Brain Structures -Functions & Mnemonic Devices
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Hippocampus
If you saw a hippo on campus, you would remember it.
F: Processes explicit memories (such as personal experiences,helps restore memories
Pituitary Gland
"Arm Pit"-Master Gland
Controls growth rate & activates other endocrine glands
What are the four lobes?
1-Parietal
2-Frontal
3-Occipital
4-Temporal
Freud Took his Pants Off
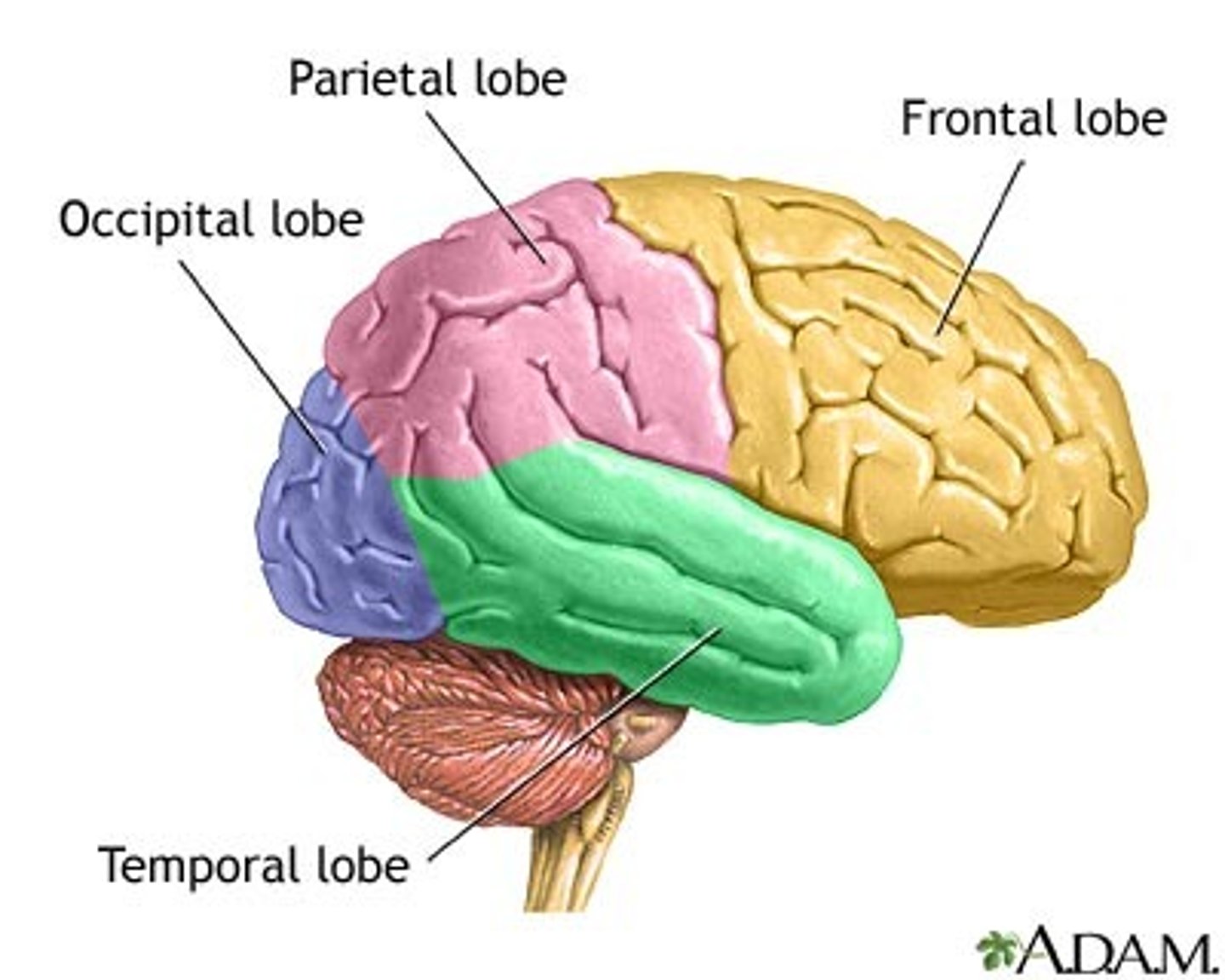
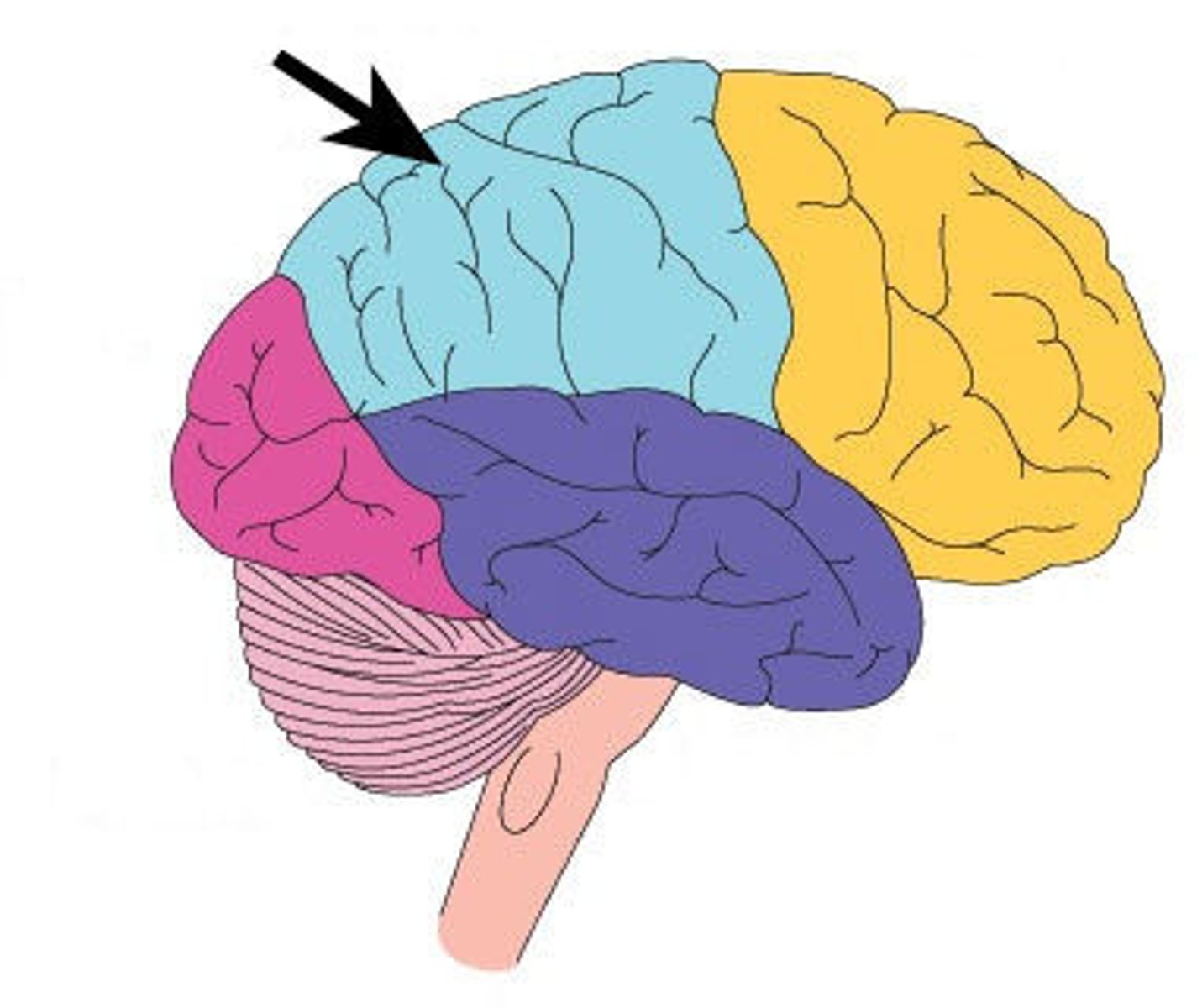
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe processes visual
information
Occ- think octopus; Picture
eyeballs instead of
suckers on the
tentacles.
