RNA, DNA replication & transcription (L3)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
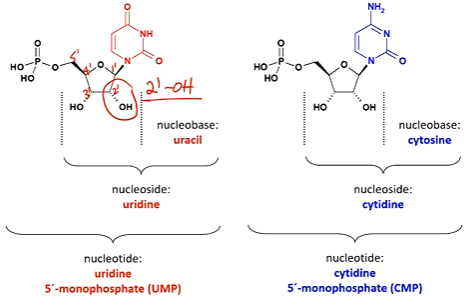
outline the main differences between DNA & RNA.
DNA | RNA | |
|---|---|---|
sugar | deoxyribose | ribose |
nucleobase | thymine | uracil |
secondary structure | double stranded | single stranded |
size | bigger | smaller |
what group is missing in the ribose sugar of DNA but not in RNA?
the 2’ OH group
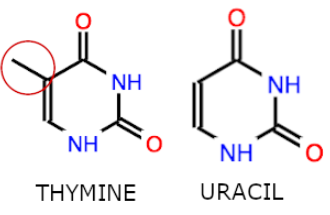
thymine & uracil are the same except uracil is missing the ______ group.
methyl group
RNA is ____ stable than DNA.
RNA is less stable than DNA.
why is RNA less stable than DNA?
the presence of the 2’ hydroxyl group in the ribose, which renders it more susceptible to hydrolysis and destruction.
what is mRNA?
a single strand of RNA that relays the code for a protein from DNA to the protein production site.
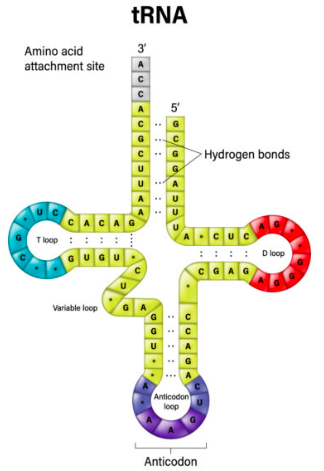
what is tRNA?
The adapter unit linking the triplet code on mRNA to specific amino acids.
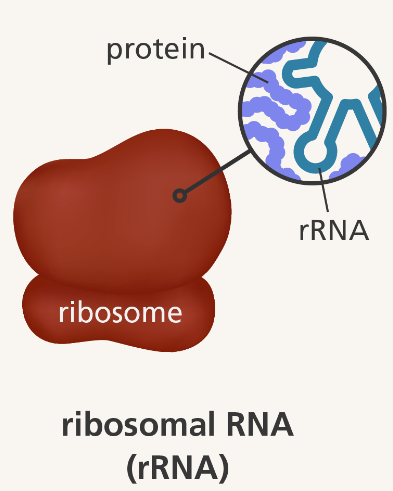
what is rRNA?
non-coding RNA present in ribosomes (site of protein synthesis)
RNA cannot adopt a _-form structure.
B-form structure
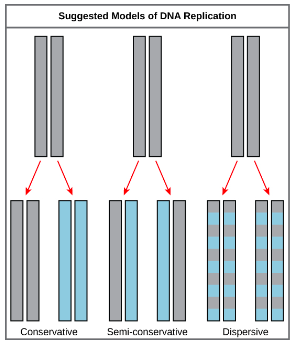
what were the 3 postulated methods of DNA replication?
semi-conservative
conservative
dispersive
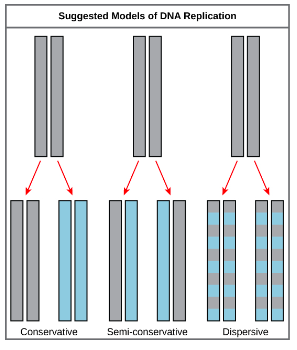
what is the difference between these postualted methods?
semi-conservative - 2 strands split & acts as a template resulting in 2 DNA molecules with a new & original strand.
conservative - replication resulting in 2 dna molecules, 1 identical to the original & 1 with 2 new strands.
