Plate Tectonics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
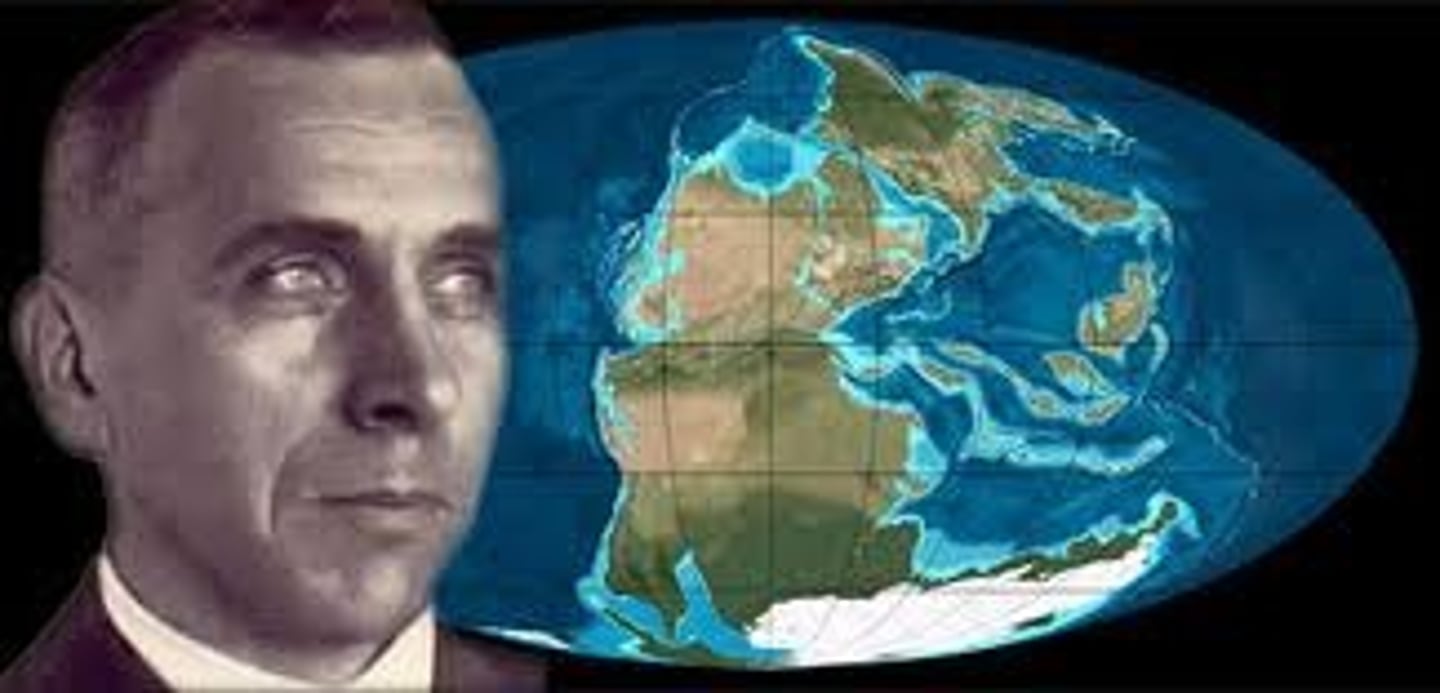
Alfred Wegener
A German scientist who proposed the theory of continental drift
Harry Hess
A naval scientist who proposed the theory of sea-floor spreading
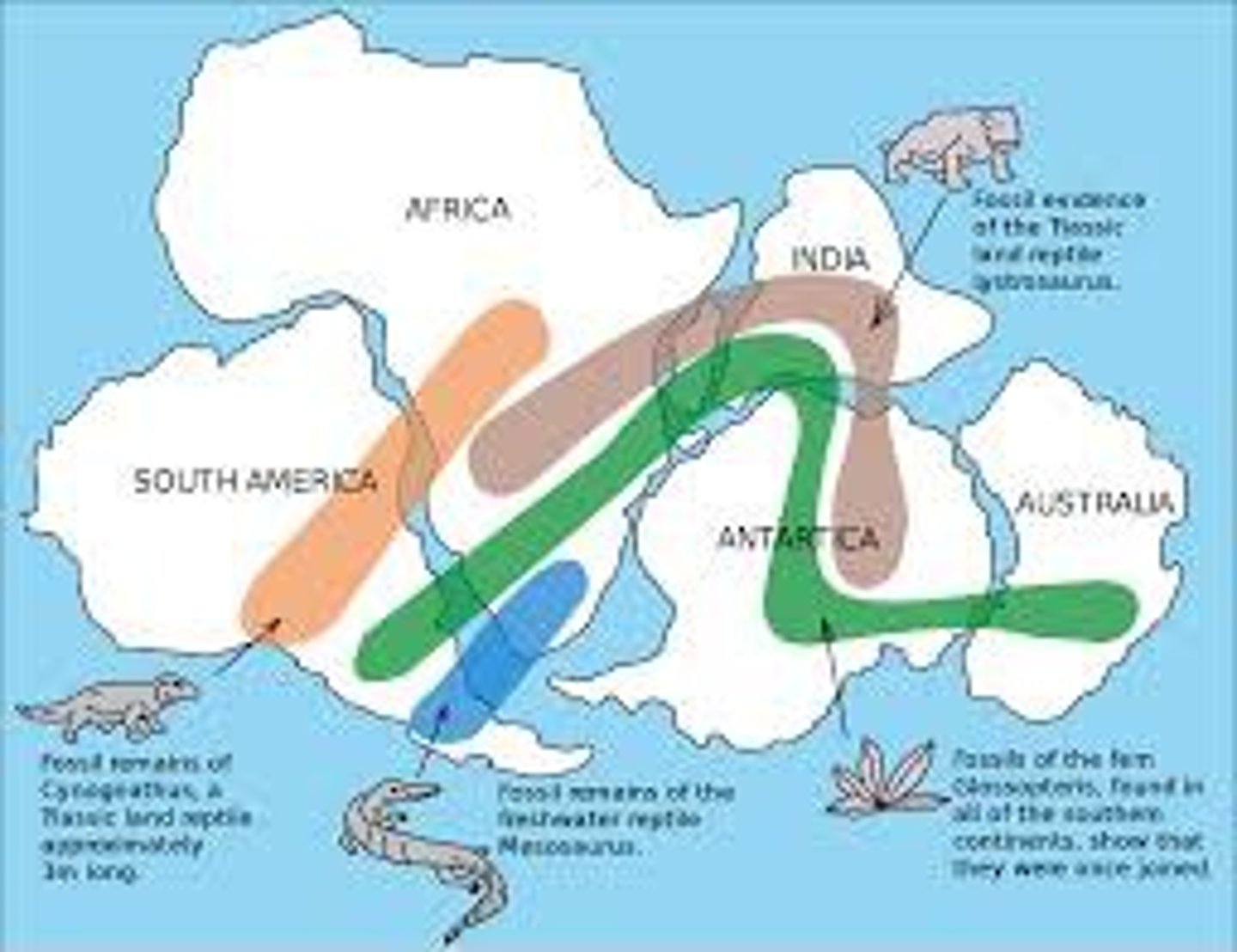
evidence for Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift
Fossil Evidence, Fit of the Continents
evidence for Harry Hess' theory of seafloor spreading
Magnetic Striping, Age of Seafloor, Sediment Thickness
magnetic striping
The pattern of alternating normal and reversed magnetic polarities found in the seafloor on either side of the spreading center.
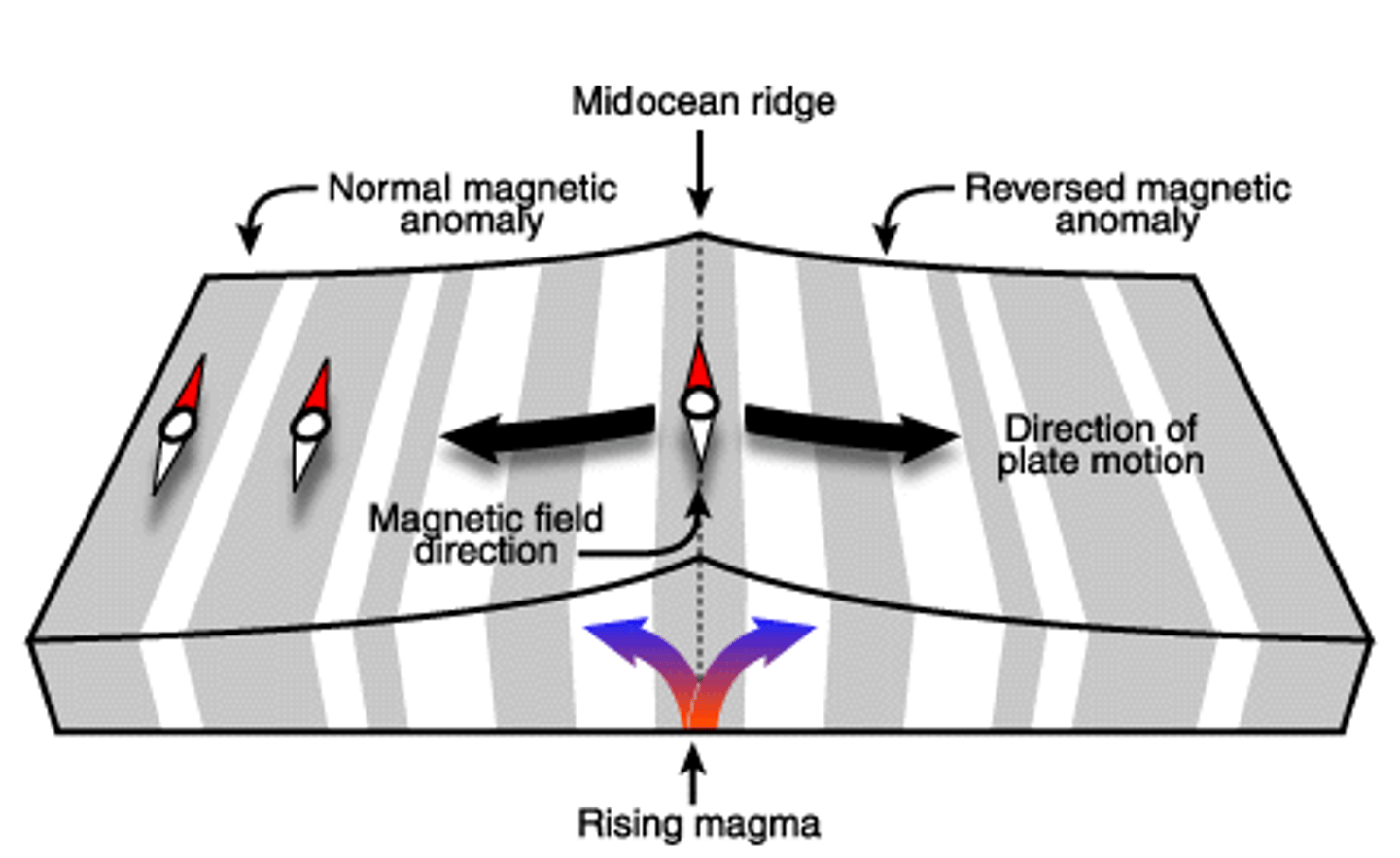
Magnetite
magnetic material found in the seafloor
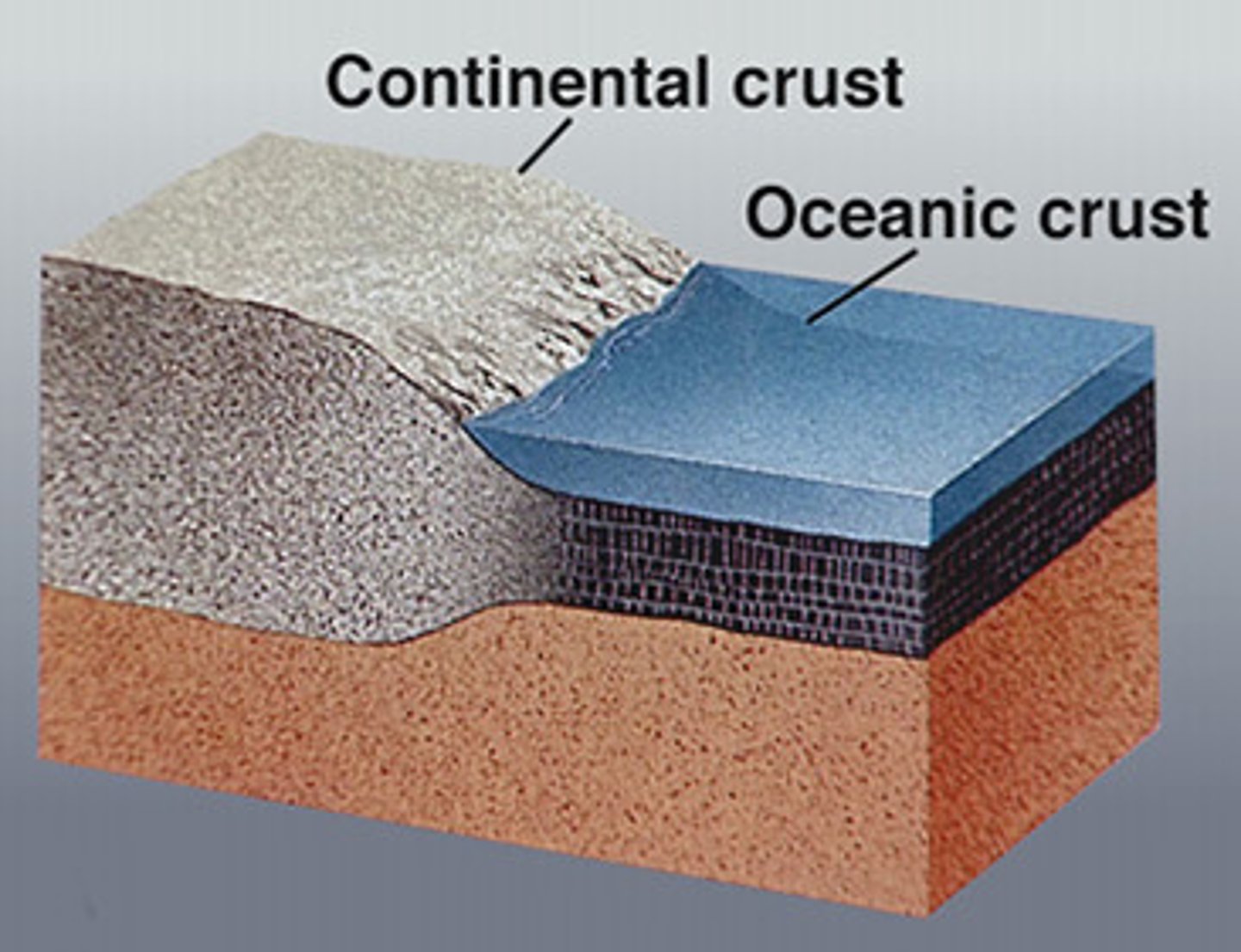
continental crust
crust that lies beneath the Earth's continents and is about 25-70 km thick. Less dense.
