10: Lipids
5.0(1)Studied by 97 people
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:08 AM on 12/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains how many carbons long?
Most commonly, they are found with chains about how many carbons long?
Most commonly, they are found with chains about how many carbons long?
Fatty acids are carboxylic acid hydrocarbon chains 4 to 36 carbons long.
Commonly, they are found 12-24 carbons long.
Commonly, they are found 12-24 carbons long.
2
New cards
Describe the carbon-skeleton nomenclature system for labelling fatty acids. For example, what does 18:2(Δ⁹,¹²) mean?
The left side of the colon denotes the number of carbons in the chain.
The right side of the colon denotes the number of double bonds in the chain.
The Δ and following numbers denote the locations of the double bonds.
The right side of the colon denotes the number of double bonds in the chain.
The Δ and following numbers denote the locations of the double bonds.
3
New cards
In most monounsaturated fatty acids, the double bond is found at which carbon?
Carbon 9.
To be more clear, it is found between C9-C10.
But it is labeled as A:1(Δ⁹)
To be more clear, it is found between C9-C10.
But it is labeled as A:1(Δ⁹)
4
New cards
Double bonds of polyunsaturated fats are typically separated by what?
A methylene group.
5
New cards
Nearly all unsaturated fatty acids have their double bonds in the ____ (cis/trans) configuration.
cis
6
New cards
What kind of polyunsaturated fats are especially important regarding human nutrition? What kind of nomenclature is used to refer to these fats?
Fatty acids with a double bond between the C3-C4 FROM THE END of the chain.
These are known as omega-3 fatty acids.
These are known as omega-3 fatty acids.
7
New cards
Physical properties of fatty acids are largely determined by what?
Length and degree of unsaturation of the hydrocarbon chain.
8
New cards
Describe the effect of increasing/decreasing length and degree of unsaturation on the solubility of a fatty acid.
As nonpolar hydrophobic chain length increases, solubility decreases.
As double bonds increase, solubility increases.
As double bonds increase, solubility increases.
9
New cards
Describe the effect of increasing/decreasing length and degree of unsaturation on the melting point of a fatty acid.
Saturated fatty acids have less kinks, allowing it to easily remain solid at higher temperatures. This means more unsaturation lowers the melting point.
As the chain length increases, melting point also increases.
As the chain length increases, melting point also increases.
10
New cards
Describe how double bonds affect the melting point of different fatty acids?
Melting point refers to how easy it is for fatty acids to "pack together," so if there are less "kinks" in the chain, it packs together more easily into a solid form.
11
New cards
What are the molecular components of a triacylglycerol? What bond connects them?
Three fatty acids all ester-linked to a glycerol.
12
New cards
Are triacylglycerols polar or nonpolar? Why?
Nonpolar. While glycerol has polar hydroxyls and the fatty acids have polar carboxyls, they are joined in ester linkages, rendering the molecule as a whole nonpolar and insoluble in water.
13
New cards
What is an adipocyte? What is an enzymatic component within adipocytes? What does that enzyme do?
A cell that specializes in storing fats. They usually contain LIPASES. Lipases catalyze hydrolysis of stored triacylglycerols.
14
New cards
What is the main function of triacylglycerols? What is a secondary function found in some animals?
Triacylglycerols are primarily for usage as stored fuel.
In some animals, they are used as cellular insulation. (E.g. "blubber" in seals, walruses, penguins, etc.)
In some animals, they are used as cellular insulation. (E.g. "blubber" in seals, walruses, penguins, etc.)
15
New cards
Name 2 advantages of using triacylglycerols as stored fuel instead of polysaccharides like glycogen or starch.
1) Fatty acid carbon atoms are more reduced than those in sugars, so upon oxidation, they release more energy gram for gram compared to sugars.
2) Triacylglycerols are hydrophobic. Because they do not dissolve in water, the cell does not have to push the "water-weight" associated with transporting soluble energy such as sugars.
In short: it's easier, faster, and releases more energy.
2) Triacylglycerols are hydrophobic. Because they do not dissolve in water, the cell does not have to push the "water-weight" associated with transporting soluble energy such as sugars.
In short: it's easier, faster, and releases more energy.
16
New cards
What occurs during hydrogenation of a fatty acid? Why is this done to commercially marketed fats?
Hydrogenation involves the conversion of cis-double-bonds to single bonds.
This is done commercially to prolong the shelf life of fats. Single bonds are much less susceptible to oxidation.
