Stem Cells - Possible Alternatives Therapies in Dentistry
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
True or False: All dental treatment is related to stem cells
True ==> either to preserve stem cells or to stimulate them to differentiate towards the right direction
symmetric division of stem cells
stem cell divides into 2 daughter cells w/ the same capacity = self renewal
*how stem cells divide
asymmetric division of stem cells
stem cell divides to produce a 1 differentiated cell & 1 daughter stem cell = potency
*how stem cells differentiate
Which kind of stem cell division results in self-renewal ?
symmetric division
Which kind of stem cell division results in differentiation?
asymmetric division
embryonic stem cells
stem cells derived from the undifferentiated inner cell mass of blastocyst = pluripotent stem cells
adult stem cells
= somatic stem cells = postnatal stem cells =undifferentiated cells found among differentiated cells of a specific tissue (confined w/in differentiated tissue)
*not just found in adults (present in infants once they are born)
multipotent stem cells
iPSCs Cells
induced pluripotent stem cells ( somatic stem cells that were genetically engineered in a lab to go back to being pluripotent)
perinatal stem cells
stem cells from embryonic cord & placenta
-have great differentiation potential
- saved my some parents for use just in case baby develops a disease (can use stem cell therapy fro Tx)
cancer stem cells
stem cells from cancerous tissue (ex: HeLa Cells)
True or False: Stem cells maintain the same differentiation potential throughout life
False ==> stem cells don't have as wide a differentiation potential after birth
Organization of Stem Cells (Most to least differentiation potential)
totipotent--> pluripotent --> multipotent --> oligopotent --> unipotent
totipotent stem cell
capable of differentiation & forming a new individual (can become placenta/birth sac cell or any cell for embryo/future body)
ex: fertilized egg (zygote)
pulripotent stem cell
stem cell capable of giving rise to several different cell types
ex: -embryonic stem cells
-iPS cells
Multipotent stem cell
stem cells that can differentiate into a range of cell types in the body
ex: -mesenchymal stem cells (adult stem cells)
-dental stem cells
oligopotent stem cells
stem cells that can only differentiate into close-related cell types
ex: Hematopoietic stem cells (adult stem cells)
unipotent stem cells
stem cells can only change into one cell type in the body
ex: muscle stem cells
Embryonic Stem Cells v Adult Stem Cells