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory
information
Use a
"piranha" fish as your
mnemonic. The
piranha bites you on
the top of the head
(where the parietal
lobe is located)That's a sensation the
parietal lobe would
process.
Frontal Lobe
The
frontal lobe is where
complex thinking
occurs. Use "front
door" as your
mnemonic. Put the
front door on your
forehead and put
Einstein (complex
thinker) behind the
door.
Temporal Lobe
is
where auditory
processing occurs.
Use "tempo" as your
mnemonic and picture
a metronome above
your ear (where the
temporal lobe is
located)
Hypocampus
involved in
memory. Use
"compass":
picture someone
(perhaps
yourself) who is
lost and can't
remember how to
get home, so you
need a compass.

Amygdala
involved in your
fear responses.
Picture a scary
wig (rhymes with
"myg") with
dollars in the hair
(similar to
"dala").
Thalmus
the
thalamus relays
information from
the body to
different areas of
the brain for
processing.
The Secretary

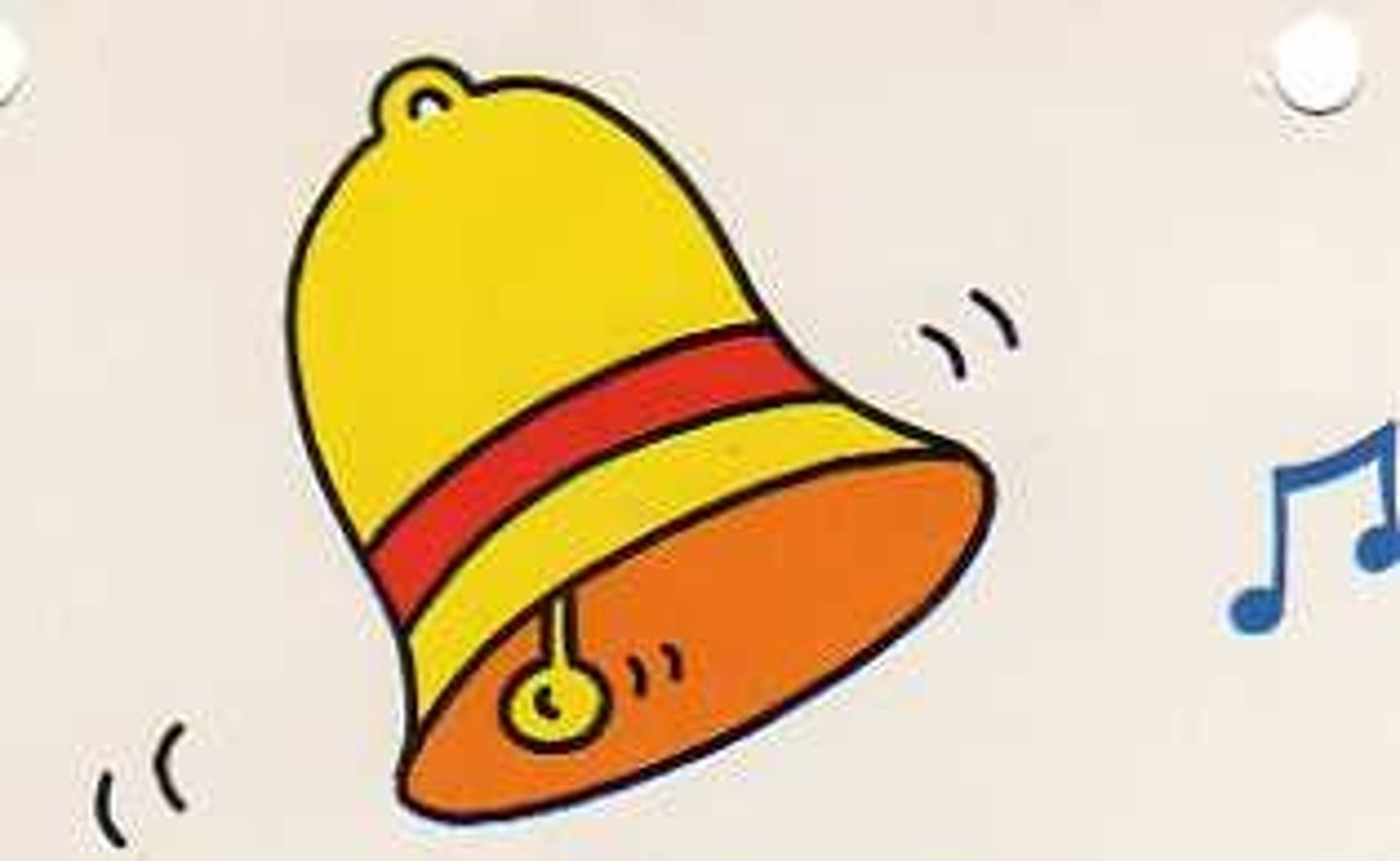
Cerebellum
involved in
helping you maintain
balance. Picture a tight walker using bells for
balance. Or picture your
favorite athlete trying to
balance a bell on his/her
head.

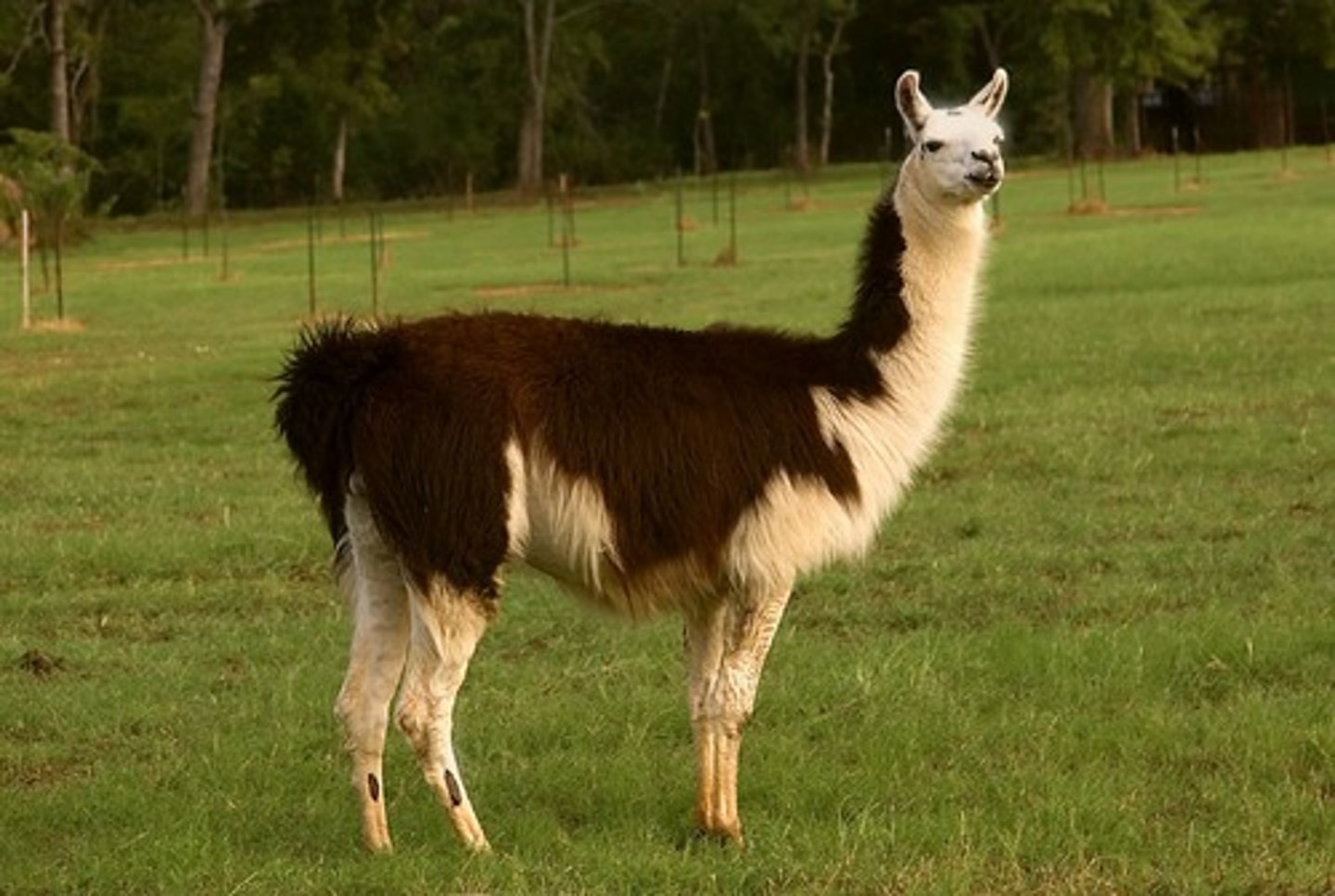
Hypothalamus
the
hypothalamus regulates
many of the body's
metabolic processes,
thirst, hunger and body
temperature. Use "hypo
-
the
-llamas" as your
mnemonic. Picture a
hypo spraying two thirsty
llamas with water to
quench their thirst and
cool them down.

What are the parts of the brain stem?
Pons,Reticular Formation and Medulla
Pavlov's Really Frikin' Mad!
Pons
the pons is the part of the
brain that regulates waking and
relaxing. Put a "d" in pons and
you have "ponds". Ponds are
relaxing to look. Your pons is
activated when you look at a
calm, relaxing pond.

Reticular Formation
is involved
in motivation and alertness.
Use "tickle" as your mnemonic.
If you (or your roommate) were
asleep and someone tickled
you, your reticular formation
would wake you up.

Medulla
regulates
the autonomic activity of the
heart and lungs. Use medals as
your mnemonic and stick the
medals in a bloody heart and
lungs. Or picture an Olympic
athlete wearing gold medals
around her neck and covering
her heart and lungs.

The parts of neurons
Dendrites,Soma,Axon,Myelin Sheath,Nodes of Ranvier, Synaptic Vescles,Synapse
Dang! Skinner Ate Mice? Not Very Smart.
Dendrites
Signals from muscles and other neurons enter the neuron through branches
"Rites" rhymes w. kites. Kites
often fly into tree branches, and
lightening can strike kites, so
picture lightening striking kites
which are attached to the branches
of the soma.
