Equine reproductive physiology
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
what type of oestrus cycle does a mare have?
seasonal polyoestrous
what does seasonal polyoestrous mean?
multiple cycles during one season
what causes cycling in mares and so when is there season?
long days cause cycling and season is April to August usually
what are the three stages of the oestrus cycle?
anoestrus
transition phase
cycling
what occurs during anoestrous?
not cycling, winter months and ovaries are dormant
when does the transition phase occur?
50-70 days prior to first ovulation
what are the two stages in cycling?
dioestrus - 16 days
oestrus - 5 days
how does light affect oestrous?
light detected by eye which then goes to the pineal gland
this activates brain centres
decreased melatonin secretion with decreasing periods of dark
release of gonadotropins (FSH and LH)
activates ovary, which stimulates the development of follicles
Follicles then produce progesterone and oestrogen
influences behaviour and receptivity
changes the uterine environment to produce eggs and allow fertilisation to occur
what hormones do follicles release?
oestrogen and progesterone
what does the release of oestrogen and progesterone from follicles cause?
influences behaviour and receptivity of mare
alters uterine environment to produce eggs and allow fertilisation to occur
ways to manipulate seasonality of mares and stallions?
artificial change to photoperiod by putting mares and stallions under light during winter months
physical change to photoperiod by moving mares and stallions from northern to southern hemisphere biannually
what occurs in oestrus?
luteolysis, follicular phase and oestrogen increase
what happens in dioestrus?
luteal phase, high progesterone
how long is dioestrus and what are the hormone levels?
16 days with high progesterone levels
why is dioestrus the luteal phase?
there is a CL on the ovary
how long is oestrus and what are the hormone levels?
5 days and high oestrogen
why is oestrous the luteolysis phase?
CL is removed and multiple follicles are produced
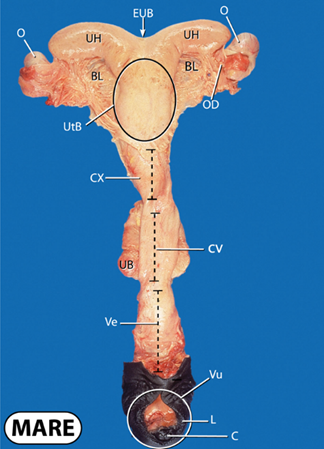
what does O stand for?
ovary
what does UH stand for?
uterine horns
what does BL stand for?
broad ligament
what does EUB stand for?
external uterine body

what does OD stand for?
oviduct
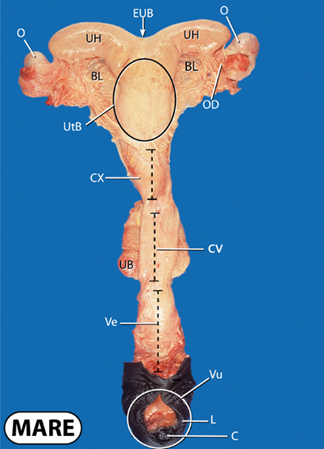
what does UtB stand for?
uterine body
what does CX stand for?
cervix
what does UB stand for?
urinary bladder
what does CV stand for?
cervical canal
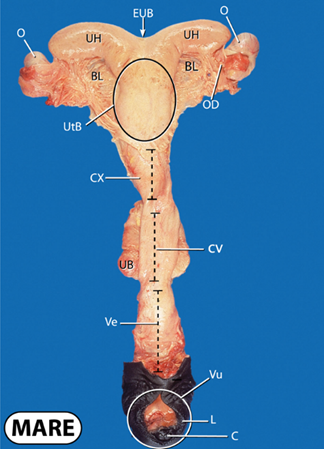
what does Ve and Vu stand for?
