TExES Core Subjects EC-6 (291) - Fine Arts, Health, & Physical Education
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
What are the four main strands in the Texas state curriculum for fine arts and visual arts?
Perception, Creative Expression, Historical/cultural Heritage, and Critical Evaluation
Seven Basic Concepts of Visual Art
Line, Space, Shape, Form, Texture, Value & Color
Concepts of Line
Outline, Contour, Gesture, Sketch, Calligraphy, Implied
Characteristics of Line
Width, length, direction, focus, feeling
Space
the emptiness around or within objects
Concepts of Space
Positive space, Negative space, Picture Plane, Composition, Focal Point, Depth (used perspectives)
Perspective Types
Nonlinear + Linear
(used to create depth)
Shape
Formed when a line(s) cross to enclose a space, giving an object height + width but no depth
Concepts of Shape
Geometric vs Real; Positive vs Negative; Static vs Dynamic
Form (art)
3-D Shape (height, width + shape)
Concepts of Form
Real (actual shape) vs Implied (visual representation of 3D shape using line, space, shape, color + value)
Concepts of Texture
Real vs Implied (using line, space, color + value)
Value
the lightness or darkness of an artwork
Concepts of Value
Tint: adding white to make lighter
Shade: adding black to make darker
Value Scale: gradual changes light to dark
High-Key: all on light side
Low-Key: all on dark side
Contrast
Color
spectrum of light broken down by it hitting an object and reflecting onto the eye
Concepts of Color
Hue: range of colors
Intensity: strength of color
Value
Temperature: warmth or coolness
What are the primary and secondary colors?
Primary: red, yellow, blue
Secondary: green, orange, violet
Green: blue + yellow
Orange: red + yellow
Purple: red + blue
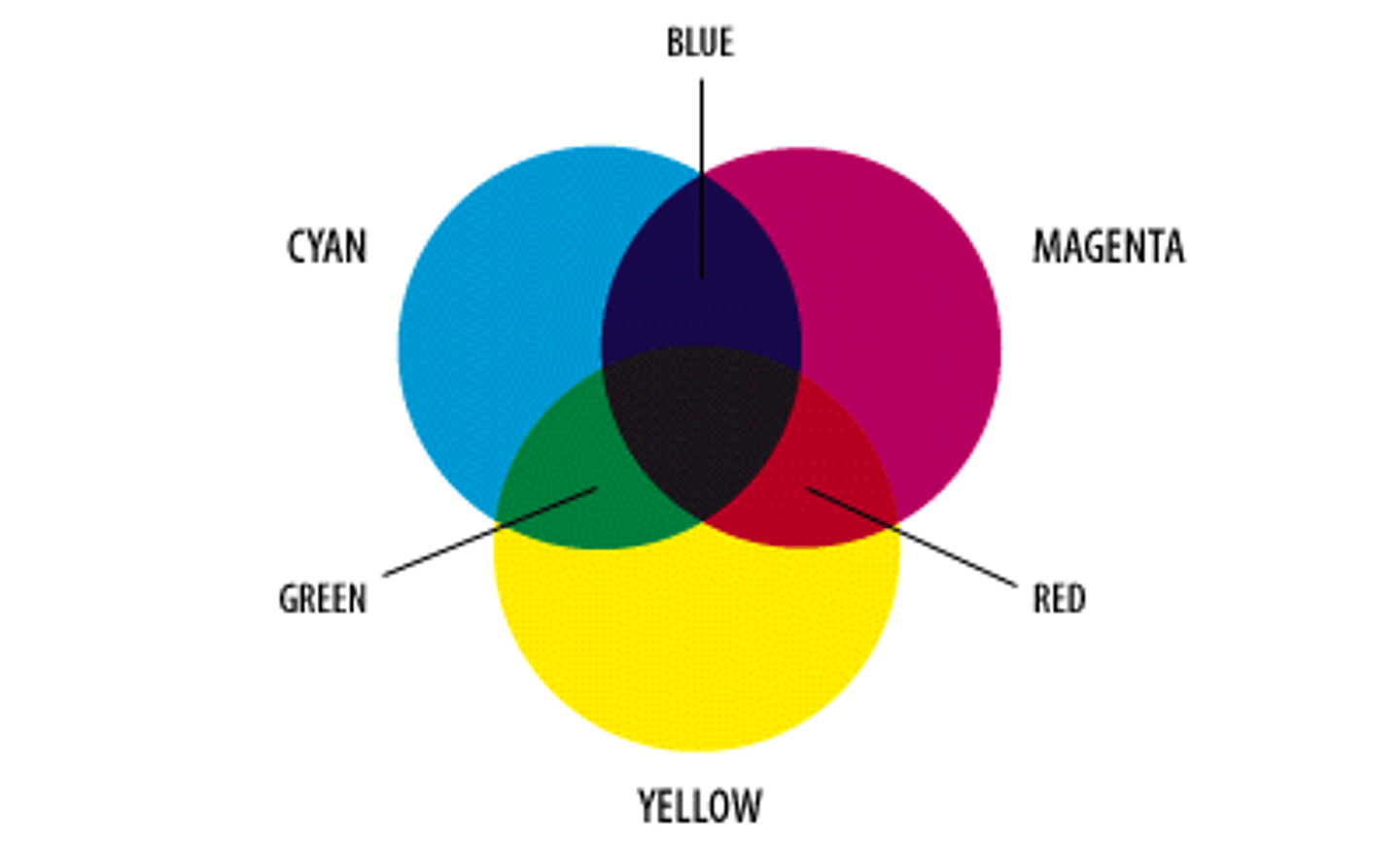
What are complementary colors?
Opposites on color wheel (red + green; blue + orange; yellow + purple)
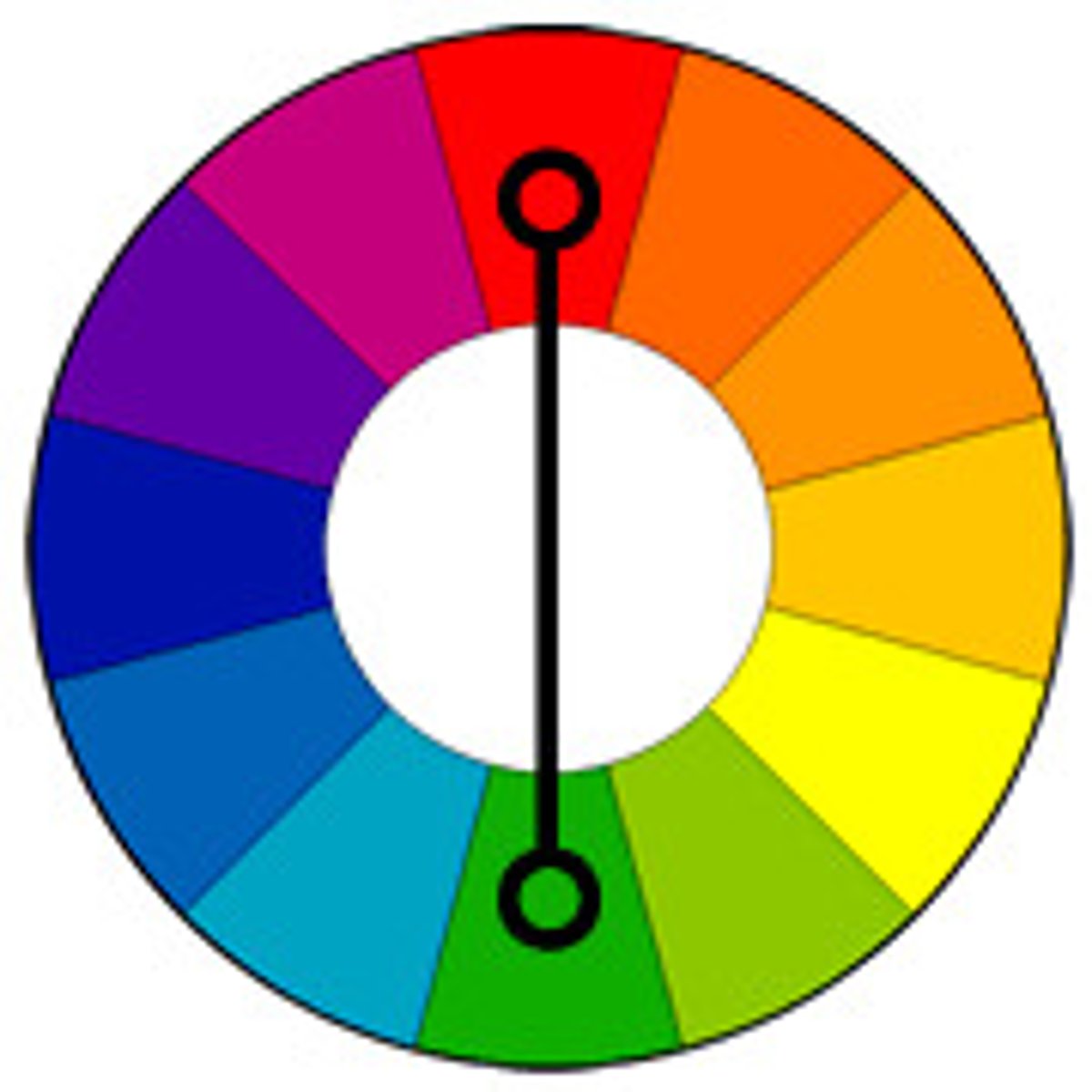
What are analogous colors?
Colors that are next to each other on the color wheel