Soma
is the cell body of the neuron
Use "ma" or "someone's ma"
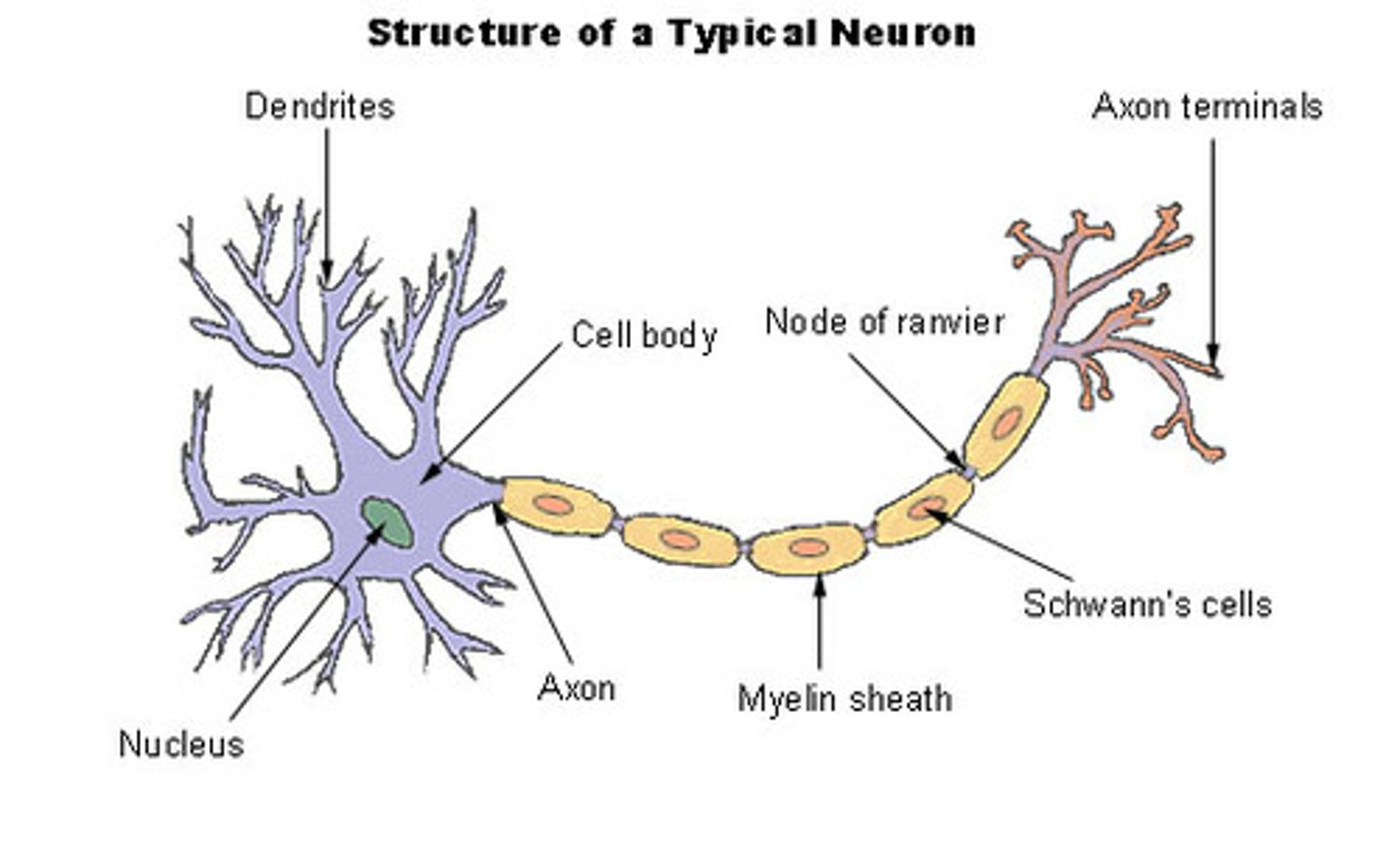
Axon
Extends out from the soma; use "ax" & picture an ax that has been stuck into "someone's ma".