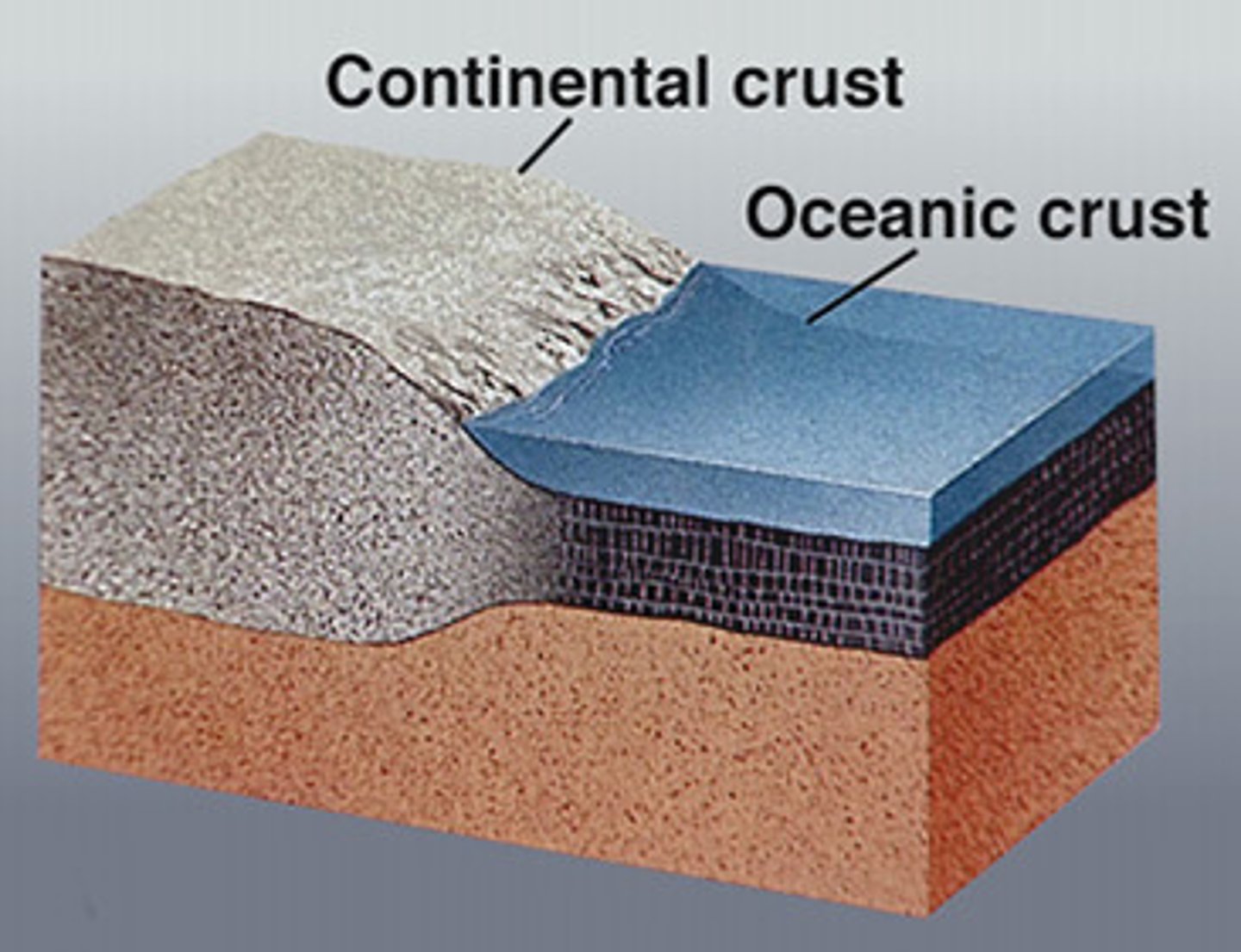
oceanic crust
crust that lies beneath the ocean and is usually 7-10 km thick. More dense.
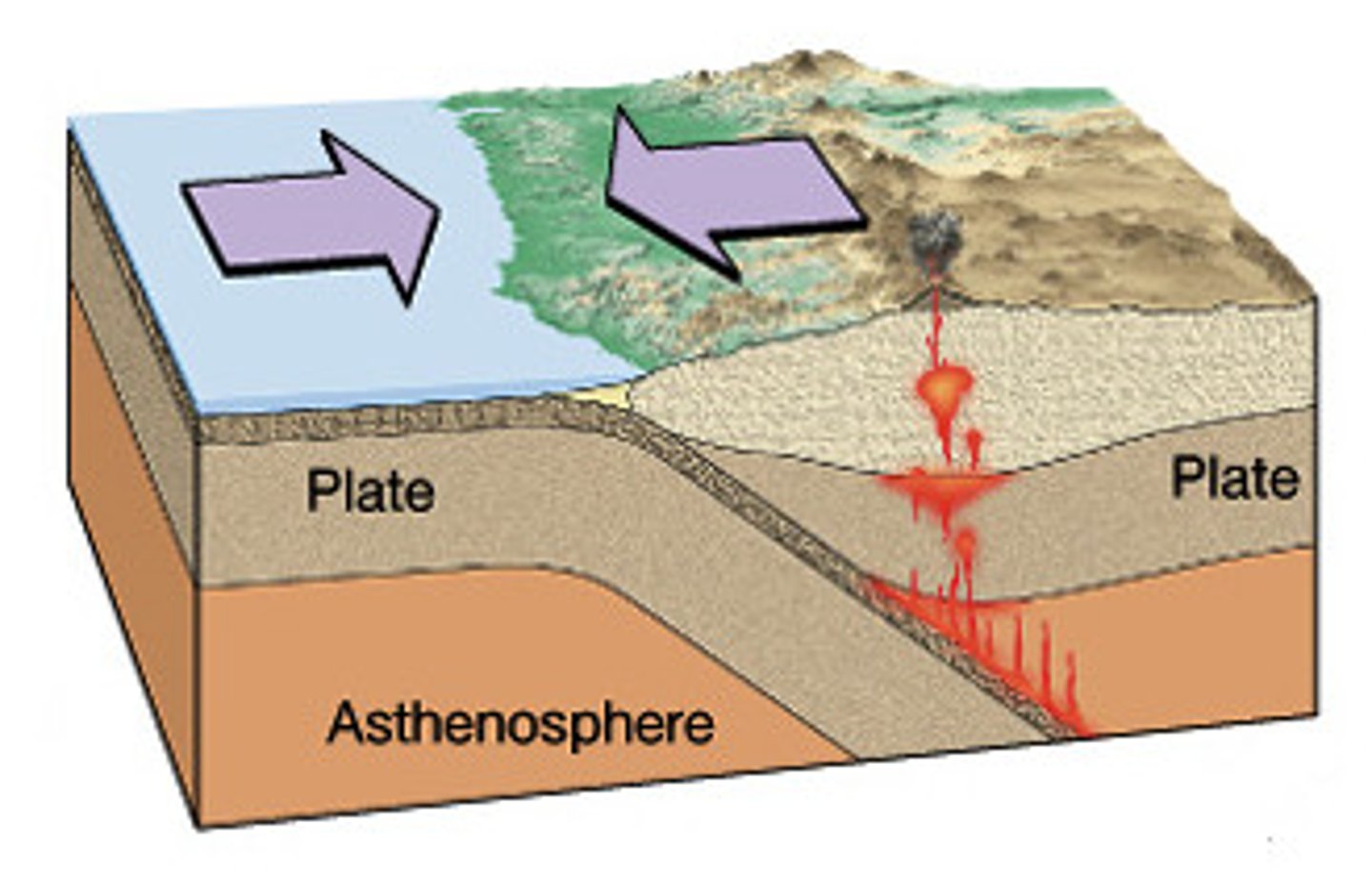
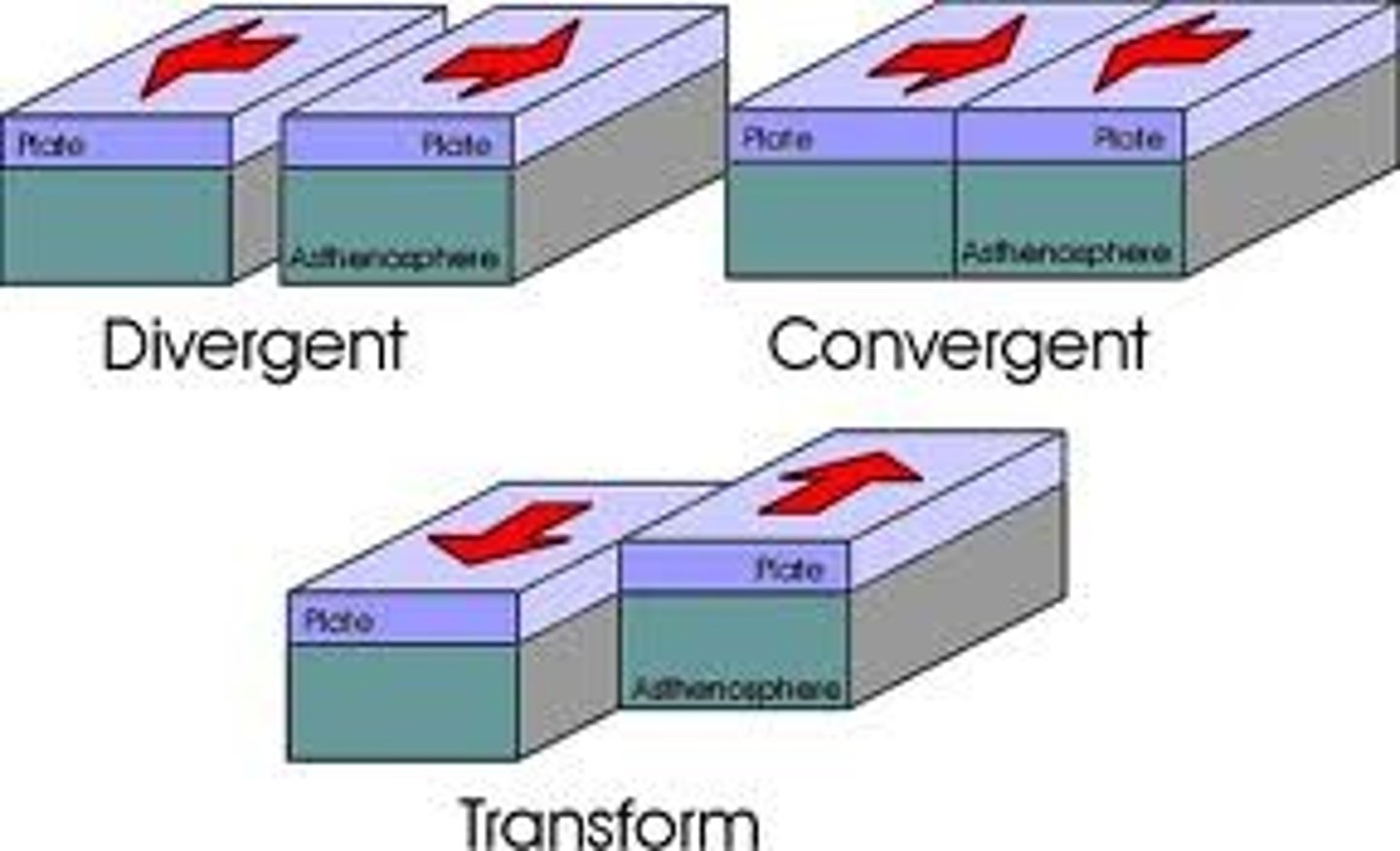
convergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
oceanic trench
Deep, narrow trough in the ocean floor where subduction is taking place.
