Musculoskeletal & Burns
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What are common patterns of burns with developmental levels?
hot water scolds are common in toddlers, so turn the pot handle away on the stove
electrical burns are common in young children, so cover sockets
flame related burns are more common in older children
chemical burns depend on agent and duration
child abuse
Children playing with matches or lighters count for how many house fires?
they count for 1 out of 10 house fires
Which kind of burns are the most common in children?
thermal burns are the most common in children
How are burns classified?
it is classified by the extent of the injury described in terms of total body surface area: age related charts
depth of injury
severity of injury
What is a first-degree burn?
only redness on skin
superficial
involve the epidermal layer only
no blisters
What is a second-degree burn?
blistering
partial thickness
all the way through epidermis and some of the dermis
What is a third-degree burn?
can see fat layer
full thickness
extends through epidermis, dermis, and nerve endings
What is fourth-degree burns?
can see bone
full thickness
underlying tissue exposed
What is a minor burn?
<10% of TBSA and partial thickness
treat outpatient
maybe 1-2 day admit
What is a moderate burn?
10-20% of TBSA and partial thickness
treat inpatient with expertise in burn treatment
What is a major burn?
>20% if partial thickness
all full thickness burn
treat in a specialized burn center
How are minor burns managed and treated?
usually managed outpatient
wound cleansed with tepid water and soap
blister removal is controversial, some think it promotes bacterial growth
antimicrobial ointment and dressing per provider order
tetanus vaccine
What kind of burns will always be popped?
chemical burns will always be popped b/c they don't want to leave that chemical agent in contact with the skin
What is always priority with major burns?
airway, and if any respiratory involvement is suspected, were going to give 100% oxygen
severe facial edema or altered LOC will get intubated
What is crucial within the first 24 hrs of major burns?
fluid replacement therapy with NS or LR is crucial
What does nutrition look like with major burns?
they're going to have enhanced metabolic demands
high protein
high calorie
Oral feedings are encouraged, if possible, but if more than what percent of body has been burned, they will receive enteral feeds?
if t25% or more of the person’s body is burned
What vitamins are given to promote wound healing?
vitamin A
vitamin C
zinc
What kind of meds are used for major burns?
abx
pain meds (fentanyl more common)
sedatives (nitrous oxide for procedural pain)
What is an allograft?
it is human cadaver skin
What is a xenograft?
it is a graft pig skin or another animal
What are the complications of burns?
airway compromise
body temperature
infection
profound shock
pneumonia
pulmonary edema
emboli
aspiration
renal failure
loss of function in burned area
What do we need to teach about scar tissue?
we tell patient and their family that scar tissue doesn't grow and expand as child does, so they may need further surgeries demanding on the burn
How do you know if child abuse related to a burn is suspected?
when the history doesn't match to the injury
Are nurses required to report suspicions of child abuse to CPS?
yes, nurses need to report any and all suspected child abuse to CPS and put in an order for a social service consult and document thoroughly
What is traction?
it is forward force produced by attaching weight to a distal bone fragment
What is countertraction?
it is backward force provided by the body weight
What is frictional force?
it is provided by patients contact with the bed
What is the function of traction?
it immobilizes a bone or fracture site to promote healing and prevent complications
What is manual traction?
it is applied to the body part by the hand placed distal to the fracture site
may be provided by application of a cast, but more commonly when a closed reduction is performed
What is skin traction?
it is applied directly to the skin surface and indirectly to the skeletal structures
pulling mechanism is attached to the skin with adhesive or elastic bandage (brace, splint)
What is skeletal traction?
it is applied directly to the skeletal structure by pins, wires, or tongs through the diameter of the bone distal to the fracture site
halo, femur fracture
What is Bryant traction?
is a type of skin traction
used for less than 3 years old and/or less than 17.5 kg (35lbs)
with femur fracture or congenital hip dysplasia
position the pt on back, bottom lifted off of bed - weights pulling up & hanging over bed
How should traction weights hang?
ropes, pulleys, and weights should hang freely
Can you, as the nurse, release traction weights?
you can never release traction unless told by provider
What are the 6 P's?
