W1 L1: Genomes: Structure and Analysis
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Mendel's experiments
He worked on the garden pea Pisum sativum
Peas normally self-pollinate but may be cross-pollinated.
Self pollination for many generations can yield pure-breeding individuals (in other words, we can be pretty sure of the characteristics of the offspring)
Discovered 3:1 ratio
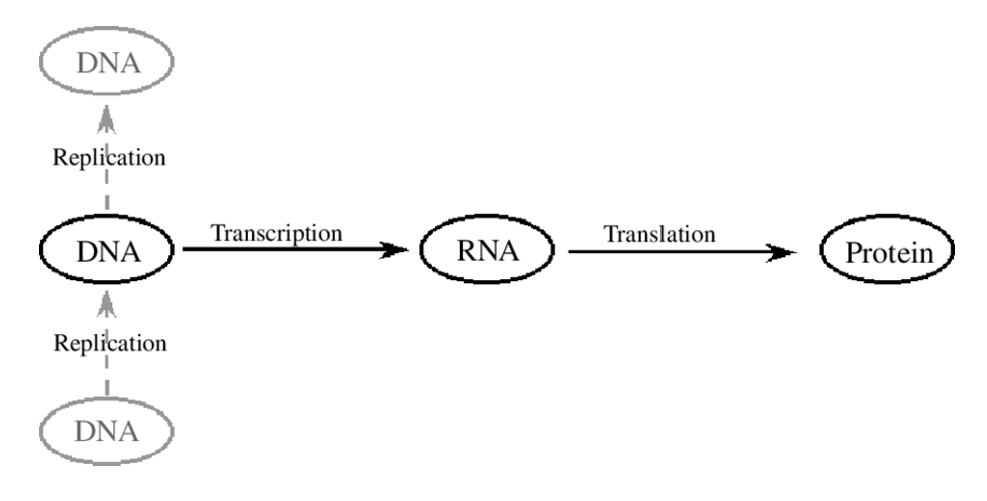
Uses of DNA
DNA replicates - can diversify
DNA can be transcribed to RNA then translated into proteins
Nucleic acids
DNA - Deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA - Ribonucleic acid
Both composed of repeats of a basic unit or monomer called a nucleotide
