ACC3200
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
What are the financial investment measurements?
Return on Investment
Residual Income
Economic Value Added
What is ROI?
Use to evaluate the financial performance of investment centres
Profit/ investment capital
% or a ratio
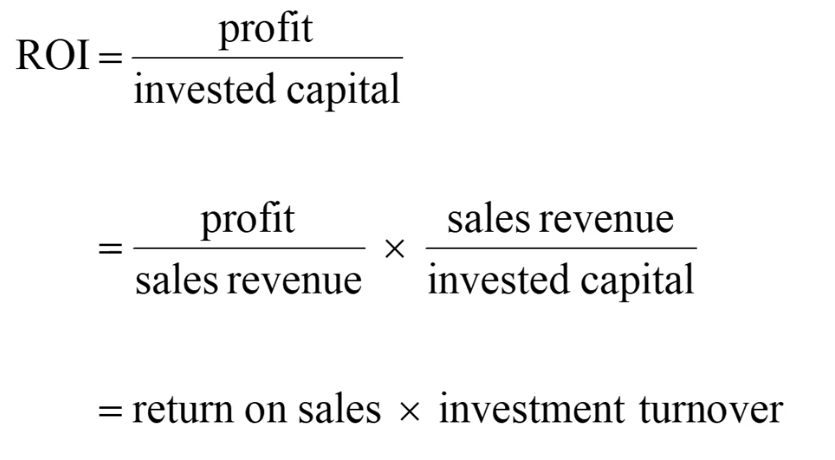
How to improve ROI?
Increase return on sales through increase selling price or sales revenue or decrease expense
Increase investment turnover through increase sales revenue or reduce invested capital
What are the advantages and limitations of ROI?
Advantages:
Focus on both the profit and the assets required to generate those profits
Can be used to evaluate the relative performance of investment centres
Limitations:
May encourage managers to focus on improving short term financial performance = may impact future competitiveness - use multiple measures
May encourage managers to defer assets replacement to maintain high ROI - consider alternative ways of measuring invested capital
Prevent goal congruence
Discourage managers to take on other projects
How to minimise behavioural problems of ROI?
Use multiple performance measurements
Consider different ways to measure invested capital
What is RI?
Profit - (invested capital * imputed interest rate)
Required rate of return = imputed interest rate charge
$ amount
What are the advantages and limitations of RI?
Advantages:
More likely to promote goal congruence compared to ROI
Takes into account of the organisation's measurement of required rate of return on performance/ investments
Encourages investment in projects that yield a positive RI to the organisation
Limitations:
Cannot use to compare performance of businesses that are different sizes
Formula is biased in larger businesses
Can encourage short orientation
What is EVA?
Measures the value added over an accounting period
The spread between the return generated by business activities and the cost of capital
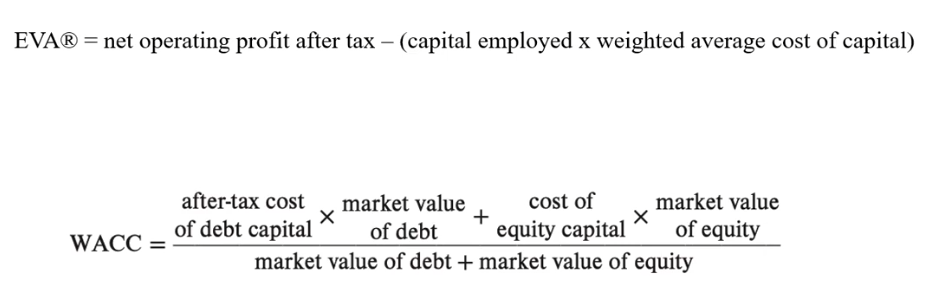
How can EVA be improved?
Increase profitability without employing additional capital
Borrowing additional funds
Pay off debt by selling assets
What is Shareholder value added (SVA)?
The worth of the business from a shareholder's perspective

What is Invested Capital?
Total assets
Total productive assets
Total assets less current liabilities
What is Value-based management?
Framework for making key business decisions that add economic value to the business
Strategies or decisions that achieve a return on capital greater than the cost of capital
What is incentive scheme?
