Tooth Developmental Defects
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential vocabulary related to tooth developmental defects, providing definitions for key terms from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Anodontia
Total lack of tooth development.
Hypodontia
A condition where a few teeth are missing, usually 6 or less.
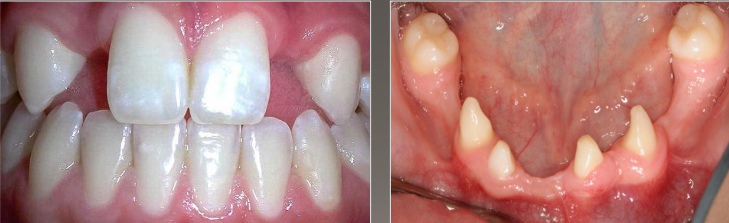
Hyperdontia
Development of an increased number of teeth, commonly known as supernumerary teeth.
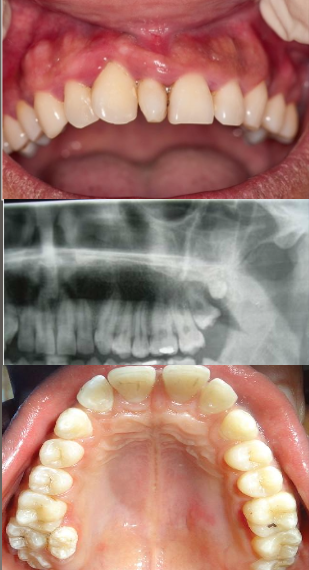
Dentinogenesis
The formation of dentin.
Dilaceration
An abnormal bend or curve in the root of a tooth.
Gemination
A single enlarged tooth in which the tooth count is normal when counted as one.
Fusion
A single enlarged tooth created by the joining of two tooth buds, resulting in a missing tooth in the count.
Macrodontia
Abnormally large teeth.
Microdontia
Abnormally small teeth.
Amelogenesis Imperfecta
A genetic condition affecting the enamel of both deciduous and permanent teeth, leading to soft, thin enamel that is easily damaged.
Dentin Dysplasia
A hereditary condition affecting dentin, resulting in abnormal dentin formation.
Regional Odontodysplasia
A non-hereditary developmental anomaly characterized by large pulps with minimal dentin and enamel, often referred to as 'ghost teeth'.
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
An inherited condition where multiple ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop.
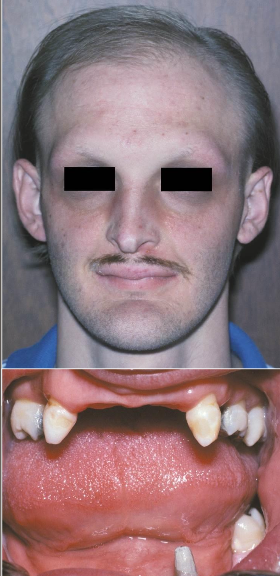
What are some clinical presentations of Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
Heat intolerance
Fever
Hypodontia
Fine, sparse hair
Reduced eyebrows and eyelashes
Periocular skin shows wrinkling and
hyperpigmentation
Concrescence
Union of two teeth by cementum alone.
Dens Invaginatus
A developmental anomaly where there is an invagination of enamel into the tooth.
Turner’s Hypoplasia
A form of enamel hypoplasia that occurs due to trauma or disease in a primary tooth affecting the permanent tooth beneath.
Cleft Lip and Palate
Congenital deformities resulting from improper fusion of the lip and/or palate during development.
Tetracycline Staining
Color changes in teeth resulting from exposure to tetracycline during tooth development.
Cleidocranial Dysplasia (Cleidocranial Dysostosis)
Syndrome complex characterized by dental and clavicle abnormalities.