vestibule and vulva
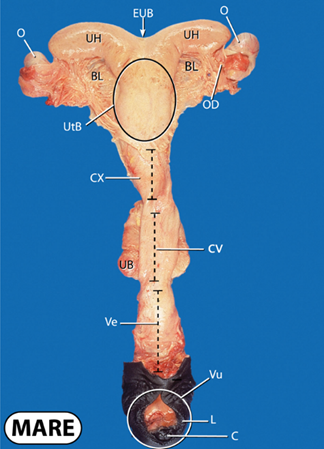
what does L and C stand for?
labia and clitoris
what is the clitoris a key area for with disease control?
key sampling point for venereal pathogen screening prior to breeding
what happens between day 2-6 with follicles?
multiple follicles form due to the 1st FSH peak
what happens to follicles between day 8-12?
follicles grow due to 2nd FSH peak
what happens to follicles day 16-18?
dominant follicle grows at a faster rate and the other follicles begin to regress
what happens at day 21?
follicle lysis and ovulation occurs due to LH
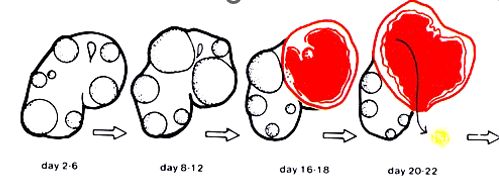
explain what is happening to the follicles at each stage
day 2-6 multiple follicles have formed due to 1st FSH peak
day 8-12 follciles are growing due to 2nd FSH peak
day 16-18 the dominant follicles grow faster and the other begin to regress
day 21 follicle lysis and ovulation due to LH
what does ovulation occur via?
ovulation fossa
what happens when the follicle ovulates?
oocyte is released
captured by fimbria of infundibulum
enters oviduct
what happens to the development of an egg if fertilisation occurs?
the fertilised embryo/egg enters uterus and develops
what happens to the egg if it is not fertilised?
oocyte degenerates in oviduct
what happens to the follicle post ovulation?
day 1-4 the ruptured follicle fills with blood and becomes corpus haemorrhagicum
day6-10 it differentiates into corpus luteum and secretes progesterone
when the CL is secreting progesterone which phase is this?
dioestrus/luteal phase
how does the CL secrete progesterone?
consists of luteal cells which secrete the progesterone
what is the definition of a CL?
soft tissue structure which releases progesterone and maintains pregnancy
what happens to CL if pregnant or not pregnant?
pregnant = CL remains
not pregnant = CL lysed by prostaglandin F2alpha
what does progesterone levels indicate the presence of?
a CL
what happens to the levels of progesterone after ovulation in mares?
rises rapidly
what is progesterone useful for measuring?
stage of cycle/ovulation
what else can be used alongside progesterone levels to monitor mares oestrus cycle?
palpation and ultrasound examination of the ovaries per rectum
what does <0 levels of progesterone show?
no CL and oestrus/anoestrus stage
what does 2.5 level of progesterone show?
CL present and dioestrus (early/late)
what does level 20 of progesterone show?
CL present and dioestrus
how do you monitor the levels of progesterone in the blood?
ELISA
when does true implantation occur?
at day 35
what happens with true implantation?
conceptus held stationary within uterine wall
sustains conceptus for remainder of gestation
what happens to the mares immune system at true implantation?
maternal immunological recognition of pregnancy
no longer seen as foreign body and prevents abortion
what is the allantochorion?
definitive placenta which sustains foetus
gas exchange occurs
what is the amnion?
surrounds foetus
poorly vascularised
what is the umbilicus?
connects allantochorion placenta to foetus
where does gas exchange happen between mother and foetus?
gas exchange and nutrient exchange occurs at the allantochorion interface with endometrium
what happens after gas exchange?
blood is then transported from the periphery of the placenta to the umbilical cord where it enter the foetus
how does oxygenated and deoxygenated blood enter and exit the foetus?
oxygen rich blood enter via umbilical vein and CO2 rich blood leaves via umbilical arteries
how does nutrient exchange vary between other animals and mares?