Process, practices and systems that are used to provide levels of pay and benefits to employees
High incentives can strive high performances
Goal congruence
What is Intrinsic motivation?
Derives from the interest and enjoyment of work
What is Extrinsic motivation?
Derives sources outside the individual
What are the Performance-related pay systems?
Individual incentive plans
Profit sharing plans
Employee share plans
Gainsharing
Team based incentive scheme
What are the disadvantages of using financial performance measures?
Focuses on the results rather the causes
Only showing one perspective of performance
Limited guidance for future actions
Some actions does not take into account of shareholder and customer value
List some non-financial measures
Customer satisfaction
Defect measures
Quality
Stock status
Accident report
Multi-skilling
Machine downtime
Delivery on time
What are the advantages of non financial measures?
May emphasise strategy
Can be a drivers of future financial performance
Easier to investigate
May be more timely
More understandable and easier to relate to
What are the limitations of non financial measures?
Inclusion of non-financial measures can be ad hoc and undirected
Trade-off can occur
Lack integrity
May not easily translate into financial outcomes
What is a balanced scorecard?
Performance measurement system
Identifies and reports on performance measures of the organisation
Translates an organisation's mission, objectives and strategies into performance measures for each key strategic area of the business
It is used to implement strategy and to monitor and manage organisational performance
May form part of an organisation's planning cycle
What are the perspectives of BSC?
Financial perspective = perspective of the shareholders
Customer perspective = achieving customer's value
Internal business process = focusing specific and critical porcess
Learning and growth = capabilities of the organisation to achieve internal business process
Define lag indicator
Measures that help managers monitor progress towards objectives
Measurements of past performance
Results of the past
Define lead indicator
Focus on factors that drive outcomes and provide actionable information
Relate to business process and activities
Predictors of future success
Improvements in these measures should, overtime, improve lag indicators
What is a strategy map?
A visual representation explaining the cause and effect relationships linking the objectives of the perspectives of the BSC and the objectives of the organisation
It communicates to managers the components of strategy and processes and systems that will help achieve it
What are the types of benchmarking?
Internal benchmarking;
Business units within the same company
Competitive benchmarking:
Identify weaknesses and strengths of competitors
Industry benchmarking:
Company with similar interests and technologies
Best in class or process benchmarking:
Best practices in an industry
Businesses may try to normalise the measures to make them comparable
Define corporate sustainability
Requires organisation to consider interrelated impacts of their activities on the economy, environment and society
What is sustainability report and what does it highlights?
Measure and communicate the economic environmental and social (ESG) impacts
Triple bottom line reports
Corporate social responsibility reports
Social audits
Social and environmental reports
What is global reporting initiative (GRI) framework?
recognised + regarded as global standards
it is the representation of the best practice
required for all reports published after 1/07/2018
Provides guidance to organisations on performance measures and methods that they can use to measure and report on sustainability-related impacts and performances
What is the SASB standards?
IFRS Sustainability disclosure standards
IFRS S1 = General requirements for sustainability related disclosures
IFRS S2 = Climate related disclosure
What is international integrated report framework (IIRF)?
Broader focus than sustainability reports
Aims to explain how an organisation creates value overtime
Integrated report: six kinds of capital (financial, manufactured, intellectual, human, social and relationship, natural)
What are the benefits of reporting sustainable performance?
Identify environmental and social changes that impact the organisation and its stakeholders
Develop a strategy to manage risk and opportunities
Create innovative new products and services
Engage in actions to grow their market share
Define natural capital
Stock of capital derived from natural resources
Issues of materiality and valutation
What is environmental management system (EMS)?
Manage environmental performance
Report and capture environmental impact of an organisation's activities
Environmental performances to be measured against policies, objectives and targets
Define environmental cost and list them.
Incurred to prevent, monitor and report environmental impacts and costs of non-compliance with regulations
Conventional costs
Direct costs associated with capital expenditure, raw materials and other operating and maintenance costs
Hidden costs
Activities such as monitoring and reporting of environmental activities and emissions, cost of searching for environmentally responsible suppliers and ongoing cost of cleaning up contaminated land
Contingent costs
Arising from failure to clean up contaminated sites, and fines and penalties for non-compliance with regulations
Relationship and image costs
Less tangible costs and benefits that relate to consumer perceptions, and employee and community relations
Societal costs
Impose on others
The environment and society
What is supply chain management?