This is done commercially to prolong the shelf life of fats. Single bonds are much less susceptible to oxidation.
17
New cards
Describe biological waxes in terms of their molecular components.
Long chain saturated and unsaturated fatty acids ester linked to long chain alcohols.
18
New cards
What are some functions of biological waxes?
Waterproofing, insulation, structure, lubrication.
19
New cards
What is the key feature of all membrane lipids?
They are amphipathic.
20
New cards
What are the four general types of membrane lipids?
Phospholipids, glycolipids, archaeal tetraether lipids, and sterols.
21
New cards
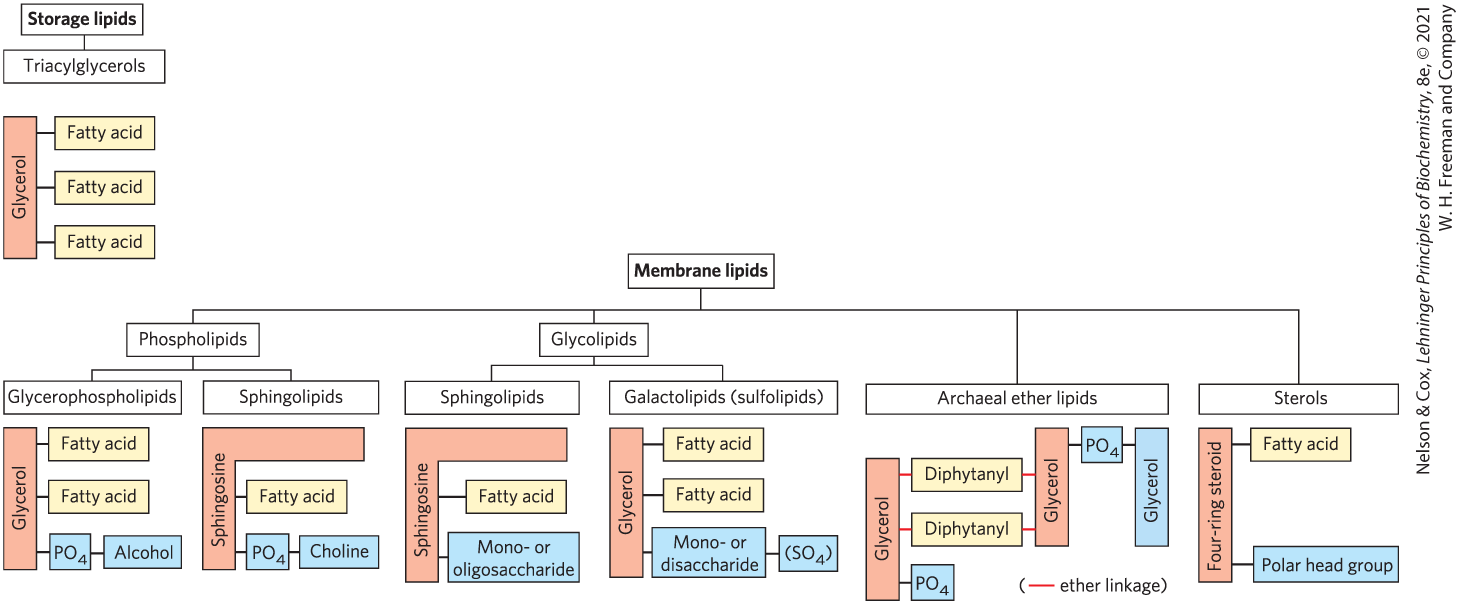
Describe the molecular components/bonds of:
Glycerophospholipids (also called phosphoglycerides)
Glycerophospholipids (also called phosphoglycerides)
Its backbone is glycerol; it contains
2 fatty acids, ester linked at C1, C2
1 phosphate head group + alcohol at C3 via phosphodiester bond
2 fatty acids, ester linked at C1, C2
1 phosphate head group + alcohol at C3 via phosphodiester bond
22
New cards
In a glycerophospholipids/phosphoglycerides, the phosphate group bears a ____ (negative/positive/neutral) charge at neutral pH.
Negative.
23
New cards
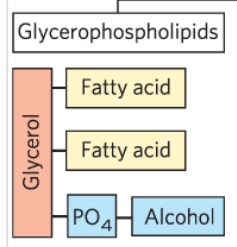
What is a plasmalogen?
