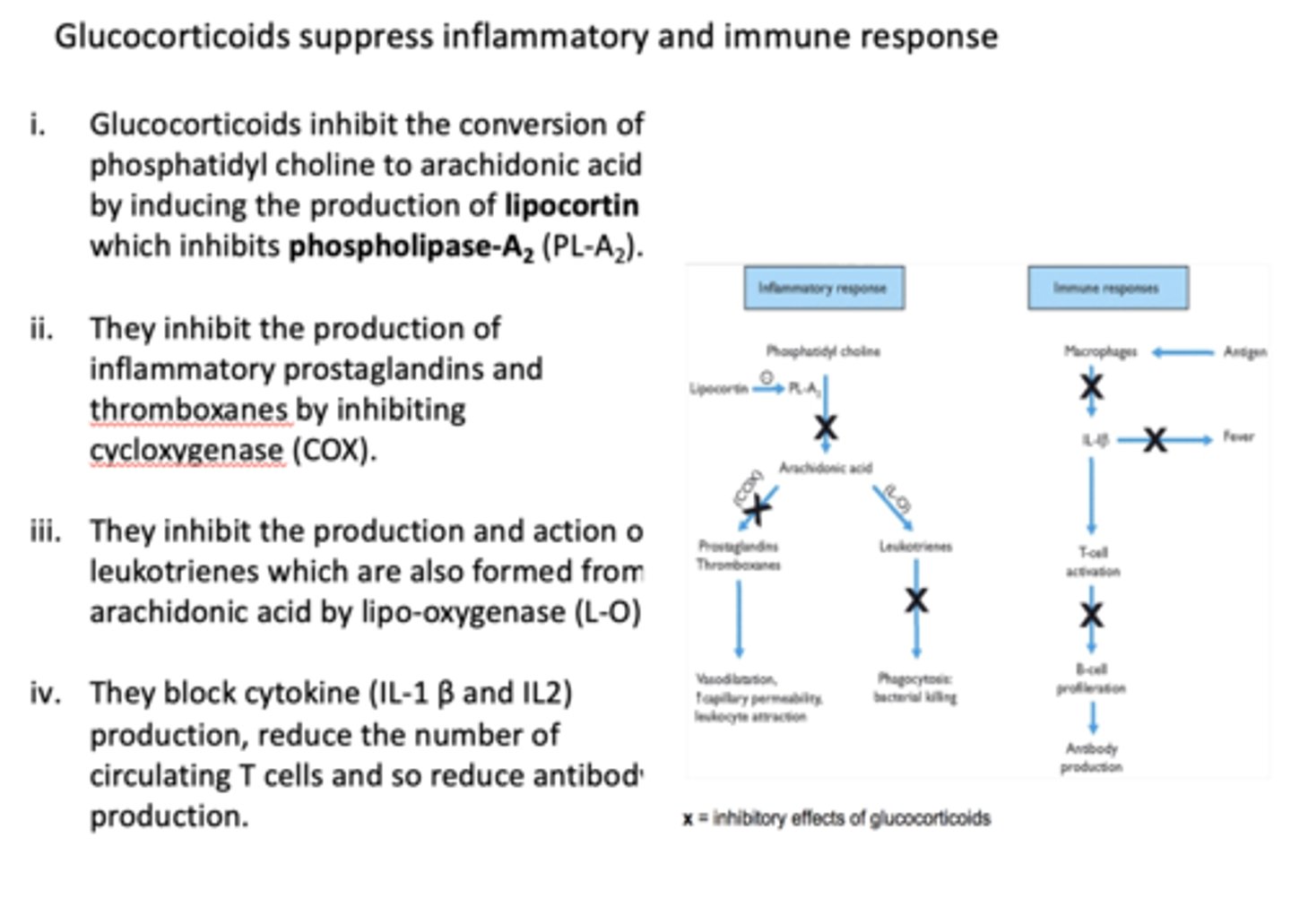
T/F: glucocorticoids suppress inflammatory and immune response
true
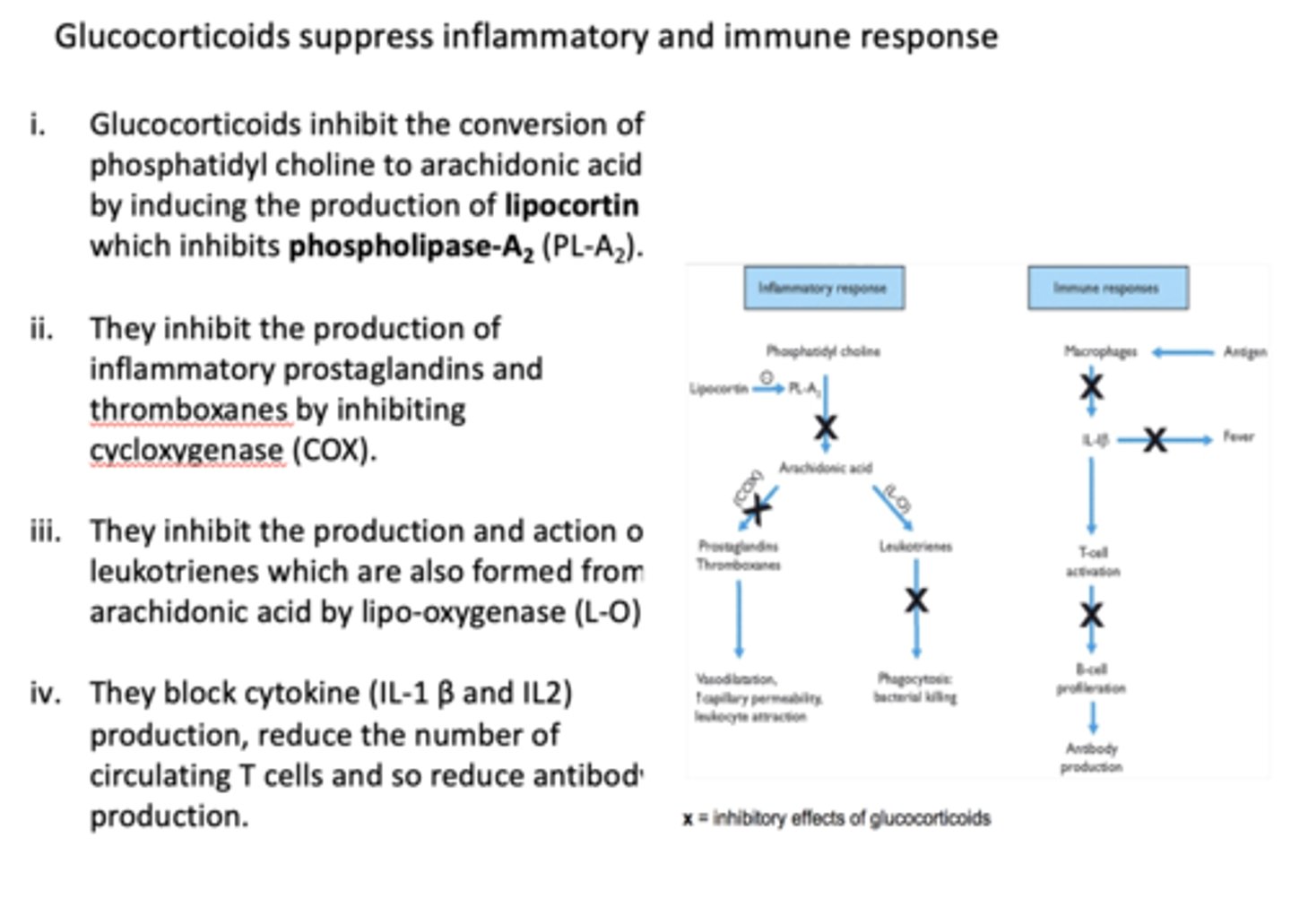
Glucocorticoids inhibit the conversion of phosphatidyl choline to arachidonic acid by inducing the production of ________ which inhibits _________
lipocortin, phospholipase A2
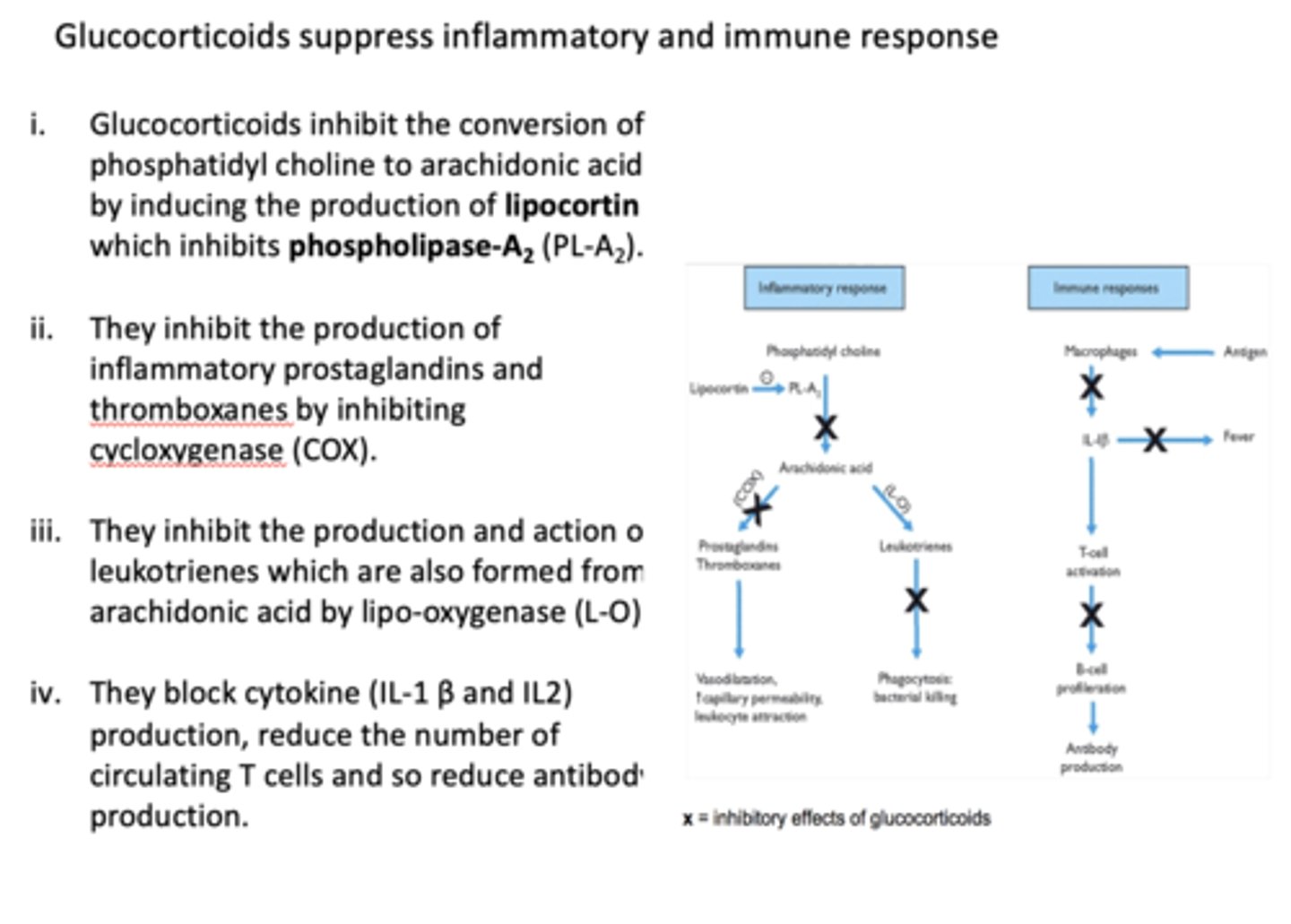
Glucocorticoids inhibit the production of inflammatory prostaglandins and thromboxanes by inhibiting ________
COX
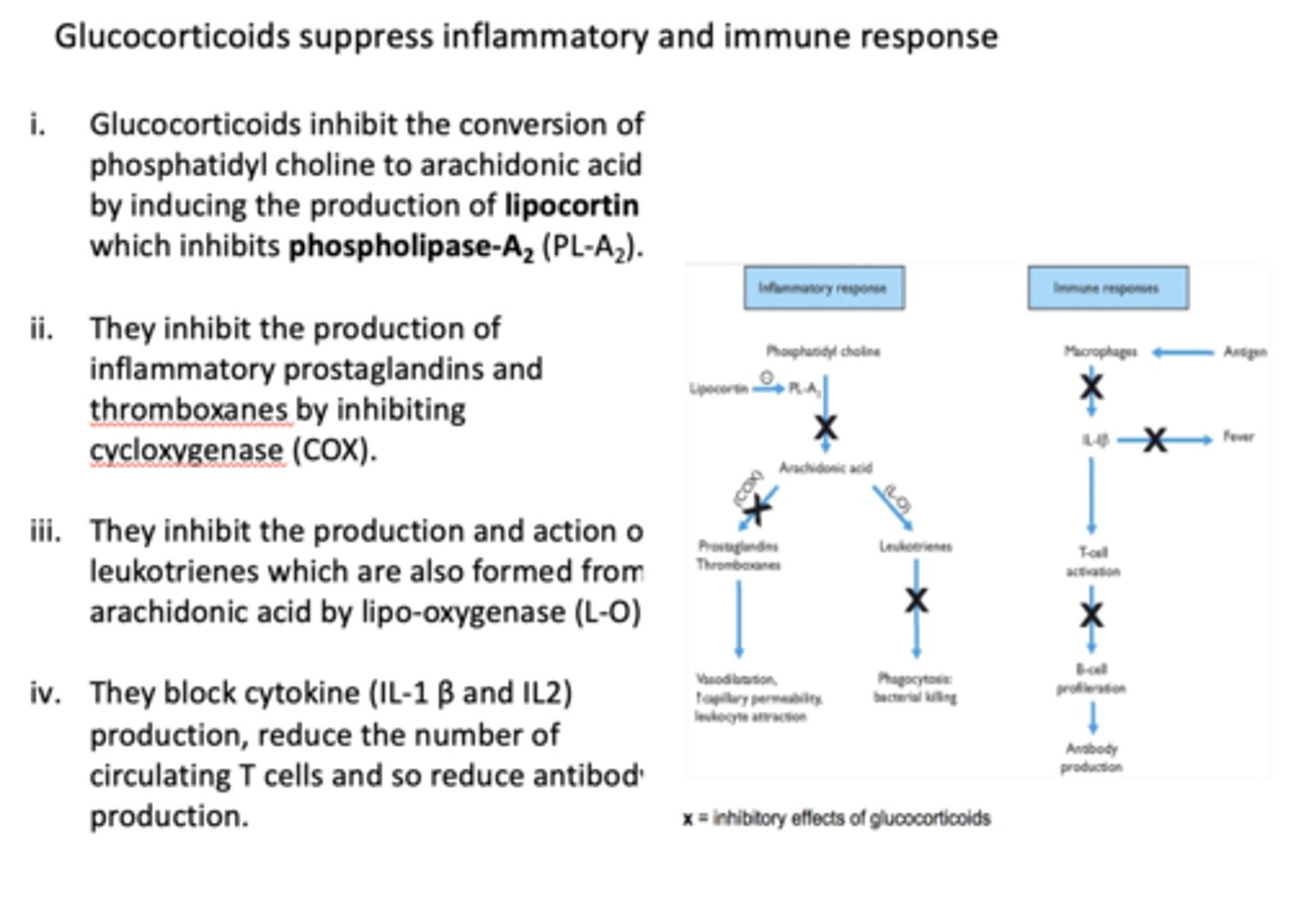