Life cycle analysis = associated impacts on the product
May lead to adoption of innovative product and process environment in each stage
Suppliers = environmentally responsible supplier cost analysis
Customers = work with to reduce the adverse environmental and social impact of products
what is International standard organisation (ISO) 14031 environmental performance evaluation?
Provides advice on how to measure environmental performance
Eco- intensity and eco-efficiency measures
Operational performance indicators
Management performance indicators
Environmental condition indicators
What is capital expenditure analysis?
Inclusion of environmental costs and benefits may affect the attractiveness of a project
Some capital expenditures driven by need to be environmentally and socially responsible
Define responsibility accounting.
A system that is built around a framework of responsibility centres
A manager is held accountable for their own responsible centre
What is strategic planning?
Long-term planning usually undertaken by senior managers
Involves decision about corporate strategy and business strategy
Might happen every 3 to 5 years
Formulated in broad terms
Directly influences the formulation of budgets
What is a budget?
Detailed plan of future operating activities
Acts as financial model of future operations
Core component of an organisation's planning and control system
Critical way of providing information to managers
Short-term plan, covering year by year
What is the purpose of budgeting?
Planning = expresses a plan of action in financial terms
Facilitating communication and coordination between all managers
Allocating resources
Controlling profit and operations = serves as a benchmark for comparing actual results
Evaluating performance and providing incentives
What is included in an operating budget?
sales budget
cost budget for manufacturing business
What does sale budget do?
Detailed summary of estimated sales units and revenues
Estimating which products will be sold and in what quantities = can be done through market research
Internal and external factors should be considered
What does cost budget for manufacturing do?
Production budget shows number of units to be manufactured
Budgets for direct materials, direct labour and overheads
Budget for selling and administrative expenses
What does cost budget for retail and wholesale business consist of?
Purchases budget to determine the quantity and costs of goods to be purchased for resale
Budgets for selling and administrative expenses
What does cost budget for service firm consist of?
Budgets for costs incurred to provide services
Overhead budget
What is included in financial budget?
Cash budget:
Expected cash receipts and planned cash payments for the budget period
Timing of all cash movements
Allows businesses to plan financial resources
Budgeted income statement:
Shows expected revenue and planned expenses
Budgeted balance sheet:
Shows expected assets and liabilities at the end of the budget period
Capital expenditure budget:
A plan for the acquisition of long-term assets
May involve cash flows over many years
What is budgeting like for not-for-profit organisations and government agencies?
No sales budget if services are provided for no charge
Other revenue sources may be estimated, including government grants, donations and sponsorships
Services levels drive the resources that are needed and form the budget cost
Define administration
Formal processes are typically used to collect data and prepare the budget
The process is often the responsibility of the senior accounting manager
A budget committee consists of key senior executives who advise the accountant during the preparation of the budget
What is a budget manual?
Who is responsible for providing information
When the information is required
What form it will take
What are the main issues for budgeting?
participative budgeting
Budgetary slack
Budget difficulty
Define participative budgeting and its benefits and costs
Develop initial budget estimates for own area of operations
Negotiation and revisions of budget estimates
Managers at all levels have input
Top-down budgeting = senior managers impose budget targets
Bottom-up budgeting = lower managerial and operations levels active in setting own budgets
Benefits:
Encourage coordination and communication between managers and wider organisation
More accurate budget estimates
Individuals identify more closely with budget targets
Employee empowerment due to higher degrees of authority and independence
Costs:
Expensive and time consuming
Can cause delays and indecisiveness
May aggravated differences and disagreements
Provides opportunities for padding budgets
Define budgetary slack and what reduce opportunities for budgetary slack?
Managers may intentionally underestimate revenues or overestimate costs
Refers to the difference between the revenue or cost projection and a realistic estimate of revenue or cost
Reduce opportunities for budgetary slacks:
Use benchmarking
Senior managers regularly involve themselves in the tasks of subordinates
Promoting and fostering values and norms unfavourable to budgtary slack
Linking rewards to predictive accuracy
Using stretch targets
What is budget padding and reasons for it?