dispersive - replication resulting in hybrid (a mixture) of parental & daughter DNA
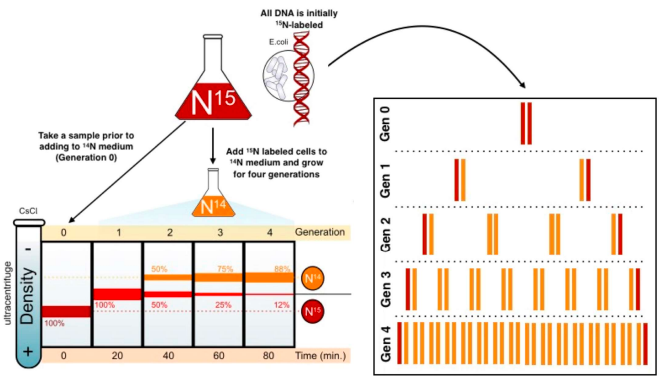
describe the Meselson & Stahl experiment
E.coli were grown in a medium containing heavy isotope 15N and also in a medium containing light isotope N14. (when DNA samples from both are spun in a centrifuge, light DNA settles higher up the test tube than heavy DNA).
after many generations E.coli from the heavy nitrogen (15N) was taken out and put in the light nitrogen (14N). after several generations, DNA samples are centrifuged on a salt density gradient.
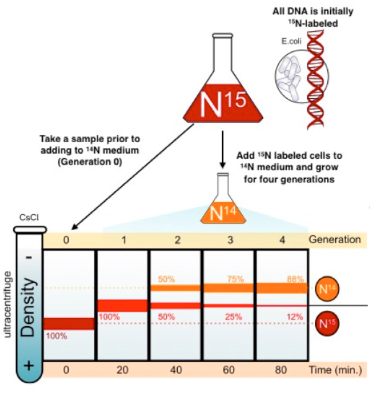
what occured when the 1st gen was centrifuged & what does it mean?
a single band centrifuged & was higher & intermediate in density between the heavy DNA and light DNA.
that replication is not conservative as the first round of replication was a hybrid of light & heavy DNA
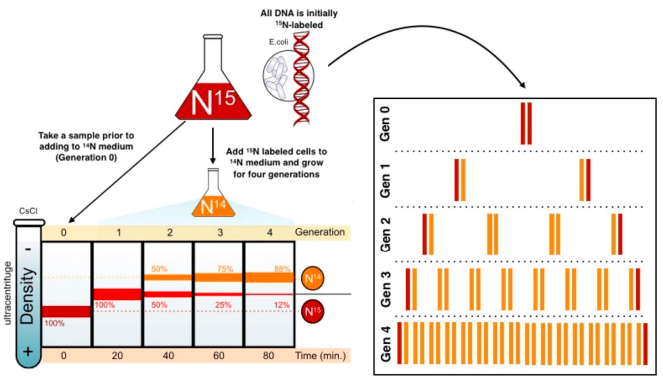
what occured when the 2nd gen was centrifuged & what does it mean?
2 bands were produced: 1 in the same position as the intermediate band & 1 in a higher position indicating semi-conservative replication
it cant be dispersive as all the molecules would have bits of old & new DNA, making it impossible to get a "purely light" molecule.
what does DNA polymerase require
template strand
primer - a short nucleic acid sequence that acts as the starting point for DNA synthesis.
DNA polymerase synthesises DNA only in the _’ to _’ direction.
DNA polymerase Synthesises DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction.
what is the replication fork?
a structure formed when the double helix of DNA unwinds at the origin of replication, creating two separate strands.
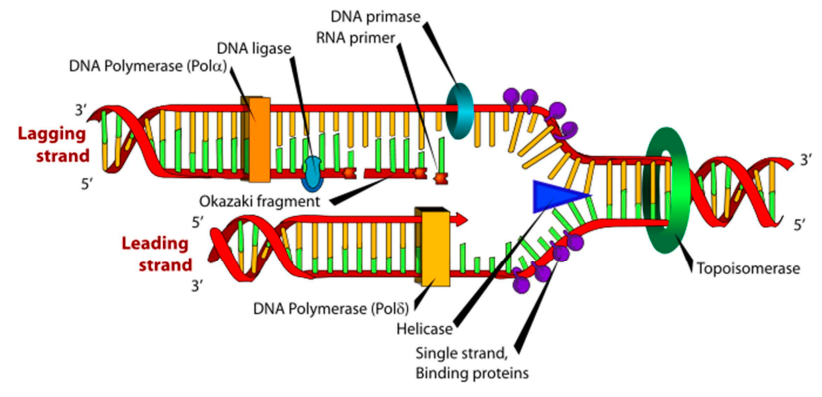
define the leading strand.
the DNA strand synthesised continuously in the 5' to 3' direction during DNA replication.