DNA molecules are composed of linear polymers of nucleotides i.e. polynucleotides
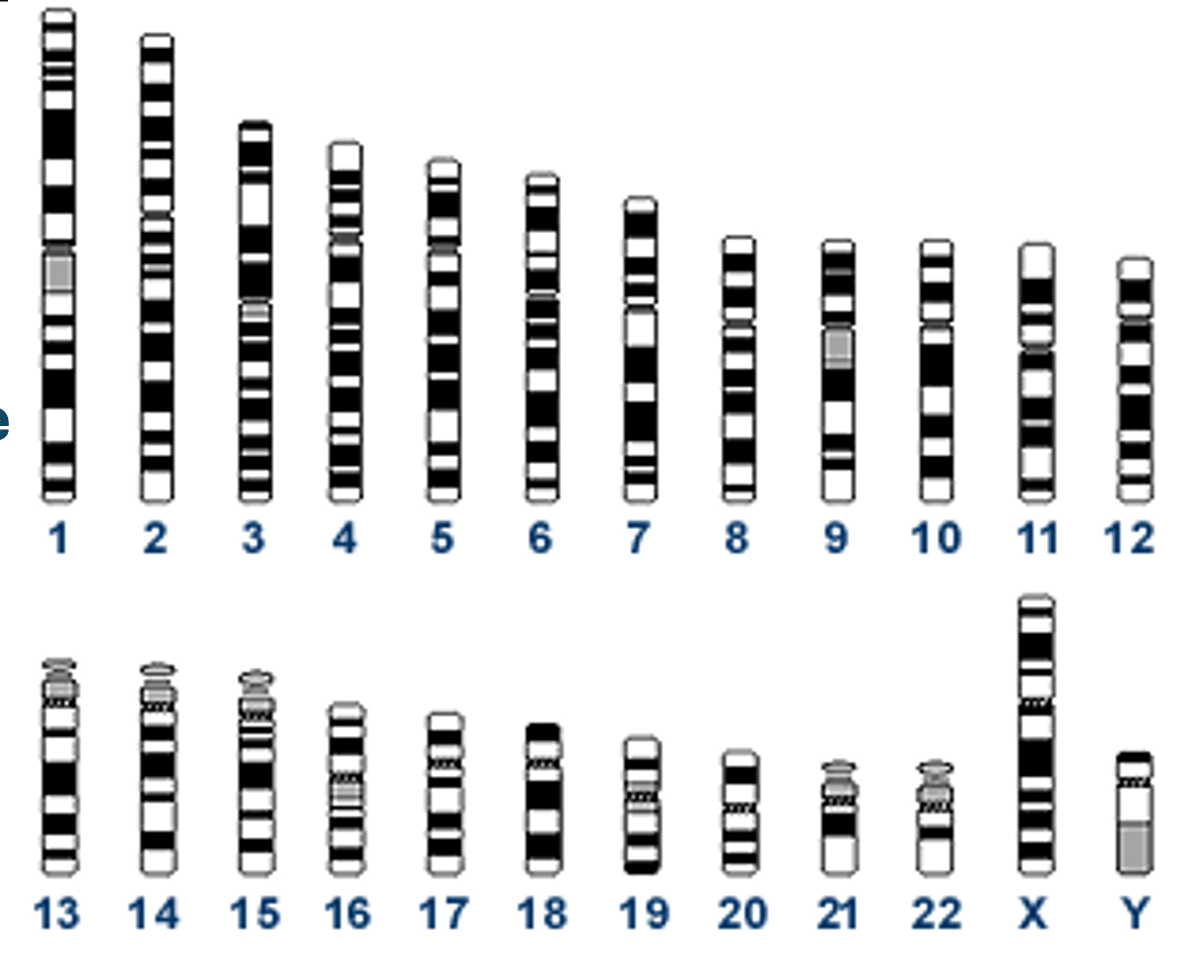
Human karyotype
Look for a change in the size or position of a chromosome
Proteins
Enzymes - e.g. lysozymes in tears
Structural proteins - e.g. keratin in hair and nails, parts of the cell wall, etc.
Majority of the cell components