pain
pallor
paresthesia
paralysis
pulse
pressure
What is developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
it is when the femoral head slips in and out of socket
can be related to incorrect swaddling or congenital factors
breach is a high risk factor
What are the signs and symptoms of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
shortened limb
restricted abduction
asymmetry of gluteal and thigh fat folds
telescoping of thigh
What is the Ortolani assessment for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
it is when the hip clicks with abduction
What is the Barlow assessment for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
is dislocation of the hip with adduction
What is the Allis assessment for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
it is when one knee is lower than the other leg when flexed
Does the nurse preform Ortolani, Barlow, and Allis assessment for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
only a provider can perform these assessments
What is education about the prevention of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
educate about correct swaddling
What is the pavlik harness?
it is a harness used for developmental dysplasia of the hip that
used in newborns to around 6 months of age
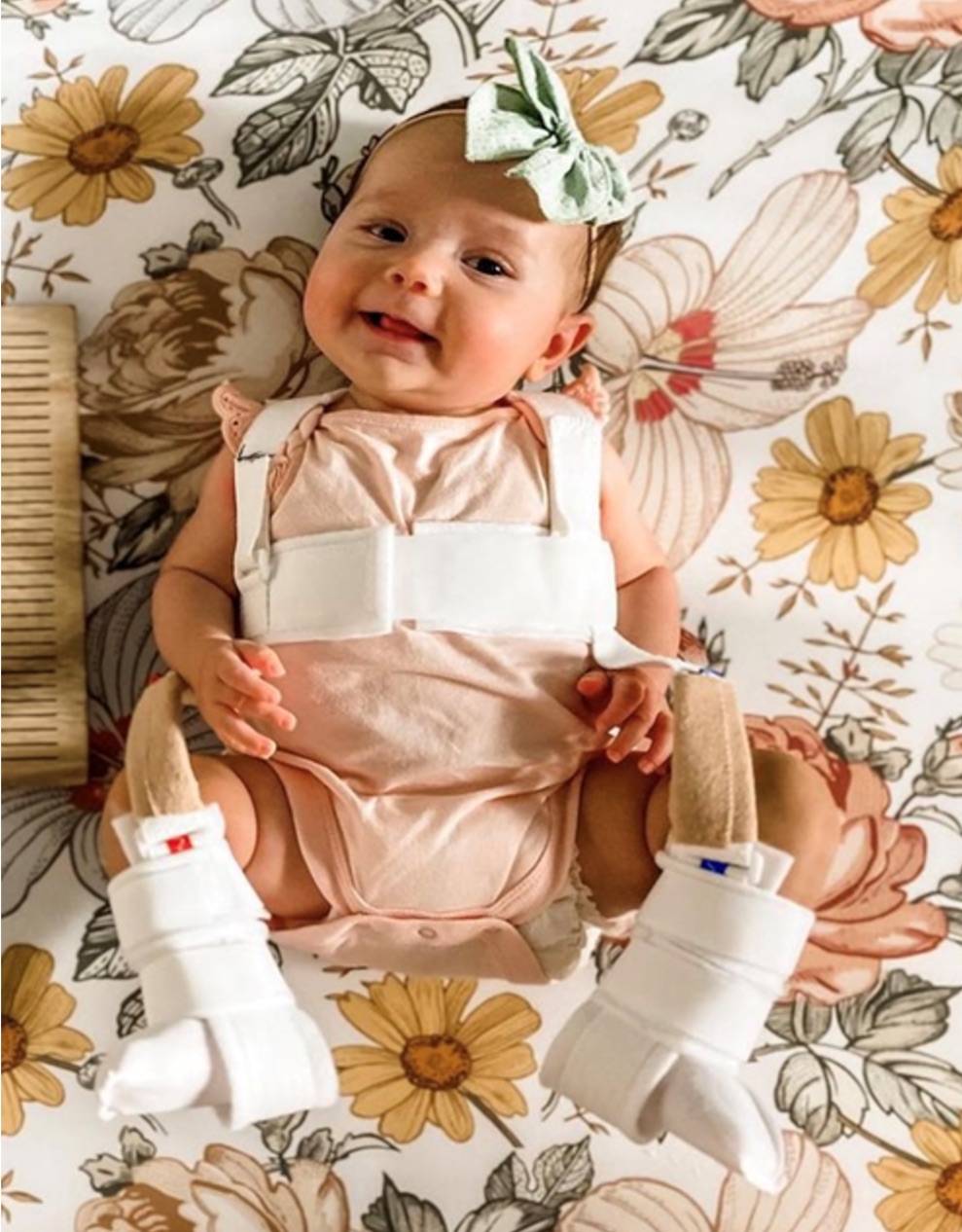

How long does a baby wear a palvik harness?