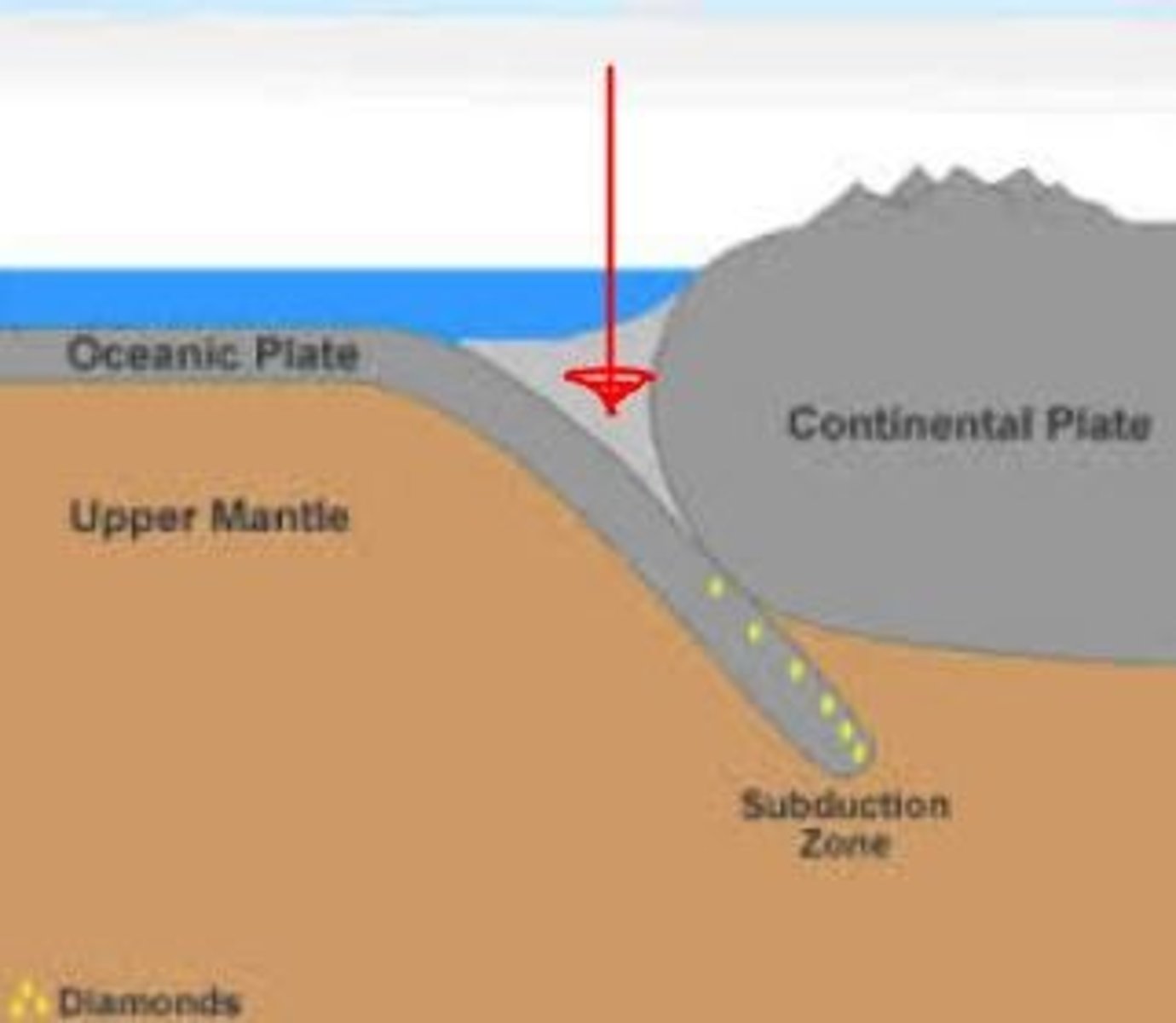
Subduction
The process by which one plate is pushed underneath another plate at a convergent boundary
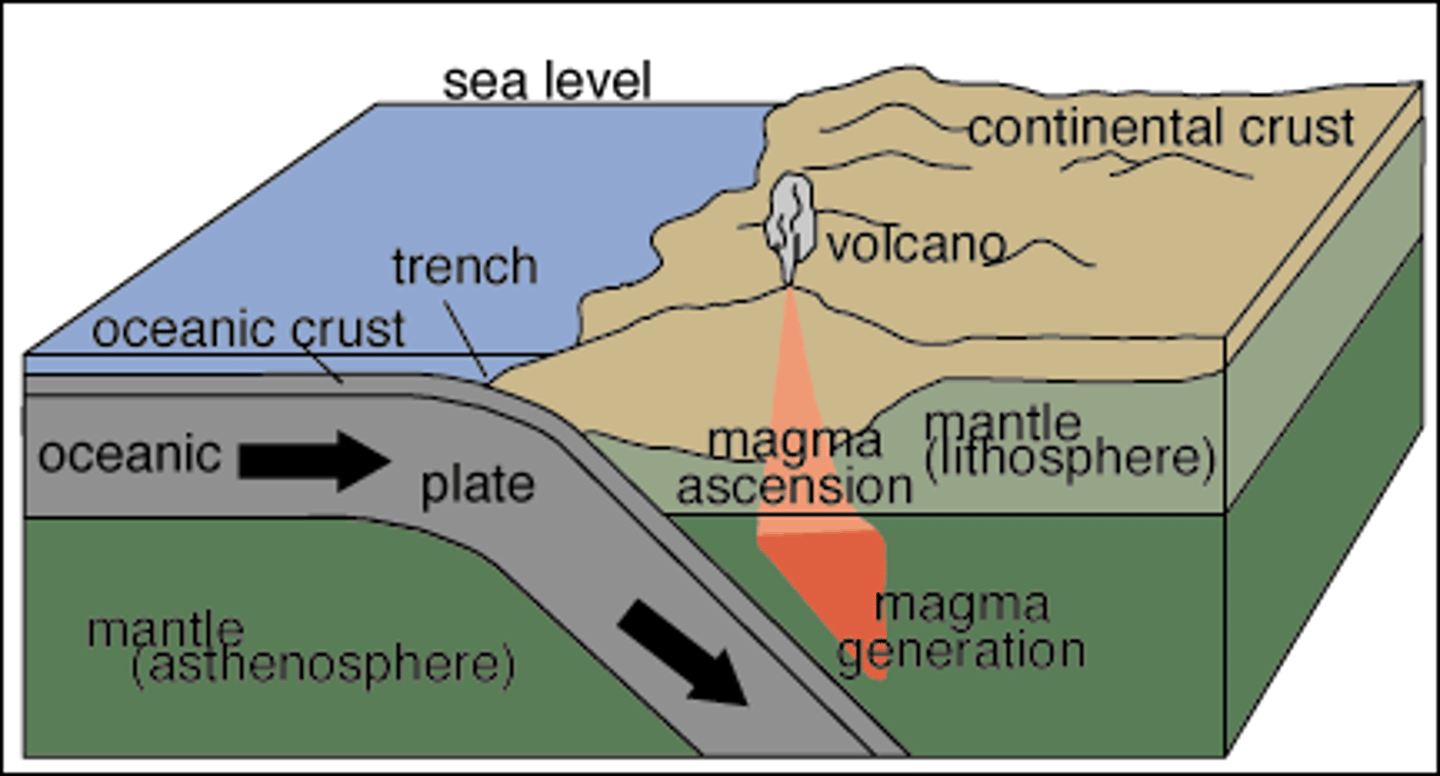
volcanic island arc
a series of volcanoes formed at a subduction zone at a oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary.
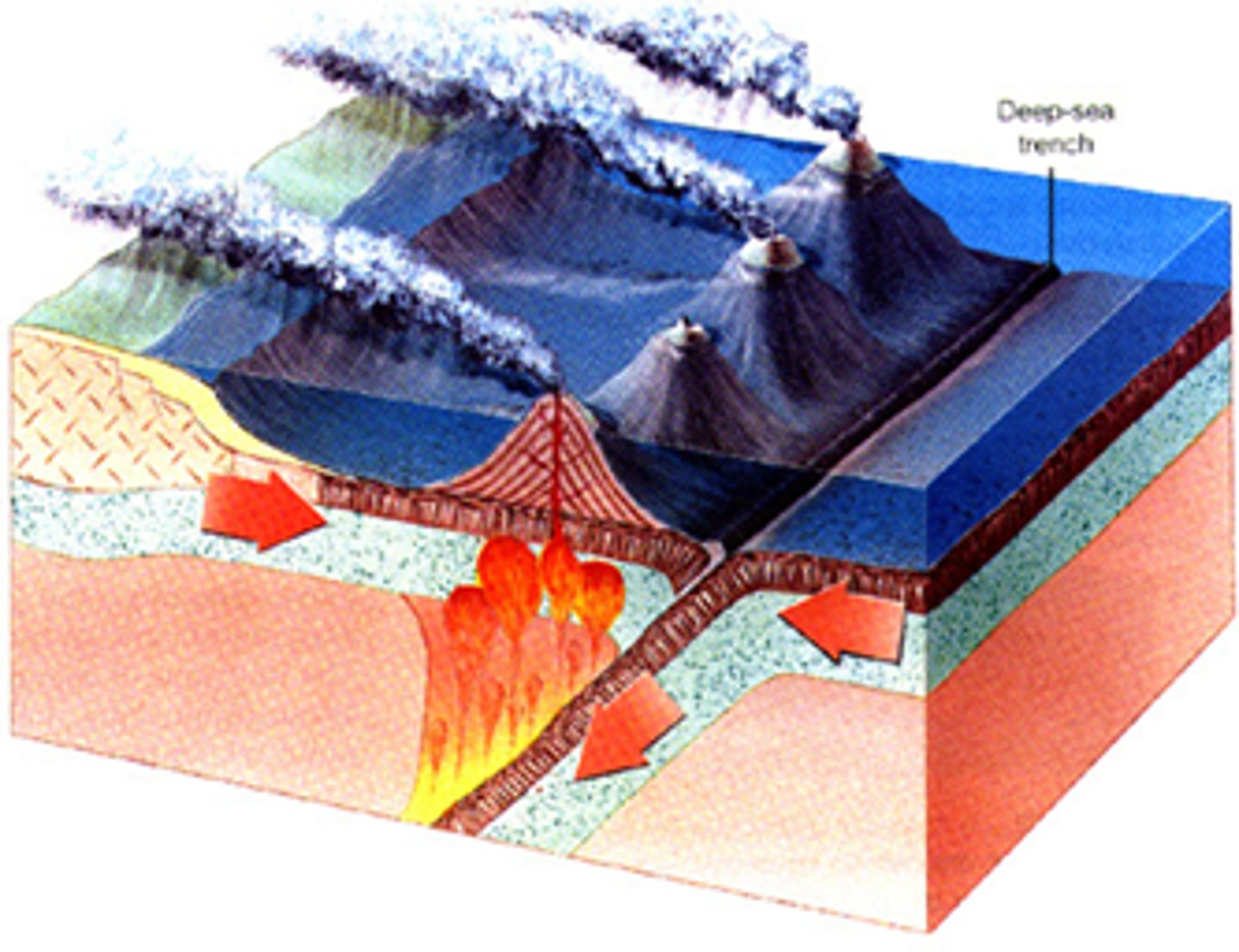
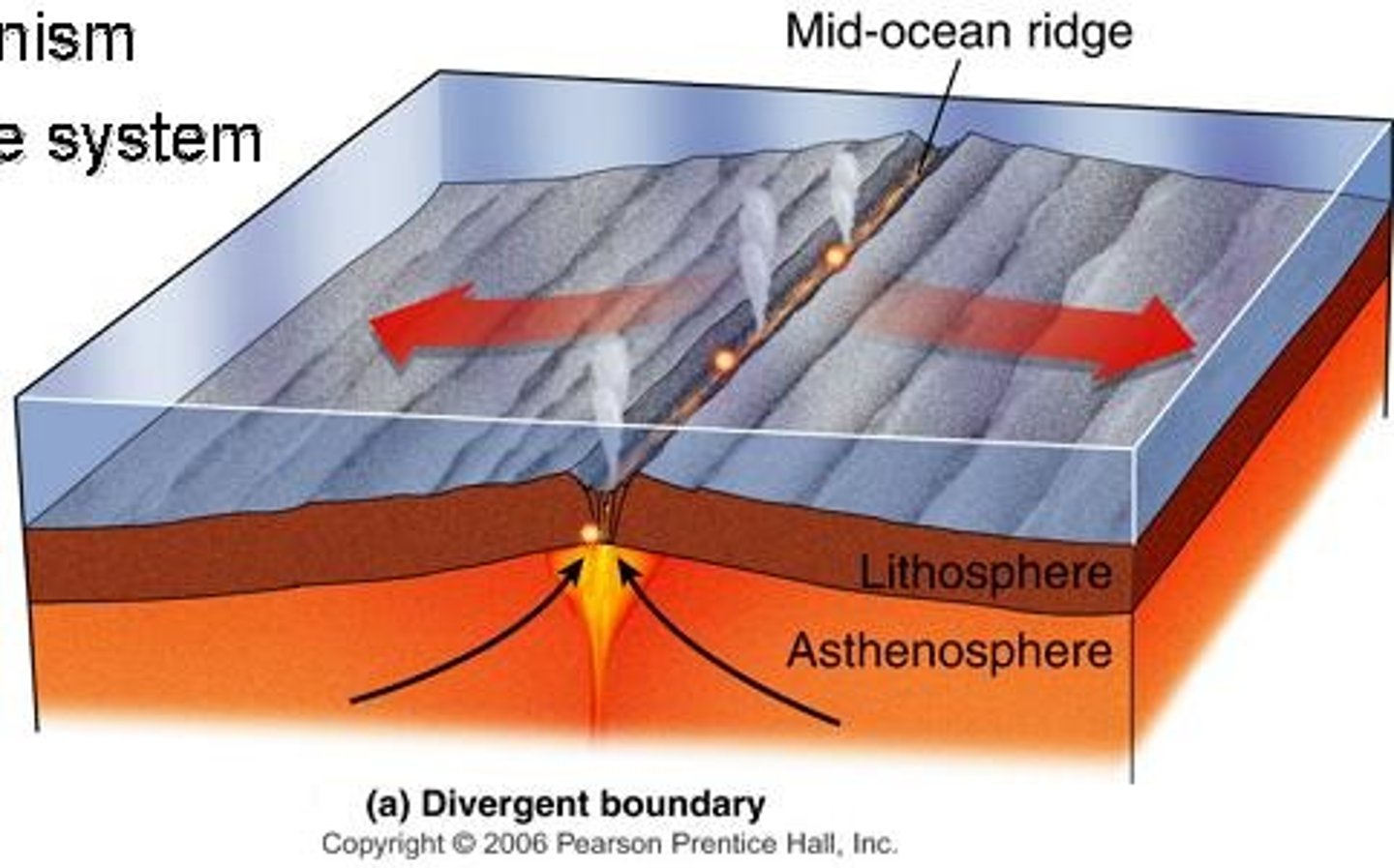
divergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
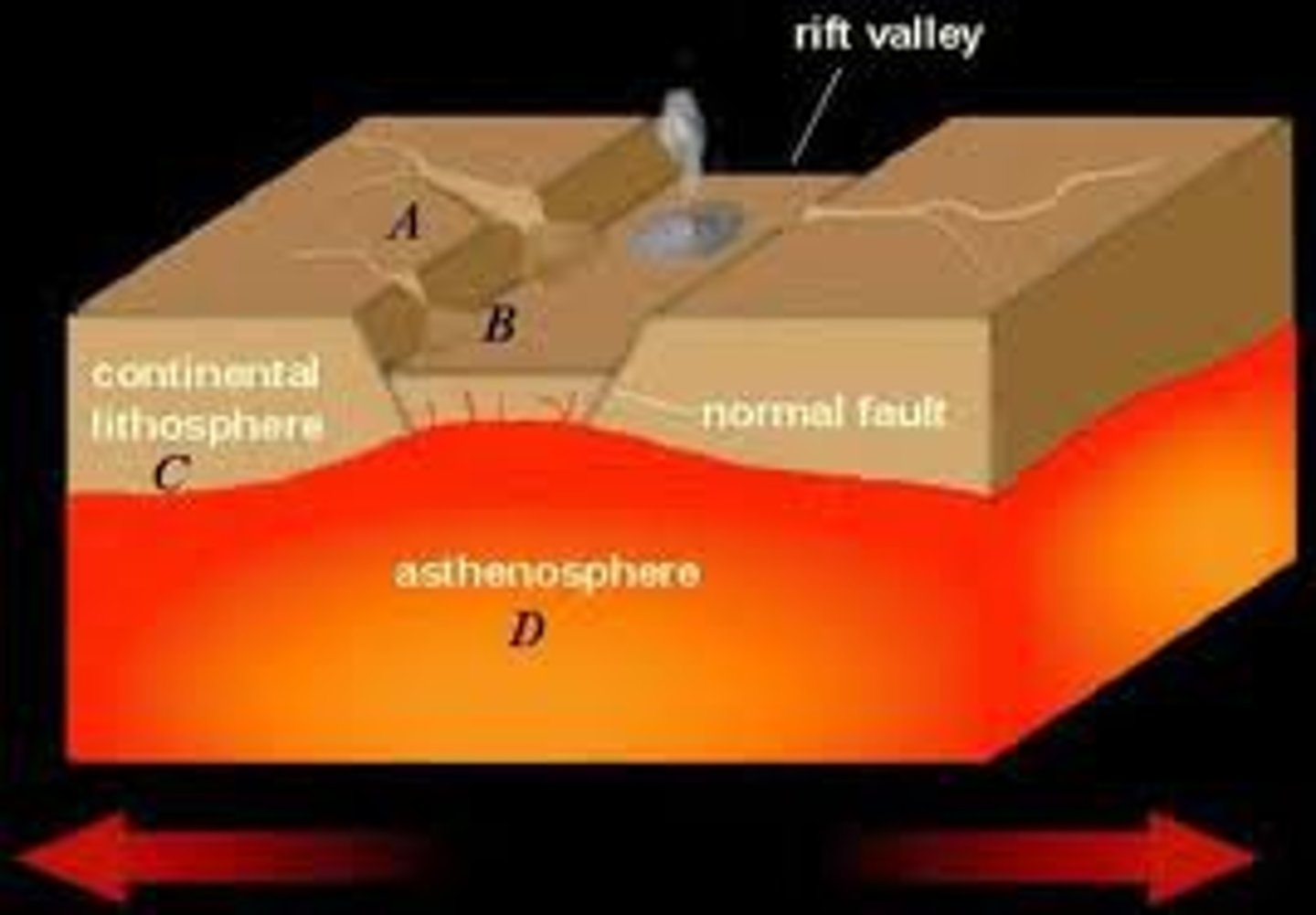
Rifting
the process by which Earth's crust breaks apart; can occur within continental crust or oceanic crust
mid-ocean ridge
An underwater mountain chain where new ocean floor is formed
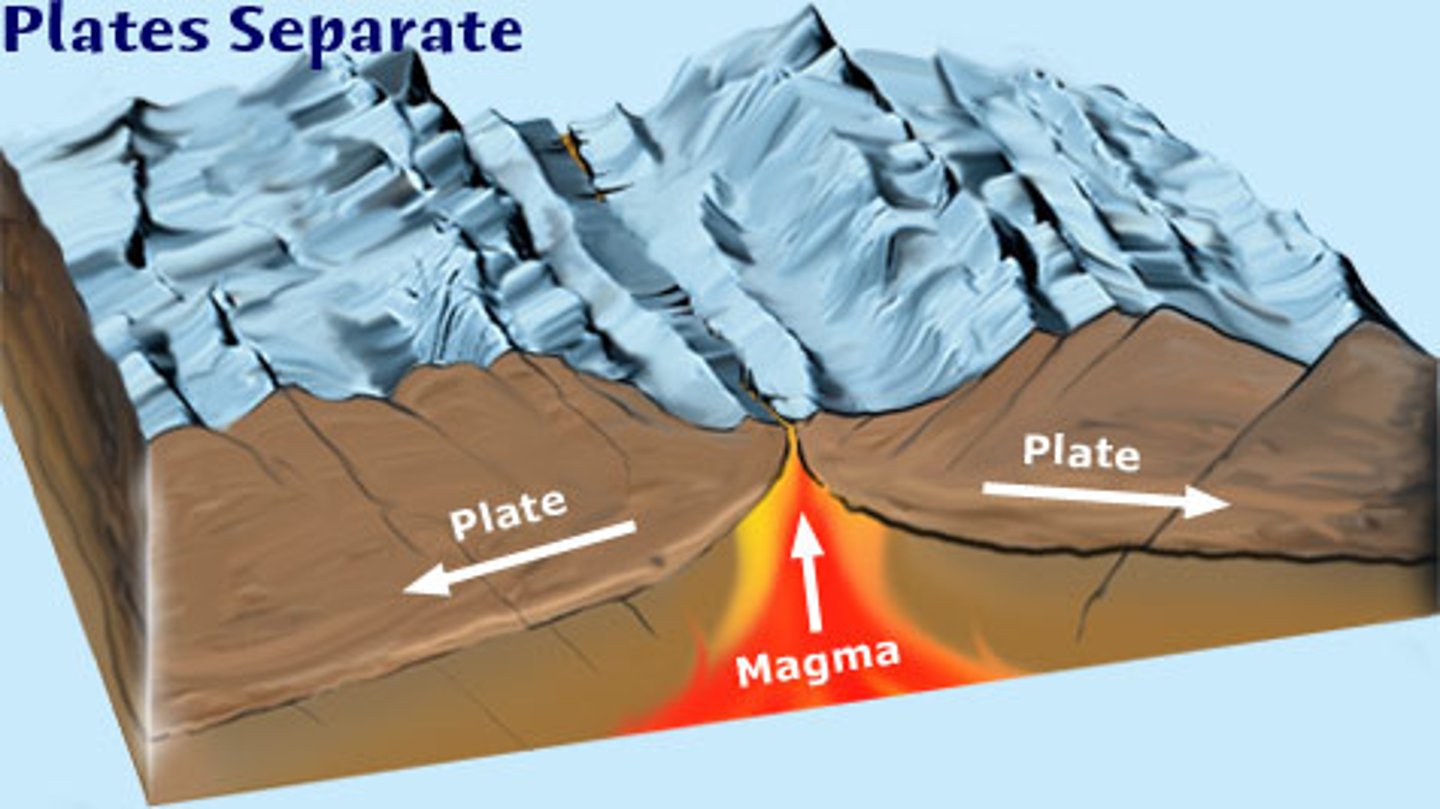
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
