chapter 6 the importance of cells 1
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
all cells are related by their? IDK
descent from earlier cells
(idk if this is still right)
all organisms are made of ____, the ____ collection of matter that can support ____.
cell ____ is correlated to cellular ____
cells; simplest; life
structure; function
all organisms are made of cells except for:
viruses and prions
biologists use ____ and the tools of ____ to study cells
microscopes; biochem
cells are extremely ____ although they are usually too ____ to be seen by the ____
complex; small; naked eye
scientists use ____ to visualize cells too small to be seen with the ____
microscopes; naked eye
how do light microscopes (LM) work?
visible light passes thru specimen + glass lenses, which magnify image
the minimum resolution of LMs is about 200 nm, the size of:
a small bacterium
what are our biggest cells?
nerve cells (neurons)
LMs can magnify to about ____ times the size of the actual specimen
1000
various techniques enhance ____ and enable cell components to be ____ or ____
contrast; stained; labeled
most subcellular structures (______) are too _____ to be resolved by a LM
organelles; small
a _____, ____ microscope is most commonly used in teaching + research labs. how does total magnification work?
compound, optical
o Eyepiece: 10x
o Objective: 4x, 10x, 40x, maybe 100x
o Total Mag: 40x, 100x, 400x, maybe 1000x
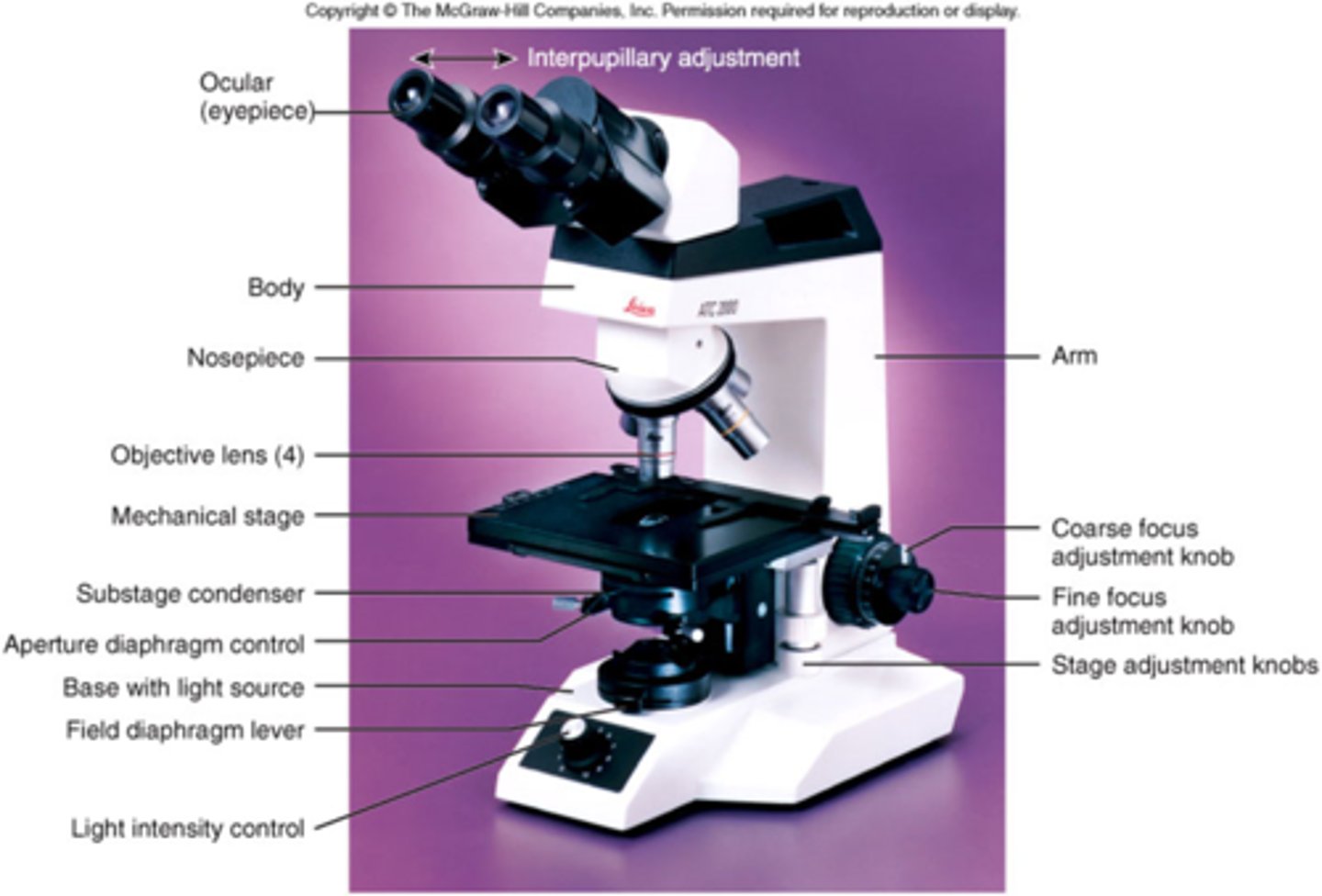
3 techniques to enhance contrast via staining
1. brightfield (unstained specimen)
