Cartilage and joints
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the two types of skeletons?
Axial skeleton
Appendicular skeleton
What are the functions of cartilage?
Foetal precursor to bone development
Cushioning at joints between bones
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Elastic cartilage
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
Free-moving joints as articular cartilage
Where is fibrocartilage found?
Intervertebral discs of the spine and knee
Where is elastic cartilage found?
Makes up the external ear and the auditory tube
What are the two categories of joints?
Functional
Structural
What are the three types of functional joints?
Immovable
Slightly moveable
Freely moveable
What are the three types of structural joints?
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
What are fibrous joints?
Dense tissue forming immobile joints between bones
What are the three types of fibrous joints and where are they found?
Suture (cranium)
Syndesmosis (closely related bones)
Gomphosis (between teeth and jaw)
What are cartilaginous joints?
Hyaline or fibrocartilage that form flexible joints
What are the two types of cartilaginous joints and what are they made from?
Synchondrosis (hyaline cartilage)
Symphysis (fibrocartilage)
What are synovial joints?
Freely mobile joints covered by cartilage
What are the six types of synovial joints?
Plane joint
Hinge joint
Pivot point
Condyloid/ellipsoid joint
Saddle joint
Ball and socket joint
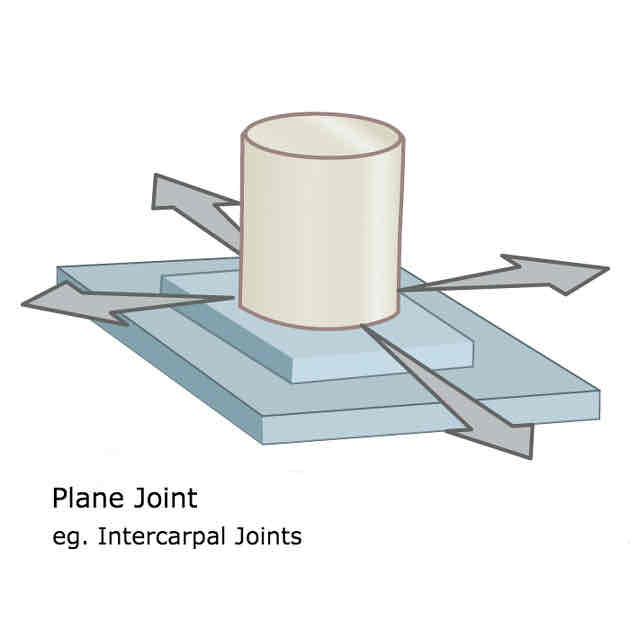
What is an example of a plane joint and what movements are possible?
Between tarsal bones
Enables bones to slide over each other
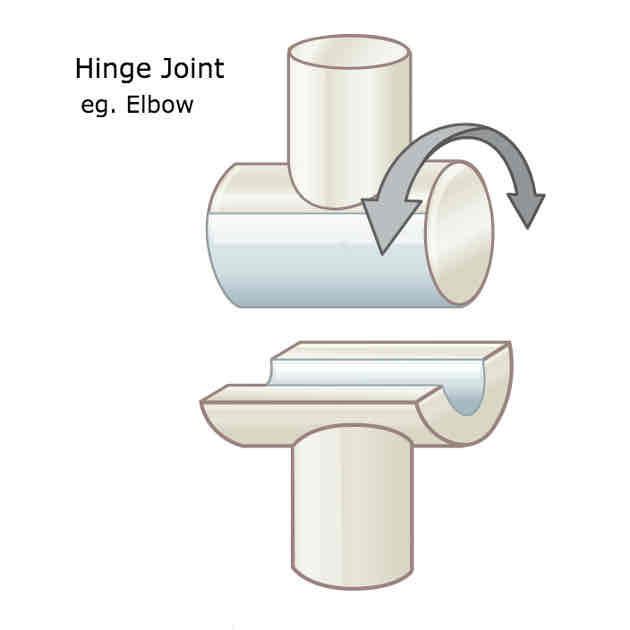
What is an example of a hinge joint and what movements are possible?
Elbow, knee and interphalangeal joints
Allows for movement in one plane
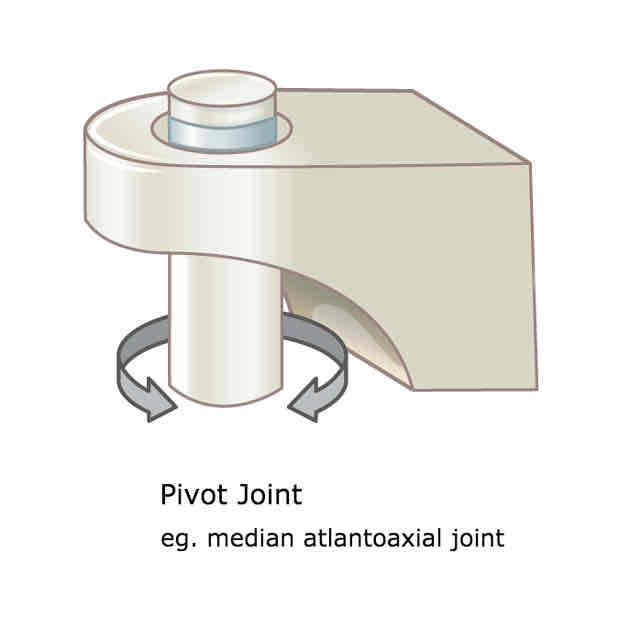
What is an example of a pivot joint and what movements are possible?