Autosomal Dominant (AD) inheritance.
Features:
Prolonged retention of deciduous teeth.
Delay or failure of eruption of permanent teeth.
Abnormally shaped teeth.
Numerous unerupted permanent and supernumerary teeth.
Gardner syndrome
AD / Mutation chromosome # 5 (APC)
Clinical features:
Colorectal (adenoma) polyps which can become malignant ( 100% if not treated)
Multiple osteoma
Epidermoid cyst of skin
20% have supernumerary teeth
Thyroid carcinoma
Pigmented ocular fundus (90%)

In which conditions are supernumary teeth found?
Gardner Syndrome and Cleidocranial Dysplasia
Micro vs Macrodontia
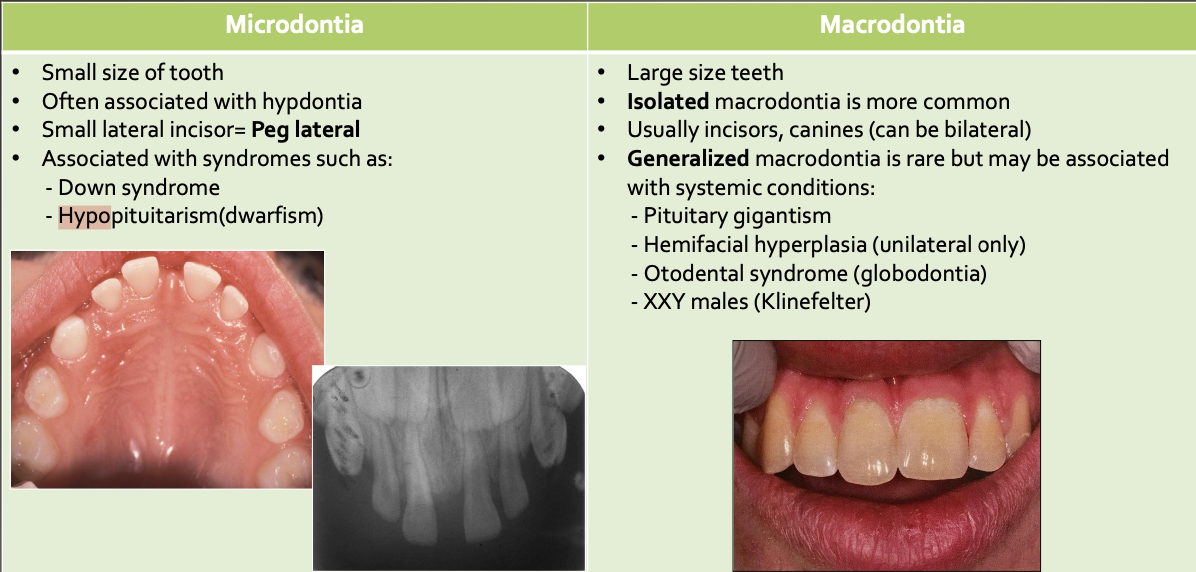
Cusp of Carabelli
Accessory cusp on palatal surface of ML cusp of maxillary molars
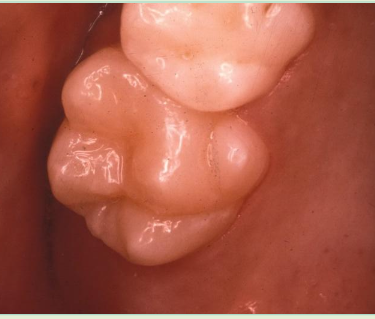
Talon Cusps
Accessory cusp on lingual of incisor; usually maxillary lateral incisor; usually has pulp tissue inside
Dens Evaginatus (occlusal pearl)
Elongated “cusp” extending from central occlusal surface; mandibular premolars, maybe molars, usually has pulp tissue, problem: occlusal trauma
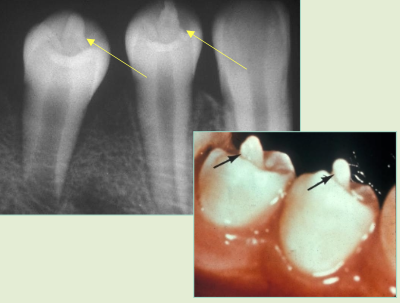
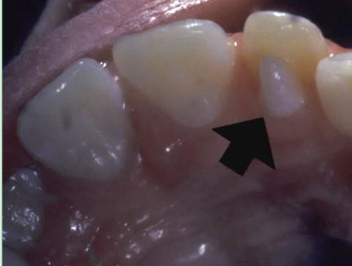
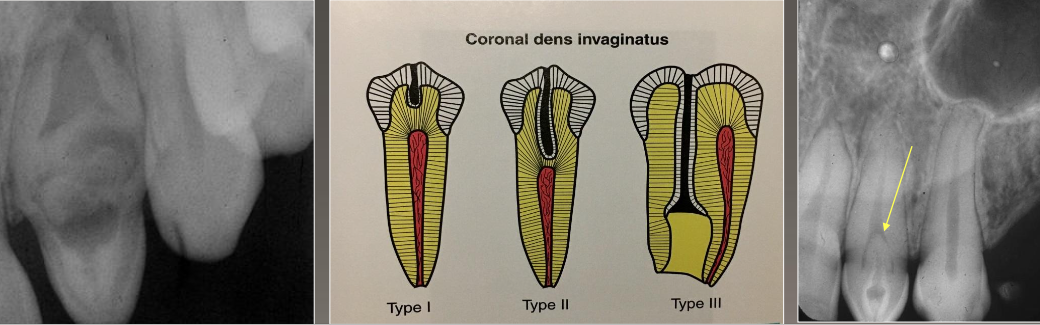
Dens Invaginatus “dens in dente”
Deep surface enamel invagination of the crown or root “ tooth within tooth”
Can be coronal (most frequent) or radicular
Type I: Invagination is confined to the crown
Type II: Invagination extends below the CEJ
Type III: Invagination may extend through the root
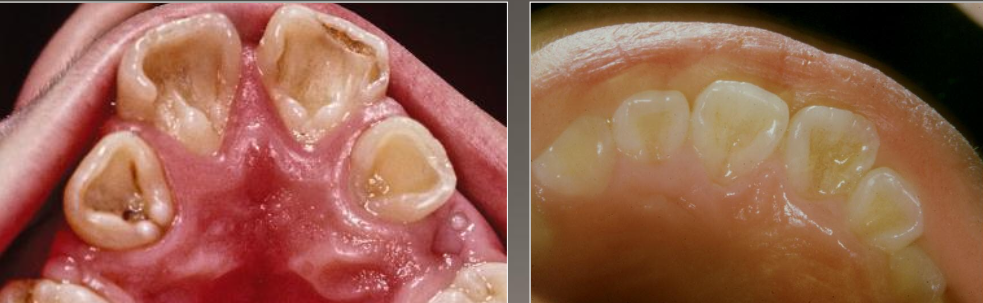
Shovel shaped teeth
Prominent marginal ridges on maxillary incisors (esp centrals)
Associated with dens evaginatus
Usually bilateral
Most common in Asians
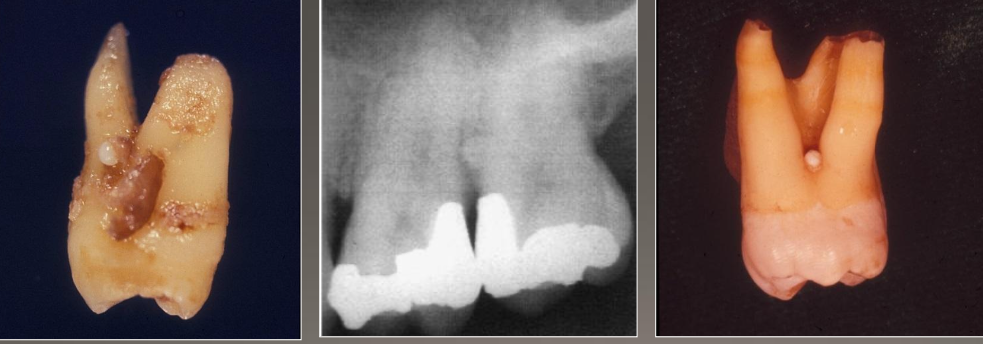
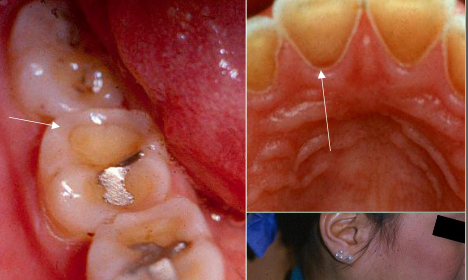
Enamel Pearl
Enamel nodules at furcation of multi-rooted teeth
Most common site: Maxillary molars
May have pulp tissue, usually without dentin
Problem: Perio defect and pulp exposure
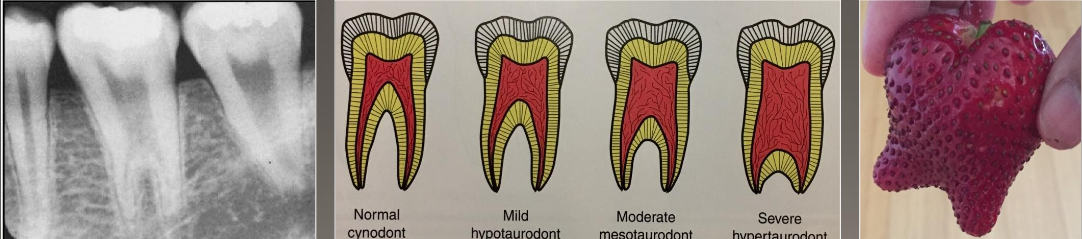
Taurodontism
Enlargement of the body and pulp chamber
Most common mandibular molars and premolars
No treatment
Associated with many syndromes
Dilaceration
From trauma or infection of tooth bud as root forming
Tooth vital
Usually 3rd molars
No problem unless endo is needed
What are some local factors of hypercementosis
Abnormal occlusal trauma.
