Grade 8: Forces between and not touching
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Big Idea: Forces between objects act when the objects are__________
in direct contact and when they are not touching.
field
area around any object in which forces can act without touching
gravity
force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses;
magnet
any material that attracts iron or materials containing iron
electromagnetism
the interaction between electricity and magnetism
electromagnet
solenoid with a soft iron core inside
Gravitational force increases as ________________ increases.
mass
Gravitational force decreases as ___________________ increases.
distance
electromagnetic induction
process of creating a current by changing a magnetic field
2 components of projectile motion
horizontal movement and vertical movement
terminal velocity
the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of gravity is balanced by the force of air resistance
electric force
the force between two charged objects
electric field
a region around a charged object where a force is exerted on other objects
electric generator
a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction
electric motor
a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
magnetic poles
ends of a magnet that have opposing magnetic qualities
free fall
when the only force acting on an object is gravity such as in a vacuum or space
static electricity
A buildup of charges on an object (clothes from a dryer; comb or balloon on hair)
3 ways an object can become charged
friction, conduction, induction
charging by friction
two objects rub together and one becomes positively charged and the other becomes negatively charged (cloth on glass rod, hair on balloon)
charging by induction
the rearrangement of electrons on an uncharged object caused by a nearby charged object
charging by conduction (contact)
Transfer of charge between objects by allowing them to come into contact with one another
solenoid
A coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current
How can magnetic field of a solenoid or electromagnet be increased?
1. increasing the number of loops in the coil
2. increasing the electric current in the wire
electromagnet
a coil that has a soft iron core and that acts as a magnet when an electric current is in the coil
Properties of magnets
1. Magnets attract objects of iron, cobalt and nickel.
2. Whether a material is magnetic or not depends on the material's atoms.
2. The force of attraction of a magnet is greater at its poles than in the middle.
3. Like magnetic poles repel each other.
4. Opposite magnetic poles attract each other.
magnetic field
The area of magnetic force around a magnet
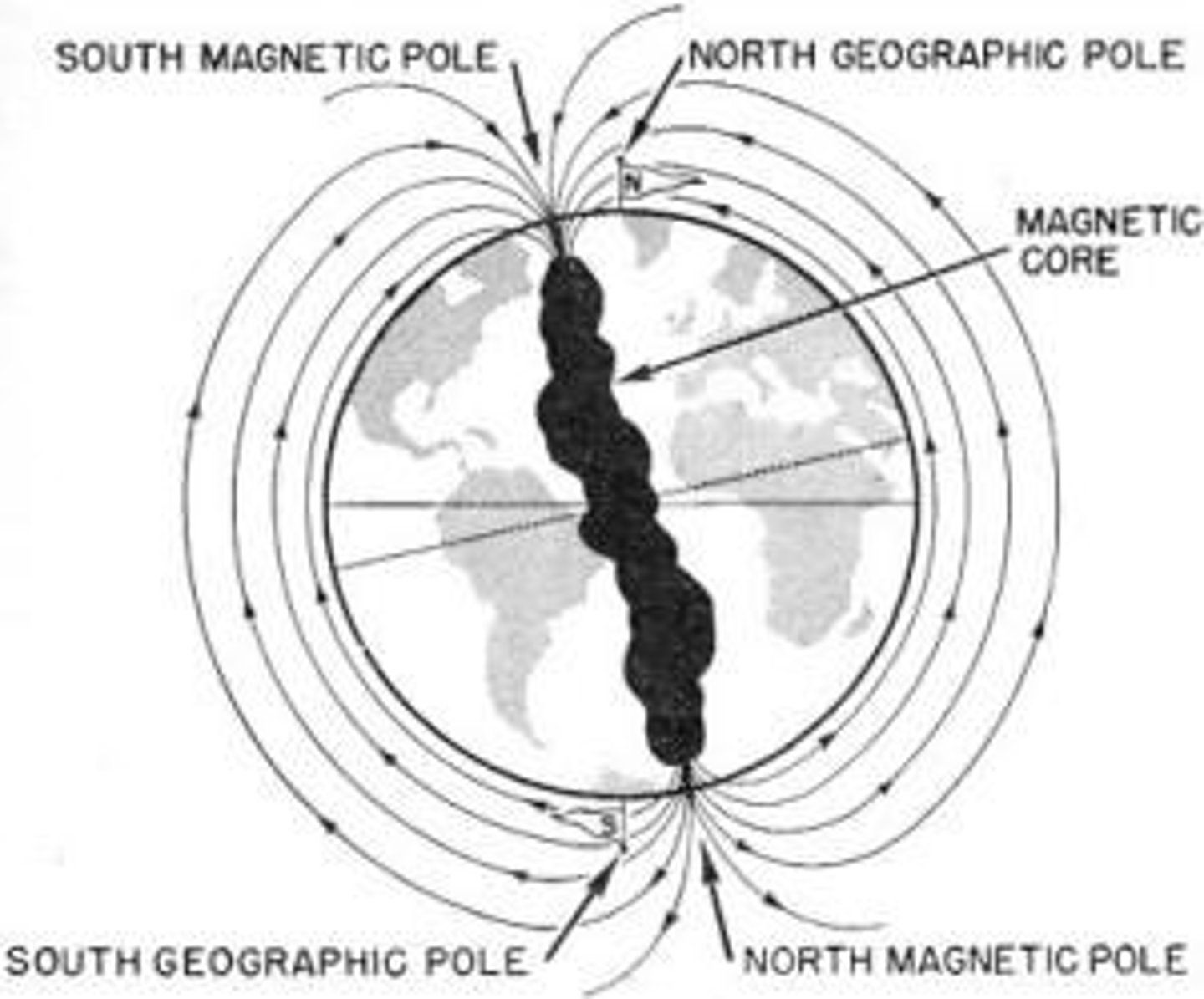
Earth's Geographic and Magnetic Poles
1. Earth acts like a giant magnet.
2. Earth has a magnetic field.
3. Compass needles and north poles of magnets point to Earth's magnetic south pole which is near Earth's geographic north pole.
How does lightning form?
Friction in the clouds creates charges.
Induction from the cloud creates a charge in the ground.
The charges are released through a static discharge event as the electrons are conducted to the other parts of the cloud/ground.
What has to happen for a feather and a bowling ball to fall at the same rate?
There would have to be no air resistance for them to fall at the same acceleration.