-embryonic = pluripotent differentiation potential
-adult stem cells = multipotent differentiation potential
-ethical concern regarding destruction of blastocyte w/ embryonic stem cells
-embryonic stem cells have high proliferative capacity --> divide indefinitely
-adult stem cells have limited proliferative capacity --> limited expansion = cells die eventually
-embryonic stem cells have a higher risk of tumor formation than adult stem cells
Tissue Engineering Triangle
model for using stem cells for regenerative medicine ==> stem cells (1st factor) attach to a scaffold (2nd factor) & are induced to differentiate towards a certain lineage via receiving a signal from biological factors (3rd factor of triangle)
-cell transplantation = regeneration done using extra stem cells (either endogenous or exogenous; from the pt or from somebody else)
-cell homing = just scaffold added to induce the stem cells in that tissue to migrate to it & attach & differentiate into what you need it to be
*don't always need all 3 factors, but scaffold likely needed when repairing larger area of tissue damage (if you wanna regenerate a big area of tissue, you need a scaffold)
Cell Transplantation
tissue engineering in regenerative medicine that utilizes endogenous (stem cells from the area) or exogenous (other source) stem cells to regenerate tissue
Cell Homing
tissue engineering in regenerative medicine where a scaffold & biological factors are added to get the endogenous stem cells to migrate there --> attach to the scaffold --> differentiate into desired tissue
ex: bone graft
Autologous stem cells
stem cells from the patient (use own stem cells for Tx)
allogenic stem cells
stem cells from the same species as the subject/patient
syngeneic stem cells
stem cells from identical twin (if pt has a ID twin they can use their stem cells for tissue engineering
True or False: Stem Cell-Based Therapy = Regenerative Medicine
False ==> b/c regenerative medicine may or may not use stem cells
What kind of stem cells does the majority of stem cell research use?
mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
True or False: It's better to use older cells for stem cell therapy
False ==> better to use younger stem cells
What is stem cell research used for?
-regeneration studies
-drug testing
-study development
stem cell niche
where the stem cells are located in the body--> migrate out of niche & differentiate when they receive a signal
Bone Marrow Stem Cells
-hematopoietic stem cells (most commonly used clinical stem cell therapy) --> Tx pts w/ immune diseases
-mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) --> can attach to a growth plate & start growing
*bone marrow transplantation is most used stem cell based therapy --> bone marrow commonly isolated from the iliac crest ( = bone marrow aspiration)
Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs)
stem cells with great differentiation potential derived from adipose tissue
*Characteristics
-plastic adhesion
-low immunogenicity = pt's immune system doesn't usually reject them
-multi-lineage capacity
-self -renew
*Clinical Applications
-wound healing
-breast augmentation
-cosmetology
-hair regeneration
-anti-aging
*doesn't have as much a differentiation potential as bone marrow stem cells
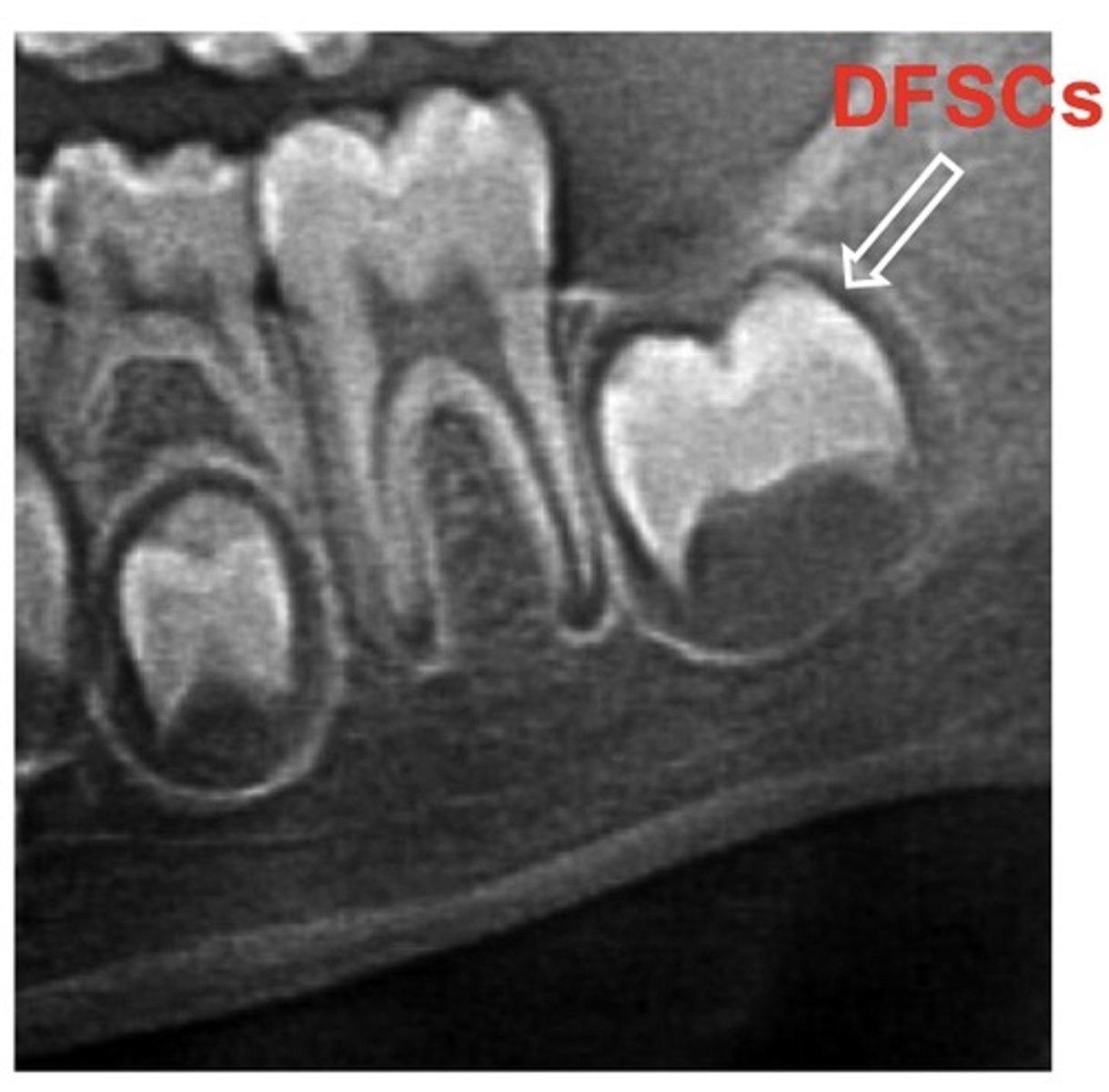
Dental Follicle Stem Cells (DFSCs)
ectomesenchymal stem cells found in the dental follicle (surrounding of the tooth germ) of developing tooth bud --> can differentiate into osteoblasts, adipocytes, chrondrocytes, & neuronal cells
Tooth Germ Progenitor Cells (TGPCs)
stem cells found in the developing tooth bud
-fibroblast-like cells in the dental papilla
- epithelial cells make up the enamel organ
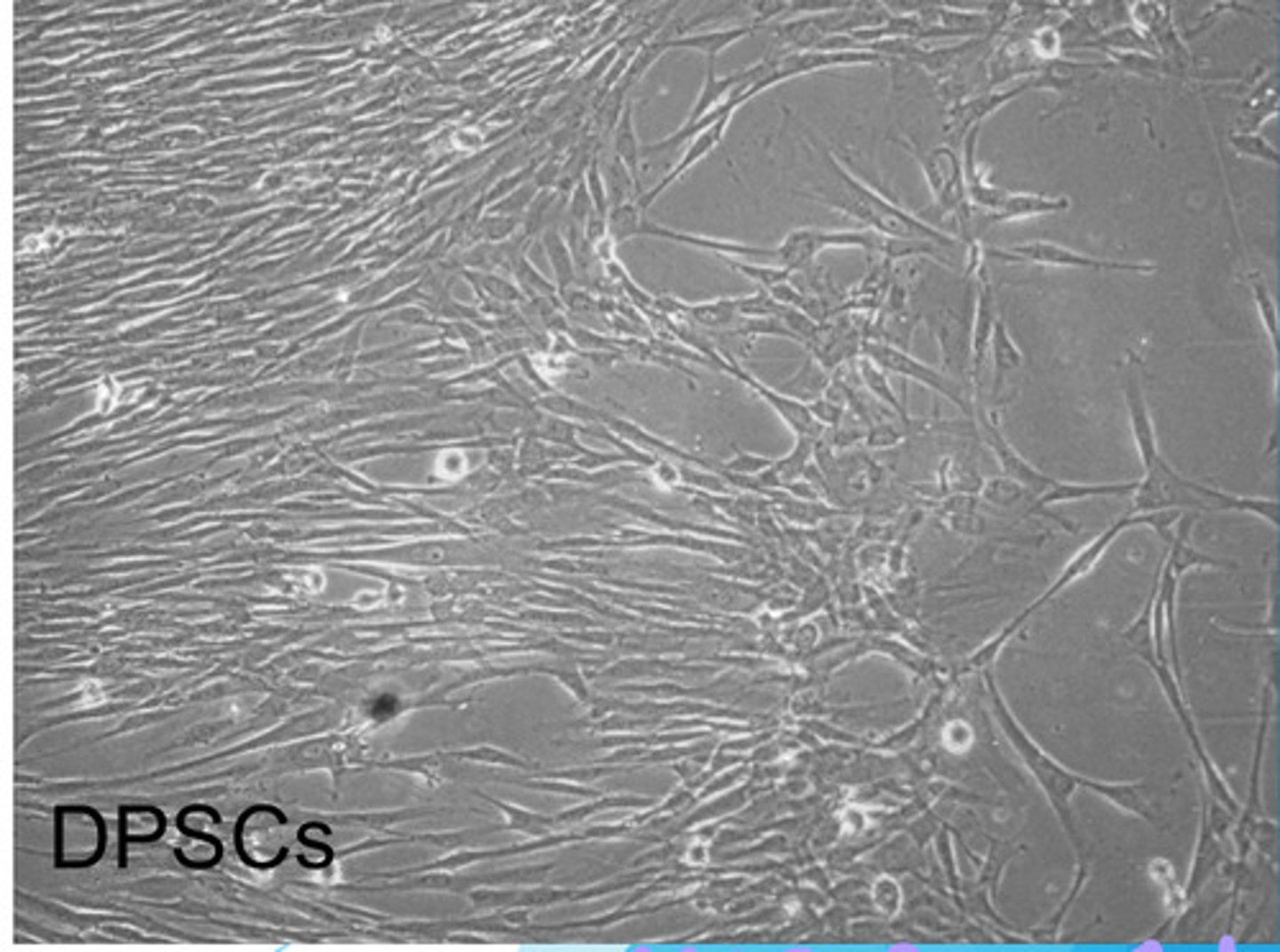
Dental Pulp Stem Cells (DPSCs)
fibroblast-like, neural crest-derived mesenchymal stem cells found in perivascular niches of the cell-rich zone of the pulp & in pulp core of permanent tooth (1st & most studied dental stem cells)
- multipotent
-greater proliferation rate than BMSCs (bone marrow stem cells)
- more suitable than BMSCs for mineralized tissue regeneration
- demonstrate chondrogenic potential in virto (can become a chondrocyte)
*will migrate out niche & differentiate into odontoblasts upon damage & forms more nerves & blood vessels to further repair the pulp
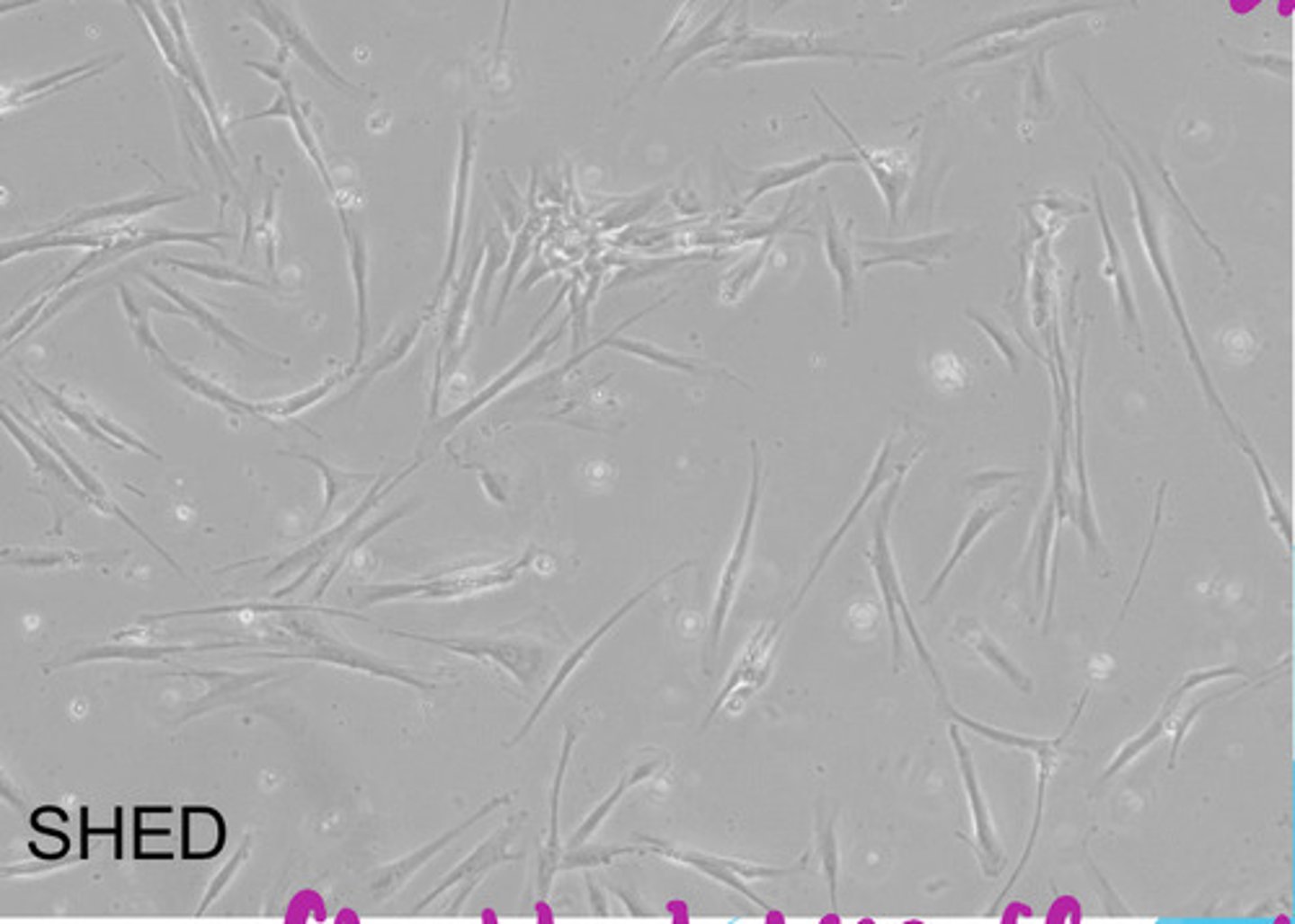
SHED cells
stem cells isolated from the pulp remanent of exofoliated deciduous teeth
-greater proliferation rate & higher capability for differentiation than BMSCs & DPSCs
-can differentiate into osteoblasts, odontoblasts, adipocytes, & neuronal cells
*fibroblast-like appearance
Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells (PDLSCs)
stem cells found in the periodontal ligament derived from neural crest cells; dental follicle-derived mesenchymal cells
-exhibit characteristics similar to mesenchymal stem cells
- like BMSCs exhibit immunomodulatory ability (can regulate the immune system
-can differentiate into osteoblasts, cementoblasts, adipocytes, chondrocytes, periodontal ligament, cementum-like tissue, tenocytes, cardiac myocytes, pancreatic islet cells ....
