Respiration
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
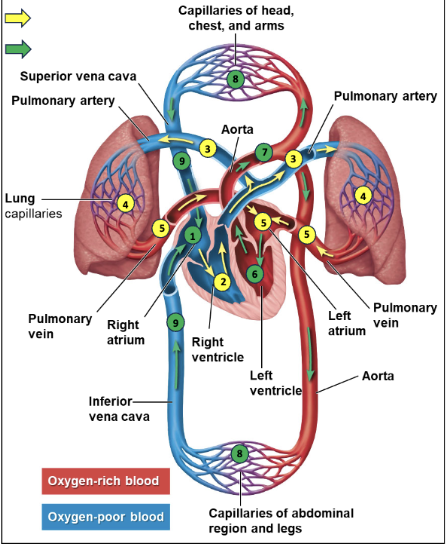
Path of blood
Right atrium receives oxygen poor blood from vena
cavaeBlood is pumped from right atrium to right ventricle
Right ventricle pumps blood to pulmonary arteries
oxygenated at lungs
Pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to left
atriumBlood flows from left atrium to left ventricle
Delivered to body tissues
Veins (ultimately vena cavae) return blood to right
atrium
Gas
substance with no fixed shape or volume, and widely separated particles, that expands to fill a “container”
Gas Exchange:
Needed because of cellular respiration: O2 consumed and CO2 produced as byproduct
Molecular mechanism of exchange: diffusion
Molecules of each type of gas in mixture diffuse from region of higher partial pressure to lower partial pressure
Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
Four attributes for effective respiration:
Gas exchange region must be moist: moisture allows gases to become/stay dissolved as they cross the gas exchange region
Gas exchange region must be thin: diffusion works best over short distances
Gas exchange region must have a large surface area
Concentration gradient must occur between the regions where gas diffuses (moves from high to low)
Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system
Lungs: exchange gases between environment and
bodyTake in O2 from air and release CO2 into it
Adults average 12-20 breaths per minute
Left lung is slightly smaller to accommodate heart
Path of airflow
Nose/mouth → pharynx → larynx → trachea (“windpipe”) → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
“Air conditioning” along the path of airflow:
nasal hairs: filters/trap out large particulate debris
nasal cavity warms and humidifies the air
air is sampled for odors
mucus surfaces capture fine particulates
Alveoli
tiny air sacs, surrounding capillary beds are ideally adapted for gas exchange
very high surfaces in direct physical contact with capillaries and the environment
one cell layer thick
O2 diffuses into the blood across alveoli
CO2 diffuses out of the blood across alveoli
Surfactant: lipid and protein mixture preventing alveoli epithelium from sticking together
Breathing
the alternate inhalation and exhalation of air (aka ventilation)
diaphragm and intercostal (between ribs) muscles move lungs
Inhalation: Diaphragm/intercostals contract and expand/lower – volume increase sucks air into lungs
Exhalation: diaphragm/intercostals relax– volume decrease pushes air out of lungs
Important lung volumes
total capacity ~5-6L
tidal volume
vital capacity
residual volume
Tidal volume
volume of air inhaled/exhaled in one normal breath
Resting Tidal Volume ∼ 500 mL
Vital capacity
maximum volume one can inhale/exhale in one maximum breath (typically 3 - 5 L)
Residual volume
(20 – 50% of lung volume) remains in the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli
Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
Air (or fluid) gets into the area between the lung and chest wall and lung can not fill with air
The diaphragm contracts and moves downward during?
Inhalation
What is the primary stimulus causing breathing rate to increase during exercise?
Increasing level of CO2
Regulation of breathing
Rising CO2 levels decrease blood pH levels
Body cannot tolerate much
Sensors in blood vessels; brain detects drop in pH
Brain signals rib muscles and diaphragm to increase breathing rate and depth
Human circulatory system connection
The human heart is two pumps in one with two separate circuits:
The right side pumps oxygen-poor blood (blue)to the lungs
Pulmonary circuit: To and from lungs
The left side pumps oxygen-rich blood (red) to body tissues
Systemic circuit: To and from body tissues
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the
blood
Blood and its contents
Blood
Plasma
red blood cells
white blood cells
platelets
Blood
involved in transport, immune defense, and temperature regulation
Plasma
Liquid part of blood
Red blood cells
AKA erythrocytes, transport oxygen
White blood cells
AKA leukocytes, resist infections
Platelets
repair damaged blood vessels
Hemoglobin
has 4 heme groups, each containing an iron atom that binds one O2 molecule
~250-300 million hemoglobin per red
blood cellOxygen diffuses across the alveolus and into the blood plasma, then into red blood cells where it binds to hemoglobin
Hemoglobin binds and releases oxygen
The partial pressure of O2 (Po2) is the relative amount of O2 available. O2 moves from high to low
In the lungs (high Po2), hemoglobin will “pick up” O2; in the tissues far away from lungs the (low Po2), hemoglobin will release O2.
Partial pressure gradient of O2 in body tissues determines how much is “unloaded from” hemoglobin
O2 released rapidly during exercise as it is used quickly
The human fetus exchanges gases with the mother’s blood
Fetal gas exchange occurs in the placenta; blood supplies do not directly mix
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for O2 than maternal hemoglobin
Fetal hemoglobin binds oxygen as maternal hemoglobin releases it
Smoking during pregnancy reduces the supply of oxygen to the fetus by up to 25%
How many O2 molecules can each hemoglobin carry?
4