206 Heart Development
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
sinus venarum
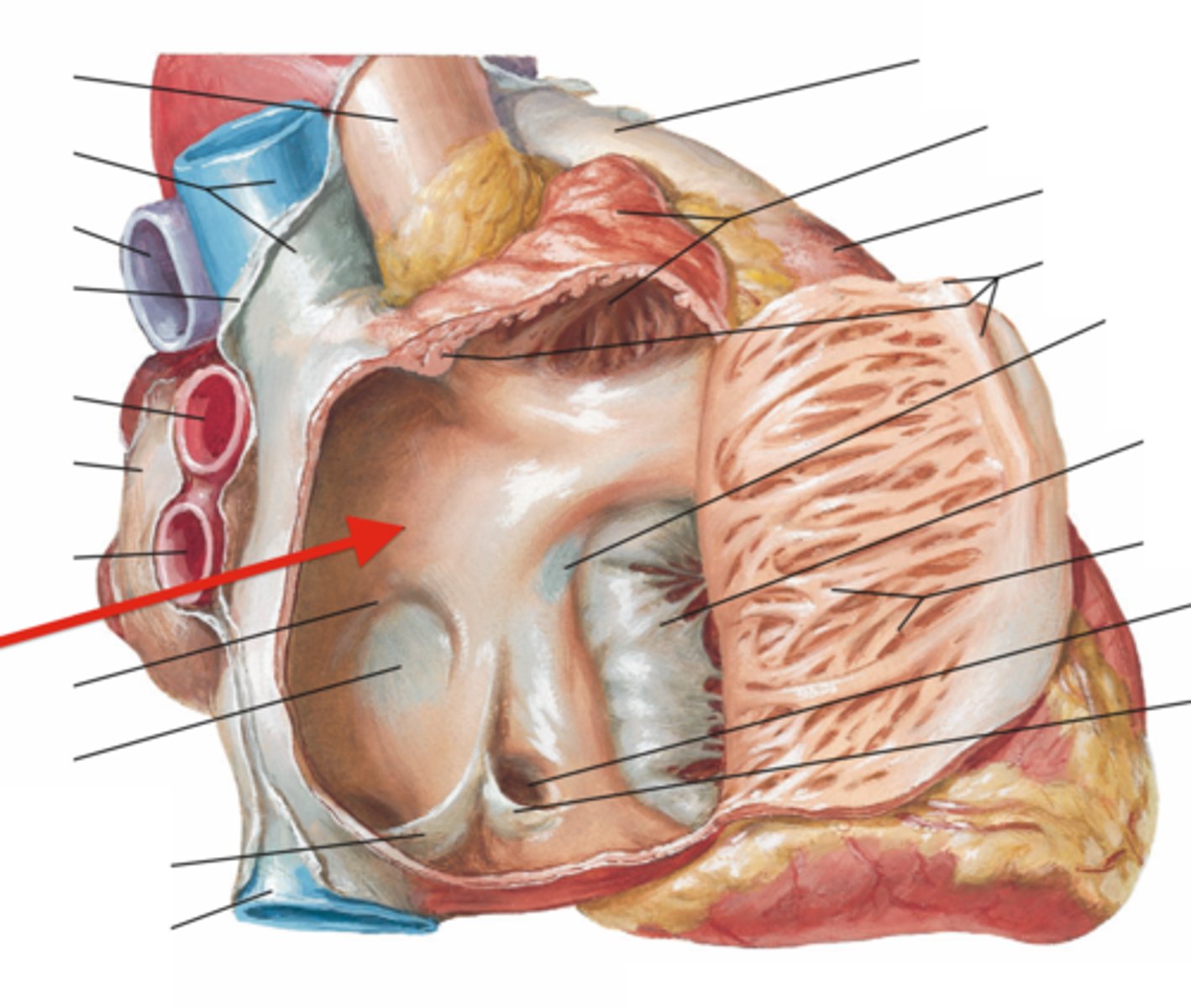
crista terminalis
identify the structure
septal defects
what are the most common heart defects?
mesoderm
the heart and its components form form what embryonic layer?
lateral
what part of the mesoderm gives rise to the heart and its compnents?
fibrous pericardium
the somatic layer of the lateral plate of the mesoderm will give rise to the:
endocardium and myocardium (the heart organ)
the visceral layer (splanchnic) of the lateral plate of the mesoderm will give rise to the:
pericardial cavity
The intraembryonic coelom between the two layers will form the:
neck
the heart develops first in the ______ then moves to the thorax
dorsal mesocardium
Prior to heart looping to form the 4-chambered heart, what must be removed?
dorsal mesocardium
the tissue from which the heart tube is suspended:
transverse pericardial sinus
the breakdown of the dorsal mesocardium results in what formation?
vasculogenesis
formation of blood islands, dorsal aortae:
myogenesis
Cardiac myoblast induction, formation of myocardium, heart tube:
cranial
which end of the embryo does the heart develop?
right
in which direction does heart looping occur:
situs inversus totalis
defective ciliopathy can lead to what as the heart develops?
vitelline veins
these extraembryonic circuits run from the yolk sac:
vitelline veins
these become incorporated into the liver as hepatic sinusoids
umbilical veins
these extraembryonic circuits run from the placenta:
sinus venosus
the region where the veins come together to enter the common atrium is called:
coronary sinus
The left sinus horn will become the:
left sinus horn
the coronary sinus arrises from what fetal structure?
left umbilical vein
what vein will persist through development, bringing maternal blood to the fetus
ductus venosus
passage for the left umbilical vein to pass through the liver to the heart?
right cardinal v.
the SVC arises from what fetal structure?
right sinus horn
what fetal structure is incorporated into the wall of the atria?
right sinus horn
what fetal structure becomes the sinus vernarum
crista terminalis
what structure separates the sinus vernarum and pectinate muscles?
intussusception
incorporation of sinus venosus wall into both atria:
septum intermedium
The two atrioventricular canals are separated by endocardial cushion tissue known as the:
ostium primum
Complete fusion at the septum intermedium does not initially occur, however, yielding a persistent opening known as the:
septum primum
Atrial septation begins with growth of the _______ from the atrial roof toward the septum intermedium.
apoptosis
the ostium secundum, forms by:
foramen ovale
The remaining exposed portion of the septum primum will form the entrance to the:
muscular ventricular septum
In ventricular septation, myocardial growth forms the:
membranous septum
In ventricular septation, endocardial cushion tissue growth forms the
ascending aorta
pulmonary trunk
the conotruncus develops into what two structures?
conotruncus
the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk arise from what embryonic structure?
conus cordis and truncus arteriosus
wha structures make up the conotruncus?
neural crest
cells from the ______ contribute to the formation of the conotruncal septation
transposition of the great vessels
If the spiraling does not happen, a defect known as ____________ occurs, where the left ventricle empties into the pulmonary trunk and the right ventricle empties into the aorta.
persistent truncus arteriosus
Failure of the two septa to completely divide the aorticopulmonary septum results in a defect known as ____________.This common trunk allows mixing of oxygenated and unoxygenated blood to occur.
tetralogy of Fallot
Anterior displacement of the aorticopulmonary septum results in: a) unequal division of the common tube b) the resultant failure of the aorticopulmonary septum to meet with the interventricular membranous septum results in a ventricular septal defect; c) the widened ascending aorta thus overrides the two ventricles resulting in a mixing of oxygenated and unoxygenated blood:
week 3
folding of the heart tube, beating commences when?
week 4
septum formation happened when?
week 4
valve formation happens when?