color theory terms
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
refraction
bending of a beam when it enters a medium where its speed is different. eg water and diamonds
absorption
occurs when a ray of light strikes a surface. energy of light is transferred to the surface material where the trabsfer creates heat preventing reflection or diffusion of light striking on the surface
transmission
unimpeded passage of light through a transparent object
reflection
light arriving at a smooth-surfaced material change their direction of travel on impact and are returned
scattering
change of direction suffered by direction on impact
interference
temporary splitting of light waves
diffraction
combined effect of scattering and interference. when light waves hit an obstacle it bends around the edges of the obstacle
Light, observer, object
three requirements to see color effect
synesthesia
neurological condition in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to automatic, involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway
Grapheme-color synesthesia
numbers and letters associated with the experience of colors
Chromesthesia
sound-to-color synesthesia. experiencing colors through a musical sound
color blindness
color vision deficiency or CVD. inability to see or perceive color differences, under normal lighting conditions.
deuteranopia
red-green color blindness
hue, saturation, value
3 dimensions of color
hue
true colors of the spectrum. describes the actual color.
color
refers to the name for any color
broken hue
combination of unequal proportions of all the primaries. earth colors
color wheels
color arrangements or structures that enable us to organize and predict such color reactions an interactions
pigment wheel
the kind that designers and artists use today. It's the basis for working with subtractive color, it imparts information about the reactions colors have when they are actually mixed
Muddy black
the result when red, yellow and blue pigments are combined using the pigment/mixing wheel
primary colors
consist of 3 unique colors, red-yellow-blue
secondary colors
produced from the mixing of one primary color with another. colors are orange-green-violet
tertiary colors
created when mixing one secondary and one primary color
process wheel
mostly used for photography, printing and ink manufacture. gives 3 basic primaries--yellow, magenta and cyan which is seen to result in purer hues. has 12-24 hues
gray-black
color result when the 3 primaries of a process wheel are combined
light wheel
based on the additive color system and provides information concerning light rays and transparent color; combinations of colored light; used for theatrical lighting and projection and is now the basis for video and computer graphics
white
color result when the 3 primaries of a light wheel are combined
Cool hues
hues that recede and suggest sky, water, distance, foliage, shadows. it is quiet, restful, far, airy and light
blue-green
the coolest hue
warm hues
hues that advance and suggest aggression, sunlight, heat, blood, arousal and stimulation; appear heavier
red-orange
the warmest hue
color saturation
tingkad; intensity, brightness or dullness of a color
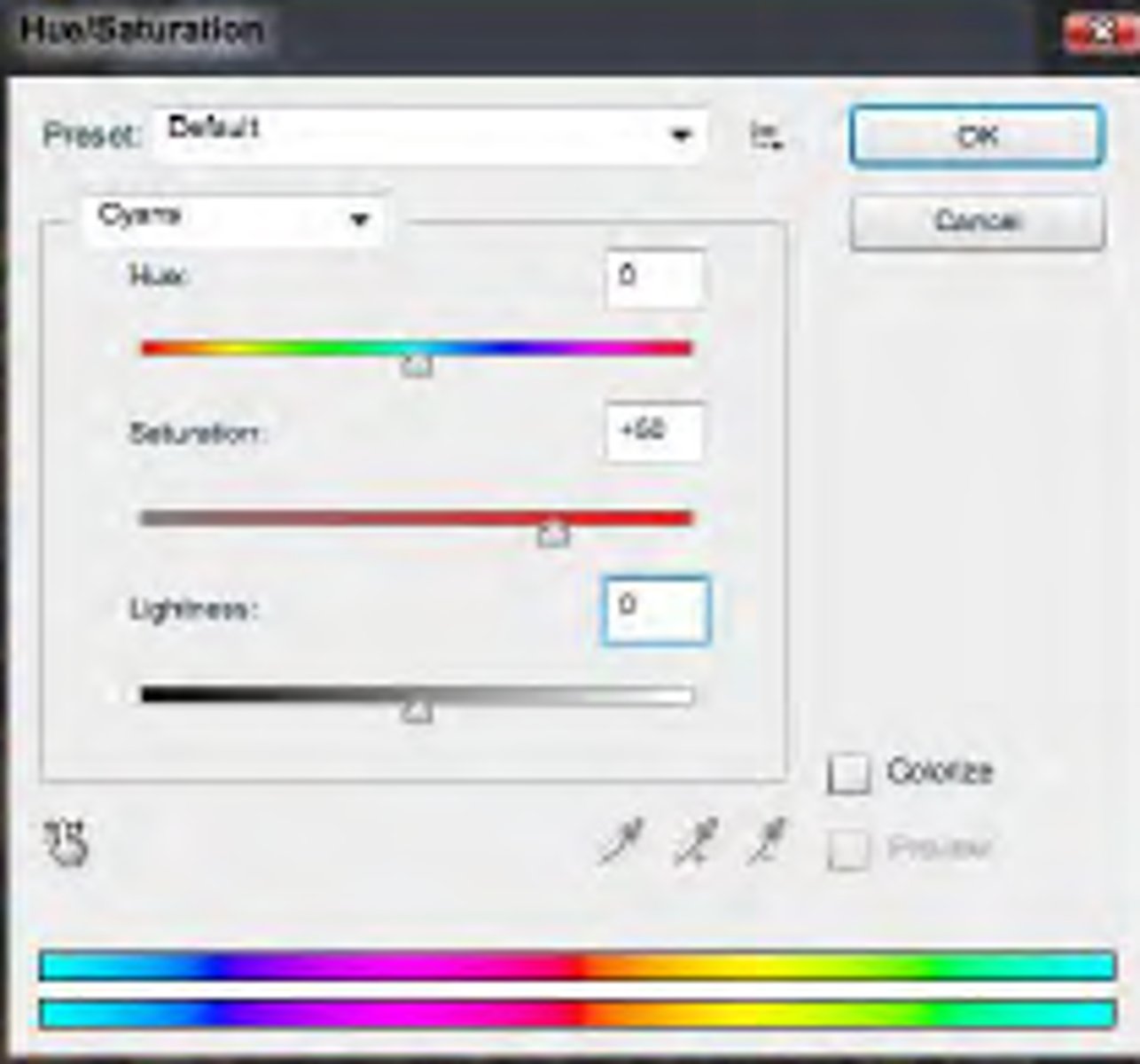
gray
a fully saturated color has no _____ in it
tones
addition of gray to pure hue; pang pa labo ng kulay
color value
lightness and darkness of a color
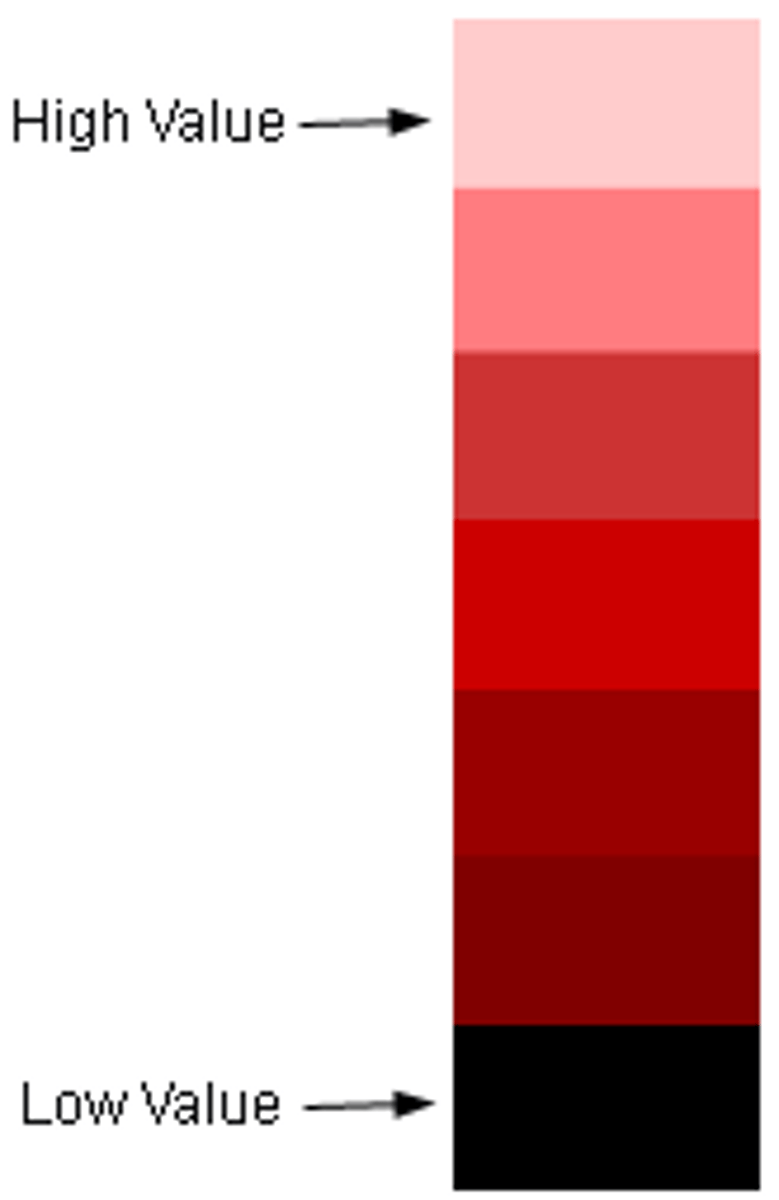

tint
hue with a presence of white
shade
hue with a presence of black
red
pink is a tint of what hue?