Glucocorticoids inhibit the production and action of leukotrienes which are also formed from arachidonic acid by
lipo-oxygenase (L-O)
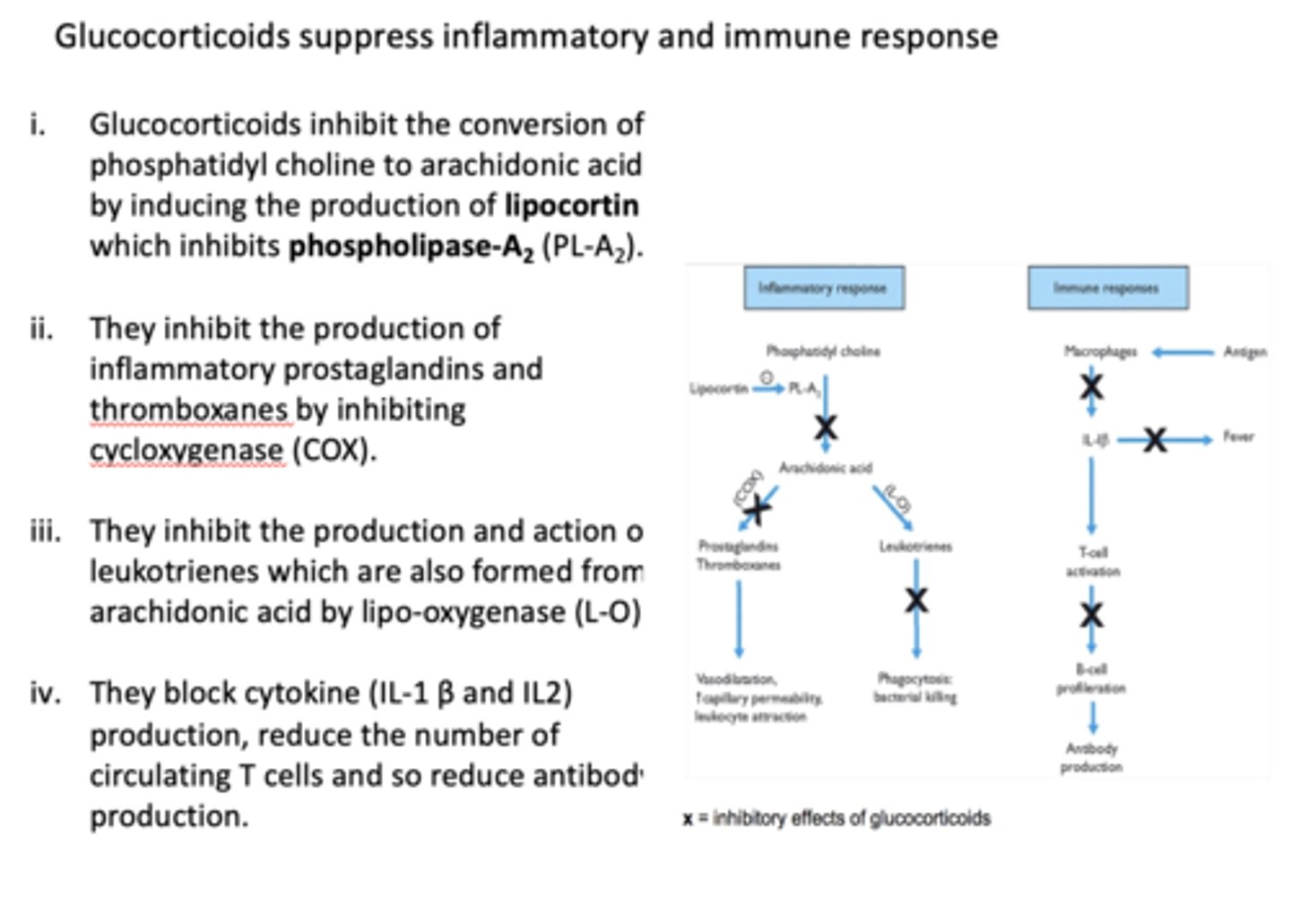
Glucocorticoids block cytokine (IL-1 β and IL2) production, _______ the number of circulating T cells and so ______ antibody production.
reduce
Mineralocorticoids are released only from where?
Zona Glomerulosa
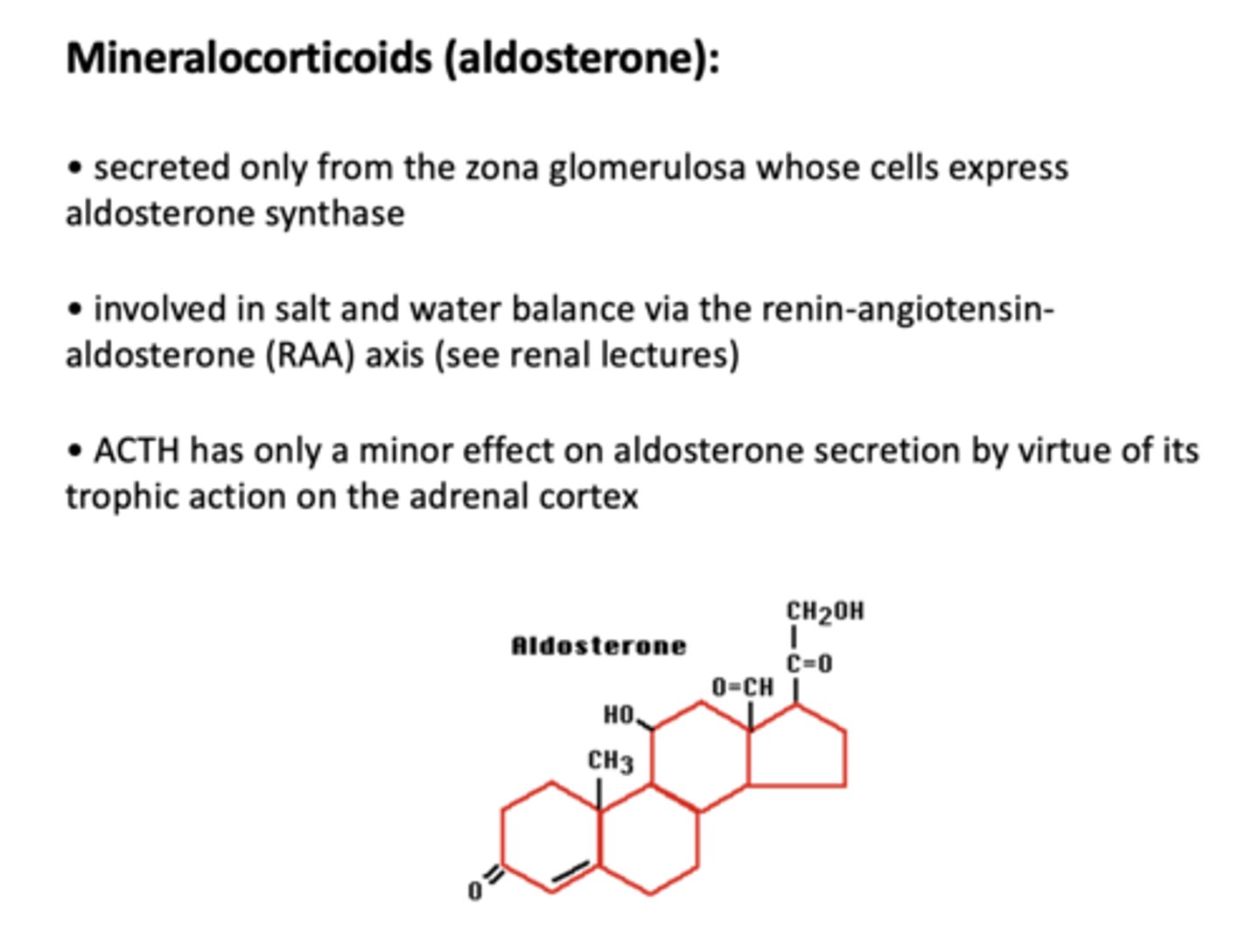
what hormones are involved in salt and water balance via the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) axis?