Adjacent inflammation.
Unopposed teeth (super eruption).
Repair of vital root fracture.
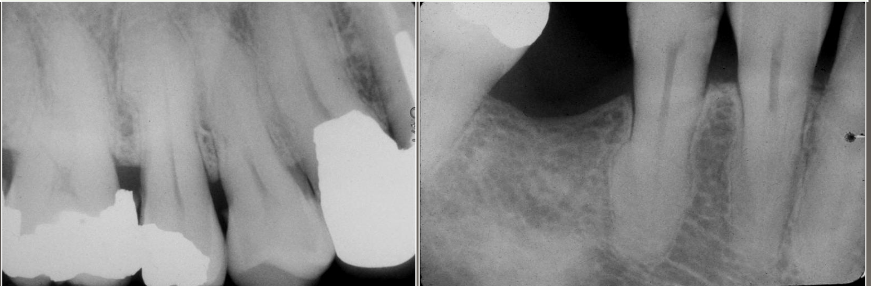
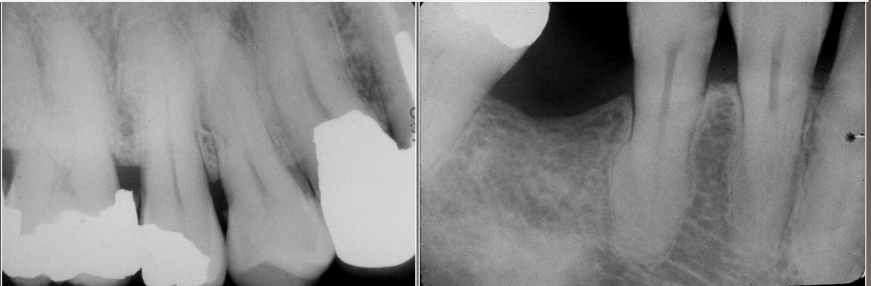
What are some systemic factors of hypercementosis
Acromegaly and pituitary gigantism.
Arthritis.
Calcinosis.
Paget disease of bone*.
Rheumatic fever.
Thyroid goiter.
Gardner syndrome*.
Vitamin A deficiency (possibly)
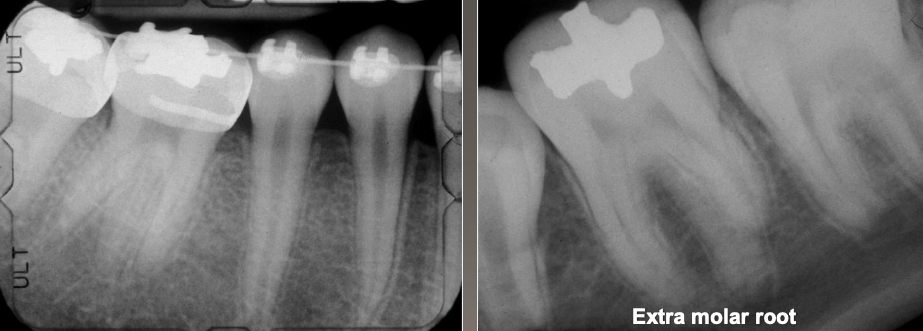
What is a supernumerary root?
Increased number of roots
Both deciduous and permanent
Most affected: mand 3rd molars > cuspids and bicuspids
No treatment but detection is important if endo treatment is needed
What is Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI)
Autosomal dominant (AD), recessive (AR), X-linked
Both deciduous and permanent dentition are diffusely involved
Affects enamel, soft and thin, easily damaged and susceptible to decay
Dentin is exposed
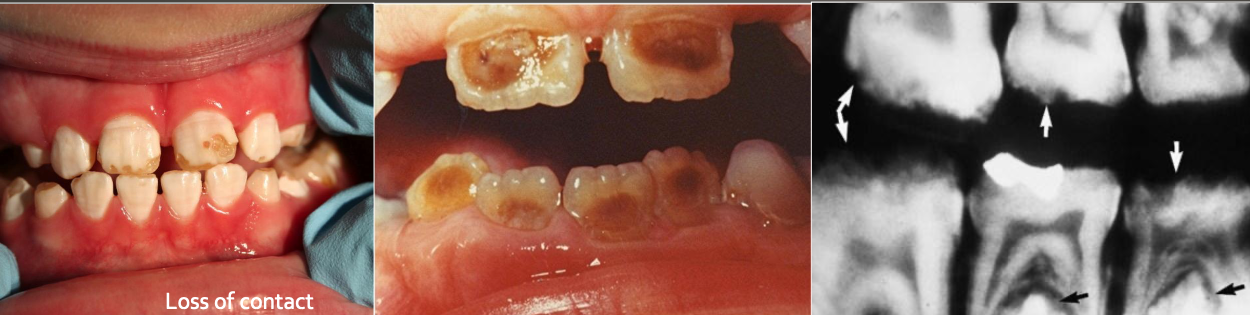
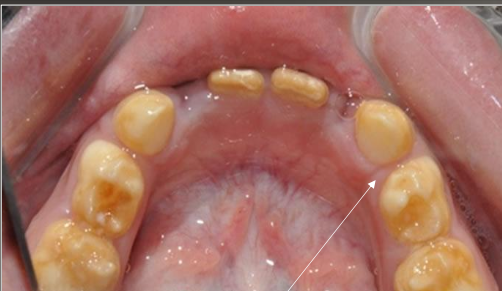
What do you see in Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI)
Yellow-brown to white pitted lesions
Open bite ,loss of contact
Types:
Hypoplastic (pitted)
Hypomaturation /hypocalcification (snow capped)
AI with taurodontism
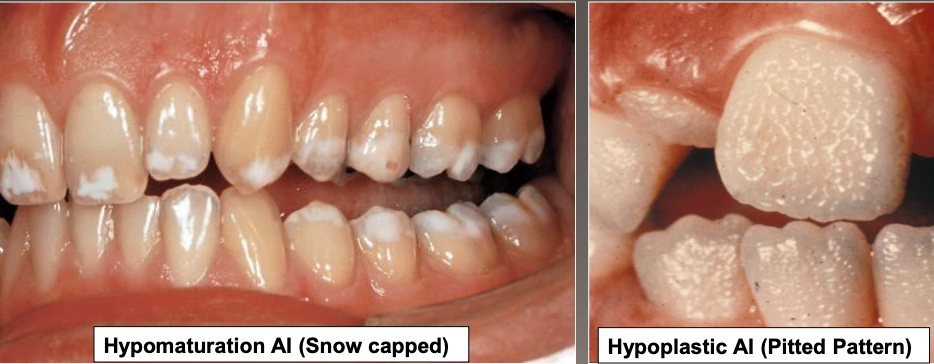
What does hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta look like?