blue
navy is a shade of what hue?
intervals
a step of change between color samples
parents
term used for the samples on either side of intervals
descendant
term used for the visual step between two "parents"
gradient
series of progressive intervals that are so close that individual steps cannot be distinguished; seamless transition between color differences
achromatic
gray, white and black. have lightness but no hue or saturation. They can be created by mixing complementary colors together.
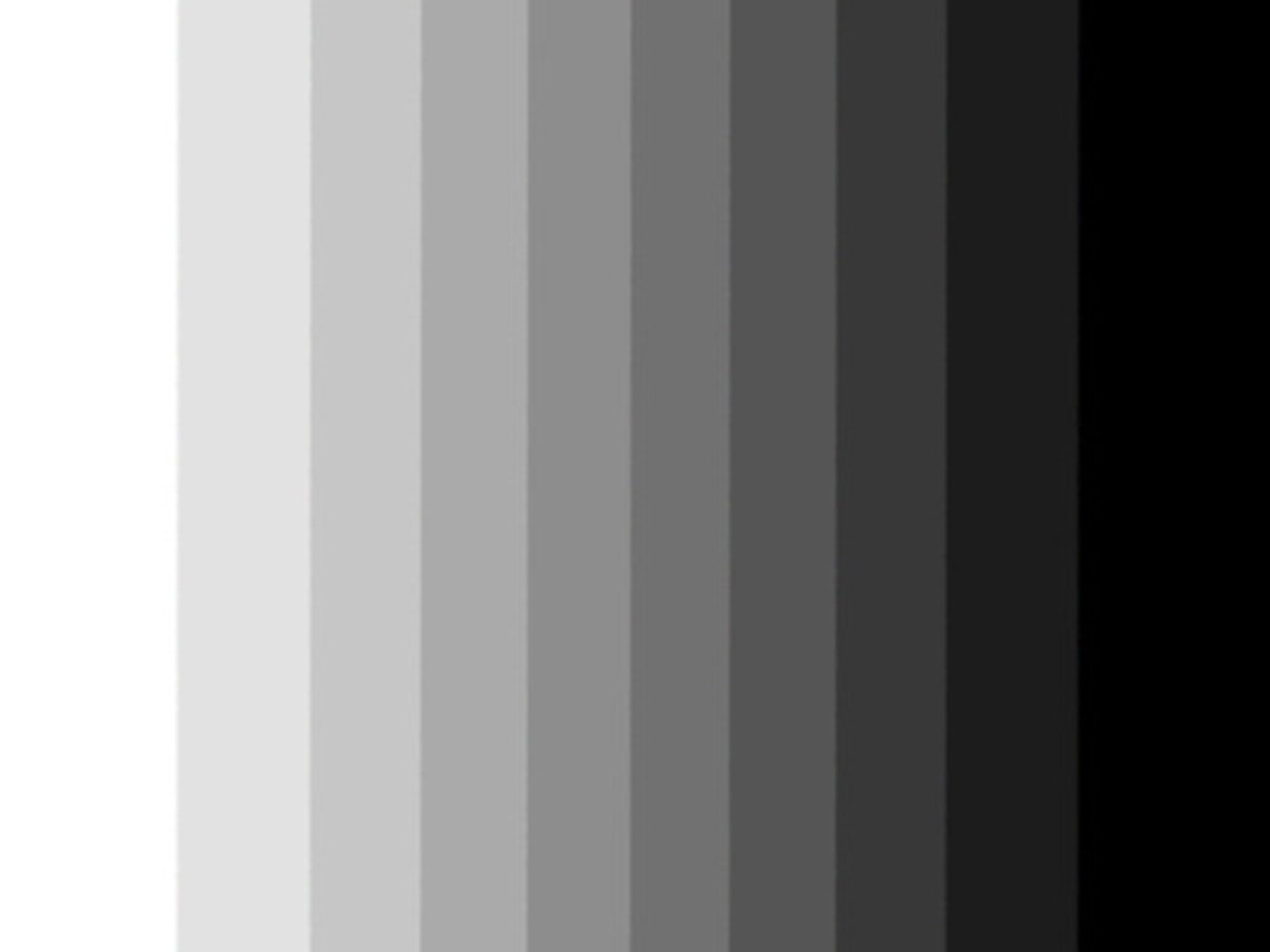
chromatic
any color which has even the slightest amount of hue are called
Advancing
Colors lower in value, more highly saturated and are warmer in hue are regarded as
receding
colors higher in value, lower in saturation, and cooler in hue are regarded as
color harmony
refers to the visual agreement of all parts of a work; these are time-tested combinations that work well together
color chords
other term for color harmony
Monochromatic
single base hue and extended using its shades, tones and tints.
