5&6: Beats, Doppler Effect, and Human Hearing in SPH 3U1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Beat
A periodic change in sound intensity caused by the interference between two nearly identical sound waves.
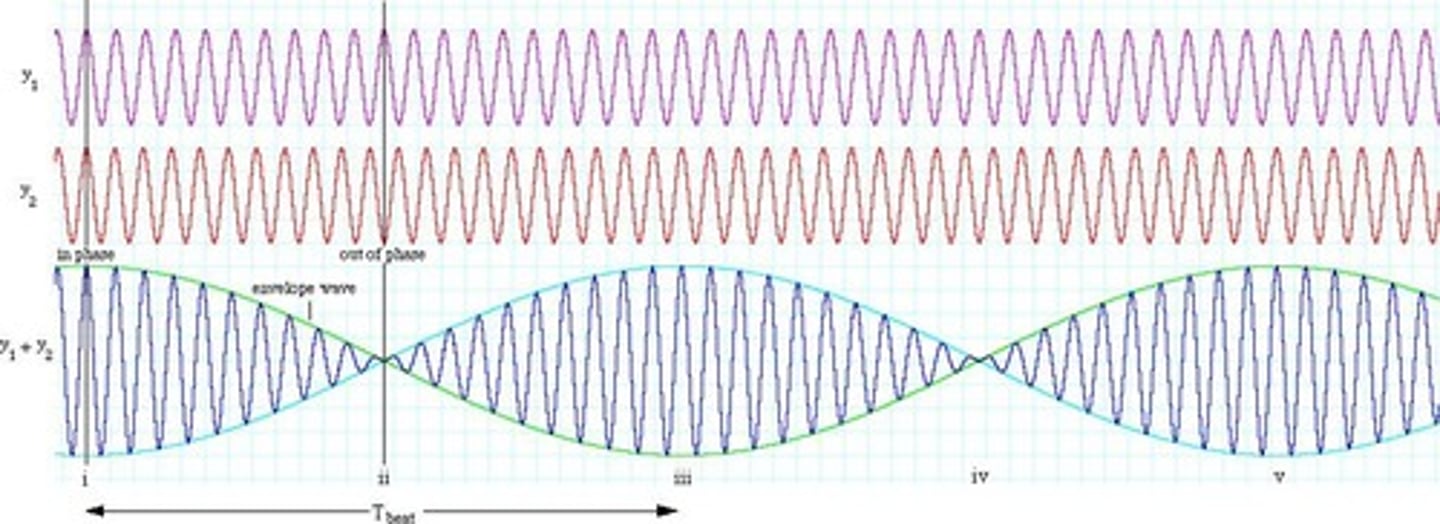
Beat frequency
The frequency of beats produced by the interference of two waves with slightly different frequencies.
Beat frequency formula
Beat frequency = |f1 - f2|
Example of beat frequency
A beat frequency of 6 Hz is heard when two notes are played. If one note is known to be 512 Hz, the frequency of the other note can be calculated.
Doppler Effect
When a source of sound approaches an observer, the observed frequency of the sound increases; when the source moves away from an observer, the observed frequency of the sound decreases.