they wear it for 22-24 hrs a day
What kind of cast in used for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in children who are older than 6 months?
closed reduction surgery w/ spica cast
spica cast is a lower extremity cast
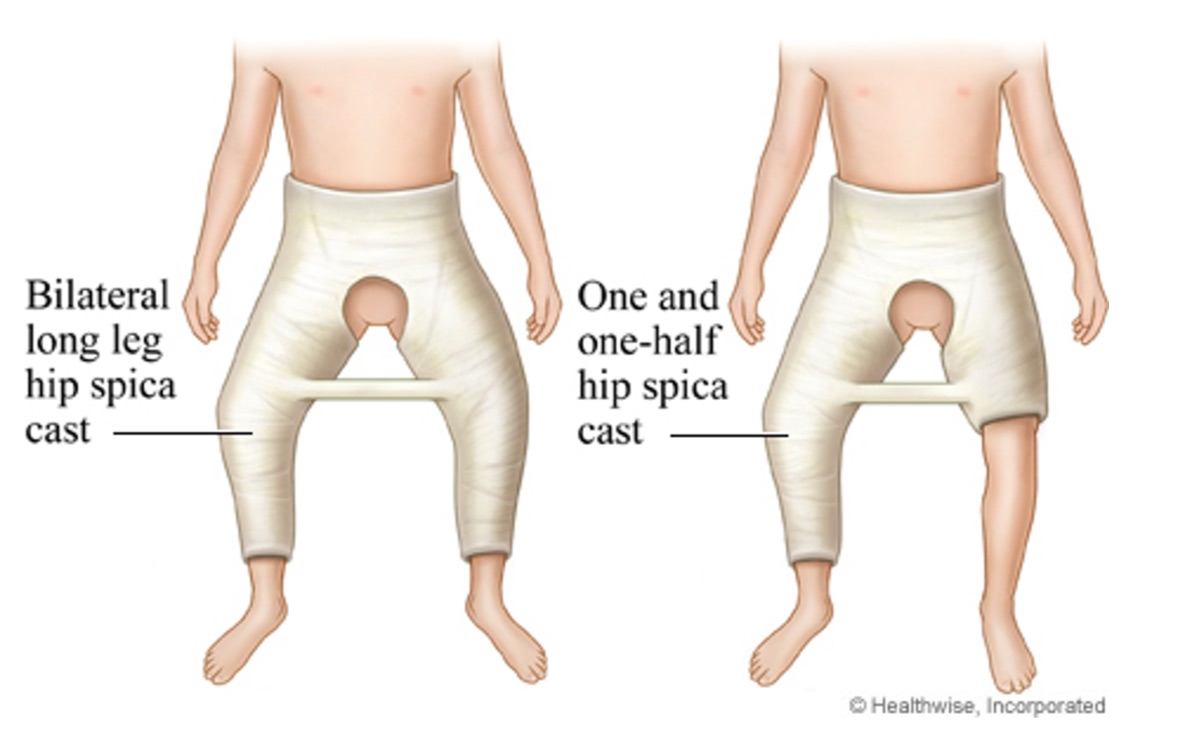
What are education points for the spica cast?
don't lift or turn the child by the crossbar
keep the cast dry
keep small toys and items away from putting things in the cast
What is clubfoot?
