CNIT 176 Exam 2
1/472
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
473 Terms
What is a basic model
It is a processing speed or program execution
It is determined primarily by ability of I/O operations to stay ahead of processor
What are I/O requirements
Means for addressing different peripheral devices
A way for peripheral devices to initiate communication with the CPU
An efficient means of transferring data directly between I/O and memory for large data transfers since programmed I/O is suitable only for slow devices and individual word transfers
Buses that interconnect high-speed I/O devices with the computer must support high data transfer rates
Capability of handling devices operating at varying speeds with varying delays
Means for handling devices with extremely different control requirements
Simple I/O configurations
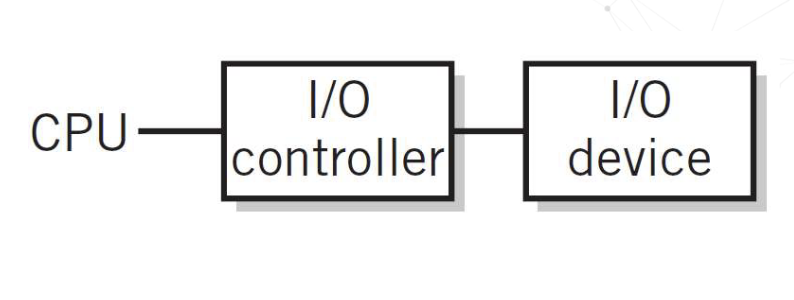
What is a Northbridge in relation to I/O
Special chip to handle communication between CPU, GPU, and RAM
What is a Southbridge in relation to I/O
Special chip to handle communication between northbridge and interfaces such as the USB and SATA (harddrive) interfaces
More Complex I/O Module, Intel Xeon
Separate IO controller chips might have been present for Ethernet, Audio, if not part of Southbridge
Is the northbridge apart of the CPU in the Intel Core Series
True
The northbridge is now part of the CPU
What are different advanced I/O techniques
Programmed I/O
CPU controlled I/O
Interrupt Driven I/O
External input controls
Direct Memory Access Controllers
Method for transferring data between main memory and a device that bypasses the CPU
Programmed I/O
I/O data and address registers in CPU
One word transfer per I/O instruction
Address information for each I/O device
Full instruction fetch/execute cycle
What are the primary uses of programmed I/O
Keyboards
Communication with I/O controllers
What are interrupts
Signal that causes the CPU to alter its normal flow of instruction execution
