Functional Response to Predators
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
A species interactions where one species feeds on another which enhances the fitness of the predator but reduces the fitness of the prey
Predation
An organism that is killed and eaten by other animals
Prey
An animal that kills and eats other organisms
Predator
Prey-predator system between Paramecium and Didinium in oat medium without sediment
Cyclical Oscillations
Interaction between two animals where one will be eaten by the other
Carnivorous predation
The consumption of plant material by animals, and herbivores are animals adapted to eat plants (browsers and grazers)
Herbivory
An individual organism, the parasite, consumes nutrients from another organism, its host, resulting in a decrease in fitness to the host
Parasitism
Predators eyes face forwards to give them a clear view of their prey
Eye position
Have sharp claws that the predators use to hold onto prey while they are killing it
Feet
sharp, pointed teeth for grabbing and cutting their food. Predators don’t usually chew the meat completely. It is swallowed whole or in chunks
Teeth
Characteristics of predators
eye position
Feet
Teeth
Characteristics of prey
eyes
Feet
Located on the side of the head so they can see if predators are approaching
Eyes
Made for running
Feet
Predation influences the?
Predation influences the fitness of both predators and prey. individuals must both feed and avoid being eaten to survive and reproduce
How has predation influenced evolution
Coevolution
The influence of closely associated species on each other in their evolution
Coevolution
also known as cryptic coloration
A defense mechanism or tactic that organisms use to disguise their appearance, usually to blend in with their surroundings