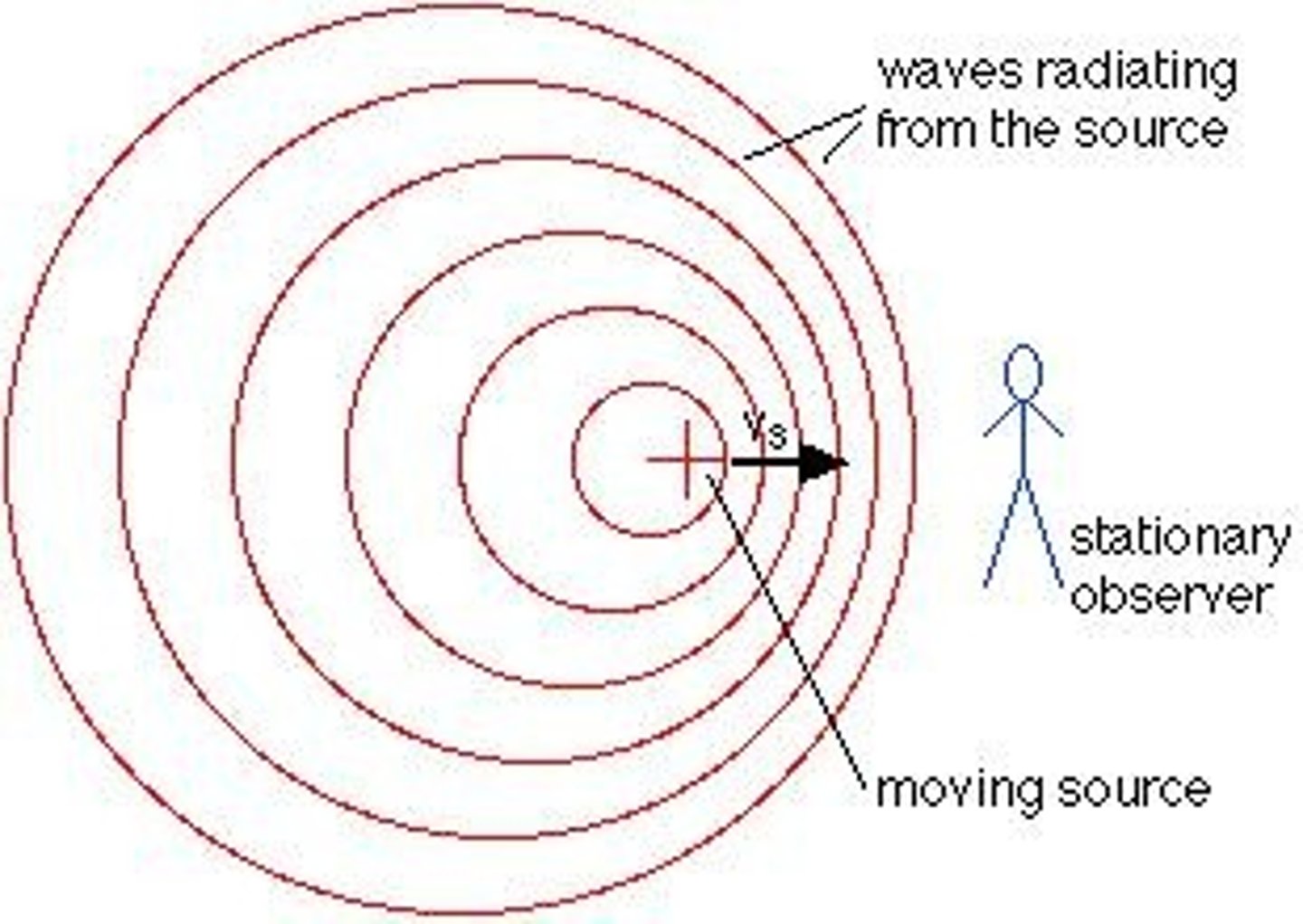
Wavelength change in Doppler Effect
As the source moves towards an observer, the distance between the wave crests is decreased, therefore the wavelength decreases.
Wavelength change when moving away
As the source moves away from an observer, the distance between the wave crests is increased, therefore the wavelength increases.
Universal Wave Equation
States that the frequency will change; increasing when the wavelength decreases, and decreasing when the wavelength increases.
Doppler Effect calculation variables
fobs - observed frequency, f - frequency of the source, v - speed of sound, vs - speed of the source.
Doppler Effect source movement
If the source is moving towards the observer, use '-'; if the source is moving away from the observer, use '+'.
Doppler Effect frequency detection
Calculate the frequency detected by the observer as the fire truck approaches and after it passes by.