2. brightfield (stained specimen)
- what we use
3. phase-contrast
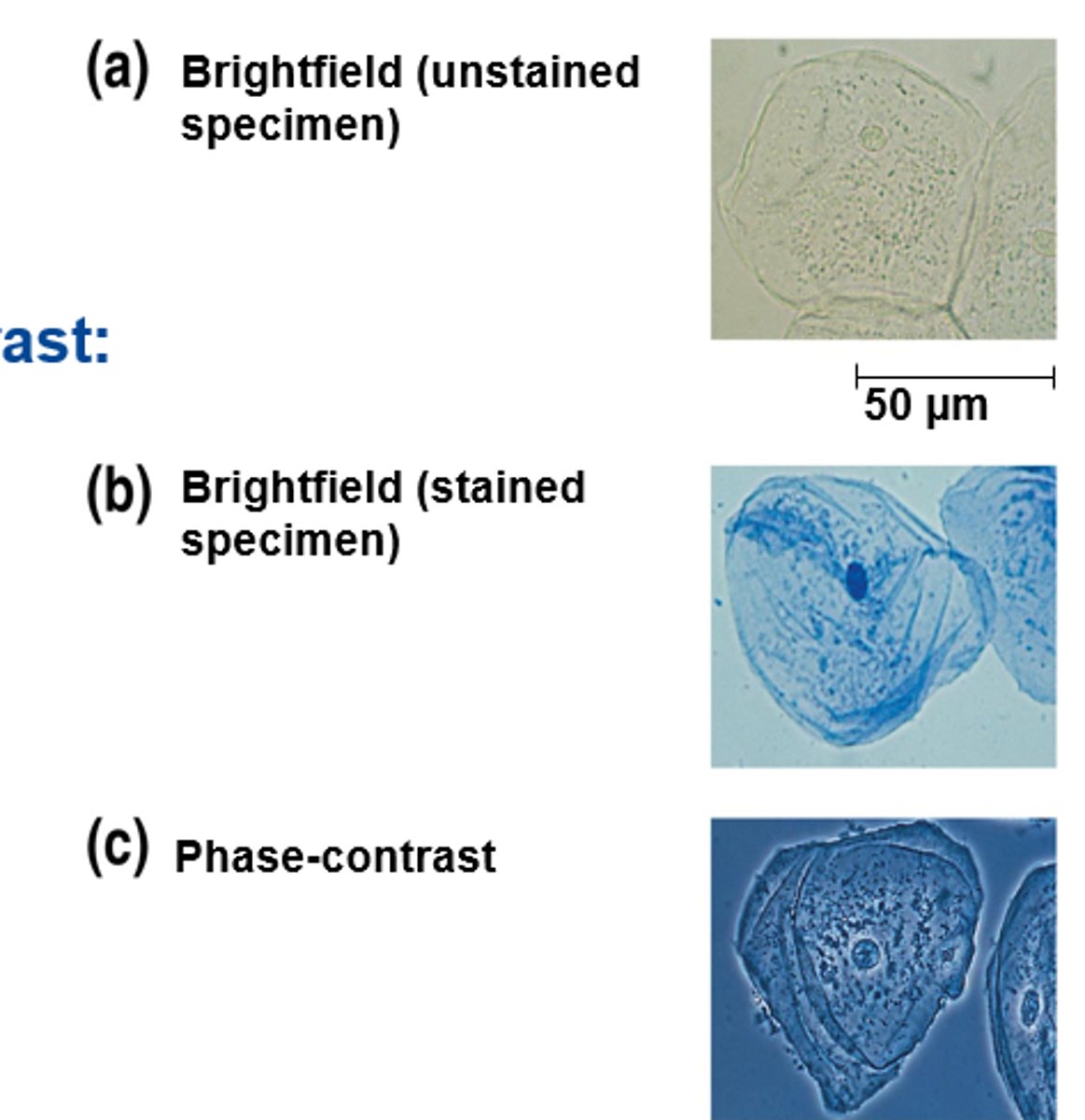
3 techniques to enhance contrast via labeling cellular components for visualization
1. differential-interference-contrast
2. fluorescence
3. confocal
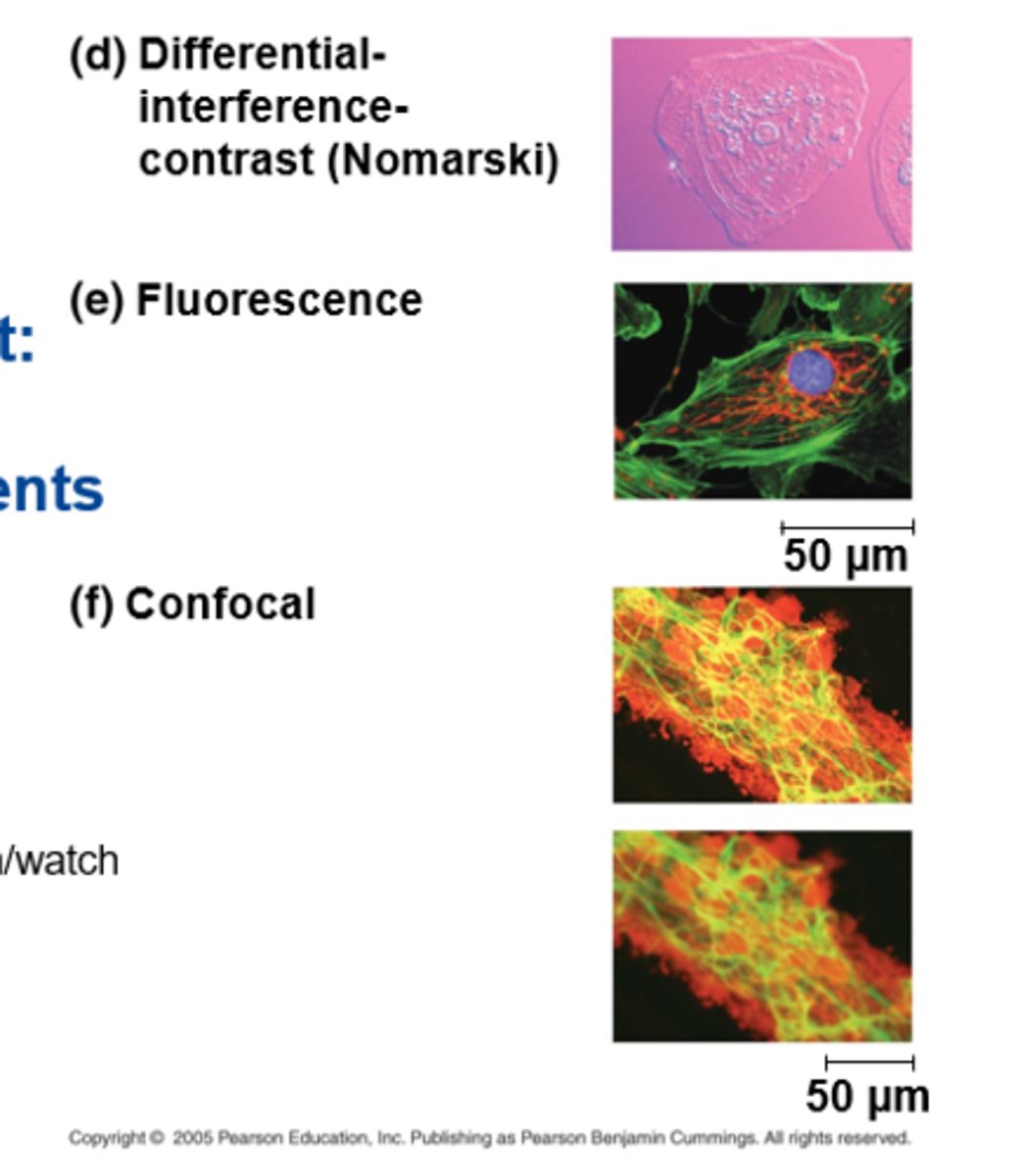
what are electron microscopes used to study?
VERY SMALL particles or cell organelles
electron microscopes (EMs) are used to study:
subcellular structures
2 basic types of electron microscopes
1. scanning electron (SEMs)
- focus electron beam onto surface of specimen, providing images that look 3D
-- scans surface of cell
2. transmission electron (TEMs)
- focus electron beam thru specimen to study internal ultrastructure of cells
what types of microscopes would you use to visualize:
1. human/eukaryotic cell
2. bacterial/prokaryotic cell
3. virus
4. protein
1. light
2. light + electron
3. electron
4. even smaller than electron bc they make viruses
one biochemical technique to study cells is:
isolating organelles by cell fractionation
what does cell fractionation do? what does it enable scientists to do?
takes cells apart + separates major organelles from each other
- enables scientists to determine organelle functions
what do ultracentrifuges do?
fractionate cells into their component parts
what force does cell fractionation use?
centrifugal
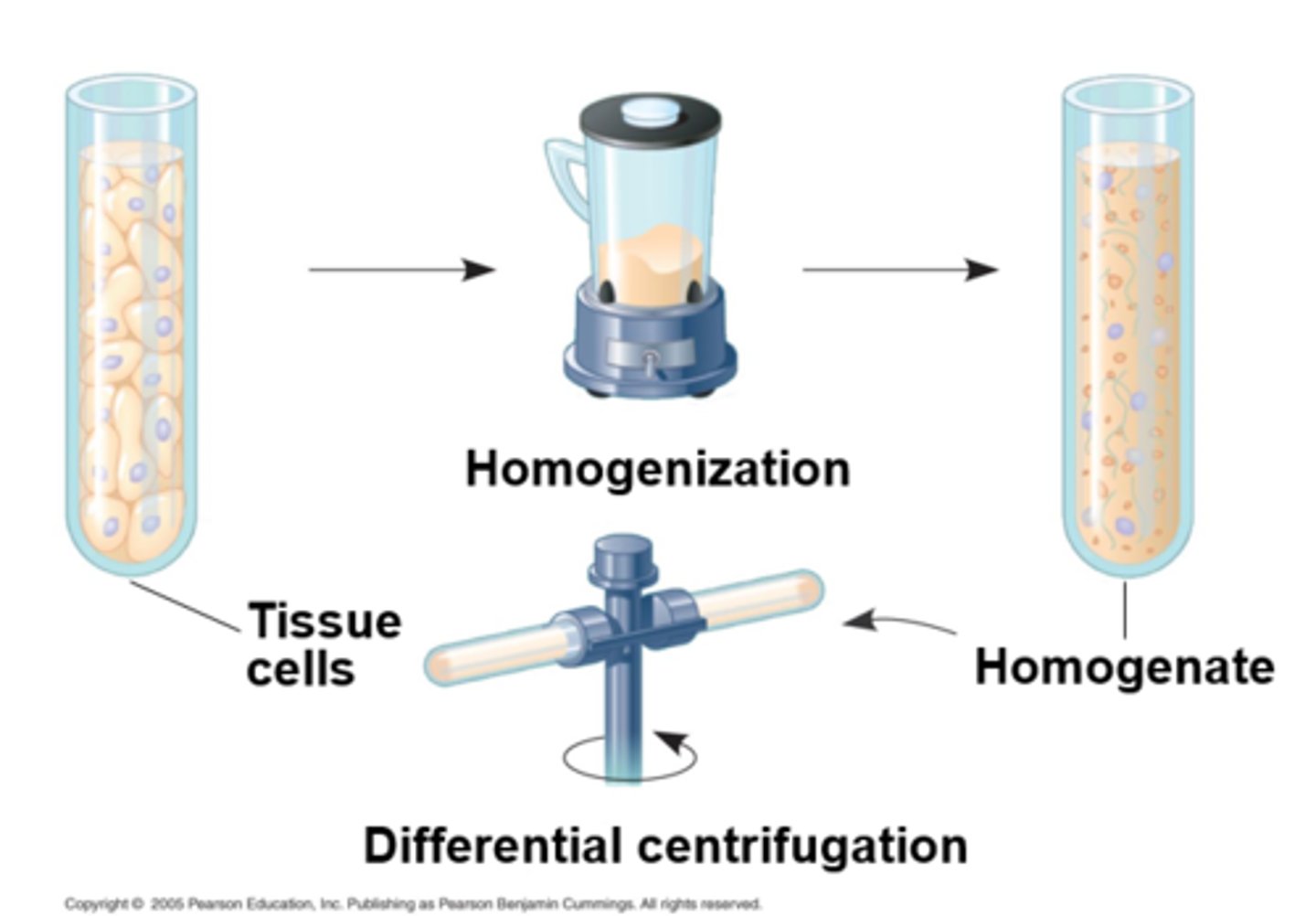
ultracentrifuges fractionate ____ from a ___ ___
organelles; cellular extract

eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that ____ their ___.