Snow capped
What does hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta look like?
A pitted pattern
Example of amelogenesis imperfecta: loss of contact
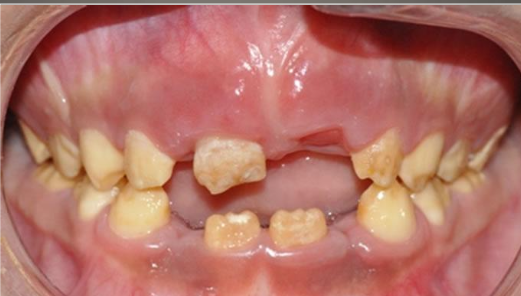
Example of amelogenesis imperfecta: loss of enamel
What is enamel dysplasia?
It can be developmental OR genetic or acquired
What is hypoplasia in enamel dysplasia?
Thickness deficit
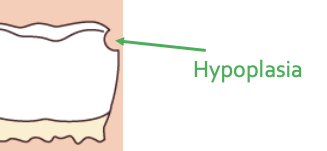
What is hypomineralization in enamel dysplasia?
It is a mineral deficit
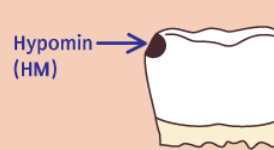
What categories fall under hypomineralization?
Hypomaturation and hypocalcification
What is hypomaturation
Amelogenin-rich
What is hypocalcification
Amelogenein-poor
What is molar hypomineralization?
A type of hypocalcification of enamel dysplasia that can be
Albumin-rich
Amelogenin-poor
Or an acquired defect
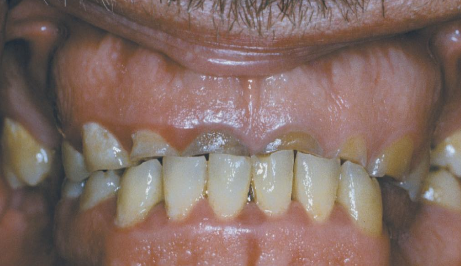
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta (DGI): What is it?
A hereditary condition affecting dentin.
Happens without any systemic disease.
Also known as Hereditary Opalescent Dentin
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Inheritance Pattern
Autosomal Dominant (AD) inheritance.
Passed down from parent to child.
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta vs Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)
DGI and OI have different genetic mutations.
They are not related, even though they were once thought to be the same condition
Shields Classification: Type 1
Clinical Presentation: Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
Features:
Opalescent Teeth.
Bone fractures
Shields Classification: Type 2
Isolated opalescent teeth.
Most common
Hereditary Opalescent Teeth
Shields Classification: Type 3
Isolated opalescent teeth.
Large pulp chambers (Shell teeth).
Pulp exposure.
Periapical radiolucencies.
"Brandywire" appearance of teeth
Important Notes on Dentinogenesis Imperfecta (DGI) and osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)
DGI is caused by a mutation in Dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP).
OI is caused by a mutation in COL1.
They are not the same.
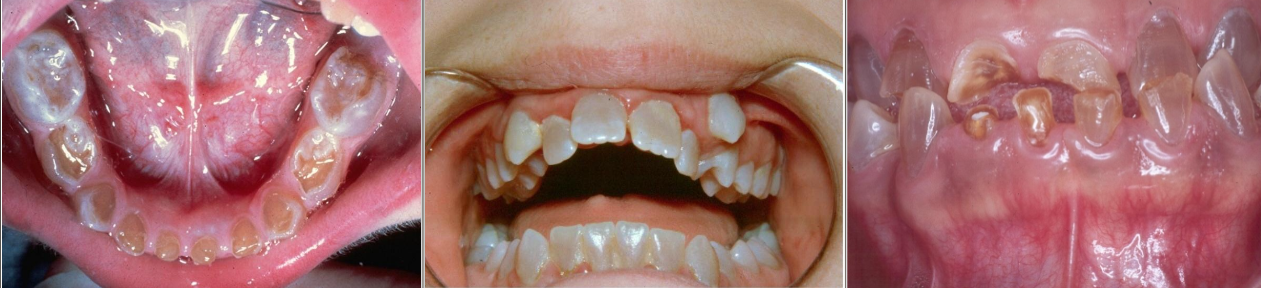
What is this an image of?