in other animals they have cotyledons whereas horses have micro cotyledons
what do mature endometrial cups secrete?
equine chorionic gonadotropins (eCG)/ pregnant mare serum gonadotropin (PMSG)
when are micro cotyledons fully present?
day 150-term
how are micro cotyledons present on the placenta?
they are diffusive across the whole outer layer
what stimulates parturition?
foetal hormonal signals
what are the three stages of parturition?
initiation of myometrial contractions 1-4 hours
expulsion on the foetus (within its amnion) 10-30 minutes
expulsion of the foetal membranes via additional abdominal contractions up to 3-4 hours post foaling
what would be the normal time placenta should have been passed?
1 hour
what prevents foals getting too big in the mares?
when foetus is at full size which is limited to the size of the placenta of the mare it secretes hormones ready for birth
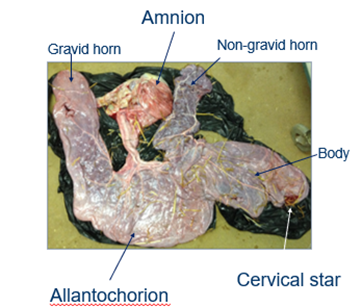
what is the gravid horn?
where the foal developed in the uterus
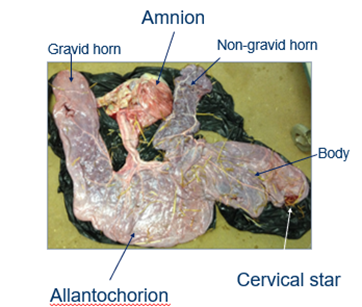
what is the non gravid horn?
the horn the foal didn’t develop in
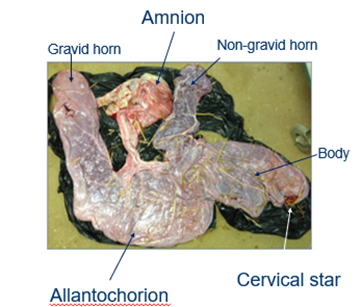
what is the cervical star?
where the placenta attaches to the cervix
what must you check once placenta has been excreted?
that it is fully intact by laying out in F shape
when do foals usually stand and suckle after birth?
attempt to stand within 30 minutes and suckle within 2 hours
when should foals get their colostrum intake?
24-36 hours
what happens when the tip of the non-gravid horn is left in the mare?
can cause sepsis and can lead to laminitis
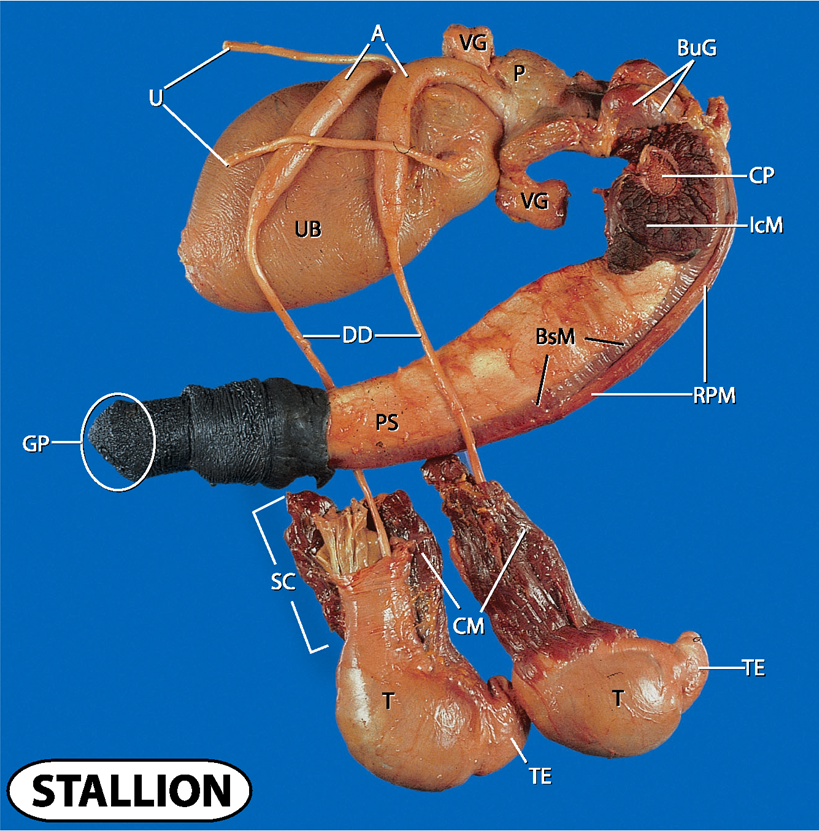
what does A and U stand for?