Frees CPU from waiting for events
Provides control for external I/O initiation
What are examples of interrupts
Unexpected input
Abnormal situation
Illegal instructions
Multitasking, Multiprocessing
Interrupt Terminology
Interrupt lines (hardware)
Interrupt requests
Interrupt handlers
Context
What are interrupt lines
One or more special control lines to the CPU
What are interrupt handlers
Program that services the interrupt
What are interrupt handlers also known as
Interrupt routine
Device driver
What is context (in relation to interrupt terminology)
Saved registers of a program before control is transferred to the interrupt handler
Allows program to resume exactly where it left off when control returns to interrupted program
What are different uses of interrupts
Notify that an external event has occurred
Real-time or time-sensitive
Signal completion
Printer ready or buffer full
Allocate CPU time
Time sharing
Indicate abnormal event (CPU originates for notification and recovery)
Illegal operation, hardware error
Software interrupts
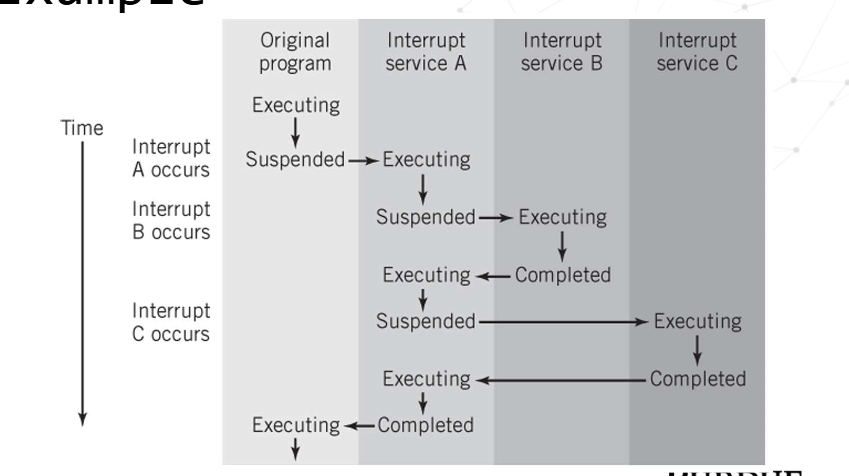
The CPU - The Interrupt Cycle
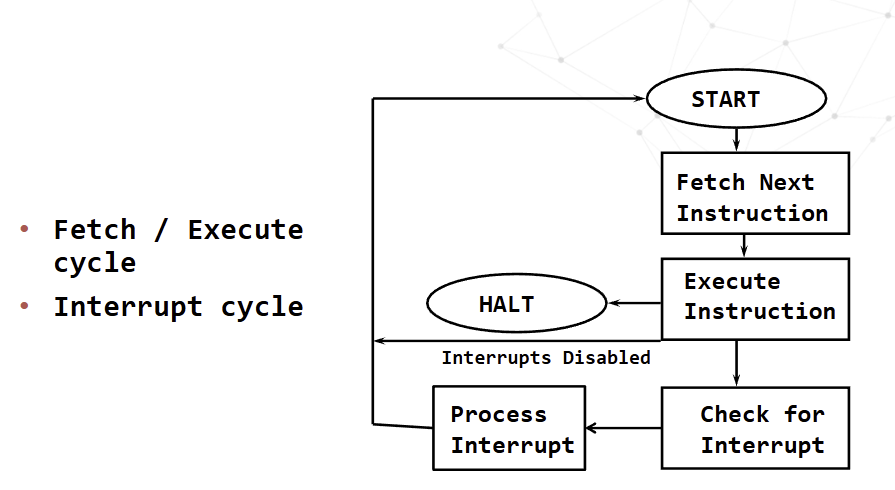
What is servicing the interrupt
Lower priority interrupts are held until higher priority interrupts are complete
Suspend program in progress
Save context, including last instruction executed and data values in registers, in the PCB or the stack area in memory
Branch to interrupt handler program
Print Handler Interrupt
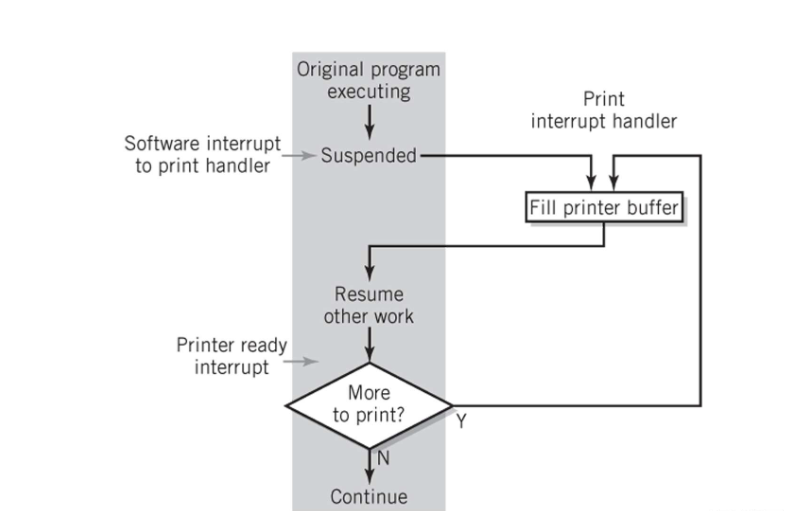
Using an interrupt for Time Sharing
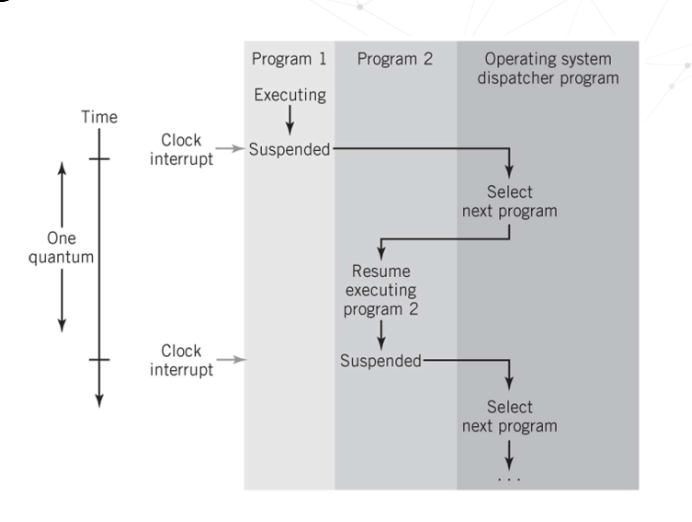
What are the different interrupt processing methods
Vectored interrupt
Polling
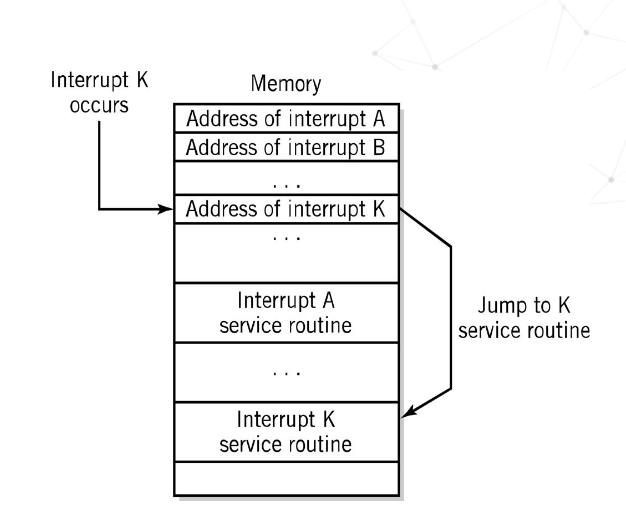
What is vectored interrupt
Address of interrupting device is included in the interrupt
Requires additional hardware to implement
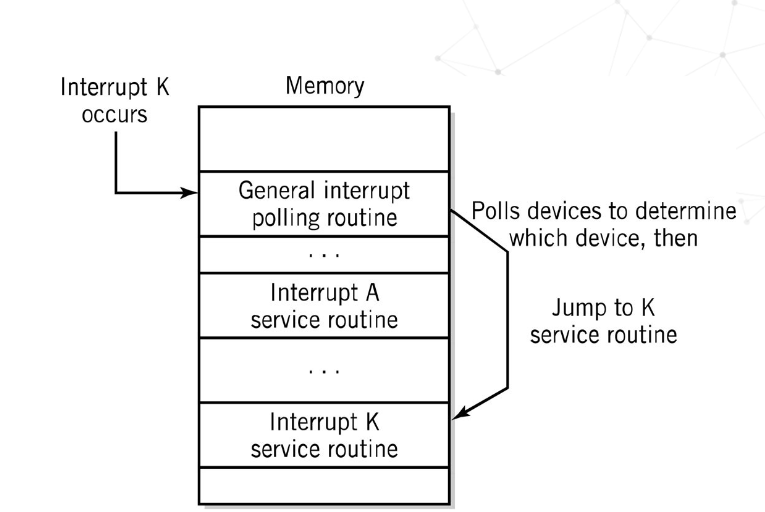
What is polling
Identifies interrupting device by polling each device
General interrupt is shared by all devices
