Common Equipment In Vet Med
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is a stethoscope used for in veterinary medicine?
Tool for listening to internal body sounds
Heart: detect murmurs (valve issues) & arrhythmia (abnormal rhythms; common in dogs, rare in cats)
Lungs: assess breathing and air movement
Gut: check digestive sounds
Can also listen near the nose for airflow
How is a rectal thermometer used in veterinary medicine?
Common and accurate method
Always use protective covers
Often preferred by DVMs

How is an aural (ear) thermometer used in veterinary medicine?
Measures temperature in the ear canal
Add +1°F to reading in animals (controversial)
Less accurate than rectal
Always use protective covers

What is a ophthlamoscope and how is it used in veterinary medicine?
Corded or handheld tool
Used to examine the inside of the eye
Helps detect ulcers, damage, and other eye issues

What should a veterinary assistant check when preparing an ophthalmoscope?
Ensure it is in good working order
Make sure it is charged or has working batteries

What is an otoscope and how is it used in veterinary medicine?
Corded or handheld tool
Used to examine the inside of the ear

How does otoscope size vary with the patient?
The bigger the animal, the bigger the plastic tip used

What’s the difference between an ophthalmoscope and an otoscope?
Ophthalmoscope: used to examine the eye (ulcers, damage, etc.)
Otoscope: used to examine the ear (inner ear health, infections, etc.)
Both can be corded or handheld tools


What is a laryngoscope used for in veterinary medicine?
Used for intubation
Used to examine the oral cavity

What should a veterinary assistant check on a laryngoscope before use?
Ensure the small light bulb is working

What are the two main types of laryngoscope blades?
Macintosh blade: curved, round like an apple; used for brachycephalic breeds (Bulldogs, Frenchies, dogs with short faces)
Miller blade: straight; used for regular dogs

![<p>Why might you choose a Macintosh blade over a Miller blade? [<strong>Laryngoscope</strong> blades]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a3e9b5e3-d59d-4029-895f-ace384760200.png)
Why might you choose a Macintosh blade over a Miller blade? [Laryngoscope blades]
Better for dogs with short, smushed faces that often have breathing difficulties

What is the purpose of a steam autoclave in veterinary medicine?
Sterilizes equipment and tools (kills all microorganisms)
Not the same as disinfecting

What type of equipment can be sterilized in a steam autoclave?
Only metal equipment and tools

What is the purpose of an ultrasonic machine in veterinary medicine?
Increases the disinfection of items
Often called “The Jiggler”

What types of items can be cleaned in an ultrasonic machine?
Plastic ✅
Metal ✅
Other materials that cannot be exposed to high heat

How does the ultrasonic machine work?
Shakes at a high frequency, creating bubbles from a cleaning chemical
Bubbles help remove bacteria and debris

What is the primary job of thumb forceps in veterinary medicine?
To grasp items, both during surgery and outside of surgery

What is the main purpose of bandage scissors in veterinary medicine?
To cut bandages safely and efficiently

What are the characteristics of Knowles bandage scissors?
Good size blades for getting under bandages
Very sharp (can even cut animals if not careful)
Sharpness helps cut bandages more easily

What are the characteristics of Lister bandage scissors?
Not as sharp
Safer for both the animal and the user
What are hemostats commonly used for in veterinary medicine?
Stop the flow of blood from a vessel during surgery
Pluck ear hair
Clamp and grasp items using the locking jaws
What are the two common types of hemostats?
Kelly
Crile
How can hemostats be shaped?
Straight
Curved
Lead Gown

Lead Gloves / Mittens

Thyroid Shield

Lead Goggles


Dosimetry Badge (Ring)
Measures how much radiation you are exposed to
Radiology Calipers
Used to measure the thickness of the body part being measured

Sandbag

V Trough (The Couch)


Radiology Markers
Shows up on radiograph
Demonstrates left and right
Dental X-Ray Unit

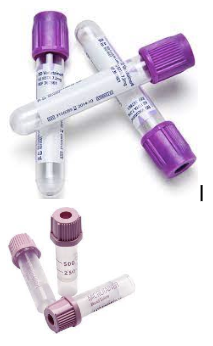
Lavender Top Tube = LTT
Contains EDTA (anticoagulant)
Keeps blood whole and homogeneous
CBC, BG, HCT, Blood Sears, HW, 4DX, Triple Snap, Procyte, & more
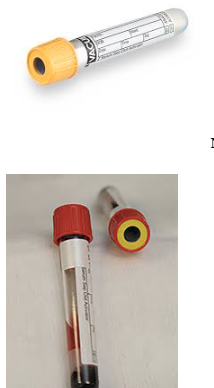
Serum Seperator = Tiger Top
Chem 10
Chem 17
Biochemical analysis of blood
aka chemistry
Catalyst Dx

Red Top Tube
No additive
Commonly used for testing phenobarbital levels
NO gel separator
Do not tip post centrifuge

White Top Tube = WTT
Contains nothing
Is considered sterile if unopened
Used for sterile urine samples
Also, once no longer sterile = great small containers
Ex = extracted teeth for owners
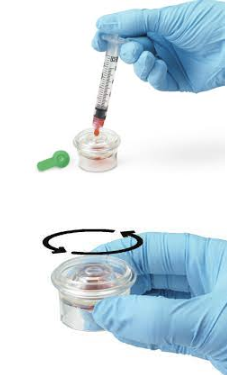
Heparin Spinner
(IDEXX Lithium Heparin Whole Blood Separator)
Specific to the Catalyst Dx Analyzers
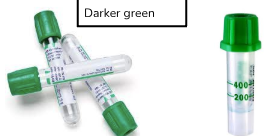
Green Top Lithium Heparin Tubes
Heparin is an anticoagulant, preventing clotting
Will generate plasma after being spun in a centrifuge
No gel at the bottom
Darker green
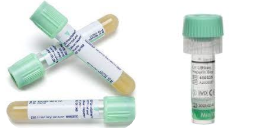
Green Top Sodium Heparin Tubes
Heparin is an anticoagulant, preventing clotting
Will also generate plasma after being spun in a centrifuge
Has gel on bottom
Lighter green
Fecal Container
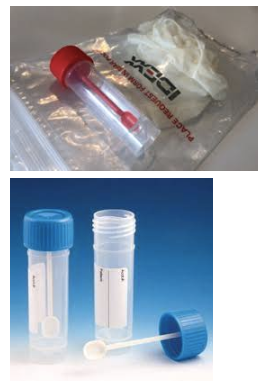
‘Non Sterile’ Urine Container
Sterile if sealed and unopened, BUT you must open the container to put the urine in. Therefore, the sterility must be broken to use

Formalin Jar
Used to send biopsy (bx) samples to the lab for testing
Preserves the specimen for the most accurate results
Is a Carcinogen (causes cancer)
DO NOT let formalin touch your bare skin
Wear gloves!!!

Refractometer
USG = Urine Specific Gravity
TS = Total Solids aka SP = Specific Protein
Compared against distilled water with a SG of 1,000

Centrifuge & Stat Spin
Spins sample at a high rate of speed, separating into different densities
Heavier content will sink, while lighter content rises to top

Microscope
Objective strength x Ocular strength = the magnification of image
Ocular lenses always 10x magnification
Common objective lenses are 4x, 10x, 40x (high dry), and 100x (oil immersion)
Ex. 10x x 4x = 40x total magnification