Lecture 6 - Muscarinic Agonists and Antagonists
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
necessary SAR aspects of a muscarinic agonist
Quaternary Ammonium (-N+(CH3)3) Charge is required for binding (A basic nitrogen that is ionized at physiological pH is also adequate for binding (3º amines) —> size of alkyl group needs to be methyl or smaller on ionized nitrogen
SAR aspects of a muscarinic agonist
Quaternary Ammonium (-N+(CH3)3) or 3º amine for receptor binding
Ester linkage (group that can act as H-bond acceptor is sufficient (carbamates, amides for example)
Ethylene bridge (increase or decrease in chain length results in decreased activity)
Alkyl substitutions on the alpha carbon of ethylene bridge result in compounds with…
increased nicotinic receptor selectivity
Alkyl substitutions on the beta carbon of ethylene bridge result in compounds with…
increased muscarinic receptor selectivity and an increase in duration of action (slows ester hydrolysis)
what happens if we add groups bigger than methyl to basic structure of muscarinic agonist
loss of activity
Ings rule of 5 for CHAIN agonists
5 atoms = agonist, 6-8 atoms = partial agonist, 9+ atoms = antagonist (atoms meaning atoms between ionized amine and carbonyl group of ester)
configuration/conformation preferentialness of agonists
ubstituent on the beta carbon creates a chiral center. S>>>>>>R in muscarinic agonism + Extended conformer (trans) is a better muscarinic agonist than the folded conformer (cis)
Ring-containing muscarinic agonists do/don’t follow Ing’s rule
DO NOT!!!!!!!!!
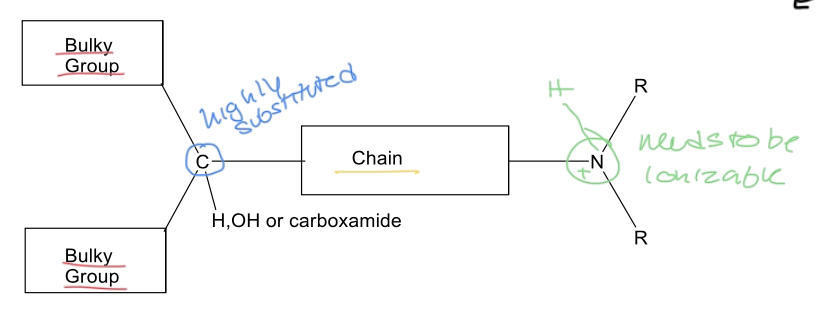
SAR of muscarinic antagonist/anticholinergic
1. Aromatic or aliphatic groups; rings better than chains (Bulk important for antagonism)
2. Tertiary carbon with a branching substituent preferably an H-bond donor or acceptor or both improves affinity (binding) for muscarinic receptor
3. Spacer (chain) could be an ester bridge, ether, hydrocarbon. Separates the bulk from the positively charged amine.
4. Cation at physiological pH is important requirement for binding to the muscarinic receptor. Could be a basic tertiary amine or a quaternary ammonium (always positively charged).
arakyl group (not necessary) near ionized amine increases affinity for muscarinic receptors
Tropane-based Anticholinergics of Historic Significance MOA
muscarinic receptor antagonists
Tropane-based Anticholinergics of Historic Significance targets
bronchi, pupil, urinary bladder
metabolism of Umeclidinium
molecule undergoes CYP2D6 mediated oxidative O-dealkylation (deactivation), ortho and para aromatic hydroxylation (deactivation), and Phase II glucuronide conjugation due to no ester
how do acetylcholinesterase inhibitors work
inhibition of AChE will increase the half-life of ACh in the synapse
reversible vs pesudo-irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
reversibles have exposes esters, pesudo-irreversibles have carbamates instead that aren’t prone to ester hydrolysis and form covalent bond with serine on AChE receptor site
if antagonist has quarternary ammonium, then…
can only work in periphery