congenital abnormality where foot is twisted out of normal position
can be unknown cause or occur isolated in association with other disorders
can be unilateral or bilateral
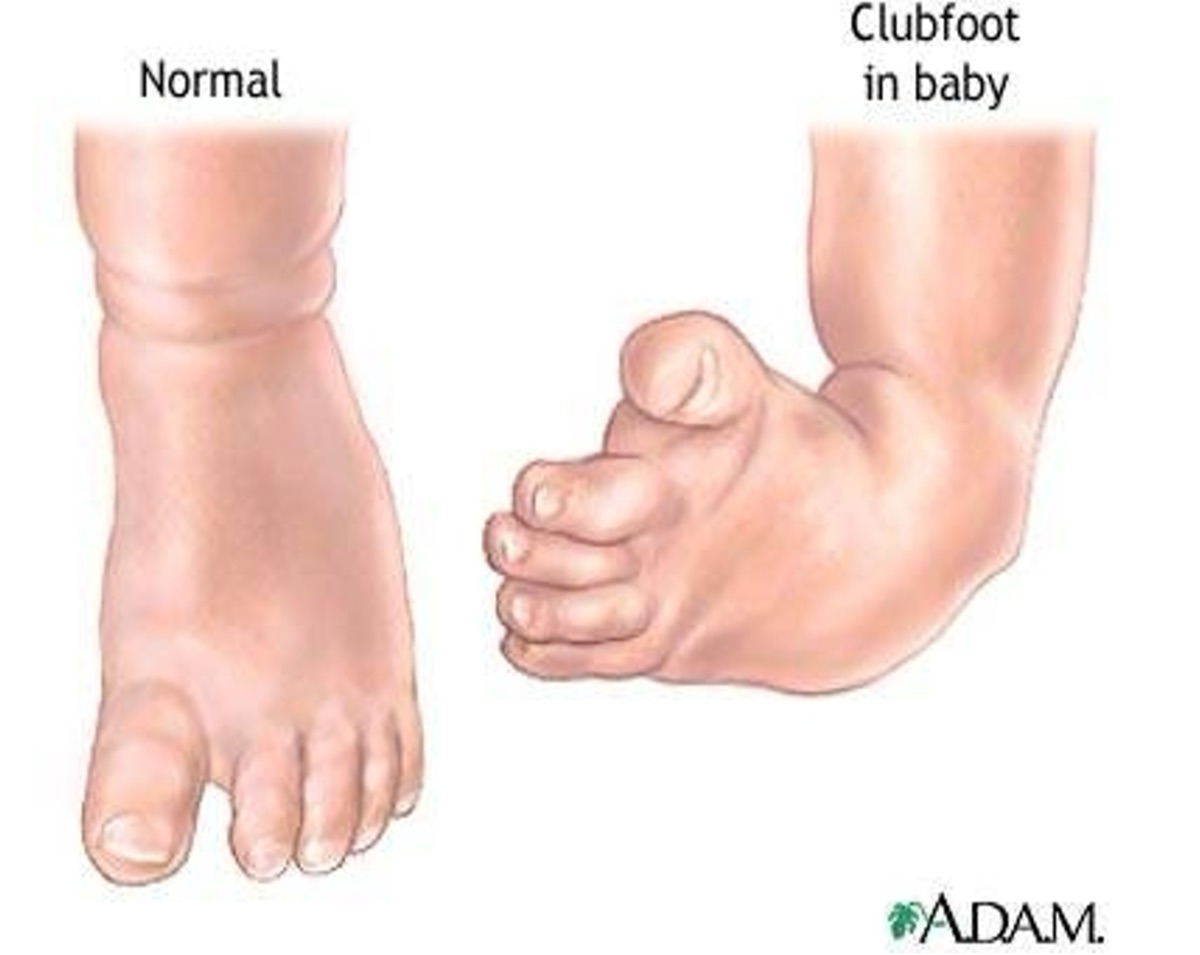
How is treatment done for clubfoot?
done in stages
correct the deformity
maintain the correction until the child has good muscle balance (casting)
prevent the deformity from re-occurring (shoes, boots)
What is the treatment of choice for clubfoot?
serial casting for 6-10 weeks at a time ASAP after birth is the treatment of choice b/c the short bone in the foot haven't ossified yet
What are the other treatments for clubfoot?
corrective shoes they can wear after the casting
surgery if the deformity is not addressed by shoes and casting
What is osteogenesis imperfecta?