Mineralocorticoids
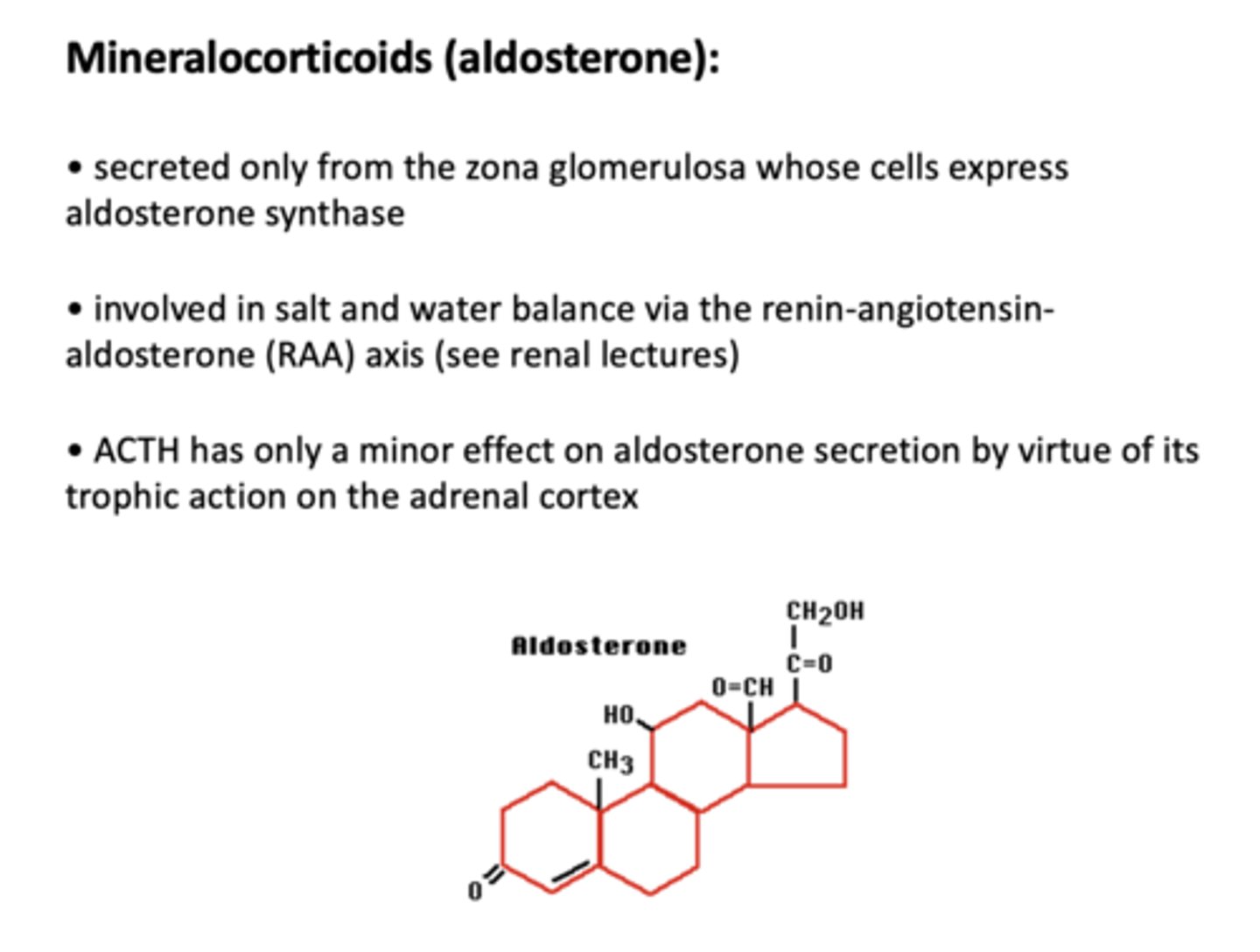
T/F: ACTH has only a minor effect on aldosterone secretion by virtue of its trophic action on the adrenal cortex
true
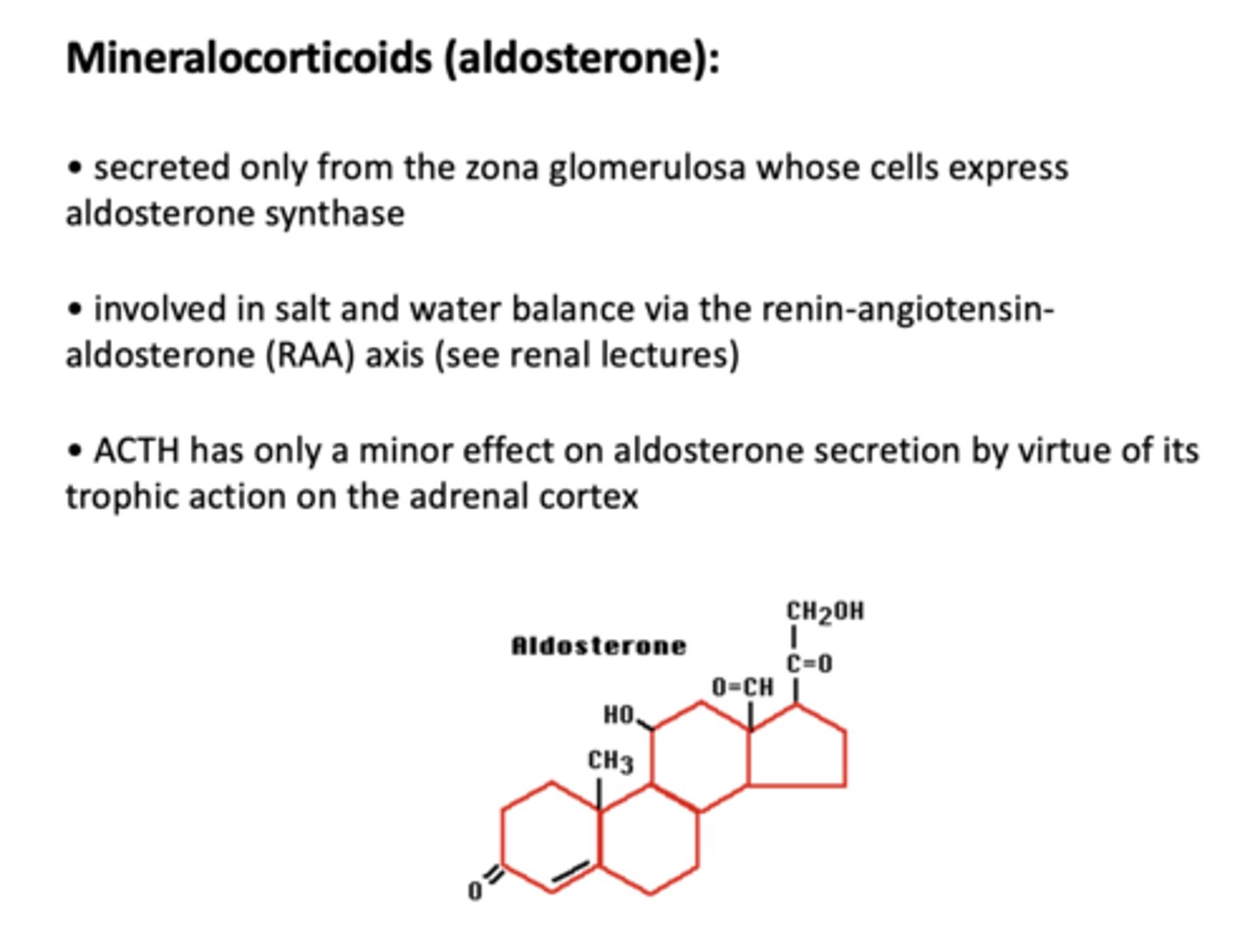
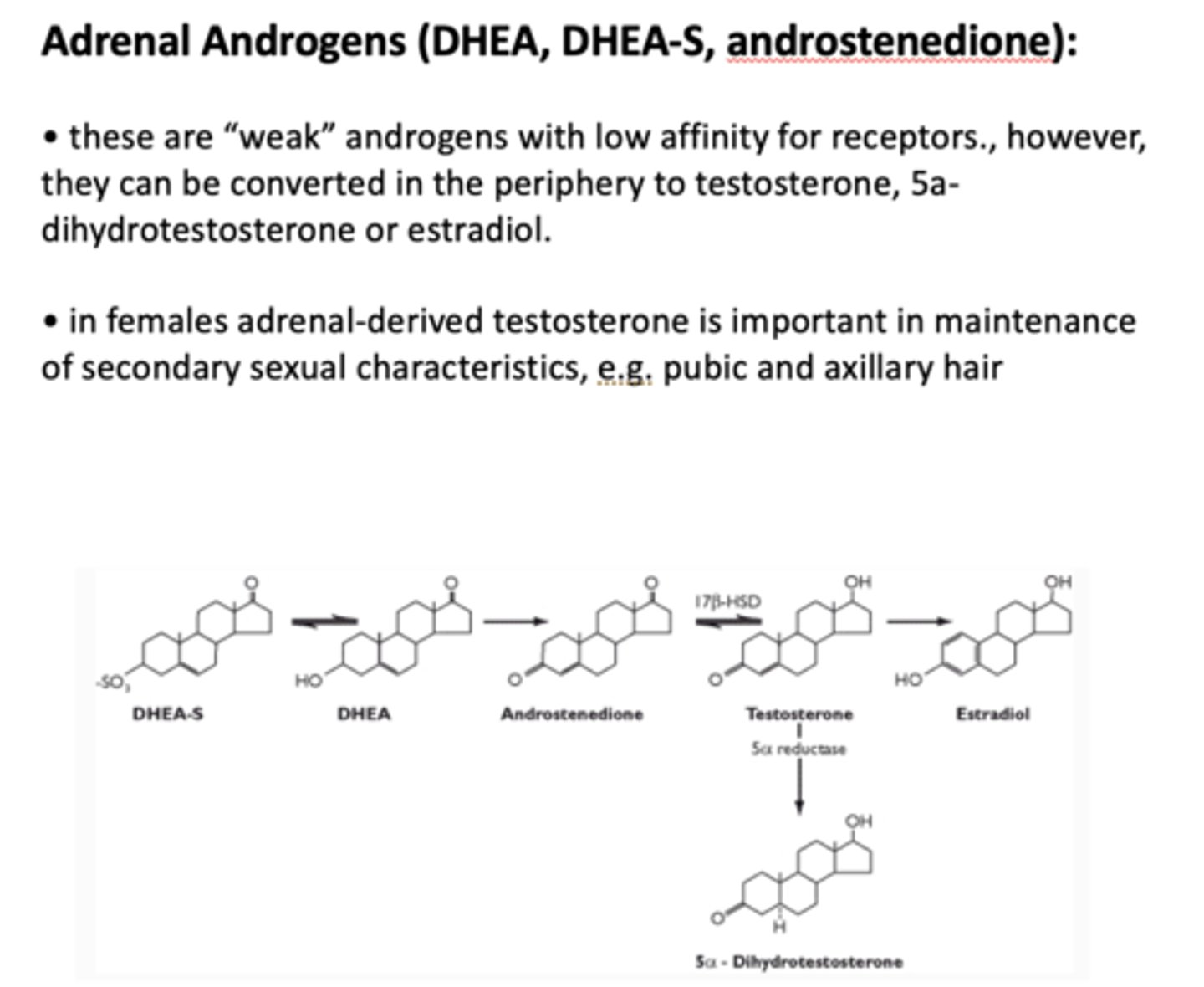
Adrenal androgens (DHEA) are _____ androgens with low affinity for receptors
weak (but can be converted to testosterone)
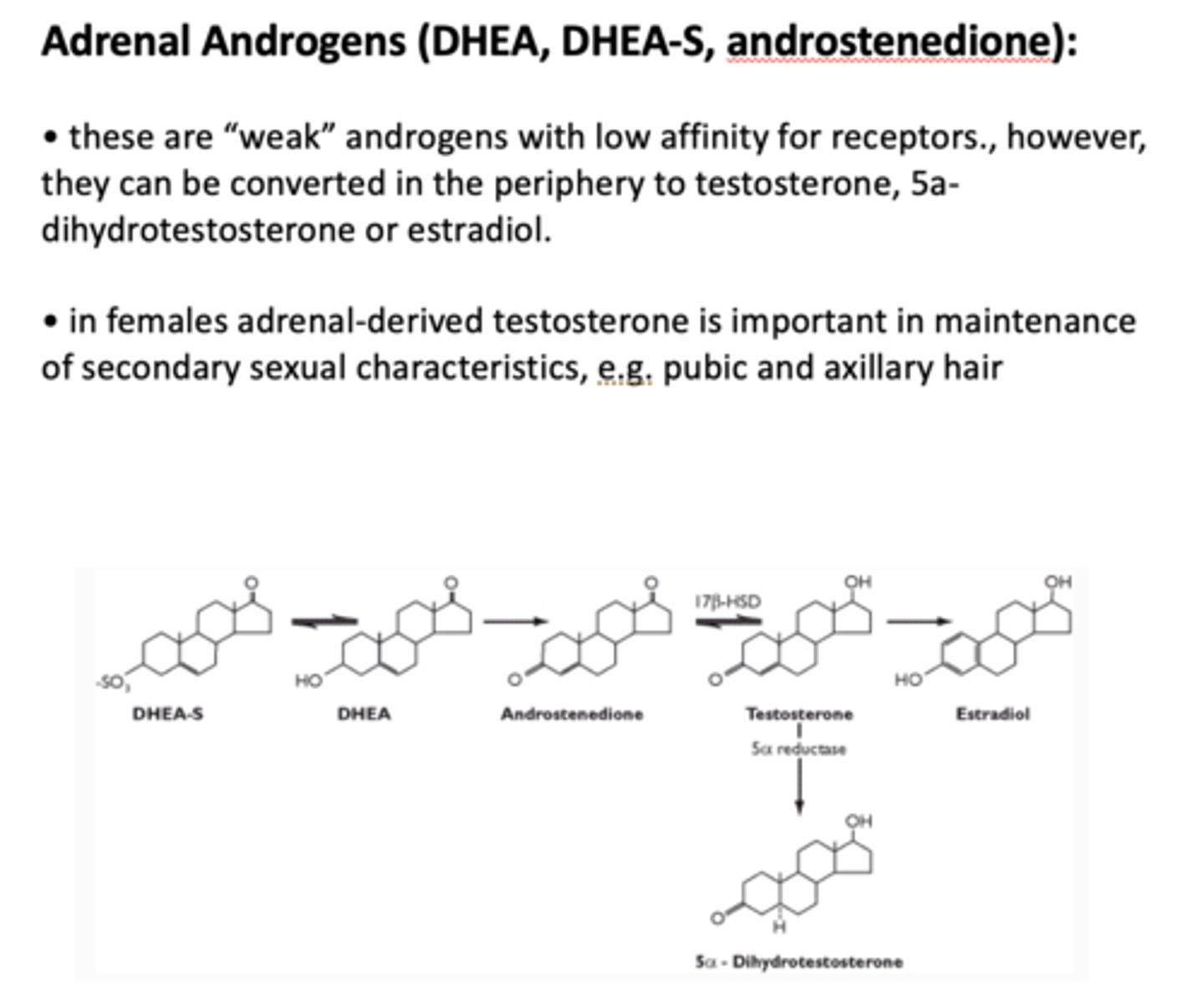
In females, adrenal-derived testosterone is important for what?
secondary sex characteristics
What condition is most commonly caused by exogenous steroid administration?