Achromatic
without color (gray, black, white)
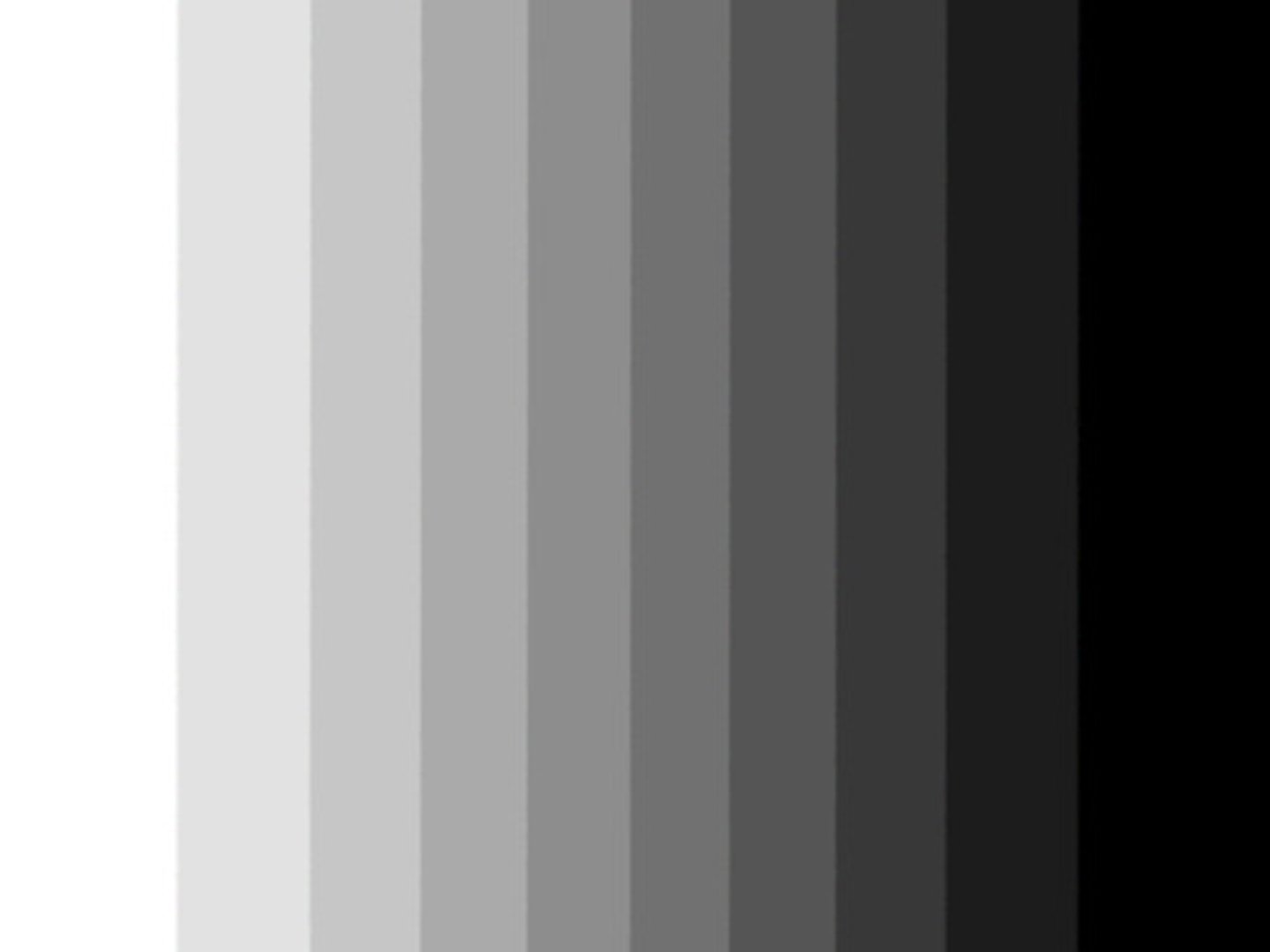
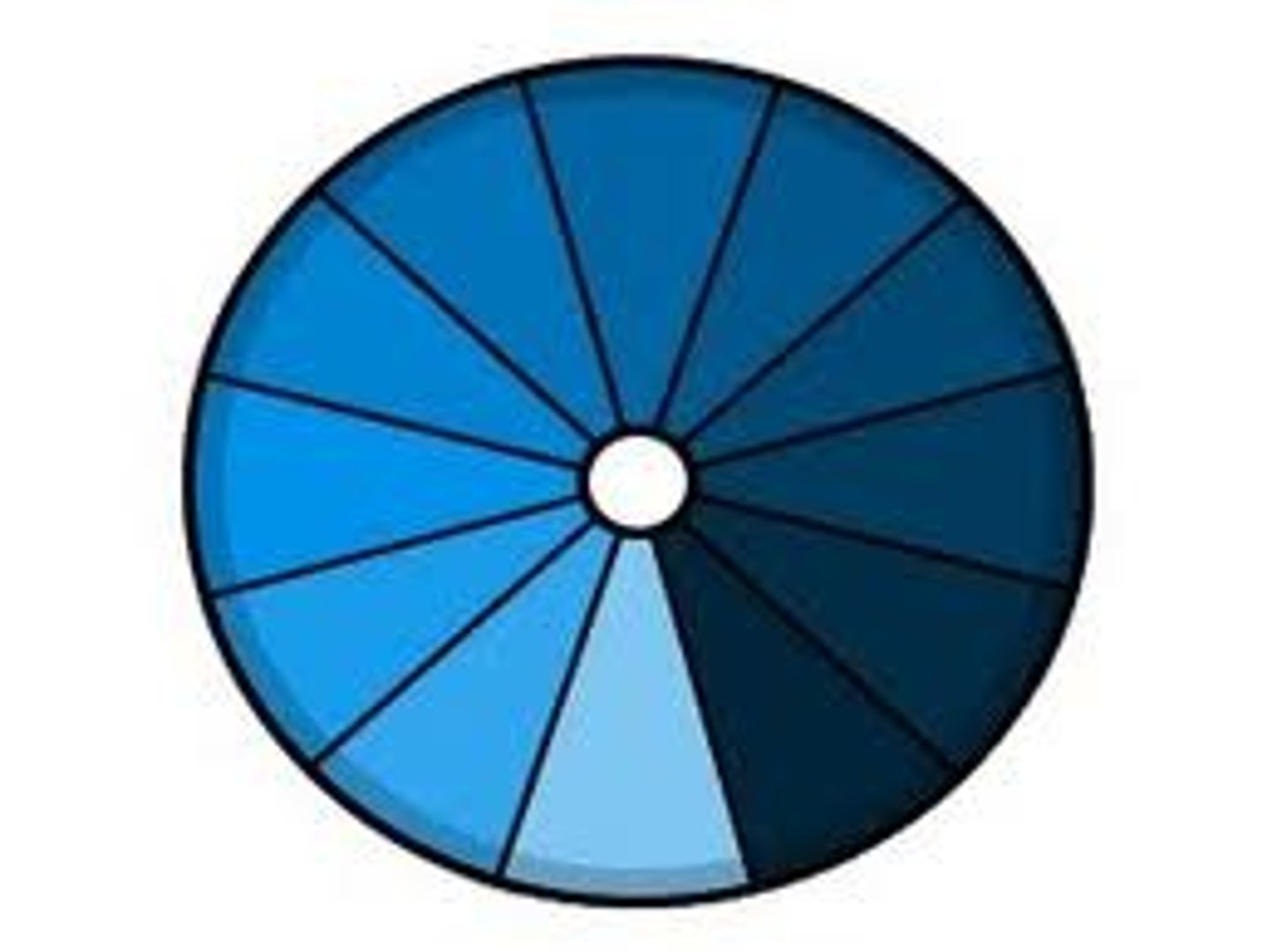
Monochromatic
have tints (white) , tones (gray) + shades (black) of single hue
Proportion (art)
art principle relates directly to math skill of measurement
Style
an artist's manner of expression
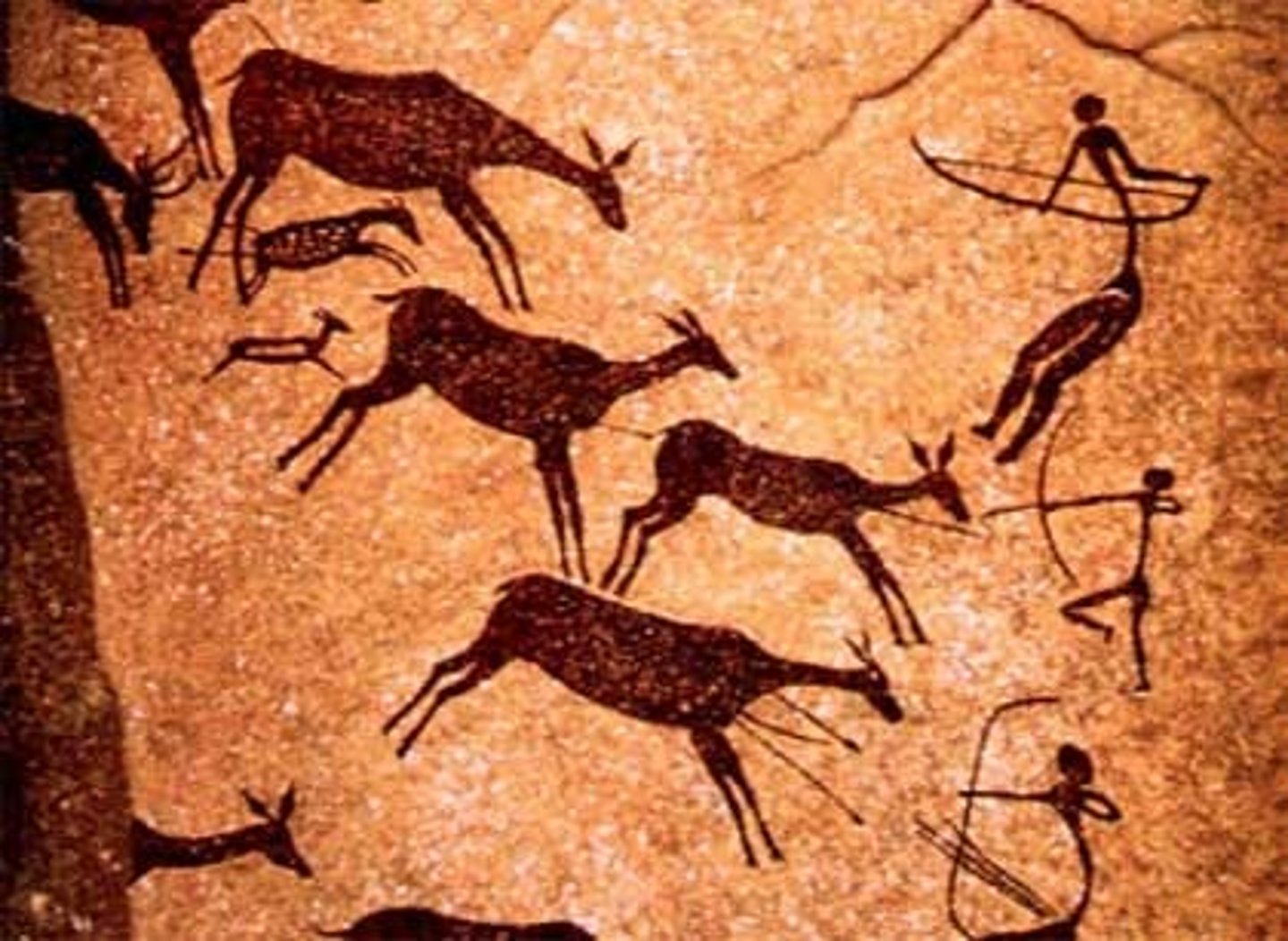
Prehistoric period
characterized by paintings that represent the daily activities of a group of people

Tempo
the speed of the underlying pulse of music
What cultures produced art in the Ancient period?
Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians, Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans
Classical period
Occurred about 1000 years after the Ancient period; Greeks were fascinated by beauty
What did Roman culture focus on during the Classical period?
engineering and building; they built temples, roads, bathing complexes, civic buildings, palaces, and aqueducts; ex. the Pantheon
Medieval period
500-1400 CE
Romanesque architecture
round arches, vaulted ceilings, heavy walls that are ornately decorated, primarily with symbolic figures of Christianit
Gothic architecture
ribbed vaulting and pointed roofs; flying buttresses, pointed arches and vaults; included sculptures and stained-glass windows that for the worshippers were visual encyclopedias of Christian teachings and stories
Renaissance period
14th-16th century; developed new forms and revived classical styles and values; more references to classical iconography and the pleasures of an idyllic golden age; ex. include Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael, Titian, Correggio, Giorgione, and Bellini
Baroque style
17th century in Europe; used exaggerated motion and elaborate artwork; produced drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur; ex. includeCarravagio and Rembrandt