it is an inherited disorder (brittle bone disease)
What are the clinical manifestations of osteogenesis imperfecta?
frequent fractures
blue sclera
thin, soft skin
short stature
hearing loss
delay in walking
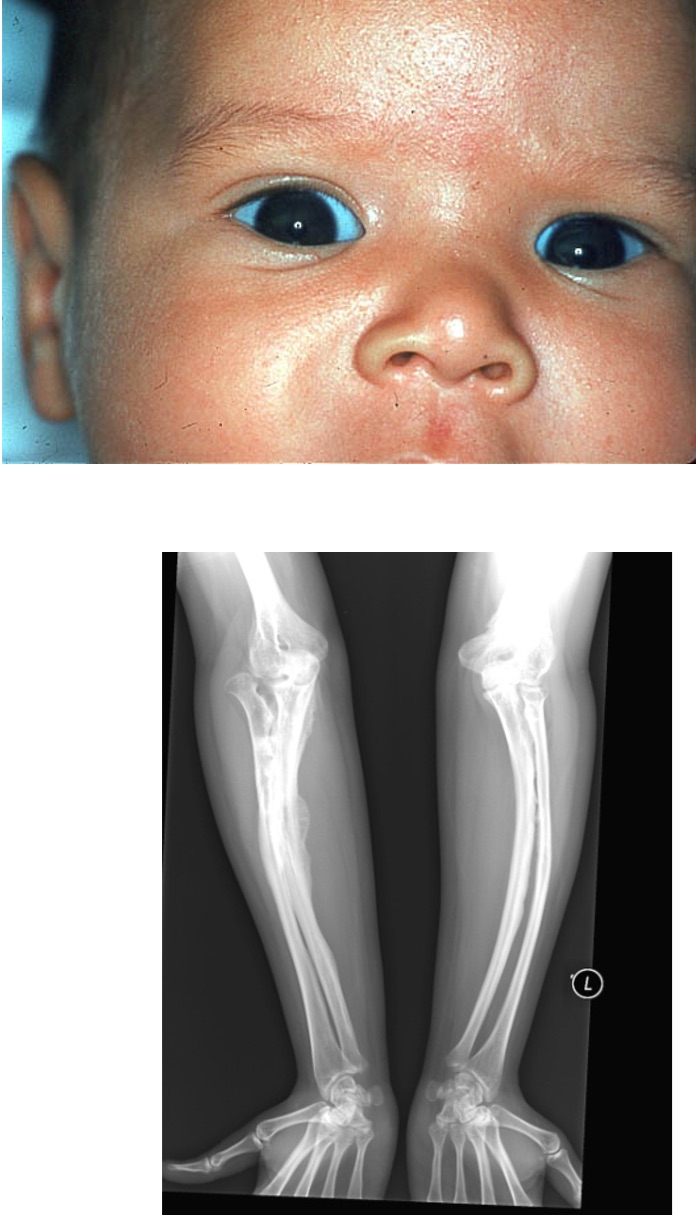
What can osteogenesis imperfecta be mistaken for?
it can be mistaken for child abuse
What are the medical managements for osteogenesis imperfecta?
no cure, only medication that can slow the release of calcium from bones (IV pamidronate)
physical therapy can help strengthen muscles and support bone density
casting, bracing, or splinting
What are some nursing managements we can do for osteogenesis imperfecta?
sliding diapers under instead
of lifting legs
use blankets for positioning
non-weight baring activities (swimming)
What is slipped capital femoral epiphysis?