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
Affects both dentition
Steel-gray/translucent/opalescent crows
Brittle enamel, breaks off
Radiograph of Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
Bulbous crown
Cervical constriction
Pulp obliteration varies
Expanded pulp = shell teeth
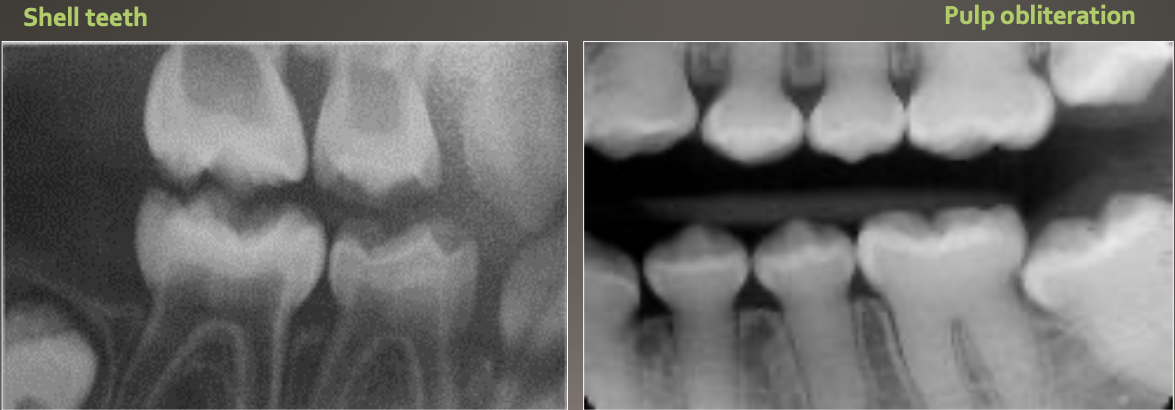
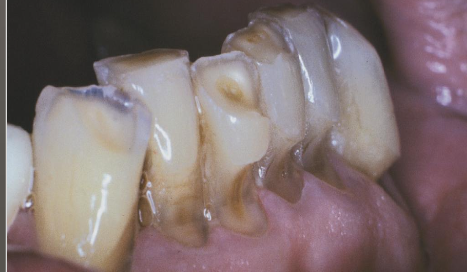
What is Dentin Dysplasia
A hereditary condition affecting dentin
Autosomal dominant
Both dentition affected
2 types
DD1- radicular
DD2- coronal
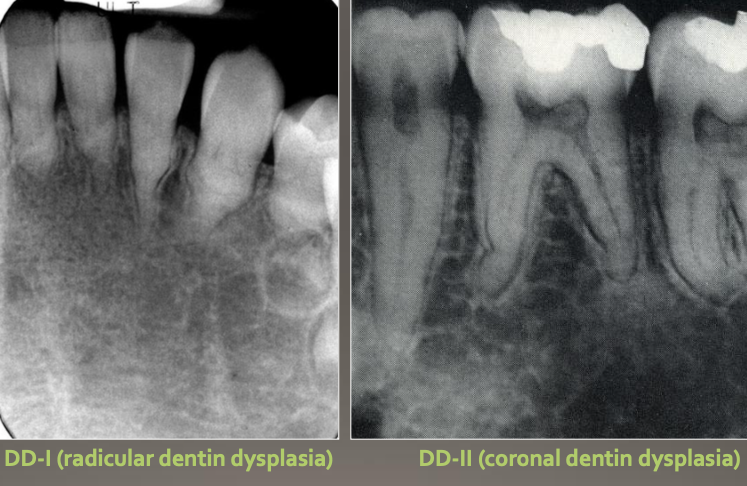
Dentin Dysplasia type 1 (DD-I)
4 types
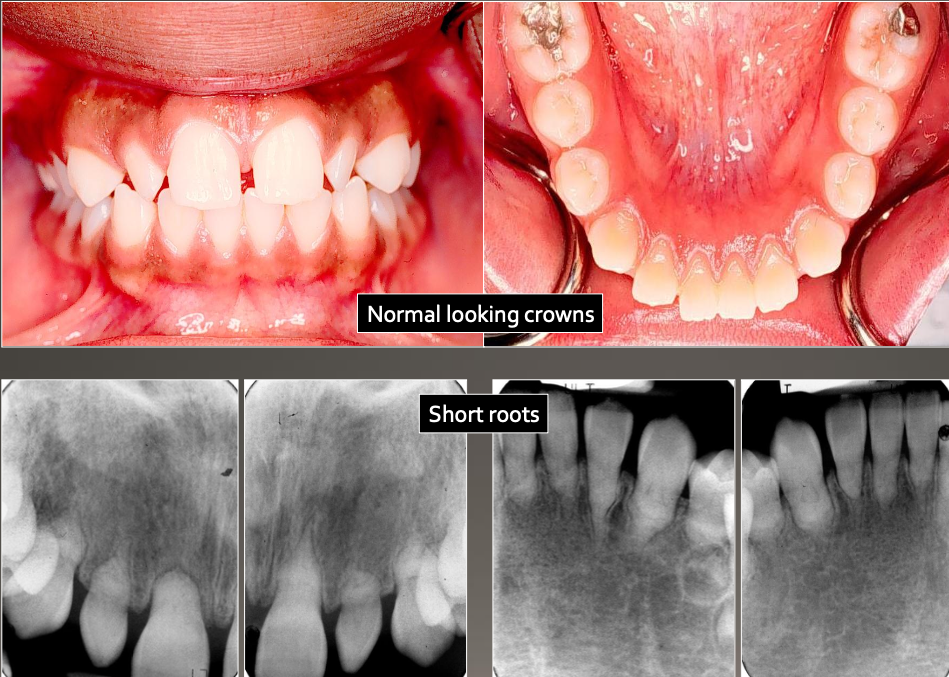
Normal clinical crown
Short roots
Periapical radiolucencies
Chevron pulp chambers
“ROOTLESS”
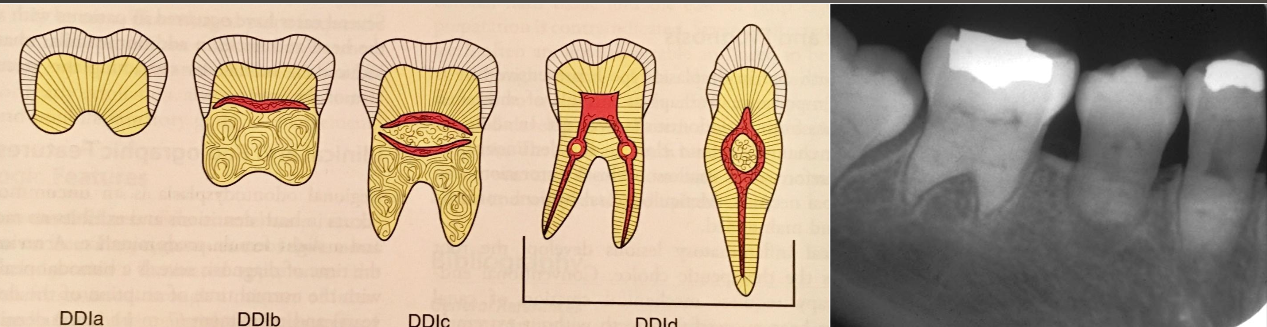
Dentin Dysplasia type 2 (DD-II)
Primary Dentition
Blue-amber-brown translucence
Bulbous crown
cervical constriction
thin roots, normal length
early obliteration of pulp
Permanent Dentition
Normal color clinically
Pulp chamber is enlarged = thistle tubs or flames shaped
Pulp stone
Normal Root
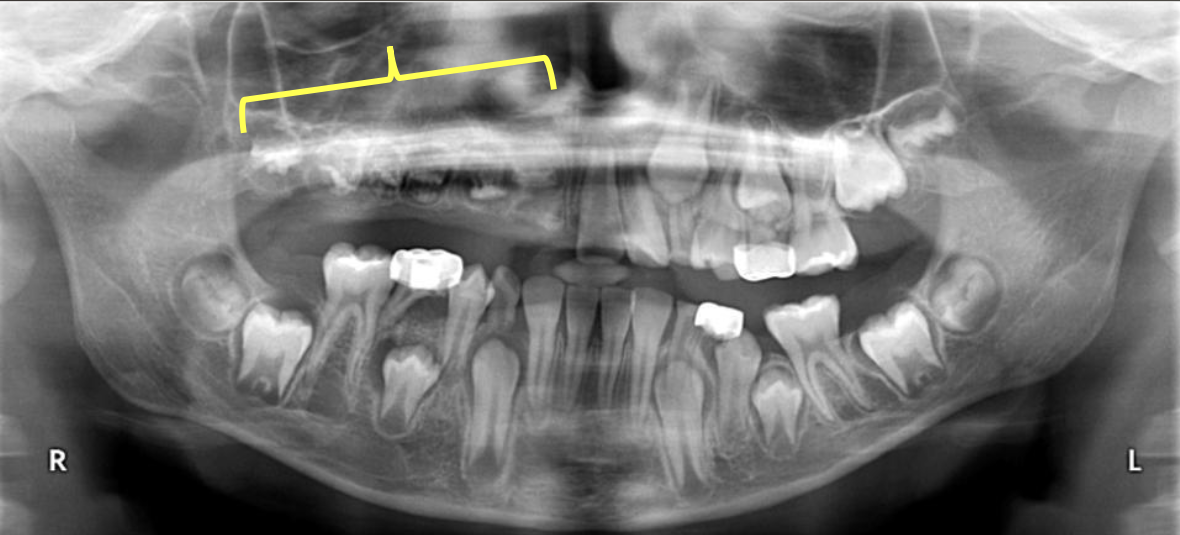
