Introduction to X-ray History/Principles
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen
Who discovered x-rays in 1895?
Vitascope
Thomas Alva Edison invented the fluoroscope _____, which allows us to see x-rays move
Pedoscope
A _____ is a shoe-fitting fluoroscope
William Coolidge
_____ invented the Coolidge tube in 1913
Hot
Today's x-ray tubes are _____
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
_____ allows us to see function and began in the 1950s
Matter
_____:
- Takes up space
- Has mass
- Different forms (solid, liquid, gas, plasma)
- Cannot be created or destroyed
- Smallest unique quality is the atom
Atoms
_____ are comprised of protons (+), electrons (-) and neutrons
Number of protons
Atoms are grouped into elements based on the _____
Neutral
Atoms are normally electrically _____
Bohr model
The _____ is based off a miniature solar system. Electrons reside in established orbits (energy levels) and revolve around a nucleus (protons and neutrons)
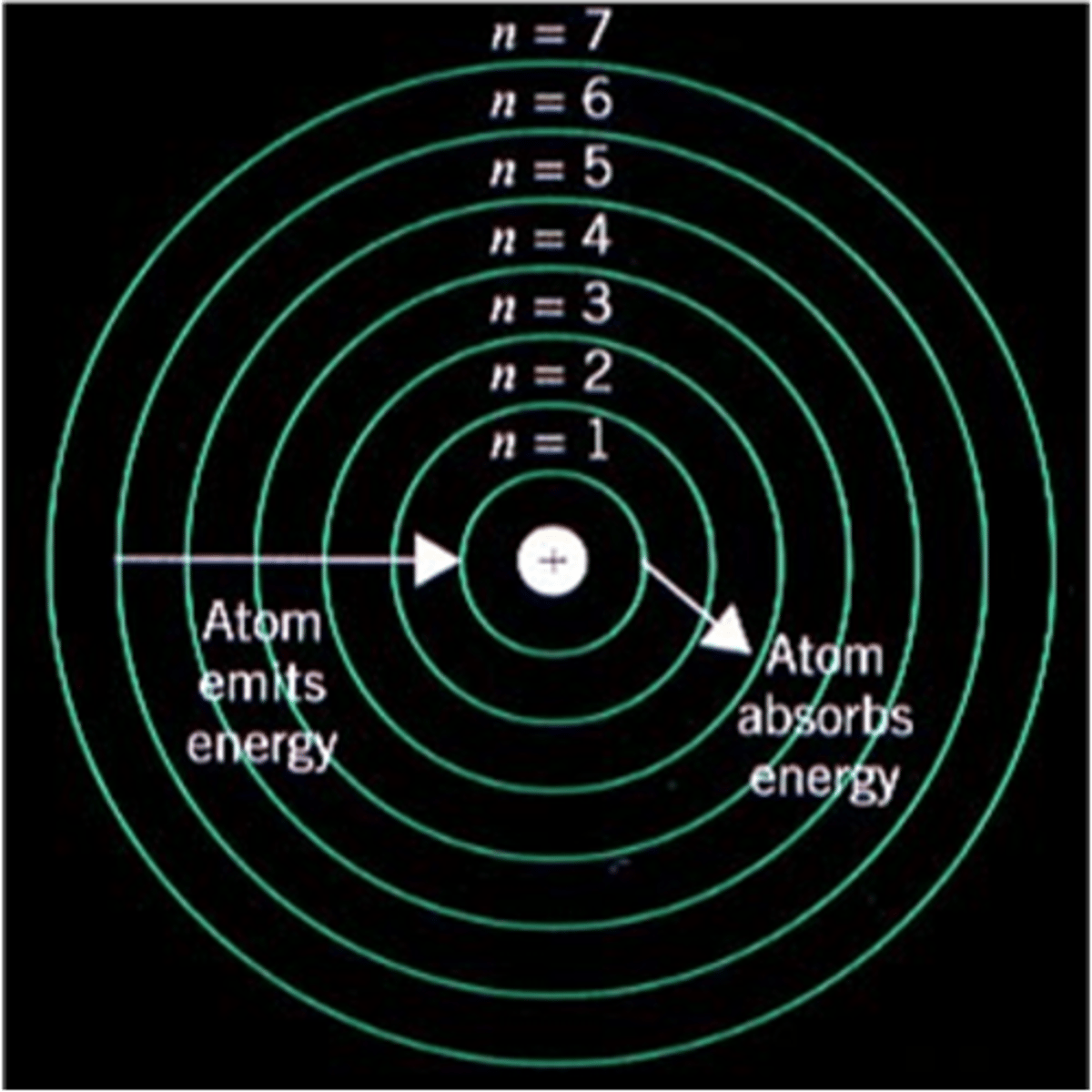
Nucleus
The _____ consists of protons and neutrons and has a mass about 2000x greater than an electron
Electron cloud
An _____ revolves around the nucleus in precise, fixed orbits

Electron orbits
_____ are also referred to as "energy levels" or "shells"
2n^2
The maximum number of electrons per shell can be calculated using the equation _____, where n equals the shell number
Electron binding energies
_____ refers to the strength of attachment of an electron to the nucleus
Energy
The movement of electrons from a higher shell (L, M, etc.) to a lower one (K) is typically accompanied by the emission of _____
Ionization
_____ occurs when the transfer of energy to an orbital electron results in ejection of the electron from the atom
True
T/F Work cannot be created or destroyed
Quantum
What is the smallest quantity of work?