it is when the femoral head slips off neck of femur
happens more in the adolescent and growth spurt years
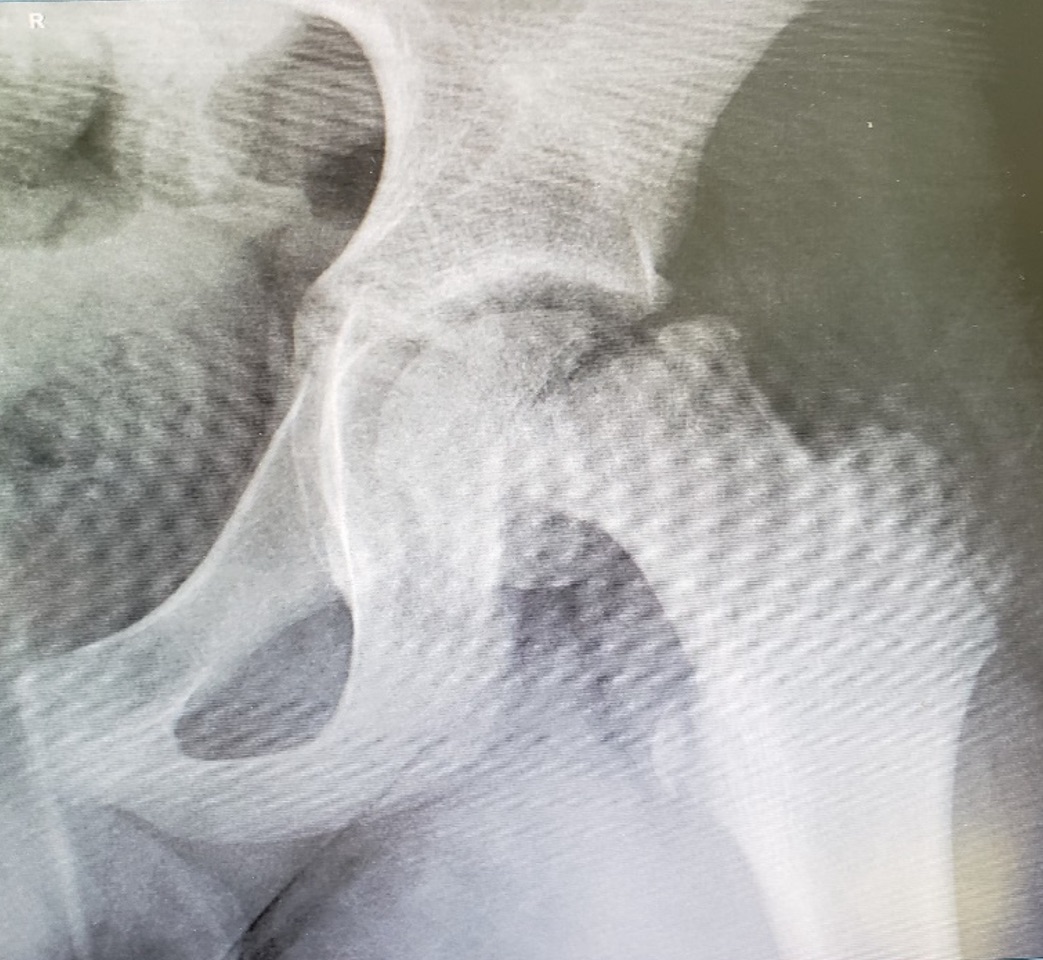
What are the signs and symptoms of slipped capital femoral epiphysis?
hip pain that radiates to the groin or thigh
limping
stiffness
loss of motion
can't bear weight on the affected side
What is the medical management of slipped capital femoral epiphysis?
x ray to confirm dx
non weight bearing to prevent further injury
surgery within 24 hrs
What is osteomyelitis?
it is an infection of the bone
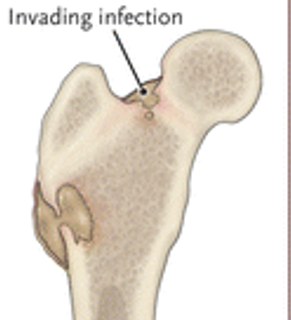
What children do we see osteomyelitis more in?
it is common to see in children under 10-years-old d/t staph infection or trauma to the bone
What are the general sign and symptoms of osteomyelitis?
very ill
irritability
fever
rapid pulse
dehydration
What are the local signs and symptoms of osteomyelitis?
tenderness
warmth
swelling
pain
tense and resistant to passive movement
What are the treatments for osteomyelitis?
empirical therapy with abx (before culture) and change once they get sensitivity back
surgery if severe enough
What is the management of osteomyelitis?
non-weight bearing in the acute phase
position for comfort
What labs are we going to check for osteomyelitis?
ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate)
CRP (c reactive protein)
-these are markers that check inflammation in the blood