Forms from a linear amino acid sequence into a complicated folded structure
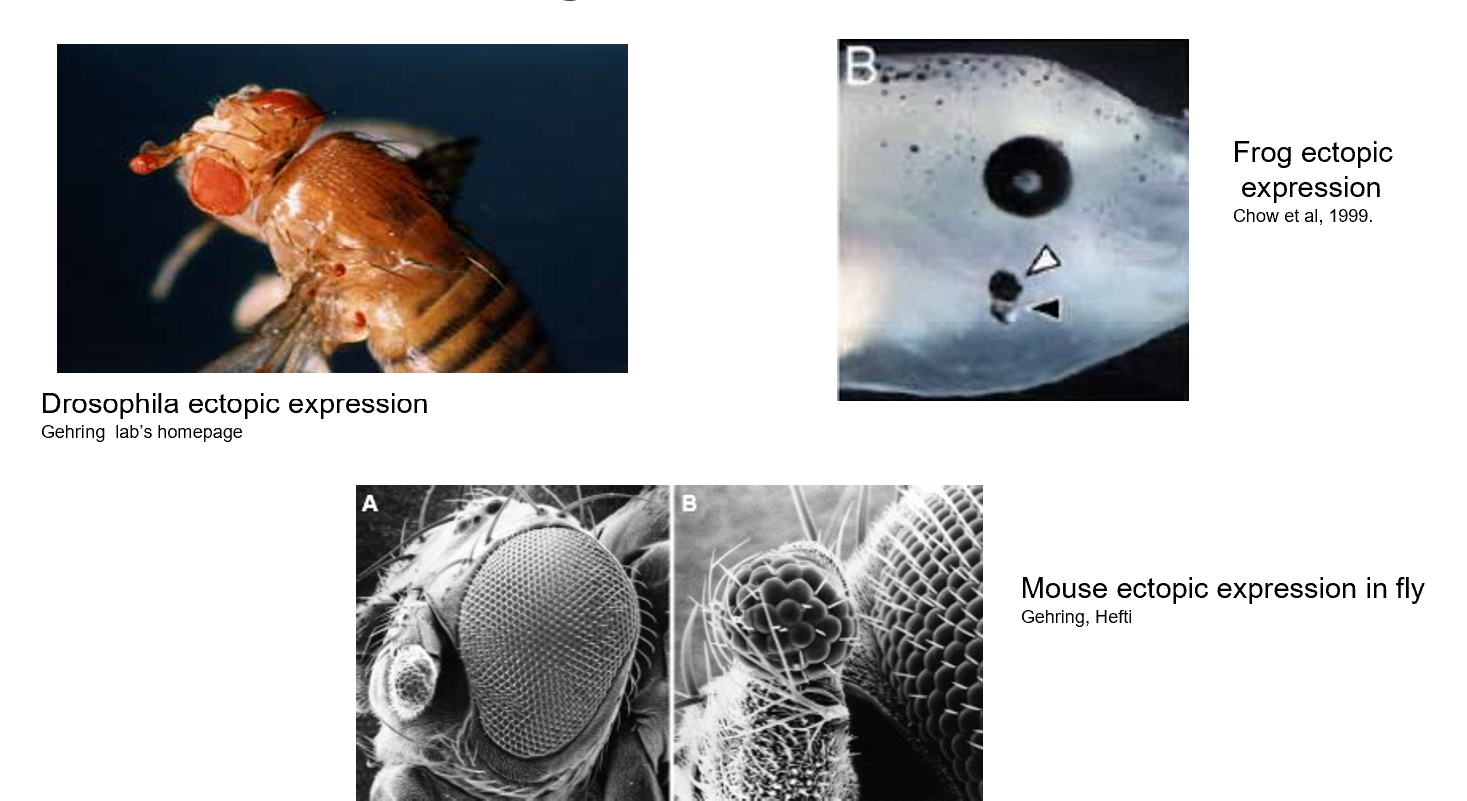
Pax6 low expression
Pax6 is important for eye development
Can lead to no eyes being developed in most organisms
Similar phenotypic output in all types of organisms
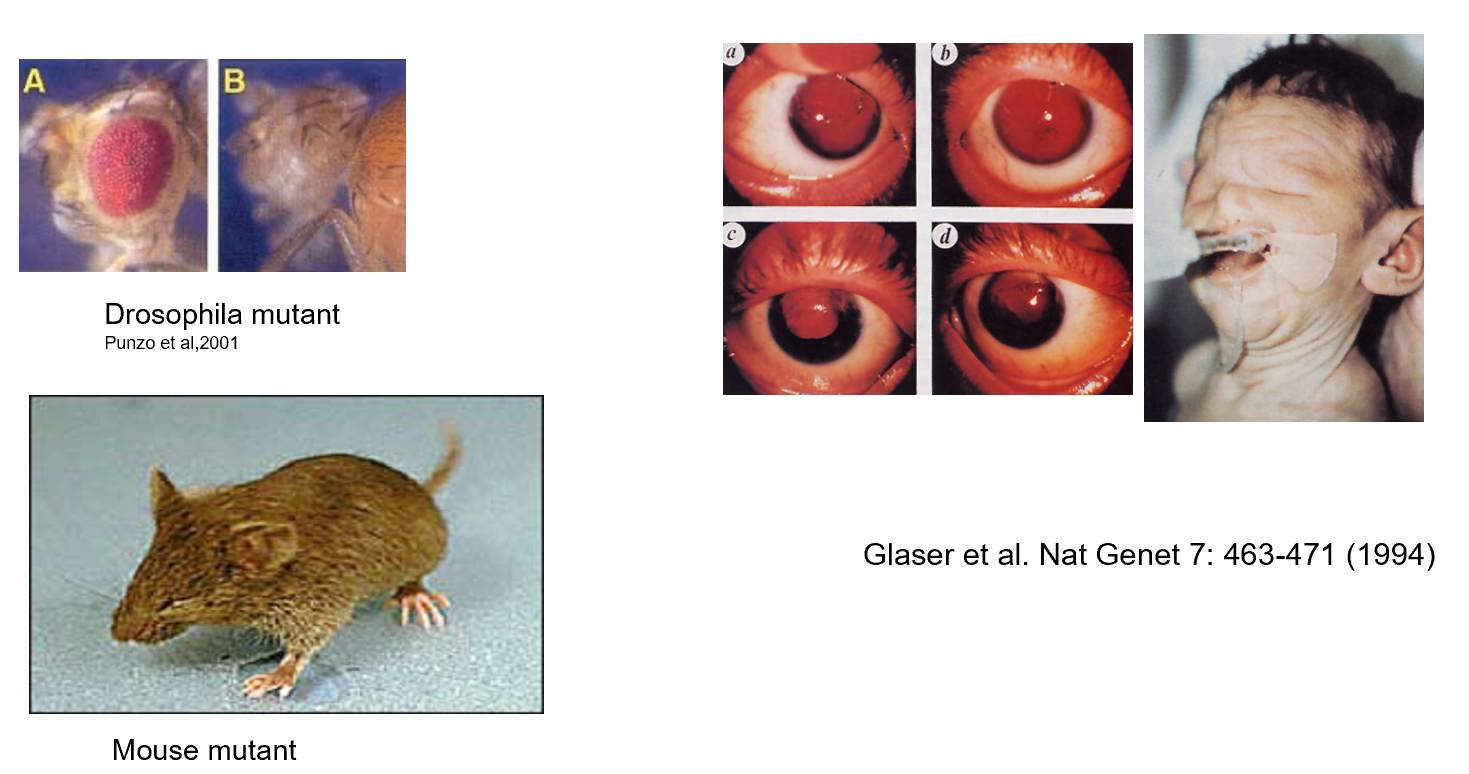
Pax6 overexpression