A type of glycerophospholipid with an ether-linked chain and double bond between C1 and C2.
24
New cards
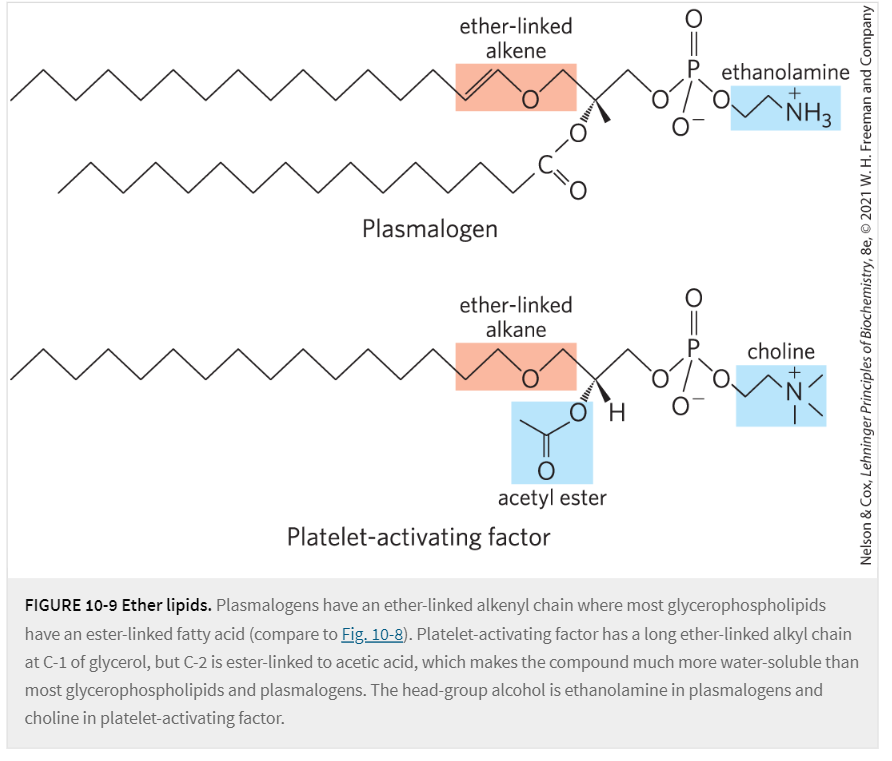
Describe the molecular components/bonds of:
Glycolipids (also called sulfolipids)
Glycolipids (also called sulfolipids)
Its backbone is glycerol; it contains
2 fatty acids, ester linked at C1, C2
1 mono/di-saccharide head group at C3 via glycosidic linkage
2 fatty acids, ester linked at C1, C2
1 mono/di-saccharide head group at C3 via glycosidic linkage
25
New cards
What is the most abundant membrane lipid in the biosphere?
Galactolipids; they are a type of glycolipid abundant in thylakoid membranes. They make up 70%-80% of the total membrane lipid content of vascular plants.
26
New cards
Describe the linkages within membrane lipids within some archaea living within ecological extremes.
In other words, how are their membranes so resistant to high temperature or low pH?
In other words, how are their membranes so resistant to high temperature or low pH?
They have their fatty acid chains linked via ETHER bond instead of ester bond; ether groups are much more resilient against hydrolysis at these ecological extremes.
27
New cards
Describe the molecular components/bonds of:
Sphingolipids
Sphingolipids
Sphingolipids are a subtype of both glycerophospholipids AND glycolipids.
Its backbone is sphingosine; it contains
1 long nonpolar chain (part of sphingosine)
1 (nonpolar) fatty acid chain
1 polar head group;
Head group is either a phosphate or sugar.
(attached via phosphodiester bond or glycosidic linkage)
Its backbone is sphingosine; it contains
1 long nonpolar chain (part of sphingosine)
1 (nonpolar) fatty acid chain
1 polar head group;
Head group is either a phosphate or sugar.
(attached via phosphodiester bond or glycosidic linkage)
28
New cards
Describe what makes a sphingolipid a ceramide.
When the fatty acid is attached to the sphingosine's C2 via amide linkage.
29
New cards
What are the functions of ceramides?
Regulation of protein kinases, cell division, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis.
30
New cards
What are the three subclasses of sphingolipids? What do all of them have in common, and where do they differ?
Sphingomyelins, glycosphingolipids, and gangliosides.