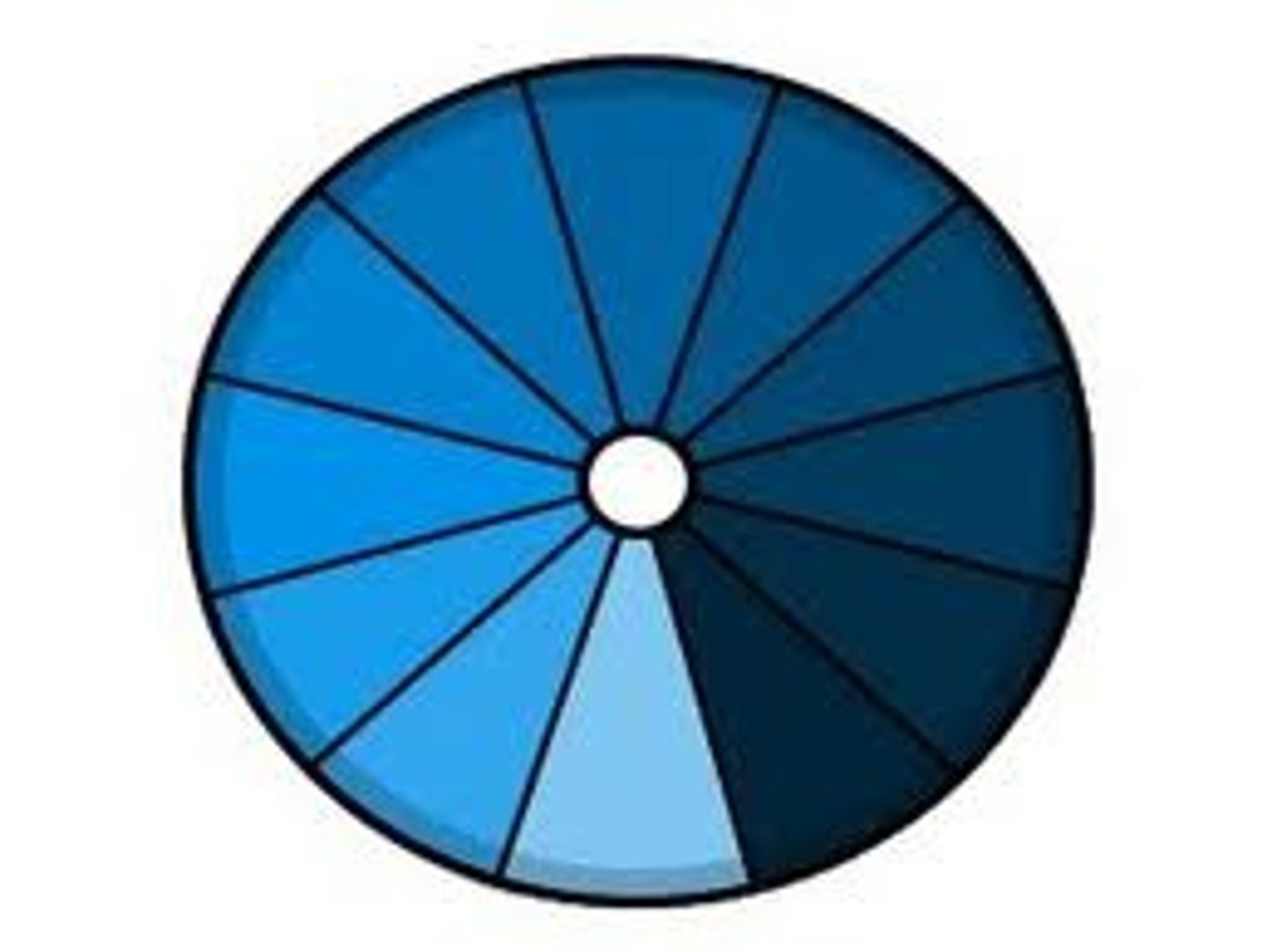
analogous
any three colors which are side by side on the color wheel; non-contrasting colors
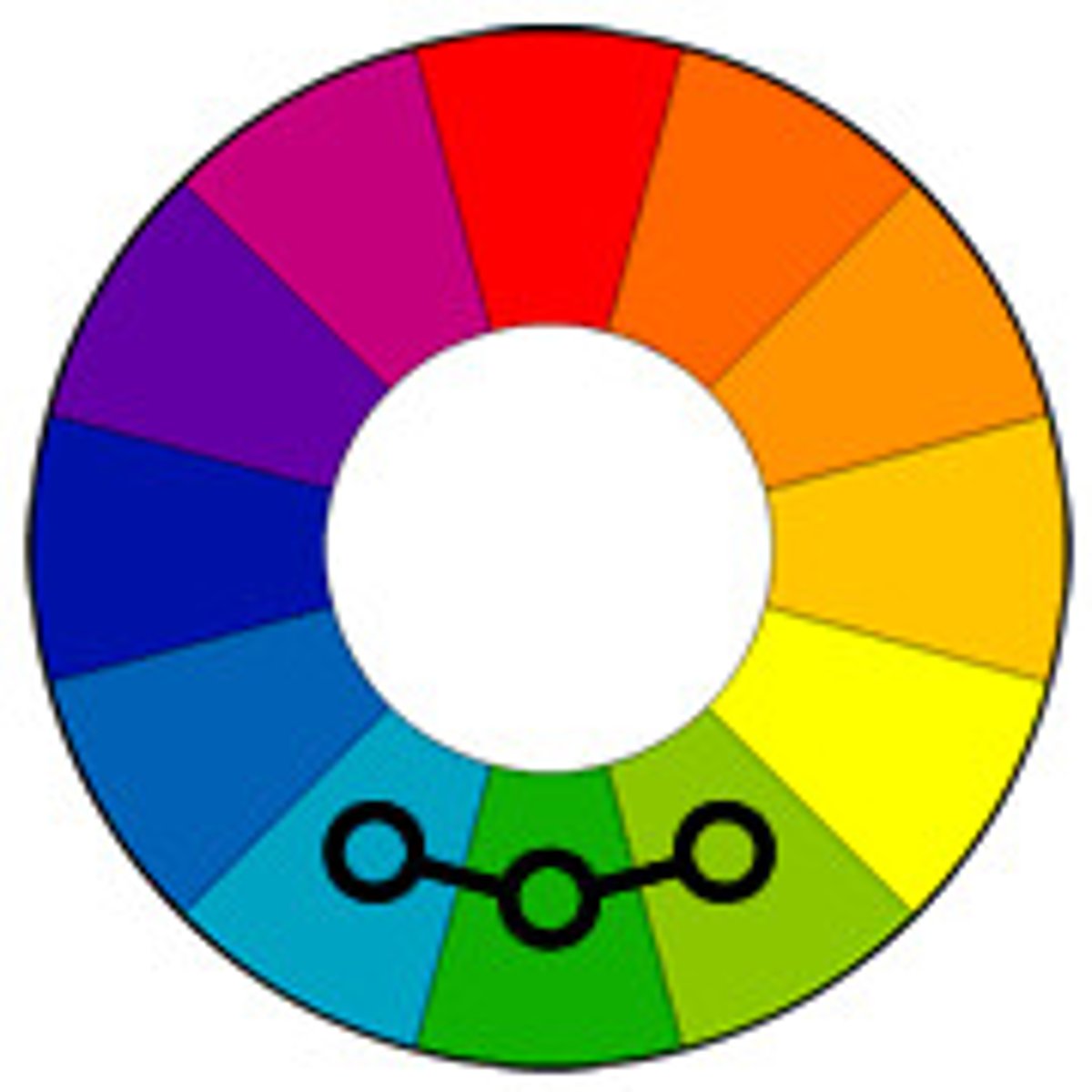
direct complementary
2 hues that lie directly opposite one another on the color wheel
near complementary color
one of the hues lies to one side of what would otherwise be a direct complementary
split complementary
forms a Y shape. one hue and 2 hues that lie on either side of its direct complement
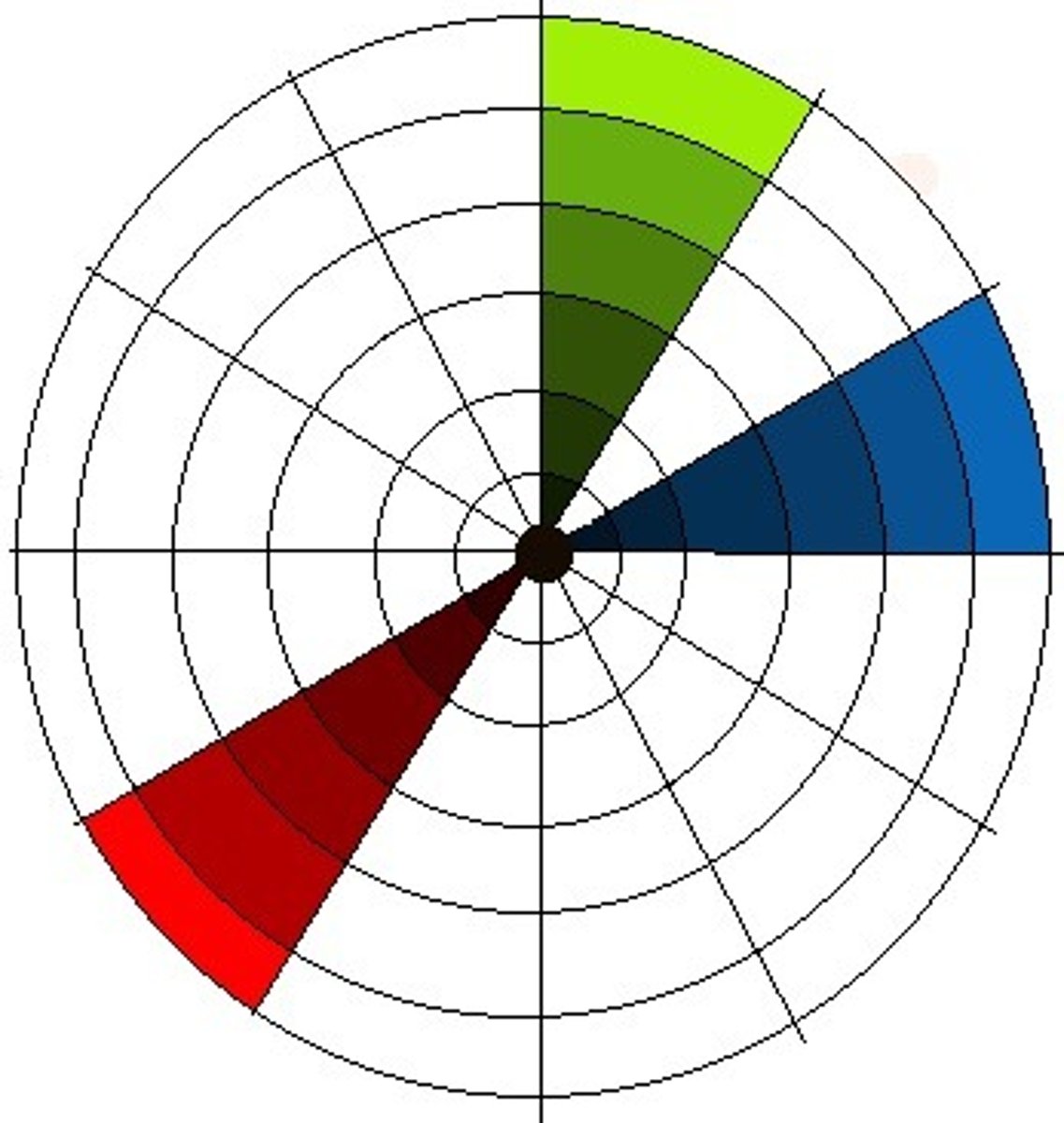
triadic