Myelin Sheath
Protects the axon & speeds the signal down the axon. (Picture sheep sitting on the axon, keeping it warm and also yelling at the signal to move it along the axon; "my yelling sheep"
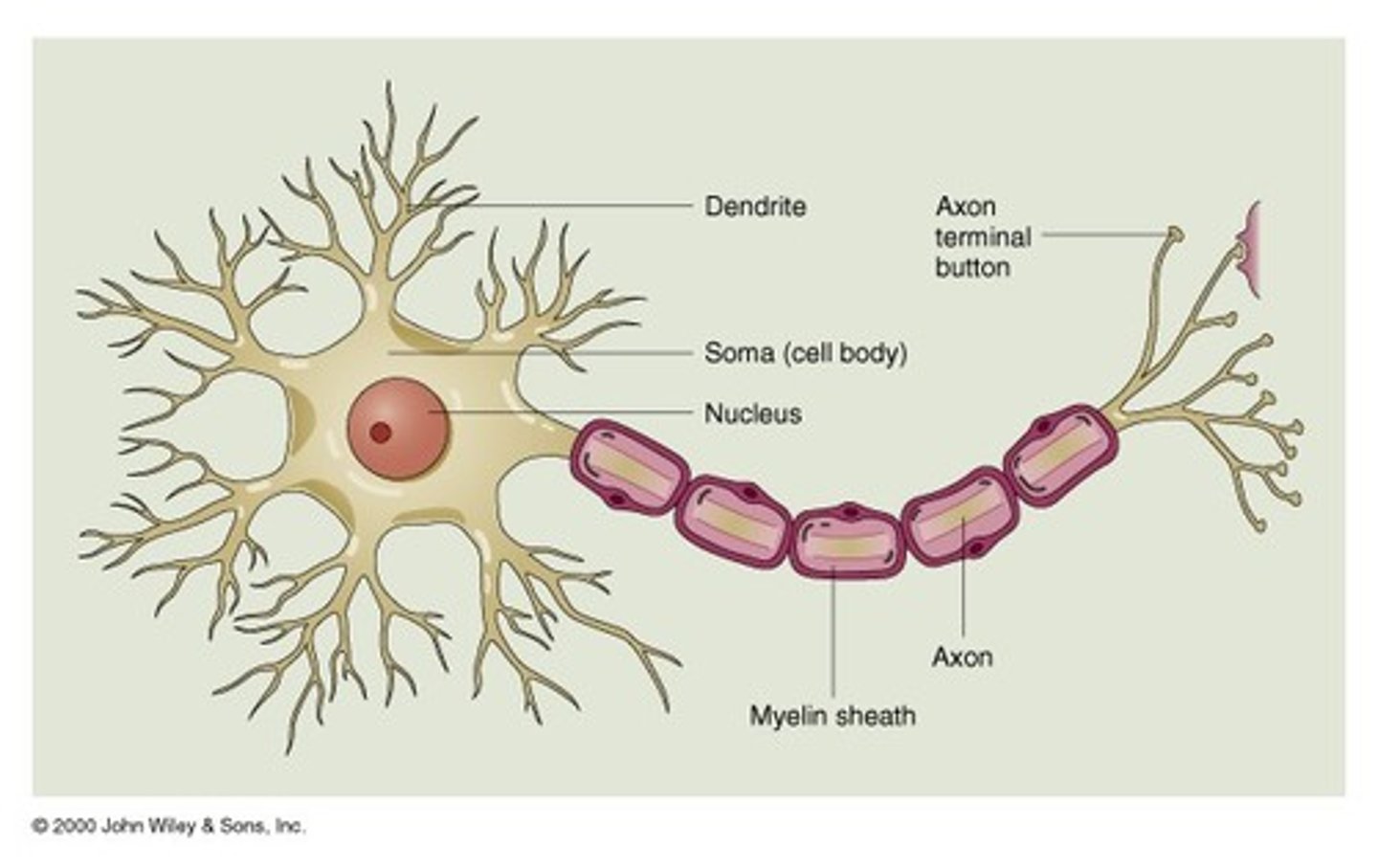
Nodes of Ranvier
Are the spaces between the myelin sheath. As the signal travels down the axon it actually jumps from one node to another. Go with "noses' and picture noses between the "sheep" the signal jumps from one nostril to another.