What do vectored interrupts look like
What do polled interrupts look like
What do multiple interrupts look like
What is Direct Memory Access
Used to transfer large blocks of data
It is a direct transfer to and from memory
The CPU isn’t actively involved in transfer itself
What are the required conditions for Direct Memory Access
The I/O interface and memory must be connected
The I/O controller must be capable of reading and writing to memory
Conflicts between the CPU and the I/O controller must be avoided
Interrupt required for completion
What does DMA stand for
Direct Memory Access
DMA Instructions
Application program requests I/O service from operating system
To initiate DMA, programmed I/O is used to send information
Interrupt to the CPU upon completion of DMA
What is the following information that the programed I/O is used to send to initiate DMA
Location of data on I/O device
Starting location in memory
Size of the block
Direction to transfer: read or write
What are I/O controller functions
Recognizes messages from device(s) addressed to it and accepts commands from the CPU
Provides a buffer where the data from memory can be held until it can be transferred to the device
Provides the necessary registers and controls to perform a direct memory transfer
Physically controls the device
Copies data from its buffer to the device/from the CPU to its buffer
Communicates with CPU
Interconnects Example
What are peripherals
Devices that are separate from the basic computer
Not the CPU, memory, or power source
What are peripherals classified as
Input, Output, and Storage
How do peripherals connect
Ports and Interface to system bus
What are different types of secondary storage
Online storage
Offline storage - loaded when needed
Network file storage
File servers, web servers, and database servers
What is flash memory
It is a solid state drive
With large capacity flash memory units
What does flash memory replace as long-term storage
Magnetic dish drives