Cushing's syndrome
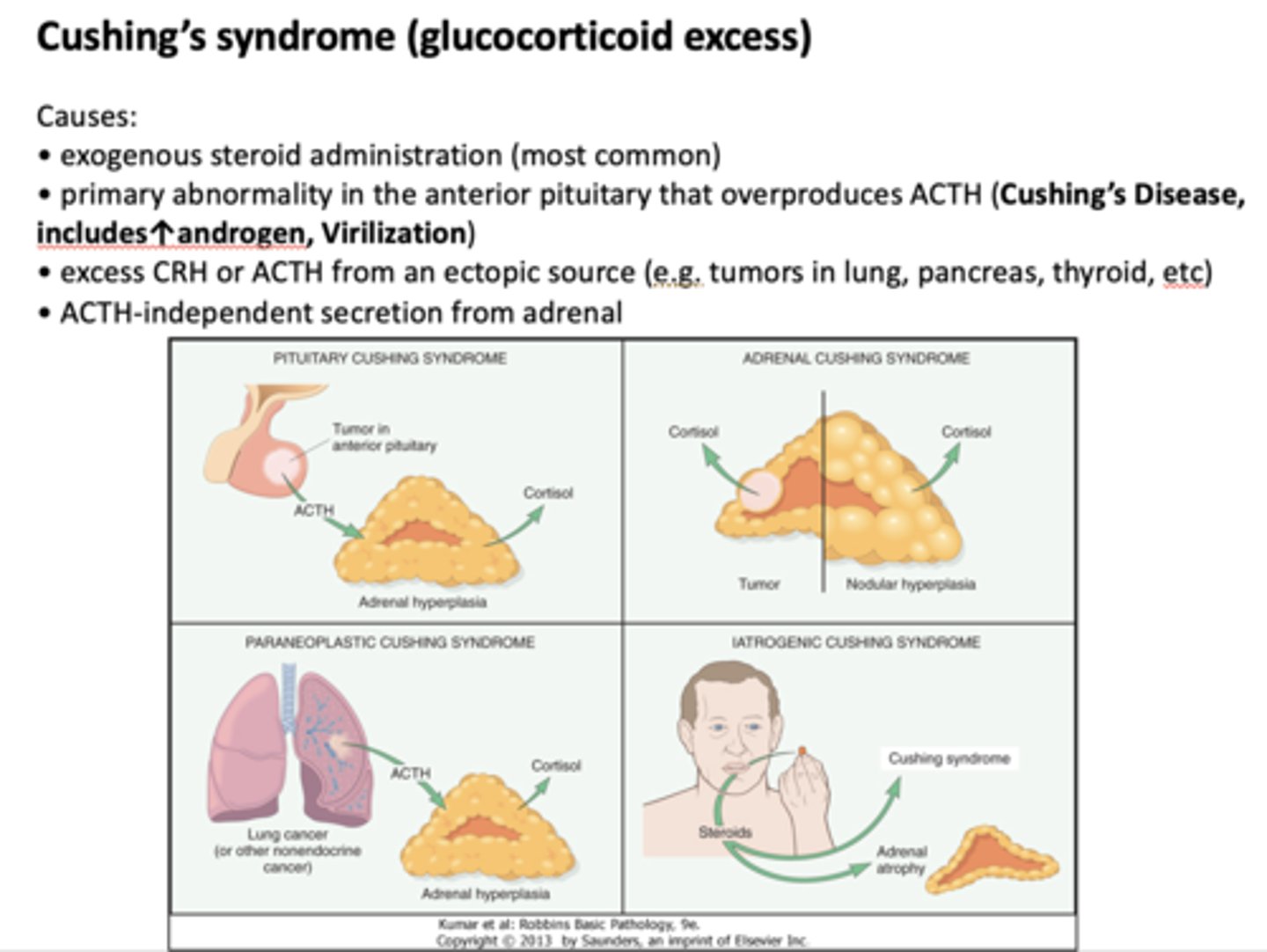
Cushing's syndrome is caused by excess of what?
glucocorticoid excess
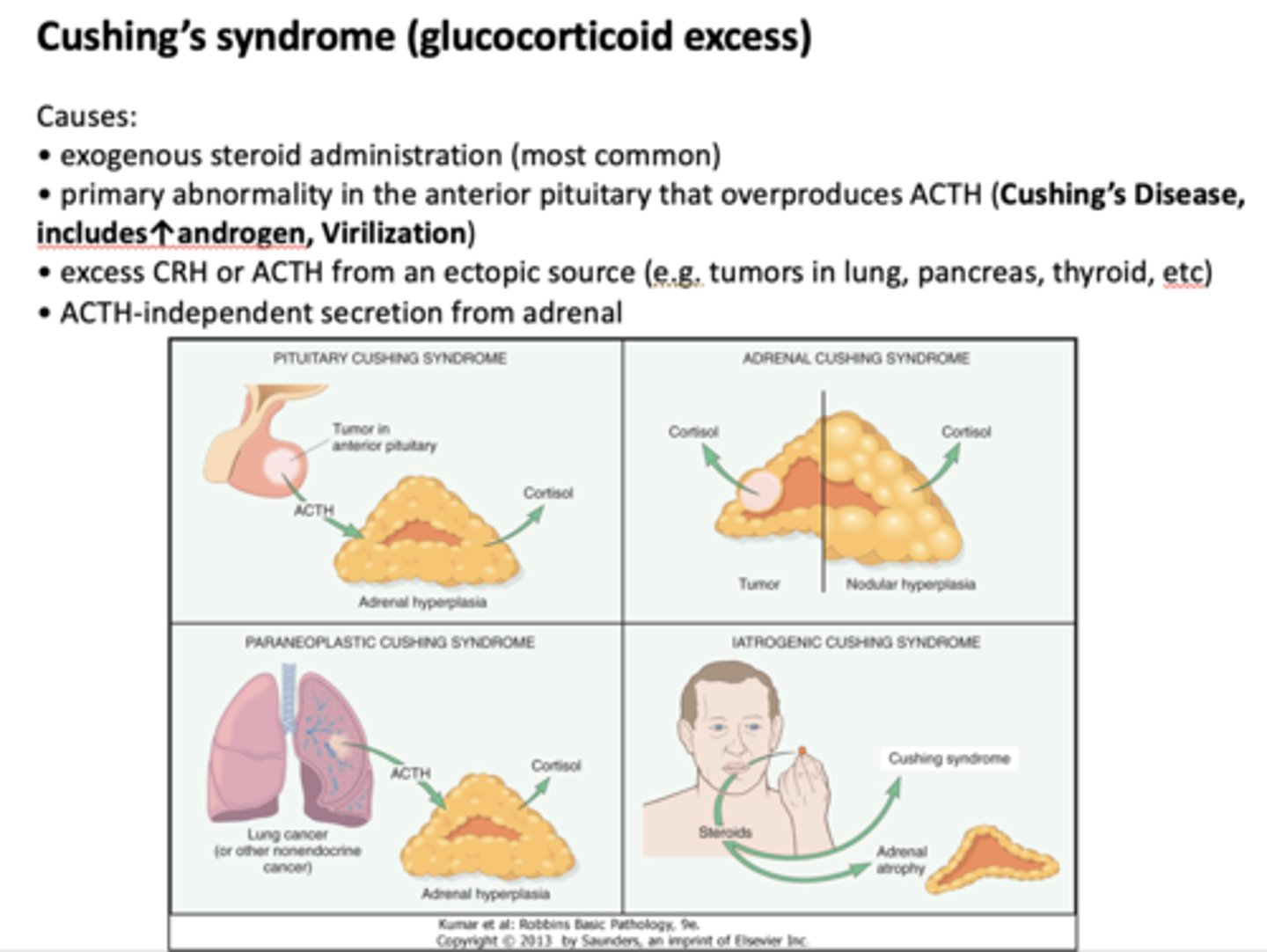
A primary abnormality in the anterior pituitary that leads to cushings disease is caused by what?