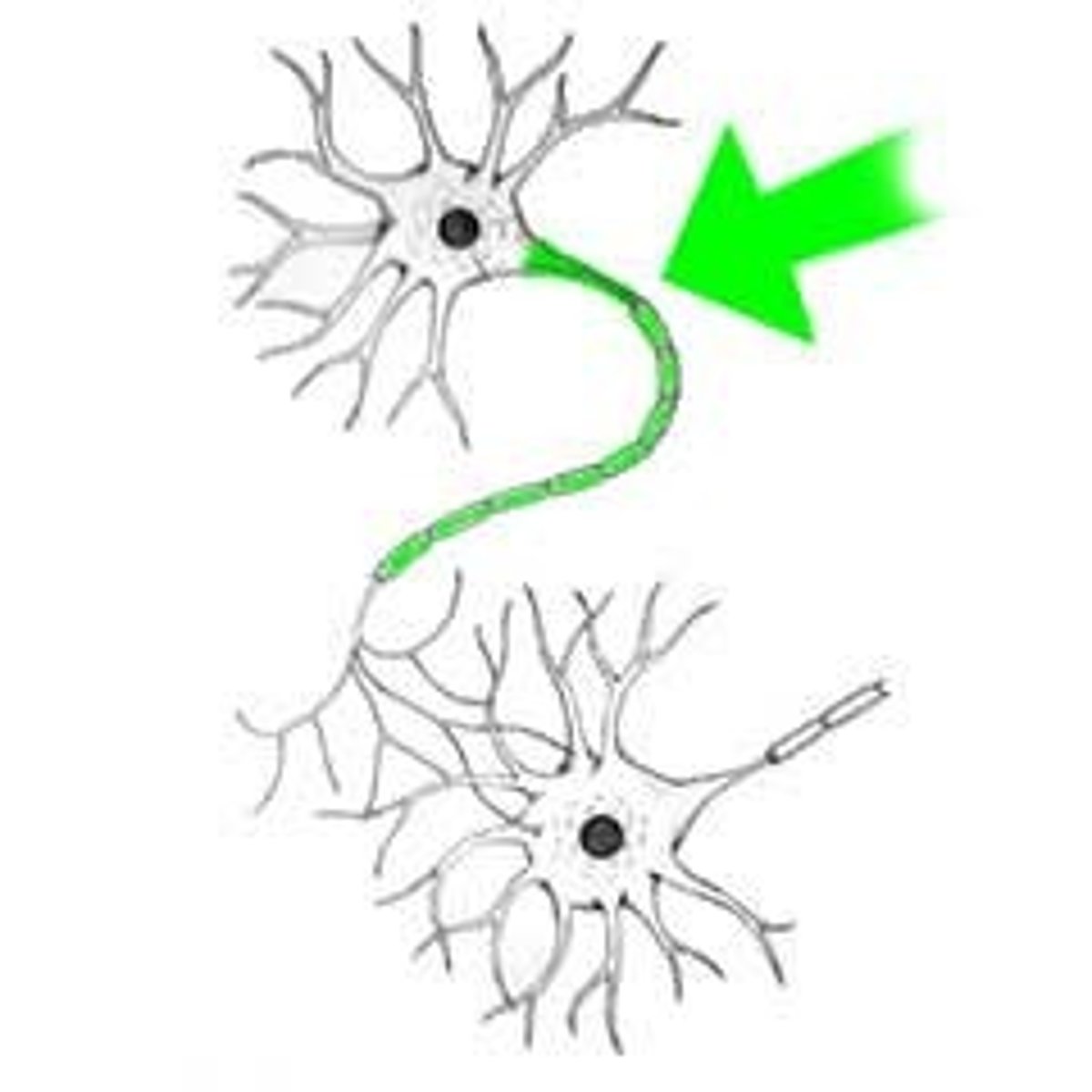
Synapse
found at the end of the
axon. It is the space
between one neuron and
another or between one
neuron and a muscle.
Use the "naps" part of
synapse and picture
someone taking a nap
between two neurons.
What are the types of neurotransmitters?
Dopamine, Acetylcholine ,Serotonin,and Endorphins - also there's GABA,Substance P & Acetylcholine(ACh)
THINK; DASE
Serotonin
"Sir Rotten" - always in a rotten mood; affects mood,sleep,appetite,impulsivity, aggression
GABA
Facilitates neural inhibition in the CNS - assoc. w. anxiety & seizure disorders
Substance P
Sends pain messages, it's after the endorphinsend
Dopamine
Associated with Parkinson's disease,Schizophrenia & ADHD
Glutamate-amino acid
Active in areas of the brain involved in learning,thought and emotion; associated w. BIPOLAR DISORDER & MIGRAINES