Regional Odontodysplasia- “ghost teeth”
Nonhereditary developmental anomaly
Most believe it is due to an alteration in vascular supply
Most commonly involves maxillary anterior teeth
Usually involves one quadrant; rarely can affect more
Very large pulps with minimal dentin & enamel
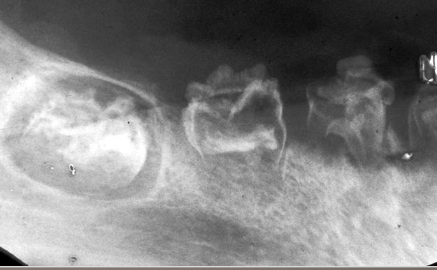
Pano of “Ghost teeth”
Attrition image
Abrasion image
Erosion (chemical) image
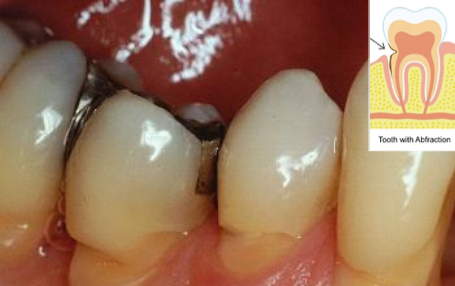
Abfraction d/t occlusal stress image
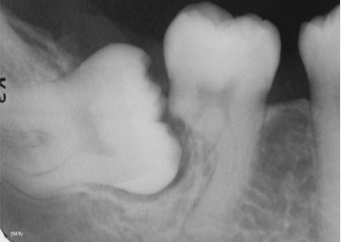
External resorption
Commonly occurs apically/ mid root and is associated with
Cysts and tumors
ortho
excessive occlusal stress
reimplantation of avulsed tooth
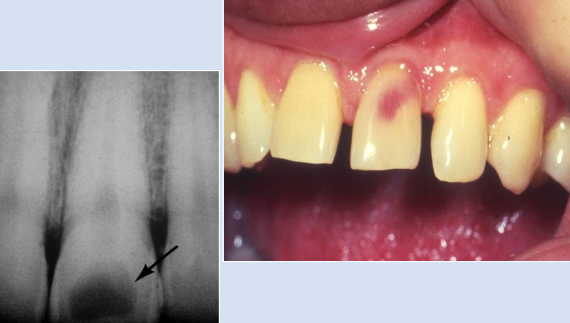
Internal resorption
Rare, injury to pulpal tissue (TRAUMA), when crown is affected known as pink tooth of mummery
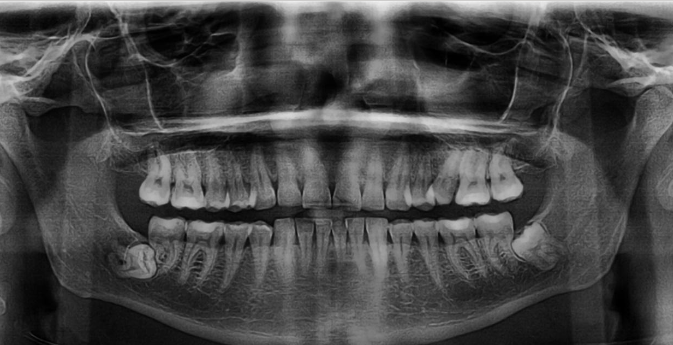
Localized Disturbances in Eruption
Impaction: Tooth is obstructed by a physical barrier.
Embedded: Tooth lacks eruptive force to emerge.
Rarely occurs in deciduous teeth
Ankylosis: What is it?
Cessation of eruption after the tooth emerges.
Fusion of cementum with bone.