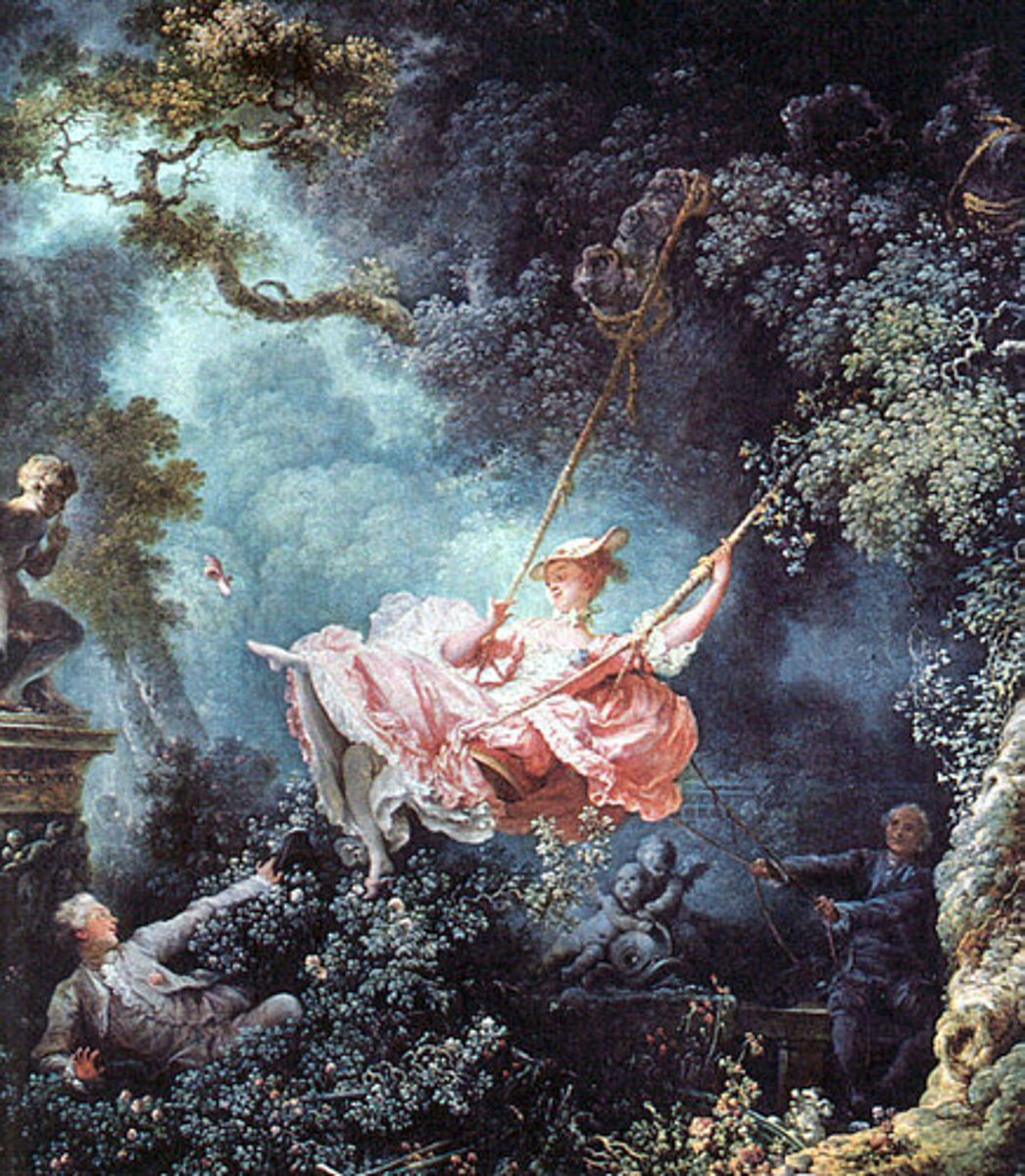
Rococo art
early 18th century; turned the drama of the Baroque period into light, pastel toned, swirling compositions that seem placed in an idyllic land of a golden age; ex. include Elisabeth Vigee-Lebrun, Francisco Goya, Jean-Antoine Watteau

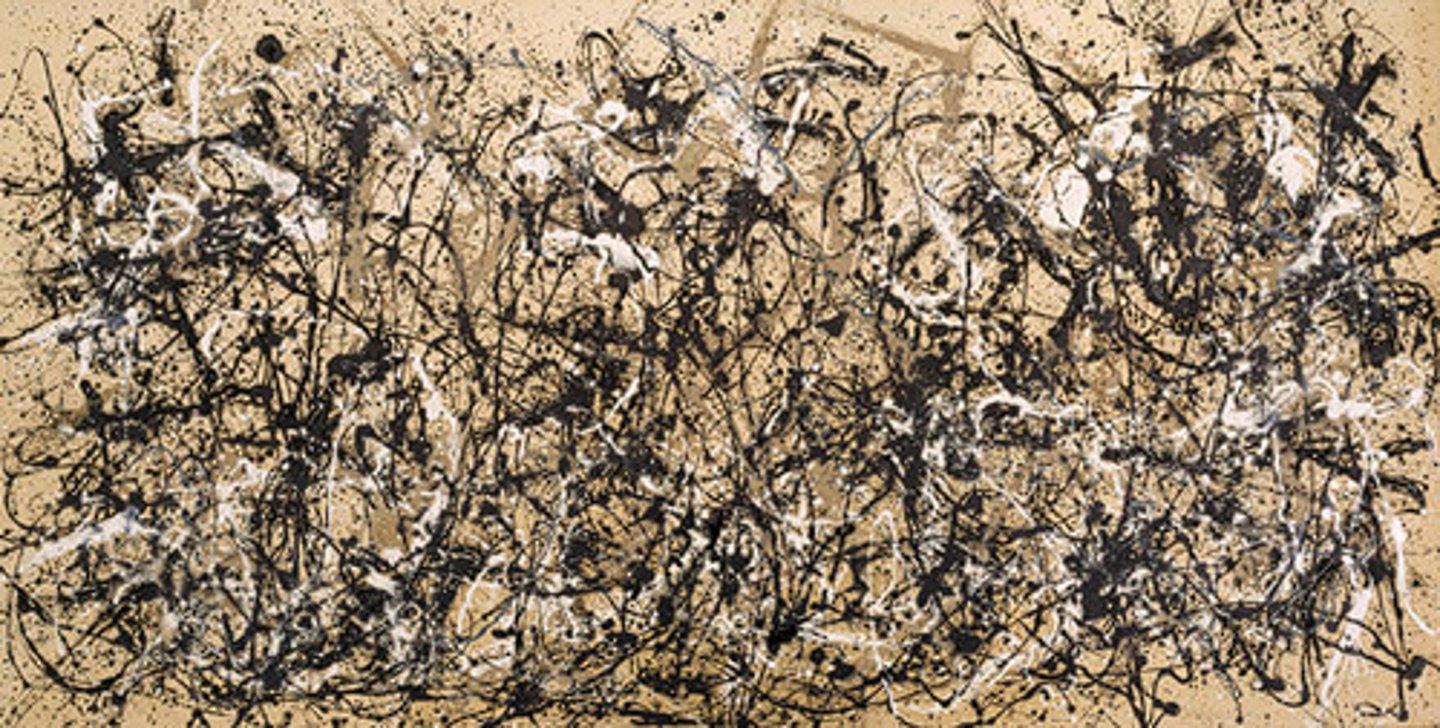
Jackson Pollack
"Action Painting" dripped and poured paint over large surfaces

Eduard Vuillard
Pointillism
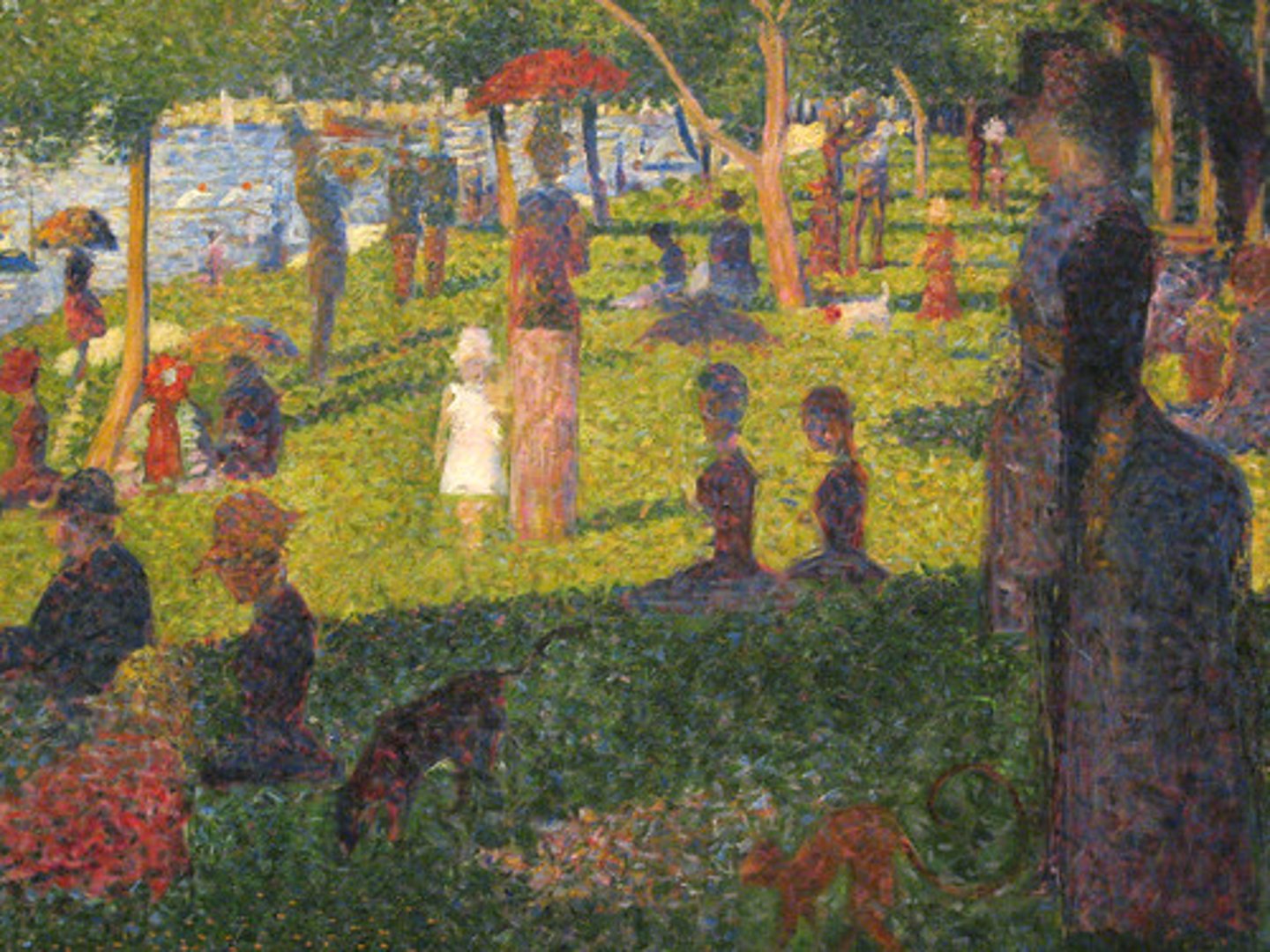

Pointillism
small, distinct dots of color are applied in patterns to form an image
Artists: Eduard Vuillard + George Seurat + Paul Signac
Ukiyo Art
wood block prints centered around everyday people of Japan (not imaginary)
- pop themes: beautiful women, kabuki actors, sumo wrestlers, folk tales
- 17-19th c.

What three elements characterized 19th century art?
Romanticism, realism, and impressionism
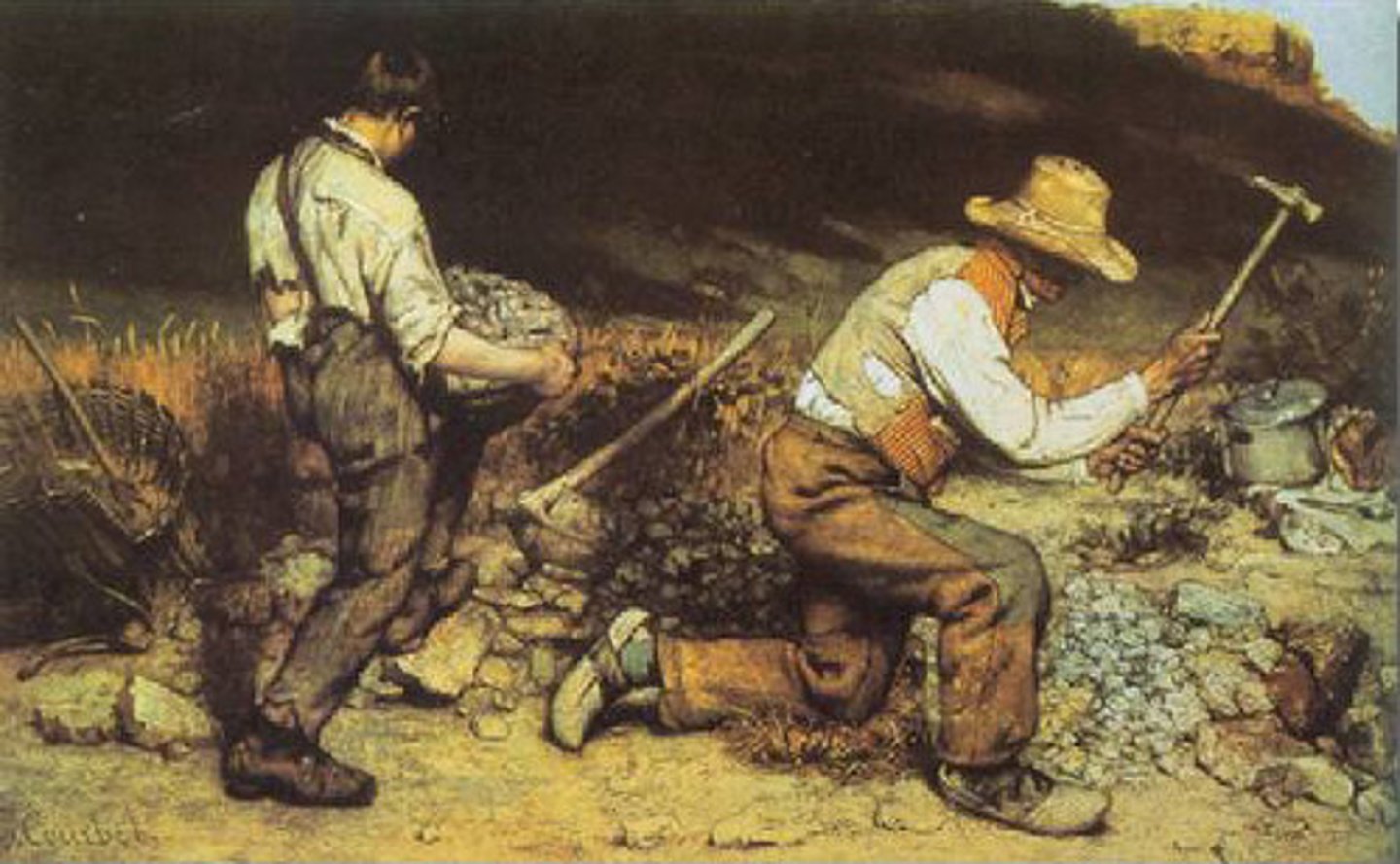
Realism
rejected traditional means of composing a picture, academic methods of figure modeling and color relations, and exact rendering of people and objects; focused on quickly observed and sketched moments of life, the relation of shapes and forms and colors, the effects of light, and the act of painting itself