Camouflage
the act or art of copying or imitating other organisms
Mimicry
batesian mimicry
Mullerian mimicry
the use of warning coloration to inform potential predators that an animal is poisonous, venomous or otherwise dangerous
Aposematic coloration
Two categories of plant defense against herbivory
tolerance
Resistance
Constitutive or induced defenses
Resistance
What are examples of physical defenses
Thorns on roses, spines on a cactus

This are secondary metabolites
Chemical defenses
carbon-based defenses and nitrogen-based defenses
Some plants can attract natural enemies to herbivores-indirect defense (e.g ants reduce herbivory)

Changing the number of prey can cause 2 types of responses which are?
Functional response
Numerical response
describes the change in the number of prey consumed by an individual predator as prey density changes
Rate of consumption vs. prey density
Predation rate change with increasing prey abundance
Functional response
describes the change in predator population density as prey density changes Rate
Increase in prey density leads to increase in predator population density
Numeric response
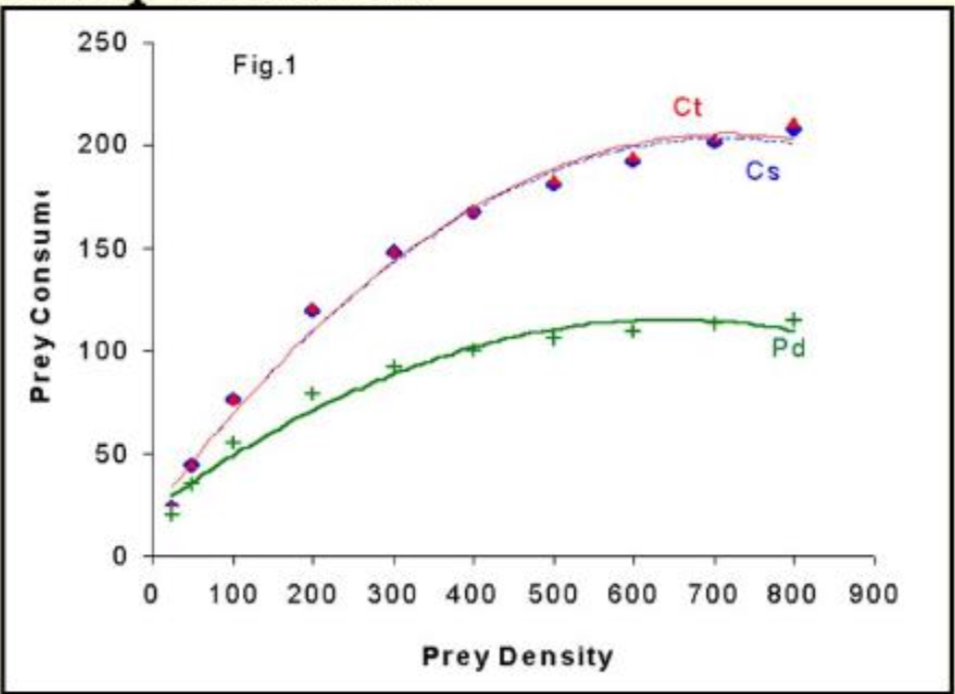
prey are consumed in direct proportion to their availability
Known as Type I functional response
Predators never satiate
No limit on the growth rate of predators
Lotka-Volterra
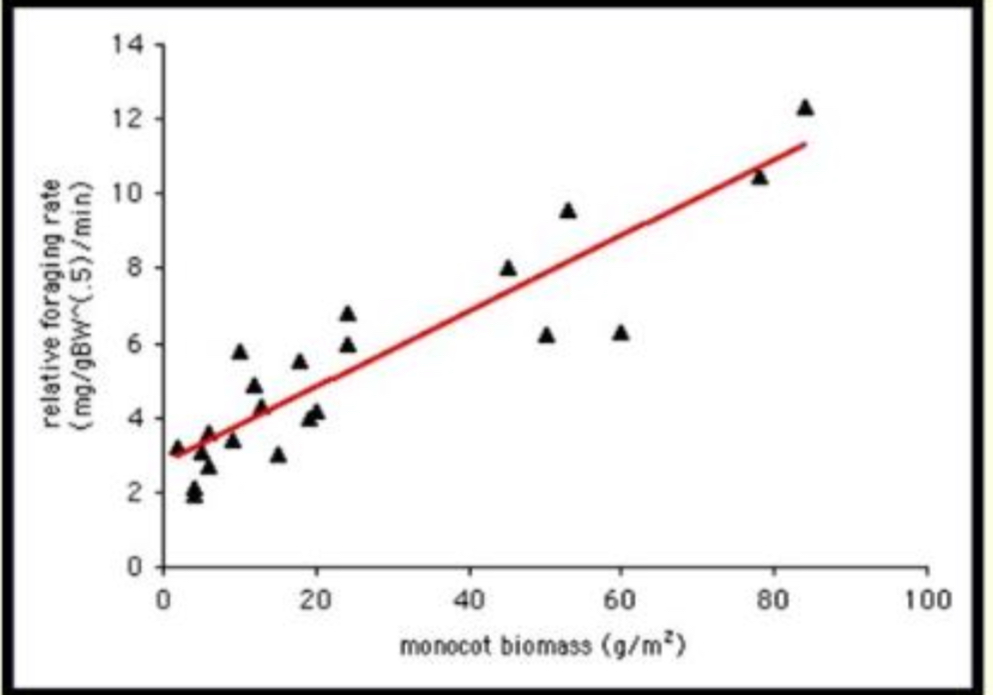
Consumption rate increases at first, but eventually predators satiate (upper limit on consumption rate)
Type II functional response
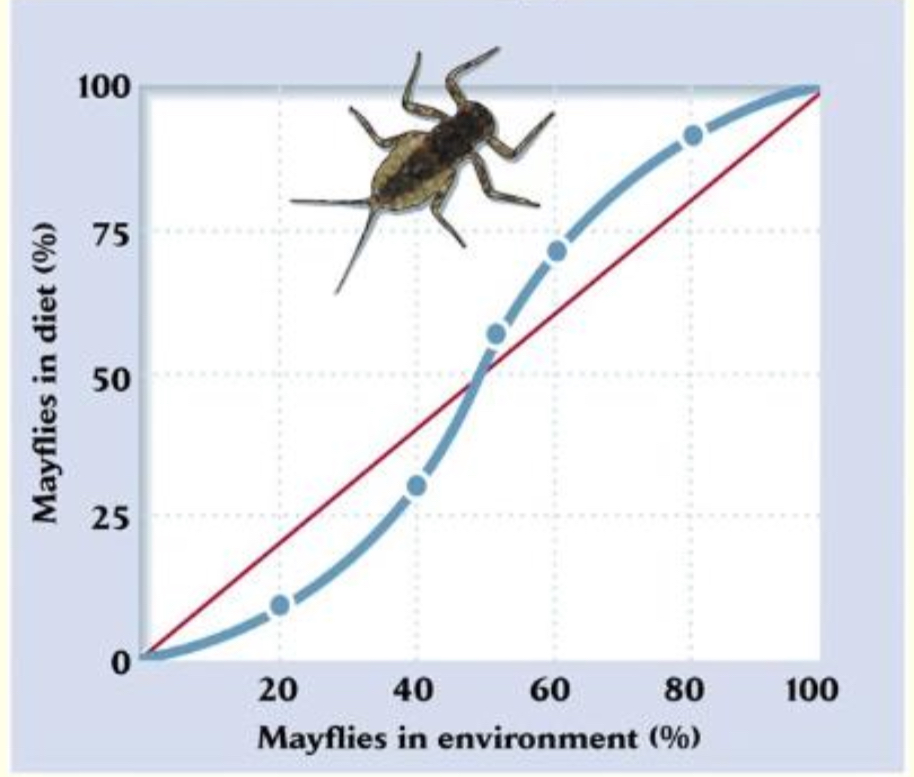
Consumption rate is low at low prey densities, increases, and then reaches an upper limit
Type III functional response