Is flash memory immune to physical shocks
True
Does flash memory produces lots of heat and noise
False
It generates little heat or noise
How is data read/written in flash memory
It is read/written in blocks
Extra facts on flash memory
Wear-leveling used to extend life
Controller logic used to manage memory space and provide fast reads/writes
What are magnetic disks made of
It is a platter made of glass, metal, or plastic with a magnetic coating
How is magnetic polarization determined in magnetic disks
Magnetic polarization is determined by 1s and 0s
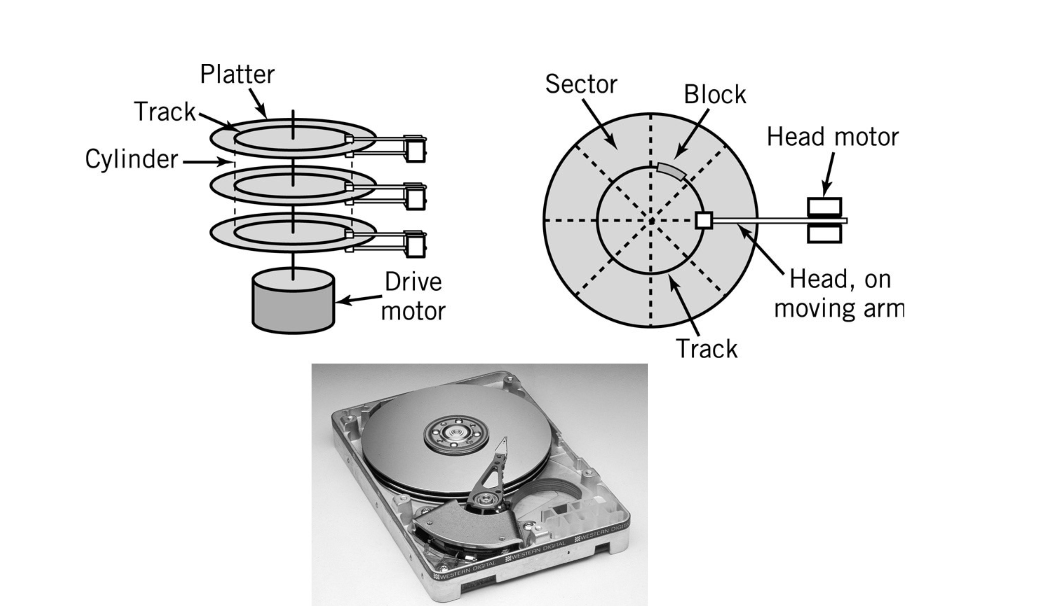
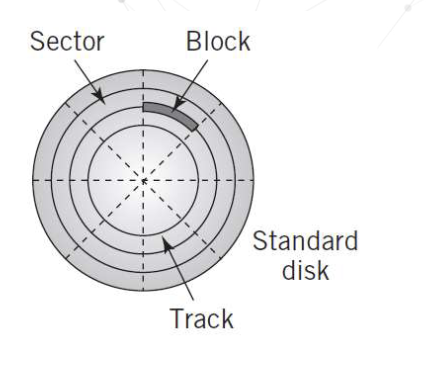
Parts of a Magnetic Disk
Track - Circle
Cylinder - Same track on all platters
Block - Small arc of a track
Sector - Pie-shaped part of a platter
Head - Reads data off the disk as disk rotates at high speed
What is the high speed the head rotates on a magnetic disk
5400-10000+ RPM
What is the layout of a Hard Disk
What are the different disk layouts
CAV and CLV and Multiple Zone
What does CAV stand for
Constant Angular Velocity
What is CAV
Number of bits on each track is the same; denser towards the center
Spins the same speed for every trackc
What does CLV stand for
Constant Linear Velocity
What is CLV
All tracks have the same physical length and number of bits
Constant speed reading data off a track
Drive has to speed up when accessing close to the center of the drive and slow down when accessing towards the edge of the drive
What is Multiple Zone Recording also known as
Zone Bit Recording (ZBR)
Zone-CAV Recording (Z-CAV)
Is multiple zone a compromise between CAV and CLV
True
It is a compromise between CAV and CLV
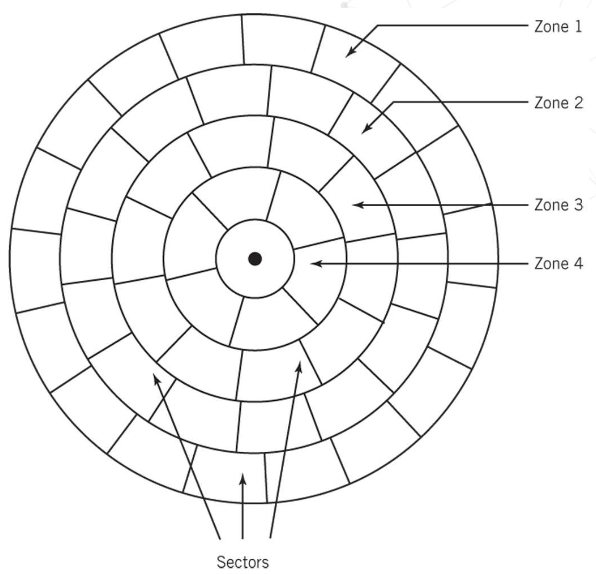
What is Multiple Zone
Disk divided into zones
Cylinders in different zones have a different number of sectors
Number of sectors in a particular zone is constant
Data is buffered so the data rate to the I/O interface is constant
Multiple-Zone disk configuration
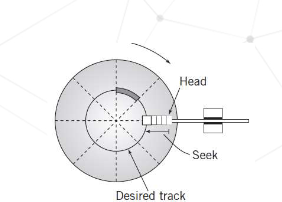