Pinna
The outer ear that directs sound waves into the auditory canal toward the middle ear.
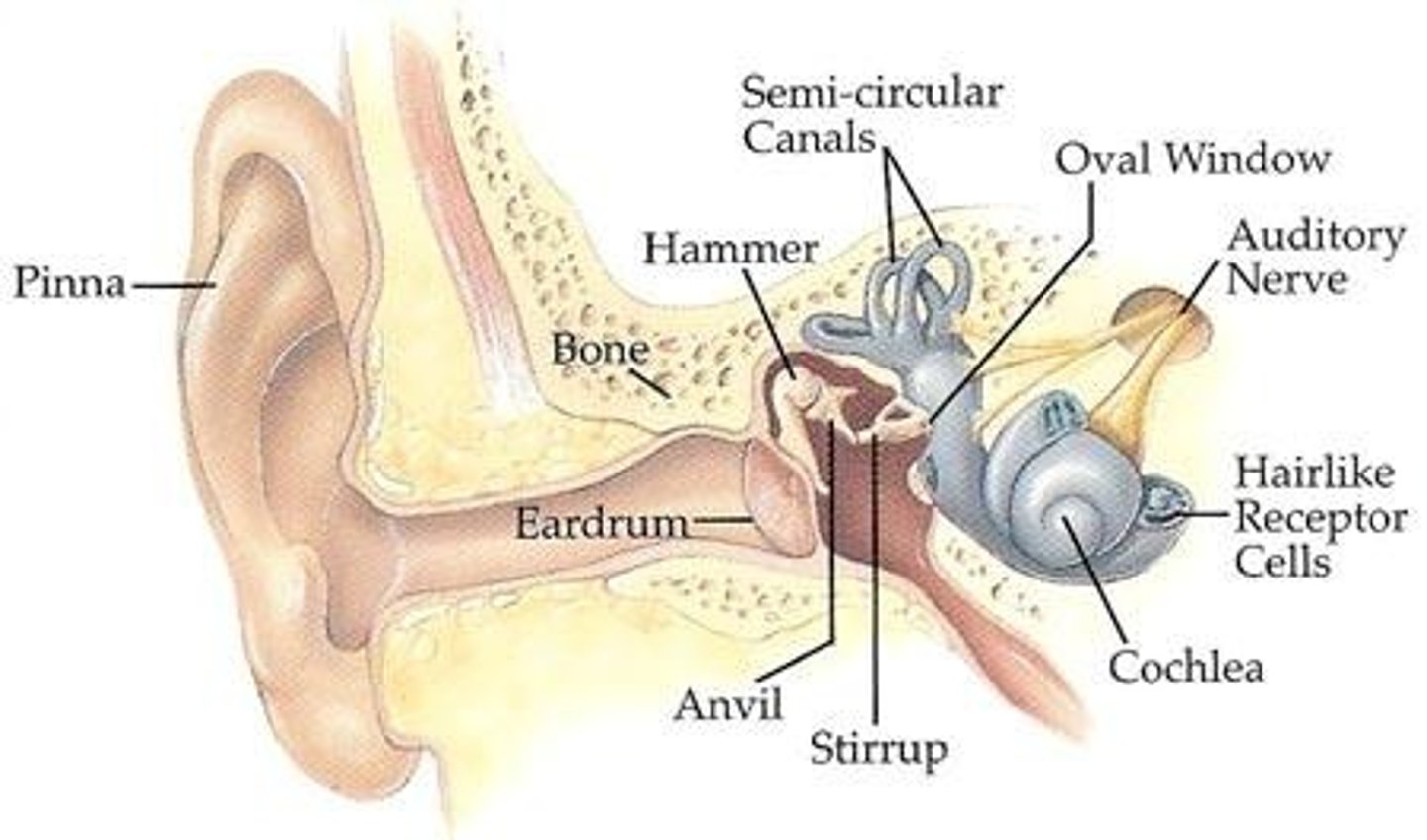
Eardrum
Also known as the tympanic membrane, it is a tightly stretched, cone-shaped membrane about 0.1 mm thick, very sensitive to sound.