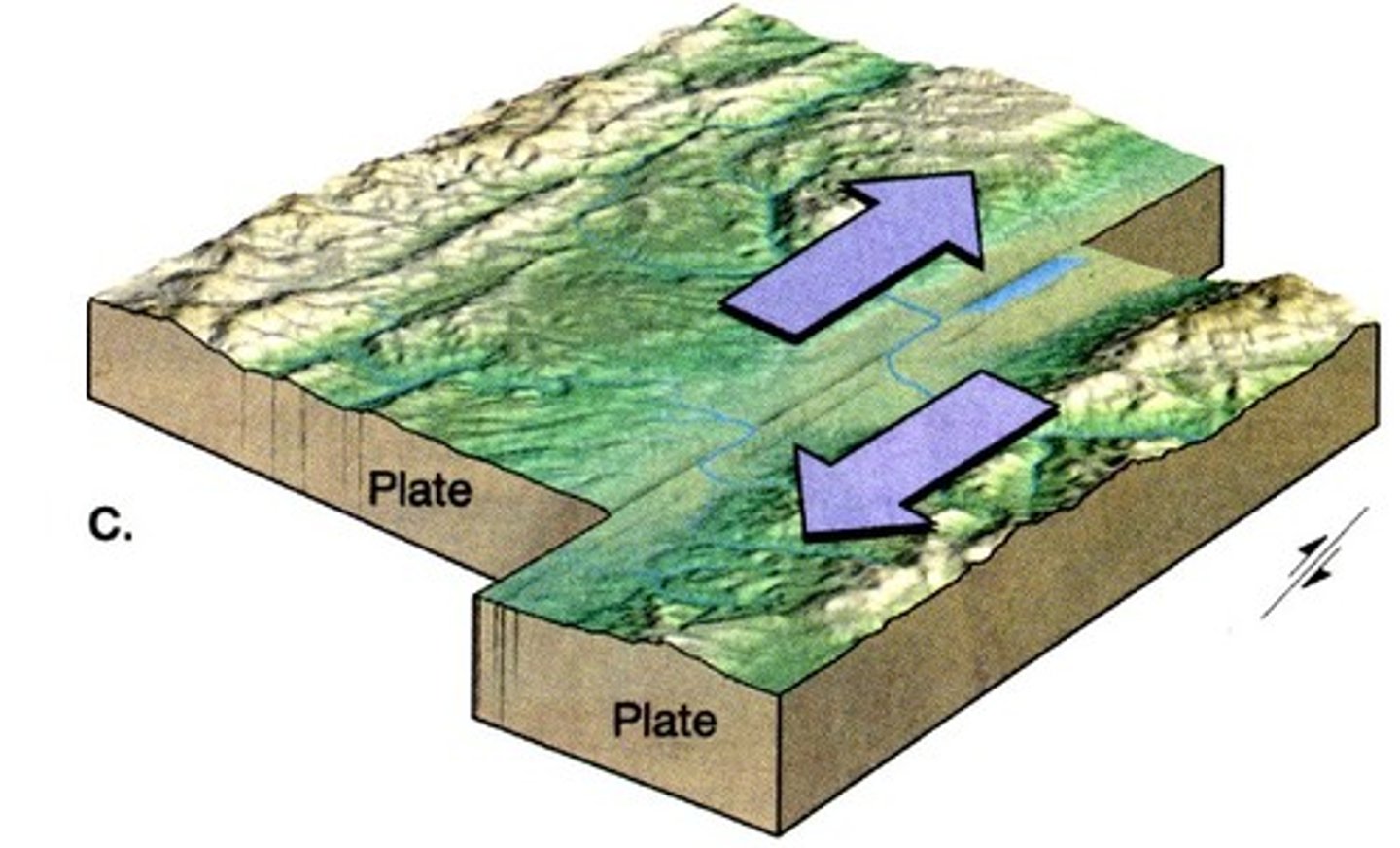
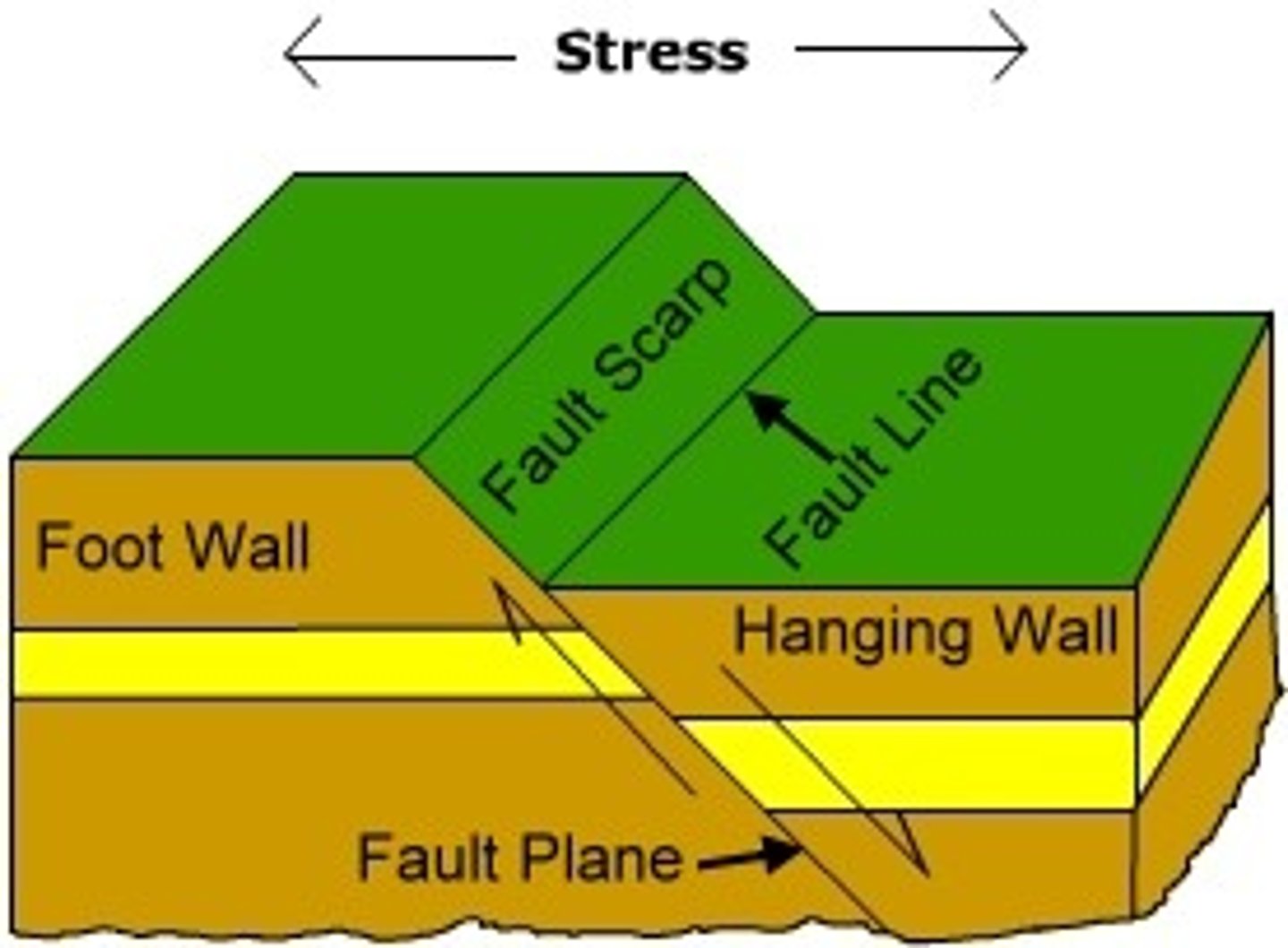
fault line
a crack in Earth's surface caused by moving plates
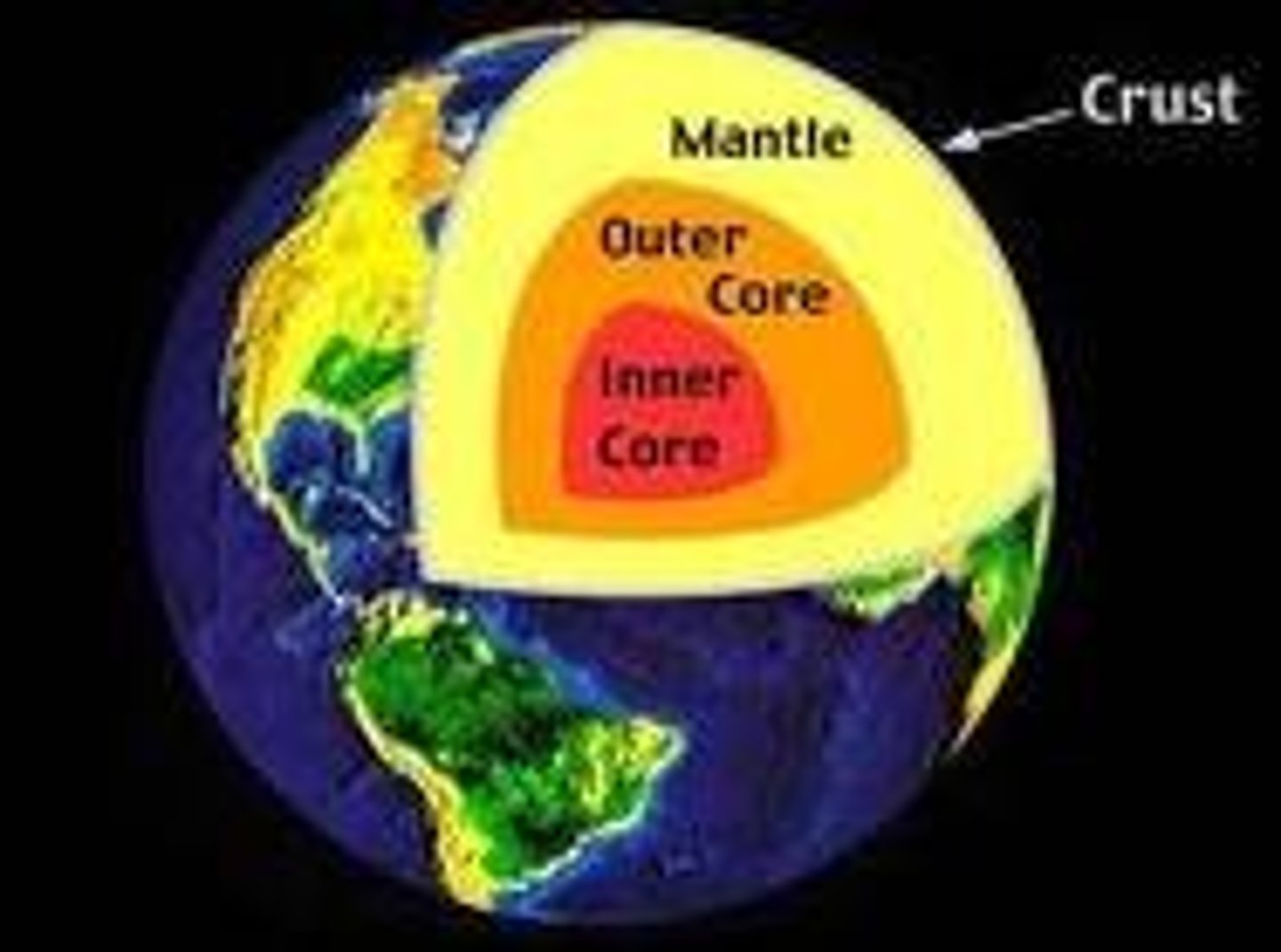
Mantle
The layer of hot, solid material between Earth's crust and core.
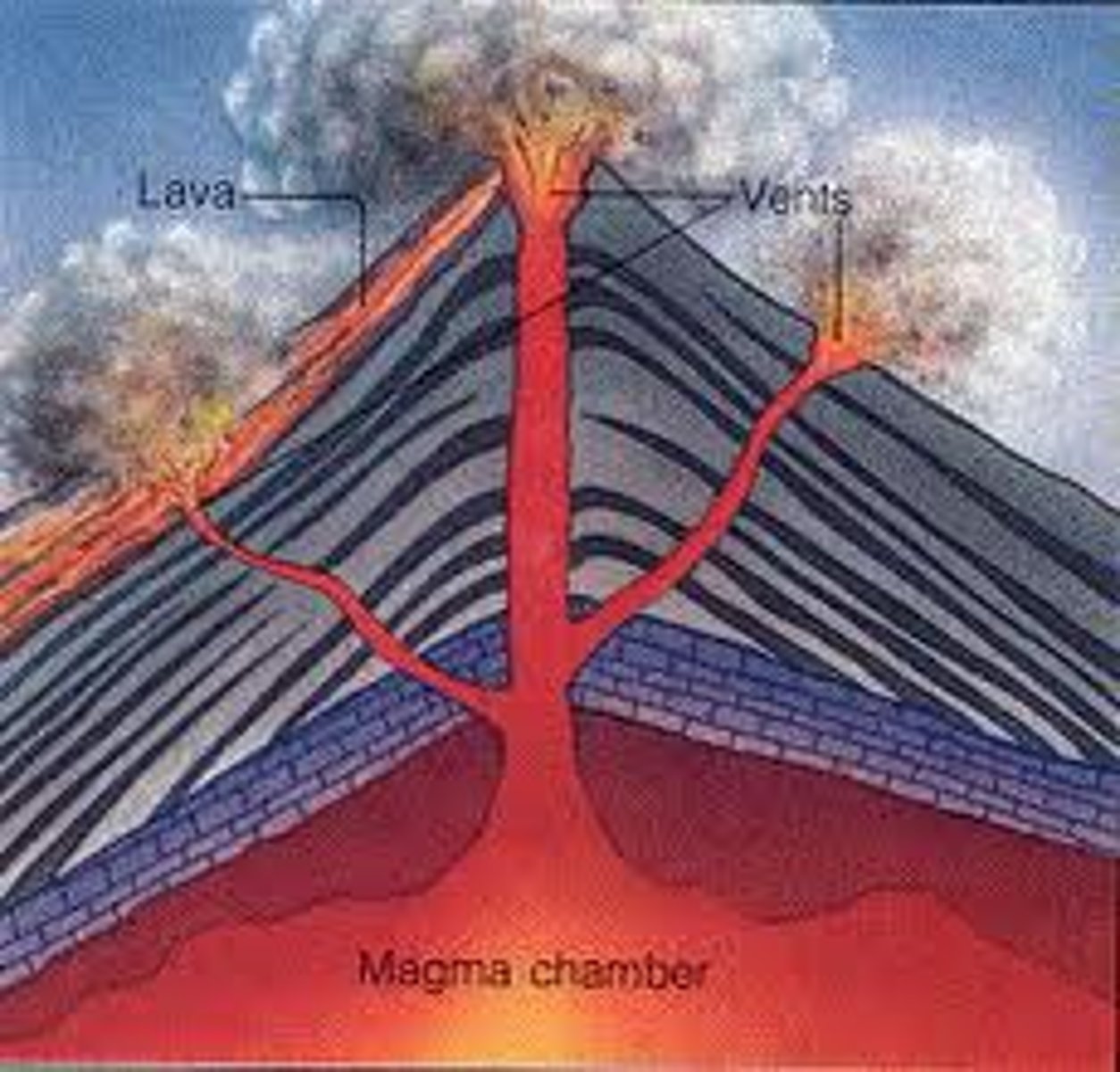
Magma
A molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle
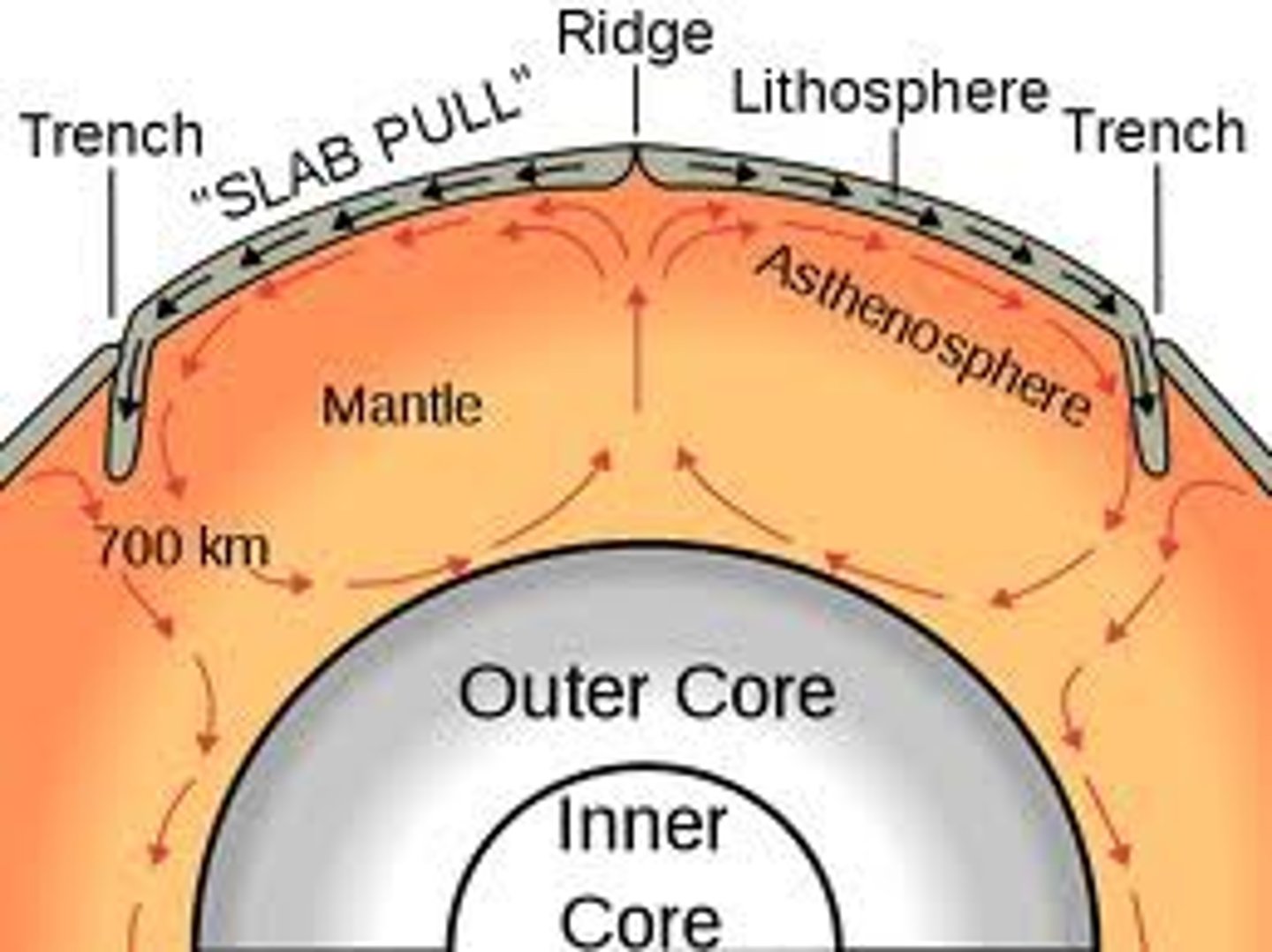
slab pull
the pulling of a tectonic plate as its edge subducts deep into the mantle
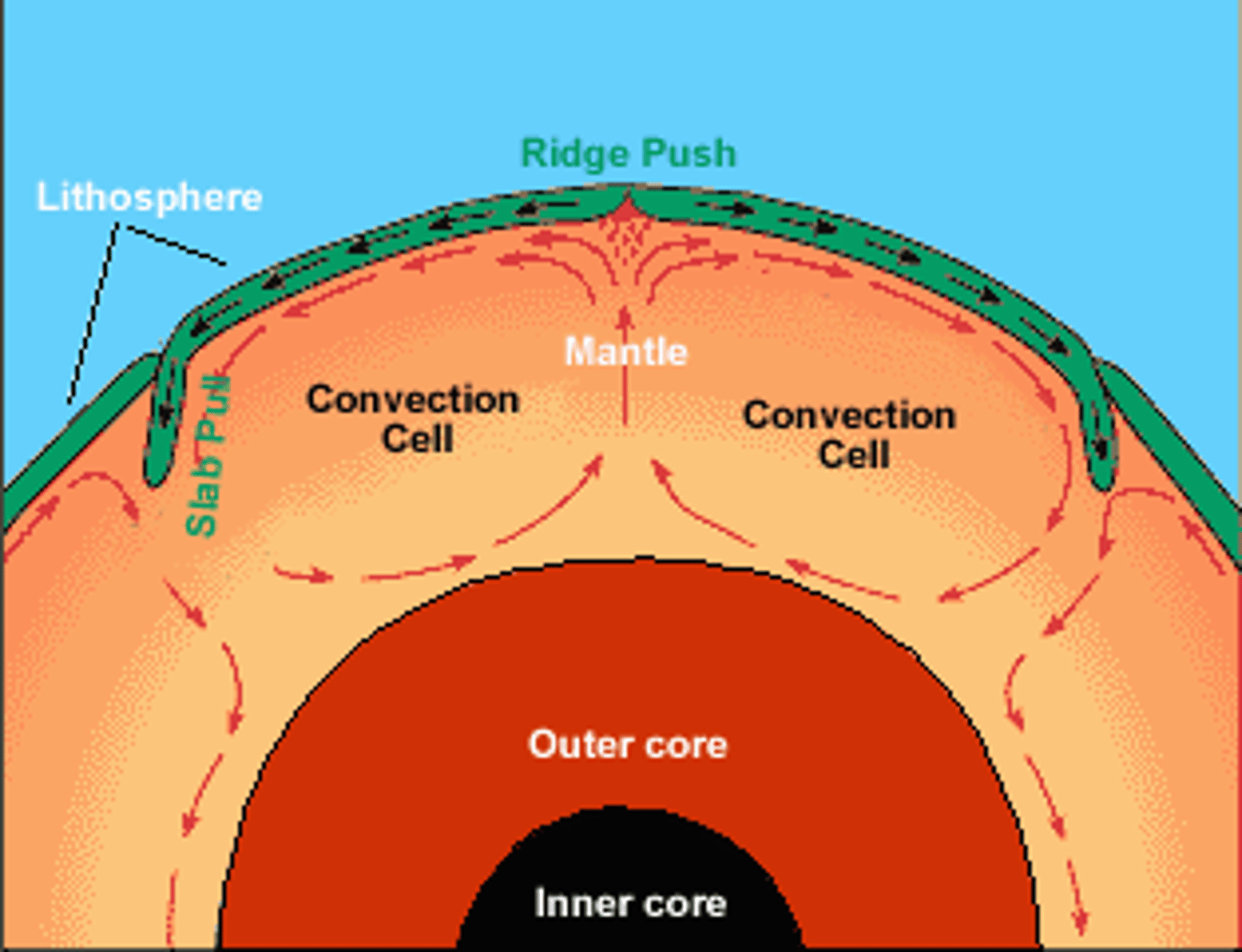
ridge push
when the force of gravity moves a plate downward and away from a ridge
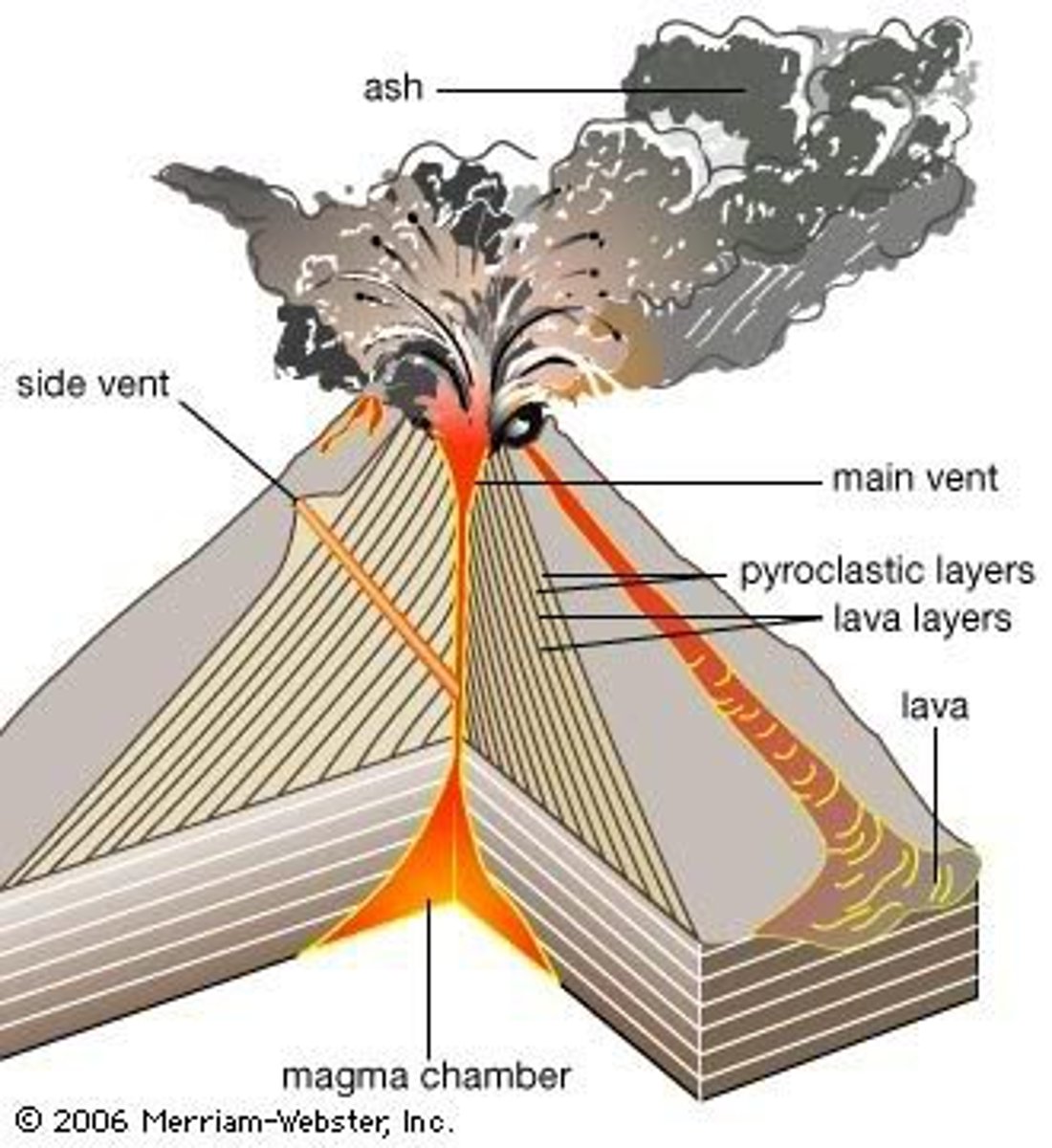
Volcanoes
an opening in the Earth's crust through which molten lava, ash, and gases are ejected.