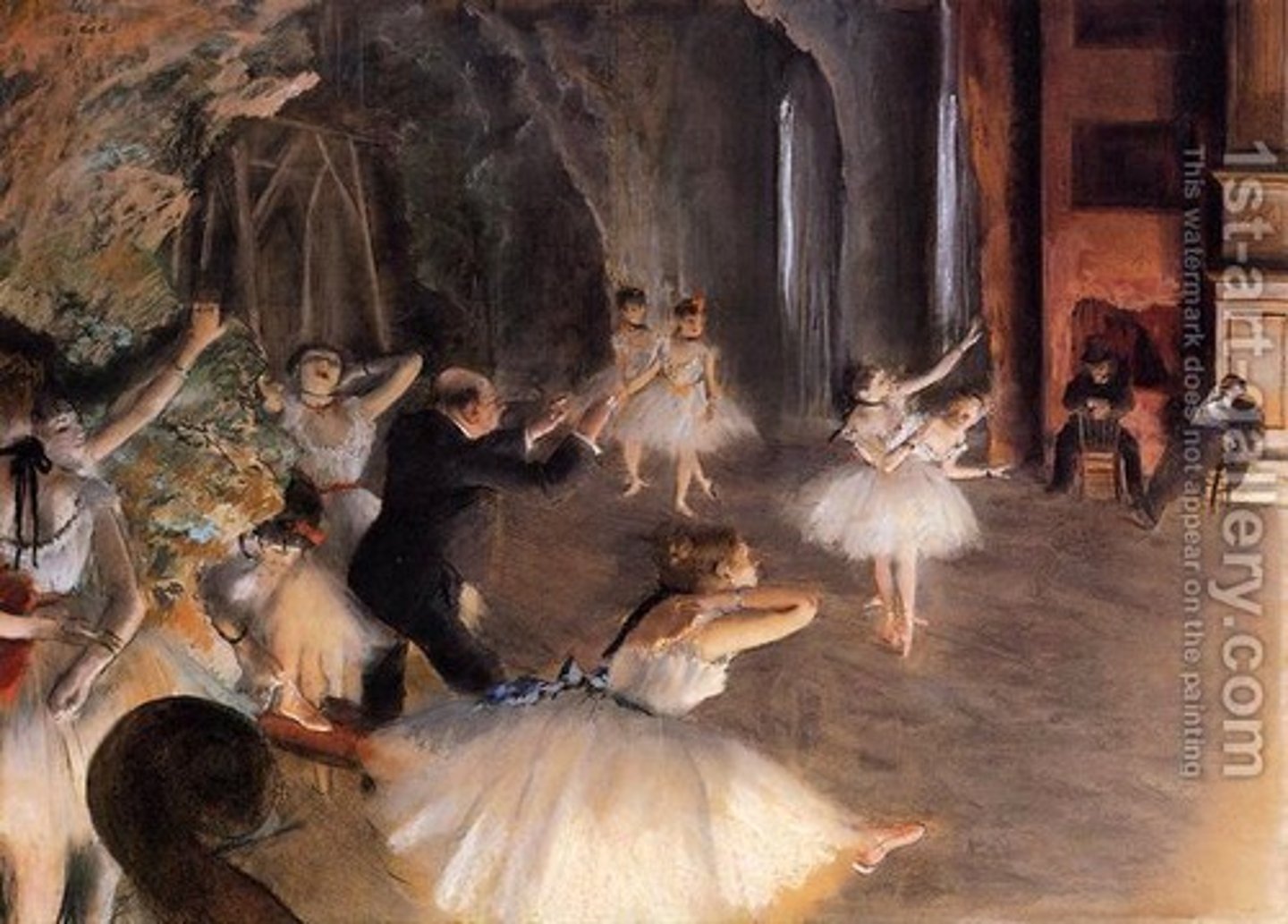
Impressionism
using light and color to capture the impression of images as opposed to the "real image"; ex. Edouard Manet, Claude Monet, Camille Pissaro, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Alfred Sisley, and Edgar Degas

Surrealism
artists made the subconscious and the metaphysical important in their work; inspired by psychoanalytic writings of Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung; ex. Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Frida Kahlo
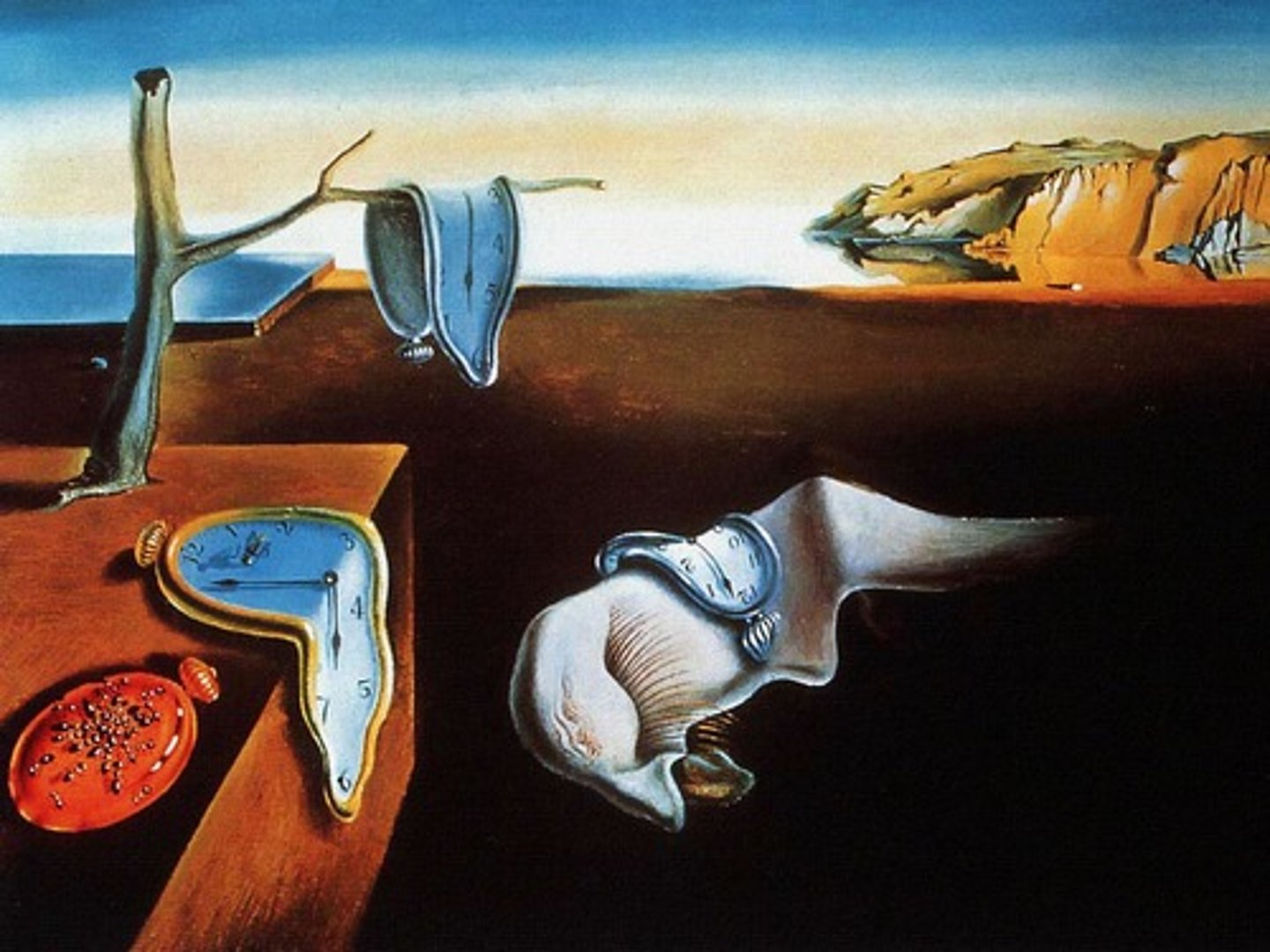
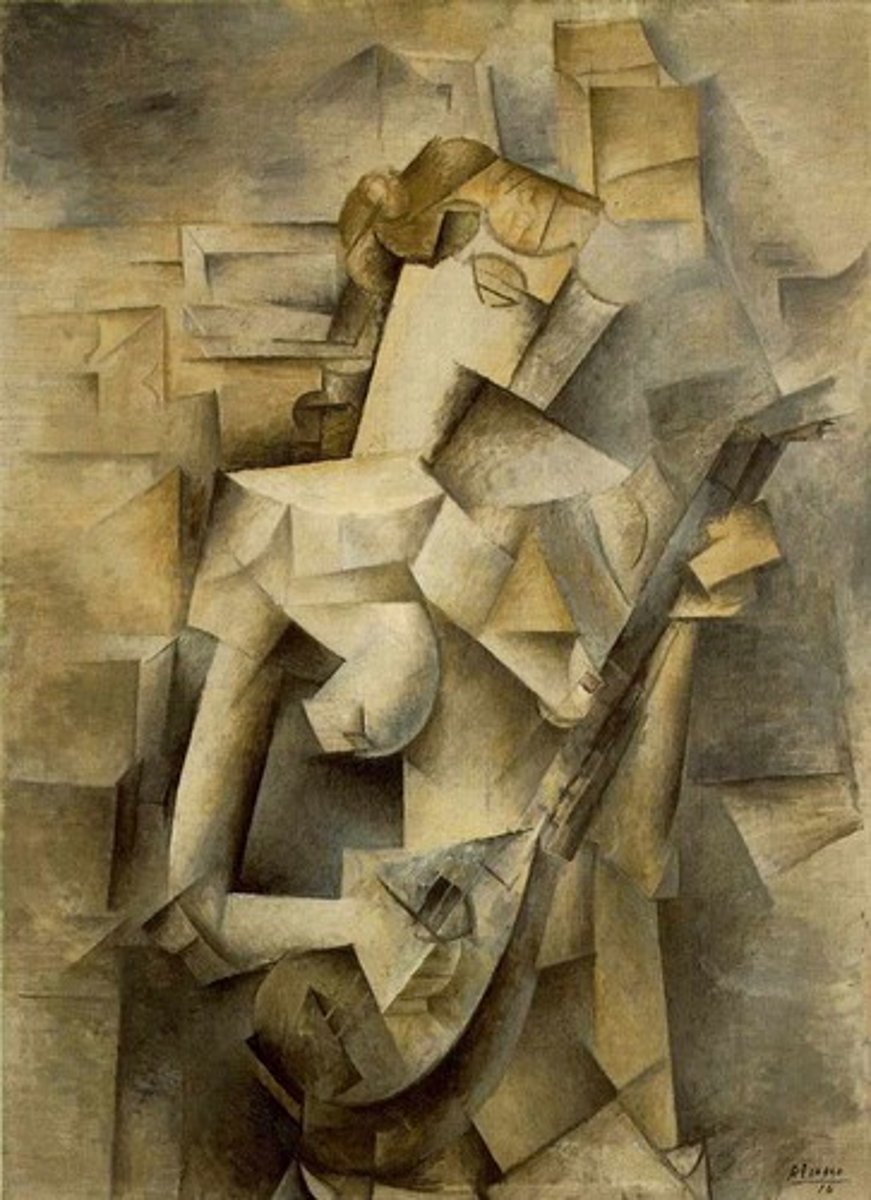
Cubism
Characterized by geometric shapes
Artists: Pablo Picasso + Georges Braque
challenged common realistic conventions to create new representations of reality or imagination; objects are analyzed, broken up and reassembled in an abstracted form—instead of depicting objects from a single viewpoint, the artist depicts the subject from a multitude of viewpoints to represent the subject in a greater context