they also partition the cell into ____
compartmentalize; functions; organelles
the basic structural and functional unit of every organism is one of two cells:
prokaryotic or eukaryotic
only organisms of the domains _____ and ___ consist of prokaryotic cells
bacteria; archaea
(4) consist of eukaryotic cells
1. protists
2. fungi
3. animals
4. plants
4 basic features of both pro and eukaryotic cells (all cells)
1. plasma membrane
2. cytosol (semifluid substance)
3. chromosomes (carry genes)
4. ribosomes (make proteins)
3 aspects of prokaryotic cells
1. no nucleus
2. DNA in nucleoid (unbound region)
3. no membrane bound organelles
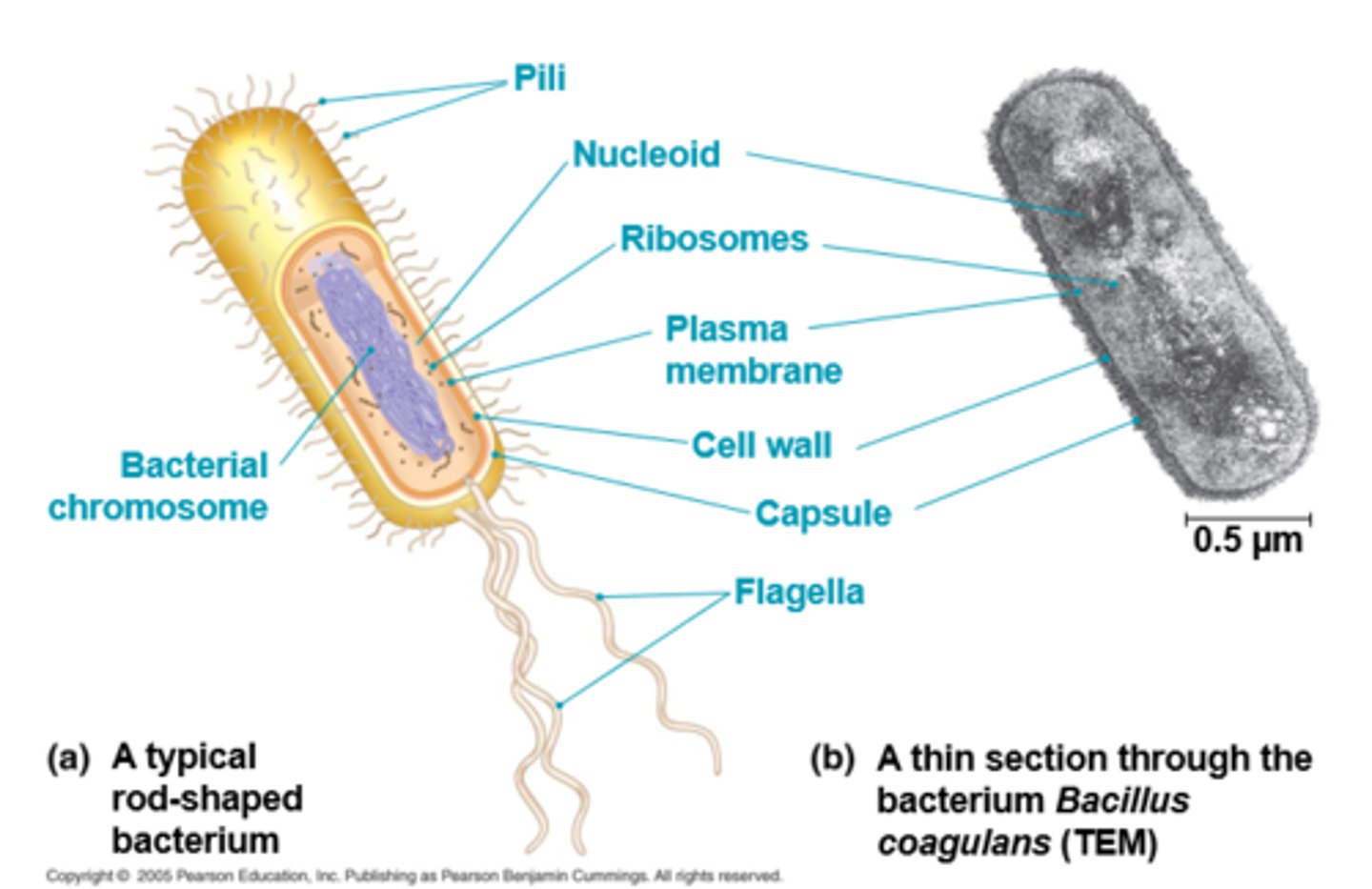
3 aspects of eukaryotic cells
1. DNA in nucleus bounded by nuclear envelope
2. larger than pro
3. membrane bound organelles
the logistic of carrying out ____ sets limits on cell ____
cellular metabolism; size
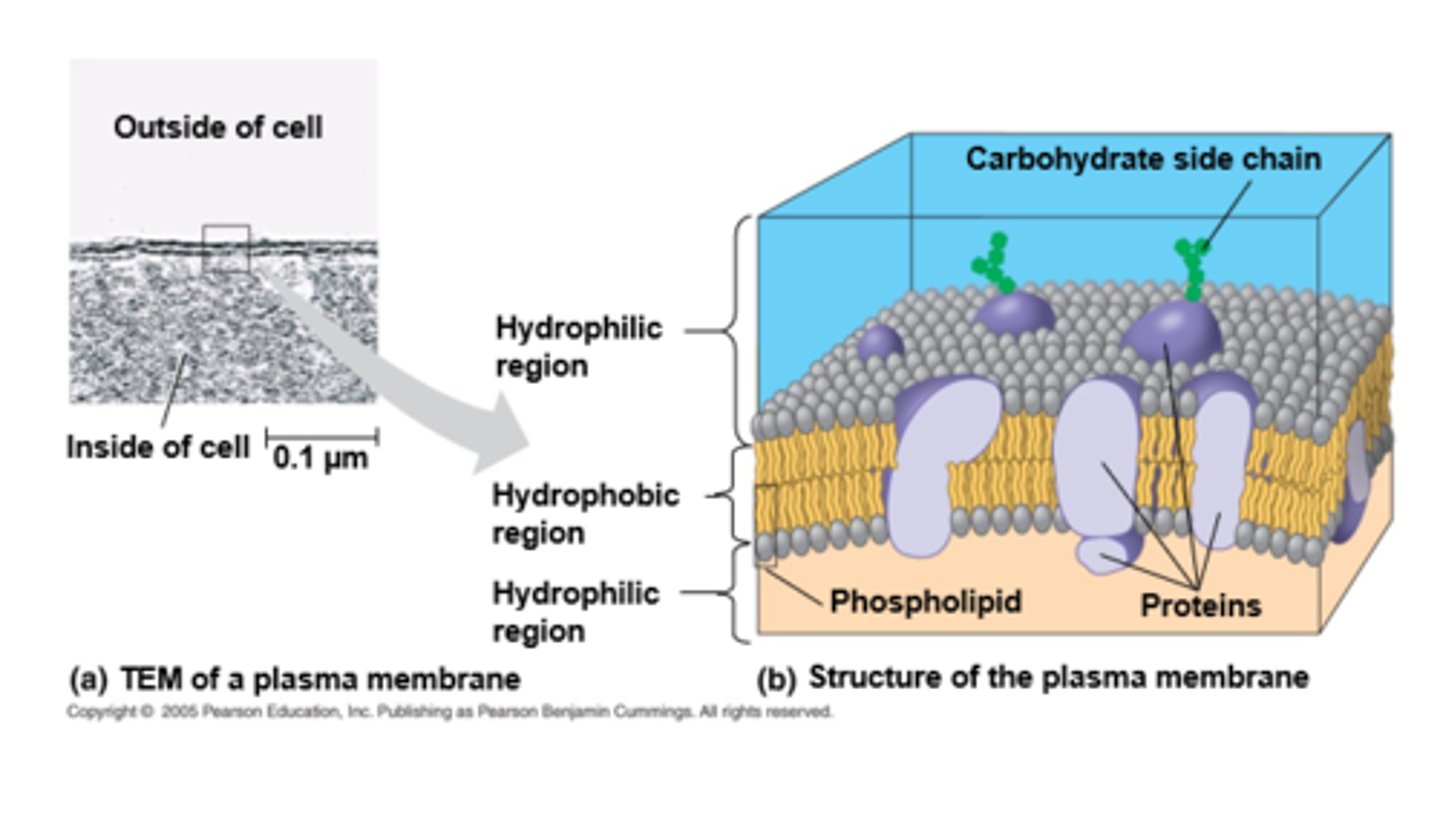
what is the plasma membrane?
selective/semipermeable barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, & waste to service volume of cell