ACTH overproduction
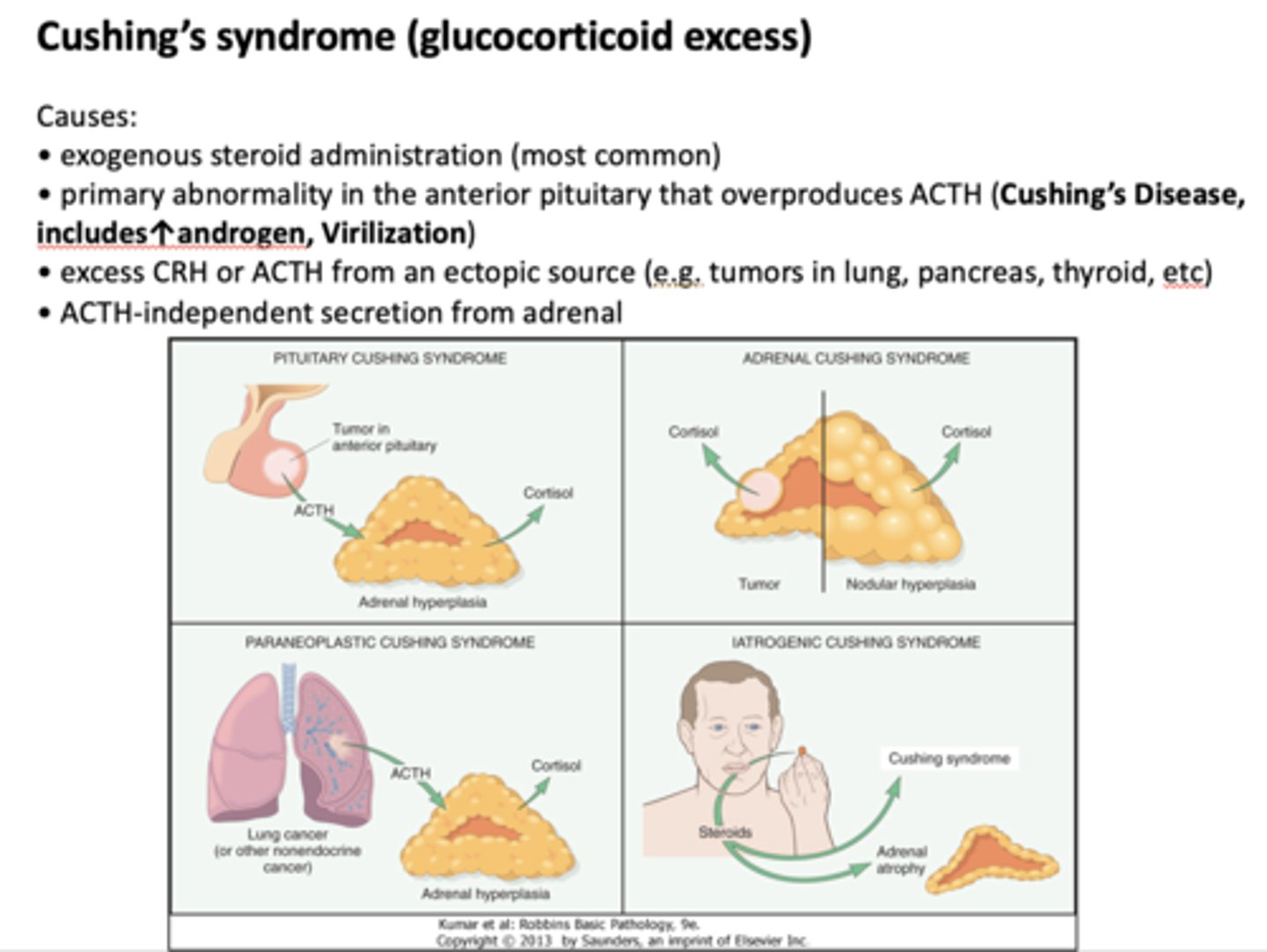
Excess ___________ and ___________ from an eptopic source (tumors in lungs, pancreas, etc) can cause cushings disease
CRH, ACTH
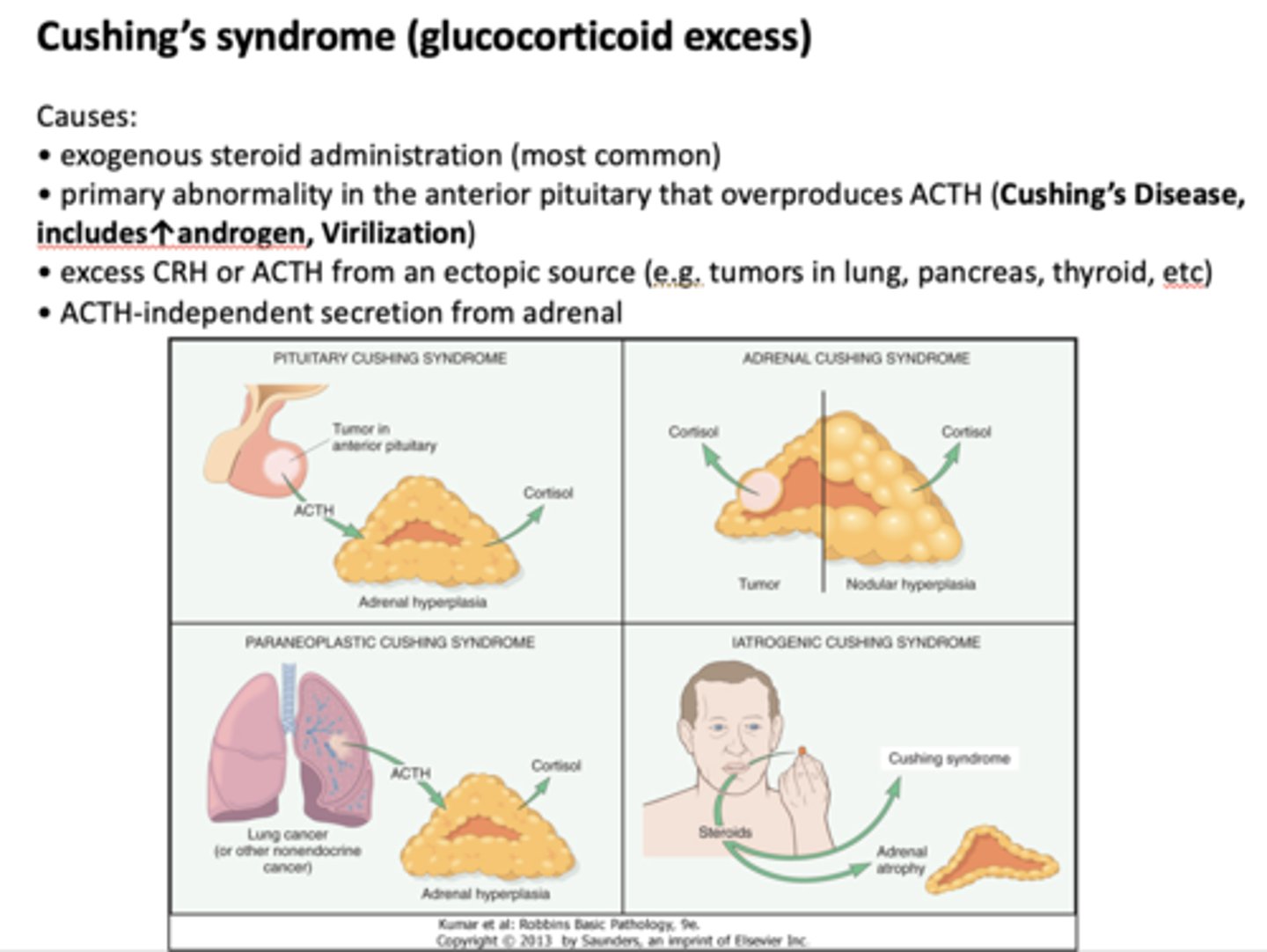
These are symptoms of what?
- Hyperglycemia
- Central obesity
- Virilization
- Skin striae, bruising and poor wound healing due to decreased collagen formation and immune suppression
- Osteoporosis
- Neuropsychiatric disorders
- Moon face
- Buffalo hump
Cushings syndrome
What condition is a primary adrenal insufficiency?
addison's disease
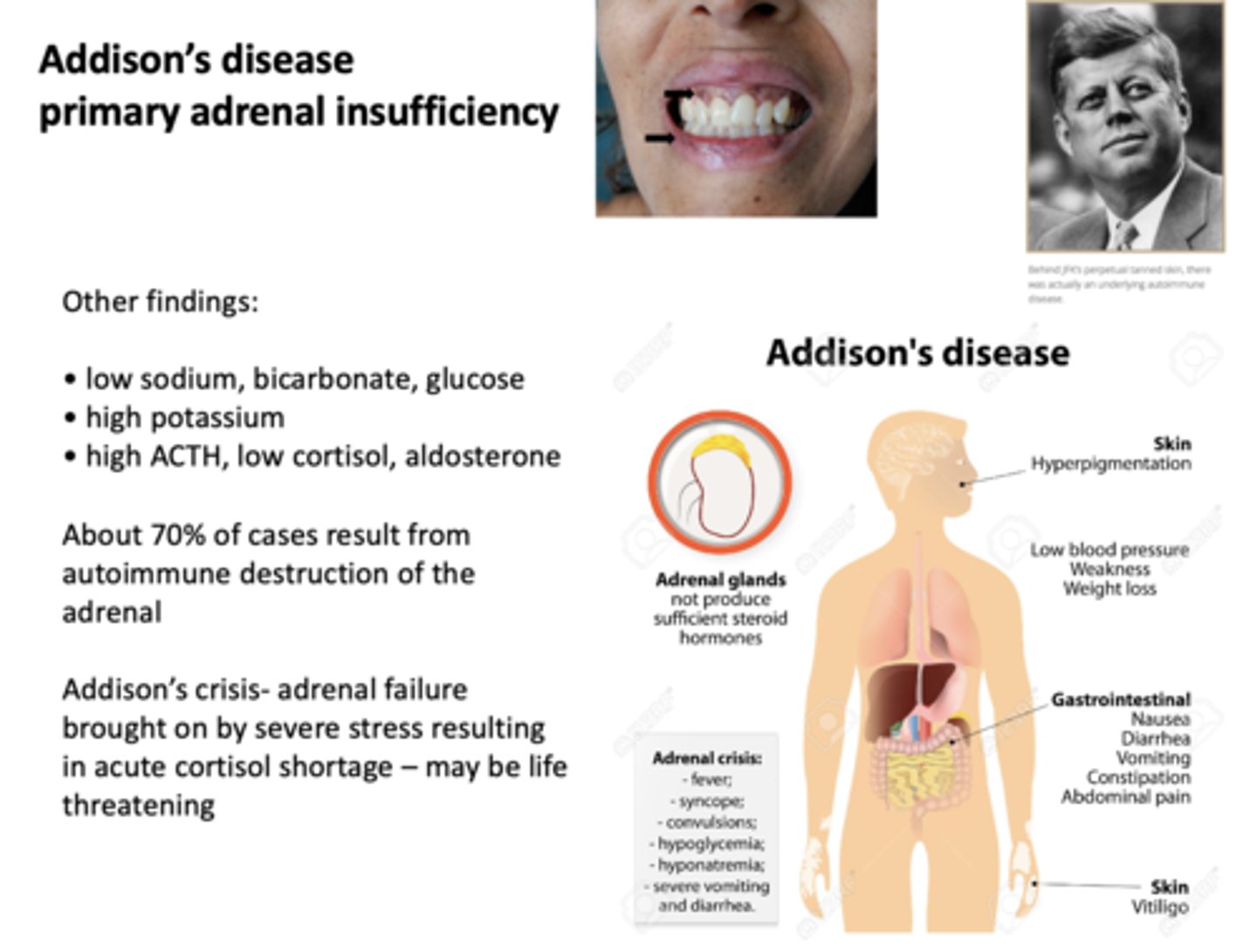
These are other findings of what?
- Low sodium, bicarbonate, glucose
- High potassium
- High ACTH, low cortisol, aldosterone
addison's disease
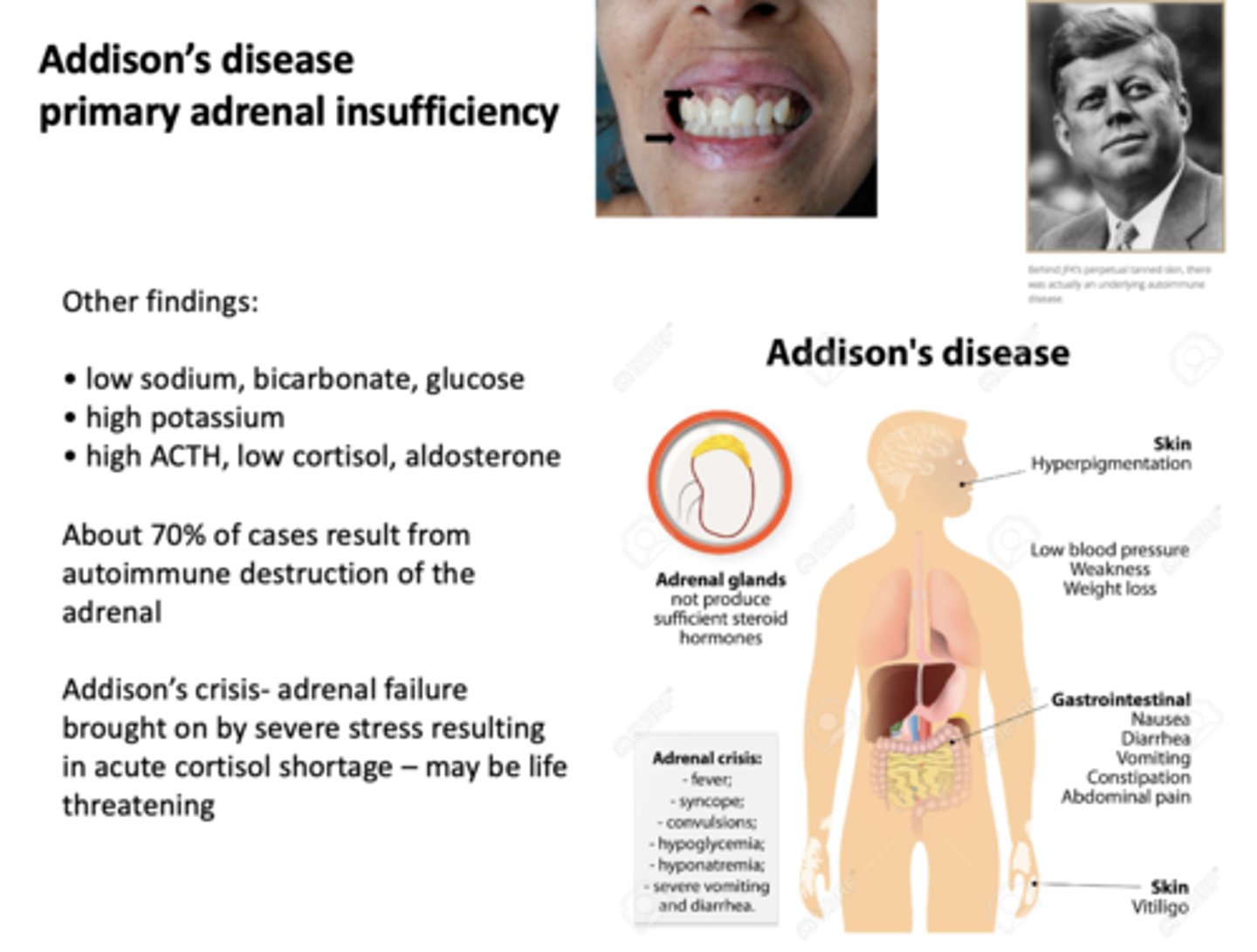
About 70% of Addison's disease are caused by what?
