PUBH 1101
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
demographic transition
describes the impact of falling childhood death rates and extended life spans on the size and age distribution of populations
epidemiological transition (public health transition)
implies that as social and economic development occurs, different types of diseases become prominent
nutritional transition
implies that countries frequently move from poorly balanced diets often deficient in nutrients, proteins, and calories to a diet of highly processed food, including fats, sugars, and salt
BIG GEMS
"social determinants of health"
Behavior
Infection
Genetics
Geography
Environment
Medical care
Socioeconomic-cultural
high-risk approach
focuses on those with the highest probability of developing disease + aims to bring their risk close to the levels experienced by the rest of the population
ex. mammography, screening ages
improving-the-average approach
focusing on the entire population and aims to reduce the risk for everyone
PERIE Process
framework for defining, analyzing, and addressing a wide range of public health issues
1) Problem
2) Etiology
3) Recommendations
4) Implementation
5) Evaluation
PERIE: Problem
describes burden, course, and distribution of disease
burden of disease
occurrence of disability and death due to disease
morbidity
disability
mortality
death
course of disease
asks how often the disease occurs, how likely it is to be present currently, and what happens once it occurs
incidence rates
measure the chances of developing a disease over a period of time
- comparing incidence rates is often a useful starting point when trying to establish cause of problem
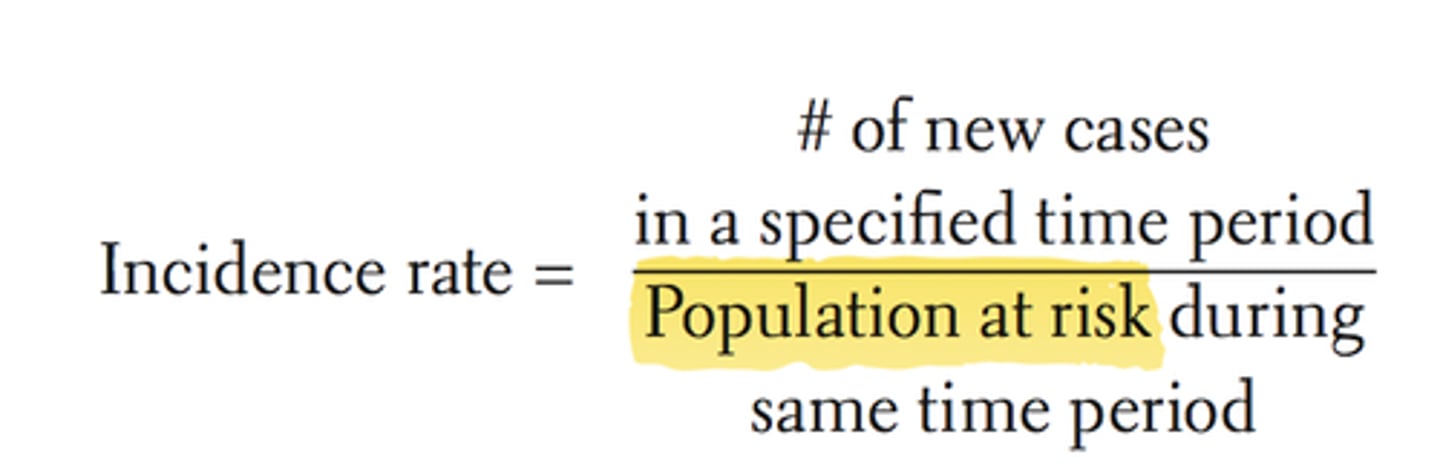
prevalence rates
the proportion or % of individuals who have the disease at a point in time

case-fatality
the chances of dying from a condition once it is diagnosed
distribution of disease
who gets the disease? where are they located? when does the disease occur?