Unknown pathogenesis (cause not fully understood)
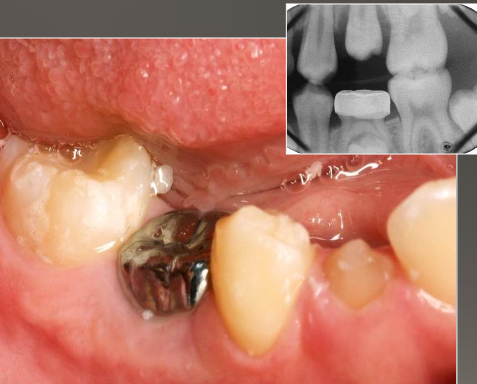
Turner’s Hypoplasia
Common causes:
Fever
Periapical inflammatory disease of overlying deciduous tooth
Trauma
Clinical: Enamel can be white, yellow, brown and/or have different degrees of hypoplasia
Location: Most common in bicuspids because of their relationship with the deciduous molars
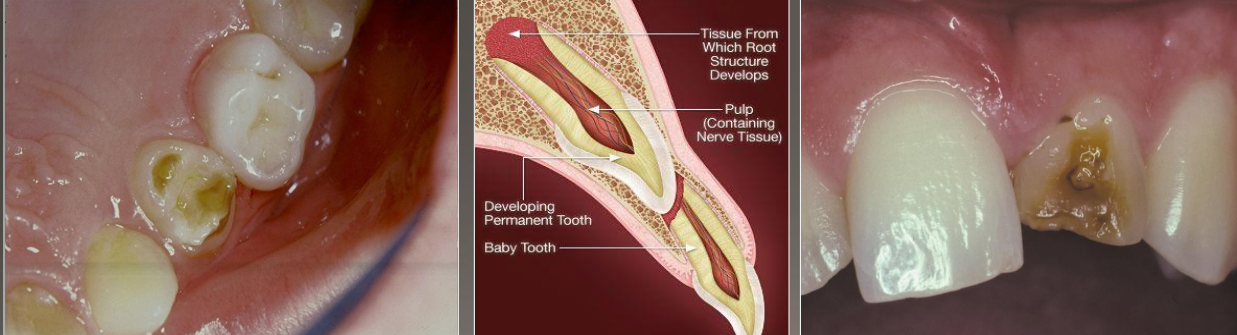
What are some other names for Congenital Syphilis?
hutchinson’s incisors and mulberry molars
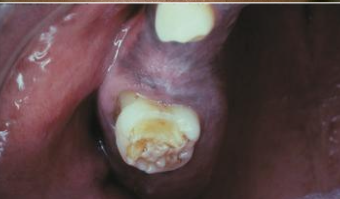
How is congenital syphilis transmitted:
From active syphilis in mother during last trimester
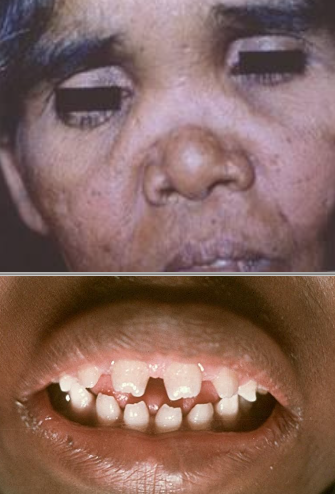
What are the intraoral clinical manifestations of congenital syphillis?
Hutchinson’s incisor (screwdrivers)
Mulberry molars (1st molars develop irregular nodules of enamel on occlusal surface)
What are the health and neck effects of congenital syphilis?
Mental degeneration, cartilage septal destruction of nose (saddle nose), blindness and deafness d/t nerve 8
What is the hutchinson triad?
Hutchinson teeth
Ocular
8th nerve deafness
What is fluorosis?
Mottled enamel; hypomineralization- creating chalky white areas; severity is dose dependent; ingestion of excess amount of fluoride; retention of amelogenin protein in enamel
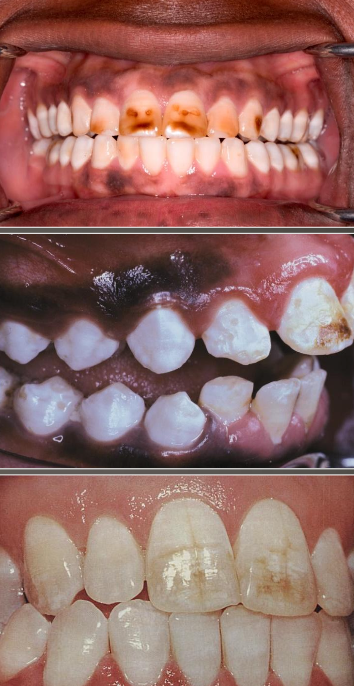
What are the clinical manifestations of fluorosis?
Must be bilateral symmetrical distribution with previous exposure to Fl
Trauma of a non-vital tooth
Pulp death after RCT
Age
Gets darker with time
Tooth is brittle
cannot bleach enamel
color doesn’t change with new RCT
Post and crown
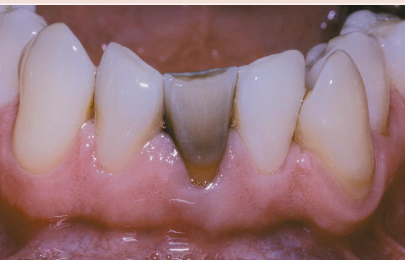
Trauma: internal resorption
Rare
Injury to pulpal tissue
When crown is affected known as Pink tooth of mummery
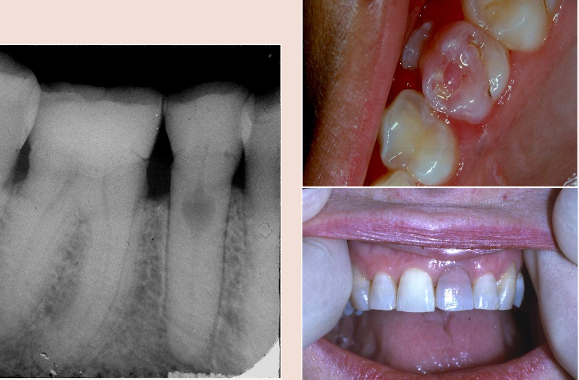
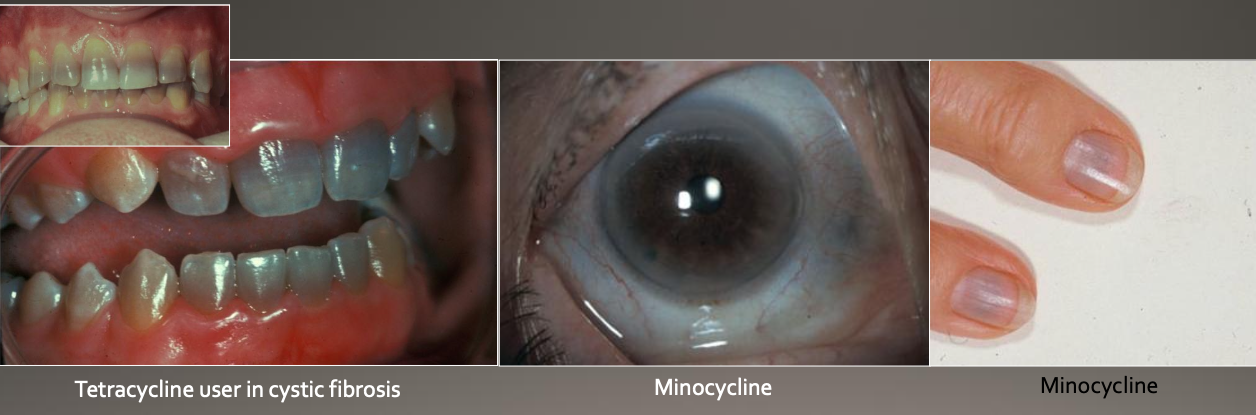
What is the cause of tetracycline staining?