Common: All derivatives of ceramides.
Differ: Head groups
Common: All derivatives of ceramides.
Differ: Head groups
31
New cards
Describe sphingomyelins.
Out of the four general types of membrane lipids, which does this fall under?
Out of the four general types of membrane lipids, which does this fall under?
Sphingomyelins are sphingolipids, specifically ceramides, whose head groups are phosphocholine or phosphoethanolamine.
Sphingomyelins are phospholipids.
Sphingomyelins are phospholipids.
32
New cards
Describe glycosphingolipids
Out of the four general types of membrane lipids, which does this fall under?
Out of the four general types of membrane lipids, which does this fall under?
Glycosphingolipids are sphingolipids whose head groups are one or more saccharides connected directly to the C1-OH of the ceramide.
Glycosphingolipids are glycolipids because their head groups are sugars
Glycosphingolipids are glycolipids because their head groups are sugars
33
New cards
What are the two subtypes of glycosphingolipids called? What differentiates them?
Cerebrosides: One sugar head group.
Globosides: Two or more sugar head groups.
Globosides: Two or more sugar head groups.
34
New cards
Describe gangliosides.
Out of the four general types of membrane lipids, which does this fall under?
Out of the four general types of membrane lipids, which does this fall under?
Gangliosides are sphingolipids whose head groups are comprised of oligosaccharides with N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) at the ends.
35
New cards
What distinguishes gangliosides from globosides?
Gangliosides, due to their Neu5Ac end groups, are negatively charged at neutral pH.
Globosides are uncharged at neutral pH.
Globosides are uncharged at neutral pH.
36
New cards
What enzymes within the lysosome degrade glycerophospholipids?
Phospholipase A removes one fatty acid, degrading the glycerophospholipid into what is called a lysophospholipid.
Then, a lysophospolipase cleaves the remaining fatty acid
Then, a lysophospolipase cleaves the remaining fatty acid
37
New cards
sandpeanut jelly butterwich
38
New cards
Describe the molecular components/bonds of:
Sterols
Sterols
Sterols are characterized by the steroid nucleus, made up of four fused rings.
All sterols in eukaryotes are made from isoprene subunits.
Side groups are as follow:
Fatty acid chains attached at C17
Polar head group attached at C3
All sterols in eukaryotes are made from isoprene subunits.
Side groups are as follow:
Fatty acid chains attached at C17
Polar head group attached at C3
39
New cards
What are other functions of lipids, aside from structure and storage?
Signaling, acting as cofactors, becoming pigments.
40
New cards
What is PIP2? What is its function?
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate
Its function is to serve as a reservoir of signaling molecules.
Upon cleavage by phospholipase C, it yields signaling molecules.
Its function is to serve as a reservoir of signaling molecules.
Upon cleavage by phospholipase C, it yields signaling molecules.
41
New cards
What signal molecules does PIP2 release upon hydrolysis?
inositol 1,4,5 triphosphate (water soluble, travels)
diacylglycerol (remains membrane-associated)
diacylglycerol (remains membrane-associated)
42
New cards
What is PIP3? What is its function?
Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate
It serves as the nucleation point (beginning molecule) for supramolecular complexes of signaling proteins to form.
It serves as the nucleation point (beginning molecule) for supramolecular complexes of signaling proteins to form.
43
New cards
What is an eicosanoid? What are their general functions in the body?
Paracrine hormones; meaning a hormone that only acts on cells adjacent to the site of its synthesis.
They are involved in reproductive function, inflammation, fever, etc.
They are involved in reproductive function, inflammation, fever, etc.
44
New cards
What molecules are eicosanoids derived from? (hint: eikosi, Greek for "20")
Arachidonic acid, 20:4(Δ5,8,11,14)
Eicosapentaenoic acid, 20:5(Δ5,8,11,14,17)
Eicosapentaenoic acid, 20:5(Δ5,8,11,14,17)
45
New cards
What are the four major classes of eicosanoids?
prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, and lipoxins
46
New cards
Describe the characteristic molecular components of prostaglandins.
What are their functions?
What are their functions?
Prostaglandins are characterized by their 5-membered ring.
Their functions include:
uterus contraction during menstruation and labor,
blood flow to specific organs,
the wake-sleep cycle,
regulating responsiveness of certain tissues to hormones, elevation of body temperature
causation of inflammation and pain.
