Sleep
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Sleep
A regularly occurring ASC that typically occurs spontaneously and is characterised by a loss of conscious awareness
Ways to Study Sleep
Electroencephalograph - detects, amplifies, and records electrical activity in the brain.
Electromyograph - detects, amplifies, and records the electrical activity of the muscles.
Electro-oculargram - detects, amplifies, and records eye movement by monitoring the tiny muscles that allow the eye to move.
Sleep diaries - Questionnaires on sleep problems, recordings of time asleep/awake, etc.
Video monitoring - for thoughts & feelings and measurement of sleep behaviours.
Electrical activity of the brain -
How does the Circadian Rhythm work?
Regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN, the ‘master’ biological clock of the body), which is located in the hypothalamus.
SCN receives info about the amount of light from the eyes and adjusts our sleep-wake cycle (SWC) accordingly.
In the morning, light stimulates neural pathways in the retina.
The retina sends a message to the SCN and triggers a rise in body temp and the release of cortisol.
A message is also sent to the pineal gland to decrease the release of melatonin.
Melatonin induces feelings of sleepiness + encourages sleep, and is also sensitive to light + is released in greater quantities in the dark.
What’s an Ultradian rhythm (URR)?
A biological rhythm that occurs with a frequency of less than 24 hours.
The sleep proportion of the SWC consists of URR.
In ~90min cycles, sleep has alternating REM and NREM stages, which are examples of a URR.
Other e.g. feeling hungry at certain times, blinking, heartbeat.
The Sleep Cycle
NREM Sleep
Lasts 70-90mins in adults (80% of sleep time)
REM Sleep
Length of periods increases throughout the sleep cycle so that it is longer just before we awaken than it is in the earlier periods of sleep.
Most adults typically experience 4 or 4 cycles of ^ per night, but the very deepest stages of sleep may not occur towards the end of the sleep period (last 2 cycles).
Stages of The Sleep Cycle

NREM Stages - Being Drowsy
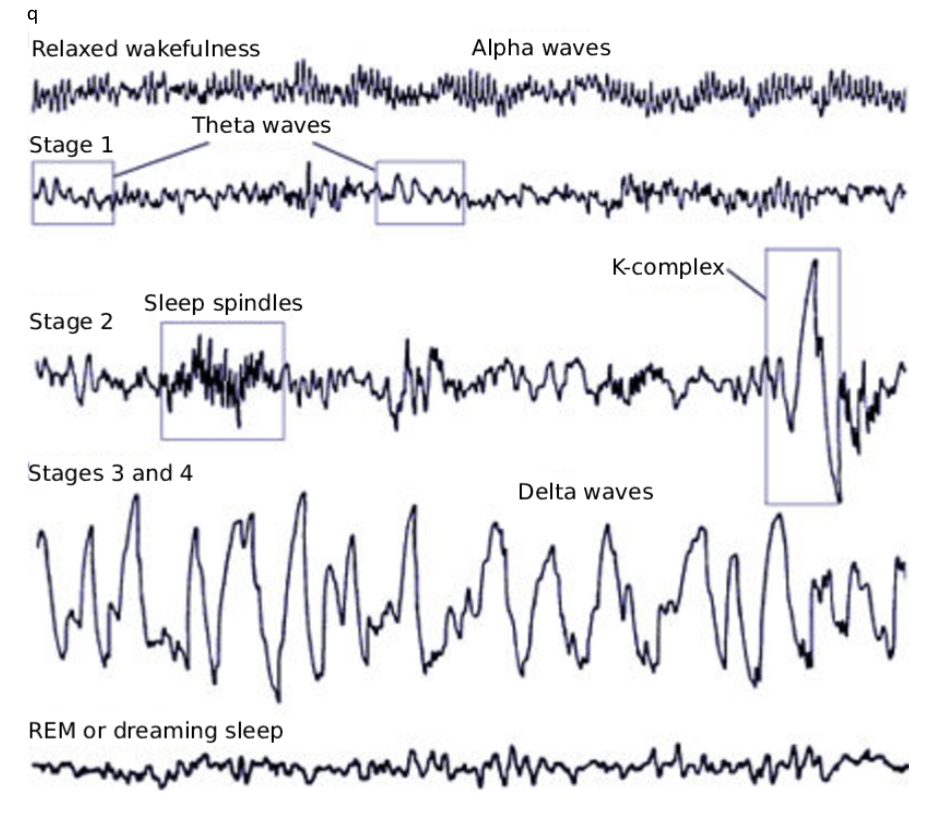
Just before we fall asleep (when we close our eyes & relax), our brainwave patterns are predominantly alpha waves, which are slower (<freq) and slightly brighter (>amp) than beta waves (<freq, >amp, occur when we r awake & alert).
NREM Stage1
When we transition from being awake to sleep, or falling asleep, we enter a stage known as a hypnagogic state (very light sleep from which we can be easily awakened).
Lasts for 5-10 mins
Alpha waves begin to be replaced by theta waves.
Decrease in heart rate, respiration, body temp, and muscle tension.
NREM Stage 2
Lasts for 20 mins per cycle.
Accounts for ~50% of our total sleep
Mostly theta waves, along with sleep spindles (short bursts of rapid brainwave activity)
+ characterised by K Complex waves (single, sudden high amp waves) → body movements lessen, breathing becomes more regular, BP, temp & heart rate continue to decrease.
NREM Stage 3
Brief, ~10mins, eyes barely move, muscles relaxed → transitional phase, marks the start of deep sleep (slow wave sleep).
Slower (<freq) & larger (>amp) delta waves become more common.
We become less responsive to external stimuli and more difficult to awaken.
If awoken, very groggy & disoriented feeling.
NREM Stage 4
The deepest stage of sleep - very difficult to be woken, no eye movement, heart/breathing rates at the slowest, little/no mucle activity.
If woken, up to 10 mins taken to be orientated + poor memory of sleep events.
Initially lasts ~30mins, and decreases as sleep progresses.
Brainwaves → regular, slow, and large delta waves for >50% of the time.
REM Sleep
A period during which the eyeballs rapidly move beneath the eyelids, darting back/forth and up/down.
First period ~10mins, then lengthens (up to 1h)
The brain is very active; EEG patterns resemble those of an awake/alert person.
Compared to stage 3/4, brainwaves are irregular (desynchronised), faster (>freq), and smaller (<amp).
Sawtooth patterns may be found among these random and fast beta-like waves with >freq & <amp.
SLEEP STAGES IN GRAPHS
Dreams in terms of NREM & REM
Most occur during REM, which causes dreams to be more vivid and memorable. NREM Dreams are less frequent and difficult to remember due to being briefer, less intense, and without a real storyline.
Sleep deprivation (SD)
Partial sleep deprivation: an insufficient amount or quality of sleep
Total sleep deprivation: results in no sleep for more than a 24h period
Psychological Effects of SD - Affective (emotional) disturbances
Amplified emotional responses such as high emotionality, confusion and irritability, feelings of sadness, mood disturbances, feelings of fatuigue.
Psychological Effects of SD - Behavioural difficulties
Problems performing motor tasks, especially simple, monotonous tasks and those requiring sustained attention or concentration. Performance on short, complex, difficult tasks is not as greatly affected by SD.
Psychological Effects of SD - Cognitive difficulties
Difficulties maintaining attention and concentrating. Difficulty thinking and poor reasoning, poor decision making, reduced ability to cope with and make decisions under stress and reduced spatial awareness.
Physiological effects of SD
Slower physical reflexes
Hand tremors
Droopy eyelids
Difficulty in focusing the eyes
A heightened sensitivity to pain
Headaches
Lower energy levels
Microsleeps