Ampulla and ureters
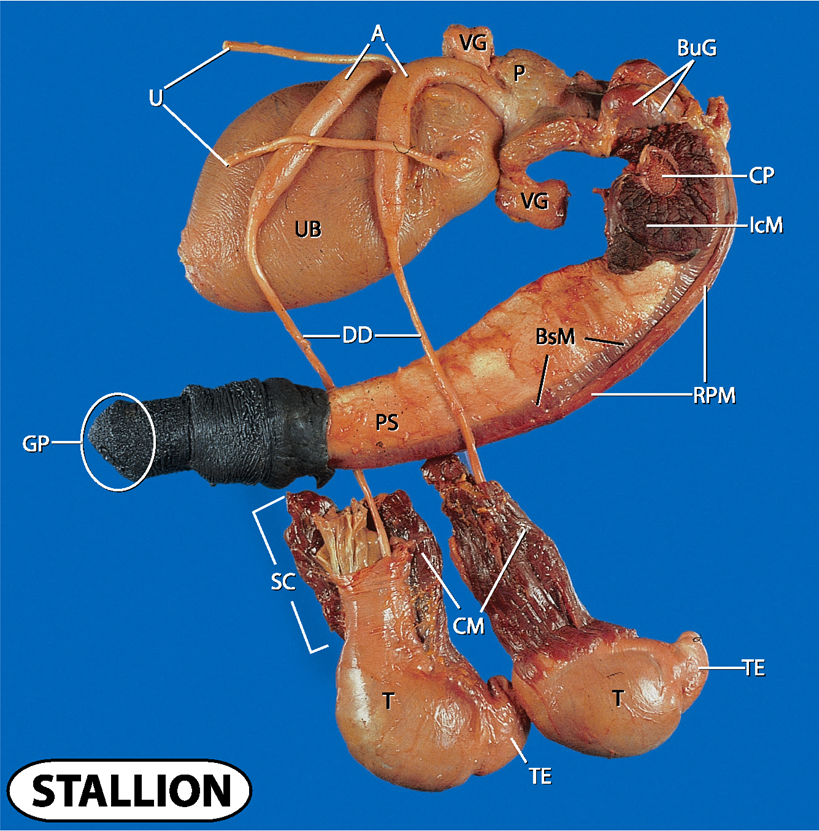
what does UB and VG stand for?