What is Seek Time
Time required to move from one track to another
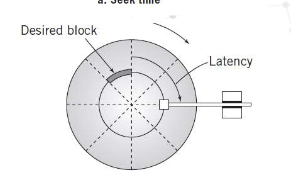
What is Latency
The time required for disk to rotate to beginning of correct sector
What is Transfer Time
Time required to transfer a block of data to the disk controller buffer
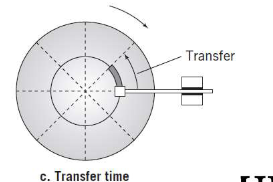
What is average seek time
Average time to move from one track to another
What is average latency time
Average time to rotate to the beginning of the sector
What is the formula to find the average latency time
½ * 1/rotational speed
What is the formula to find the average transfer time
1/(# of sectors * rotational speed)
What is the formula to find the total time to access a disk block
Average seek time + average latency time + average transfer time
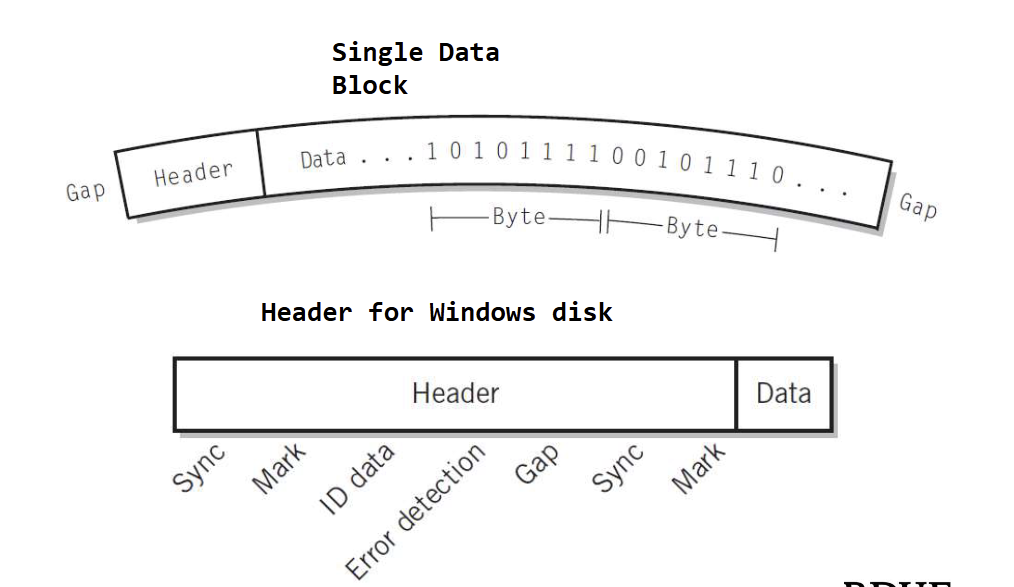
What are the components in a data block format in relation to magnetic disks
Interblock gap
Header
Data
What is a formatting disk
Establishes the track positions, blocks, and headers needed before use of the disk
What does a disk block format look like
What is a disk array
Grouping of multiple disks together
What does RAID stand for
RAID → Redundant Array of Independent/Inexpensive Disks
What are the different types of RAID Arrays
Mirrored array
Striped array
RAID 0 to RAID 5
What is a mirrored RAID array
Two or more disks contain the exact same stores of data
How does a mirrored RAID array read data
Alternate blocks of data are read from hard drives and combined
Is access time reduced in a mirrored RAID array
True
Access time is reduced by approximately a factor equal to the number of disk drives in an array
How does read failure work in a mirrored RAID array
Block is marked and then read from the mirrored drive
Extra fact about mirrored RAID arrays
When using three or more mirrored drives, majority logic is used in the event of a failure.
Fault-tolerant computers use this technique
What is a striped RAID array
A file segment is stored divided into blocks on different disks