*fibroblast-like appearance
SCAP cells
stem cells isolated from the apical papilla of a tooth that are associated w/ root formation
* can act like mesenchymal stem cells & differentiate into osteoblasts, adipocytes, chondrocytes, & neurons
True or False: Stem cells from bone marrow of craniofacial bones and the bone marrow of other skeletal bones are identical
False ==> stem cells in bone marrow of craniofacial bones is different from the bone marrow of the rest of the skeleton b/c they are derived from different germ layers
-craniofacial bones are neural crest cell (ectoderm) derived
-rest of the skeleton is derived from mesoderm
BMSCs
bone marrow stem cells (different from craniofacial bones v. rest of the skeleton)
Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells (G-MSCs)
stem cells found in the gingiva
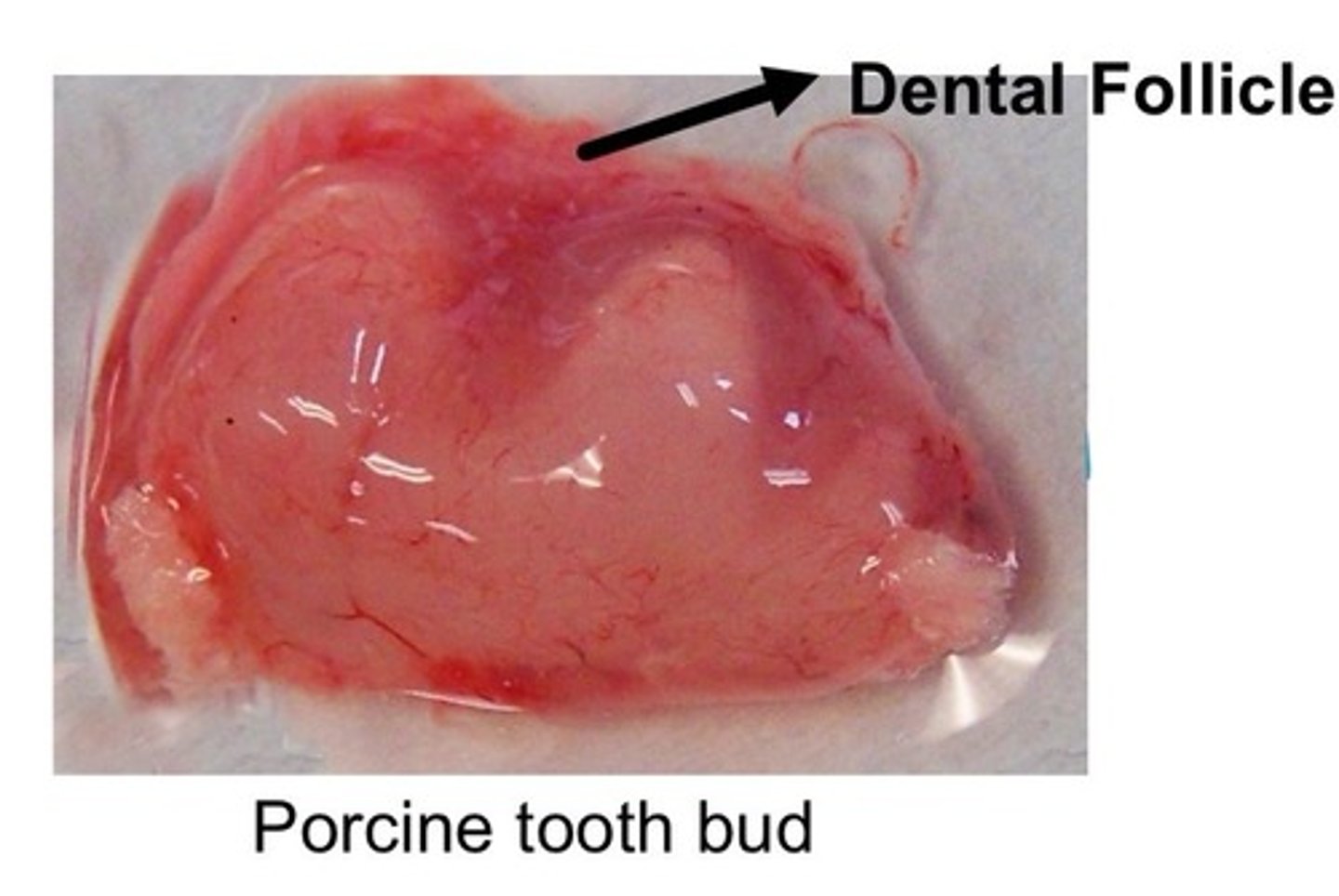
Dental Follicle
ectomesenchymal cell condensation that harbors heterogeneous population of cells that make up the periodontium (a bunch of different types of stem cells that will make up all the different types of cells of future periodontium)
hBMSCs
human bone mesenchymal stem cells from the jaw bone (mandible)
What kind of stem cells are found in the enamel organ of tooth bud?