urinary bladder and vesicular glands
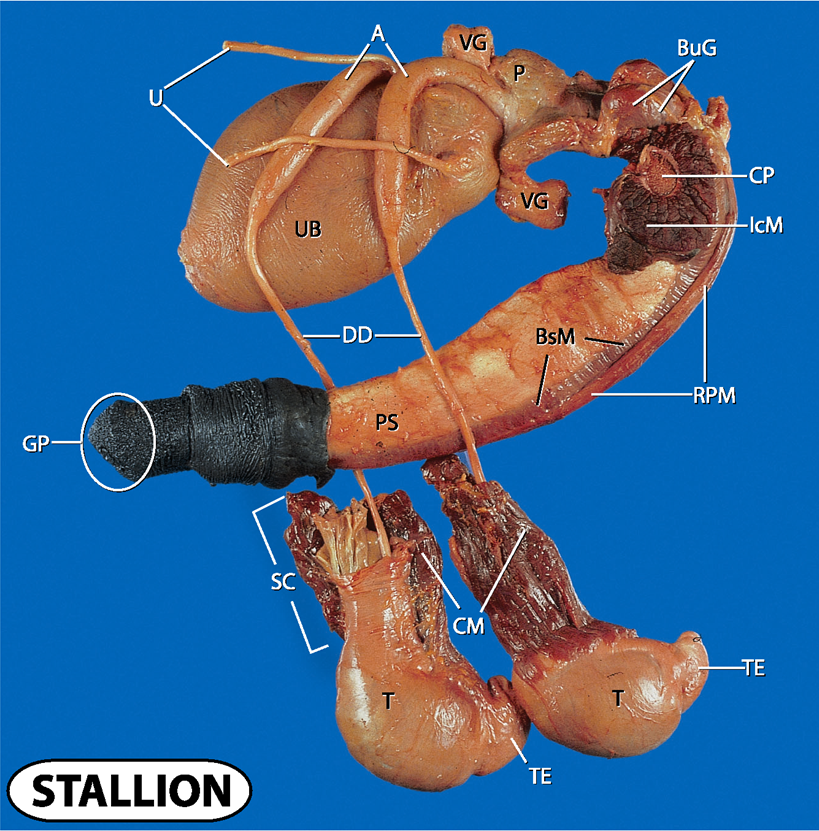
what does P, CP and BuG stand for?
prostate, crus penis and bulbourethral glands
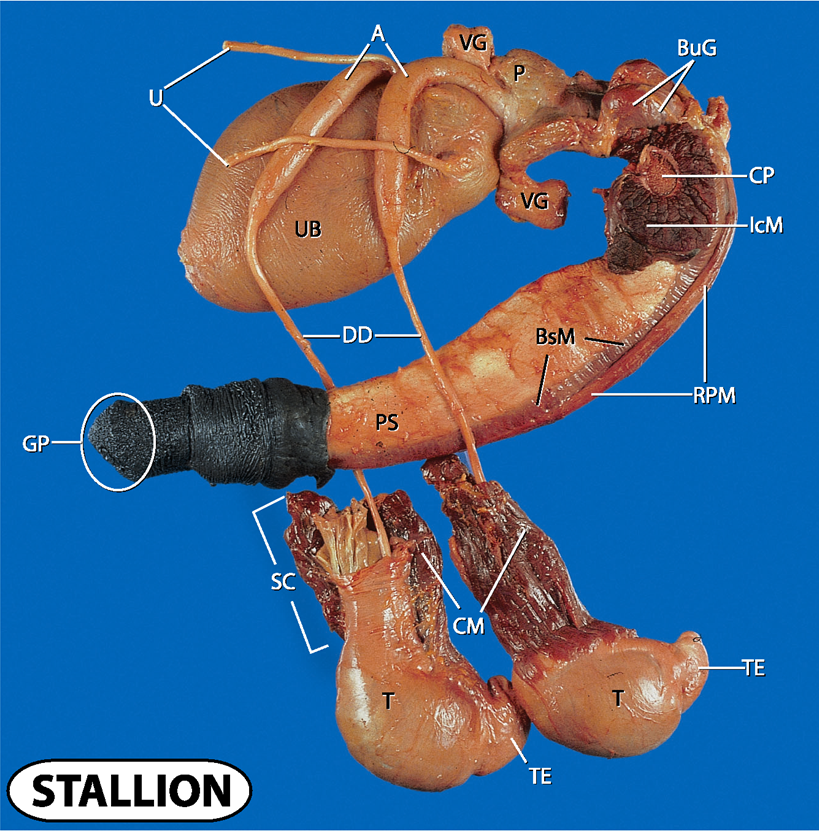
what does IcM, BsM and RPM stand for?