Extra eye tissue growing in other places
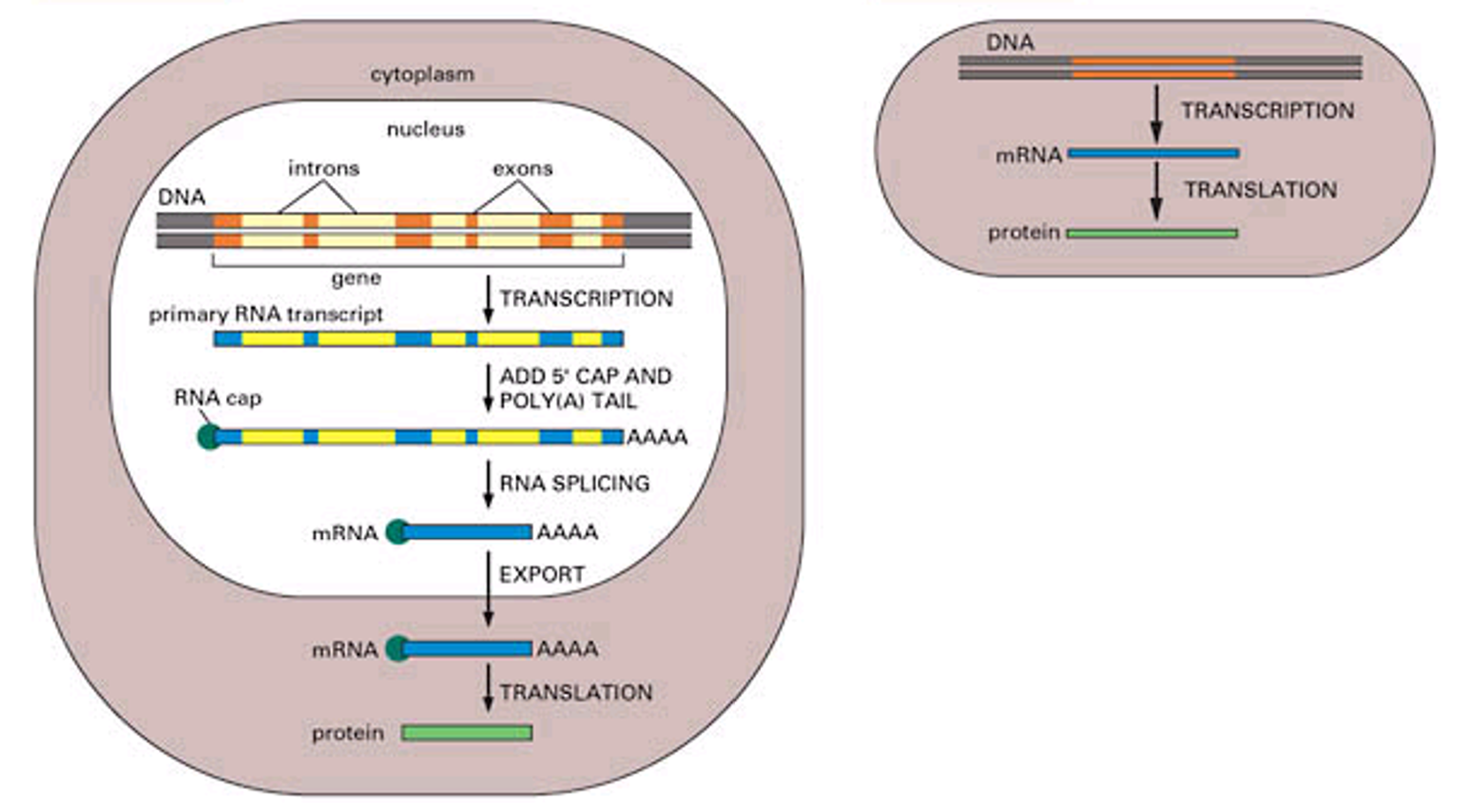
Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes: Protein coding region in DNA transcribes into mRNA, then translates into protein, no nucleus
Eukaryotes: Mostly in the nucleus, highly compartmentalised, very large, DNA from protein coding gene gets