3 hues that are equidistant from one another on the color wheel; forms a triangle
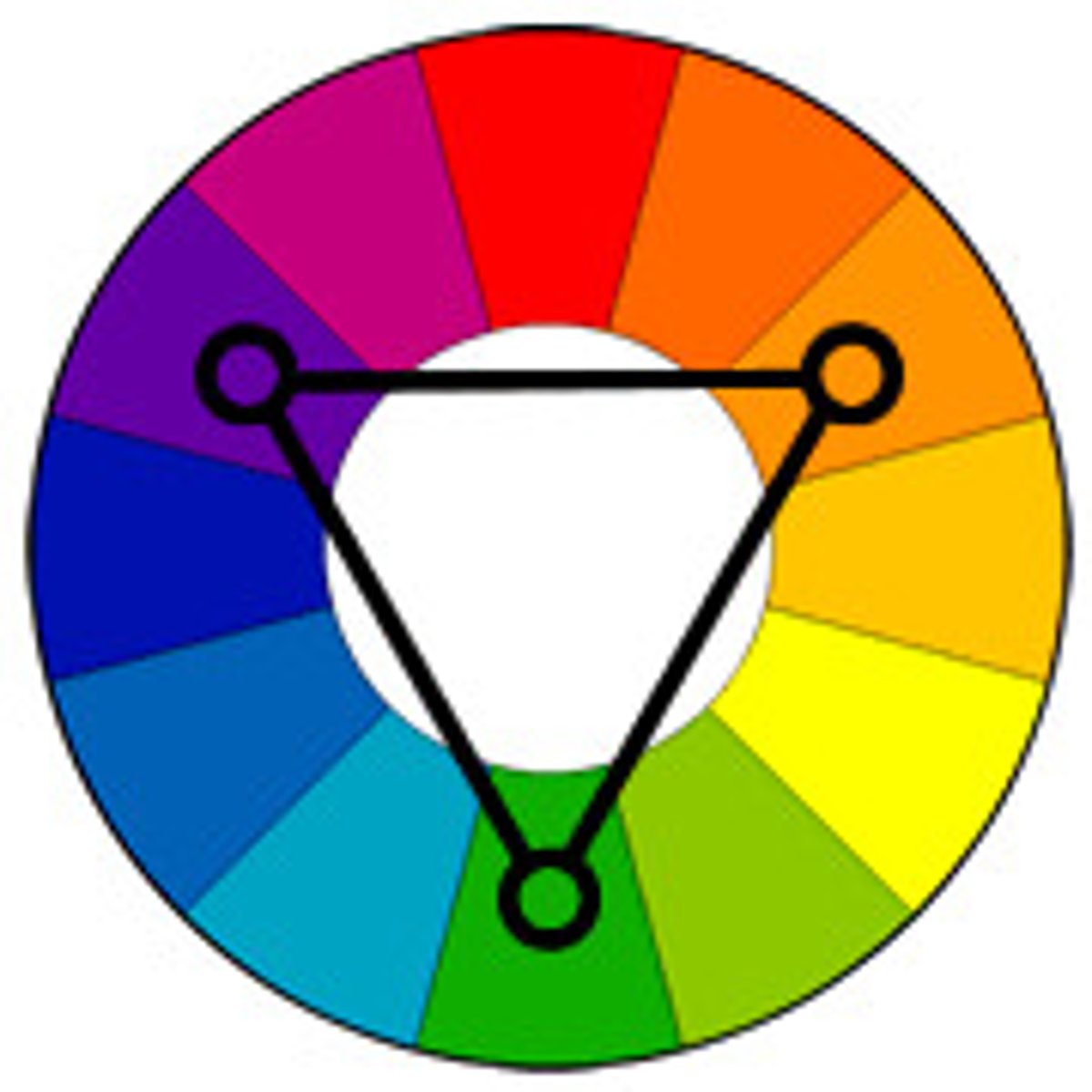
tetradic
4 equidistant hues; forms a square
neutral colors
grays and browns

one hue with neutral
harmony that utilizes one accent hue in full saturation combined with neutral colors or b&w. uses only one hue.
subtractive color
pigments, dyes--colorants. It is the process of mixing pigments together, such as seen in paintings. blended pigments absorb more light, hence, reflecting less light.
mixing of hue pigments is based on?
colorant
material that changes the light absorption characteristics of another material to w/c it is applied
dyes
natural or artificial colorants that absorb but usually do not scatter light and are soluble in the substrate
pigments
natural or artificial colorants that not only absorb but also scatter light and that are insoluble in the application medium or substrate
additive color
process of mixing colored light, such as in theatrical lighting or television. Lights are mixed by placing colored filters in front of a projected light ray
black
absence of light
on-screen color
additive color is sensed very differently form color reflected from a real surface. Printed colors cannot be matched exactly
CMYK mode
color display mode that imitates the results of the mixing process colors. This display mode facilitates working on-screen for print production
100
each cmyk can have a value of 0-100%. 0% equals no color (white), while ___% equals black
grayscales
made by manipulating percentages of key alone
middle gray
cmy colors mixed in equal percentages without black make a?