the general structure of a biological membrane is _____. what does this allow for?
a double layer of phospholipids; inside and outside of cell
pro vs eukaryotic cells
pro (before nucleus)
- singular circular chromosome
- include bacteria
- flagella for movement (allow 4 invasive infections
- super old/simple
- UNICELLULAR but can form biofilms
eu (true nucleus)
- 46 chromosomes (23 from each parent)
- membrane bound organelles
how does alcohol kill cells?
when you make drugs what should you watch out for?
strip lipids
antibiotic resistance + killing normal flora causes superinfections
why are carbohydrate side chains important?
are antigens that give cells identity
- how ur body knows ur cells r urs vs bacteria
- how sperm find eggs
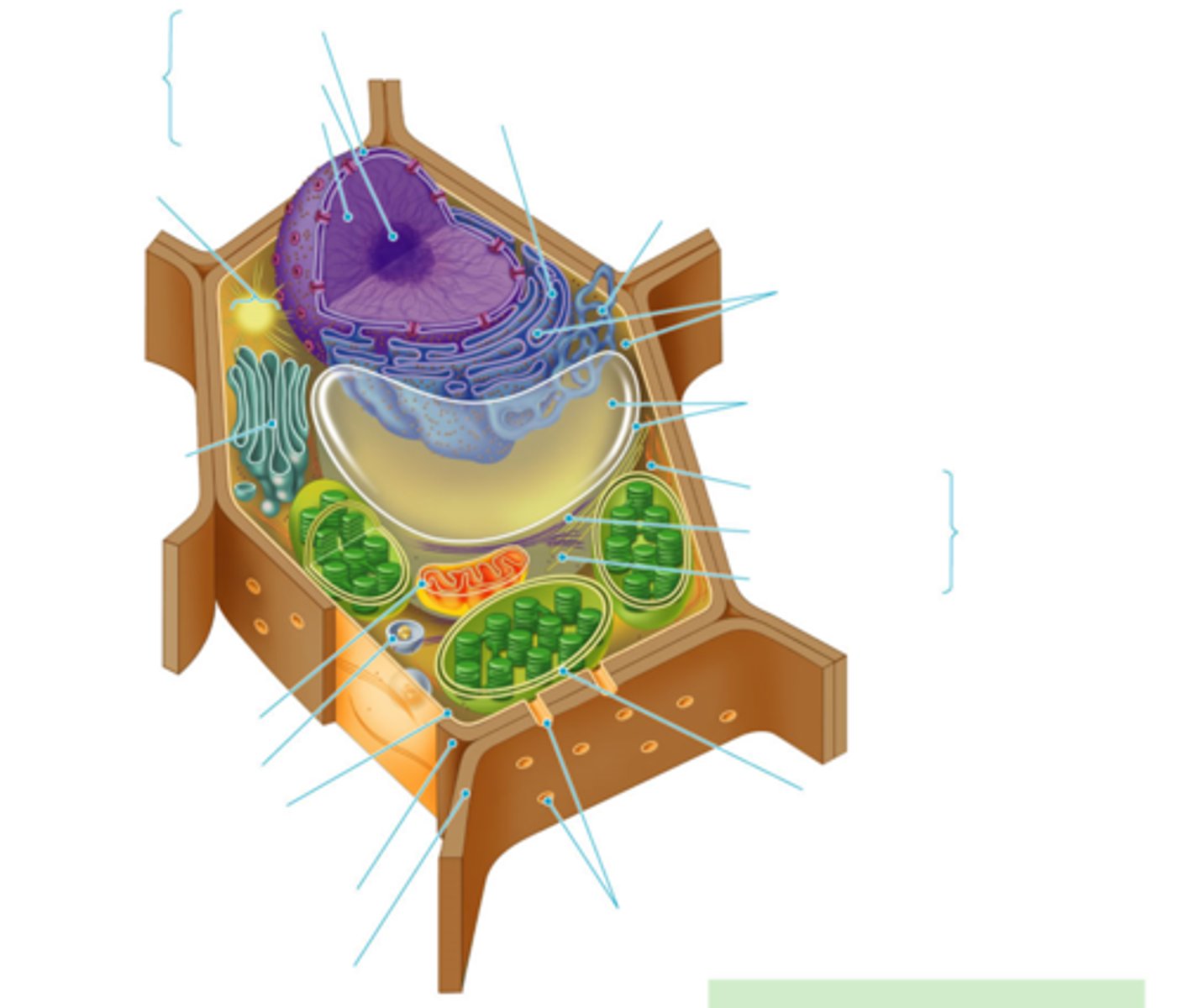
plant + animal cells have most of the same:
organelles
3 things animal cells have that plant cells don't
1. lysosomes
2. centrioles
3. flagella
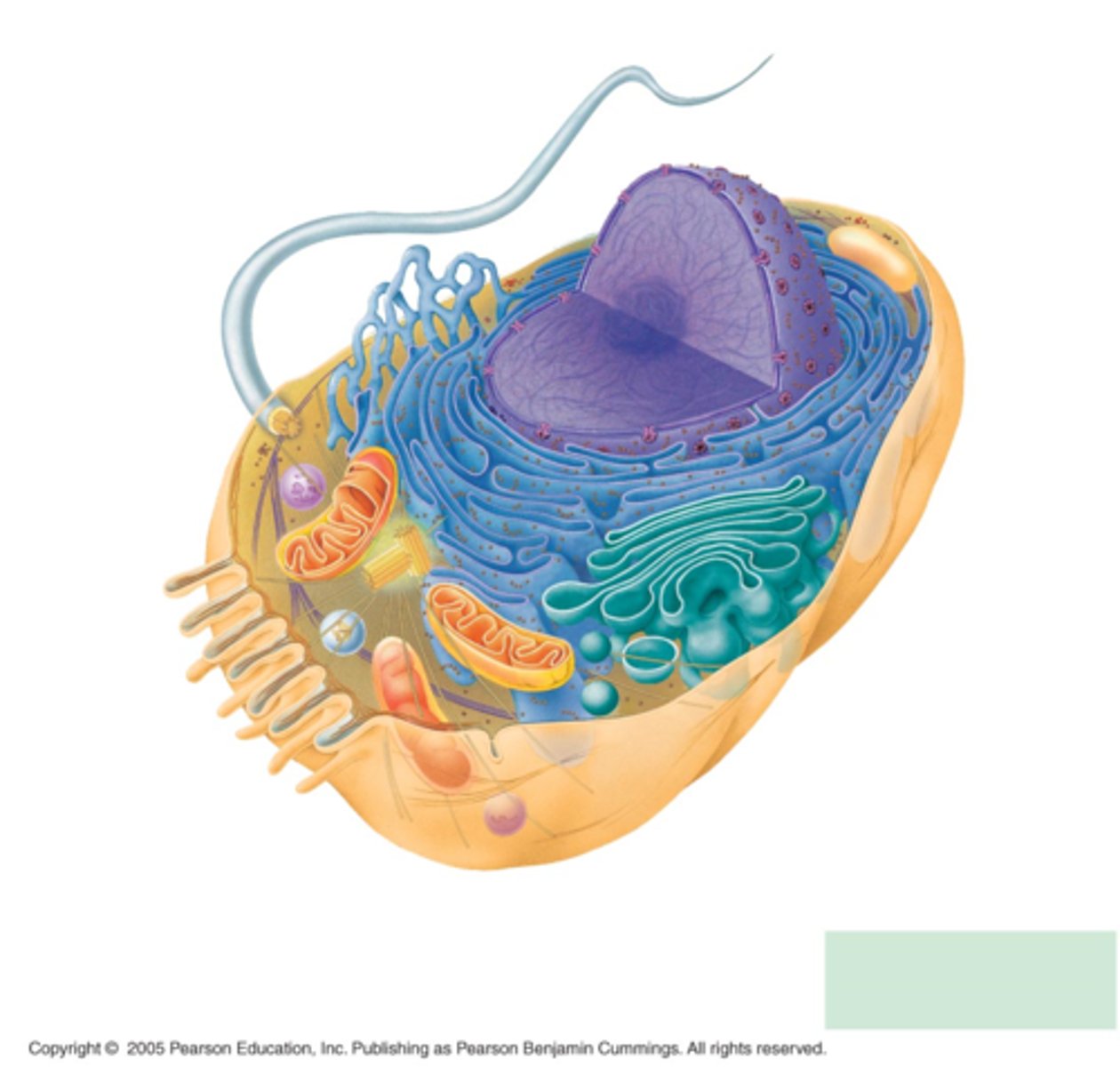