Eustachian tube
A tube that connects the middle ear to the mouth, allowing air pressure to equalize when opened.
Middle ear
The cavity containing the eardrum and three bones that transmit vibrations to the inner ear.
Hammer (Malleus)
One of the three bones in the middle ear that transmits vibrations from the eardrum.
Anvil (Incus)
One of the three bones in the middle ear that transmits vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup.
Stirrup (Stapes)
The bone in the middle ear that connects to the cochlea and transmits vibrations to the inner ear.
Cochlea
A snail-shaped structure in the inner ear, about 3 cm long, filled with fluid that transmits pressure waves.
Basilar membrane
A membrane in the cochlea that responds to different frequencies of sound.
Semicircular canals
Three hard, fluid-filled loops at right angles to each other that help maintain balance.
Hearing loss
The inability to hear, which can be caused by damage to the eardrum, middle ear, or cochlea.
Deafness
A condition where signals from the cochlea do not travel to the auditory nerve, which is not curable.
Loud sounds
Extremely loud sounds, such as explosions or loud music for too long, can burst the eardrum.
Cochlear hair damage
Damage to the hairs in the cochlea that cannot be repaired and can lead to permanent hearing loss.
Surgery for hearing loss
A potential treatment for hearing loss due to damage to the eardrum or middle ear.
Auditory nerve
The nerve that transmits electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain.
Mechanical energy conversion
The process where the mechanical energy of vibrating hairs in the cochlea is converted into electrical energy.
Frequency response
The way the basilar membrane responds to different frequencies, with higher frequencies at the start and lower frequencies at the far end.
Balance maintenance
The function of the semicircular canals that send signals to the brain to help maintain balance.
Pressure waves
Waves created by sound that move through the cochlea and cause vibrations in hair-like structures.
Vibrating hairs
Hairs in the cochlea that respond to sound frequencies and help the brain interpret sound.
Noise
Sound that originates from a source that vibrates in a random manner.
Music
Sound that originates from a combination of musical notes that originate from a source that vibrates in a uniform manner with one or more constant frequencies.
Pitch
The perception of the highness or lowness of a sound; higher frequencies produce higher pitches.
Stringed Instruments
Instruments that have a tightly stretched string fixed at both ends, resulting in a node at each end when vibrating.
Resonator
An object, usually a hollow chamber called a case box or sounding board, that vibrates in resonance with the source of sound, improving loudness and quality.
Fundamental Frequency
The lowest frequency of a vibrating string, which can change when the length of the string changes.
Wind Instruments
Instruments that act as air columns, where sound originates from air vibrating over an opening, vibrating lips, or a vibrating reed.
Percussion Instruments
Instruments that produce sound by striking one object against another.
Speed of Wave in String
The speed of the wave in the string remains the same when the length is changed.
Air Column
The space within wind instruments that allows air to vibrate, producing sound.
Plucking Stringed Instruments
Different frequencies and multiple simultaneous frequencies can be obtained depending on where a stringed instrument is plucked.
Length of String
As the length of the string changes, the frequency will change as well.
Hollow Chamber
A resonator that enhances the sound quality of stringed instruments.
Changing Frequency in Wind Instruments
In some wind instruments, the length of the air column can be changed, while in others, the frequency can be changed by opening holes in the column.
Vibrating Lips
The method of sound production in brass instruments like the trumpet.
Vibrating Reed
The method of sound production in woodwind instruments like the clarinet.
Case Box
Another term for a resonator in stringed instruments.
Sounding Board
A type of resonator that enhances the sound of stringed instruments.
Striking Objects
The method by which percussion instruments produce sound.
Node
A point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude, found at each end of a vibrating string.