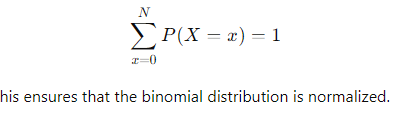The binomial distribution (1)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What does the binomial distribution describe?
It describes situations involving a fixed number of independent trials, each with two possible outcomes (often referred to as success and failure).
In a binomial distribution, what are the two possible outcomes?
The two possible outcomes are typically labelled as A (success) and B (failure)
P(A)=p and P(B)=q=1−p
What is the random variable X in a binomial distribution?
The random variable X represents the number of successes (outcomes A) in N trials, and it can take integer values from 0 to N.
How is the probability of exactly x successes in N trials calculated?
p is the probability of success.
q=1−p is the probability of failure.
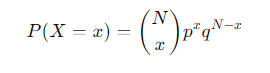
How is the number of ways to obtain x successes from N trials represented?
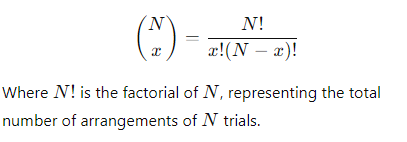
What are the conditions required for a binomial distribution?
A fixed number of trials (N)
Each trial results in a "success" or "failure"
Trials are independent
The probability of success (p) is constant
The variable xxx represents the total number of successes
What does it mean that the binomial distribution is normalized?
The binomial distribution is normalized if the sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes equals 1
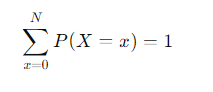
How is the binomial distribution related to the binomial series?
This shows that the sum of the probabilities in a binomial distribution is equal to 1.
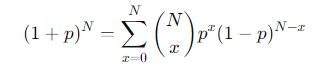
What is the result of summing the probabilities for all possible outcomes in a binomial distribution?