epithelial tooth germ progenitor cells (TGPCs)
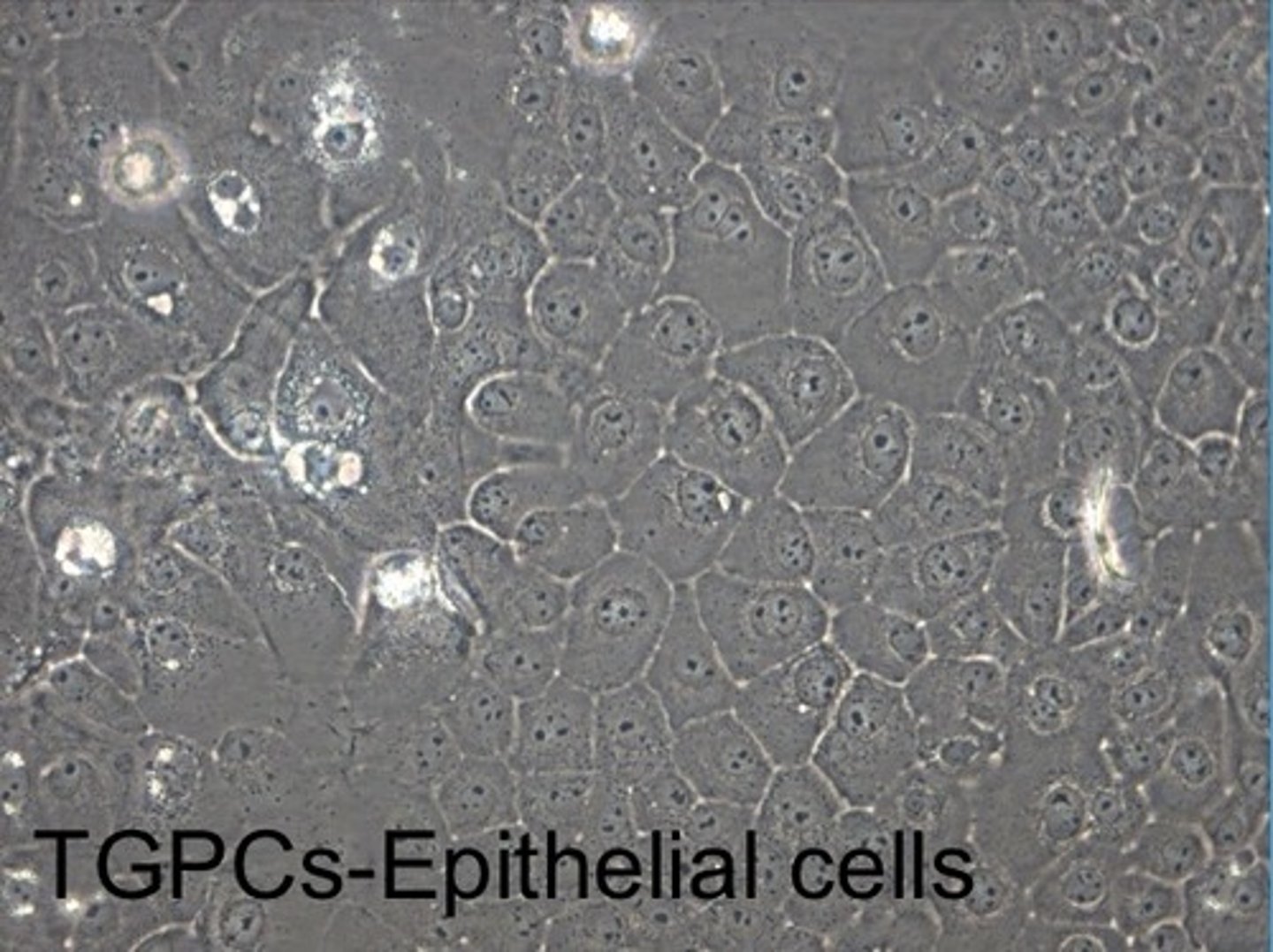
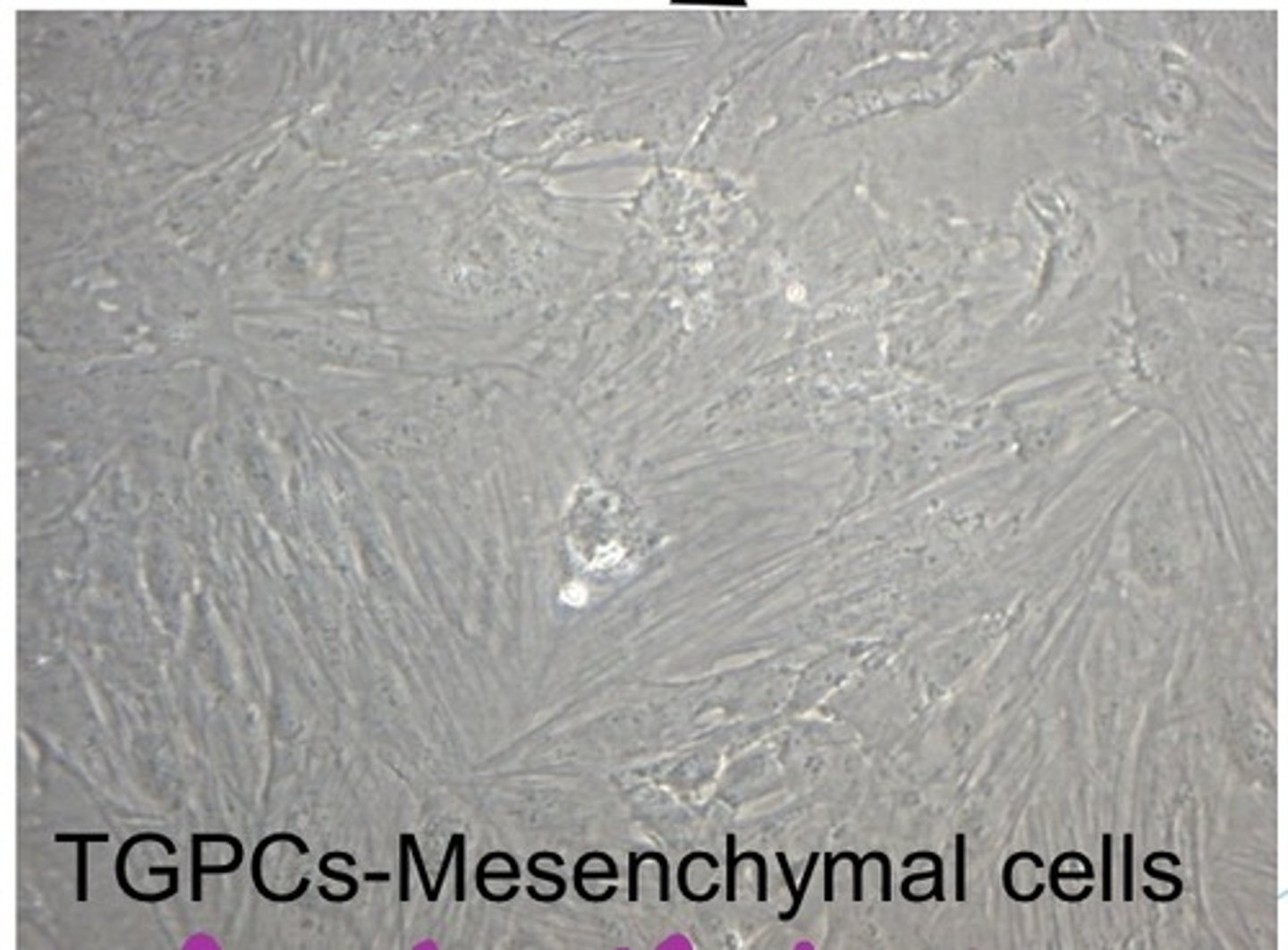
What kind of stem cells are found in the dental papilla of tooth bud?
mesenchymal tooth germ progenitor cells (TGPCs)
What kind stem cells can be isolated from deciduous teeth?