group associations (ecological associations)
two factors, such as a characteristic and a disease, occur together more often than expected by chance alone in the same group of population
- does not require that the investigator have data on the characteristics of the individuals that make up the group or population
-may suggest ideas or hypotheses about the cause, or etiology, of a disease
risk indicators/risk markers
types of factors that occur more frequently among groups with the disease than among groups w/o the disease
epidemiologists
public health professionals that investigate "person" and "place" to find associations in the frequency of a disease
artifactual
data that is actually a result of the method of data collection; due to a confounding variable
3 reasons why changes in rate are artifactual:
1) diff or changes in interest in identifying the disease
-diff or changes in the ability to identify disease
-diff or changes in the definition of the disease
age adjustment
method to make fairer comparisons between groups with different age distributions
age distribution
the # of people in each age group in a population
population comparisons/ecological studies
investigations that use info on groups or a population w/o having info on the specific individuals within the group
confounding variable
a factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment
PERIE: Etiology
understanding the reasons for disease (causation)
contributory cause
immediate cause of disease
1) the "cause" is associated with the "effect" at the individual level
2) the "cause" precedes the "effect" in time
3) altering the "cause" alters the "effect"
case-control studies (retrospective studies)
compares patients who a disease of case with patients who do not have the disease or outcome, and looks back to compare how frequently the exposure to a risk factor is present in each group to determine the relationship between the risk factor and the disease
cohort studies (prospective studies)
1+ samples (called cohorts) are followed prospectively and subsequent status evals w respect to a disease or outcome are conducted to determine which initial participants risk factors are associated w it
randomized controlled trials (experimental studies)
randomly assigns participants into an experimental group or control group
as the study is conducted, the only expected diff between the two groups is the outcome variable being studied
supportive or ancillary criteria
additional measures that helps establish existence of contributory cause
4 types of supportive criterion
1) consistency
2) strength
3) dose response
4) biological plausibility
Consistency of Relationship
studies at the individual level produce similar results in multiple locations among populations of varying socioeconomic and cultural backgrounds
Strength of Relationship
the risk for those w the risk factor is greatly increased compared to those without the risk factor
Dose-response Relationship
higher levels of exposure and/or longer duration of exposure to the "cause" is associated w increased probability of the "effect"
Biological plausibility
known biological mechanisms can convincingly explain a cause-and-effect relationship
PERIE: Recommendations
What works to reduce the health impacts?
Classification of Recommendations
A = Must
B = Should
C = May
D = Don't
I = Indeterminant
PERIE: Implementation
How do we get the job done?
"When-Who-How" approach
method to examine the options for implementation
"When"
asks about timing in the course of disease in which an intervention occurs
- timing helps categorize interventions as PRIMARY, SECONDARY, and TERTIARY
Primary: take place before the onset of the disease; aims to prevent disease from occuring
Secondary: occurs after development of disease but before symptoms appear; aimed @ early detection of disease or reducing risk while patient is asymptomatic
Tertiary: occurs after symptoms, but before irreversibility; aim to prevent irreversible consequence of the disease
"Who"
at whom should we direct the intervention?
-individual, at-risk group, general population, community
"How"
How should we implement intervention?
- information (education), motivation (incentives), obligation (requirements)
PERIE: Evaluation
How well does the intervention work in practice?
RE-AIM framework
RE-AIM framework
- used to evaluate successfulness of interventions
Reach
Effectiveness
Adoption
Implementation
Maintenance
RE: how well does intervention work in practice?
AIM: how well is the intervention accepted in practice?
public health
the totality of all evidence-based public and private efforts that preserve and promote health and prevent disease, disability, and death
health communications
the methods for collecting, compiling, and presenting health information + how we perceive info, combine info, and use info to make a decision
According to CDC, the goal of health communications is to create social change by affecting people's attitudes, external structures, and/or modify or eliminate certain behaviors
What are the seven types of quantitative data?