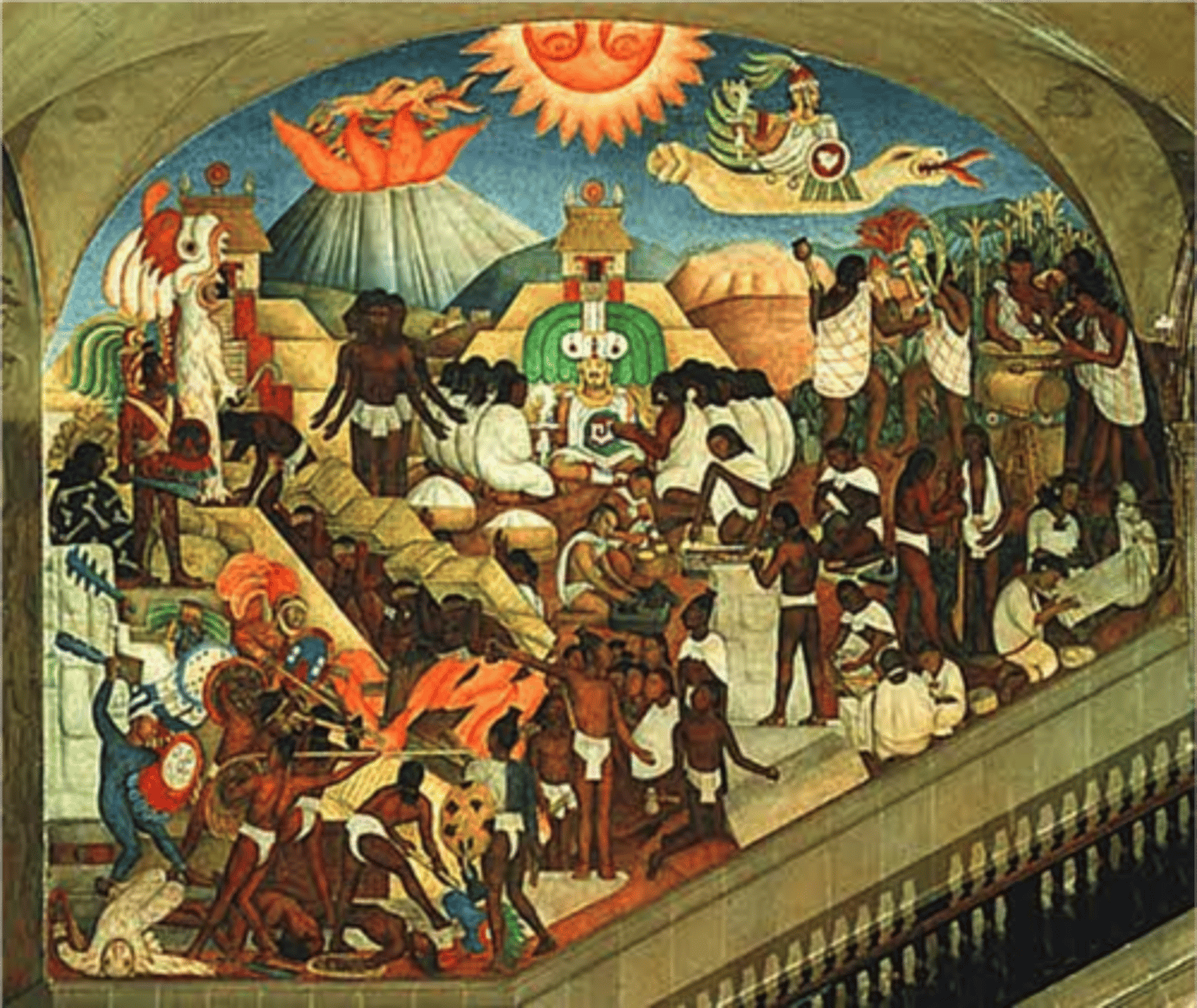
Muralists
between WW1 and WW2; created art that was physically interesting and with subjects accessible to the average person; ex. John French Sloan, George Bellows, and Diego Rivera

Photorealism
paintings resembling lifelike photos; often portraits, still lifes, or landscapes
Rhythm
the varied lengths of sounds and silences in relation to the underlying beat; patterned recurrence of a beat
(duration + tempo)
Beat
- the pulse that is felt in the music
- element of time in music (rhythmic pulse)
Quarter note

Quarter rest
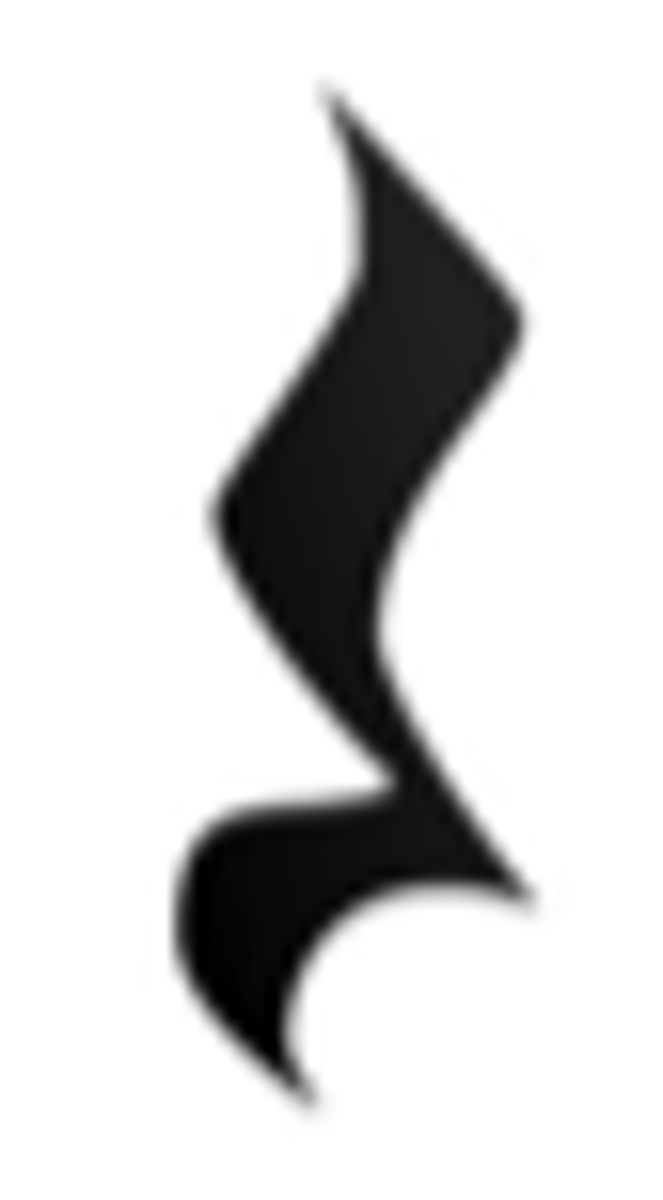
Two eighth notes
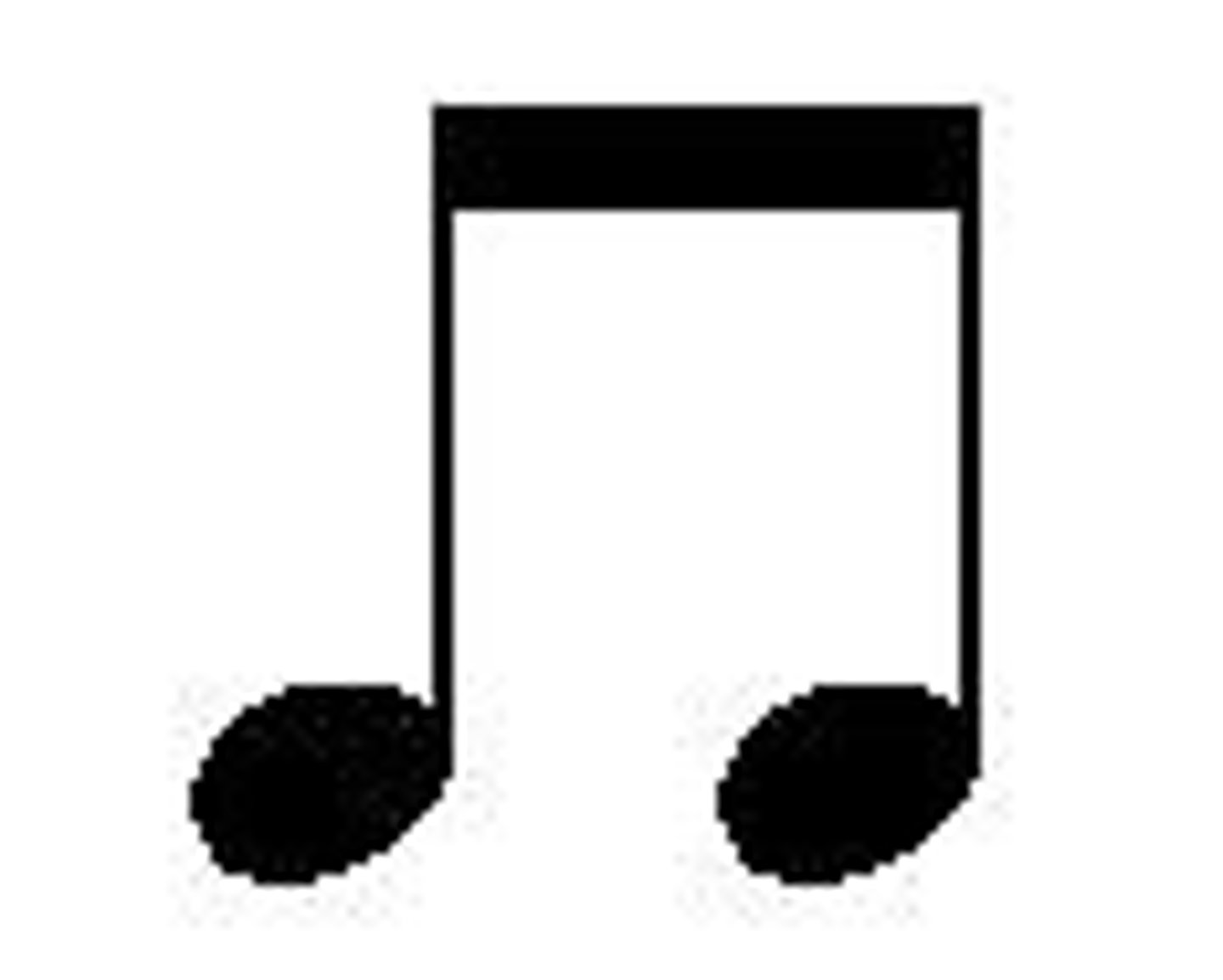