5 things plant cells have that animal cells don't
1. chloroplasts
2. central vacuole
3. tonoplast
4. cell wall
- made of cellulose we can't digest but helps digestion
5. plasmodesmata
the eukaryotic cell's genetic instructions are housed in the ____ and carried out by the ___
nucleus; ribosomes
the nucleus contains most of a eukaryotic cell's _____ and the ribosomes use the ____ from this to make ____
DNA; information; proteins
the ______ contains most of the cell's genes and is usually the most ___ organelle
nucleus; conspicuous
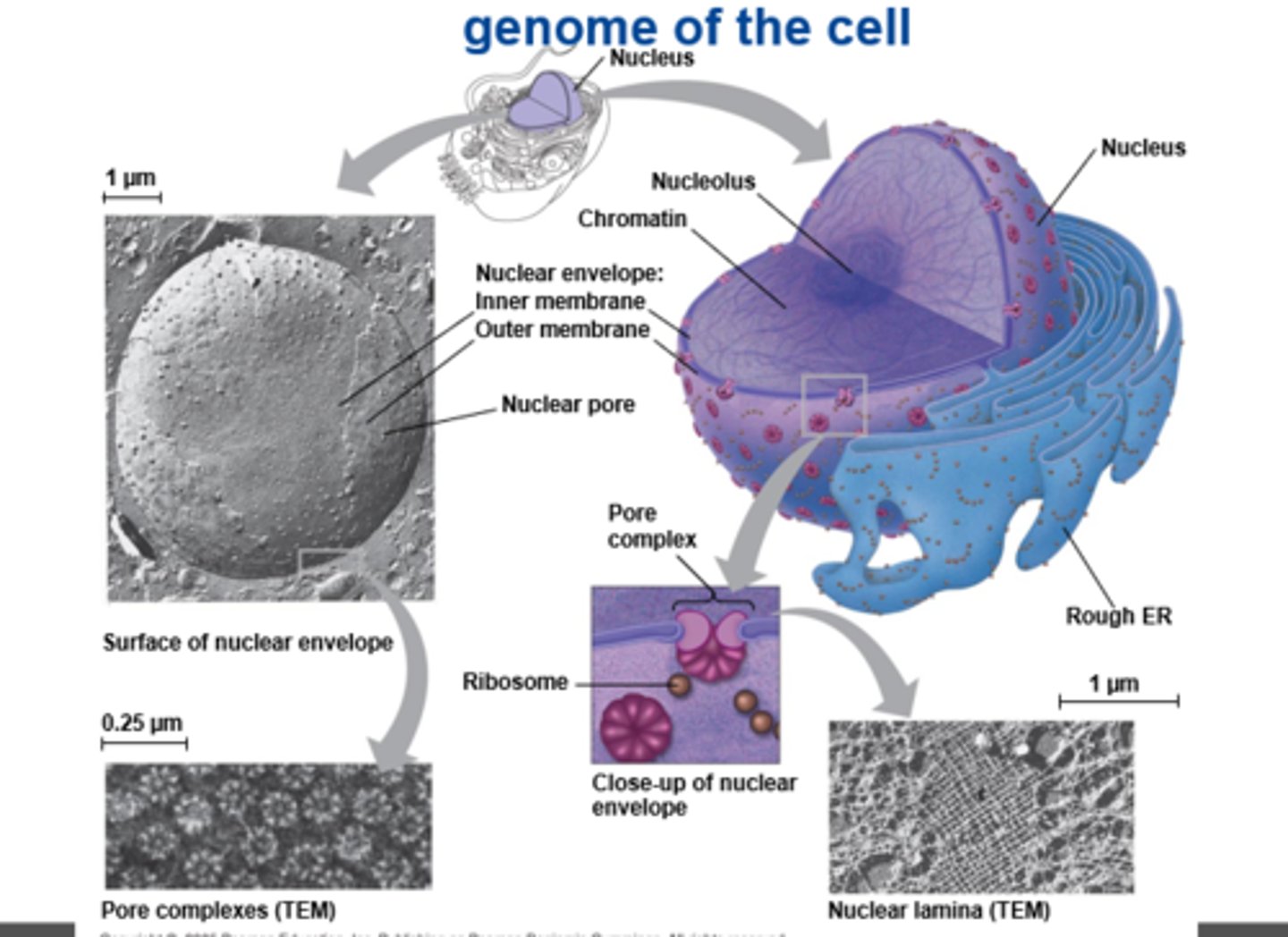
the ____ encloses the nucleus, separating it from the ____
nuclear envelope; cytoplasm
central dogma of biology
DNA to RNA (transcription)
RNA to protein translation)
ribosomes are particles made of (2)
1. ribosomal RNA
2. protein
ribosomes carry out protein synthesis in 2 locations:
1. cytosol (free ribosomes)
2. outside ER or nuclear envelope (bound ribosomes)
3 types of RNA
1. messenger RNA
2. ribosomal RNA
3. transfer RNA
how do ribosomes make proteins?
