Chapter 2 - Periodic Properties
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
In reference to the periodic table, what does a group refer to?
A group consists of elements that occupy the same column
What common characteristic do elements in a group share?
Same number of valence electrons
In reference to the periodic table, what does a period refer to?
A period consists of elements that occupy the same row
What common characteristic do elements in a period share?
Same number of electron shells
Which group of elements represents alkali metals?
Group 1
Which group of elements represents alkaline earth metals?
Group 2
Which group of elements represents noble gases?
Group 18
Which group of elements represents halogens?
Group 17
Which group(s) of elements represent transition metals?
Group 3-12
Which group of elements is most stable?
Elements found in group 18, the noble gases, are the most stable. The elements in this group have outer energy levels that are completely filled
Which group of metal elements is considered very reactive?
Group 1, alkali metals
Which group of non-metal elements is considered very reactive?
Group 17, halogens
Which period of elements represents the lanthanides?
Period 6
Which period of elements presents the actinides?
Period 7
Which element from Group 1 is not considered an alkali metal?
Hydrogen
How many elements exist as diatomic atoms?
7
What are the seven elements that exist as diatomic atoms?
Hydrogen, nitrogen, fluorine, oxygen, iodine, chlorine, and bromine
Are metals or non-metals malleable and lustrous?
Metals
Do metals or non-metals form basic oxides?
Metals
Do metals or non-metals form acidic oxides?
Non-metals
Do metals or non-metals have higher melting and boiling points?
Metals
Which physical state are most metals at room temperature?
Solid
Which physical state(s) are most non-metals at room temperature?
Gas or solid
Which metal is a liquid at room temperature?
Hg
Which non-metal is a liquid at room temperature?
Br
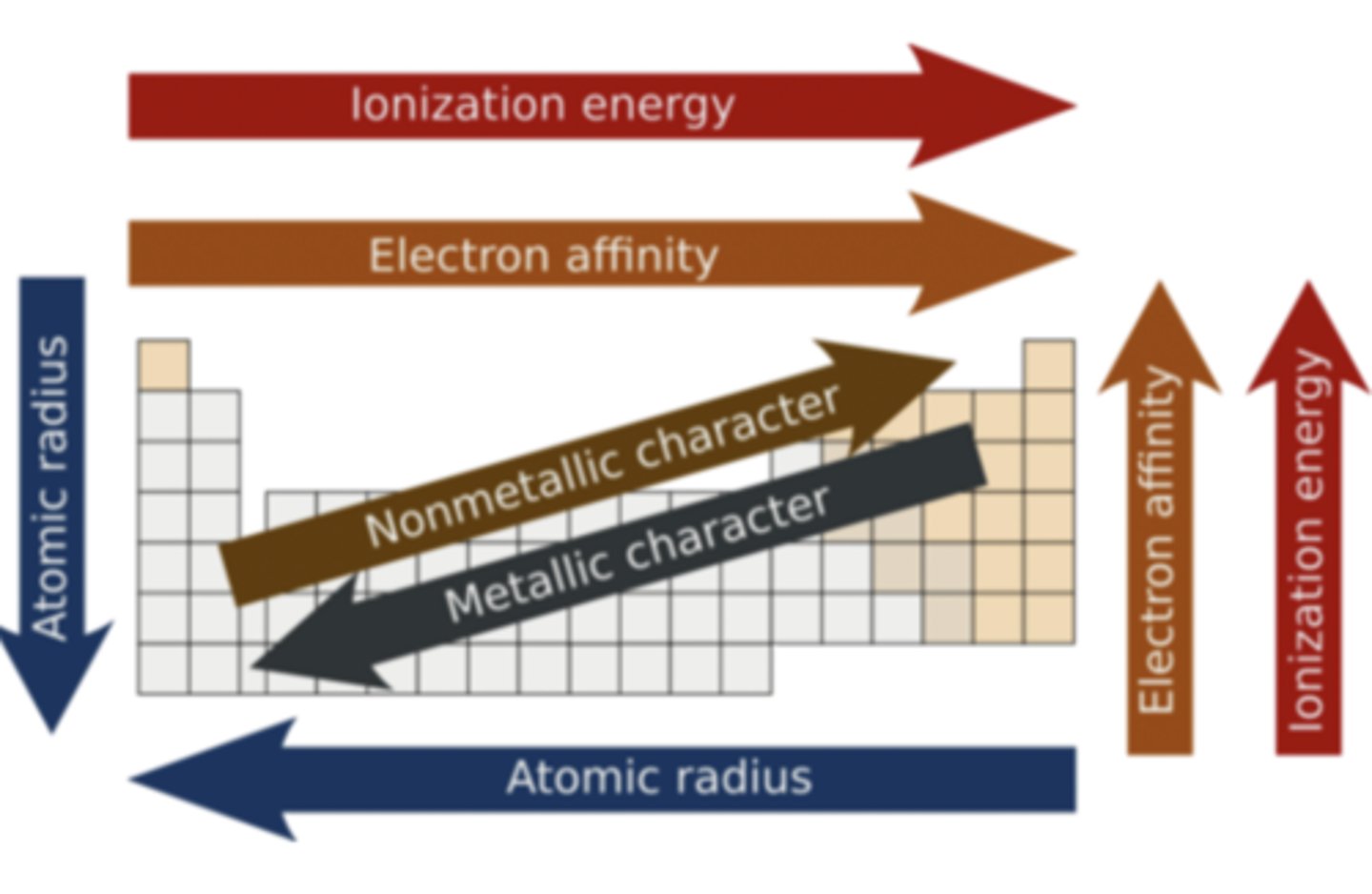
What is the trend for atomic radius as you move from left to right across the periodic table?
Radii decrease
Why does atomic radius decrease across a period?
Number of protons in an atom increases, resulting in greater nuclear attraction between the protons and electrons
What is the definition of effective nuclear charge?
The nuclear charge experienced by an electron in an atom with multiple electrons
What is the formula for calculating effective nuclear charge?
Effective nuclear charge = Z - S.
Z is # of protons; S is # of shielding electrons
What is the trend for effective nuclear charge in regards to the periodic table?
Increases across a period from left to right. Decreases going down a group
What is the definition of isoelectronic series?
Atoms and ions that have the same electron configuration, but differing numbers of protons. For example, O2-, F-, and Ne
What is the definition of ionization energy?
The energy needed to remove an electron from an atom
Is it possible for elements to have more than one ionization energy?
Yes
Are subsequent ionization energies typically smaller or larger than the first ionization energy?
Larger, because subsequent electrons are more difficult to remove
Does ionization energy increase or decrease going from left to right across the periodic table?
Increase, since there is an increase in effective nuclear charge
Does ionization energy increase or decrease going down a group on the periodic table?
Decrease, as shielding effect is increasing
What is the definition of electron affinity?
Amount of energy released when an electron is added to an atom
Does electron affinity increase or decrease going from left to right across a period?
Increases
Does electron affinity increase or decrease going down a group?
Decreases
Why does electron affinity decrease going down a group?
The attraction of an electron to the nucleus decreases due to shielding. Electron affinity, therefore, decreases
What is the definition of electronegativity?
Ability of an atom to attract electrons in a bond to itself
What does a high electronegativity imply?
The greater ability to attract an electron(s)
Does electronegativity increase or decrease going from left to right across a period?
Increases
What is the most electronegative element?
Fluorine
Which group of elements does not possess electronegativity?
Noble gases (group 18) as they have full valence shells and do not need additional electrons
Summary of periodic trends for review