Eighth note
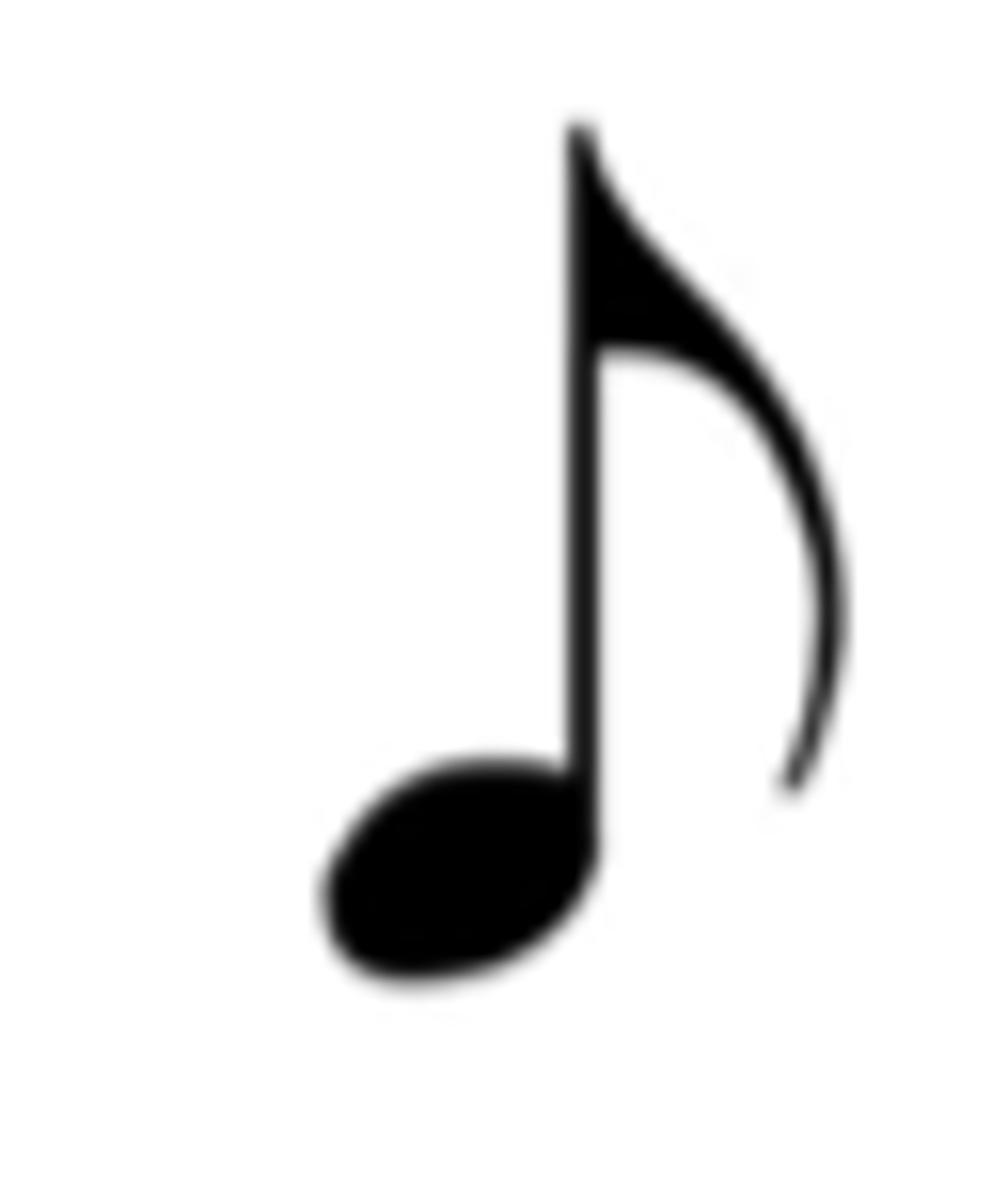

Eighth rest

Half note

Half rest
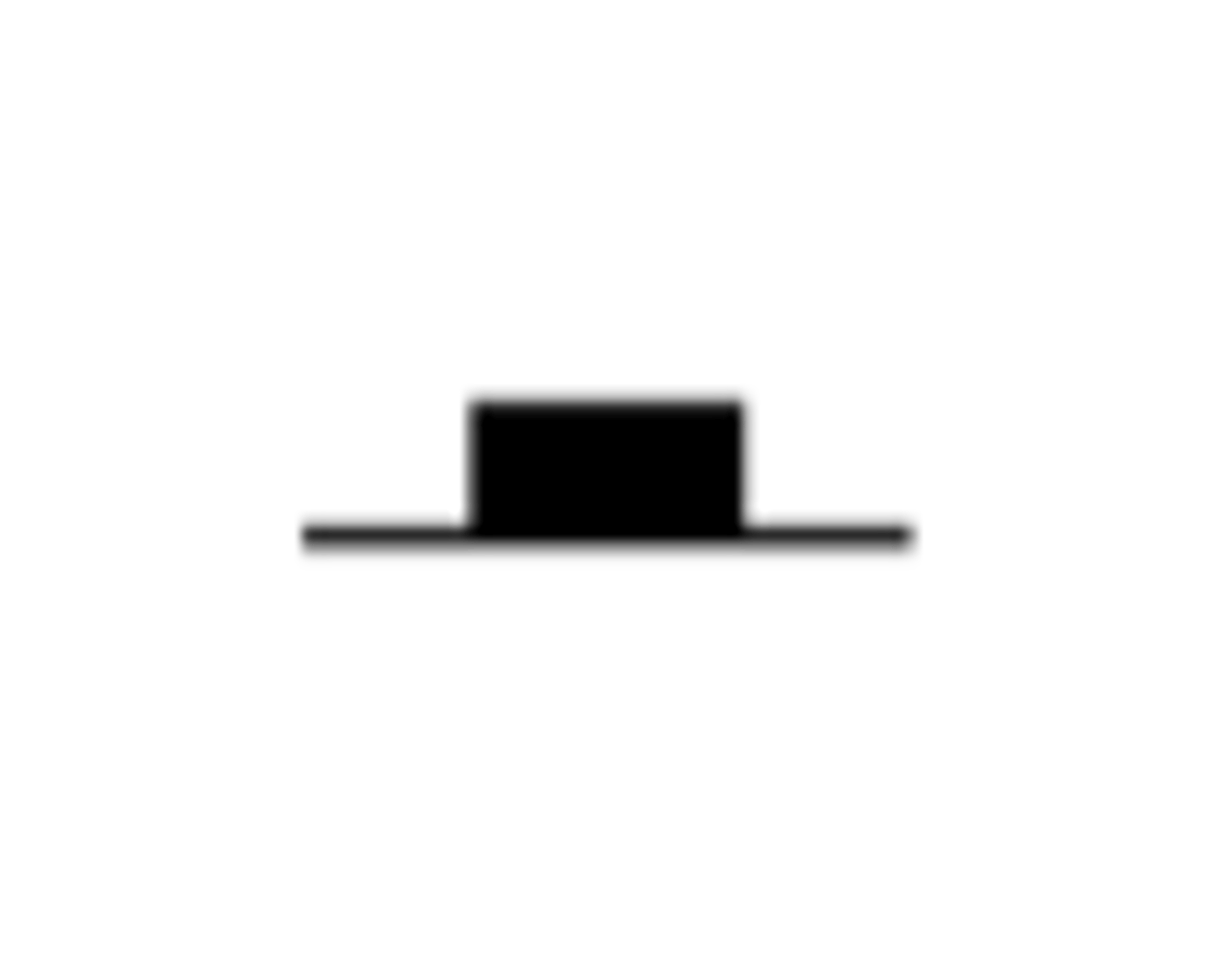
Whole note
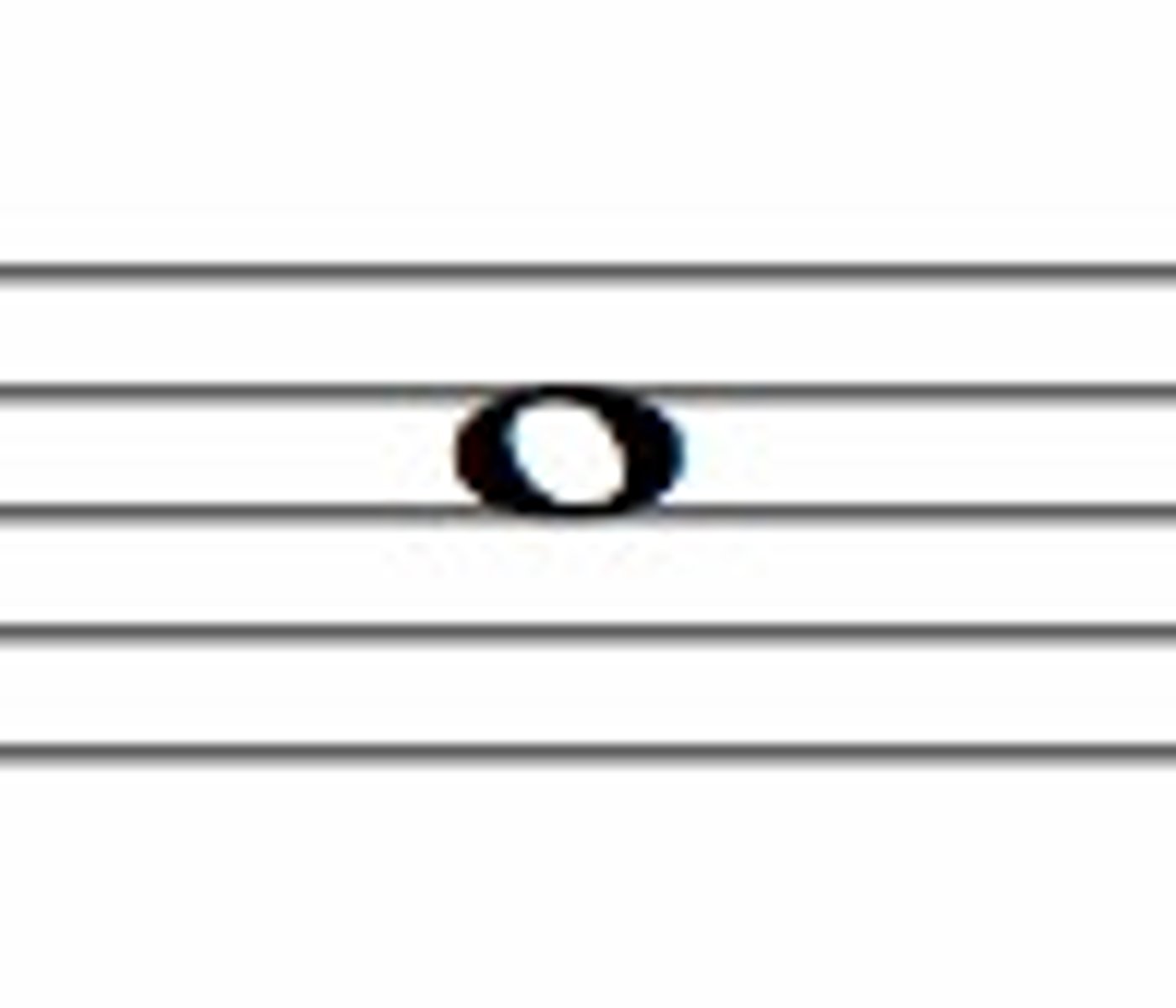

Whole rest

Meter
how musicians group the steady beats; grouped in 2s = duple meter; grouped in 3s = triple meter (waltz)
What are the letters of the musical alphabet?
A, B, C, D, E, F, and G
Clef signs
determine the pitch level, either higher or lower