SHED & PDLSCs ==> have to be isolated from the primary tooth before exfoliation
Exfoliated Deciduous Tooth
primary tooth with resorbed roots & pulp
*hard to extract stem cells from here once tooth is exfoliated
What kind of stem cells can be extracted from adult teeth?
-PDLSC
-SCAP
-DPSCs
*main sources = impacted wisdom teeth, teeth removed for orthodontic purposes, & supernumerary teeth
True or False: PDLSCs are extracted from the gingiva surrounding the teeth
False ==> PDLSCs are scraped off the hard tissue on the roots
Why is it better to extract dental stem cells from an impacted wisdom tooth than any other adult tooth in the dentition?
only able to isolate a limited amount of stem cells from pulp of tooth that has a fully developed root --> impacted wisdom teeth have underdeveloped roots = more stem cells can be extracted
True or False: Dental stem cells are only used to regenerate pulp
False ==> dental stem cells can also be used to regenerate other body cells (neuron-like cells, cardiomyocytes, adipocytes, insulin secreting beta cells, hepatocytes)
*good option b/c
-nonwasteful --> come from medical waste
-minimally invasive isolation method (unlike painful bone marrow isolation)
-immunomodulatory/immunosuppressive --> can downregulaet the immune response --> decrease possibility of immuno-rejection
dental tissue-derived iPSCs
dental stem cells that have been reprogrammed to be pluripotent
-great differentiation potential --> hepatocyte like cells, retinal pigment epithelial-like cells, neuron-like cells, mesenchymal stem cell-like cells, neural crest-like cells, dental epithelial stem cells, & osteoblast-like cells
-autologous cell source
- can form teratoma (tumors) like embryonic stem cells
Which stem cells are used for dental tissue regeneration?
-dental tissue-derived iPSCs
-bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs)
-adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs)
-Human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) --> used to generate blood vessels that facilitate dental tissue regeneration
Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell (HUVEC)
stem cells from the umbilical cord ==> can be used to generate blood vessels that facilitate dental tissue regeneration
Endodontic Disease
infection or inflammation of dental pulp
*common cause = caries & trauma
*when odontoblasts are damaged by caries, stem cells migrate from the pulp & differentiate into odontoblasts & make reparative dentin
Why is the dental pulp vulnerable?
-small volume of pulp cavity
-narrow connection to surrounding blood supply
-confined in calcified tissue walls
*pulp can easily die due to these things
What is a possible consequence of injuring the dentin?
injury to dentin can pull nerve fibers & odontoblasts into tubules causing damage & pain
Why is keeping the pulp functional important? (Why aim to save the pulp?)
-artificial pulp (guttapercha) can't sense microleakage --> only pts w/ vital pulp will feel pain & seek attention of the dentist
>living pulp required to maintain dentin & tooth sensitivity
-teeth w/ non-vital pulp become brittle & break over time
What does the dental pulp consist of?
-odontoblasts --> most distinct
-fibroblasts --> most abundant
-defensive cells --> macrophages & other immunocompetent cells
-undifferentiated ectomesenchymal cells or progenitor cells
Where are DPSCs located in the pulp?
-perivascular niche in cell-rich zone of pulp
-pulp core
Current Therapies for Endodontic Disease
- direct/indirect pulp capping
-root canal treatment
-pulpotomy --> pulp chamber removed but pulp canals remain
-guided pulpal repair
-antibiotics
Direct/Indirect Pulp Capping
treatment for reversible pulpitis where a calcium hydroxide liner is placed w/ glass ionomer & composite to form barrier & stimulate stem cells to form odontoblasts --> makes dentin bridge that protects the pulp
*type of cell homing that allows for partial pulp regeneration
Pulpotomy
treatment for reversible pulpitits where the pulp chamber is removed but the pulp canals remain --> sterile cotton pellet w/ formocersol solution placed w/ zinc oxide-eugenol cement
Purpose of Dental Pulp Regeneration
-regenerate dentin-pulp complex via stimulation of odontoblasts to deposit dentin
-regenerate blood supply (angiogenesis/vasculogenesis) & nerve supply (neurogenesis)
*can be partial pulp regeneration or whole pulp regeneration==> done via regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs), pulp revascularization, & pulpal revitalization
Whole Pulp Regeneration
pulp regeneration after endodontic treatment via exogenous stem cells that migrate to the tooth via bloodstream come in through apical blood vessels
* more possible w/ immature pulp stem --> need to culture stem cells & then implant them into mature pulp
Tissue Engineering Triangle for Dental Pulp Regeneration
-possible cell sources --> DPSCs SHED, SCAP
-scaffolds --> scaffold-free, collagen, hydrogel, synthetic polymer
-biological factors --> TGF-B1, BMP-2
Which biological factors are used for regeneration of dental pulp?
-Transforming growth factor B1 (TGF-B1)
-Bone morphogenetic proteins 2 (BMP-2)
What are the tooth-supporting tissues?
bone-PDL-cementum complex = highly organized collagen fibers that insert perpendicularly to cementum & bone--> act as a buffer of force when you chew food
*successful regeneration of PDL forms perpendicular fibers
Regeneration of the Periodontal Ligament
regeneration of cementum, PDL fibers, & alveolar bone (bone-PDL-cementum complex)
Function of Periodontal Ligament
-support & stabilize the tooth
-nutrition
-sensory
-formative & remodeling --> vital PDL is important for ortho Tx
-transmission of occlusal forces from teeth to bone
Why do implants need to be replaced over time?
Implants don't have a PDL --> force of biting/chewing goes straight to the bone--> bone resorbs over time --> implant will need to get replaced
*this is the reason bone graphs are needed before implants are placed
Why can't implants be moved with orthodontic treatment?
can't move implants b/c they don't have a PDL (implants are anchored in straight bone)
True or False: Partial periodontal tissue regeneration happens after deep pocket cleaning
True
True or False: Partial periodontal tissue regeneration happens around dental implants
False ==> full periodontal tissue regneration happens around dental implant (remember that av bone is a periodontal tissue --> av bone regenerates around the implant not PDL!)