ischocavernosus muscle, bulbospongiosus muscle and retractor penis muscle
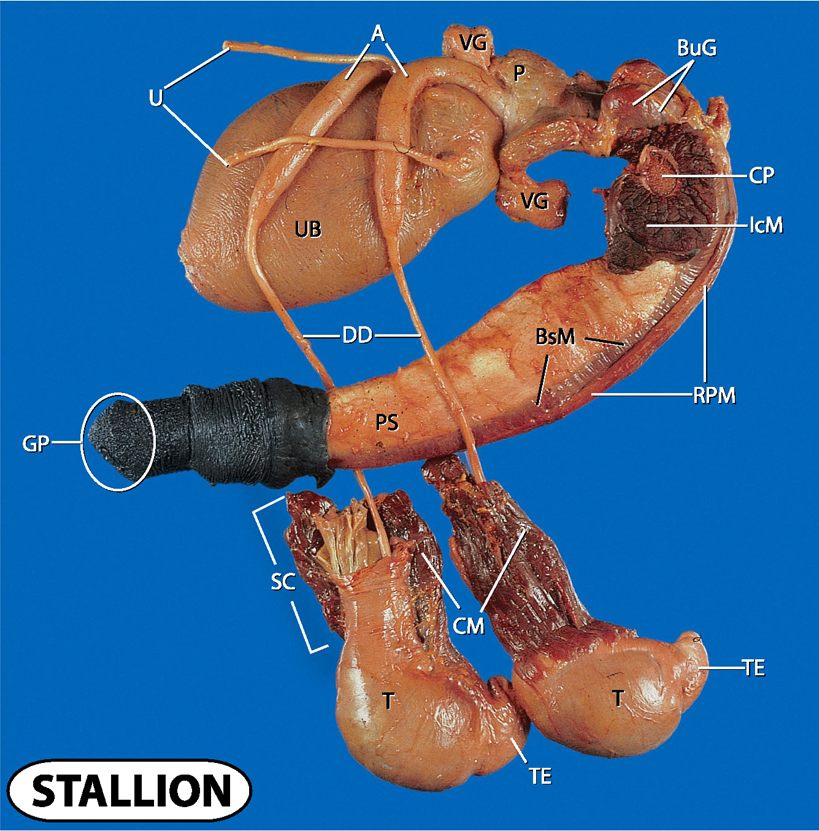
what does UB and DD stand for?
urinary bladder and ductus deferens
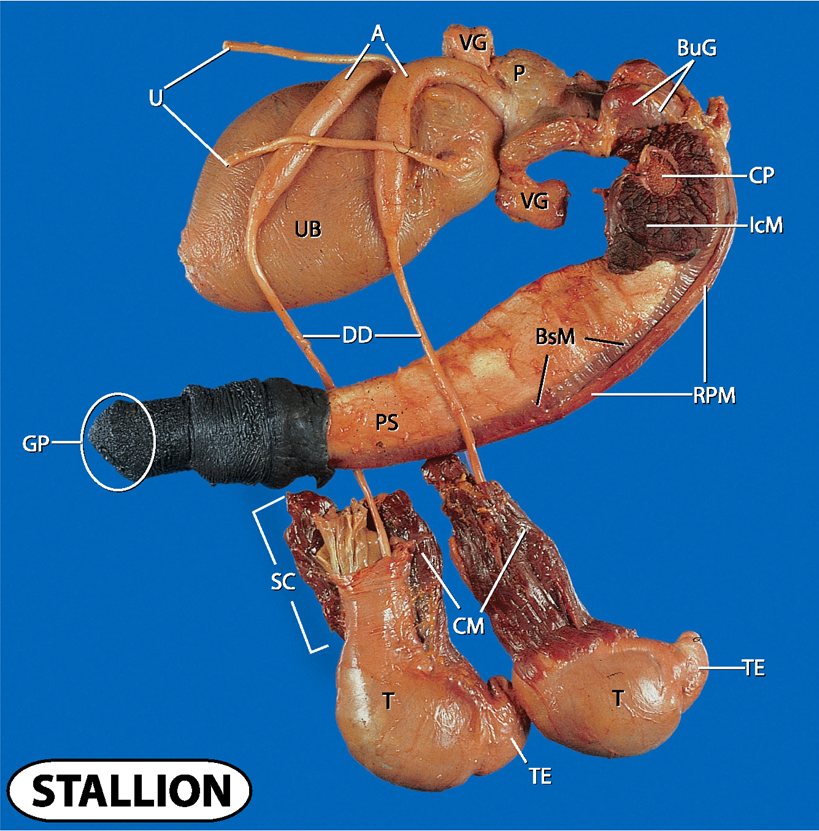
what doe PS and GP stand for?
