Bio98 Lecture 15: Regulation of PDH and TCA Cycle; Intro to Fatty Acids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
The net ATP and electrons calculation
Glycolysis: 5-7 ATP equiv.
PDH + TCA: 25 ATP equiv
-2.5x ATP per NADH & 1.5x ATP per FADH2
-Total ATP formed: 30-32
Irreversible steps are most regulated:
-Prequel: ?, TCA: ?
-Prequel: Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
-TCA: Citrate synthase (CS), isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH), alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (KGDH)
Modes of regulation
1) product inhibition: ATP, NADH, intermediates
2) Energy depletion: activation
3) Ca²+ is a signal for muscle contraction: I need more ATP!
(IRREVERSIBLE rxns are usually the MOST regulated)
The regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
-2 mains modes of regulation:
1) product inhibition
- E1 = CO2; E2 = Acetyl-CoA; E3 = NADH
- ACETYL-CoA inhibits E2 SUBUNIT
- FATTY ACIDS also inhibit E2 SUBUNIT
- HIGH NADH levels INHIBIT E3 SUBUNIT
- activity is ACTIVATED by HIGH levels of CoA-SH + NAD+
2) phosphorylation
- ATP inhibits E1 and AMP activates it ; phosphorylation disturbs E1 active site
-Ca²+ : activates the phosphatase to give back active E1
- Phosphorylation = direct covalent modification of the E1 subunit
TCA Regulation: Step 1 (irreversible)
Condensation of Acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate (OAA) through citrate synthase to make citrate
1st irreversible step
ATP inhibits allosterically @ citrate synthase to prevent citrate from being produced
High ATP = abundant energy, TCA not needed
TCA Regulation: Step 3 (irreversible)
- regulated in lots of ways
- ATP & NADH both bind & inhibit allosterically @ isocitrate dehydrogenase to prevent isocitrate from turning into alpha-ketoglutarate
phosphorylation also regulates IDH activity
Activated by ADP (low energy state)
-Net result of turning off isocitrate dehydrogenase: citrate rises bc of the equilibrium of the aconitase rxn ; feeds back towards the production of citrate by econotase
Citrate transports out of mitochondria back into the cytoplasm, where it feeds into lipid biosynthesis
It leads into the production of acetyl-CoA → leads into production of fats and the storage of energy.
Phosphorylation (TCA)
Step 3 (cont.):
- KINASE uses ATP —> PHOSPHORYLATES IDH = INACTIVE IDH
- DEPHOSPHORYLATED IDH = ACTIVE IDH
- lots of material to go for TCA —> KINASE INHIBITED so that IDH is ACTIVE
TCA Regulation: Step 4 (irreversible)
α-ketoglutarate transformed into succinyl-CoA
—> 3rd IRREVERSIBLE reaction
- reaction + regulation is SIMILAR to PDH (production inhibition):
- HIGH SUCCINYL-CoA levels (acetyl-CoA) = E2 INHIBITED
- HIGH NADH levels = E3 INHIBITED
Why do we need fat?
Sources of energy, hormones, and cell membranes
-Why fat?
more energy density than other materials (kJ/g)
less water → 6Xs more energy than glycogen per gram
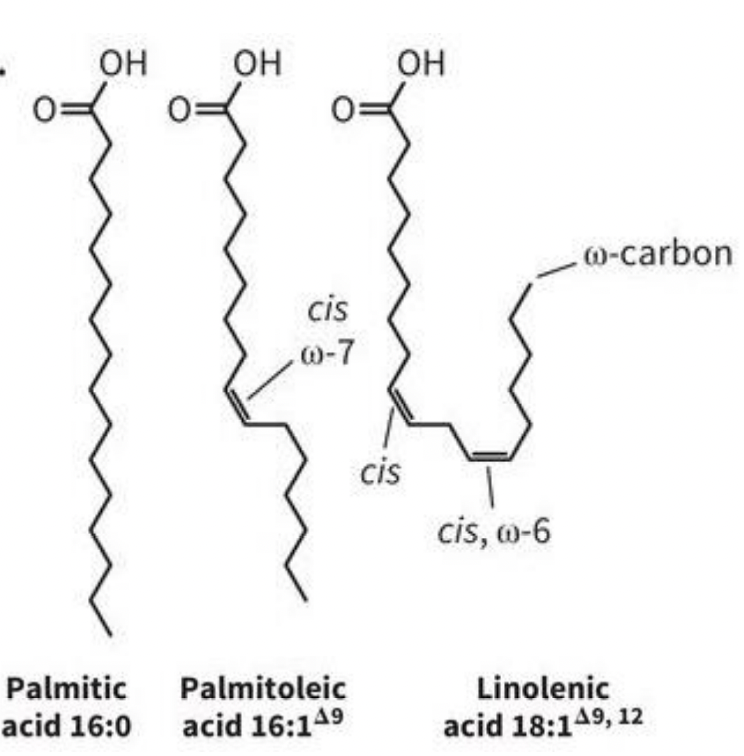
What’re Fatty Acids (FAs)?