From use of tetracycline during tooth development
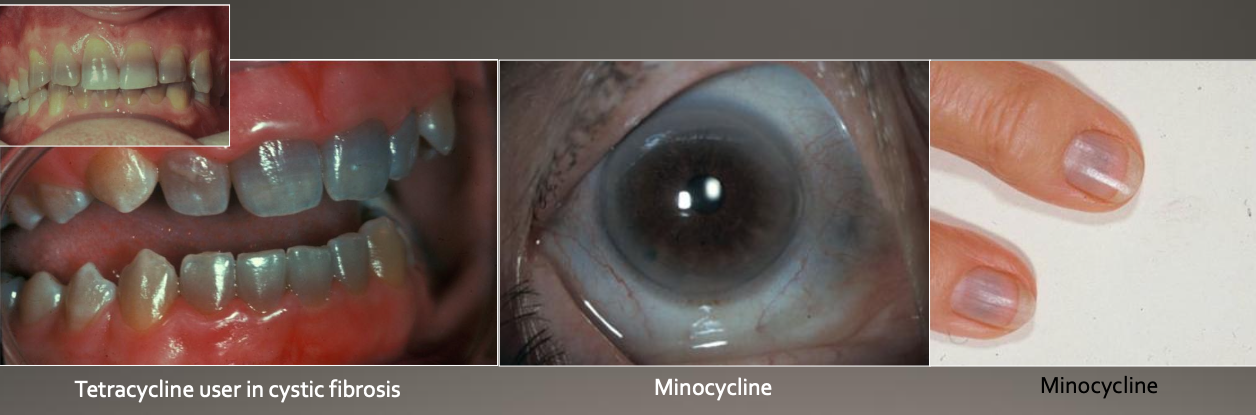
How does tetracycline work cellularly?
Minocycline (a type of tetracycline) binds to collagen in:
Dental tissues
Pulp
Dentin
Bone
May also discolor skin, sclera, and thyroid
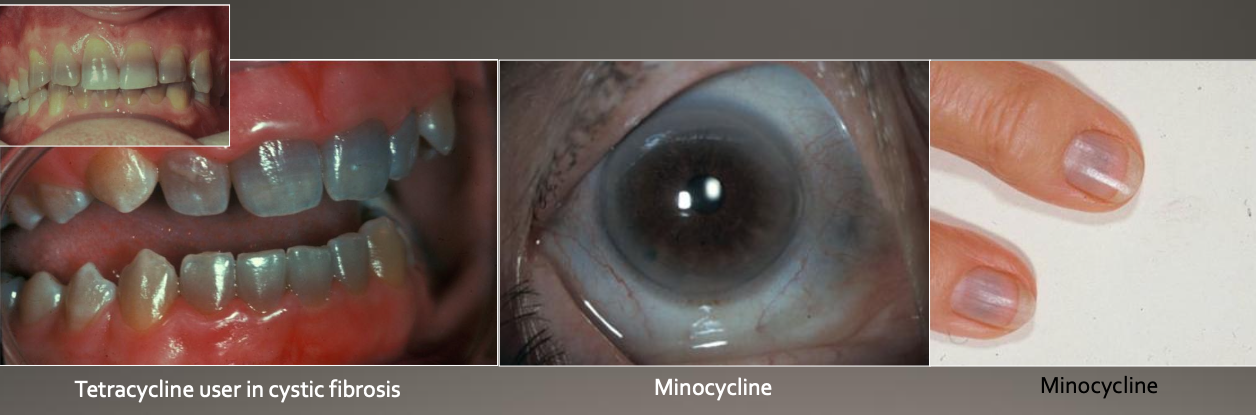
Tetracycline Staining: Uses and Precautions
Rx: Often prescribed for:
Acne
Cystic fibrosis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Precaution: Avoid tetracycline use during:
Pregnancy
Up to 8 years of age (due to risk of staining developing teeth).
What is a clinical feature you see in Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia?
Screw driver teeth
What is the mode of inhertance in Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasisa?
Autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and x-linked
In hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, what structures fail to develop?
2+ ectodermally derived anatomic structures like skin, ahir, nails, teeth and sweat glands
What does paramolar mean?
Situated lingually or bucally to a molar
What is the order in which you’d see hyperdontia?
Max incisor, max 4th molar, mandibular 4th molar
What is the mode of inheritance for cleidocranial dysplasia?
Autosomal dominant
What is the most of inheritance for gardner syndrome?
Autosomal dominant
What is a peg lateral?
A small lateral incisor associated with microdontia
What are the conditions you see in microdontia?
Down syndrome, hypopituitarism
What features do you see in macrodontia
Isolated macrodontia (only 1 tooth is larger than the rest)
Generalized macrodontia is rare but could happen
Where do you commonly see a talon cusp?
Maxiallary lateral incisor linguallyW
WHere do you normally see dens evaginatus (occlusal pearl)
mandibular premolars
What is type 1 dens invaginatus
Confined to crown
What is type 2 dens invaginatus
Extended below the CEJ
What is type 3 dens invaginatus
Extended through root
What condition is associated with shovel shaped teeth?
Dens evaginatus
Paget disease of bone and Garder syndrome are associated with this
Systemic hypercementosis
Where would you most commonly see a supernumeray root?
Mandibular 3rd molar