penis shaft and gland penis
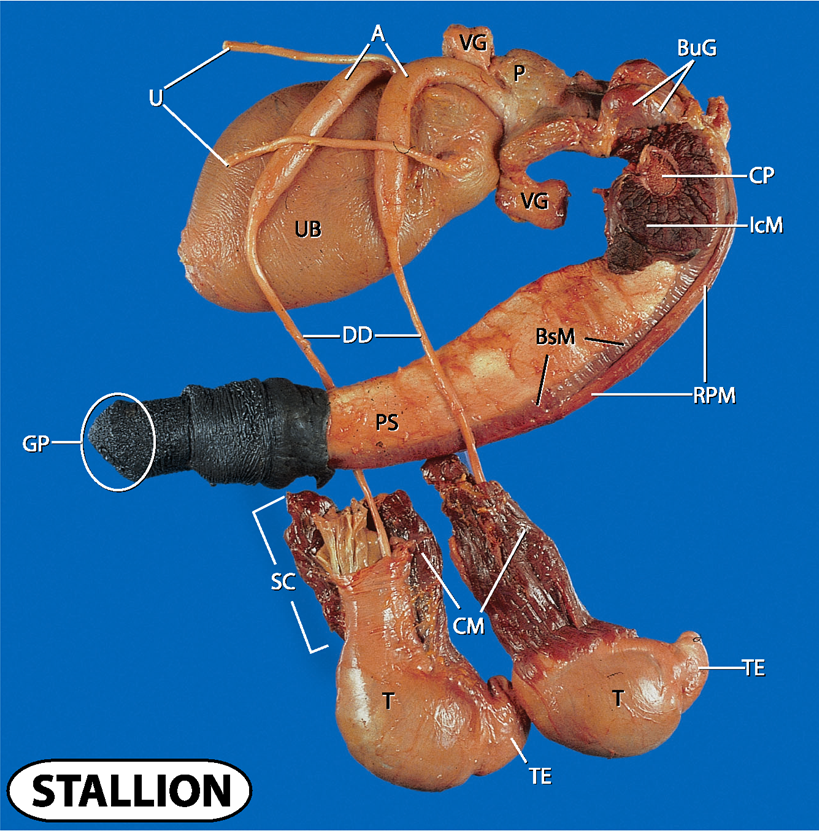
what does SC, CM, T and TE stand for?
spermatic cord
cremaster muscle
testes and tail of epididymis
what happens in the testes?
spermatogenesis and testosterone release
what happens in the epididymis?
spermatozoa maturation for 9 days
what does the spermatic cord do?
suspends testicles within the scrotum
what does the ductus deferens do?
transports semen from epididymis
what is the important role of the cremaster muscle?
temperature regulation of the testes as they have to be 4-6c cooler than the body temp
what does the ischiocavernosus muscles and the retractor penis muscles do?
IcM = maintains erection
RPM = retracts penis when not in use
what does the ureter do?
transports urine from kidneys to the bladder