read RNA
the endomembrane system regulates _____ and performs ____ in the cell
protein traffic; metabolic functions
7 components of the endomembrane system
1. nuclear envelope
2. endoplasmic reticulum
3. golgi apparatus
4. lysosomes
5. vacuoles
6. vesicles
7. plasma membrane
components of the endomembrane system are ____ of the cell composed of a ____ that do what?
regions; membrane; transport things btwn diff cell compartments
the plasma membrane encases the ____ and contains the ___ holding all of the ____
entire cell; cytoplasm; organelles
endomembrane system components are either ____ or ____ via ____
continuous; connected; transfer by vesicles
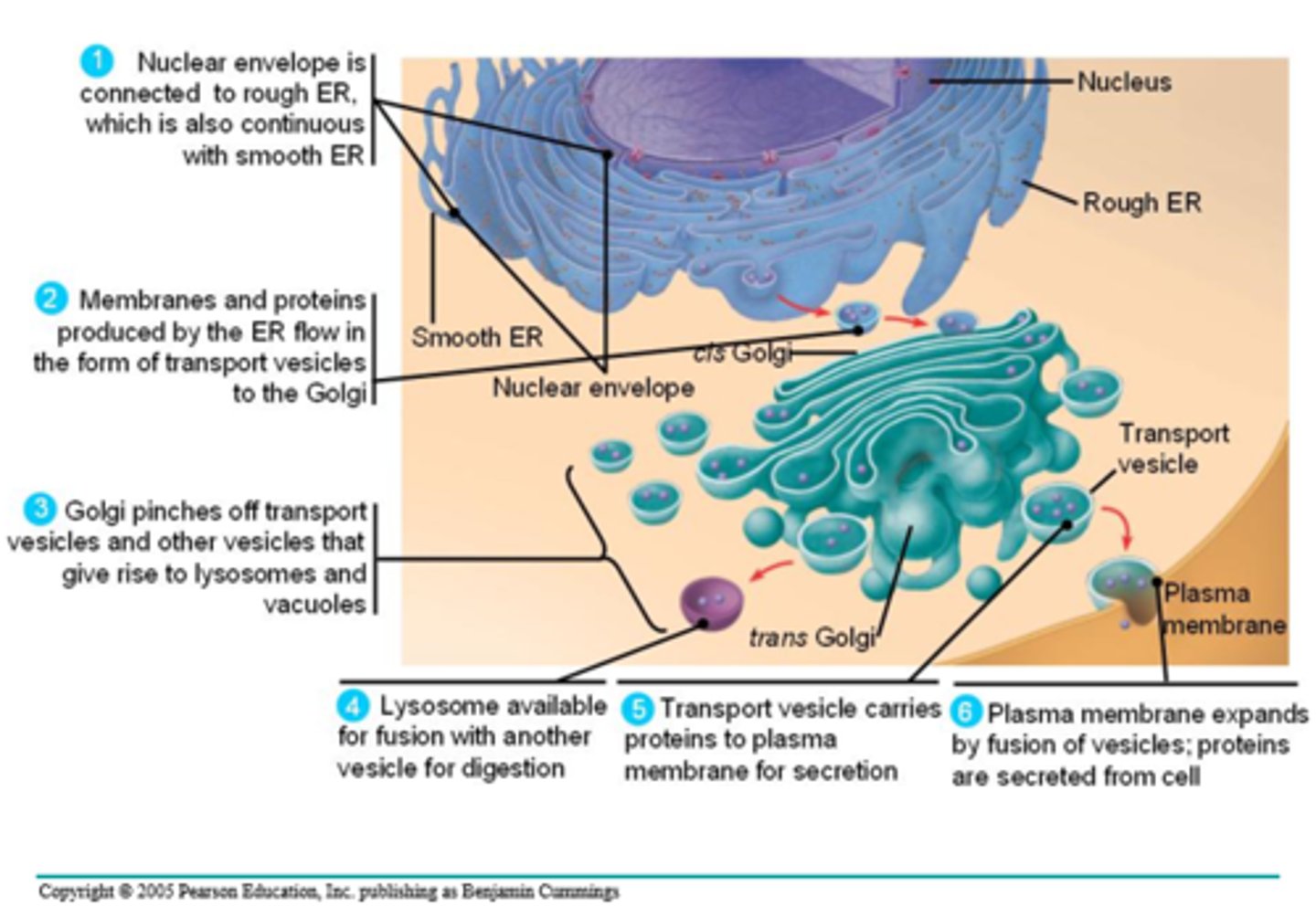
explain 6 parts of the endomembrane system
1. nuclear envelope connected to rough ER, which is continuous with smooth ER
2. membranes + proteins produced by ER flow in transport vesicles to golgi
3. golgi pinches off transport vesicles + vesicles that become lysosomes/vacuoles
4. lysosome available for fusion w/another vesicle for digestion
5. transport vesicle carries proteins to plasma mem for secretion
6. plasma mem expands by vesicle fusion + proteins r secreted
how are proteins made?
1. DNA in nucleus holds cell directions
2. mRNA starts in nucleus bc DNA can't leave
3. mRNA leaves thru nuclear pores into rough ER
4. ribosomes here turn RNA into proteins
cells can either make proteins for itself or send it elsewhere. what are examples of each?
keep: myosin + actin used for muscle contraction
sent: antibodies + mucous sent to battle disease
ur rate of protein production is limited by?
the food u eat
what is the biosynthetic factory?
endoplasmic reticulum
the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) accounts for more than ____ of the total membrane in many ____ cells
half; eukaryotic
the ER membrane is continuous with the ____
nuclear envelope
4 functions of smooth ER
1. synthesizes lipids
2. metabolizes carbs
3. stores calcium
4. detoxifies poison
2 functions of rough ER
1. produces proteins + membranes
2. membrane factory for cell
the rough ER produces proteins and membranes which are distributed by:
transport vesicles
how are the rough ER and smooth ER related?
rough ER makes proteins
smooth ER refines them
the rough ER receives stuff from the ____.
nucleus
ribosomes diff btwn rough and smooth ER
rough: ribosomes bind to/stud its surface
smooth: lacks ribosomes
what part of your body has the most smooth ER?
the liver
the golgi apparatus is like a ____/____ _____ and consists of what?
shipping/receiving center (UPS)
flattened membranous sacs (cisternae)
3 functions of golgi
1. modifies products of the ER (proteins
- post-translational protein modifications are performed in cisternae
2. manufactures certain macros
3. sorts/packages materials into transport vesicles
what are the two faces of the golgi apparatus?
1. cis "receiving"
2. trans "shipping"
what is a cistern? how is this related to the cisternae of the golgi?
cistern: big holding container
rough ER send protein vesicles to cisternae: which hold + modify proteins
lysosomes (____) is a membranous ____ of ____
(digestive compartments); sac; hydrolytic enzymes
hydrolytic enzymes perform ______. lysosomes technically perform a form of _____
hydrolysis; digestion
why are vesicles important for lysosomes?
don't want digestive enzymes outside of vesicles bc they can be harmful
what can lysosomal enzymes do?
hydrolyze proteins, fats, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids
what process can lysosomes do?