Their functions include:
uterus contraction during menstruation and labor,
blood flow to specific organs,
the wake-sleep cycle,
regulating responsiveness of certain tissues to hormones, elevation of body temperature
causation of inflammation and pain.
47
New cards
Describe the characteristic molecular components of thromboxanes.
What are their functions? (hint: what are they produced by?)
What are their functions? (hint: what are they produced by?)
Thromboxanes are characterized by their 6-membered ring containing an ether.
Produced by thrombocytes (blood platelets)
Their functions include:
formation of blood clots and reduction of blood flow to the site of a clot.
Produced by thrombocytes (blood platelets)
Their functions include:
formation of blood clots and reduction of blood flow to the site of a clot.
48
New cards
Describe the characteristic molecular components of leukotrienes.
What are their functions?
What are their functions?
Leukotrienes are characterized by their linear chain with 3 conjugated double bonds.
Their functions include:
contraction of smooth muscle (leukotrienes are the cause for asthmatic attacks)
Their functions include:
contraction of smooth muscle (leukotrienes are the cause for asthmatic attacks)
49
New cards
Describe the characteristic molecular components of lipoxins.
What are their functions?
What are their functions?
Lipoxins are characterized by their linear chain containing hydroxyl groups.
Their functions include:
Anti-inflammation response
Their functions include:
Anti-inflammation response
50
New cards
What is a steroid?
A derivative of sterols, they are potent hormones related to molecular signaling.
51
New cards
What are the two classes of vitamins?
Give an example of some from each class?
Give an example of some from each class?
Water Soluble: B, C
Fat Soluble: A, D, E, and K
Fat Soluble: A, D, E, and K
52
New cards
Vitamin D:
What is it commonly called?
Describe its function.
What does deficiency cause?
What is it commonly called?
Describe its function.
What does deficiency cause?
Name: D3; Cholecalciferol, D2; Ergocalficerol
Function: Involved in the regulation of calcium uptake and levels in the intestines, kidneys, and bone.
Deficiency causes defective bone formation.
Used as a dietary supplement in dairy
Function: Involved in the regulation of calcium uptake and levels in the intestines, kidneys, and bone.
Deficiency causes defective bone formation.
Used as a dietary supplement in dairy
53
New cards
Vitamin A:
What is it commonly called?
Describe its function.
Describe the function of its derivatives.
What does deficiency cause?
What is it commonly called?
Describe its function.
Describe the function of its derivatives.
What does deficiency cause?
Name: A1; all-trans-retinol/b-carotene
Functions: cell development, growth, differentiation, and vision.
Derivative: regulation of gene expression for embryonic development, stem cell differentiation, and proliferation
Deficiency causes dry skin, dry eyes, night blindness, and in pregnant women causes growth problems and congenital malformations.
Functions: cell development, growth, differentiation, and vision.
Derivative: regulation of gene expression for embryonic development, stem cell differentiation, and proliferation
Deficiency causes dry skin, dry eyes, night blindness, and in pregnant women causes growth problems and congenital malformations.
54
New cards
What are carotenoids?
Where are they found?
What vitamin do they contain?
Where are they found?
What vitamin do they contain?
Carotenoids are compounds produced in nature characterized by their extensive conjugated double bond systems, which contributes to its high absorption of visible light, lending to its vibrant color.
They are found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and other yellow vegetables.
They contain b-carotene, which is a form of vitamin A.
They are found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and other yellow vegetables.
They contain b-carotene, which is a form of vitamin A.
55
New cards
Vitamin E:
What are its characteristic features?
Describe its function.
Describe the function of its derivatives.
What does deficiency cause?
What are its characteristic features?
Describe its function.
Describe the function of its derivatives.
What does deficiency cause?
Vitamin E refers to a group of lipids called tocopherols which contain a substituted aromatic ring and a long isoprenoid chain
Functions: biological antioxidant. destroys free reactive oxygen species; prevents oxidative damage.
Deficiency causes scaly skin, weakness, and sterility.
Functions: biological antioxidant. destroys free reactive oxygen species; prevents oxidative damage.
Deficiency causes scaly skin, weakness, and sterility.
56
New cards
What isoprenoid compounds function as lipophilic electron carriers that drive redox reactions related to ATP synthesis?
Ubiquinone (mitochondria) and plastoquinone (chloroplast).
57
New cards
What is a dolichol?
A dolichol is an isoprenoid alcohol that are strongly associated to membrane lipids. They are involved with the attachment of sugar units to lipids or proteins.