If manager performance evaluations depend on budgetary benchmarks being achieved, managers may try to "beat the budget", manage uncertainty or compete for resources
Incentives to underestimate revenue or overestimate costs
Deploy tactics to influence budget negotiations, such as witholding information, promising performance improvements, emphasising the role of business conditions, or appealing to decision maker's emotions
There are three primary reasons for padding the budget:
Some managers believe their performance looks better when they exceed their budget
It is a way of coping with uncertainty
To guard against initial budget requests being cut back by senior management
When does budget difficulty occur?
Goal congruence occurs when the organisation's goals coincide with an individual's goals
When is budget acceptance occur?
Budget acceptance is more likely when:
Developed participatively
Considered achievable
There is frequent feedback on performance
Employees are held responsible for activities within their control
Achievement is accompanied by rewards
What is zero based budgeting?
The process where all activities in the organisation are initially set to zero
Managers must justify each activity in order to receive an allocation of resources
Can be time consuming and expensive to implement
Not useful to identify areas of waste, redundant activities or ways to improve performance
Can be too introspective
What is program budgeting?
Budgets are prepared for individual programs and program objectives as opposed to line item budgeting
Control is achieved through quantitative and qualitative performance measures
It is often associated with budgeting in government departments
Focus on outputs and outcomes
What is rolling budgeting?
Continually updated
Add a new time period
Drop the period just completed
Identify any gaps between what it is expected
What is flexible budgeting?
Detailed budget prepared for a range of levels if activity = compared to a static budget which relates to one specific planned level of activity
Allows us to select the most appropriate benchmark for cost control
A valid basis for comparing actual and expected costs to budget, for the actual level of activity
What does a control system consist of?
Predetermined performance level
Measure of actual performance
Comparison between standard performance and actual performance
What is standard cost?
Serves as a benchmark
Part of the control system
Important for planning and control
Estimated costs that is going into making a unit of product
Budgeted costs, based on estimates of the cost of material, labour and overhead resources
Actual cost is compared to standard cost to determine variance cost
Define standard cost variance
Used to evaluate actual performance and control costs
Define Setting standards
Analysis of historical data
Engineering methods
Combined approach
What is service organisation?
May be non-repetitive
Firms may develop standard quantities to capture the time taken for key activities and processes
What are the types of standards?
perfect or ideal standard
practical standard
Benchmarking cost standard
Define ideal or perfect standard
Peak efficiency
Lowest material and labour prices
Use of the best quality materials
No production disruptions
Motivation to achieve the lowest cost = can cause employee to feel discourage as standards are not possible to achieve
May sacrifice product quality
Define pratical standard
Minimum attainable costs under normal operating conditions
Allowances made for downtime and wastage
May encourage more positive attitudes towards targets as it is more achievable and realistic
May encourage inefficiency and wastage
Define benchmarking cost standard
Identify the company that has the best cost performance
Identifies areas need to improve cost performance
Cost standards may be formulated to achieve external performance standards
More difficult to benchmark against competitors = but will create a competitive advantage once succeed
What is static-budget variance?
The difference between the actual result and the corresponding static budget (master budget) amount
What are the cost and benefits of investigation?
Cost:
time spent investigating
disruption to the production process
cost of implementing corrective actions
Benefits:
Reduce future cost if the cause of the variance is eliminated
Improve work practice
What is standard costing system?
can be used for product costing
all inventories recorded at standard cost
variances are closed off at the end of the period
Limitation of variance analysis
variances are too aggregated
variances focused on the consequences rather than the causes of the problems
variances report may be too late to be useful
tendency to focus on cost minimisation
takes departmental rather than a process perspective
What is the purpose of performance measurement?
Communicate business' strategy and plans, align employee's goals
Track management performance against targets
Evaluate and reward subordinate's performances
Guide future development of strategies and operations
Compare actual results with what's on targets
Allows for goal congruence
What is an effective performance measurement system?
Links to strategies and goals
Recognises controllability
Embraces participations and empowerment
Simple and understandable measures
Emphasises the positives
Reported in a timely manner --> to take corrective actions
Includes benchmarking
Limited number of measures
Links rewards
What is decentalisation?