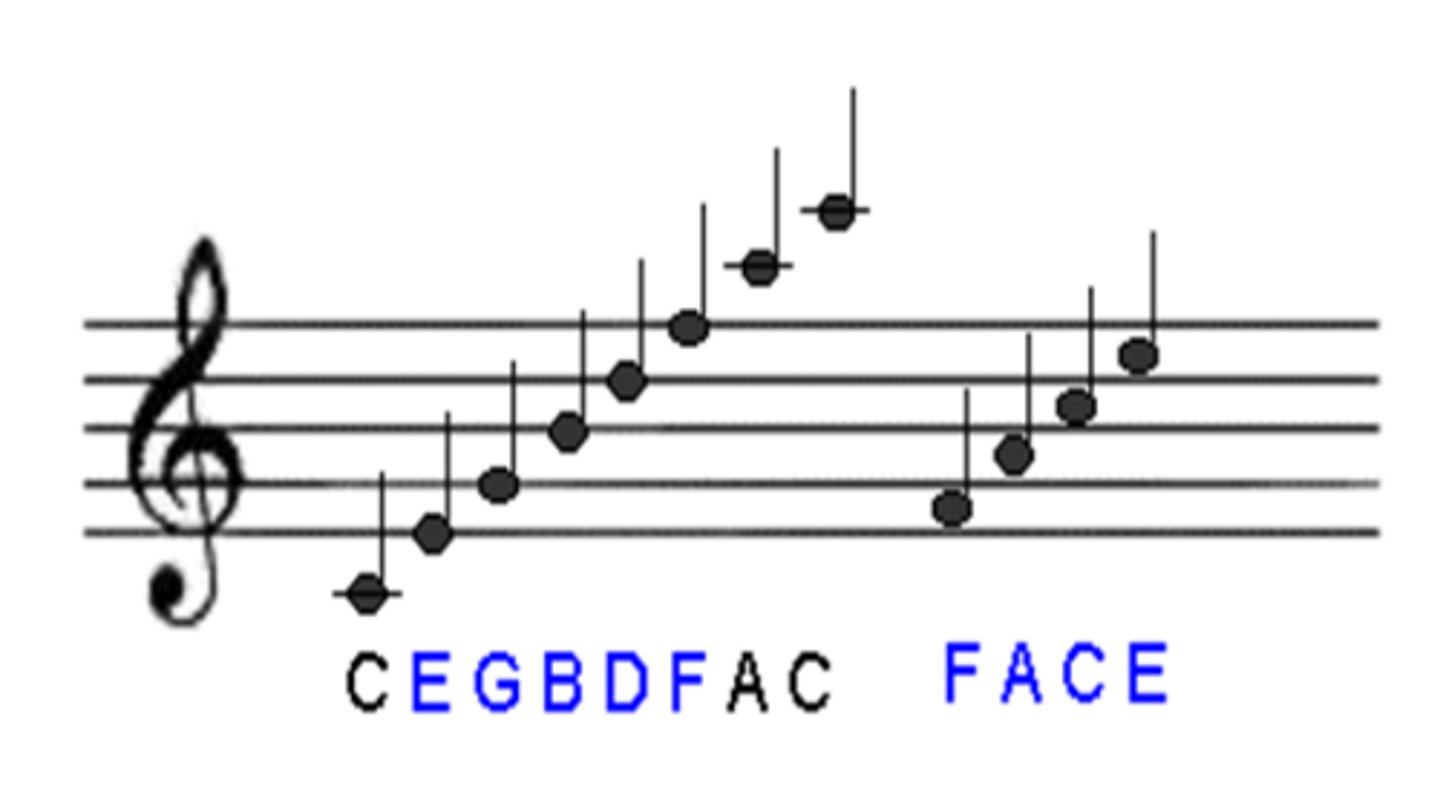
What are mnemonics for remembering the lines and spaces of the treble clef?
Lines: Every Good Boy Does Fine (E, G, B, D, F)
Spaces: FACE

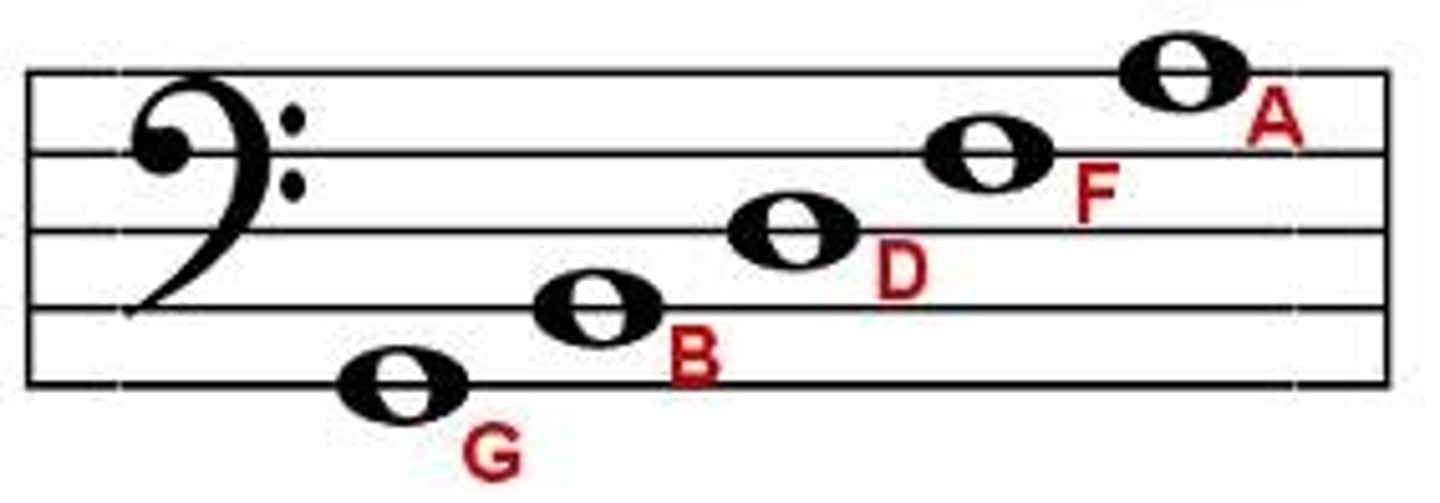
What are mnemonics for remembering the lines and spaces of the bass clef?
Lines: Good Boys Do Fine Always (G, B, D, F, A)
Spaces: All Cows Eat Grass (A, C, E, G)
What are all the articulations in music?
Staccato, marcato, legato, martele, pizzicato
Interval
the distance between two pitches
Unison
two sounds of an identical pitch
Octave
the distance between one pitch and the next pitch with the same name eight steps apart
Crescendo/Decrescendo
process of gradually getting louder (crescendo) or quieter (decrescendo) --> DYNAMICS IN MUSIC
Harmony
- use of different pitches simultaneously
- supporting infrastructure/sounds for melody
ex: chords in a guitar
Melody
tune; part you can hum/whistle/sing
Expression (music)
More than just the notes - comes from the performer
Form (music)
the structure of design (organization) of the music
- repetition, contrast, unity, variety
Phrase (music)
a musical line that contains groups of pitches; similar to a sentence in language
Pitch
the highness or lowness of a sound
Timbre
difference in sounds
(flute + trumpet play same exact note but sound different bc of timbre)
Dynamics (music)
term used by musicians to represent the louds and softs in music or the volume of the sound
-pianissimo, piano, mezzo-piano, mezzo-forte, forte, fortissimo
-Crescendo + decrescendo
Articulations (music)
attack and decay of tones + how they're produced, structure an event's start and end, determining the length of its sound
- They can also modify an event's timbre, dynamics, and pitch.
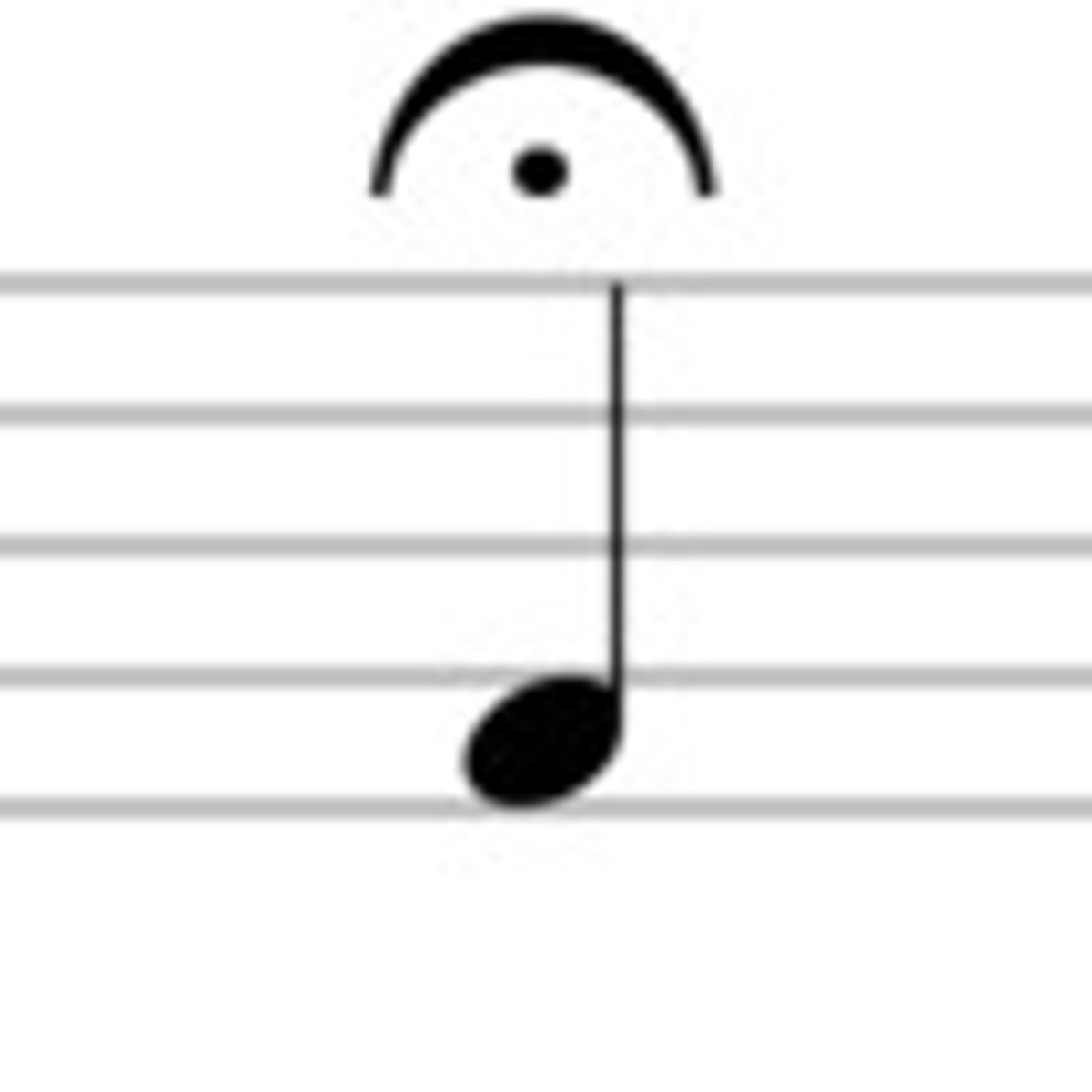
Fermata
a pause of unspecified length on a note or rest