58
New cards
Lipids containing which linkages can be hydrolyzed?
Treatment with what leads to hydrolysis?
Treatment with what leads to hydrolysis?
Lipids containing ester or amide linked fatty acids can be hydrolyzed utilizing acid, base, or enzymes.
Hydrolysis yields the lipid's individual components which can then be analyzed.
Hydrolysis yields the lipid's individual components which can then be analyzed.
59
New cards
Neutral lipids are readily extracted by:
nonpolar organic solvents.
Examples include ethyl ether, chloroform, or benzene.
Examples include ethyl ether, chloroform, or benzene.
60
New cards
Membrane lipids are readily extracted by:
polar organic solvents.
Examples include ethanol or methanol.
Examples include ethanol or methanol.
61
New cards
What mixture does experimental extraction of lipids usually use?
1 : 2 : 0.8 of chloroform : methanol : water
62
New cards
What are 5 methods of lipid analysis?
(Hint: 3 are types of chromatography)
(Hint: 3 are types of chromatography)
Adsorption chromatography (HPLC)
Thin-plate chromatography
Gas chromatography
Specific Hydrolysis
Mass spectrometry
Thin-plate chromatography
Gas chromatography
Specific Hydrolysis
Mass spectrometry
63
New cards
Describe adsorption chromatography relating to the separation of lipids.
1. Silica gel is used (insoluble, polar) within the column
2. A lipid solution is run through the column;
polar lipids will bind to the silica
nonpolar lipids will pass through
Then, the columns are eluted with solvents of increasing polarity.
1. First wash: chloroform (nonpolar lipids elute)
2. Second wash: slightly polar solvent (slightly polar solvents elute)
Each successive wash, lipids of higher polarity are eluted with their respective solvents.
2. A lipid solution is run through the column;
polar lipids will bind to the silica
nonpolar lipids will pass through
Then, the columns are eluted with solvents of increasing polarity.
1. First wash: chloroform (nonpolar lipids elute)
2. Second wash: slightly polar solvent (slightly polar solvents elute)
Each successive wash, lipids of higher polarity are eluted with their respective solvents.
64
New cards
What solute elutes cerebrosides within adsorption chromatography?
Cerebrosides are eluted with acetone.
65
New cards
Describe thin-layer chromatography relating to the separation of lipids.
1. A thin layer of silicic acid (polar) is spread on a glass plate.
2. Lipid samples are spotted at one end of the plate.
3. A nonpolar, organic solvent is used to elute the lipids.
The most nonpolar lipids elute the furthest, b/c they don't bind to the silicic acid and prefer the nonpolar solvent more.
2. Lipid samples are spotted at one end of the plate.
3. A nonpolar, organic solvent is used to elute the lipids.
The most nonpolar lipids elute the furthest, b/c they don't bind to the silicic acid and prefer the nonpolar solvent more.
66
New cards
Describe gas chromatography relating to the separation of lipids.
Utilizes the volatile properties of some lipid derivatives to separate them. Most lipids require transesterification to produce derivatives that are in more volatile forms.
Similar to the principles of adsorption chromatography;
The order of elution depends on the nature of the solid adsorbent in the column and on the boiling point of the components of the lipid mixture.
Similar to the principles of adsorption chromatography;
The order of elution depends on the nature of the solid adsorbent in the column and on the boiling point of the components of the lipid mixture.
67
New cards
Describe specific hydrolysis. What is its purpose?
Specific hydrolysis is performed to determine a lipid's structure.
Essentially this process utilizes acid, base, and enzymes to cleave lipid bonds to yield their individual components.
These components can then be isolated using chromatography techniques to determine a lipid's makeup.
Essentially this process utilizes acid, base, and enzymes to cleave lipid bonds to yield their individual components.
These components can then be isolated using chromatography techniques to determine a lipid's makeup.
68
New cards
Ester linked fatty acids are hydrolyzed by
mild acid or mild base
69
New cards
Amide linked fatty acids are hydrolyzed by
harsh hydrolysis conditions
70
New cards
Describe mass spectrometry. What is its purpose?
Mass spectrometry reveals a lipid's complete structure. It is usually performed following chromatography on individual lipid components.
71
New cards
What is the "shotgun method" of lipid separation?
It avoids fractionation of a lipid and utilizes very modern high-resolution spectrometry technologies to identify components of a mixture without separating them all first.