Approximately how many adults in the world are affected by periodontal disease?
50%
Guided Tissue Regeneration Technique (GTR)
type or periodontal regeneration technique where a special membrane is inserted after cleaning bwtn the gum & bone to block unwanted tissue to allow PDL fibers & bone to grow (membrane dissolves once strong fibers attach root to bone)
True or False: Implantation of bone substitute materials into a periodontal wound forms a Long Junctional Epithelium (LJE) that has the ability to regenerate a real periodontium
False==> LJE produced but it doesn't have the ability to regenerate a real periodontium
Stem Cells that can regenerate the PDL
-PDLSCs
-DPSCs
-BMSCs
-Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs)
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
*all regenerate PDL w/ pretty good results
Clinical Trial for PDL Regeneration using Cell Sheets
PDLSCs grown on temp sensitive culture --> detach from petri dish when temp changes --> placed on periodontal ligament cell sheet --> allow cells to be placed around the tooth & implanted in layers
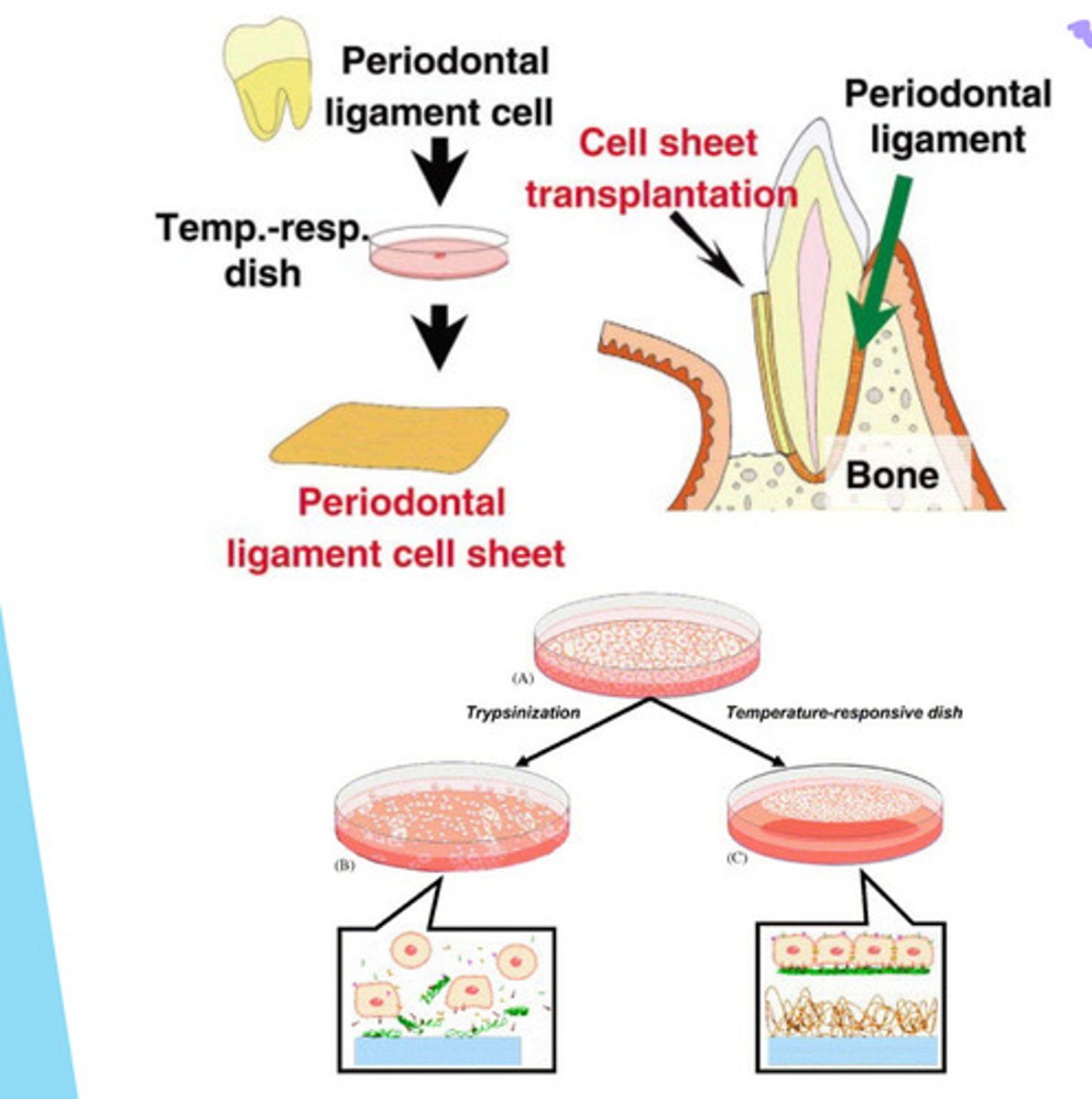
PDL Regeneration via Cell Sheet (picture only)
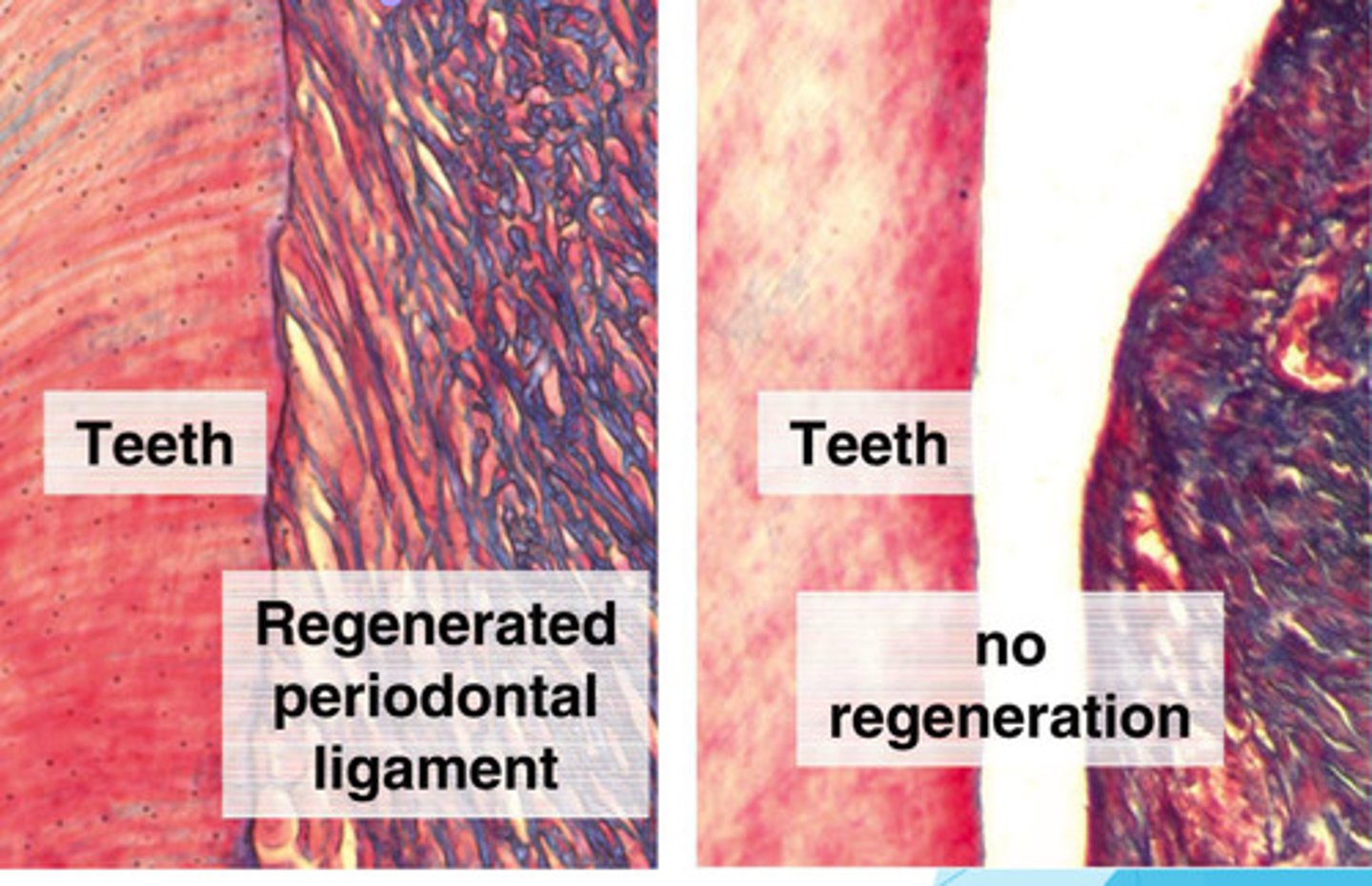
True or False: PDL regeneration can be induced via 3D printed guiding scaffold in vitro
True ==> 3D print the cementum-PDL-bone complex & then implant it
True or False: Success of PDL regeneration depends on the type scaffolding material used
Lowkey False ==> PDL regeneration tested using different scaffolding materials (GTR v autologous PDLSC sheets) & the results weren't significantly different
Why is studying epithelial-mesenchymal interaction w/in a tooth bud the key to learning to regenerate teeth?
b/c teeth develop via epithelial-mesenchymal interactions==> cross talk btwn the enamel organ & the dental papilla cells from the ameloblasts & odontoblasts that deposit enamel & dentin
Which organs form via Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions?
-hair
-salivary glands
-kidneys
-mammary glands
Why are mouse/rat dental epithelial stem cells utilized in research instead of human dental epithelial stem cells?
b/c dental epithelial stem cells in humans disappear from the cervical loop (bottom on tooth root) over time but they remain in rats/mice (this is the reason why rats/mice have continued tooth growth thru out their life) = epithelial stem cells only available in rats/mice
Tooth Generation via Organ Culture/Mouse Sub-renal Capsule
