Economics Test + Exam Year 11
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Perfect Competition
Least product differenciation, Most consumer control
Monomolistic Competition
Some product differenciation, Some customer control
Oligopoly
A lot of product differenciation, a lot of customer control
Monopoly
Only product in market, no customer control
Definition of externalities
Third-party effects (positive or negative)
Example and responces to externalities
Ex: Pollution, education
Responce: Taxes/subsidies
Definition of public goods
Non-rival, non-exclusive
Example and responces to public goods
Ex: Street lighting, defence
Responce: GOVT regulations
Definition of Common resources
Rival but non-exclusive
Example and responce to common resources
Ex: Fisheries, forests
Responce: Regulation, permits
Definition of Information failure
Buyers/sellers lack of info
Example and responce to information failure
Ex: Unsafe drugs, used cars
Responce: Regulation, disclosure
Definition of market power
Monopoly/oligopoly exploitation of consumers
Example and response to Market Power
Ex: Electricity, airlines
Response: antitrust laws
Definition of collusion
Firms cooperates to maximize joint profit (illigal in most cases)
Definition of Nash Equilibrium
Each firm chooses best stratergy given the others choice
Definition of strategic independence
Frims outcomes depend on rivals decisions
Definition of payoff matrix
Shows profits/losses for each combination of stratergies
Demand Factors (TIRES)
T - Taste/preferences
I - Income
R - Related Goods
E - Expectation of Future Prices
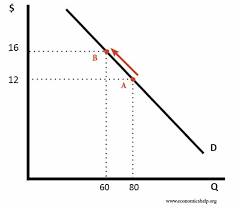
Is the following a movement along the demand line or a shift of demand?
Movement along the demand line
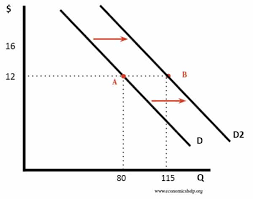
Is the following a movement along the demand line or a shift of demand?
Shift of demand
Supply Factors (TIGERS)
T - Technology
I - Input Quality
G - GOVT Intervention
E - Expectation of Future Prices
R - Resource costs (land, labour, capital)
S - Sellers in the Market
Define Elastic Goods
Consumers are highly sensitive to price
Define Inelastic Goods
Consumers are not sensitive to price
Factors that indluence ability to substitute a good (PED, SPLAT)
S - Subsitution
P - Proportion of Income
L - Luxery of Necessity
A - Addictive
T - Timely
Factors that influence ability to substitute producing a good (PES, SWEPTS)
S - Storage of goods
W - Weather conditions
E - Ease of access to specialist equitment
P - Planning perms & GOVT restrictions
T - Time to produce
S - Switching resources to new production
Forms of Maket Failure (NCE)
Abuse of market power
Assymetric Information (onesided)
Consumer demerit goods (externalities)
Production Externalities
Tragedy of the commons
Under Supply of the goods that society needs