autoimmune destruction of adrenal
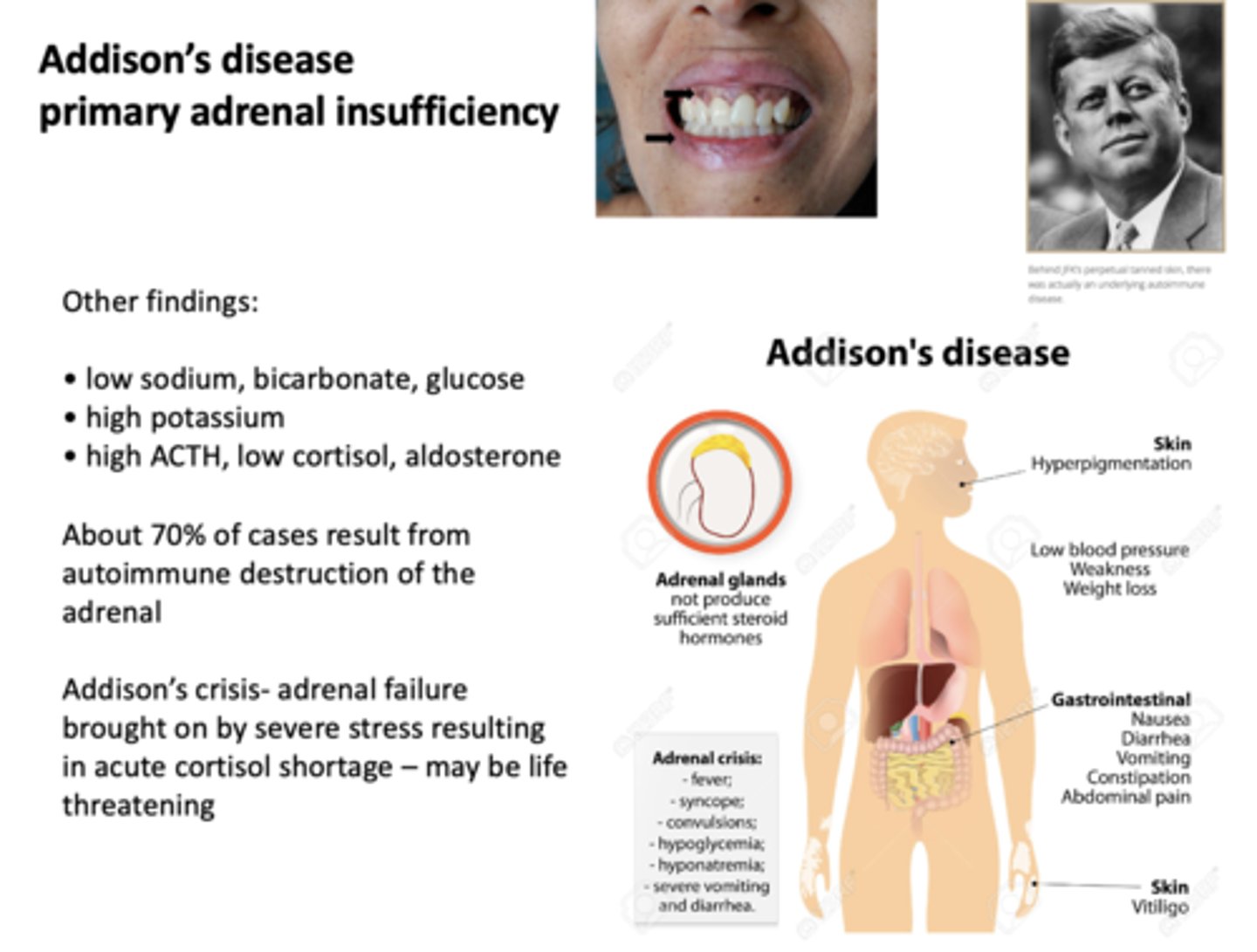
What has the following characteristics?
Adrenal failure brought on by severe stress resulting in acute cortisol shortage - may be life threatening
Addison's crisis
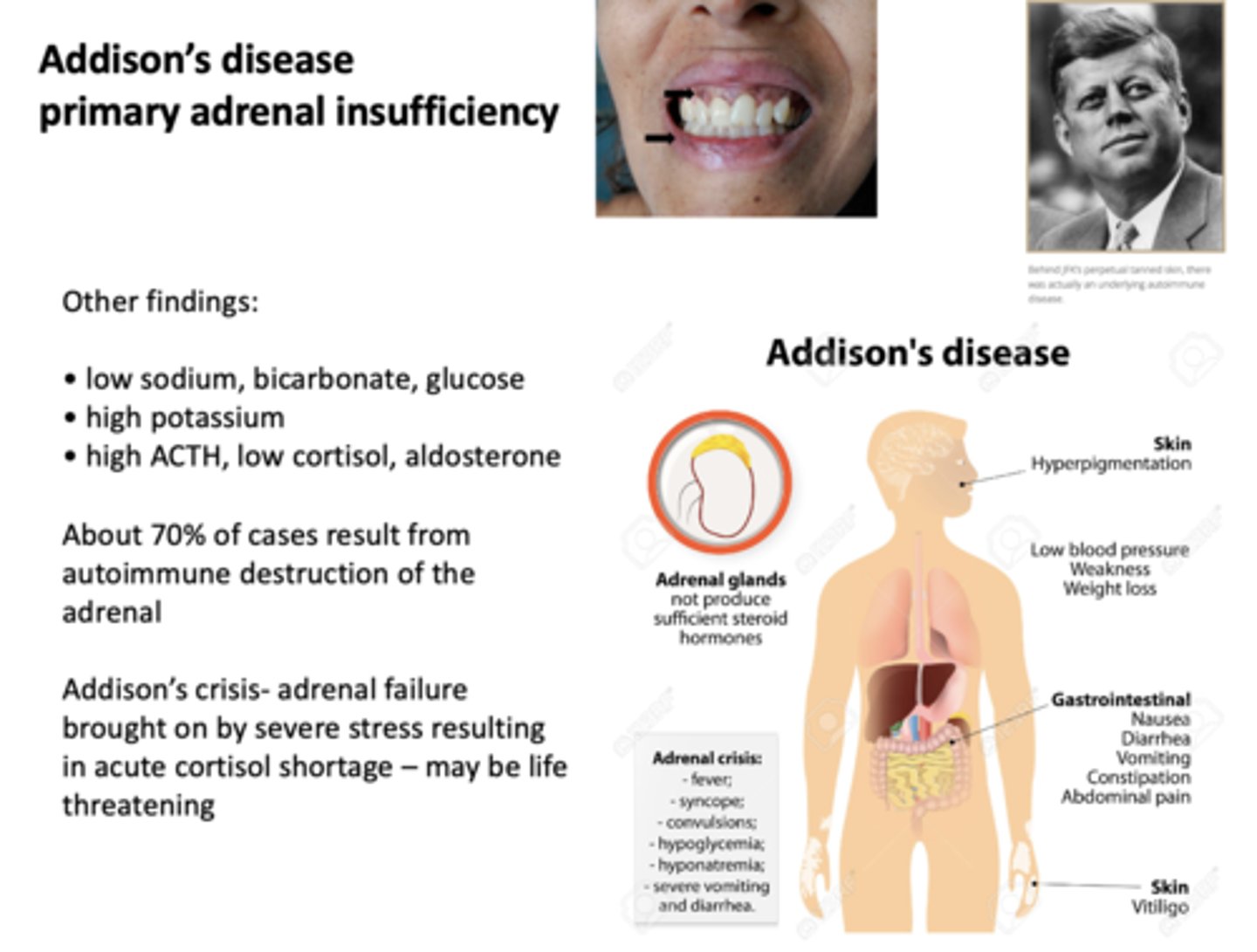
What has the following symptoms:
- Hyperpigmentation
- Low blood pressure (weakness, weight loss)
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomitting
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Vitiligo
Addison's disease
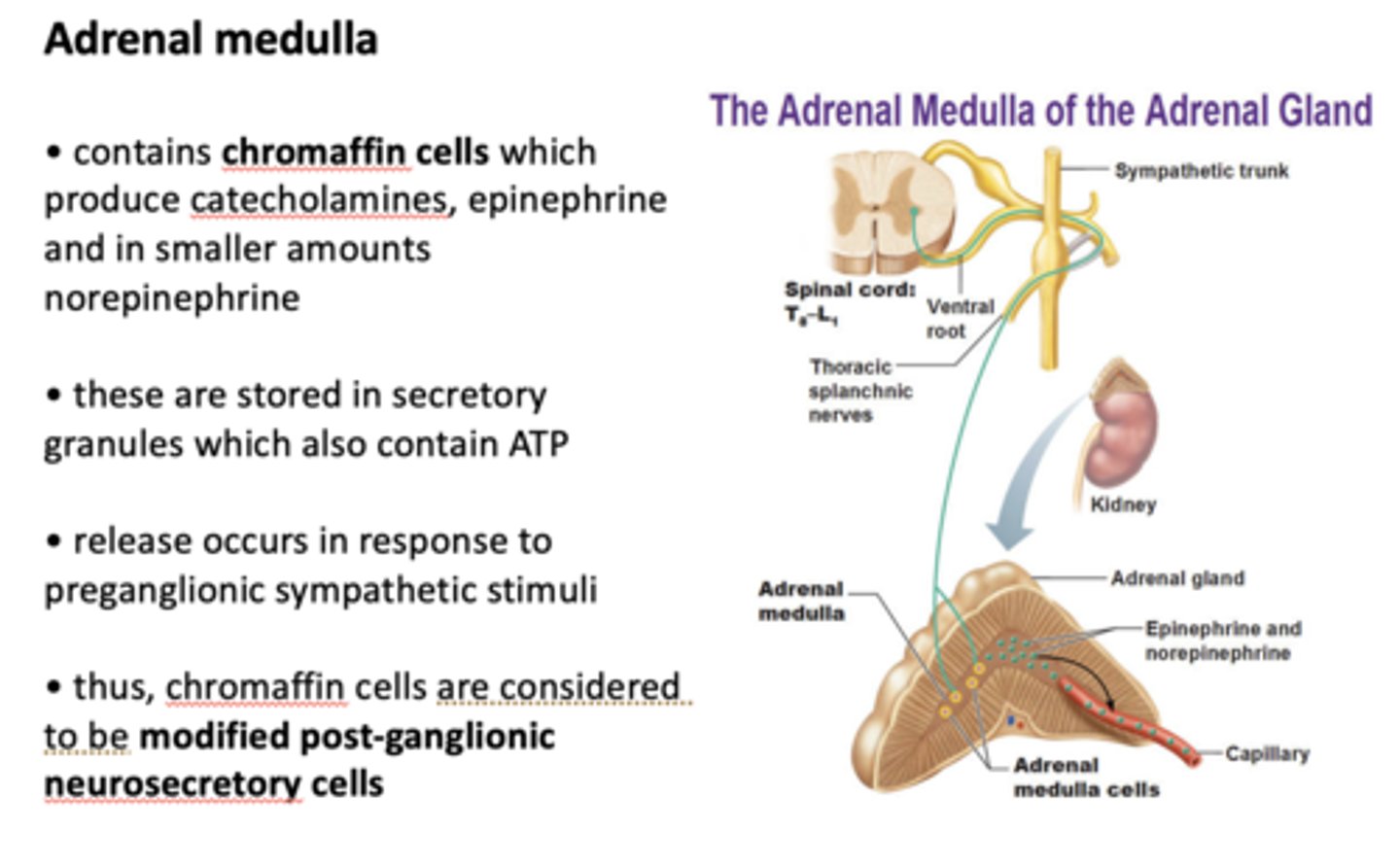
What contains chromaffin cells which produce catecholamines, epinephrine and in smaller amounts norepinephrine?