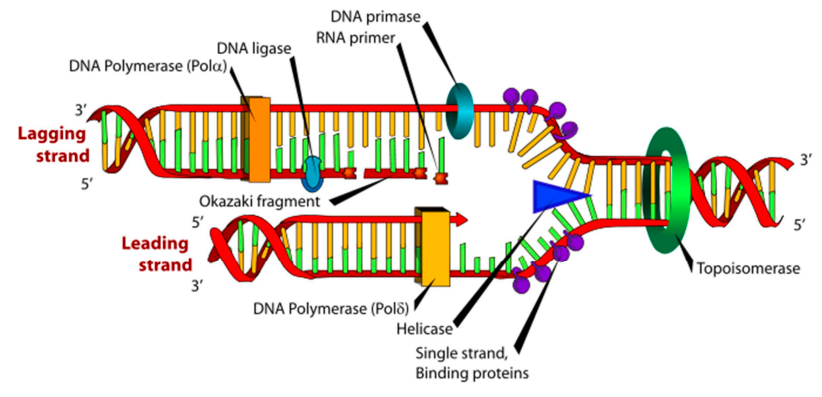
define the lagging strand.
the DNA strand synthesized discontinuously in short fragments called Okazaki fragments during DNA replication.
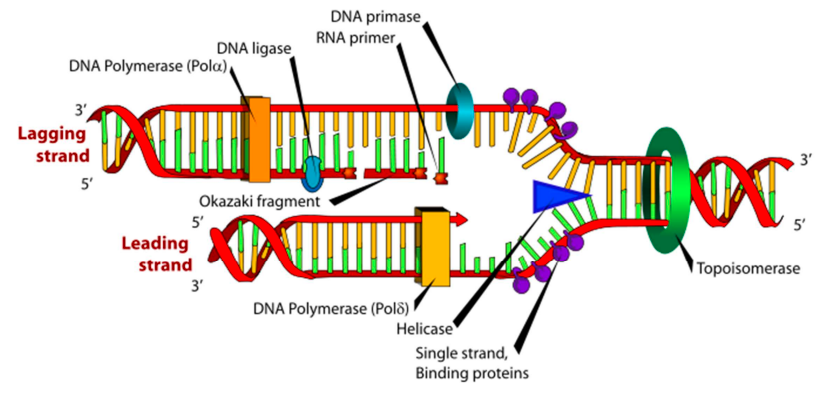
what is a key diff between the leading & lagging strand?
the leading strand only required 1 primer while the lagging strand requires 1 primer per okasaki fragment
define DNA helicase
an enzyme that unwinds DNA at the replication fork by breaking H bonds between complementary BPs.
define topoisomerase
an enzyme that acts ahead of the replication fork & prevents supercoiling. it may cut the DNA to relieve tension.
define DNA ligase
an enzyme that seals gaps between adjacent (close) okazaki fragments on the laggin strand.
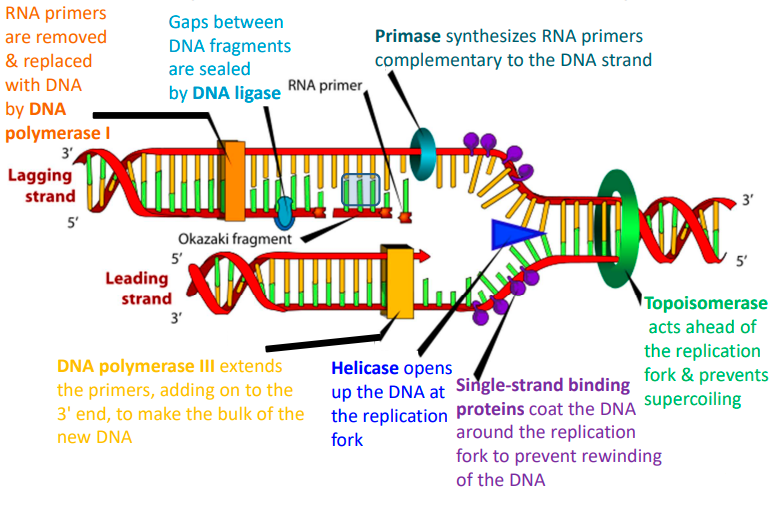
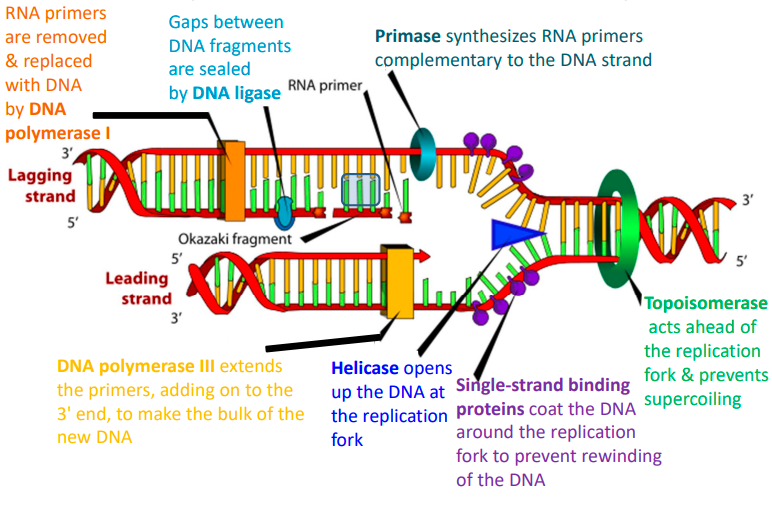
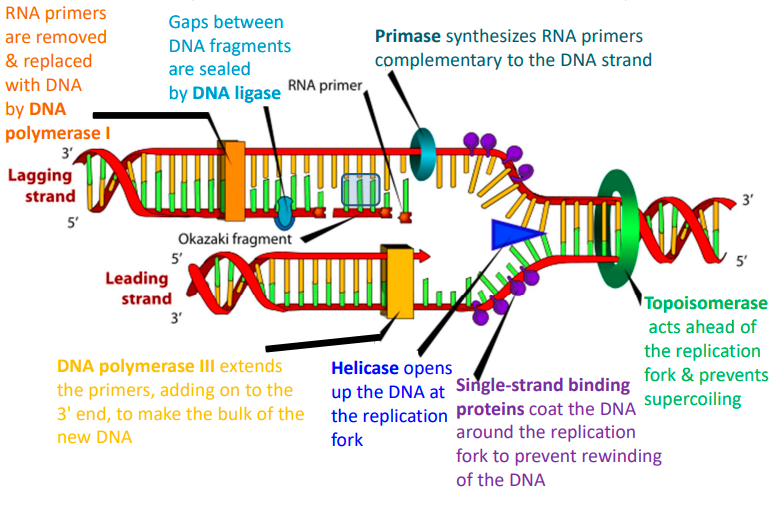
describe the process of DNA replication
DNA helicase unwinds the double helix, creating a replication fork.
DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding complementary nucleotides to the exposed single strands.
One strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction (leading strand), while the other is synthesized discontinuously in short fragments (lagging strand).