clear colors and tints
result when 2 of the CMY colors are mixed without black
RGB mode
mode of screen display parallels the behavior of light. Usually displayed in 0-255 mode. with 0 being black; the higher the number, the brighter the colors. each slider has 255 individual options
White
_____ is RGB 255, 255, 255, while black is RGB 0, 0, 0
HSV mode
or HSL mode displays a circular color map. it requires learning to mix color in a way that is associated with digital design
Gamut
range of colors reproduced in a color mode
calibration
the setting or correcting of a measuring device or base level, usually by adjusting it to match or conform to a dependably known and unvarying measure.
calibrate a monitor
to adjust the monitor so that specific combinations of red, green and blue signals produce specific on-screen
pantone color matching system
standardized color reproduction system. Created so different manufacturers in diff locations can all refer to this system to make sure colors match without direct contact with one another.
1755
how many spot colors does pantone have?
CRI (color rendering index)
a quantitative measure of the ability of a light source to reproduce the colors of illuminated objects accurately when compared to a reference light source, such as pure sunlight. scale is from 0-100 (perfect cri; sunlight)
glare
visual sensation caused by excessive and uncontrolled brightness. It can be disabling or simply uncomfortable
disability glare
reduction in visibility caused by intense light sources in the field of view
discomfort glare
sensation of annoyances or even pain induced by overly bright sources.
color temperature (k)
best describes the color appearance of the light source and the light emitted from it. the numerical value assigned to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of kelvin.
cool daylight
most preferred lighting for offices with over 6500k w/c is a bright white
3500-4000k
color temperature for hotels and environments that want to create a warm atmosphere
aristotle
greek philosopher who attempted to explain the composition of colors and how they were related. He wrote the book "de coloribus"
de coloribus
first known book about color written by aristotle. it outlines the theory that all colors (yellow, red, purple, green and blue) are derived from mixtures of black and white
leonardo da vinci
renaissance artist and scientist (1452-1519) who believed that black and white are colors. Assigned black, white, yellow, green, blue and red as primary or simple colors. author of treatise on painting published in 1651.
Simultaneous Contrast
complementary colors intensify each other when placed side by side; certain responses took place when colors are placed next to each other; theory concluded by leonardo da vinci
atmospheric perspective
method of creating the illusion of depth, or recession, in a painting or drawing by modulating colour to simulate changes effected by the atmosphere on the colours of things seen at a distance.

sir isaac newton
english physicist who was interested purely in the physics of color rather in the perception. He discovered that as a ray of white light passes and is bent, or refracted, through a prism it is broken into an array of colors, or spectral hues- roygbiv. his theory was based on the mixing of light. "light alone generates color". (1642-1727)
Moses Harris
english entomologist and engraver, wrote the natural system of colors in 1766 where he presented red, yellow and blue as the primary hues w/c he termed "primitives" and the mixture of these produced the "compound" hues of orange, green and violet. (1730-1788)
Harris wheel
divided into 18 equal hue divisions and each division was then graded by value dark to light; similar to pigment wheel but with more tertiary colors
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
German poet who published "theory of colors". One of the first modern thinkers to investigate and record the function of the eye and its interpretation of color, rather than properties of light. He explored every aspect of color and its reactions, including the role of complementary colors in creating shadows, simultaneous contrast, successive contrast and proportional color use. His focus was more on pigments. (1749-1832)
six-hue spectrum
Goethe's _______ remains the convention for artists; Newton's seven-hue model of the full range of visible hues remains the scientist's spectrum
Philip Otto Runge
german painter who wrote the color sphere. he arranged 12 hues in a spherical format. His primaries were still red, yellow and blue, and the nine remaining hues were interspersed to form a diameter of equator around the center of the sphere
michel eugene chevreul
french chemist hired by the famous french tapestry-weaving studio Gobelins to be its dye master. also known for his work The Principle of Harmony and Contrast of Colors. he verified that all hues could be obtained from mixtures of the primaries red, yellow, and blue. He also developed a more 3-dimensional color hemisphere than runge's
afterimaging
an optical reaction discovered by chevreul that occurs after we stare intensely at a hue and then shift our eyes to a white surface resulting to a second hue
Ogden rood
american who proposed that colors differed from one another as a result of three variables--purity, luminosity, and hue. (hue, saturation and tone). His experiments were concerned with the optical mixing that occurs in pointillism.
Albert Munsell
(1858-1918) the life's work or american-born color theorist led to his system being adopted by the US Bureau of Standards as the acceptable language of color.