What is the minimum amount of drives needed in a striped RAID Array
3
Minimum of three drives needed for true stripping because one drive worth of space is reserved for error checking
Is one drive reserved for error checking in a striped RAID array
True
One drive is reserved for error checking
How does Writes work in a striped RAID array
Writes - block of parity words from each block of data is created and put on the reserved error checking disk
How does Reads work in a striped RAID array
Reads - parity data is used to check original data
What are the different RAID levels
RAID 0
RAID 1
RAID 2, 3, 4
RAID 6
RAID 10
What is RAID 0
No error checking or redundancy, but data is placed across all drives for increased speed
What is RAID 1
Mirrored array
What is RAID 2, 3, 4
Arrays that are striped in different ways (deprecated)
What is RAID 5
Error checking blocks are spread across all drives
What is RAID 6
Double parity blocks, two drives per array can fail
What is RAID 10
Mix of performance of 0 with redundancy of 1 used instead of 5 or 6 if performance is important
What is optical storage
Reflected light off a mirrored or pitted surface
What is CD-ROM
650 MB of data, approximately 550 MB after formatting and error checking
Spiral 3 miles long, containing 15 billion bits
CLV - all blocks are same physical length
Block - 2352 bytes
2k of data (2048)
16 bytes for header (12 start, 4 id)
288 bytes for advanced error control
Different types of optical storage
Laser strikes land
Laser strikes a pit
What is laser strikes land
Light is reflected into a detector
What is laser strikes a pit
Light is scattered
CD Layout
Standard Disk Layout
What are the different types of optical storage
Medium-powered laser blister technology
What is medium-powered laser blister technology also used for
CD-R, DVD-R, DVD-R, DVD+R
CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, DVD-RAM
Are there file compatibility issues between the different formats
True