Primase synthesises RNA primers on the lagging strand to initiate synthesis of each Okazaki fragment.
DNA polymerase extends the RNA primers by adding DNA nucleotides to form Okazaki fragments.
DNA ligase joins the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, producing two complete DNA molecules, each consisting of 1 original strand and 1 newly synthesized strand.
define transcription
copying of a segment of DNA into RNA which codes for a specific protein.
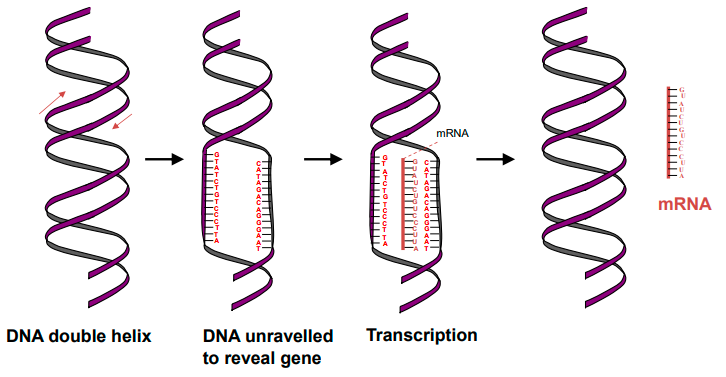
what is RNA polymerase?
an enzyme responsible for catalysing the production of complementary RNA from the DNA template strand in transcription.
describe the process of transcription.
initiated when RNA pol binds to DNA upstream (5’) of the gene at the promoter region
DNA double helix unwinds & RNA pol reads the template strand
nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the growing chain.
transcription continues until a terminator sequence
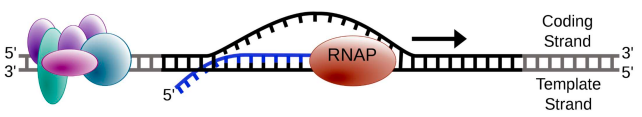
which strand is read?
the template strand
what occurs to the mRNA after transcription?
introns (non-coding DNA sequences) are removed
exons (coding DNA sequences) are spliced (joined) together