Dividing the organisation into smaller units
Each unit assigned particular operational and decision making responsibilities
Goal congruence = ensuring goals throughout the units are aligned with organisational goals
Managers assigned responsibility to run units
Managers accountable for performance of their units
What are the benefits for managers in decentralisation?
More accurate and complete local information about markets and operations
Training for future higher level managers
Greater motivations and job satisfaction
Corporate managers have more time for strategic issues
Delegation allows quicker responses to opportunities and problems as they arise
What are the cost of decentralisation?
Narrow focus on own unit's goals
Unnecessary duplication
Behavioural challenge
What is shared services?
Concentration of support services formed into a separate unit to service multiple internal customers
Aim to reduce cost and improve quality of service
High level of autonomy and incentives
Often set up as profit centres with the aim to break even
What is team based structure?
Move towards flatter organisational structures
Self managed work teams
Members of team will be multiskilled
Promote employee satisfaction
Improved customer satisfaction and improved productivity
What is financial performance reports?
Show key financial results appropriate for the type of responsibility centre
Contribution margin format
Distinguish between profit margin controllable by manager and profit margin attributable to unit
What is transfer pricing?
Internal selling used when goods and services are transferred within a decentralised organisation
The transfer price is the revenue for the supply unit and cost for the buying unit
Result in profits that are reliable and accurate
Preserve and encourage autonomy
Encourage goal congruent behaviour
Who set transfer price?
Managers of profit centres and investment centres may have considerable autonomy
Direct intervention by corporate management is contrary to decentralisation philosophy
Corporate management may develop general policies to govern transfer pricing practices
What are transfer pricing method?
Market based prices = used if there are competitive external markets
Cost plus prices = no reliable external market prices, such as intermediate products
Negotiated prices = profit and/or investment managers negotiated transfer prices
What is the general transfer pricing rule?
Provide guidance on the appropriate transfer price
Represents a minimum transfer price

What happen when An external market and spare capacity in the supplying unit?
Additional profit for supply unit
Negotiation may occur to provide incentives for the buying unit
What happen when An external market and no spare capacity in the supplying unit?
Take into account of opportunity cost of lost profits
What happen when there is no external market and spare capacity in the supplying unit?
No opportunity cost
May be based on cost plus
What happen when there is no external market and no spare capacity in the supplying unit?
Account for opportunity cost on lost sales
What is quality?
The degree to which a product meets customers' needs and expectations
Total features and characteristics of a product or service made or performed according to specifications to satisfy customer at the same time
What are the layers of quality?
Quality of design:
Degree to which a product's design specifications meet customers' expectation
Quality of performance:
Degree to which a product meet its design specification
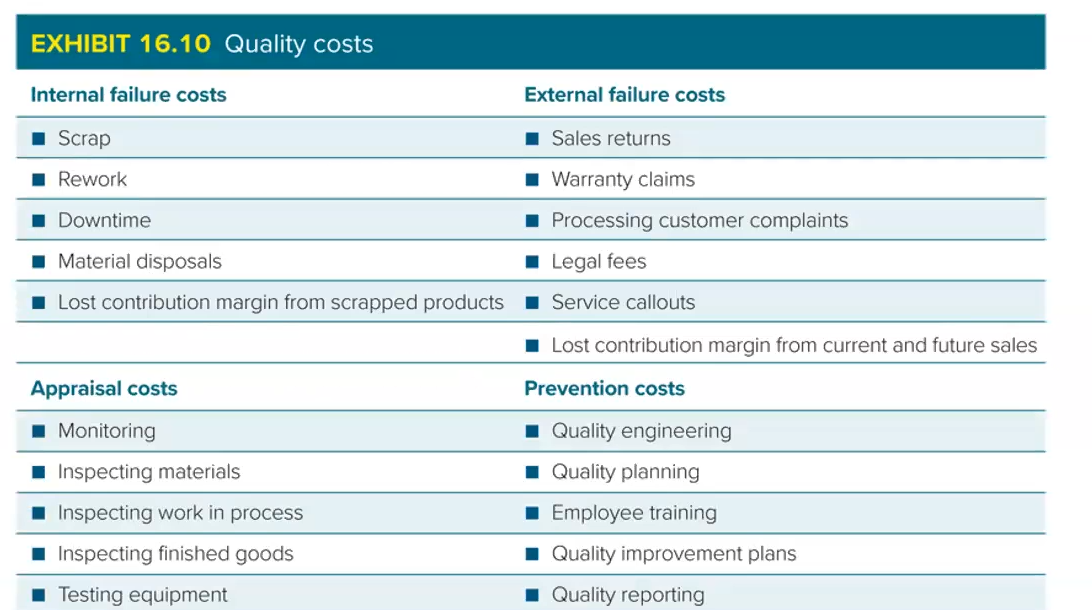
What are the types of quality cost?