7 quantitative sources
1) single case or small series
2) statistics
3) surveys (sampling)
4) self-reporting
5) sentinel monitoring
6) syndromic surveillance
7) social media
infant mortality rate
estimates rate of death in the first year of life
Under-5 Mortality: new measure used by WHO to summarize health of kids
life expectancy
measures the overall death experience of the population, incorporating the probability of dying at each year of life
Health-adjusted Life Expectancy (HALE): new measure by WHO to summarize health of populations
health literacy
the ability to obtain, interpret, understand, and apply basic health information and services
dread effect
present with hazards that easily produce very visual and feared consequences
Ex. Fear shark attacks more than drowning in a swimming pool
unfamiliarity effect
hazards we lack experience with may elicit more fear
Ex. Knowing a friend who died of lung cancer may influence how we perceive info on the hazards of smoking or presence of radon
uncontrollability effect
consider hazards that we perceive as in our control as less threatening than ones we perceive as out of our control
Ex. Car crashes seem less hazardous than plane crashes
inform of decision
implies that clinician has all the essential info and can make the decisions in patient's best interest
informed consent
patients need to give permission before major interventions
shared decision making
clinician provides info to the patient with which he can make a decision
4 P's of Social Marketing
Product: the desired behavior you are asking audience to do, and the associated benefits, tangible objects, or services that support behavior change
Price: the COST of overcoming the barriers the audience faces in making the desired behavior change
Place: where the audience will perform the desired behavior, access the program's services, or think about your issue
Promotion: the communication message, materials, channels, and activities that will effectively reach your audience
Elements of Communication
Sender, Receiver, Channel, Message
How can we evaluate quality of information?
Examine key quality standards:
- overall site quality
-authors
-information
-relevance
-timeliness
-links
-privacy
5 Steps to change someone's behavior (Peter Loge)
1.) What is the goal?
- make it specific, targeted, and measureable
2.) Who has power over the goal?
- who can make the action happen?
3.) What does the person with power find persuasive?
- figure out what your audience perceives to be true and remind them of it
4.) From whom do they find it persuasive?
5.) Do that.
Relationship between public health and social & behavioral sciences
share fundamental belief that understanding organization & motivation behind social forces + understanding behavior of individuals can be used to improve the lives of individuals and society
Social systems influence behavior by
1.) shaping norms
2.) enforcing patterns of social control
3.) providing or not providing opportunities to engage in certain behaviors
4.) reducing or producing stress for which certain behaviors may be an effective coping strategy
Ways Culture may affect health
- behavior (social practices)
- response to symptoms (level of urgency + seek care)
- types of interventions that are acceptable (reliance on self help and traditional healers)
- disease and interventions (diff in follow up and adherence to treatment)
Ways Religion may affect health
- social practices may put individuals at increased/reduced risk
- response to symptoms
- types of acceptable interventions
- response to disease
Social determinants of health
conditions in which people are born, grow up, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age, as well as the systems put in place to deal with illnesses that affect health and quality of life
-- shaped by economics, social policies, and politics
-- connected with health disparities
Key categories of social determinants of health
- social status
-social support or alienation
- food
- housing
- education
-work
-stress
-transportation
-place
-access to health services
downstream factors
directly involves an individual and can potentially be altered by individual interventions
mainstream factors
result from the relationship of an individual with a larger group or population
upstream factors
grounded in social structures and policies
Levels of Influence (Theories and Models)
1) Intrapersonal: focusing on individual characteristics
- knowledge, attitudes, beliefs, motivations, self-concept, past experiences, skills
- Health Belief Model, Stages of Change Model
2) Interpersonal: focusing on relationships between people
- other people influence behavior by sharing thoughts, advice, feelings, and support
- social cognitive theory
3) Population and Community: focusing on factors within social structures
- norms, rules, regulations, policies, laws
- Diffusion of Innovation
Health Belief Model
intrapersonal model focuses on individuals' perceptions and thought processes prior to taking health related action
-proposes people are more likely to take action if they believe:
- they are susceptible to the condition and it has serious consequences
- taking action would benefit them and benefits outweigh harms
- they have the ability to successfully perform the action
Stages of Change Model
intrapersonal model that assumes people go through a set of incremental stages when changing behavior rather than making significant change all at once
- five stages of change:
1) Precontemplaiton
2) Contemplation
3) Preparation
4) Action
5) Maintenance
Social Cognitive Theory
interpersonal model that focuses on the interaction between individuals and their social systems
- changing behavior requires understanding of:
- individual characteristics
- influences in the social and physical environment
- interaction among all these factors
- reciprocal determinism
Reciprocal Determinism (Social Cognitive Theory)
dynamic interplay among personal factors, the environment, and behavior
- changing one factor will change them all
Diffusion of Innovation
The process whereby a new product, service, or idea spreads through a population
PRECEDE-PROCEED
provides a structure to design and evaluate health education and health promotion programs using a diagnostic planning process followed by an implementation and evaluation process
-PRECEDE: Diagnostic phase
-PROCEED: Implementation and evaluation phase
heuristics
an approach to problem solving, learning, or discovery that employs a practical method not guaranteed to be optimal or perfect, but sufficient for the immediate goals.
communicable diseases
can be transmitted from person to person or from animals or the physical environment to humans
infectious disease
contains both communicable and non communicable disease
epidemic
disease that has increased frequently in a defined geographic area far above usual rate
Koch's Postulates
four conditions to establishing contributory cause; tested TB
1.) the organism must be shown to be present in every case of the disease by isolation of the organism
2.) the organism must not be found in cases of other diseases
3.) Once isolated, the organism ust be capable of replicating the disease in an experimental animal
4.) The organism must be recoverable from the animal
Modern Koch's Postulates (from NIAID)
1.) evidence of an epidemiological association
2.) isolation
3.) transmission to establish that an organism is a contributory cause of the disease
route of transmission
the anatomical & physiological methods for transmission from person to person and from animal species to humans
asymptomatic transmission
the ability to transmit the disease while humans or animals are free of symptoms of the disease
reproduction ratio
the # of new cases one individual with the disease generates on average over the course of its communicable period; provides a measure of the potential for an epidemic's development given the patterns of transmission in a particular society
passive immunity
inject antibodies into an individual for short term protection
inactivated vaccines
dead organisms injected into patient to build immunity
live vaccines
attenuated organisms used to stimulate cell-mediated immunity and create long term protection
herd immunity
the resistance to the spread of a contagious disease within a population that results if a sufficiently high proportion of individuals are immune to the disease, especially through vaccination
case finding
confidential interviewing of those diagnosed with a disease and asking for their recent close physical or sexual contacts
epidemiological treatment
treatment of contacts
Characteristics that make eradication of disease possible
-no animal reservoir
-short persistence in environment
-absence of a long-term carrier state
-disease produces long-term immunity
-herd immunity protects those who are susceptible
-vaccination also establishes long-term immunity
-easily identified disease
-effective postexposure vaccination (ring vaccination)
Four Criteria for a Screening Program
1.) disease produces substantial death and/or disability
2.) early detection is possible and improves outcome
3.) there is a feasible testing strategy for screening
4.) Screening is acceptable in terms of harms, costs, and patient acceptance
lead-time bias
early detection without improved outcome
false positives
individuals who have positive results on a screening test but do not turn out to have the disease
false negatives
individuals who have negative results on the screening test but turn out to have the disease
sequential testing
misses those who have false negative because when a negative test occurs, the testing process is over
multiple risk factor reduction
a strategy to intervene simultaneously on a series of risk factors, all of which contribute to a particular outcome
useful when the presence of two or more risk factors increases the risk more than would be expected by adding the impact of each
cost-effectiveness
combines issues of benefits and harms with issues of financial costs
population health aproach
requires the combined and integrated use of multiple interventions