Rubato & Ritardando
gradual changes of tempo + the alteration of note values in a musical composition
Rubato: slight speeding up and then slowing down
Ritardando: decreasing in speed
Pianissimo [pp]
very quiet
Piano [p]
quiet
Mezzo-piano [mp]
moderately quiet
Mezzo-forte [mf]
moderately loud
Forte [f]
loud
Fortissimo [ff]
very loud
Staccato
each note is detached or separated from others; short
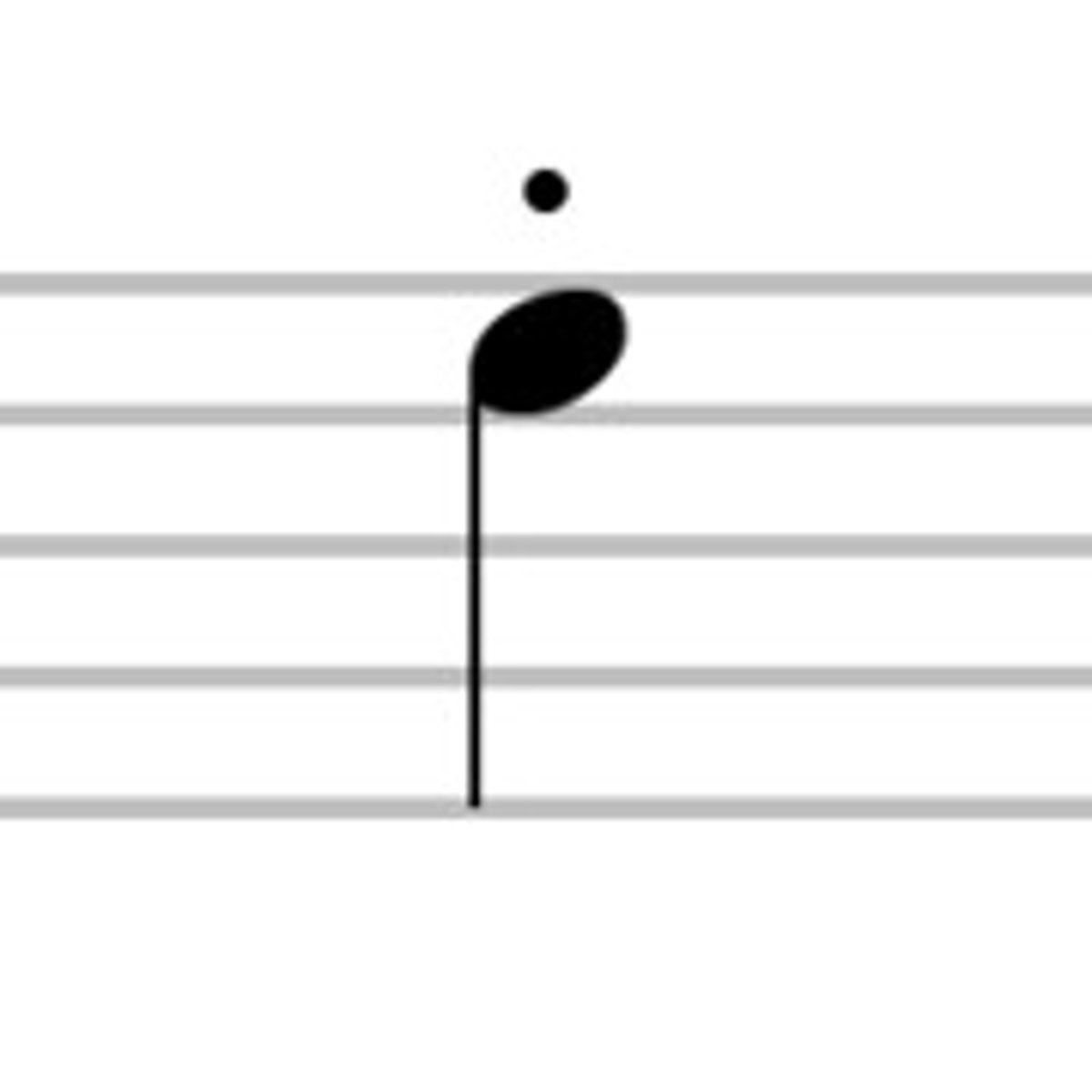

Marcato
with emphasis and louder than the rest; stressed

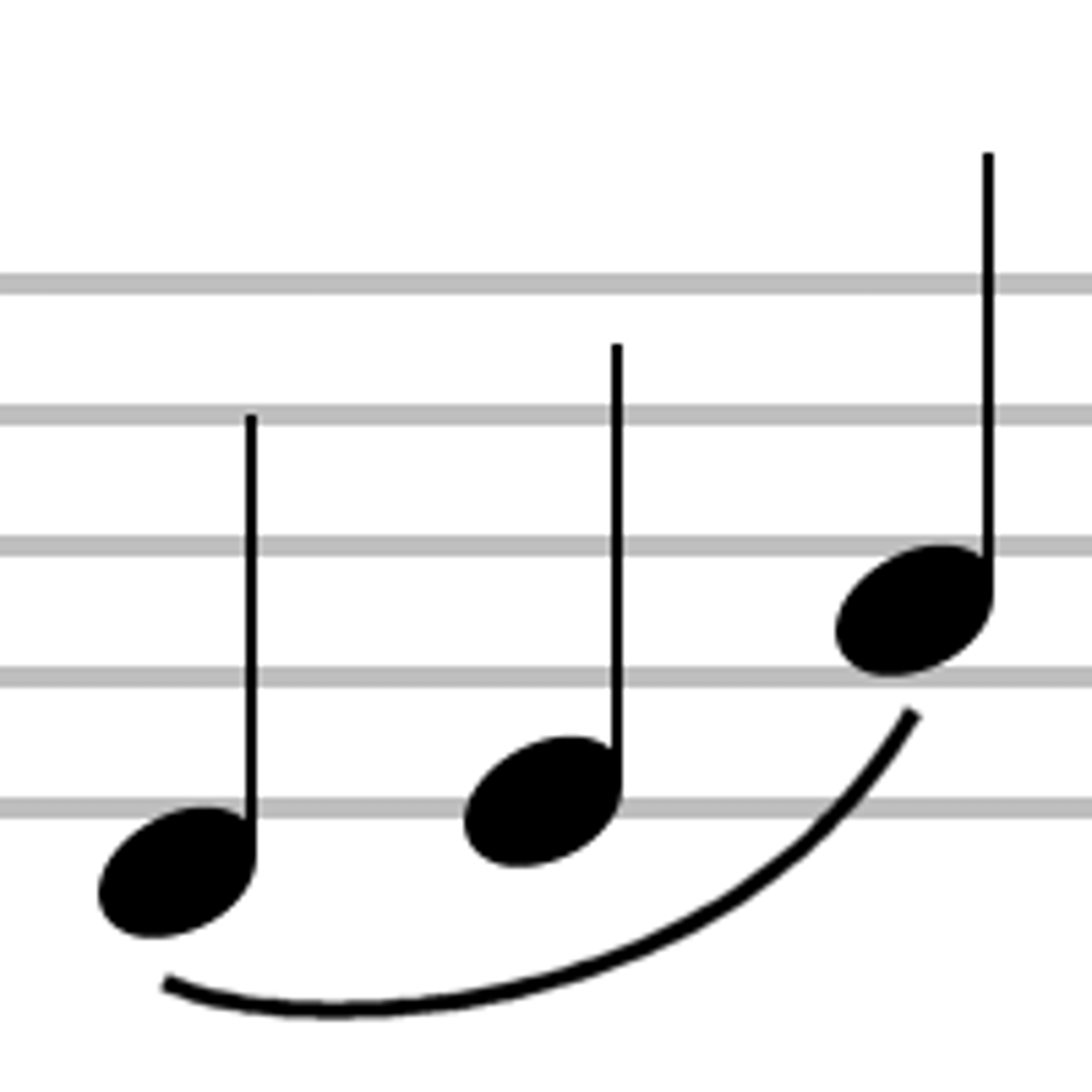
Legato
smooth + connected, no breaks in between notes

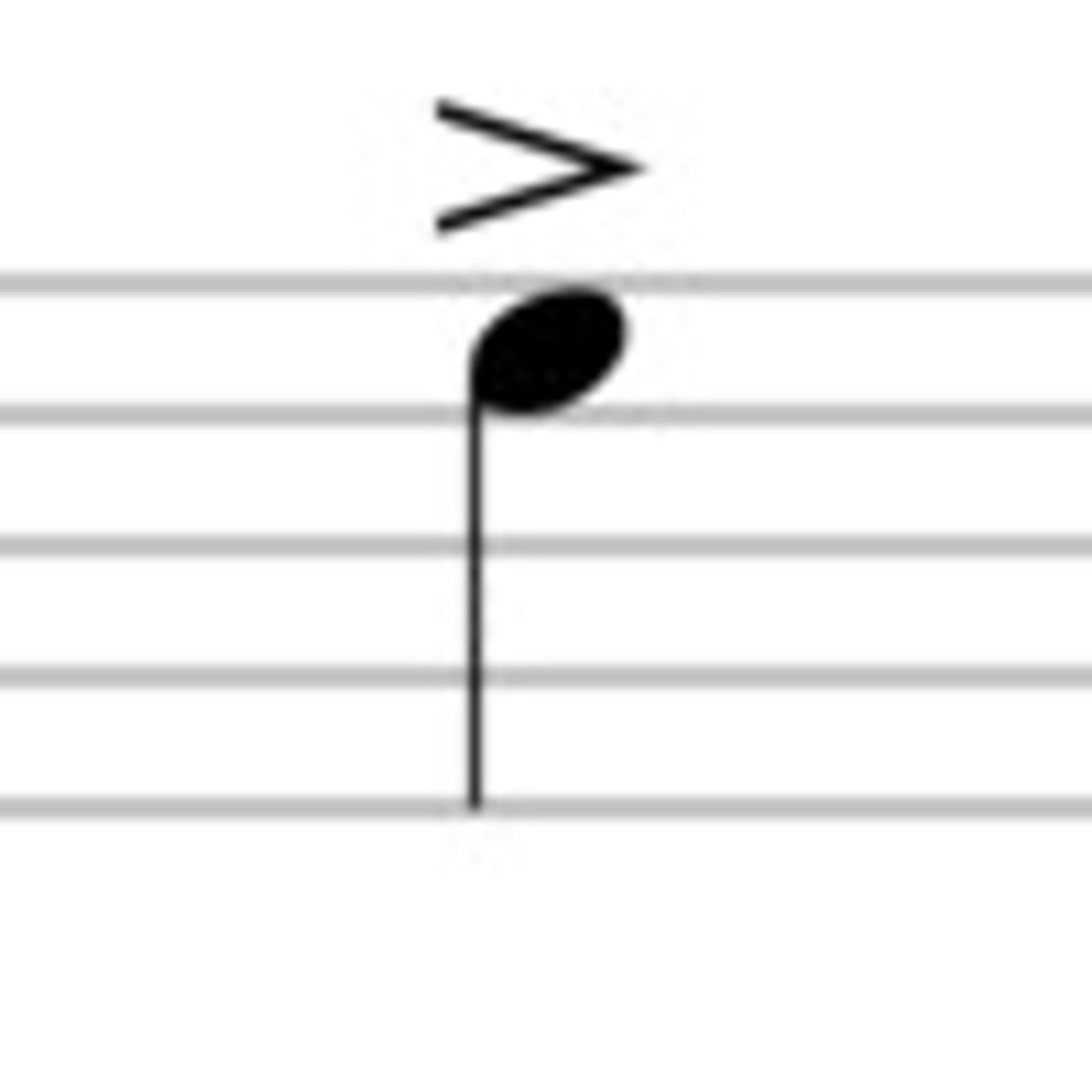
Sforzando (sfz)
Strongly accented, or playing in a forced manner
Portamento
Carrying the sound very smoothly (legato) from note to note
Martele
Bow-strike: hammered, individual dotted notes
Pizzicato
plucking the strings instead of using a bow
What is good singing posture?
feel flat on floor, shoulders back, head and chest up, back slightly forward
What are the four main strands in the Texas state curriculum for music?
music literacy, creative expression, historical and cultural relevance, and critical evaluation and response
What are the different forms of Jazz?
Dixieland, classic, swing, bebop, mainstream, blues, fusion, modern, free, cool new wave
What artists are associated with Jazz?
Swing: Duke Ellington, Goodman, Basie (1930's)
Cool Jazz: Miles Davis
Bebop: Parker, Gillespie (1940's)
Free: Coleman, Coitrane (1960's)
What are the main elements of swing, cool, bebop and free jazz?
Swing: jazz style + quality of jazz perfromenace in contrast to straight rhythm in music
Cool: laidback, slower, softer, relaxed in contrast to Bop
Bop: focus on rhythm and faster tempo
Free: broke away from harmonic.melodic and formal conventions
Which music style is from Southern Texas, uses an accordion and a bajo-sexto?
Tejano Music
Mariachi Music?
ensemble; originated in Jalisco, Mexico. Has a trumpet, violins, guitar + guitarron
the geographic location of Texas + Mexico influenced mariachi style on Texas (migration from Mexico)
Count Basie, a jazz pianist and band leader, employed which style of playing in his accompaniment?
Comping
After the game has started, which of the following what be an inadvisable method for modifying a physical activity or game?
Applying rules of elimination because the highest-skilled kids will receive all the activity/opportunity provided and the lowest-skilled kids will become spectators
Dramatic play includes a variety of activities, but it rejects what?
Memorization of lengthy dialogues