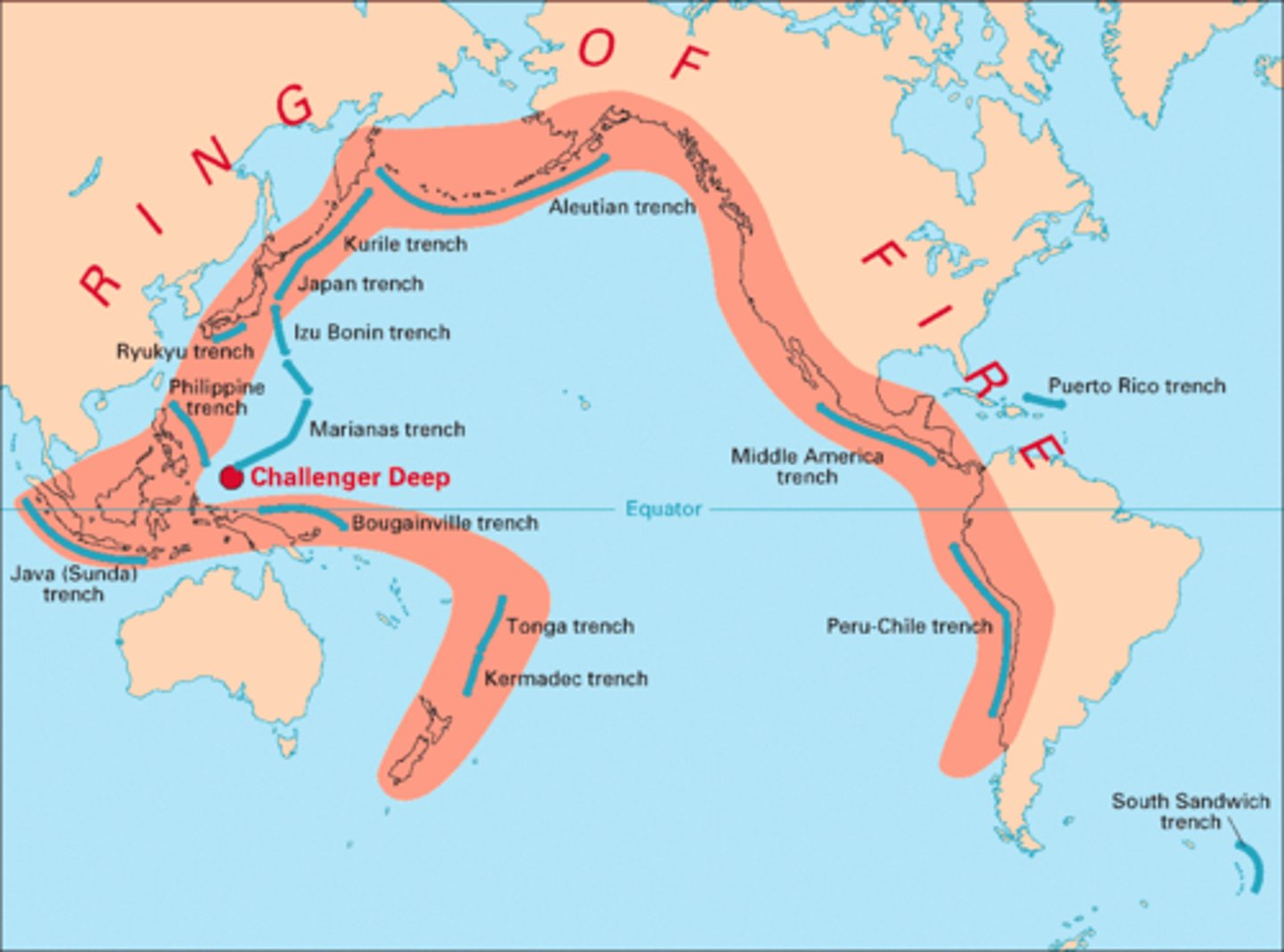
Ring of Fire
A zone of intense volcanic activity at the boundary between the Pacific plate and surrounding continental plates
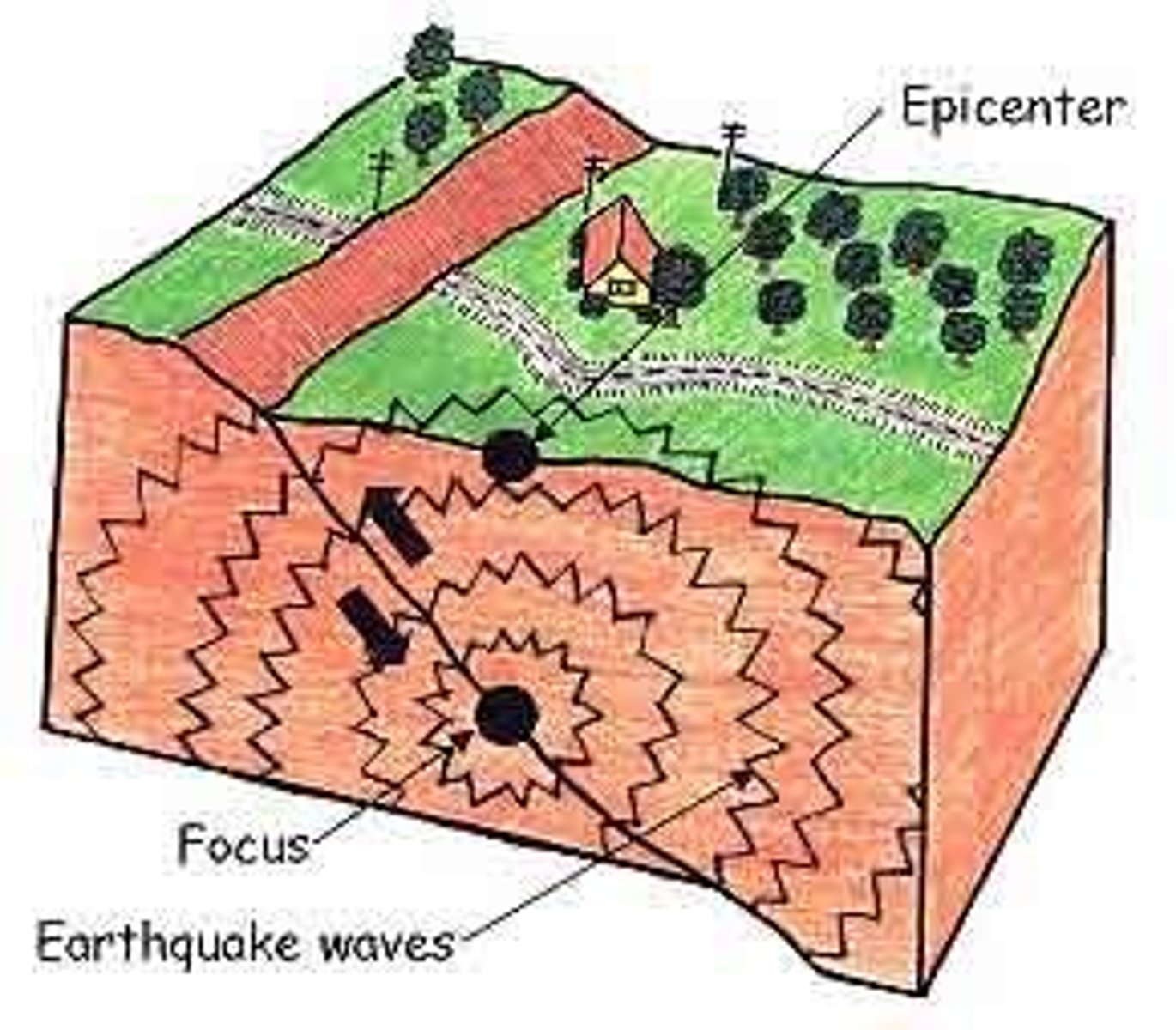
Focus
The point beneath Earth's surface where rock breaks under stress and causes an earthquake
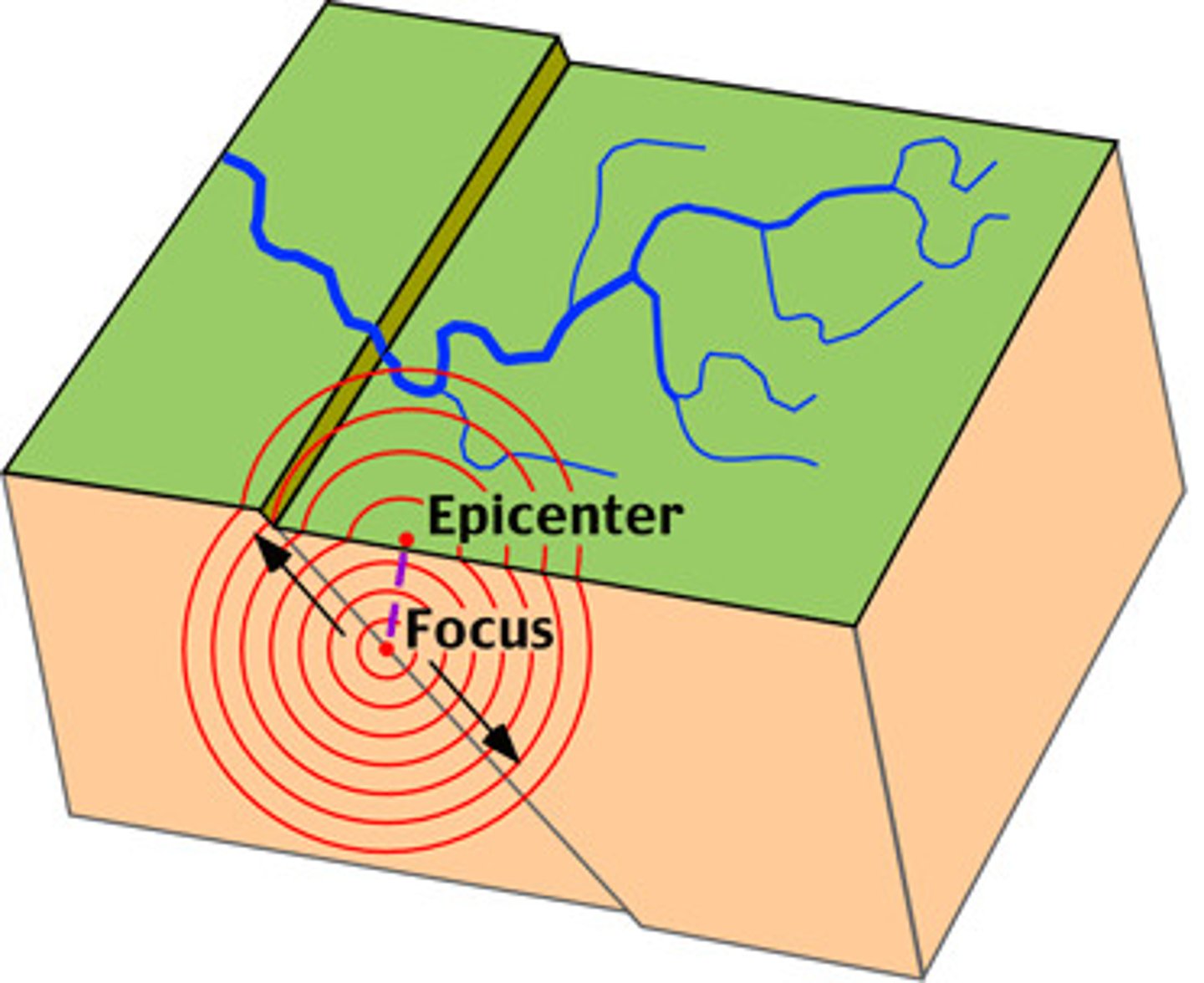
Epicentre
the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
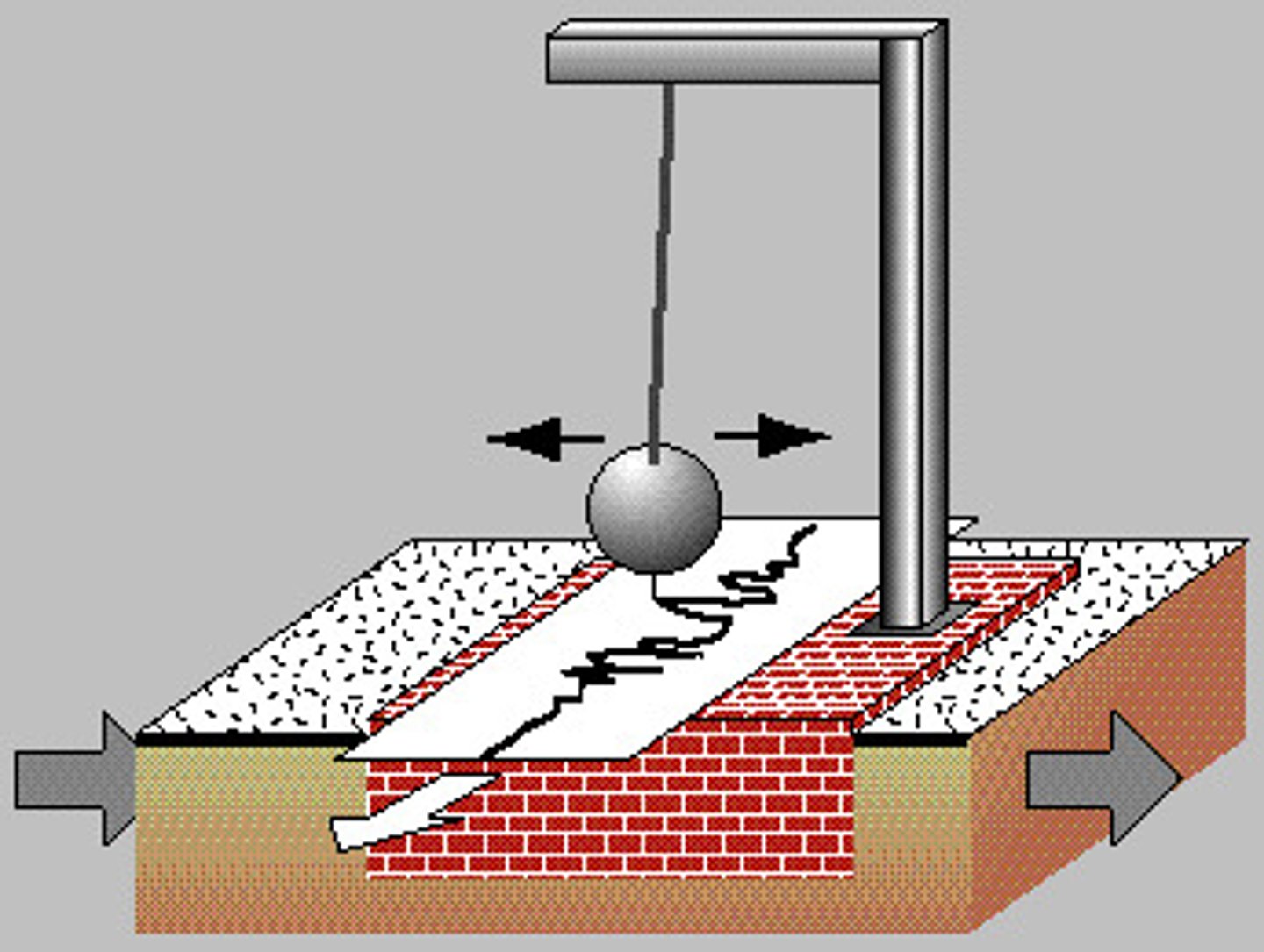
Seismometer
Instrument used to measure horizontal or vertical motion during an earthquake.