Internal failure costs:
Detective products or services are detected before leaving the business
External failure costs:
Defective products or services provided to customers
Appraisal costs:
Determine whether defects exist
Prevention costs:
Prevent internal or external failures and minimise appraisal activities
What is cost of quality report?
Places a dollar figure on the costs of poor quality to quantify them
Looks at trends over time
Classifies costs as fixed or variable
Considers interactions between the four categories
What is total quality management and what does it consist of?
Structured approach to achieving continuous improvement in process to meet customer expectations
Organisation-wide
Infiltrates all aspects of the business and involve employees
Customer driven
Define by the needs and expectation of the customers
Involves empowerment
Want employees to manage their own quality inspections and correct problems
Process perspective
Focus on the smooth flow across the organisation
Quality management system
Supported by documented quality procedures and practices to keep the TQM process under control
Continuous improvement
What is six sigma?
Approach to manage quality
Business improvement methodology that focuses on identifying and eliminating defects
Structured approach and rigorous data analysis
Company can achieve quality accreditation - ISO 9000
What is supply chain management?
Interlinked organisations involved in creation, distribution and sales of goods and services
The management of key business processes that extend across the supply chain (original supplier to the final customers)
What kind of technology involves supply chain management?
E-commerce (Business transactions through electronics = allow customers to access interactive websites and initiate and complete transactions over the internet)
Business-to-business (B2B)
Electronic data interchange (EDI) (linking a company's computer system to suppliers or customers to exchange information in a timely manner)
Business and its non-business customers (B2C)
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
Cloud computing
Internet of things
How are customers be managed?
Customer relationship management (CRM) = collecting and analysing of customer data to understand customers' behaviour patterns and needs
Seeks to develop strong customer relationships
Tailored products to customers' expectation and needs
Lead to improvements in customer service, customer retention, new customers, more effective and efficient marketing
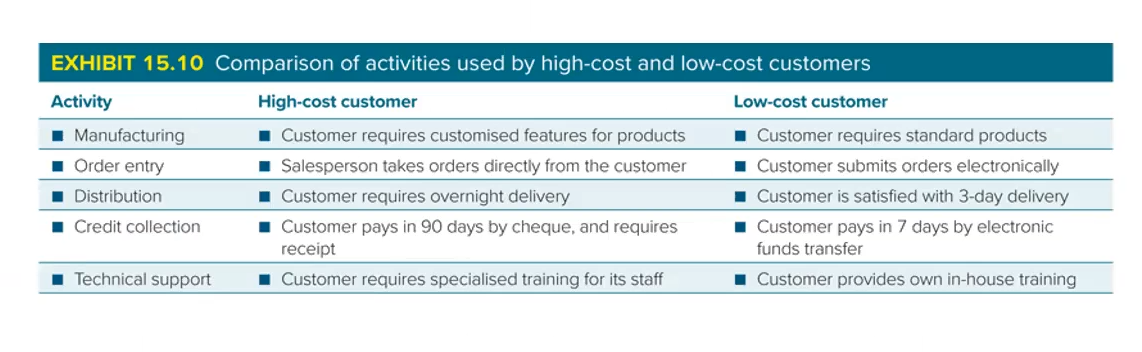
What are the types of customer profitability analysis?
Customer cost analysis = the analysis of the cost of products purchased by customers plus customer driven activities
Customer driven costs = include marketing and selling, packaging, order entry and after sales services
Activity based costing analysis may be used to determine the relative profitability