modified and spliced, transcribed into mRNA and translated into a protein
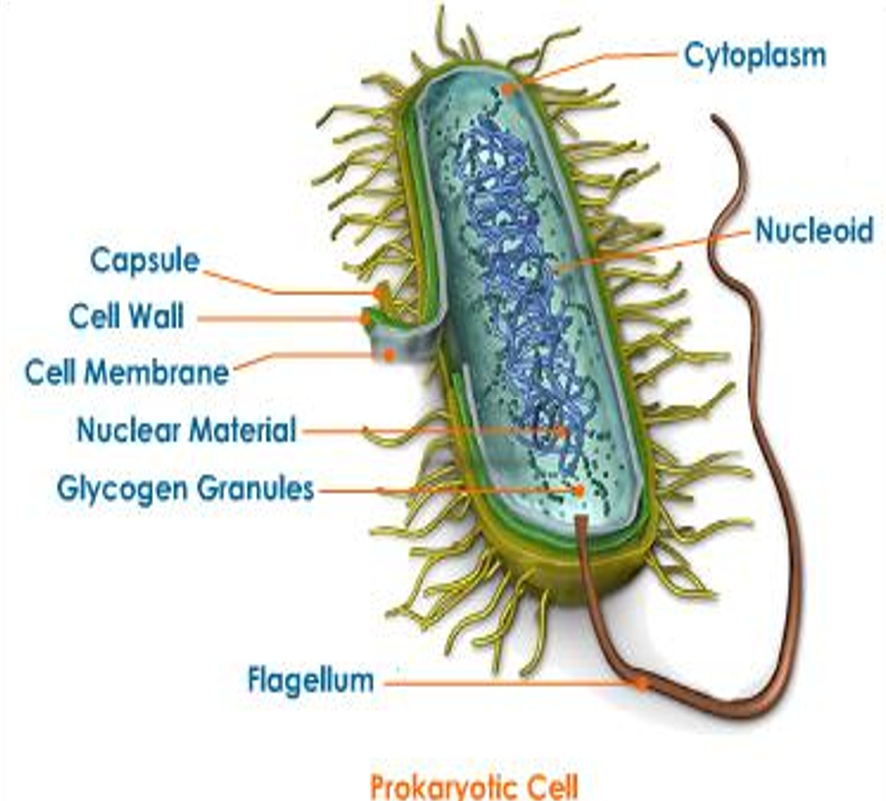
Prokaryotic cell
No compartmentalisation
The nucleoid is distributed in the cell
Translation and transcription are independent of each other
No nucleus
Free floating DNA
Unicellular only
Asexual reproduction
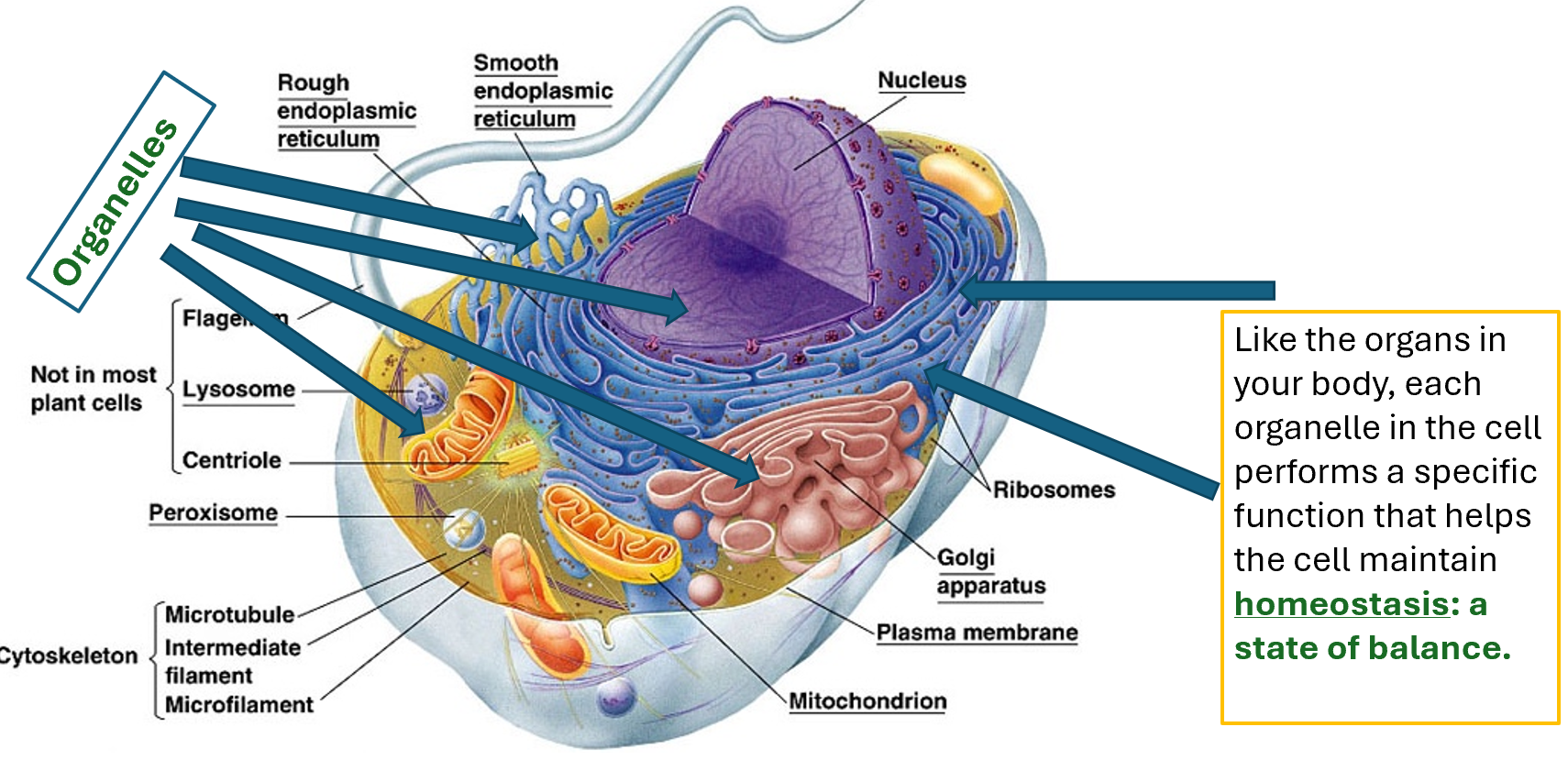