Carboxylic acid + long hydrophobic tail
-Saturated: no double bonds (packed tightly)
-Unsaturated: double bonds (packed loosely)
-Polyunsaturated: multiple double bonds
-Naming system: X:Y^ΔZ (X= # carbons, Y=number of unsaturated bonds, Z= position of unsaturated bonds)
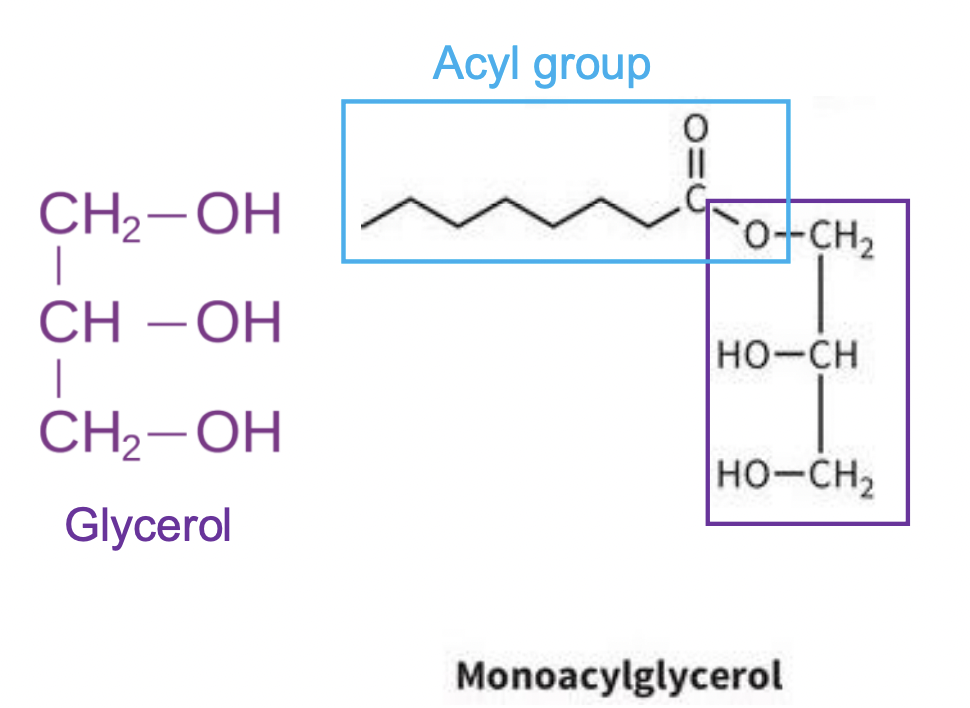
What are Fats (lipids)?
-Fatty acids: carboxylic acids and amphipathic (contain polar and nonpolar ends).
-can act as a detergent, cells don’t want these floating around
-FAs are stored as neutral lipids by reacting with a “head group” such as glycerol
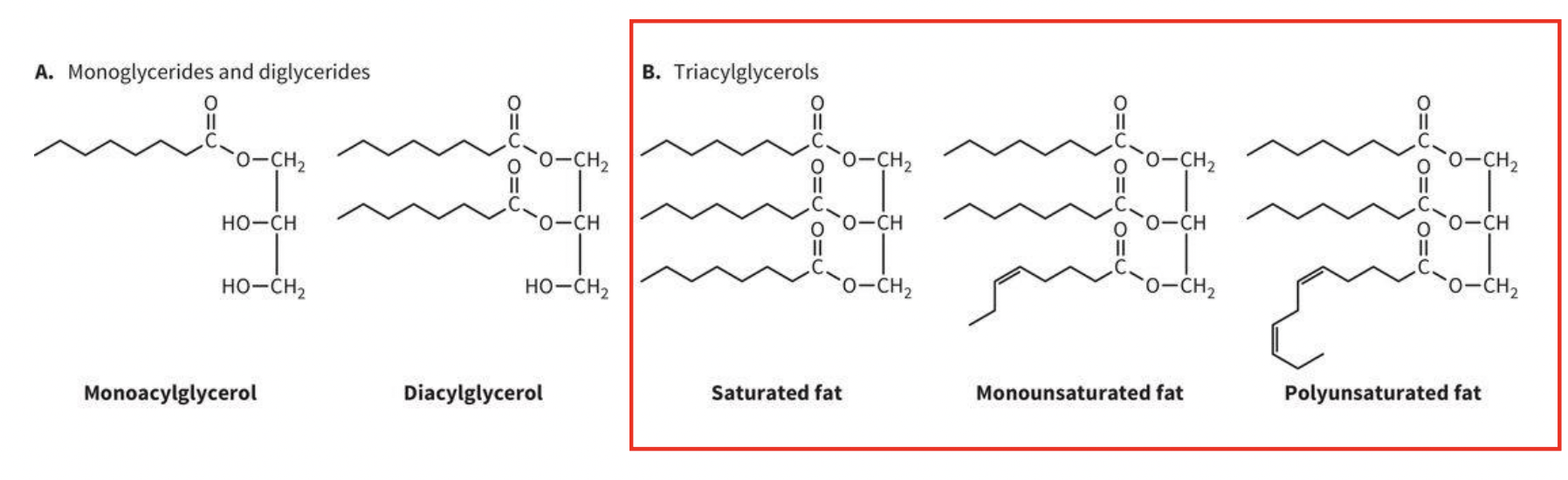
Different Types of Acylglycerols
A. Monoglycerides and diglycerides
-Monoacylglycerol
-Diacylglycerol
B. Triacylglycerols: the main source of energy storage in the body & can be broken down for energy
-Saturated Fat
-Monounsaturated fat
-Polyunsaturated fat
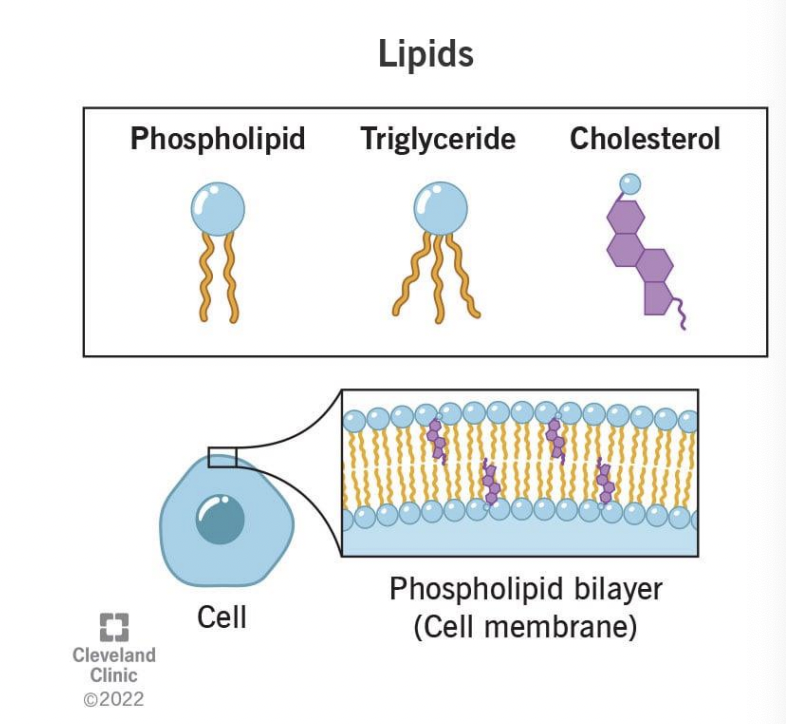
Other types of lipids
- Phospholipids are the main component of the lipid bilayer and organellar membranes
Phospholipids are fluid-like
- Cholesterol is rigid, provides important structural support in membranes.
Cholesterol: the good and the bad
Good cholesterol:
high density lipoprotein (HDL)
Bring cholesterol back to liver
High protein:fat ratio
Bad cholesterol:
low density lipoprotein (LDL)
Accumulates plagues on arterial walls → heart attack
Low protein:fat ratio
FATTY ACID OXIDATION:
- the metabolic breakdown of fatty acids (to acetyl-CoA)
—> occurs in the CYTOPLASM of fat cells
- DOWNREGULATED (inhibited) by INSULIN
—> wants to store fat
- UPREGULATED (activated) by GLUCAGON
—> wants to break down fat
- Fatty acids transported by albumin
- Glycerol -> G3P in gluconeogenesis in liver
(more about this in next lecture)
Glycerol Oxidation
- Glycerol kinase: phosphorylates glycerol but requires ATP (costs energy)
- Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NOT the same G3P from glycolysis) generates DHAP (generates NADH!)
- TIM (TPI) regenerates G3P (same one from glycolysis) from DHAP
- Either glycolysis or gluconeogenesis depending on what is needed