adrenal medulla
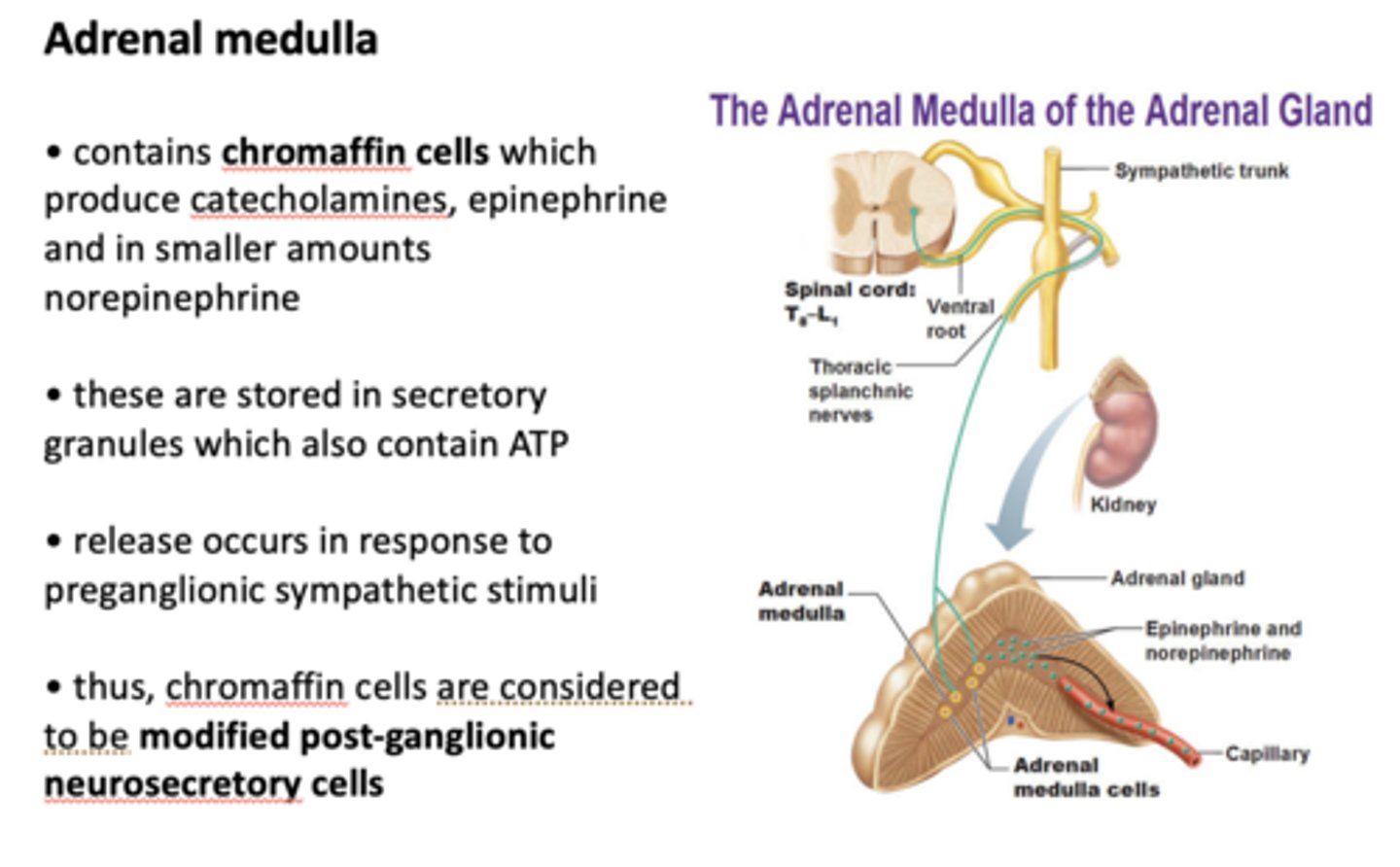
epinephrine and norepinephrine are stored in secretory granules which also contain _____
ATP
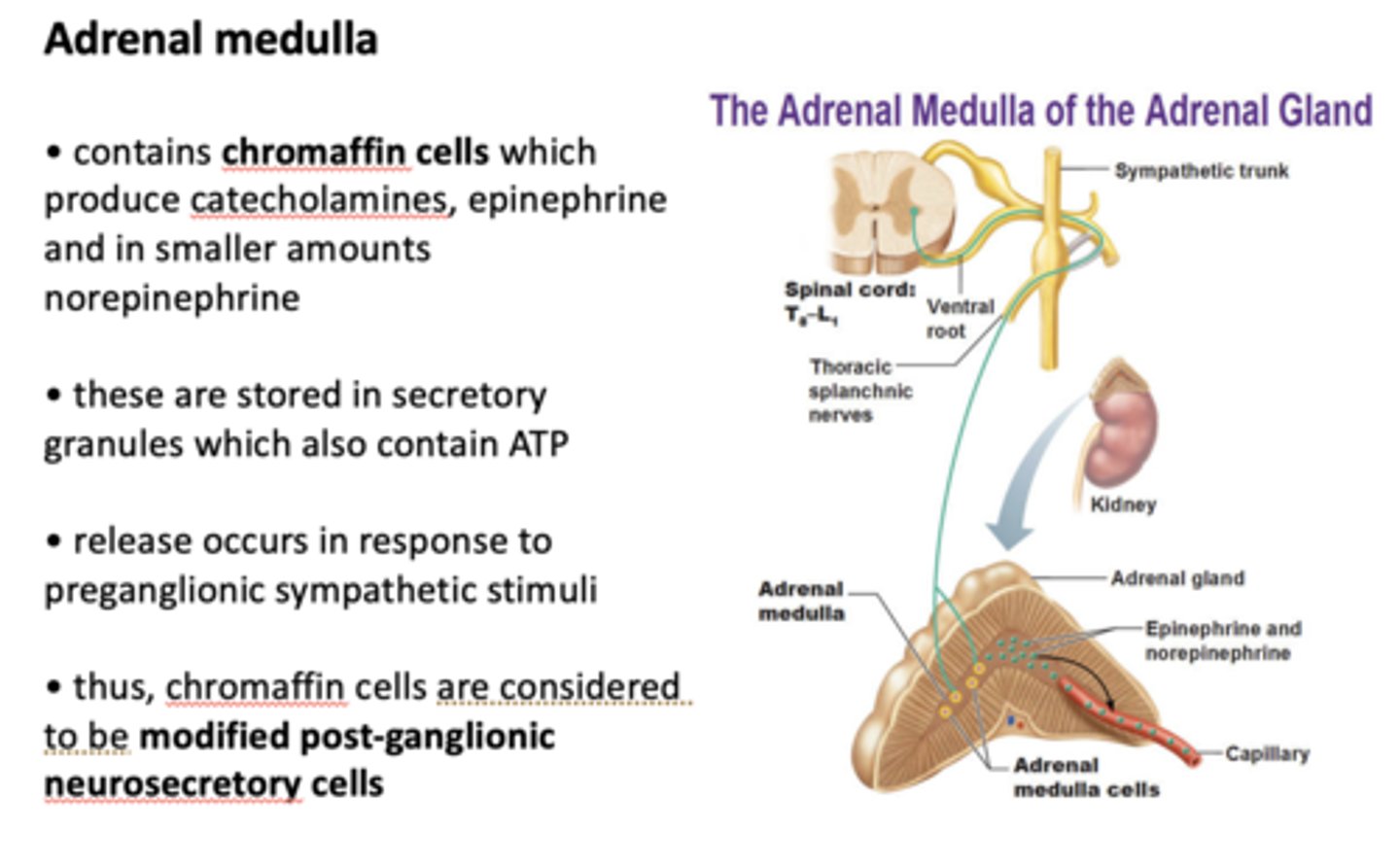
chromaffin cells are considered to be...
modified post-ganglionic neurosecretory cells
What stimulates glycogenolysis in muscle and liver and lipolysis in adipose tissue?
epinephrine

Catecholamines are responsible for what response?
fight or flight
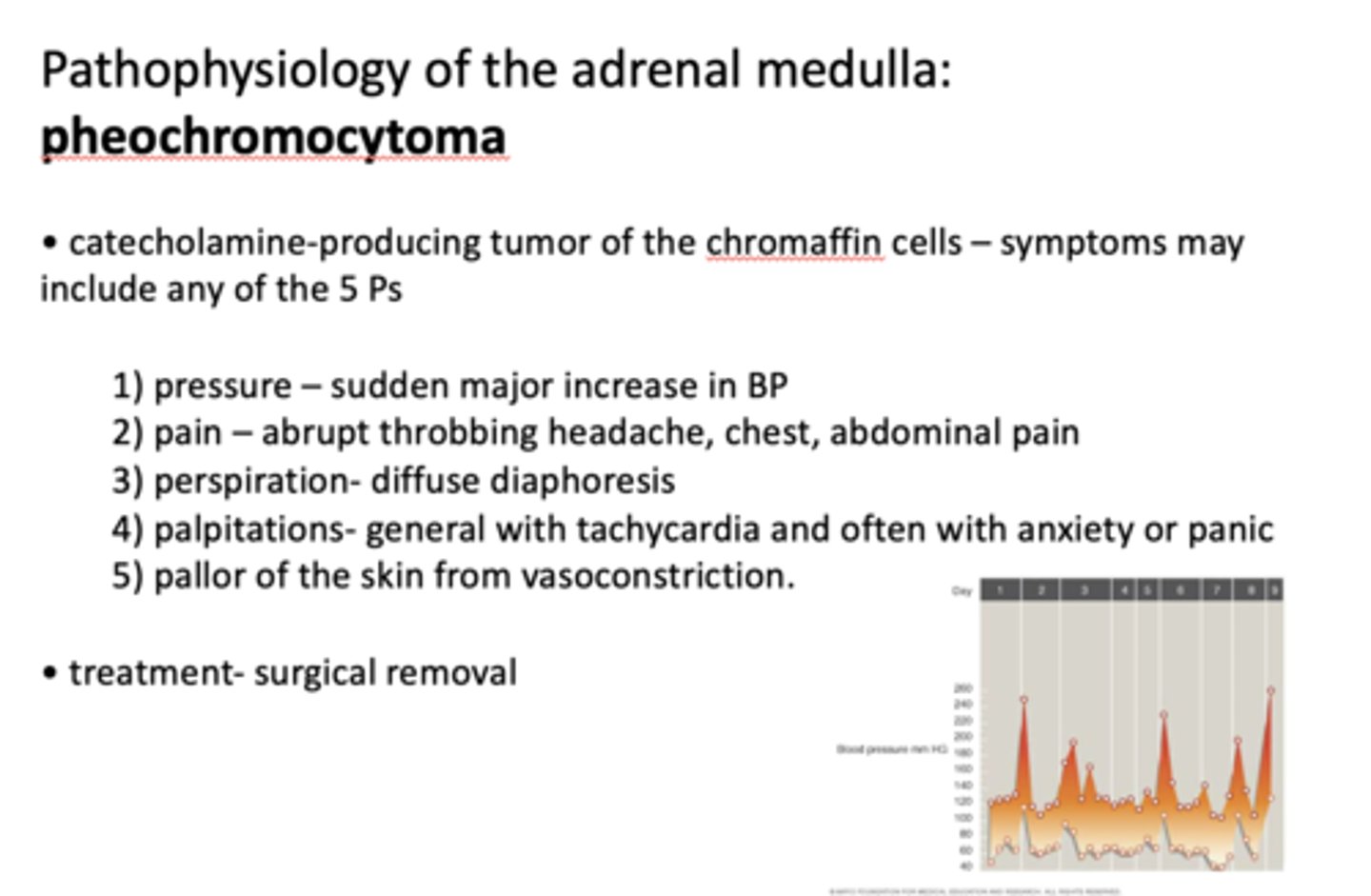
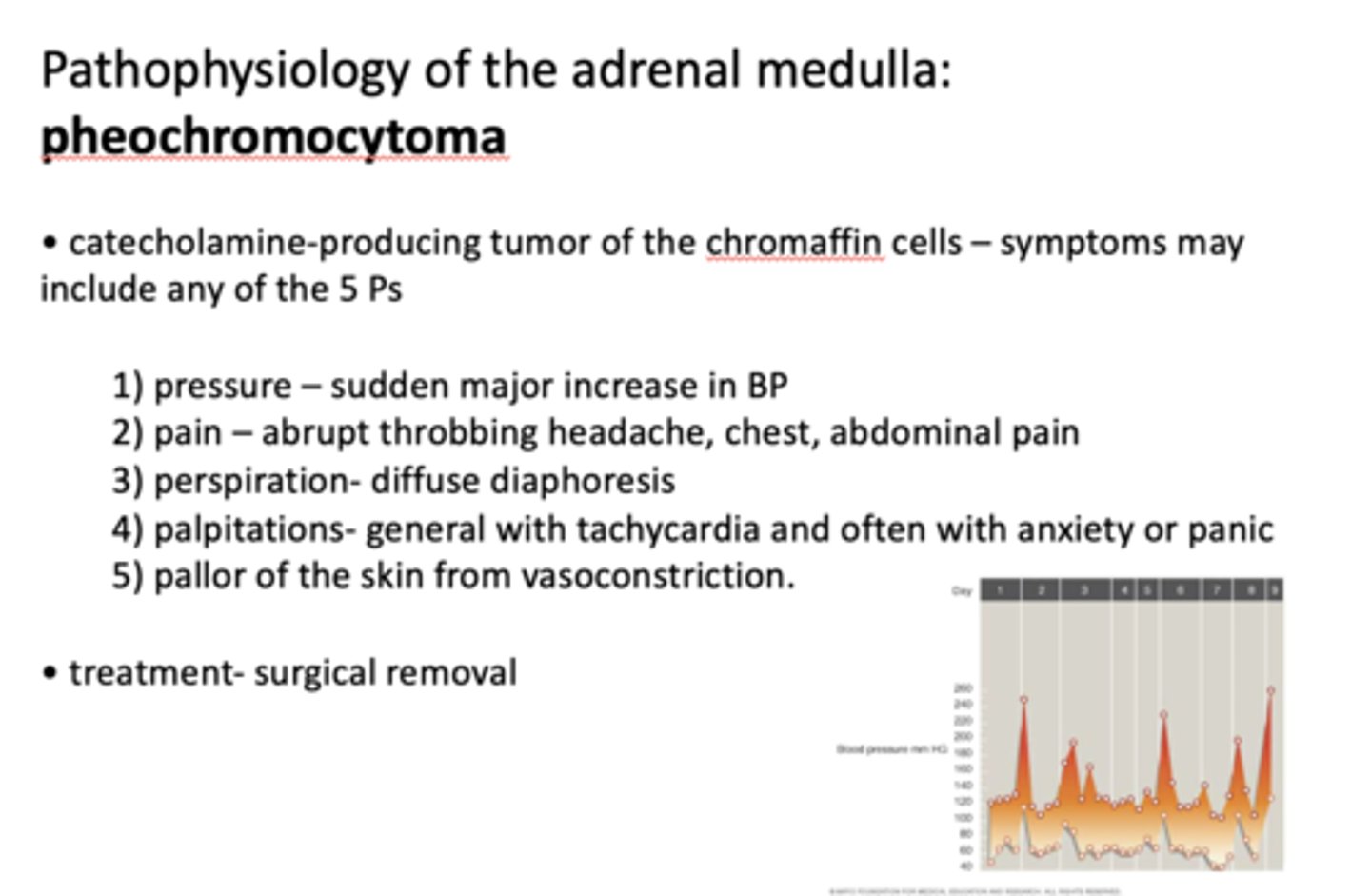
What is pathology of the adrenal medulla?