Eukaryotic cell
Highly compartmentalised
molecules trafficking
Nucleus containing DNA
Can be unicellular or multicellular
Can be asexual or sexual reproduction
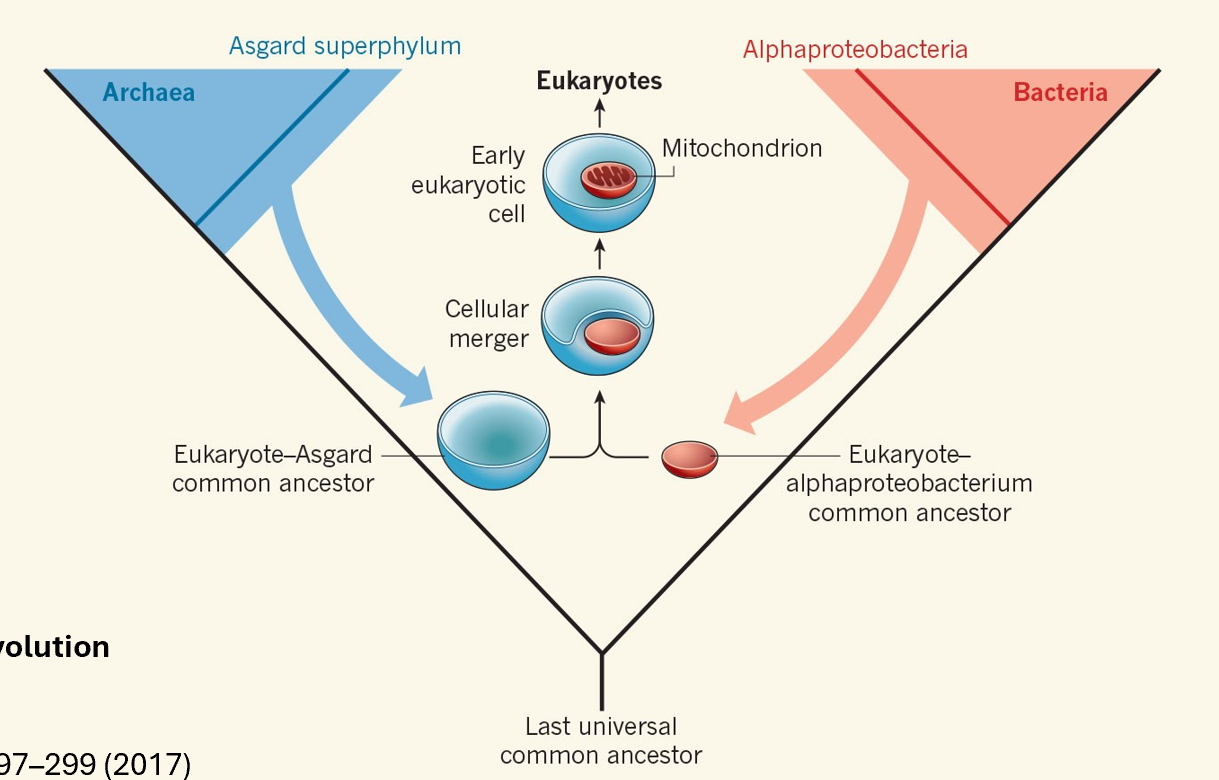
Evolution of eukaryotes
Eukaryotes merged from bacteria and archaea
Most of the genes are found in the nucleus after the fusion