digest material taken into cell from outside via phagocytosis
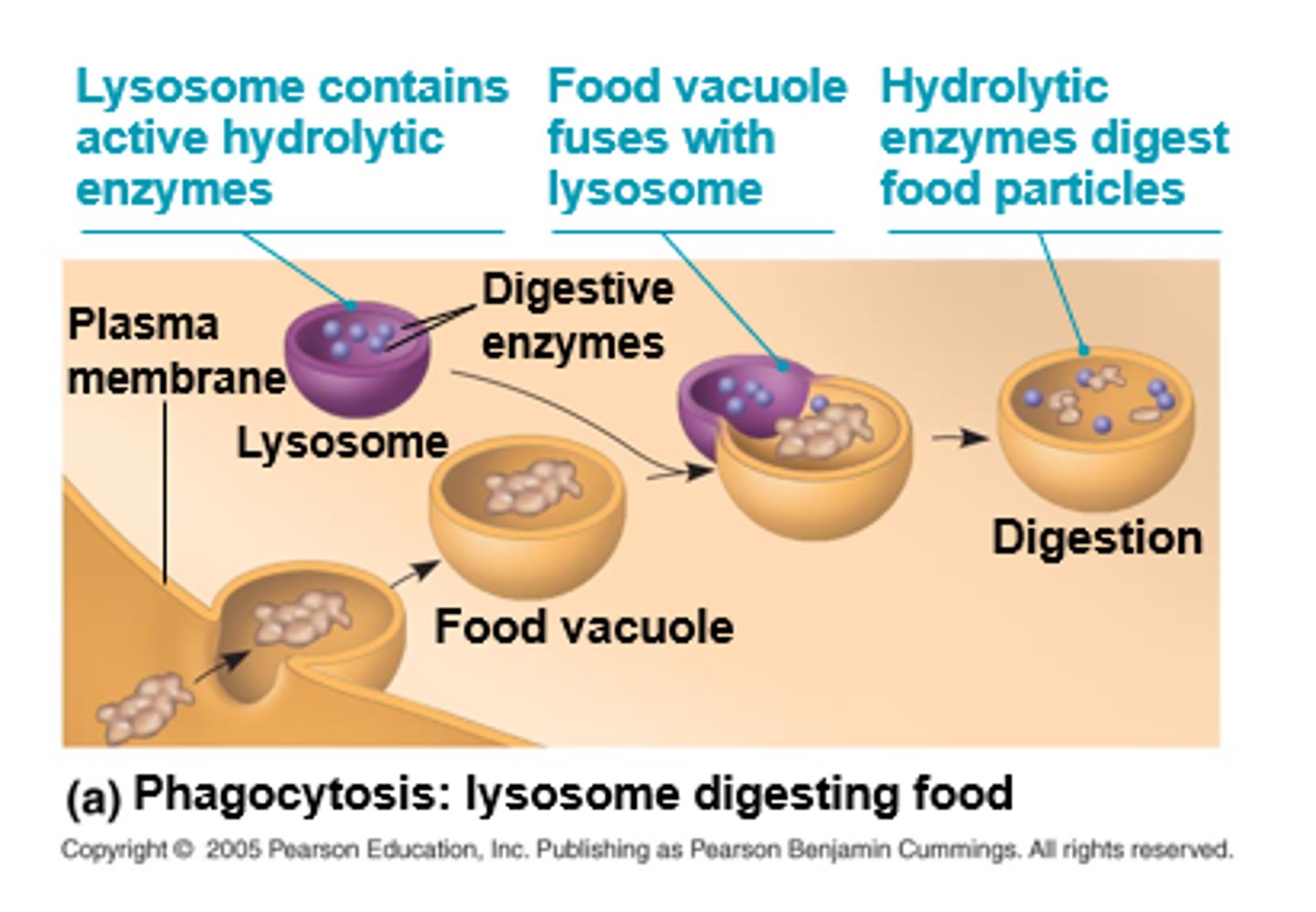
what is the 2nd function of lysosomal enzymes?
recycle organelles + macromolecules within a cell via autophagy
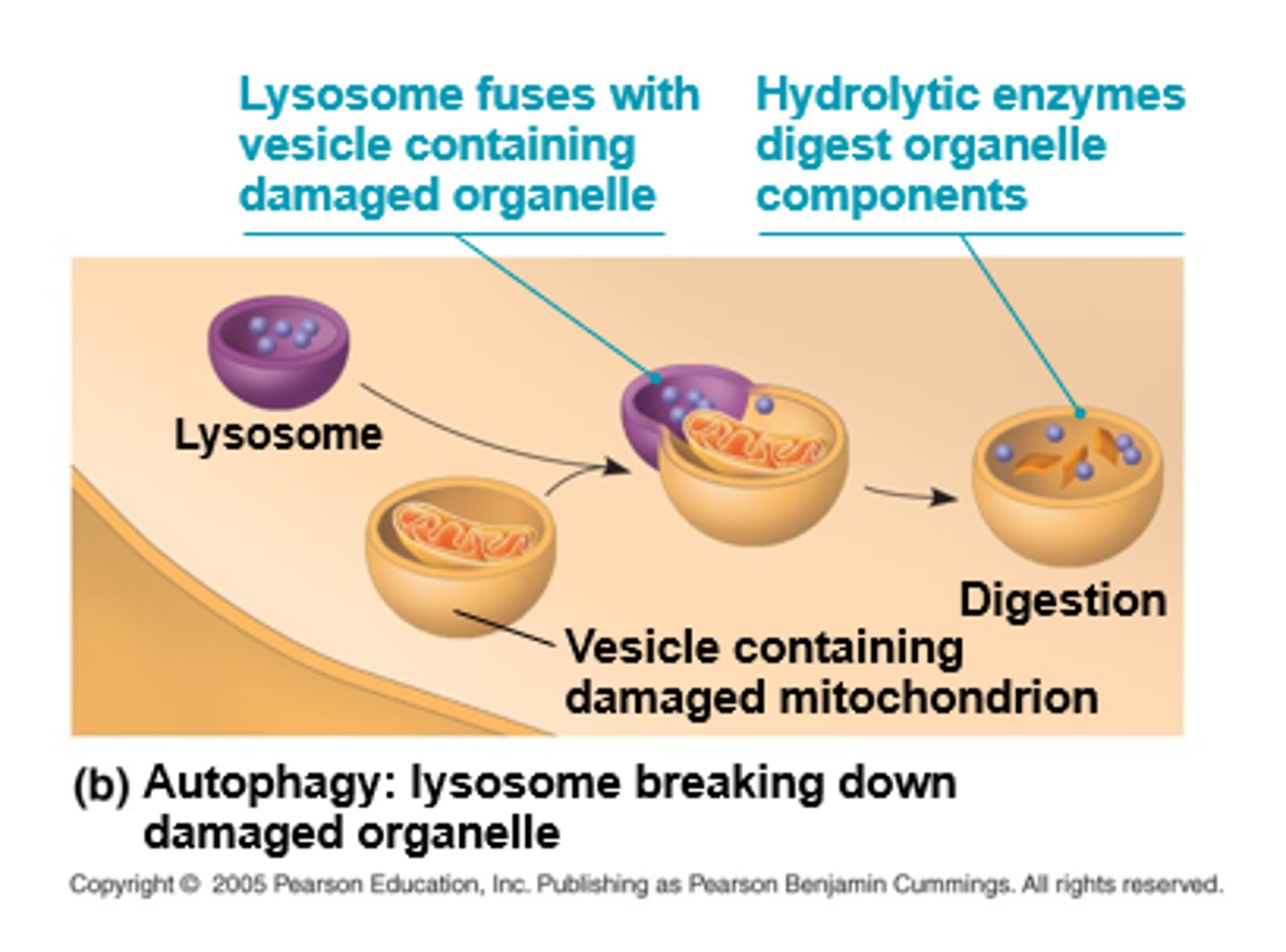
what cells do not have lysosomes?