pheochromocytoma
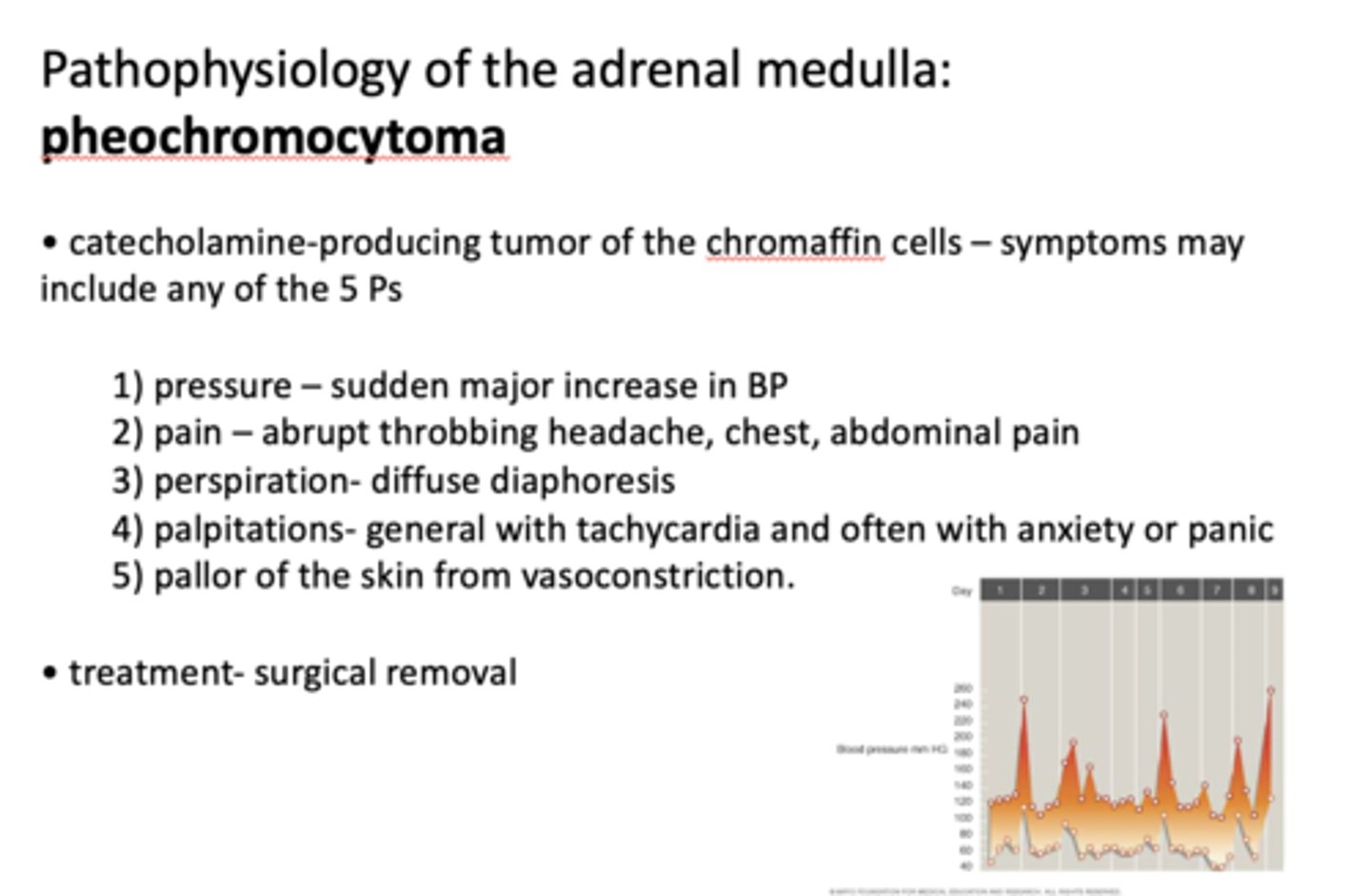
Pheochromocytoma is what?
catecholamine-producing tumor of chromaffin cells
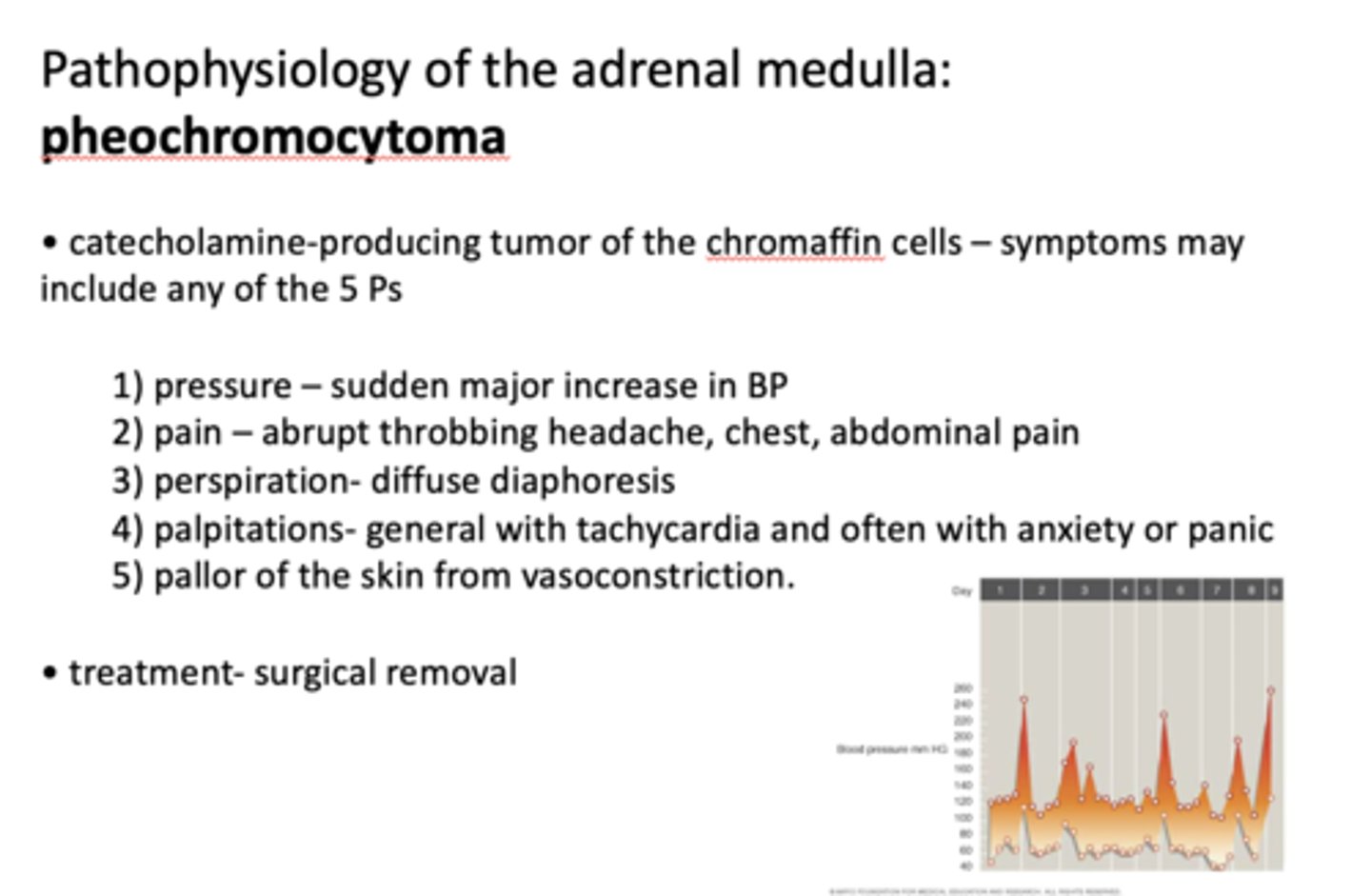
Pheochromocytoma symptoms may include any of the 5 Ps which are...
- Pressure
- Pain
- Perspiration
- Palpatations
- Pallor
Cushing's disease is
A. Caused by chronoic excessive ACTH secretion
B. Due to excessive glucocorticoid feedback inhibition of ACTH release
C. Not associated with darkening of the skin due to excessive
D. Glucocorticoid feedback inhibition of CRH release from the hypothalamus
A. Caused by chronoic excessive ACTH secretion
In woman, Cushing's disease cause masculinization/ Virilization, with increased body hair, acne and irregular menses. Why does cushing's disease have these effects in women?
The adrenal androgens DHEA, DHEAS, and androstenedione are androgen precursors. They can be converted to active androgens peripherally and provide about 50% of circulating androgens in women. In men, the role of adrenal androgens, if any, remains obscure. In women, adrenal androgens promote pubic and axillary hair growth and libido. Excessive adrenal androgens in women can lead to various degrees of virilization and ovarian dysfunction.
Which of the following substances is derived from proopiomelanocortin (POMC)?
A. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
B. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
C. Melatonin
D. Cortisol
E. Dehydroepiandrosterone
A. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)