epithelium & mesenchyme of mouse tooth germ separated--> separated further into single cells --> placed into collagen gel = high-density reconstituted tooth germ --> organ cultured for 2 days --> transplanted into kidney of mouse or organ cultured for another 14 days --> tooth bud implanted into alveolar bone of mouse --> tooth growth & eruption
*Disadvantages
-can't be replicated in humans yet
- need stem cells from a embryonic tooth bud
-mice teeth are way smaller than human teeth
Decellularized Tissues
tissues that doesn't have cells, just extracellular matrix (ECM left) --> can be used to regenerate tissue & whole organs (ex: heart valves, bladder, dermis, etc.)
*possible that decellularized tooth bud (dcTB) can regenerate a whole tooth
Whole Tooth Regeneration using Decalcified Tooth Bud
take human pulp stem cells + pig dental epithelial stem cells --> place in decellularized scaffold --> implant into pig alveolar bone -->>>get generation of tooth that's bigger than a mouse tooth but smaller than a human tooth (confirmed histologically)
-human cells = human dental pulp cells (hDM) & human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs)
-pig cells = pig dental tooth bud epithelial cells (pDE)
USAG-1
factor that stops supernumerary teeth from growing
*new tooth regrowth medicine that blocks USAG-1 with antibody (Anti-USAG-1 therapy) to allow growth or supernumerary teeth = therapy for replacement of different teeth
Anti-USAG-1 Therapy
world's first tooth regrowth medicine that uses anti-USAG-1 antibodies to block USAG-1 to allow the growth of supernumerary teeth
*goal of medication is to Tx patients w/ congenitally missing teeth (congenital adontia)
True or False: Dental stem cells can be stored in cell bank to be utilized later in case of need for tissue regeneration
True ==> whole pulp or just isolated dental pulp stem cells stored --> cheaper than preserving the umbilical cord
Stem Cell Exosomes
small extracellular vesicles secreted by stem cells that are utilized for regeneration (contains all the key components for cell-cell communication, proteins, lipids, & RNAs)
*Advantages of using exosomes instead of full on stem cells
-safer b/c they are cell-free (less immuno rejection reactions)
-stable fro storage & transport
-modifiable
-lower risk of tumor formation
Application of Stem Cells for Dental Clinic
-adequate disinfection v. stem cell survival
-cell transplant v. cell homing
-autologous v. allogenic
-time consuming
-potential risks = contamination & tumorigenesis
-cost
-possible personized dentistry via "custom-made" tooth