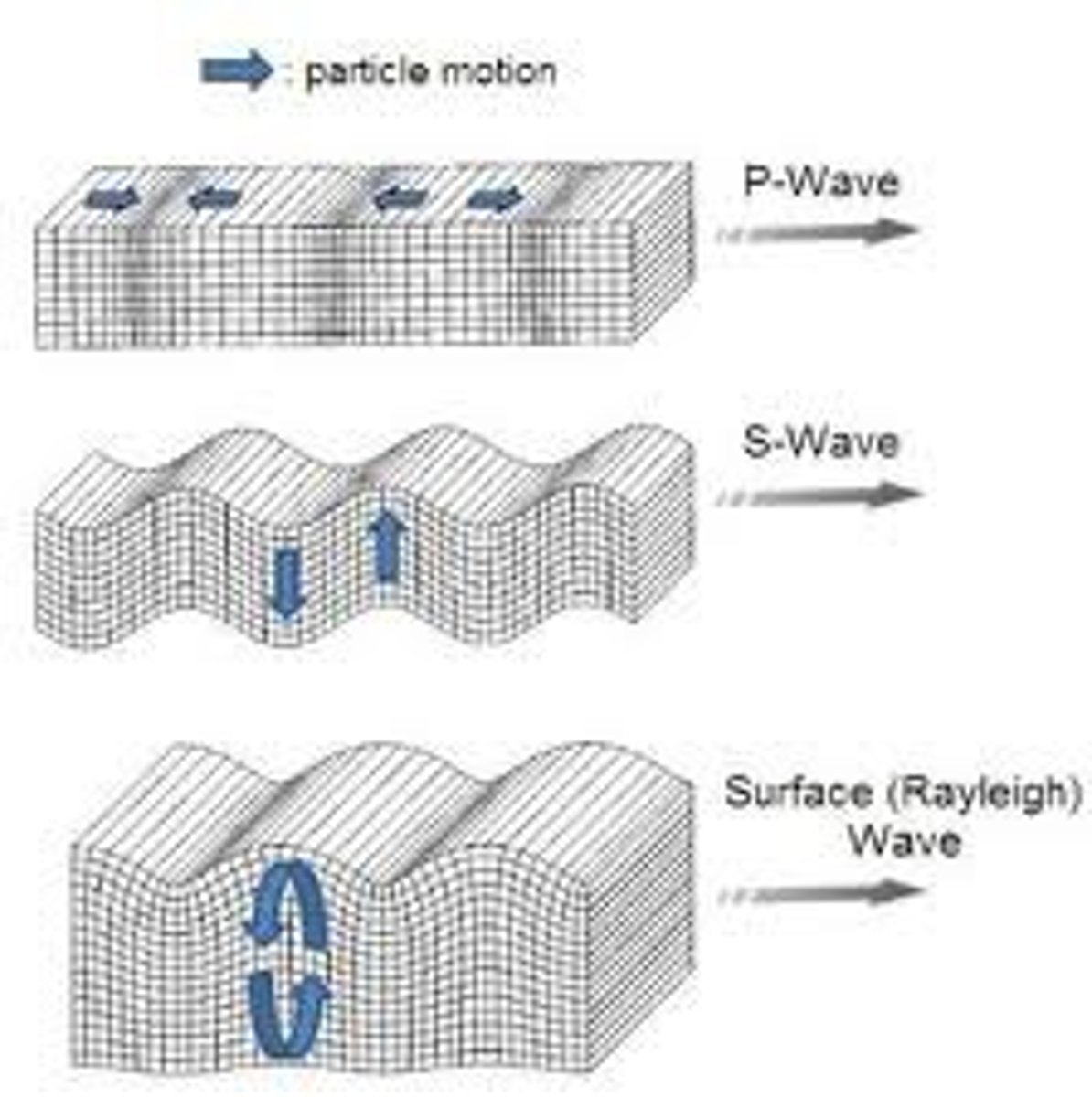
P (primary) waves
longitudinal waves (back and forth) that travel fast.
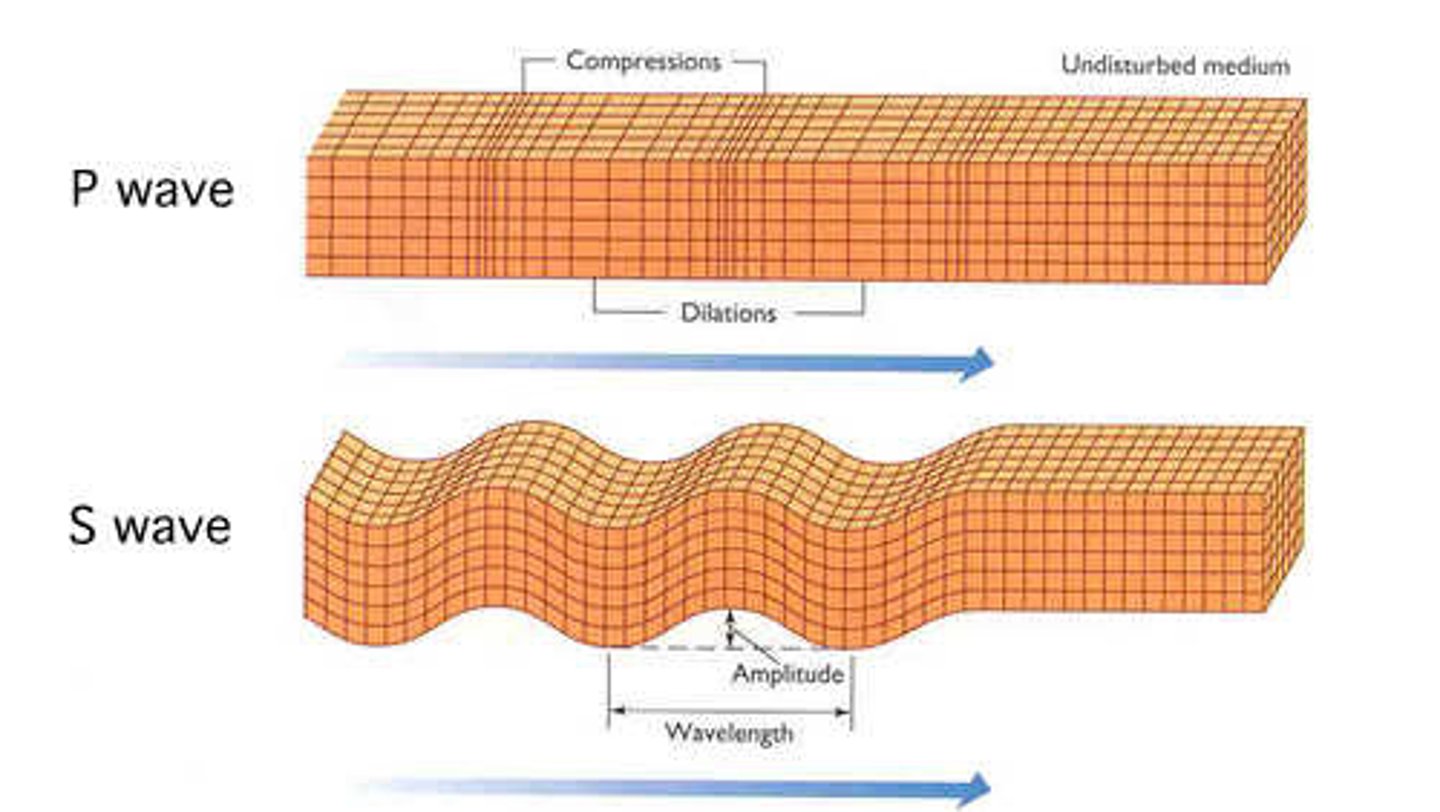
S (secondary) waves
transverse waves (up and down) travel slower than P-waves.
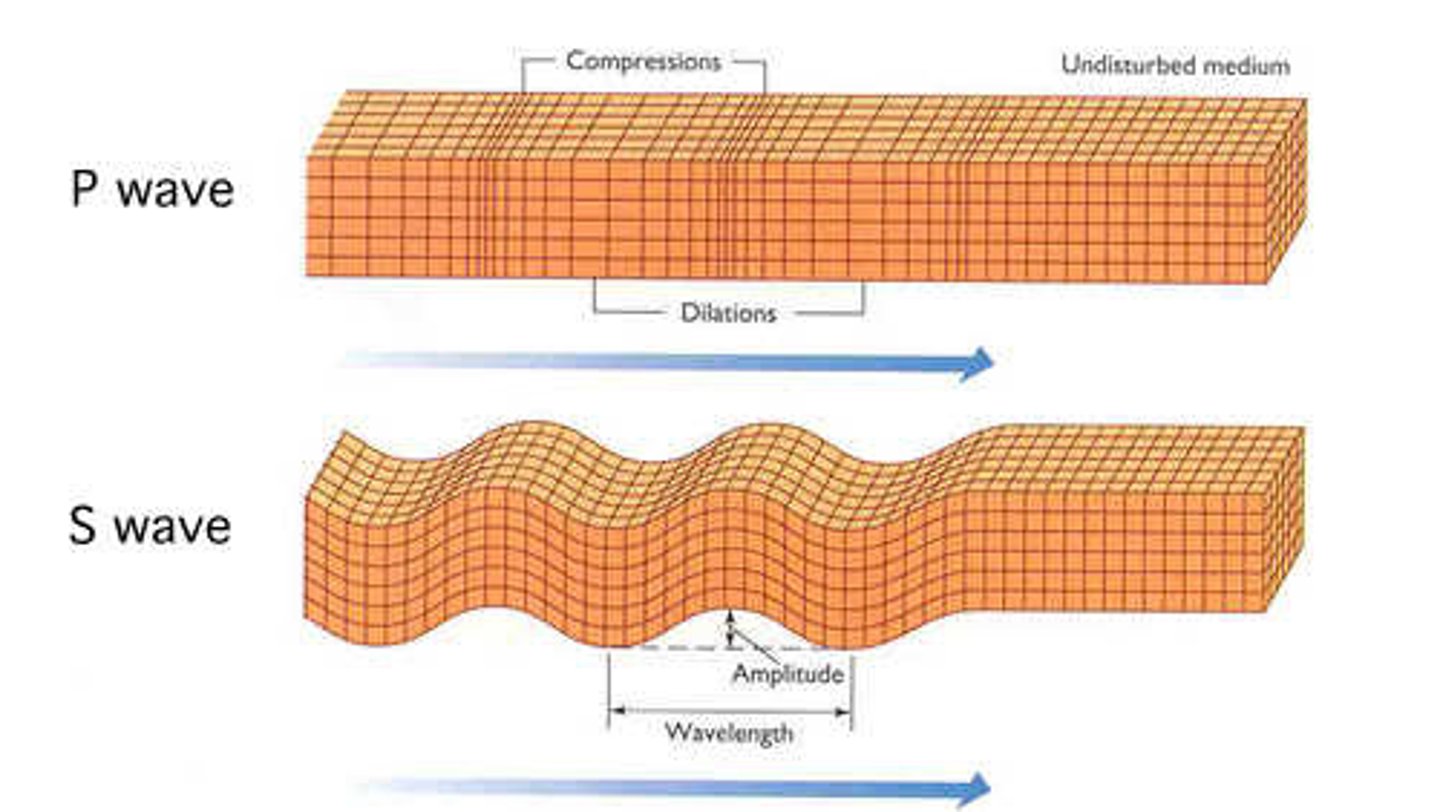
surface waves
seismic waves that travel along the Earth's surface. Causes the most destruction.
earthquake
The shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface.
Richter scale
A scale that rates an earthquake's magnitude based on the size of its seismic waves.

tectonic plates
Sections of the Earth's crust that move due to convection currents.

plate boundary
the region where two tectonic plates are in contact
Hot spot
A localized area where magma from deep in the mantle rises, not necessarily associated with a plate boundary
Continental-Continental
Pushed upwards forming large mountain ranges e.g Himalayas
Oceanic-Continental
Creates fold mountains and active volcanoes e.g. Ring of Fire
Subduction
Denser Oceanic crust is pushed underneath the Continental crust. Creates deep trenches
Oceanic-Oceanic
Faster plate undergoes subduction. Creates deep trenches and island arcs from underwater volcanoes.