Between C1 and C2 vertebrae
Allows rotation on a single axis
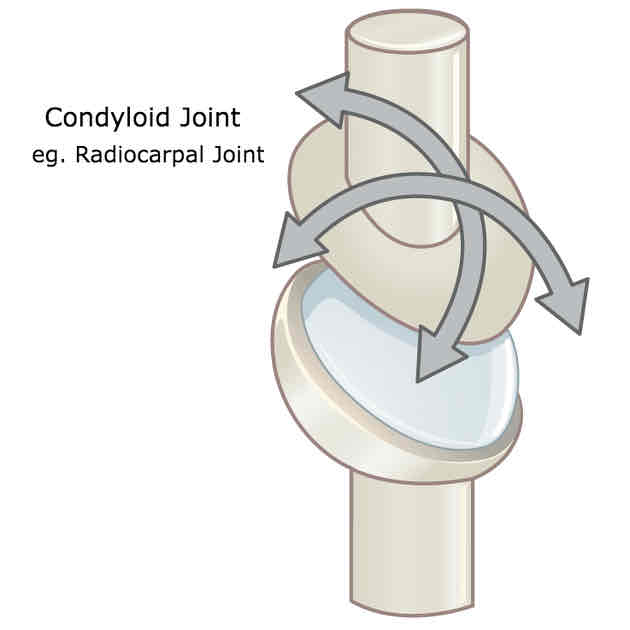
What is an example of a condyloid joint and what movements are possible?
Radiocarpal
Allows flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction
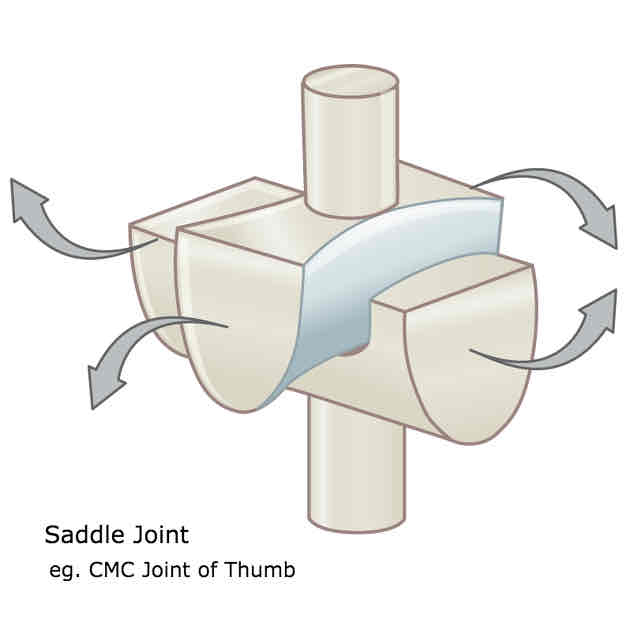
What is an example of a saddle joint and what movements are possible?
Carpometacarpal joint
Allows flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction but not axial rotation
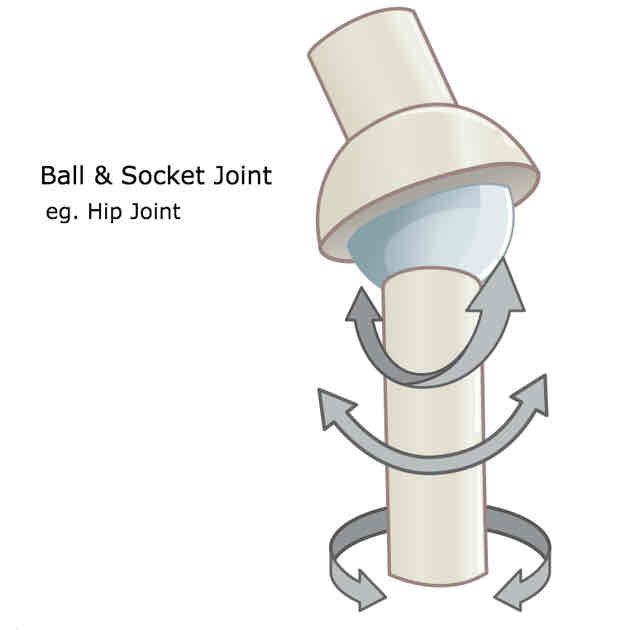
What is an example of a ball and socket joint and what movements are possible?
Shoulder joint and hip joint
Allows indefinite amount of movements
What is the function of skeletal muscles?
Provides structural support and maintains posture
What are the three types of connective tissue in skeletal muscles and where are they found?
Endomysium (around individual fibres)
Perimysium (around bundles of fibres)
Epimysium (around muscle)
What is the origin of a muscle?
Where the muscle is attached on a more stable bone
What is the insertion of a muscle?
Where the muscle is attached to a more moveable bone
What is a tendon?
Connects muscle to bone
Moves bones
What is a ligament?
Joins bones together
Stabilises structures
What are the two types of bones?
Compact bone
Spongy bone
What is the periosteum of the bones?
Covers the outer surface
What is the endosteum of the bones?
Covers the inner surface of the bones
What are the five classifications of bones?
Long bone
Short bone
Flat bone
Irregular bone
Sesamoid bone
What are the two types of ossification?
Intramembranous ossification
Endochondral ossification
What is intramembranous ossification?
Mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts
What is endochondral osiffication?
Formation of cartilage tissue which is replaced by bone
What are the four types of cells involved in bone production?
Osteocyte
Osteoblast
Osteogenic
Osteoclast
What is the function of osteocyte cells?
Mature bone cells that maintain normal bone cell activity
What is the function of osteoblast cells?
Forms bone matrix
What is the function of osteogenic cells?
Stem cells found in bone marrow
What is the function of osteoclast cells?
Resorbs (destroys) the bone