plant cells
vacuoles (_____) are ____ with varied ___
(diverse maintenance compartments); membrane-bound sacs; functions
a ____ or ____ cell may have 1 or more vacuoles
plant; fungal
food vacuoles are formed by:
phagocytosis
contractile vs central vacuoles
contractile (freshwater protists)
- pump excess water out of cell
central (mature plant cells)
- hold organic compounds + water
____ cells do not have central vacuoles
animal
vacuoles are primarily used for ____ and are only really found in ___ and ___
storage; plants; fungi
vesicles are _____ with varied ____, and are much ____ than vacuoles
membrane-bound sacs; functions; smaller
4 functions of vesicles
1. moving material btwn ER and golgi
2. moving things btwn cisternae of golgi
3. deliver things into cell from extracellular environment via endocytosis
4. deliver waste/hormones to be excreted at exterior of cell via exocytosis
order of how things are transported out of cell by vesicle movement (10)
1. a piece of mRNA is synthesized by transcription from a DNA gene
2. ribosome synthesizes protein by translation (primary structure)
3. protein enters smooth ER to be modified
4. protein folded to form secondary structure
5. protein first enters into vesicle
6. protein enters into cis golgi for modification
7. protein folded to form tertiary/quaternary structures
8. protein transported in transport vesicles btwn golgi's cisternae
9. protein leaves golgi in vesicle
10. vesicle containing protein (mucus, hormones) fuses w/plasma mem to release protein out of cell
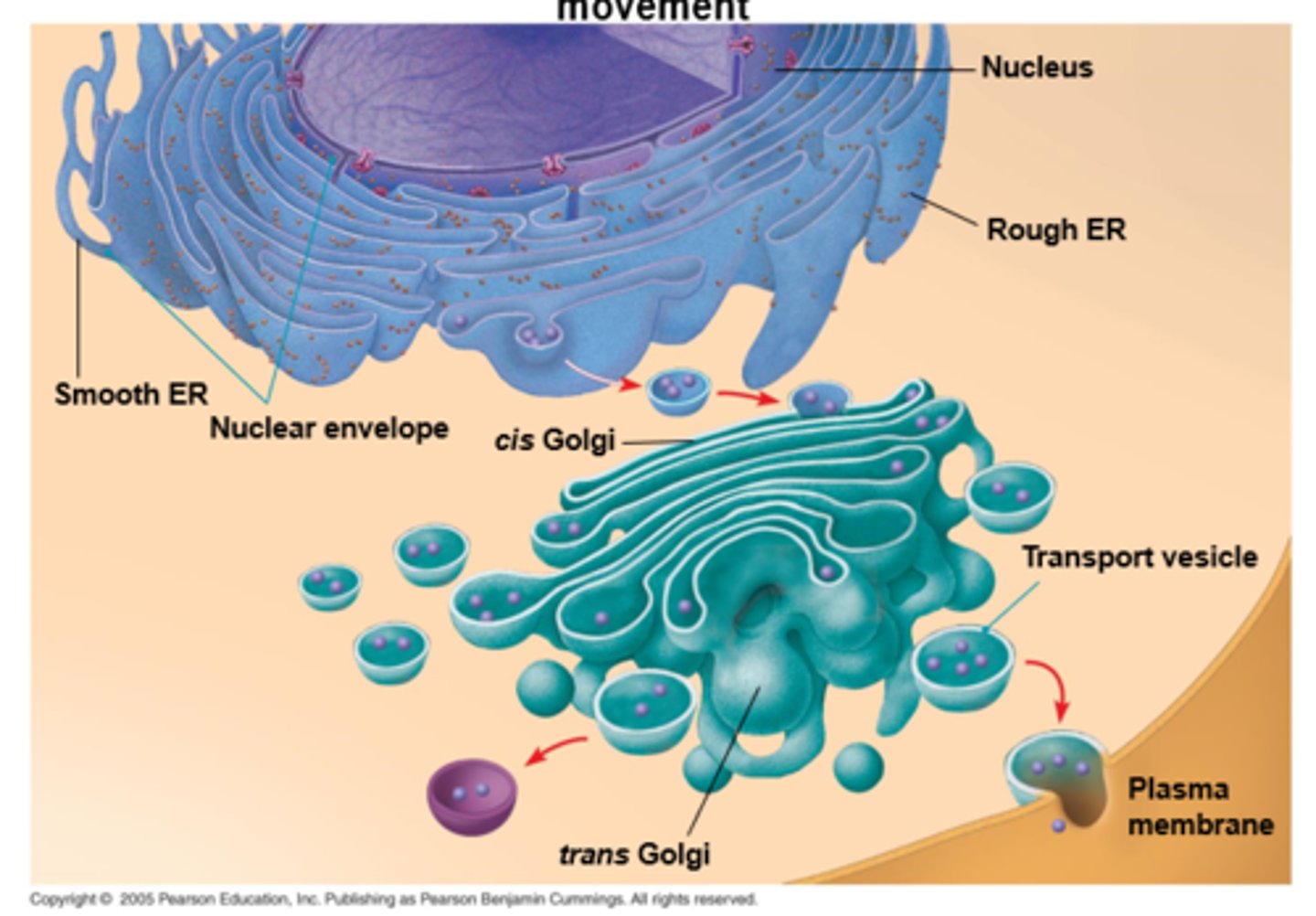
vesicles from the ER are sent to the ____ and are ____ so they work, and then (2):
golgi; refined;
1. sent out via exocytosis
2. retained (NOT ENDOCYTOSIS, just retained)
what kind of cells in your body make a lot of protein?
1. muscle
- testosterone makes them stimulate protein synthesis
2. pancreatic
- insulin/glucagon
3. hair
how big is a typical cell?
0.1-0.2 mm / 100 micrometers
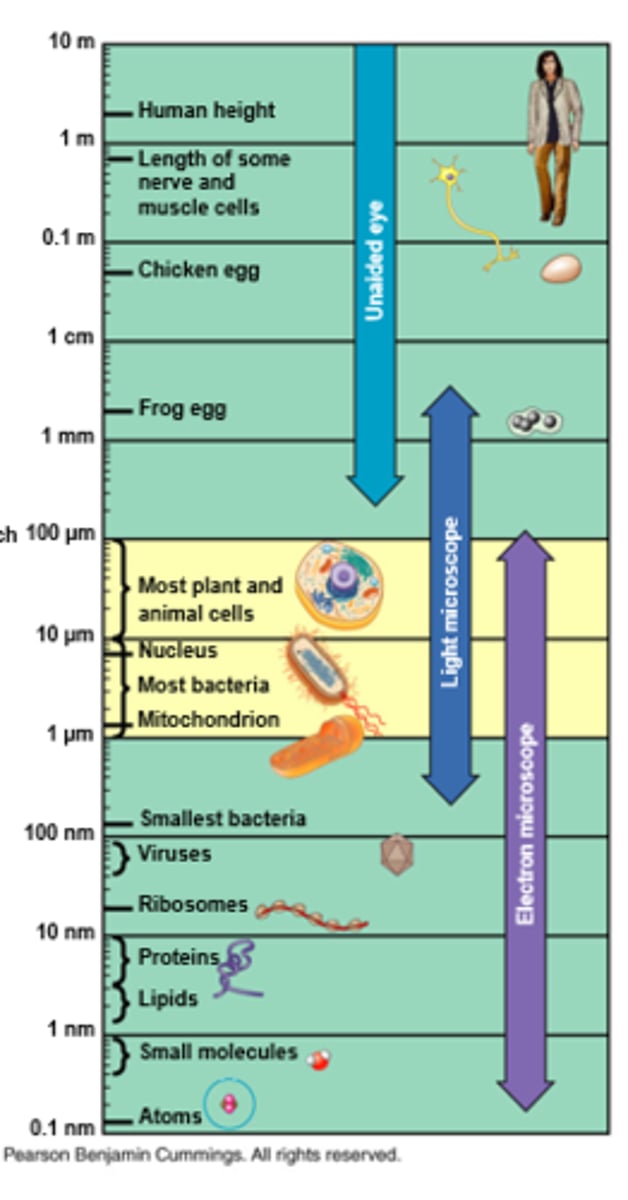
why do we fractionate a cell and then centrifuge its parts?
isolating organelles; separates parts of cell to break it down and study them
what are the steps of cell fractionation?
1. homogenization
2. centrifuge
how does a centrifuge sort cellular extract?
based on density
most to least:
1. nuclei and cellular debris
2. mitchondria
3. plasma/internal membranes (microsomes)
4. ribosomes
how does anemia or dehydration affect a centrifuge of blood?
- RBCs usually most dense bc of iron
- anemia makes RBCs lower proportion of blood
- dehydration lowers plasma proportion
a carbohydrate side chain connected to a protein is a:
glycoprotein
lysosomes are filled with _____, a kind of ____.
digestive/hydrolytic enzymes; proteins